Multi-GNSS Large Areas PPP-RTK Performance During Ionosphere Anomaly Periods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. GNSS Observation Equations
2.2. Positioning with Atmospheric Accuracy Constraint
| Items | Strategy | |
|---|---|---|
| Service-Side | User-Side | |
| Data | GPS + Galileo + BDS double-frequency with 30 s interval | |
| Elevation cutoff | 7° | |
| Satellite orbit and clock | GFZ real-time streams products [37] | |
| Tropospheric ZWD delay | Saastamoinen + VMF3 + GPT3 + random work processing [38] | Three nearby stations interpolated |
| Tropospheric ZHD delay | Saastamoinen + VMF3 + GPT3 | |
| Ionospheric delay | Estimated as white noise | Three nearby stations interpolated |
| Satellite and receiver antenna | Igs20.atx | |
| Phase wind-up | Corrected [39] | |
| Phase ambiguity | WL + NL using LAMBDA to fix [40] | |
| Station displacement | Solid earth tides, ocean tides, and pole tide displacements corrected according to IERS 2010 [41] | |
| Differential Code Biases | CAS DSB (Differential code biases) [42] | |
| Parameter estimator | Kalman filter | |
3. Observation Data and Processing Strategies
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Processing Strategy
4. Experimental Validation
4.1. UPD Estimation
4.2. Atmospheric Delay Performance Evaluation
5. Positioning Validation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zumberge, J.; Heflin, M.; Jefferson, D.; Watkins, M.; Webb, F. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar]
