Aptamer Paper-Based Fluorescent Sensor for Determination of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Apparatus
2.2. Synthesis of Nb2C MXene Nano-Quenchers
2.3. Preparation of Fluorescent Aptamer Probes
2.4. Detection Method in Tube
2.5. Paper-Based Detection System
2.6. Real Sample Analysis
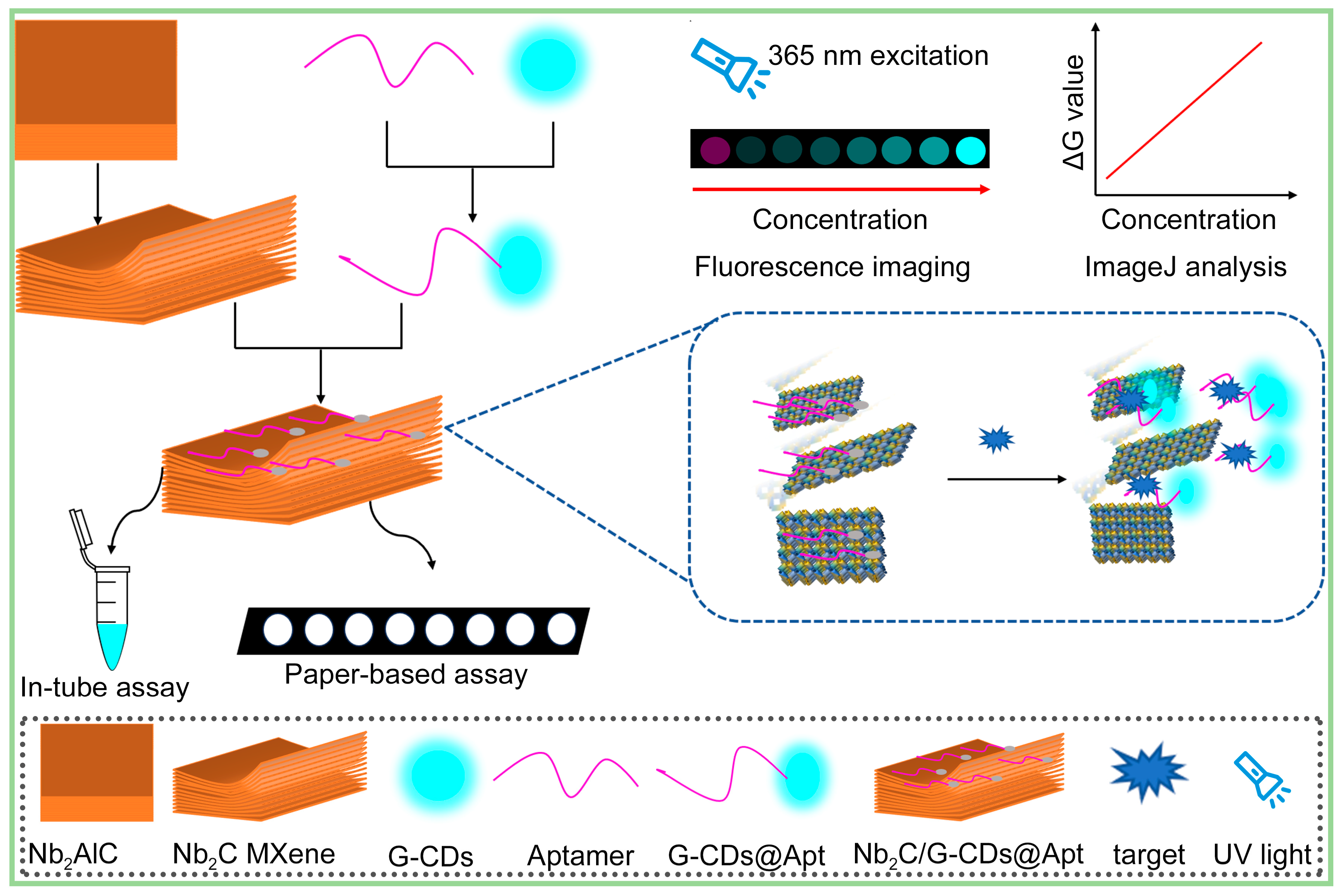
3. Results and Discussion
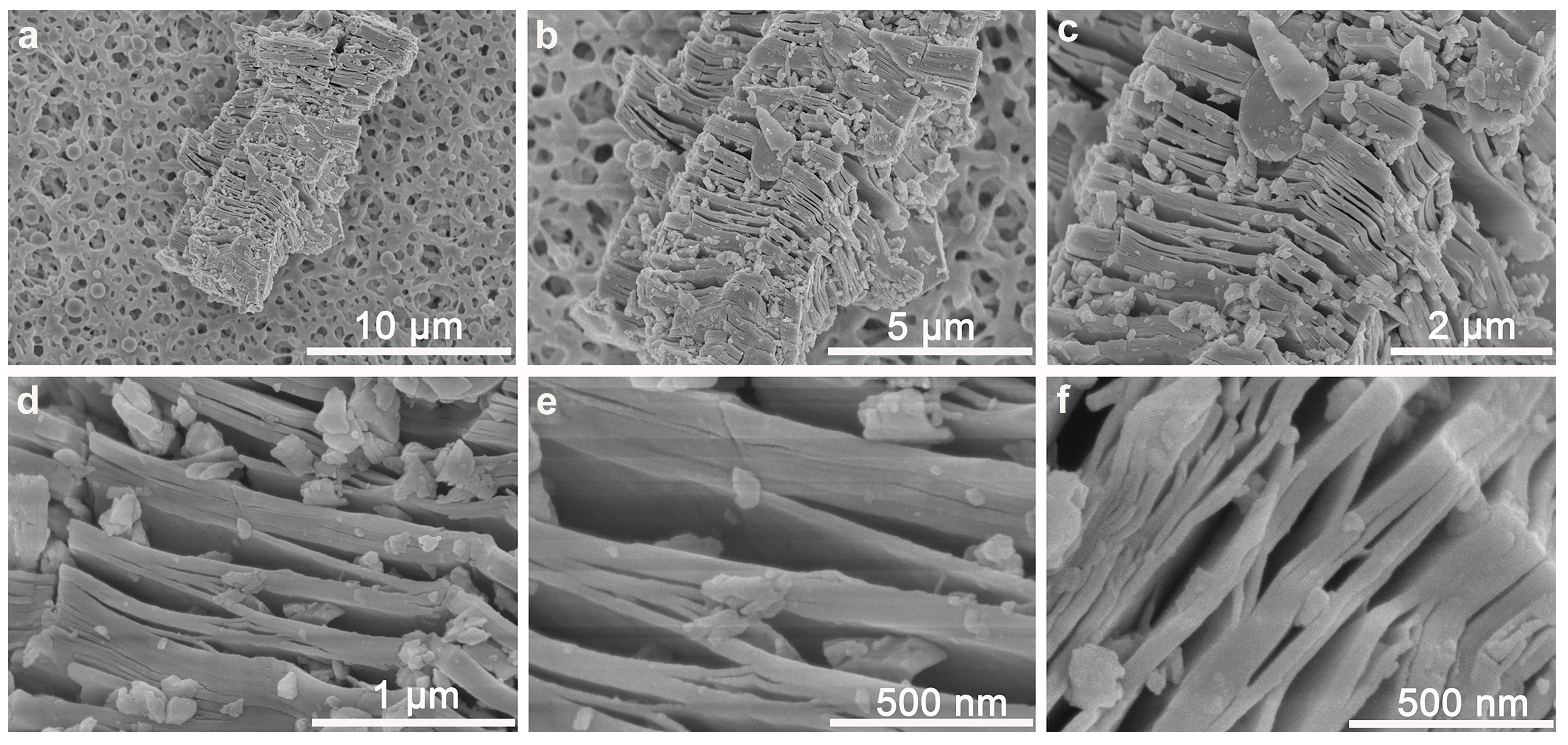
3.1. Multi-Layer Nb2C MXene Nano-Quenchers Loaded on MCE Paper Substrate
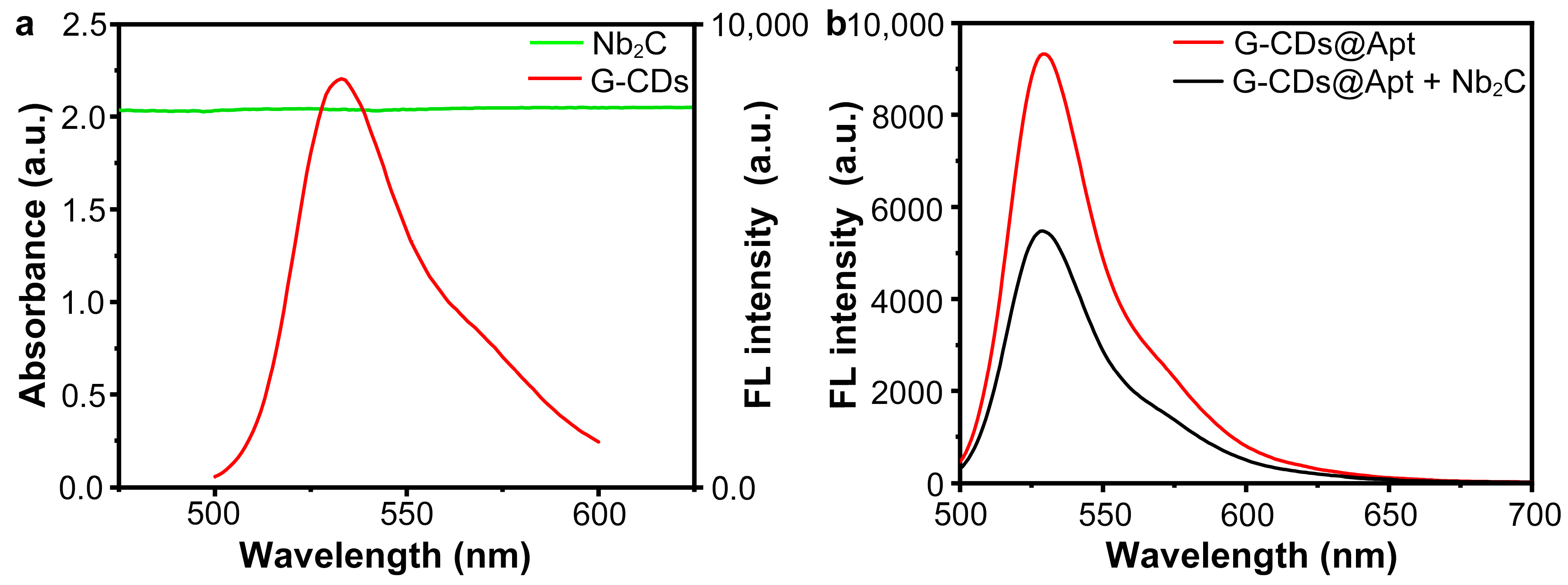
3.2. Fluorescence Quenching Due to Absorption of Aptamer Probes by Nb2C MXene Nano-Quenchers
