Exploring the Synergistic Effects of MoS2 and PVDF for Advanced Piezoelectric Sensors: A First-Principles Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of MoS2/PVDF Composite Nanofiber Film
2.2.2. Preparation of MoS2/PVDF Composite Sensor
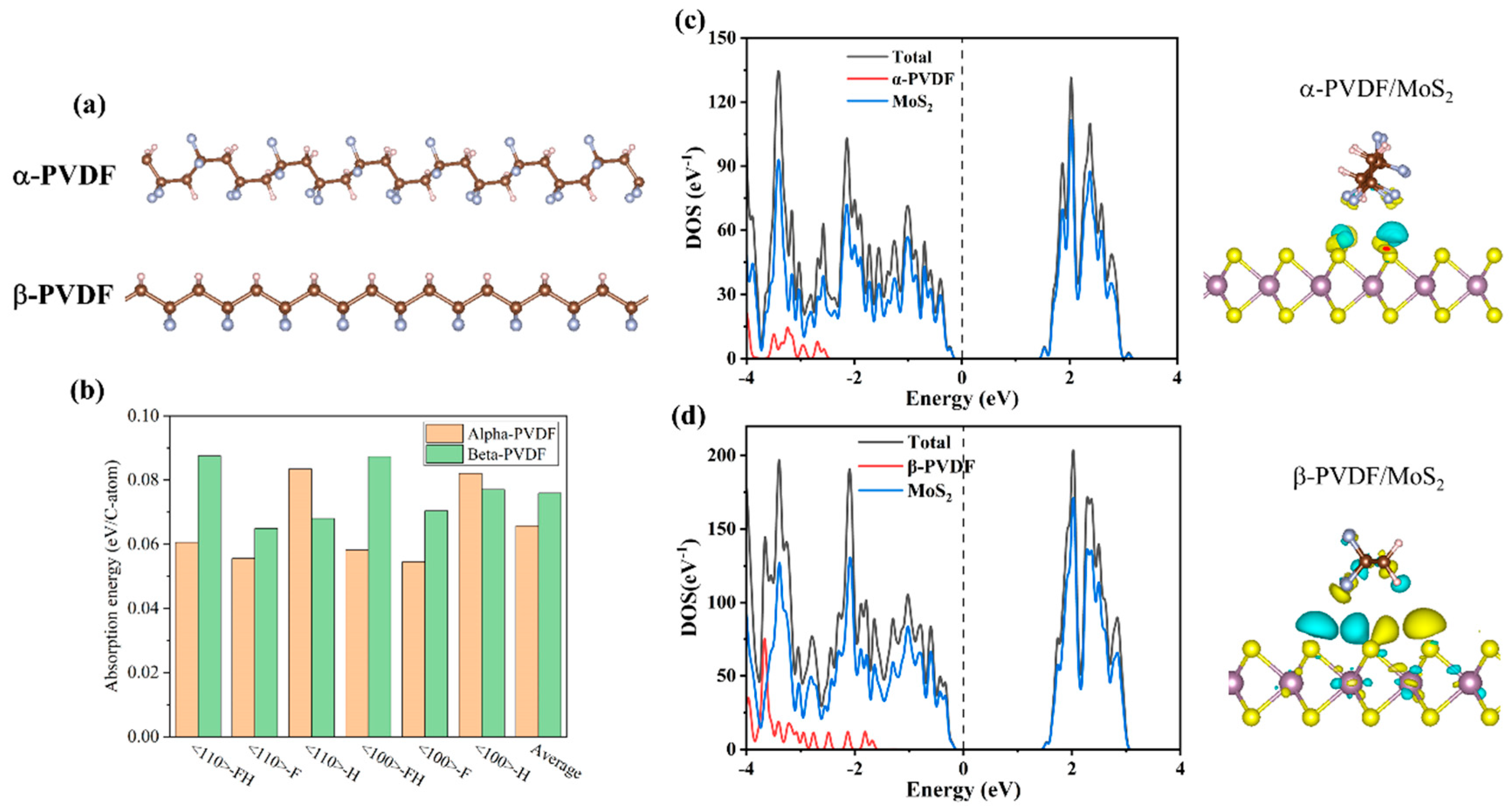
2.2.3. Density Functional Theory Calculation
2.2.4. Characterization and Testing
3. Results and Discussion
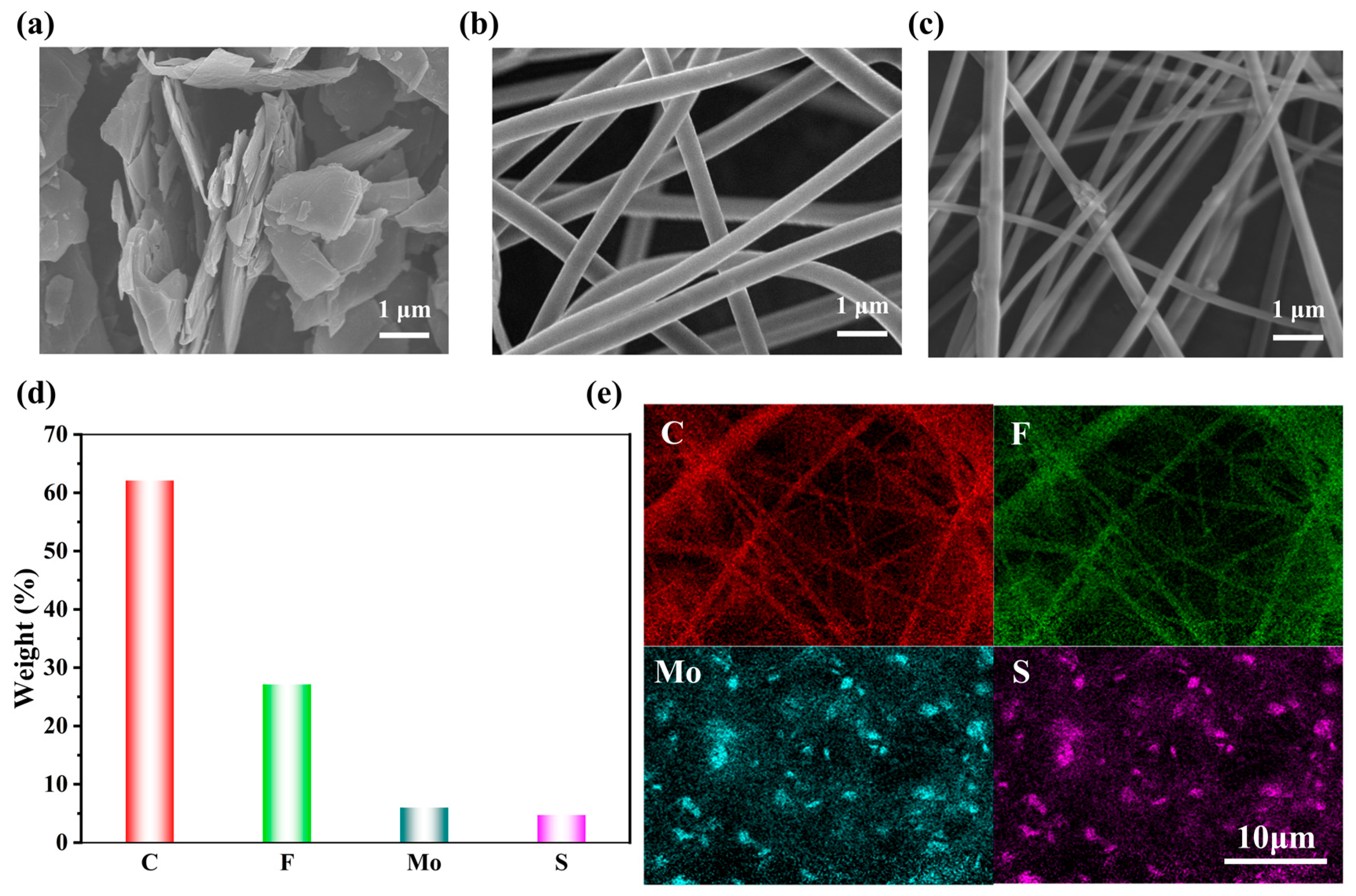
3.1. Morphology and Structure of MoS2/PVDF Composite Nanofiber Film
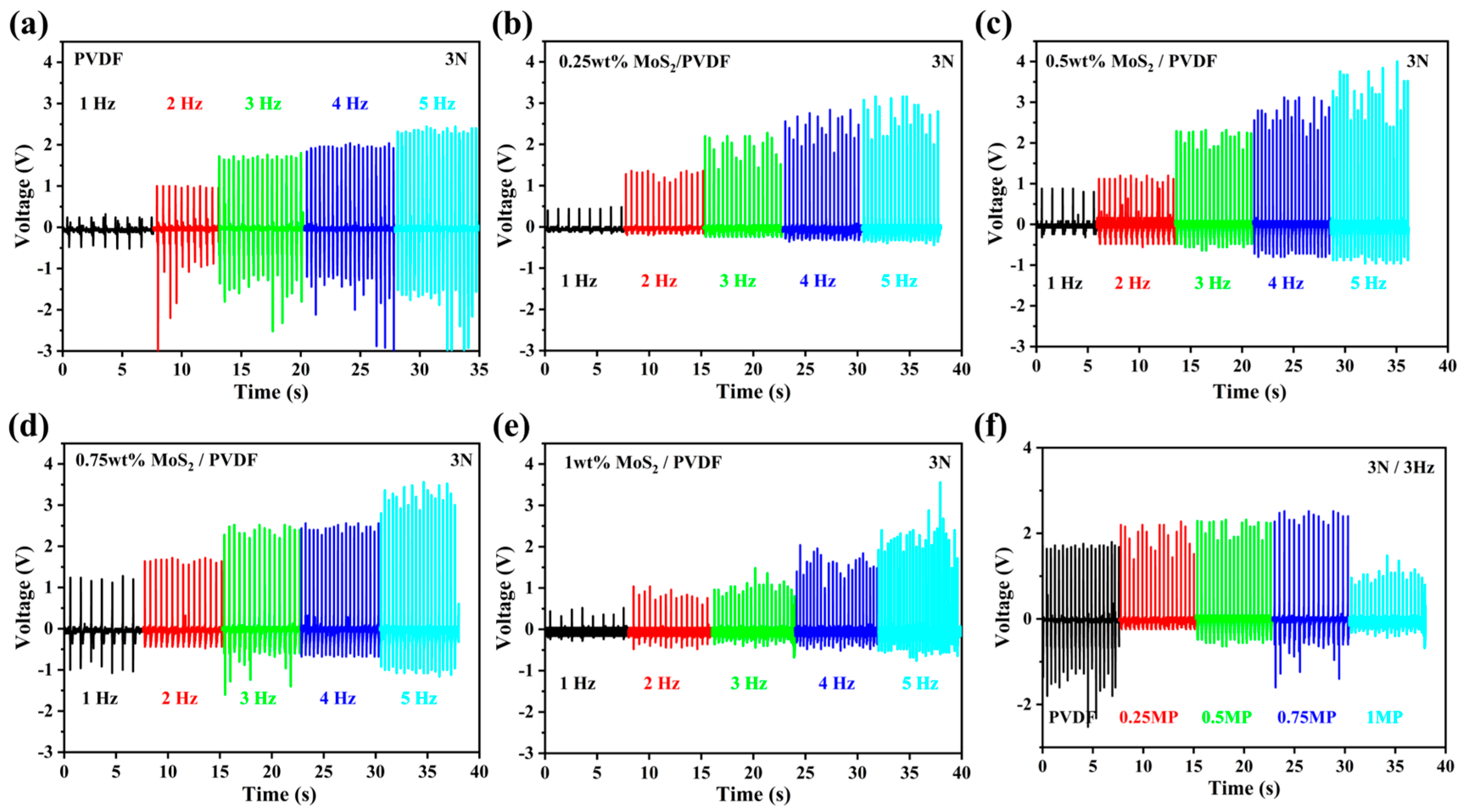
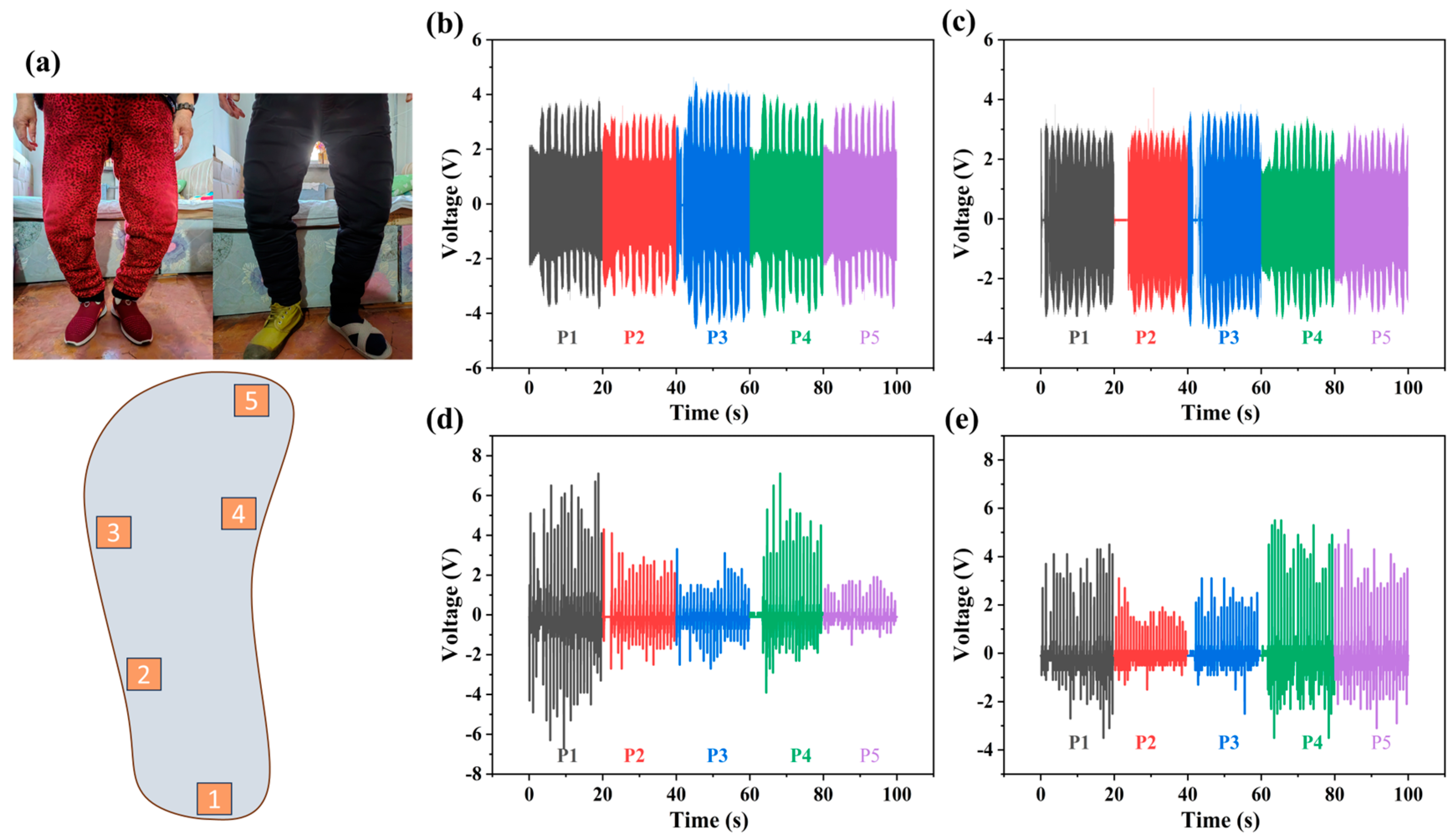
3.2. Piezoelectric Properties of MoS2/PVDF Sensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, W.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Sensing in Wearable Electronics─A Paradigm Shift Technology. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 12105–12134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, L.; Liang, F.; Li, M.; Yabuta, Y.; Iqbal, M.A.; Mayakrishnan, G.; Shi, J.; Kim, I.S. Flexible Piezoelectric Sensor Based on Two-Dimensional Topological Network of PVDF/DA Composite Nanofiber Membrane. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2024, 6, 1212–1228. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, S.; Cha, S.N.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, J.M.; Chou, L.J.; Wang, Z.L. A Hybrid Piezoelectric Structure for Wearable Nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Wu, W.; Guo, R.; Yuan, D.; Das, S.; Wang, Z.L. Wafer-Scale High-Throughput Ordered Growth of Vertically Aligned ZnO Nanowire Arrays. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3414–3419. [Google Scholar]
- Le, A.T.; Ahmadipour, M.; Pung, S.-Y. A review on ZnO-based piezoelectric nanogenerators: Synthesis, characterization techniques, performance enhancement and applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 844, 156172. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.; Jung, H.; Baek, C.; Hwang, G.