- Psychas, D.; Teunissen, P.J.G.; Verhagen, S. A Multi-Frequency Galileo PPP-RTK Convergence Analysis with an Emphasis on the Role of Frequency Spacing. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, C.; Wang, A.; Song, Z.; Zhou, J. Models and performance of SBAS and PPP of BDS. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadas, T.; Bosy, J. IGS RTS precise orbits and clocks verification and quality degradation over time. GPS Solut. 2014, 19, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhao, Q.; Verhagen, S.; Psychas, D.; Liu, X. Assessing the Performance of Multi-GNSS PPP-RTK in the Local Area. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yao, W.; Tu, R.; Du, Y.; Liu, M. Performance Assessment of Multi-GNSS PPP Ambiguity Resolution with LEO-Augmentation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmierski, K.; Zajdel, R.; Sośnica, K. Evolution of orbit and clock quality for real-time multi-GNSS solutions. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; He, Y.; Yi, W.; Song, W.; Cao, C.; Chen, M. Method for evaluating real-time GNSS satellite clock offset products. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. Improving multi-GNSS ultra-rapid orbit determination for real-time precise point positioning. J. Geod. 2018, 93, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Chen, J.; Zuo, X.; Mei, D.; Liu, W. Investigating GNSS PPP–RTK with external ionospheric constraints. