Chemical Nose-Based Non-Invasive Detection of Breast Cancer Using Exhaled Breath †
Abstract
Highlights
- Exhaled breath was analyzed using a commercial electronic nose for early breast cancer detection.
- Samples were collected with no prior requirements from the patients.
- After feature extraction, the processed data was used for model optimization and training.
- Accuracy, precision, and specificity of 91.0% were achieved by the model.
- The method could provide a path for a rapid, simple, screening technique for low-income countries.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental and Computational Methods
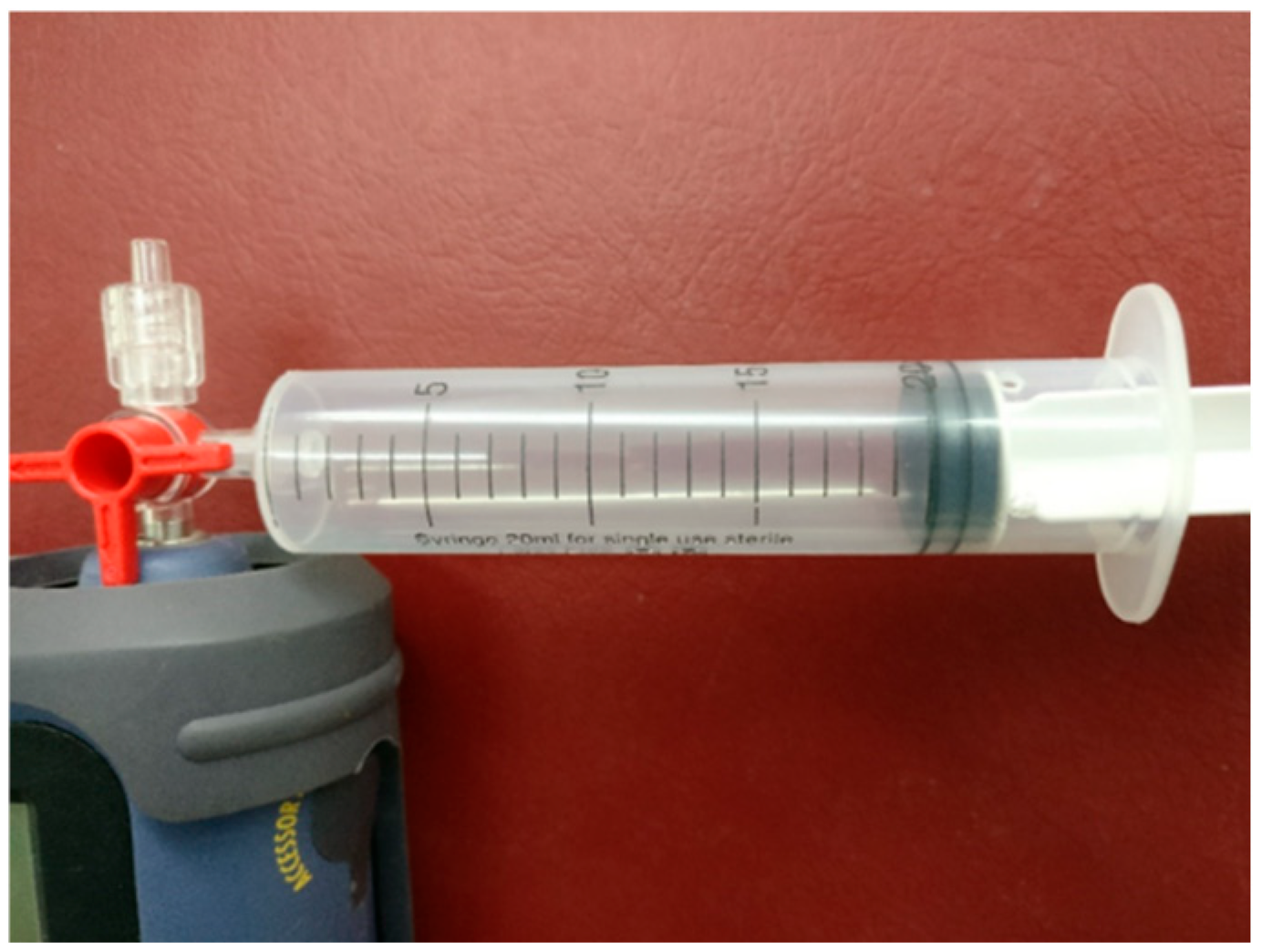
2.1. Exhaled Breath Collection
2.2. Electronic Nose
2.3. Subjects
2.4. Data Analysis Method
3. Results