-T.; Ryu, J.; Yoon, D.; Yoo, J.; Park, K.-I.; Kim, J.H. All-inkjet-printed flexible piezoelectric generator made of solvent evaporation assisted BaTiO3 hybrid material. Nano Energy 2017, 41, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, D.; Sogen, S.; Suzuki, H. Intrinsic Piezoelectricity of PZT. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2024, 6, 6384–6390. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Han, X.; Shen, Q.-D. PVDF-Based Ferroelectric Polymers in Modern Flexible Electronics. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2017, 3, 1600460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepelin, N.A.; Glushenkov, A.M.; Lussini, V.C.; Fox, P.J.; Dicinoski, G.W.; Shapter, J.G.; Ellis, A.V. New developments in composites, copolymer technologies and processing techniques for flexible fluoropolymer piezoelectric generators for efficient energy harvesting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1143–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Hang, G.; Duan, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z. Recent progress on flexible poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based piezoelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting and self-powered electronic applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 193, 114285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairagi, S.; Ali, S.W. Investigating the role of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in the piezoelectric performance of a PVDF/KNN-based electrospun nanogenerator. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 4876–4886. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Qing, X. A flexible capacitive sensor based on the electrospun PVDF nanofiber membrane with carbon nanotubes. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 299, 111579. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Lee, D.; Oh, J.; Si, H.; Kim, K. Synergy of Polydopamine-Assisted Additive Modification and Hierarchical-Morphology Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Nanofiber Mat for Ferroelectric-Assisted Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2024, 6, 1910–1926. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Wan, L.; Li, L.; Li, P. High-Performance Piezoelectric Nanogenerator of BTO-PVDF Nanofibers for Wearable Sensing. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2024, 45, 2300619. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, H. Porous, multi-layered piezoelectric composites based on highly oriented PZT/PVDF electrospinning fibers for high-performance piezoelectric nanogenerators. J. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 331–344. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, M.; Wang, J.; Su, L.; Xin, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Luan, X.; Chen, L.; Yao, Z. Versatile Lamellar Wrap-Structured PVDF/PZT/CNTs Piezoelectric Sensor for Road Traffic Information Sensing, Monitoring, and Energy Harvesting. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154554. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Fan, J. Piezoelectric Properties of Three Types of PVDF and ZnO Nanofibrous Composites. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2021, 3, 160–171. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, T.; Tian, G.; Lan, B.; Deng, W.; Tang, L.; Ao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, W.; Ren, X.; et al. Spatially Confined MXene/PVDF Nanofiber Piezoelectric Electronics. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2024, 6, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Yu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, D.; Wu, M. A core-shell structured barium titanate nanoparticles for the enhanced piezoelectric performance of wearable nanogenerator. Appl. Energy 2023, 351, 121835. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, K. A review on MoS2 structure, preparation, energy storage applications and challenges. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 998, 174916. [Google Scholar]
