Methane Concentration Inversion Based on Multi-Feature Fusion and Stacking Integration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
2.3. Stacking Ensemble Learning Model for Methane Concentration Inversion
2.4. Base Learner
2.5. Meta-Learner
2.6. Model Evaluation Metrics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Factor Selection for MFF-SEM Model
3.3. Accuracy Analysis and Comparison Between Stacking Model and Other Single Models
3.4. Seasonal Analysis of Methane Concentrations
3.5. Generalization Experiment
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The proposed MFF-SEM ensemble learning model effectively utilizes four base models (XGBoost, RF, LightGBM, and GBDT) and a Lasso meta-model in series-parallel cascade learning to capture different feature representations and pattern expressions from the original data. Through complementary advantages of multiple models, it thoroughly explores the intrinsic associations between multiple features and methane concentrations, achieving the best inversion performance with R2 of 0.9747, RMSE of 2.9294, and MAE of 1.5299.
- (2)
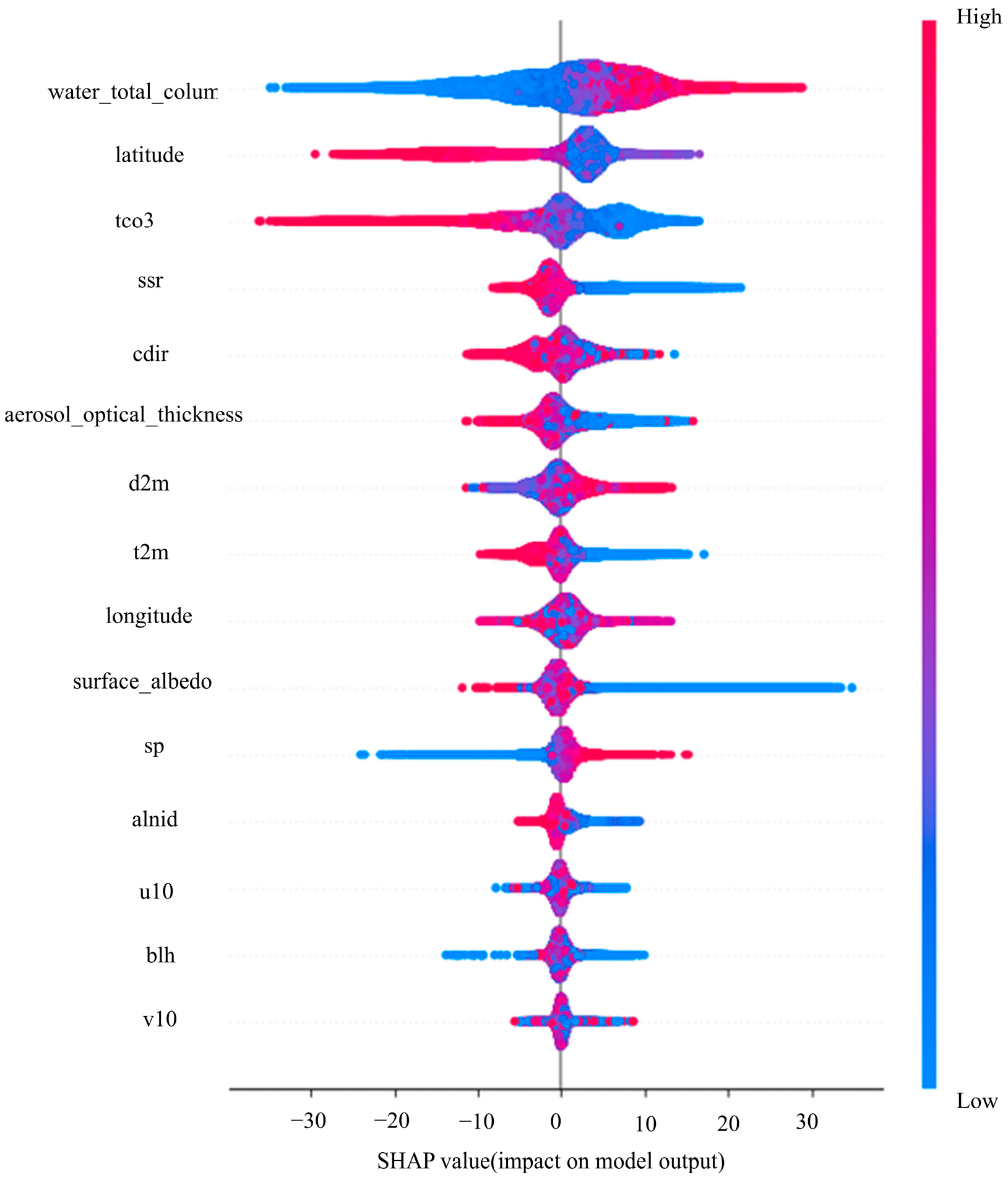
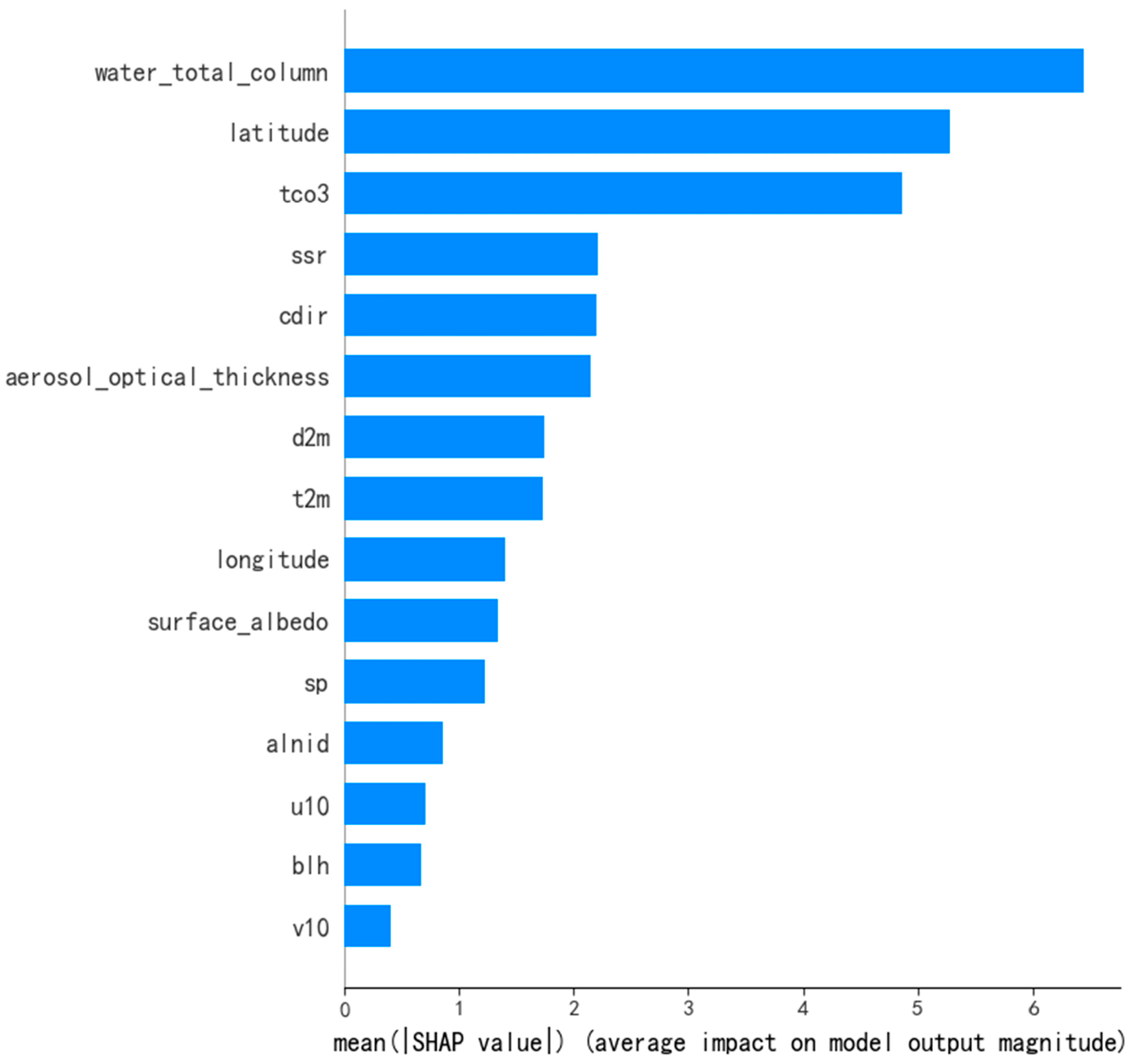
- SHAP plot analysis reveals that total column water vapor (water_total_column), latitude, and total column ozone (tco3) make significant contributions to the model in methane concentration inversion. Features such as surface pressure (sp) show positive correlations with methane concentration variations, while