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, H. Regional Real-Time between-Satellite Single-Differenced Ionospheric Model Establishing by Multi-GNSS Single-Frequency Observations: Performance Evaluation and PPP Augmentation. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z. Real-time GNSS precise point positioning for low-cost smart devices. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wübbena, G.; Schmitz, M.; Bagge, A. PPP-RTK: Precise point positioning using state-space representation in RTK net-works. In Proceedings of the 18th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2005), Long Beach, CA, USA, 13–16 September 2005; pp. 2584–2594. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, B.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, P.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. A new large-area hierarchical PPP-RTK service strategy. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabandeh, A.; Teunissen, P.J.G. An analytical study of PPP-RTK corrections: Precision, correlation and user-impact. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 1109–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Khodabandeh, A. PPP–RTK theory for varying transmitter frequencies with satellite and terrestrial positioning applications. J. Geod. 2020, 96, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Teunissen, P.J.G.; Odijk, D. A Novel Un-differenced PPP-RTK Concept. J. Navig. 2011, 64, S180–S191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D.; Khodabandeh, A.; Nadarajah, N.; Choudhury, M.; Zhang, B.; Li, W.; Teunissen, P.J.G. PPP-RTK by means of S-system theory: Australian network and user demonstration. J. Spat. Sci. 2016, 62, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D.; Verhagen, S.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Medium-Distance GPS Ambiguity Resolution with Controlled Failure Rate. In Geodesy for Planet Earth, Proceedings of the International Association of Geodesy Symposia, Kobe, Japan, 30 July–4 August 2017; Kenyon, S., Pacino, M., Marti, U., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 136, pp. 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, Z.; Duan, B.; Hugentobler, U.; Wang, L. GPS and GLONASS observable-specific code bias estimation: Comparison of solutions from the IGS and MGEX networks. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, T.; Hou, P. Ionosphere-weighted undifferenced and uncombined PPP-RTK: Theoretical models and experimental results. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, T.; Yuan, Y. GPS receiver phase biases estimable in PPP-RTK networks: Dynamic characterization and impact analysis. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 659–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y. PPP-RTK based on undifferenced and uncombined observations: Theoretical and practical aspects. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Cui, B.; Li, P.; Bisnath, S.; Zheng, K. Exploring the role of PPP–RTK network configuration: A balance of server budget and user performance. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabandeh, A. Single-station PPP-RTK: Correction latency and ambiguity resolution performance. J. Geod. 2021, 95, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Zeng, R.; Guo, J. Assessing all-frequency GPS/Galileo/BDS PPP-RTK in GNSS challenging environments. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Factor graph-based PPP-RTK for accurate and robust positioning in urban environments. J. Geod. 2024, 98, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hou, P.; Zha, J.; Liu, T. PPP–RTK functional models formulated with undifferenced and uncombined GNSS observtions. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivavaraprasad, G.; Ratnam, D.V.; Padmaja, R.S. Detection of ionospheric anomalies during intense space weather over a low-latitude GNSS station. Acta Geod. Geophys. 2017, 52, 535–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Cui, B.; Hu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. PPP-RTK considering the ionosphere uncertainty with cross-validation. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, M.; Panda, S.K.; Dodo, J.D. Assessment of long-term impact of solar activity on the ionosphere over an African equatorial GNSS station. Earth Sci. Inform. 2022, 15, 2109–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamba, T.M.; Danskin, D.W.; Nndanganeni, R.R.; Tshisaphungo, M. Space weather impacts on the ionosphere over the southern African mid-latitude region. Earth Planets Space 2023, 75, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbey, I. NASA, NOAA: Sun Reaches Maximum Phase in 11-Year Solar Cycle. Nasa.gov. 15 October 2024. Available online: https://science.nasa.gov/science-research/heliophysics/nasa-noaa-sun-reaches-maximum-phase-in-11-year-solar-cycle/ (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Ge, M.; Gendt, G.; Rothacher, M.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Resolution of GPS carrier-phase ambiguities in Precise Point Positioning (PPP) with daily observations. J. Geod. 2008, 82, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Chai, H.; Xiao, G.; Wang, M.; Yin, X.; Chong, Y. A method for undifferenced and uncombined PPP ambiguity resolution based on IF FCB. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 66, 2888–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. Calibrating receiver-type-dependent wide-lane uncalibrated phase delay biases for PPP integer ambiguity resolution. J. Geod. 2021, 95, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Nischan, T.; Bradke, M. Multi-GNSS Rapid Orbit- Clock-& EOP-Product Series. GFZ Data Services 2017. Potsdam. Available online: https://dataservices.gfz-potsdam.de/panmetaworks/showshort.php?id=escidoc:2563890 (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Saastamoinen, J. Contributions to the Theory of Atmospheric Refraction. Bull. Géodésique 1972, 105, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, J.; Möller, G.; Schindelegger, M.; Pain, G.; Weber, R. Development