3.1. Exhaled Breath Collection
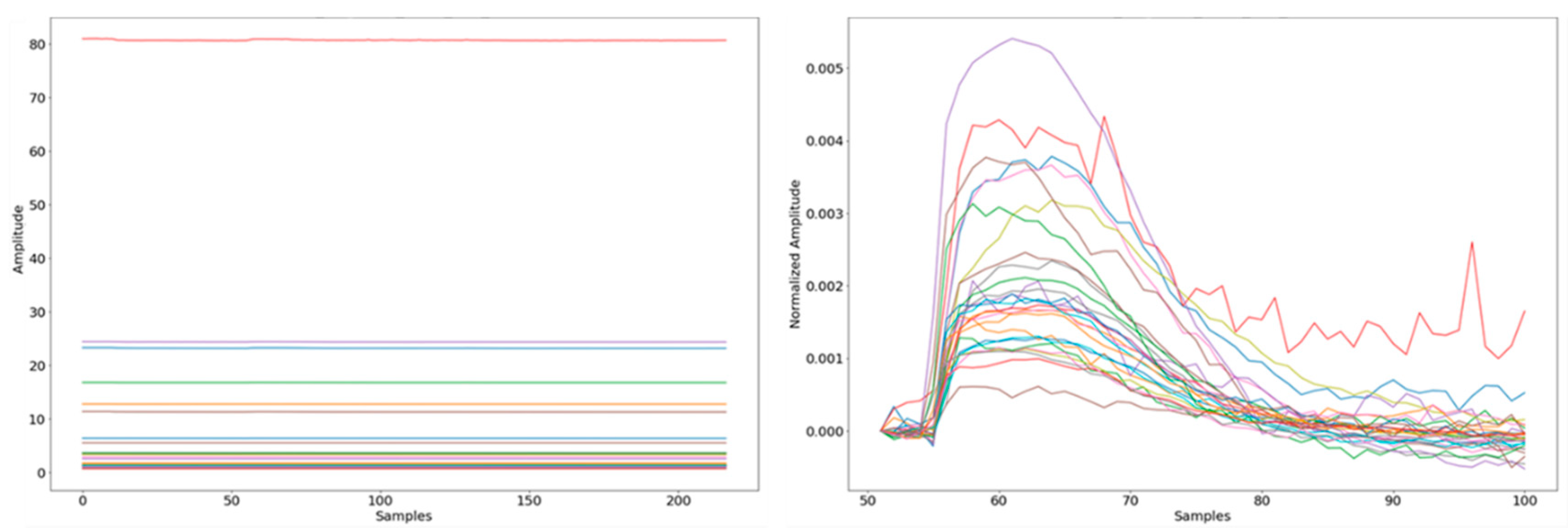
3.2. Exhaled Breath Data Processing
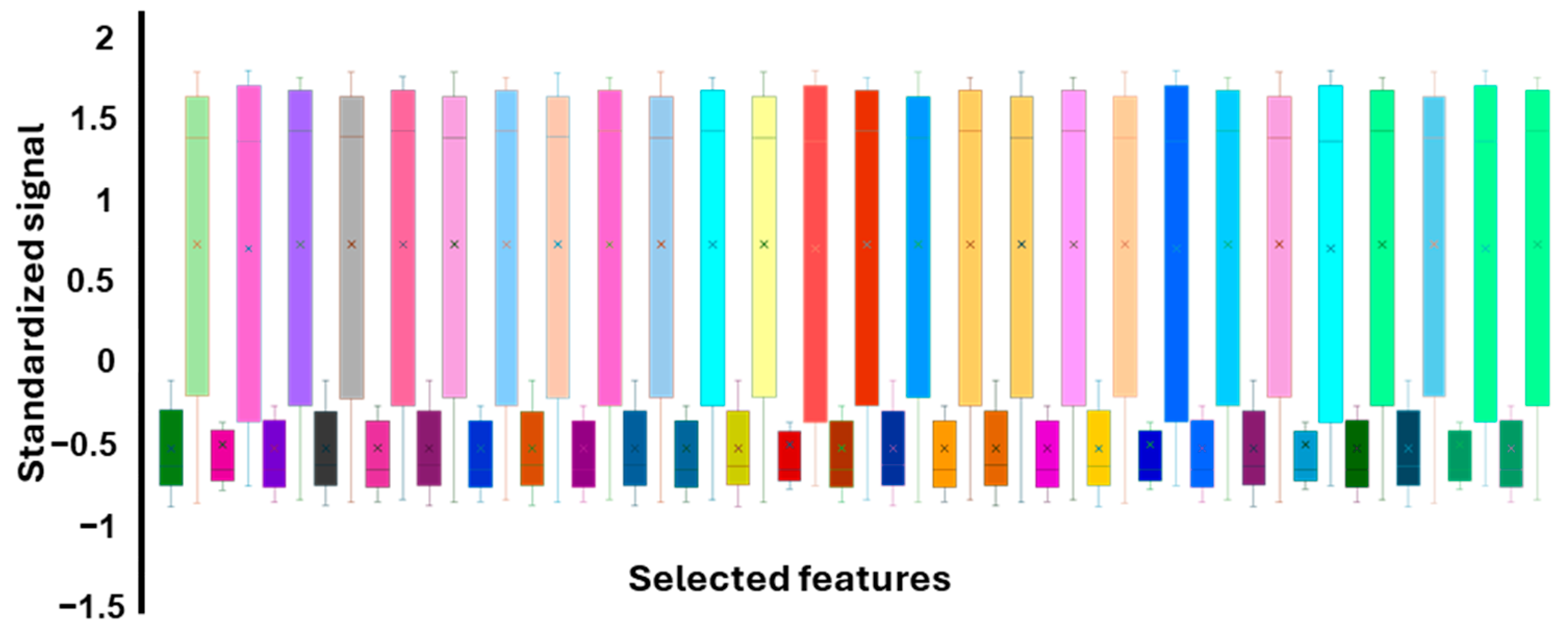
3.3. Feature Extraction
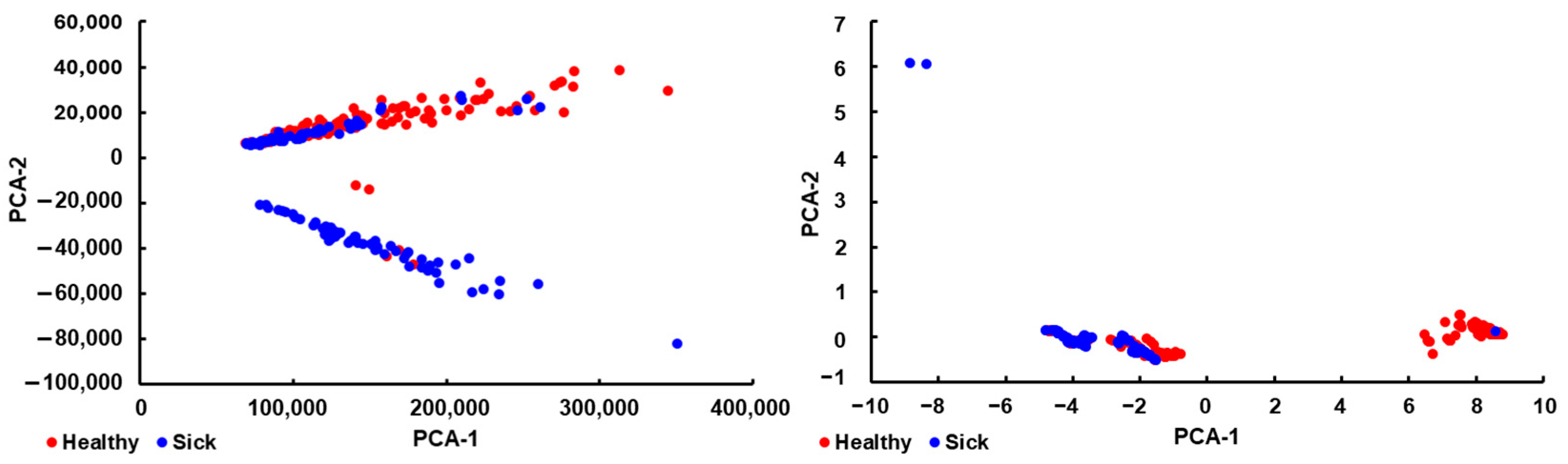
3.4. Model Selection
3.5. Model Optimization
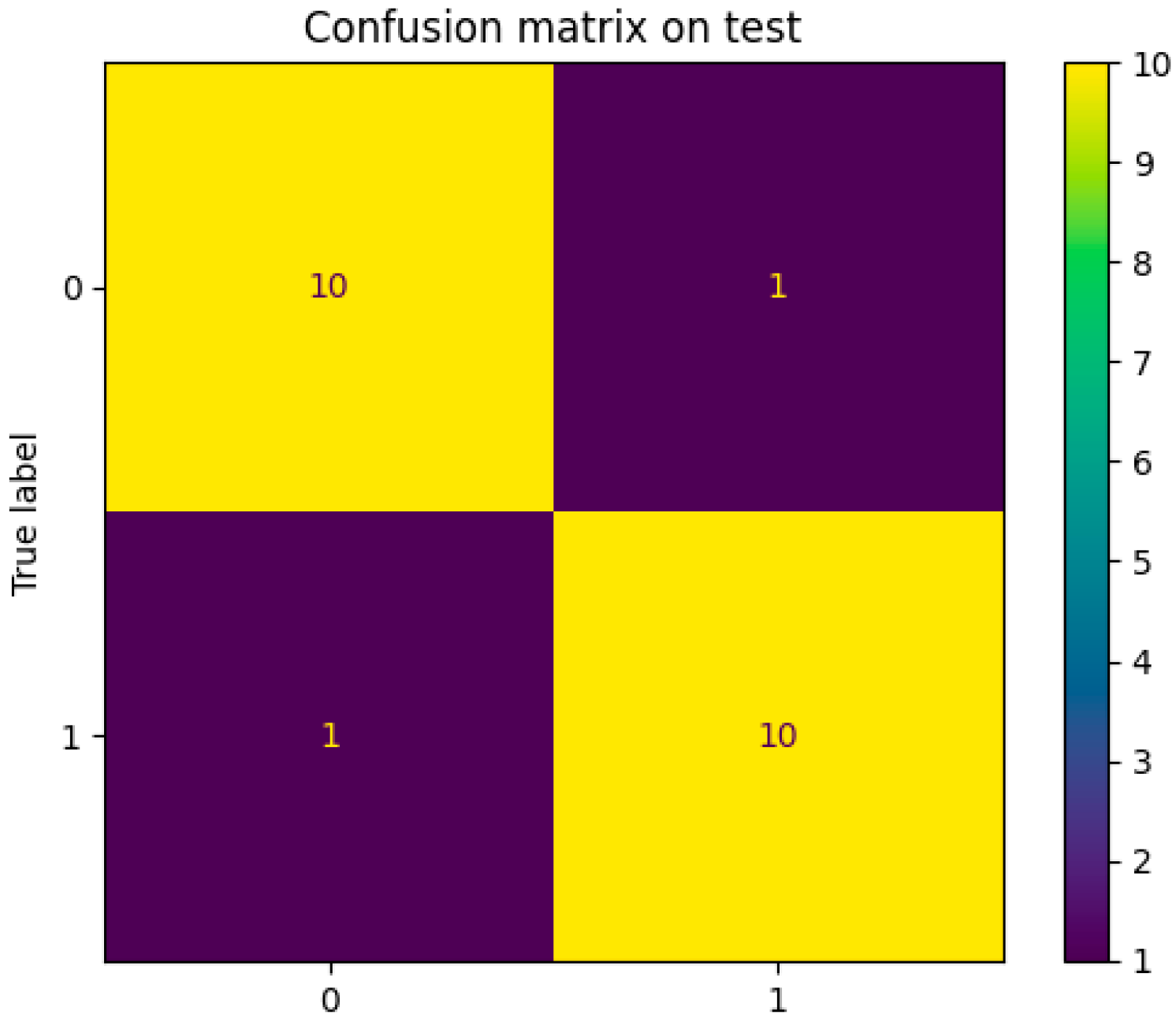
3.6. Model Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BC | breast cancer |
| VOCs | volatile organic compounds |
| EB | exhaled breath |
| EN | electronic nose |
| SVM | support vector machine |
References
- The World Health Organization. In Breast Cancer; The World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024.
- The Breast Cancer Research Foundation. In The Breast Cancer Statistics and Resources; Cancer Research Foundation: New York, NY, USA, 2024.