features like 2 m temperature (t2m) and boundary layer height (blh) exhibit negative correlations with methane concentration changes.
- (3)
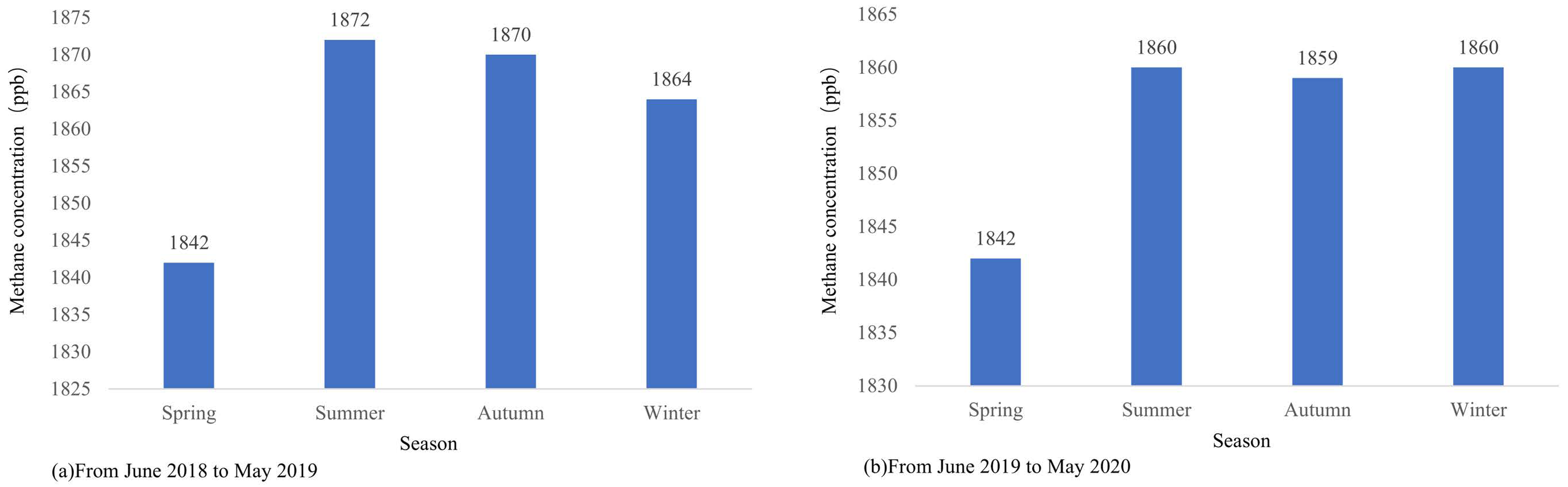
- The mean methane concentrations from June 2019 to May 2020 are higher than those of the previous year, indicating an increasing trend in methane concentrations over the years. Summer methane concentrations are typically higher, primarily due to increased temperatures promoting methane generation and release. The decrease in methane concentrations in early 2020 is mainly attributed to reduced human activities during the pandemic. Overall, methane concentrations exhibit a pattern of higher levels in summer and winter, and lower levels in spring and autumn.