of an improved empirical model for slant delays in the troposphere (GPT2w). GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.T.; Wu, S.C.; Hajj, G.A.; Bertiger, W.I.; Lichten, S.M. Effects of antenna orientation on GPS carrier phase. Manuscripta Geod. 1993, 18, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, G.; Luzum, B. (Eds.) IERS Conventions; IERS Technical Note; Verlag des Bundesamts für Kartographie und Geodäsie: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2010; Volume 36, p. 179. ISBN 3-89888-989-6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Z.; Montenbruck, O.; Tan, B. Determination of differential code biases with multi-GNSS observations. J. Geod. 2015, 90, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherniak, I.; Krankowski, A.; Zakharenkova, I. ROTI Maps: A new IGS ionospheric product characterizing the ionospheric irregularities occurrence. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Hancock, C.M.; Roberts, G.W.; Wang, Q. Analysis on the ionospheric scintillation monitoring performance of ROTI extracted from GNSS observations in high-latitude regions. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzka, J.; Stolle, C.; Yamazaki, Y.; Bronkalla, O.; Morschhauser, A. The Geomagnetic Kp Index and Derived Indices of Geomagnetic Activity. Space Weather 2021, 19, e2020SW002641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Shi, C.; Lou, Y.; Liu, J. Ionospheric effects in uncalibrated phase delay estimation and ambiguity-fixed PPP based on raw observable model. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