- Kresse, G.; Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Hafner, J. Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöchl, P.E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 17953–17979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, P.; Lopes, A.C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): Determination, processing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.H.; Singh, S.; Khare, N. Design of flexible PVDF/NaNbO3/RGO nanogenerator and understanding the role of nanofillers in the output voltage signal. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 149, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pan, H.; Xie, G.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, C.; Su, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tai, H. Flexible piezoelectric pressure sensor based on polydopamine-modified BaTiO3/PVDF composite film for human motion monitoring. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 301, 111789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Ha, J.-W.; Lee, S.G.; Sohn, E.-H.; Park, I.J.; Kang, H.S.; Yi, G.-R. Fluorinated Titania Nanoparticle-Induced Piezoelectric Phase Transition of Poly(vinylidene fluoride). Langmuir 2019, 35, 8816–8822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Choudhary, A.; Garg, A. Flexible and Robust Piezoelectric Polymer Nanocomposites Based Energy Harvesters. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 2793–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Deng, P.; Yuan, S.; Nie, Y.; He, B.; Xing, L.; Zhang, Y. CuO/PVDF nanocomposite anode for a piezo-driven self-charging lithium battery. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2615–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Pan, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, X.; Liu, J.; Zhai, J.; Xu, J. Three-dimensional polypyrrole induced high-performance flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators for mechanical energy harvesting. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 219, 109260. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.; Lei, R.; Dou, H.; Wu, Z.; Lu, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, W.; Rezakazemi, M.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; et al. Sweat permeable and ultrahigh strength 3D PVDF piezoelectric nanoyarn fabric strain sensor. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, F.; Cheng, Z.; Raad, R.; Xi, J.; Foroughi, J. Piezofibers to smart textiles: A review on recent advances and future outlook for wearable technology. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 9496–9522. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Wang, J.; Li, A.; Ma, Q.; Feng, S.; Ran, B.; Zhang, L. Exploring the Synergistic Effects of MoS2 and PVDF for Advanced Piezoelectric Sensors: A First-Principles Approach. Sensors 2025, 25, 2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072085
Li R, Wang J, Li A, Ma Q, Feng S, Ran B, Zhang L. Exploring the Synergistic Effects of MoS2 and PVDF for Advanced Piezoelectric Sensors: A First-Principles Approach. Sensors. 2025; 25(7):2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072085
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Rui, Juqi Wang, Aolin Li, Quanbin Ma, Shi Feng, Bo Ran, and Lingling Zhang. 2025. "Exploring the Synergistic Effects of MoS2 and PVDF for Advanced Piezoelectric Sensors: A First-Principles Approach" Sensors 25, no. 7: 2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072085
APA StyleLi, R., Wang, J., Li, A., Ma, Q., Feng, S., Ran, B., & Zhang, L. (2025). Exploring the Synergistic Effects of MoS2 and PVDF for Advanced Piezoelectric Sensors: A First-Principles Approach. Sensors, 25(7), 2085. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25072085