- (4)
- In terms of extrapolation performance, the proposed MFF-SEM model also outperforms other models. The model achieves its best performance in winter, with an R2 of 0.6401. However, due to the influence of other complex factors, the inversion performance is relatively low in autumn. The overall lower extrapolation performance is primarily related to limited sample size and short time span. Future research will expand the study area and time span and incorporate physical models for in-depth investigation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, D.H. Climate change science and sustainable development. Prog. Geogr. 2014, 33, 874–883. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Guan, L.; Tao, F.; Liang, M.; Sun, W.Q. Changes of CH4 concentrations obtained by ground-based observations at five atmospheric background stations in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.D.; Zuo, Q.W.; Sun, M.S.; Huang, L.Z.; Shi, J.S. Research progress of satellite remote sensing detection of methane. Remote Sens. Inf. 2024, 39, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, X.; Hu, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Bai, G.; Xiao, W. Quantification of Central and Eastern China’s atmospheric CH4 enhancement changes and its contributions based on machine learning approach. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 138, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wójcik-Gront, E.; Wnuk, A. Evaluating Methane Emission Estimates from Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Compared to Sentinel-Derived Air–Methane Data. Sustainability 2025, 17, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Xie, Y.; Han, G.; Meng, X.; Li, Z. Methane Dynamics in Inner Mongolia: Unveiling Spatial and Temporal Variations and Driving Factors. Proceedings 2024, 110, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.B. Chemical behavior of methane in atmosphere. Res. Environ. Sci. 1996, 9, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, B.; Zhang, H.; Yang, D.D. A modeling study of effective radiative forcing and climate response due to the change in methane concentration. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2017, 13, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Liao, H. Advances in the research on sources and sinks of CH4 and observations and simulations of CH4 concentrations. Adv. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Etminan, M.; Myhre, G.; Highwood, E.J.; Shine, K.P. Radiative forcing of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide: A significant revision of the methane radiative forcing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 12614–12623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Xu, L.; Deng, S.M.; Zhou, R.J. Analysis of H2O and CH4 distribution characteristics in the middle atmosphere using HALOE data. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 31, 440–448. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.Z.; Tao, M.H.; Ding, S.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Zeng, M.Y.; Chen, L.F. Spatial and temporal distribution of XCO2 and XCH4 in China based on satellite remote sensing. J. Atmos. Environ. Opt. 2022, 17, 679–692. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Langerock, B.; Vigouroux, C.; Sha, M.K.; Ramonet, M.; Delmotte, M.; Mahieu, E.; Bader, W.; Hermans, C.; Kumps, N.; et al. Atmospheric CO and CH4 time series and seasonal variations on Reunion Island from ground-based in situ and FTIR (NDACC and TCCON) measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 13881–13901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Li, Z.; Fan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Han, Y. Satellite sensors and retrieval algorithms of atmospheric methane. Acta Opt. Sin. 2023, 43, 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Yang, D.X.; Cai, Z.N.; Zhu, S.H.; Liu, Y.; Deng, J.B.; Lu, N.M. Status and trend analysis of atmospheric methane satellite measurement for carbon neutrality and carbon peaking in China. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 46, 1469–1483. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, M.; Xiong, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L. Increase of Atmospheric Methane Observed from Space-Borne and Ground-Based Measurements. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tang, J.; Wen, Y.; Worthy, D.; Trivet, N.; Zhang, X.; Ji, J.; Zheng, M.; Tans, P.; Conway, T. Characteristics of atmospheric methane concentration variation at Mt. Waliguan. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 1998, 9, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Zhang, S.; Gao, C.; Yan, Y.; Bao, J.; Su, L.; Liu, M.; Peng, N.; Liu, M. A long-term analysis of atmospheric black carbon MERRA-2 concentration over China during 1980–2019. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 264, 118687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.Y.; Lin, X.F.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y.F.; Wang, C.P.; Shi, Y.Q.; Chen, J.F.; Liu, S.H.; Xie, J.H. Study on the temporal and spatial variation of CH4 and its driving factors over China from 2010 to 2019. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 46, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Bai, W.; Zhang, P.; Wang, W. Spatiotemporal variations in mid-upper tropospheric methane over China from satellite observations. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 2804–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepers, D.; Guerlet, S.; Butz, A.; Landgraf, J.; Frankenberg, C.; Hasekamp, O.; Blavier, J.; Deutscher, N.M.; Griffith, D.W.T.; Hase, F.; et al. Methane retrievals from Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite (GOSAT) shortwave infrared measurements: Performance comparison of proxy and physics retrieval algorithms. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D10302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Xie, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, X.X.; Wang, Q.Y.; Yang, D.D. The spatial-temporal distribution of CH4 over globe and East Asia. China Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 4401–4408. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Yu, T.; Gu, X.F.; Cheng, T.H.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, D.H. Global atmospheric methane variation and temporal-spatial distribution analysis based on ground-based and satellite data. Remote Sens. Inf. 2012, 27, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.W. Ground Methane Emission Monitoring in China Based on TROPOMI Satellite Observations. Master’s Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, F.; Tao, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Methane Retrieval from Hyperspectral Infrared Atmospheric Sounder on FY3D. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Cao, X. Methane Retrieval Algorithms Based on Satellite: A Review. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.P.; Wu, X.D.; Ma, D.J.; Wen, J.G.; Xiao, Q. Remote sensing retrieval based on machine learning algorithm: Uncertainty analysis. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2023, 27, 790–801. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, T.; Li, L.Q.; Yan, S.Q.; Yang, S.Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, Z.P.; Chen, Q.C. Review of Machine Learning in Air Pollution Research. Environ. Sci. 2025, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.H.; Zhu, W.X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Y.X.; Hou, X.; Xun, N.N. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of near-surface methane concentration in China. China Environ. Sci. 2024, 44, 593–601. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.L.; Wang, W.T.; Xie, Y.; Aydana, Y.; Jiang, Y.T.; Xu, J.Q. Climate dry-wet conditions, changes, and their driving factors in Xinjiang. Arid Zone Res. 2023, 40, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.X.; Sun, R.D.; Song, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, B.W.; Yu, R.X.; Li, L. Research on ozone column concentration in Xinjiang based on OMI data. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 1498–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, R.Q.; Li, X. Comparison between the applicability of ERA-Interim and ERA5 reanalysis in Jiangsu Province. Mar. Forecast. 2021, 38, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Dutra, E.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Albergel, C.; Arduini, G.; Balsamo, G.; Boussetta, S.; Choulga, M.; Harrigan, S.; Hersbach, H.; et al. ERA5-Land: A state-of-the-art global reanalysis dataset for land applications. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 4349–4383. [Google Scholar]