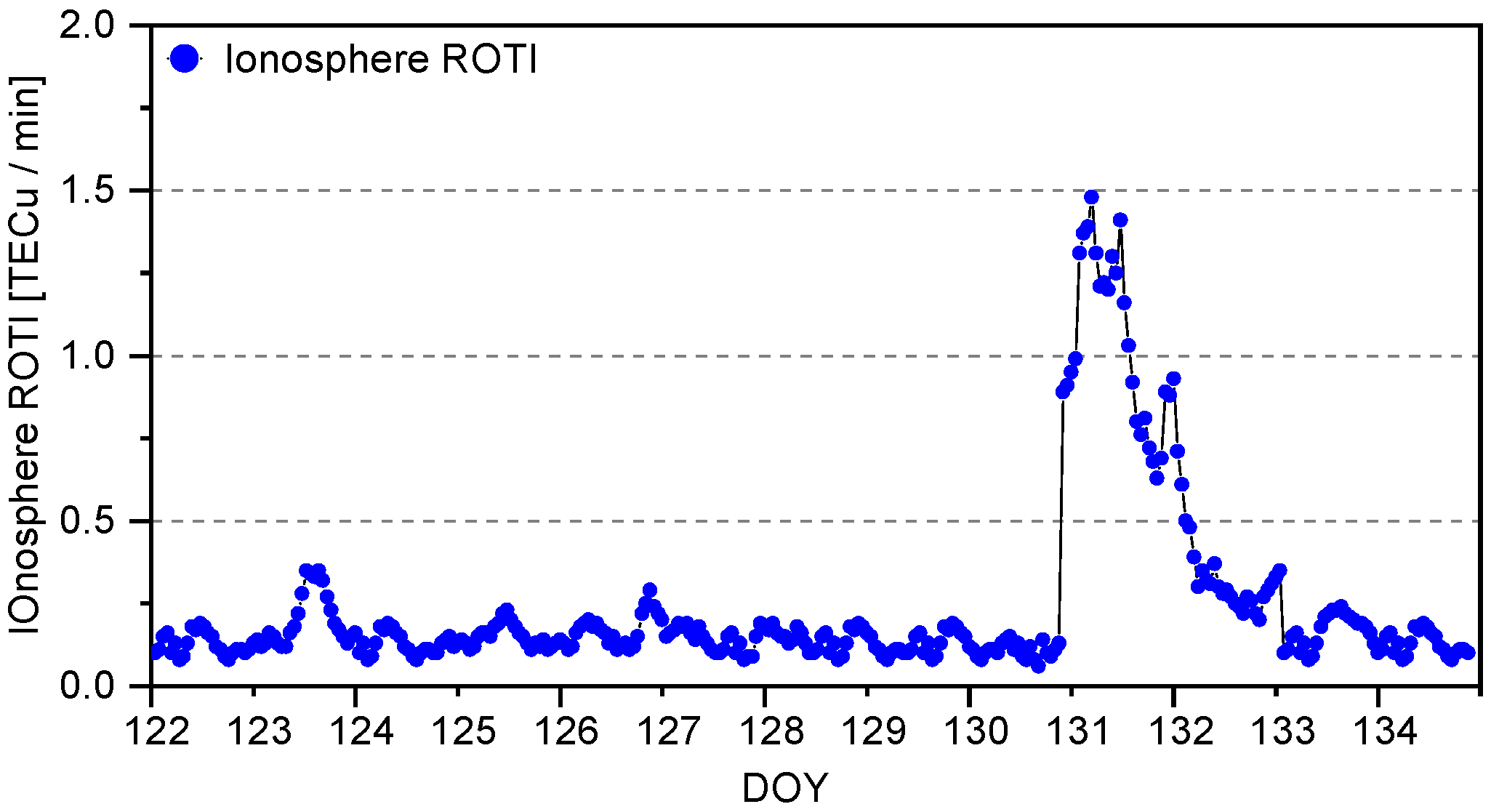

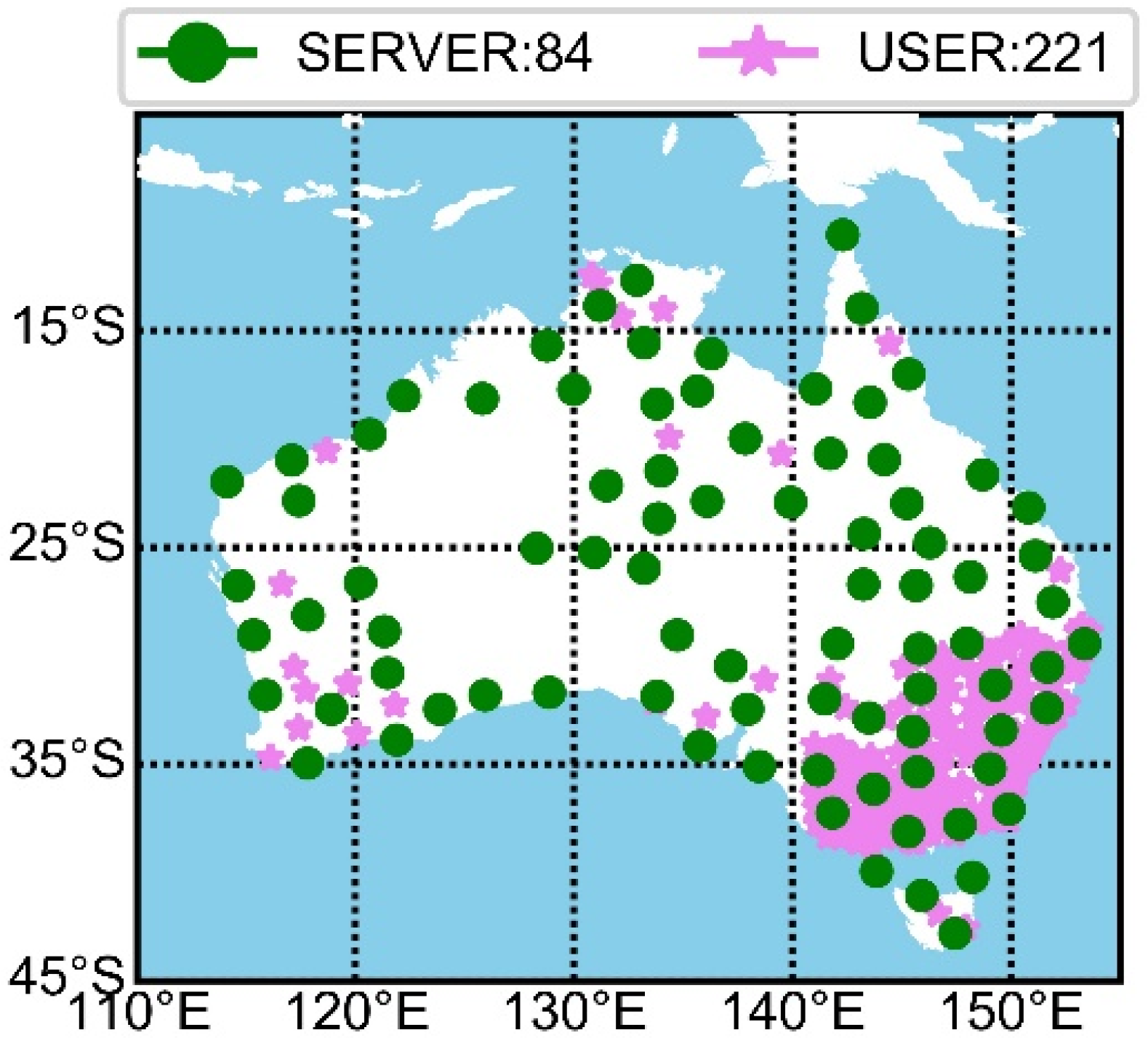
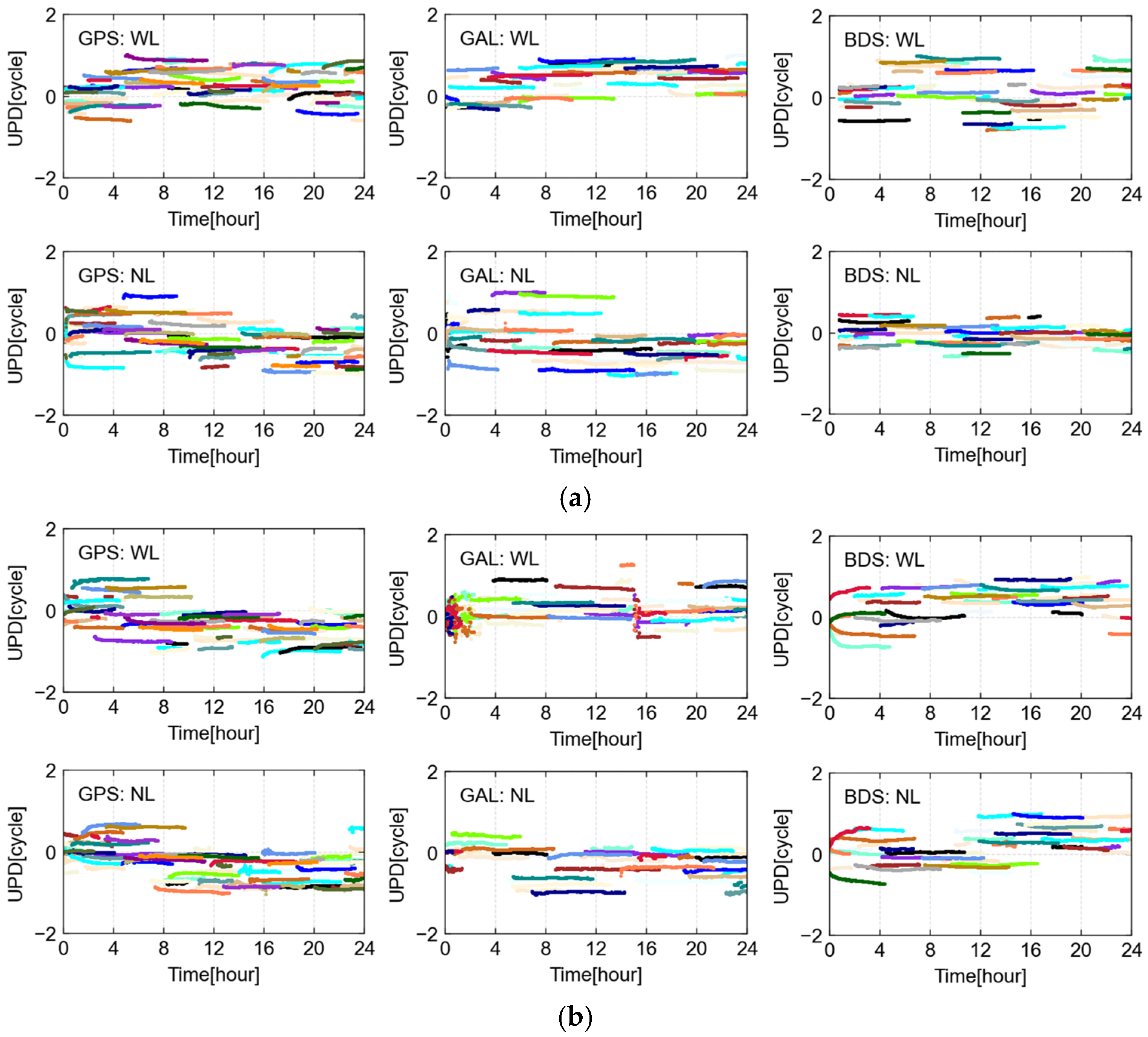
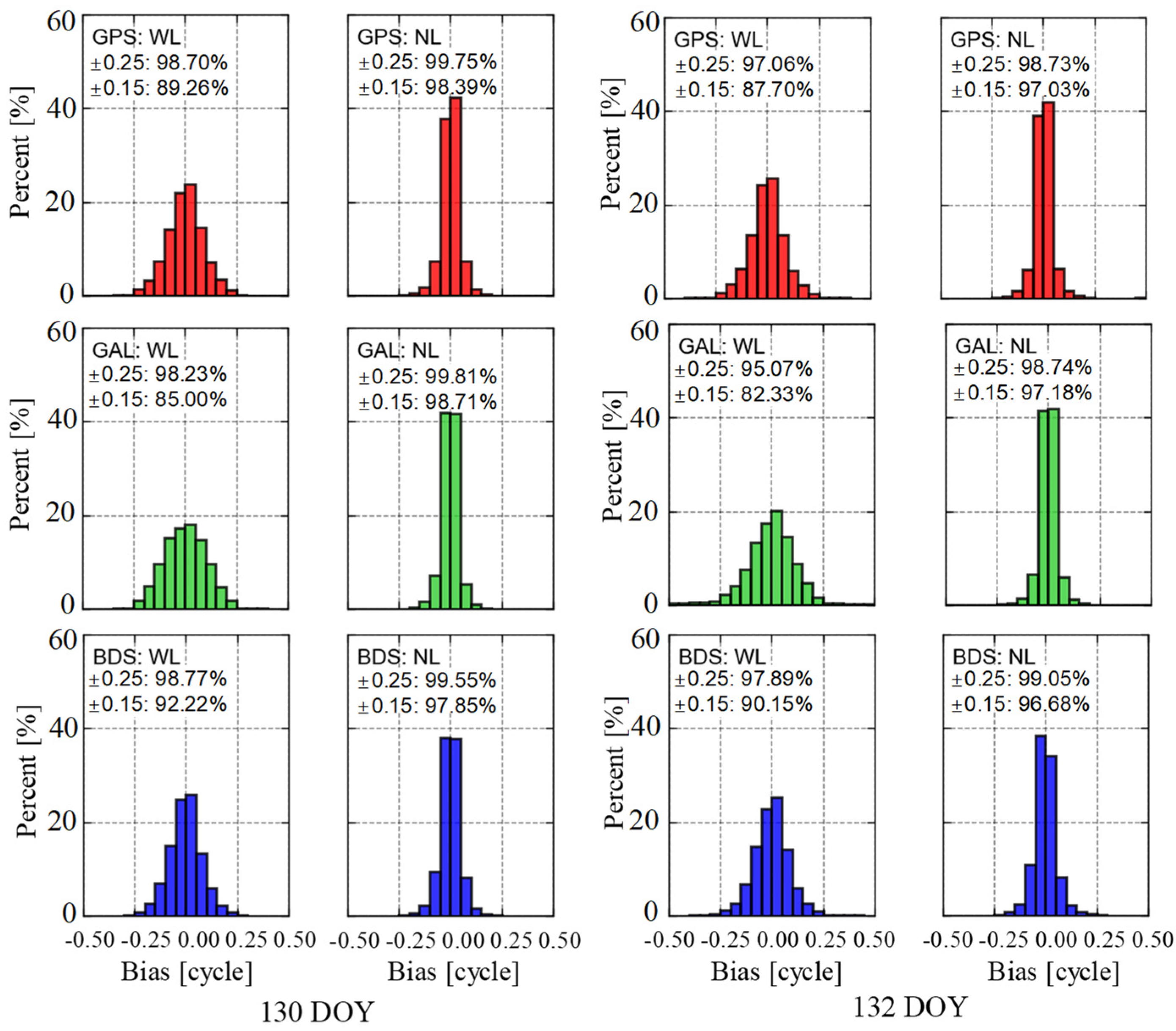

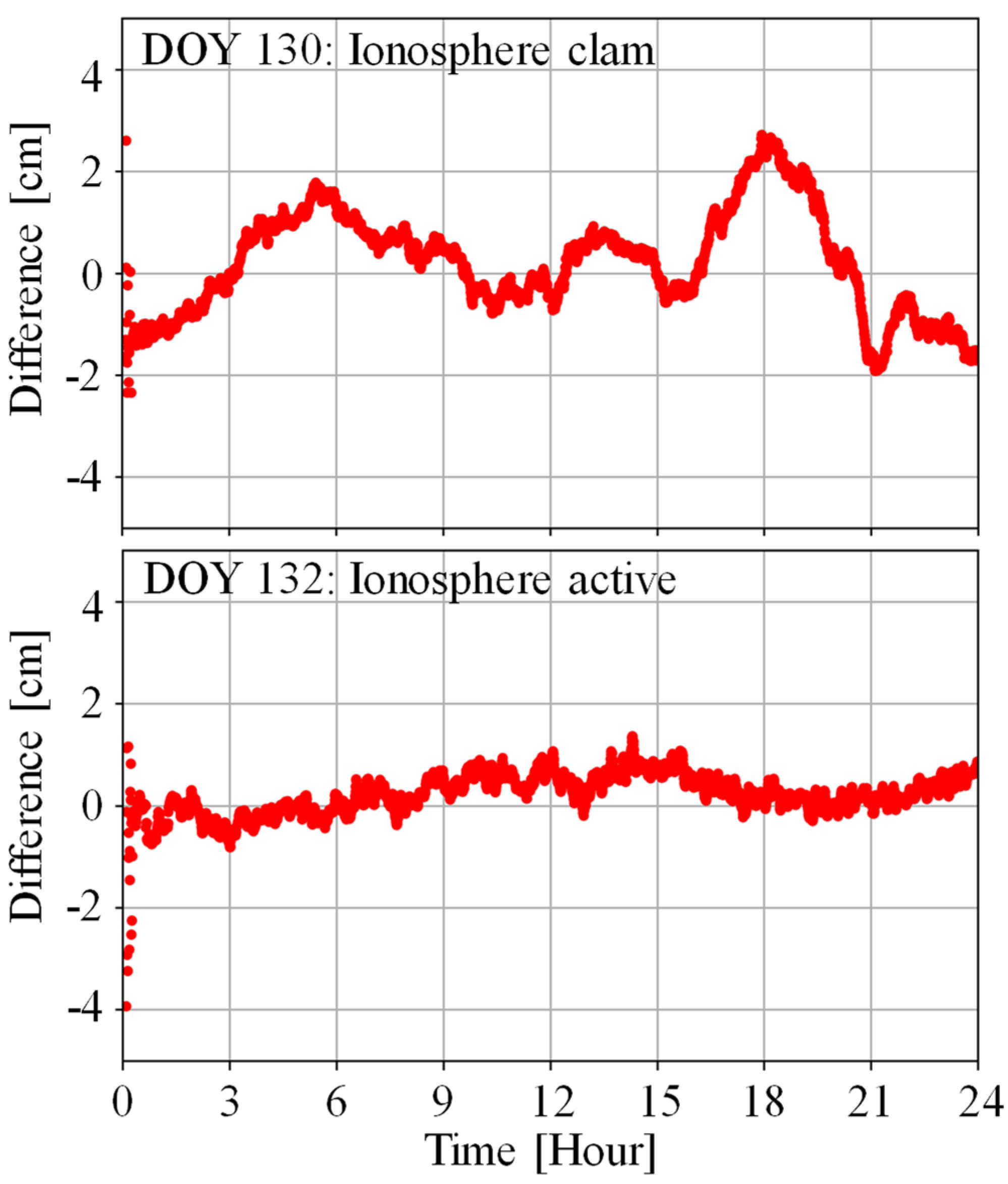

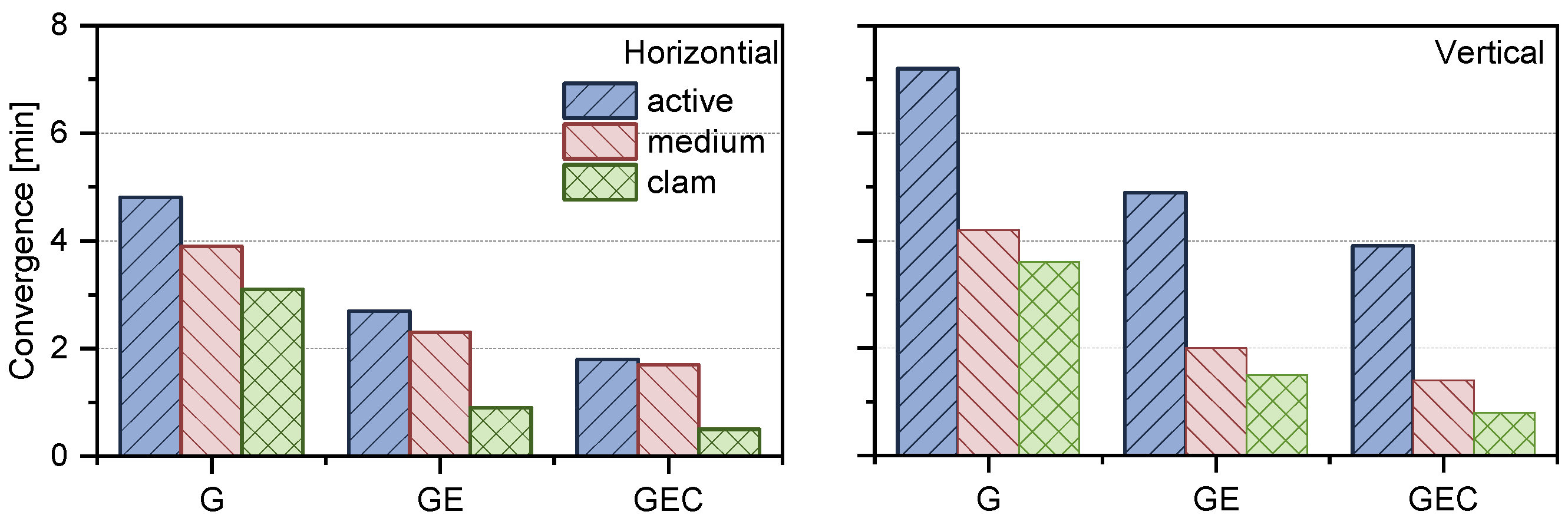
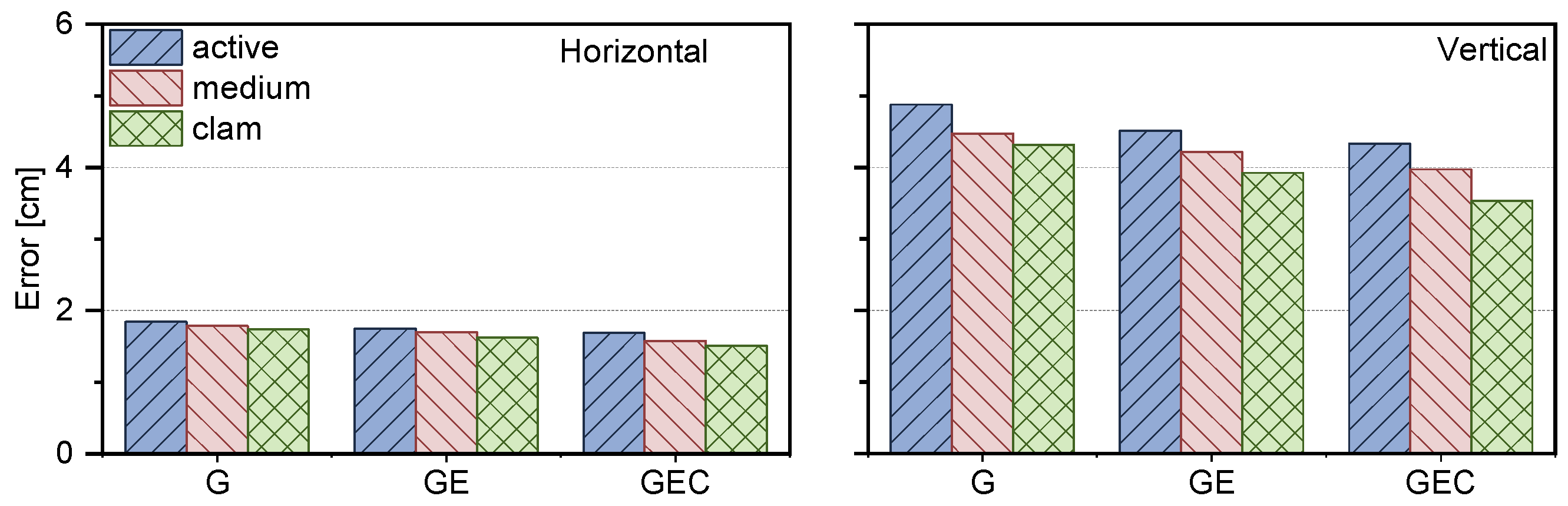
| Type | Calm [cm] | Medium | Active [cm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ionosphere | 4.97 | 7.83 | 13.86 |
| Troposphere | 1.01 | 1.15 | 1.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Yang, G.; Huang, R.; Li, M.; Zhu, M. Multi-GNSS Large Areas PPP-RTK Performance During Ionosphere Anomaly Periods. Sensors 2025, 25, 2200. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072200
Wang Z, Yang G, Huang R, Li M, Zhu M. Multi-GNSS Large Areas PPP-RTK Performance During Ionosphere Anomaly Periods. Sensors. 2025; 25(7):2200. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072200
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhu, Guangbin Yang, Rui Huang, Man Li, and Menglan Zhu. 2025. "Multi-GNSS Large Areas PPP-RTK Performance During Ionosphere Anomaly Periods" Sensors 25, no. 7: 2200. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072200
APA StyleWang, Z., Yang, G., Huang, R., Li, M., & Zhu, M. (2025). Multi-GNSS Large Areas PPP-RTK Performance During Ionosphere Anomaly Periods. Sensors, 25(7), 2200. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072200