- Wilkinson, L.; Gathani, T. Understanding Breast Cancer as a Global Health Concern. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20211033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa Vieira, R.A.; Biller, G.; Uemura, G.; Ruiz, C.A.; Curado, M.P. Breast Cancer Screening in Developing Countries. Clinics 2017, 72, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulman, L.N.; Willett, W.; Sievers, A.; Knaul, F.M. Breast Cancer in Developing Countries: Opportunities for Improved Survival. J. Oncol. 2010, 2010, 595167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaglan, P.; Dass, R.; Duhan, M. Breast Cancer Detection Techniques: Issues and Challenges. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B 2019, 100, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guan, X.; Fan, Z.; Ching, L.-M.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, W.-M.; Liu, D.-X. Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Early Detection of Breast Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shermis, R.B.; Wilson, K.D.; Doyle, M.T.; Martin, T.S.; Merryman, D.; Kudrolli, H.; Brenner, R.J. Supplemental Breast Cancer Screening With Molecular Breast Imaging for Women With Dense Breast Tissue. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2016, 207, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.S.; Moon, W.K.; Chang, J.M.; Koo, H.R.; Kim, W.H.; Cho, N.; Yi, A.; La Yun, B.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.Y.; et al. Breast Cancer Detected with Screening US: Reasons for Nondetection at Mammography. Radiology 2014, 270, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dromain, C.; Thibault, F.; Diekmann, F.; Fallenberg, E.M.; Jong, R.A.; Koomen, M.; Hendrick, R.E.; Tardivon, A.; Toledano, A. Dual-Energy Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography: Initial Clinical Results of a Multireader, Multicase Study. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knogler, T.; Homolka, P.; Hoernig, M.; Leithner, R.; Langs, G.; Waitzbauer, M.; Pinker, K.; Leitner, S.; Helbich, T.H. Application of BI-RADS Descriptors in Contrast-Enhanced Dual-Energy Mammography: Comparison with MRI. Breast Care 2017, 12, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, G.L. Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Breast Cancer: A Literature Review and Future Perspectives. WJCO 2014, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jossinet, J. The Impedivity of Freshly Excised Human Breast Tissue. Physiol. Meas. 1998, 19, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laganà, F.; Prattico, D.; De Carlo, D.; Oliva, G.; Pullano, S.A.; Calcagno, S. Engineering Biomedical Problems to Detect Carcinomas: A Tomographic Impedance Approach. Eng 2024, 5, 1594–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krilaviciute, A.; Heiss, J.A.; Leja, M.; Kupcinskas, J.; Haick, H.; Brenner, H. Detection of Cancer through Exhaled Breath: A Systematic Review. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 38643–38657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley-Girvan, I.; Davis, S.W. Breath Based Volatile Organic Compounds in the Detection of Breast, Lung, and Colorectal Cancers: A Systematic Review. CBM 2017, 21, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Ditkoff, B.A.; Fisher, P.; Greenberg, J.; Gunawardena, R.; Kwon, C.S.; Rahbari-Oskoui, F.; Wong, C. Volatile Markers of Breast Cancer in the Breath. Breast J. 2003, 9, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Ditkoff, B.A.; Fisher, P.; Greenberg, J.; Gunawardena, R.; Kwon, C.S.; Tietje, O.; Wong, C. Prediction of Breast Cancer Using Volatile Biomarkers in the Breath. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2006, 99, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Saunders, C.; Hope, P.; Schmitt, P.; Wai, J. Volatile Biomarkers in the Breath of Women with Breast Cancer. J. Breath Res. 2010, 4, 026003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, G.; Gallimidi, Z.; Reiss, A.H.; Dovgolevsky, E.; Billan, S.; Abdah-Bortnyak, R.; Kuten, A.; Engel, A.; Shiban, A.; Tisch, U.; et al. Classification of Breast Cancer Precursors through Exhaled Breath. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 126, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, S. Breathing Out. ACS Cent. Sci. 2016, 2, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlata, S.; Finamore, P.; Meszaros, M.; Dragonieri, S.; Bikov, A. The Role of Electronic Noses in Phenotyping Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Biosensors 2020, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binson, V.A.; Subramoniam, M.; Sunny, Y.; Mathew, L. Prediction of Pulmonary Diseases With Electronic Nose Using SVM and XGBoost. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 20886–20895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudiño-Ochoa, A.; García-Rodríguez, J.A.; Ochoa-Ornelas, R.; Cuevas-Chávez, J.I.; Sánchez-Arias, D.A. Noninvasive Diabetes Detection through Human Breath Using TinyML-Powered E-Nose. Sensors 2024, 24, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binson, V.A.; Mathew, P.; Thomas, S.; Mathew, L. Detection of Lung Cancer and Stages via Breath Analysis Using a Self-Made Electronic Nose Device. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2024, 24, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daulton, E.; Wicaksono, A.N.; Tiele, A.; Kocher, H.M.; Debernardi, S.; Crnogorac-Jurcevic, T.; Covington, J.A. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) for the Non-Invasive Detection of Pancreatic Cancer from Urine. Talanta 2021, 221, 121604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Podmore, I. Current Challenges in Volatile Organic Compounds Analysis as Potential Biomarkers of Cancer. J. Biomark. 2015, 2015, 981458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, G.B.; Boshier, P.R.; Markar, S.R.; Romano, A. Accuracy and Methodologic Challenges of Volatile Organic Compound–Based Exhaled Breath Tests for Cancer Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, e182815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulejko, J.E.; McCulloch, M.; Jackson, J.; McKee, D.L.; Walker, J.C.; Solouki, T. Evidence for Cancer Biomarkers in Exhaled Breath. IEEE Sens. J. 2010, 10, 185–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markar, S.R.; Wiggins, T.; Antonowicz, S.; Chin, S.-T.; Romano, A.; Nikolic, K.; Evans, B.; Cunningham, D.; Mughal, M.; Lagergren, J.; et al. Assessment of a Noninvasive Exhaled Breath Test for the Diagnosis of Oesophagogastric Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Hakim, M.; Broza, Y.Y.; Billan, S.; Abdah-Bortnyak, R.; Kuten, A.; Tisch, U.; Haick, H. Detection of Lung, Breast, Colorectal, and Prostate Cancers from Exhaled Breath Using a Single Array of Nanosensors. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Zhang, D.; Liu, D. A Novel Medical E-Nose Signal Analysis System. Sensors 2017, 17, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elia, P.; Raizelman, S. Biomarkers for the Detection of Pre-Cancerous Stage of Cervical Dysplasia. J. Mol. Biomark. Diagn. 2015, 6, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurado, C.; Giménez, M.P.; Soriano, T.; Menéndez, M.; Repetto, M. Rapid Analysis of Amphetamine, Methamphetamine, MDA, and MDMA in Urine Using Solid-Phase Microextraction, Direct On-Fiber Derivatization, and Analysis by GC-MS. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2000, 24, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman-Saffar, O.; Boger, Z.; Libson, S.; Lieberman, D.; Gonen, R.; Zeiri, Y. Early Non-Invasive Detection of Breast Cancer Using Exhaled Breath and Urine Analysis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 96, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Peng, Y.; Duan, Y. Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Based on Breath Analysis: An Emerging Method. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2013, 87, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, C.; Turner, C. Breath Analysis in Disease Diagnosis: Methodological Considerations and Applications. Metabolites 2014, 4, 465–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röck, F.; Barsan, N.; Weimar, U. Electronic Nose: Current Status and Future Trends. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 705–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnowski, W.; Dymerski, T.; Gębicki, J.; Namieśnik, J. Electronic Noses in Medical Diagnostics. CMC 2019, 26, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A. Advances in Electronic-Nose Technologies for the Detection of Volatile Biomarker Metabolites in the Human Breath. Metabolites 2015, 5, 140–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yu, J.; Dong, D.; Yao, G.; Wei, G.; He, A.; Wu, H.; Zhu, H.; Huang, Z.; Tang, Z. E-Nose Based on a High-Integrated and Low-Power Metal Oxide Gas Sensor Array. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 380, 133289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovel, J.; Greiner, R. An Introduction to Machine Learning Approaches for Biomedical Research. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 771607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binson, V.A.; Thomas, S.; Subramoniam, M.; Arun, J.; Naveen, S.; Madhu, S. A Review of Machine Learning Algorithms for Biomedical Applications. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 52, 1159–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.; Took, C.C.; Seong, J.-K. Machine Learning in Biomedical Engineering. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2018, 8, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binson, V.A.; Subramoniam, M.; Mathew, L. Detection of COPD and Lung Cancer with Electronic Nose Using Ensemble Learning Methods. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 523, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-Vector Networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujitani, M.; Tanaka, Y. Cross-Validation, Bootstrap, and Support Vector Machines. Adv. Artif. Neural Syst. 2011, 2011, 302572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, I.; Barnes, P.J.; Loukides, S.; Sterk, P.J.; Högman, M.; Olin, A.-C.; Amann, A.; Antus, B.; Baraldi, E.; Bikov, A.; et al. A European Respiratory Society Technical Standard: Exhaled Biomarkers in Lung Disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1600965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, O. Scikit-Learn. In Machine Learning for Evolution Strategies; Studies in Big Data; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 20, pp. 45–53. ISBN 978-3-319-33381-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bergstra, J.; Komer, B.; Eliasmith, C.; Yamins, D.; Cox, D.D. Hyperopt: A Python Library for Model Selection and Hyperparameter Optimization. Comput. Sci. Discov. 2015, 8, 014008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Cruz-Ramos, J.A.; Huston, J.; Ornelas, O.; Pappas, N.; Pathak, S. Prediction of Breast Cancer Risk with Volatile Biomarkers in Breath. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 170, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barash, O.; Zhang, W.; Halpern, J.M.; Hua, Q.-L.; Pan, Y.-Y.; Kayal, H.; Khoury, K.; Liu, H.; Davies, M.P.A.; Haick, H. Differentiation Between Genetic Mutations of Breast Cancer by Breath Volatolomics. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 44864–44876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz De León-Martínez, L.; Rodríguez-Aguilar, M.; Gorocica-Rosete, P.; Domínguez-Reyes, C.A.; Martínez-Bustos, V.; Tenorio-Torres, J.A.; Ornelas-Rebolledo, O.; Cruz-Ramos, J.A.; Balderas-Segura, B.; Flores-Ramírez, R. Identification of Profiles of Volatile Organic Compounds in Exhaled Breath by Means of an Electronic Nose as a Proposal for a Screening Method for Breast Cancer: A Case-Control Study. J. Breath Res. 2020, 14, 046009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Peng, H.-Y.; Huang, C.-H. Breath Biopsy of Breast Cancer Using Sensor Array Signals and Machine Learning Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; Caires, A.O.; Borges, T.D.S.; Lima, A.M.D.S.; Silva, L.O.B.; Dos Santos, W.N.L. Robustness Evaluation in Analytical Methods Optimized Using Experimental Designs. Microchem. J. 2017, 131, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; He, T.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lee, C. Artificial Intelligence Enhanced Sensors—Enabling Technologies to next-Generation Healthcare and Biomedical Platform. Bioelectron. Med. 2023, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| C | 66 |
| Coef0 | 66 |
| Degree | 10 |
| Gamma | 2.5 |
| Tol | 0.02 |
| Parameter | Train | Validation |
|---|---|---|
| Recall | 0.80 ± 0.02 | 0.80 ± 0.11 |
| Precision | 0.95 ± 0.01 | 0.94 ± 0.06 |
| Accuracy | 0.89 ± 0.01 | 0.88 ± 0.06 |
| Specificity | 0.96 ± 0.01 | 0.95 ± 0.05 |
| Parameter | Test |
|---|---|
| Recall | 0.91 |
| Precision | 0.91 |
| Accuracy | 0.91 |
| Specificity | 0.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matana, Y.; Libson, S.; Amihood, B.; Boger, Z.; Lieberman, D.; Zeiri, O.; Zeiri, Y. Chemical Nose-Based Non-Invasive Detection of Breast Cancer Using Exhaled Breath. Sensors 2025, 25, 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072210
Matana Y, Libson S, Amihood B, Boger Z, Lieberman D, Zeiri O, Zeiri Y. Chemical Nose-Based Non-Invasive Detection of Breast Cancer Using Exhaled Breath. Sensors. 2025; 25(7):2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072210
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatana, Yosef, Shai Libson, Barak Amihood, Zvi Boger, David Lieberman, Offer Zeiri, and Yehuda Zeiri. 2025. "Chemical Nose-Based Non-Invasive Detection of Breast Cancer Using Exhaled Breath" Sensors 25, no. 7: 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072210
APA StyleMatana, Y., Libson, S., Amihood, B., Boger, Z., Lieberman, D., Zeiri, O., & Zeiri, Y. (2025). Chemical Nose-Based Non-Invasive Detection of Breast Cancer Using Exhaled Breath. Sensors, 25(7), 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072210