- Schneising, O.; Buchwitz, M.; Hachmeister, J.; Vanselow, S.; Reuter, M.; Buschmann, M.; Bovensmann, H.; Burrows, J.P. Advances in retrieving XCH4 and XCO from Sentinel-5 Precursor: Improvements in the scientific TROPOMI/WFMD algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2023, 16, 669–694. [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist, H.; Kivimäki, E.; Häkkilä, T.; Tsuruta, A.; Schneising, O.; Buchwitz, M.; Lorente, A.; Martinez Velarte, M.; Borsdorff, T.; Alberti, C.; et al. Evaluation of Sentinel-5P TROPOMI Methane Observations at Northern High Latitudes. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natekin, A.; Knoll, A. Gradient boosting machines, a tutorial. Front. Neurorobotics 2013, 7, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Y.; Chen, F.; Fan, L.; Sun, D.; He, H.; Dai, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, Y. Conversion of surface CH4 concentrations from GOSAT satellite observations using XGBoost algorithm. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 301, 119697. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.L.; Zheng, H.B. Study of PM2.5 concentration prediction model based on improved machine learning. J. Dalian Univ. Technol. 2024, 64, 353–360. [Google Scholar]







| Name | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meteorological features (u10, v10, t2m, d2m, cdir, alnid, sp, ssr, tco3, blh) | 0.25° × 0.25° | 1 h | ERA5 dataset provided by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) |
| Auxiliary features | 7 km × 7 km | 1 d | Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) |
| CH4 | 7 km × 7 km | 1 d | Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) |
| Model | Parameter Setting |
|---|---|
| XGBoost | n_estimators = 200 learning_rate = 0.01 max_depth = 10 |
| GradientBoosting | n_estimators = 200 max_depth = 5 learning_rate = 0.1 |
| Random Forest | n_estimators = 200 max_depth = 15 |
| LightGBM | num_leaves = 200 max_depth = 30 learning_rate = 0.05 |
| Lasso | alpha = 1.0 max_iter = 1500 |
| Feature Combination | Feature Description |
|---|---|
| F1 | meteorological factors |
| F2 | meteorological factors and auxiliary data |
| F3 | meteorological factors, auxiliary data, and latitude and longitude |
| Model | R2 | RMSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 0.6718 | 11.9198 | 9.0477 |
| 1DCNN | 0.8885 | 6.9111 | 5.2564 |
| GBDT | 0.8643 | 7.6244 | 5.7510 |
| LightGBM | 0.9435 | 4.9206 | 3.7154 |
| RF | 0.9479 | 4.0637 | 2.1072 |
| XGBoost | 0.9673 | 3.2221 | 1.7284 |
| MFF-SEM | 0.9747 | 2.8294 | 1.5299 |
| Model | R2 | RMSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 0.4300 | 14.0324 | 11.2621 |
| 1DCNN | 0.4059 | 14.3266 | 11.5291 |
| GBDT | 0.5365 | 12.6542 | 10.2950 |
| LightGBM | 0.5715 | 12.1671 | 9.9433 |
| RF | 0.4538 | 13.7361 | 11.1318 |
| XGBoost | 0.5295 | 12.7493 | 10.3821 |
| MFF-SEM | 0.5838 | 11.9903 | 9.8294 |
| Model | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1DCNN | 0.2386 | 0.1224 | −0.0794 | 0.5078 |
| LSTM | 0.3886 | 0.1234 | 0.1459 | 0.4343 |
| RF | 0.3302 | 0.3300 | 0.0146 | 0.5174 |
| LightGBM | 0.4150 | 0.4875 | 0.2262 | 0.6075 |
| XGBoost | 0.4301 | 0.3881 | 0.1518 | 0.6066 |
| GBDT | 0.4559 | 0.4065 | 0.1947 | 0.5650 |
| MFF-SEM | 0.4733 | 0.4755 | 0.2534 | 0.6401 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Li, W.; Yi, C.; Song, G.; Zhang, Y. Methane Concentration Inversion Based on Multi-Feature Fusion and Stacking Integration. Sensors 2025, 25, 1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25071974
Han Y, Li W, Yi C, Song G, Zhang Y. Methane Concentration Inversion Based on Multi-Feature Fusion and Stacking Integration. Sensors. 2025; 25(7):1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25071974
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yanling, Wei Li, Congqin Yi, Ge Song, and Yun Zhang. 2025. "Methane Concentration Inversion Based on Multi-Feature Fusion and Stacking Integration" Sensors 25, no. 7: 1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25071974
APA StyleHan, Y., Li, W., Yi, C., Song, G., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Methane Concentration Inversion Based on Multi-Feature Fusion and Stacking Integration. Sensors, 25(7), 1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25071974