3.3. Target-Induced Aptamer Probe Detachment from Nano-Quencher and Fluorescence Recovery
3.4. Feasibility of Using Nb2C/G-CDs@Apt Test Paper for Detecting SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
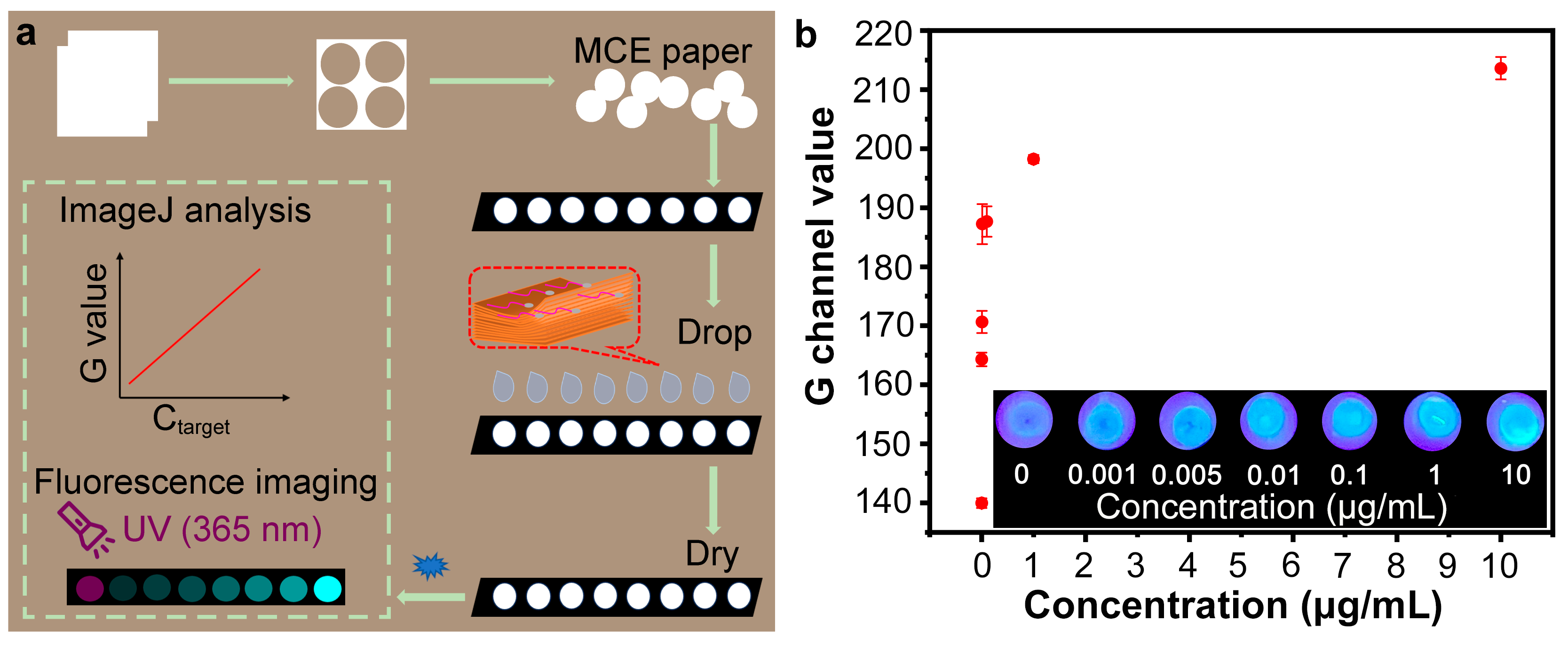
3.5. Optimization of Paper-Based Analytical Method
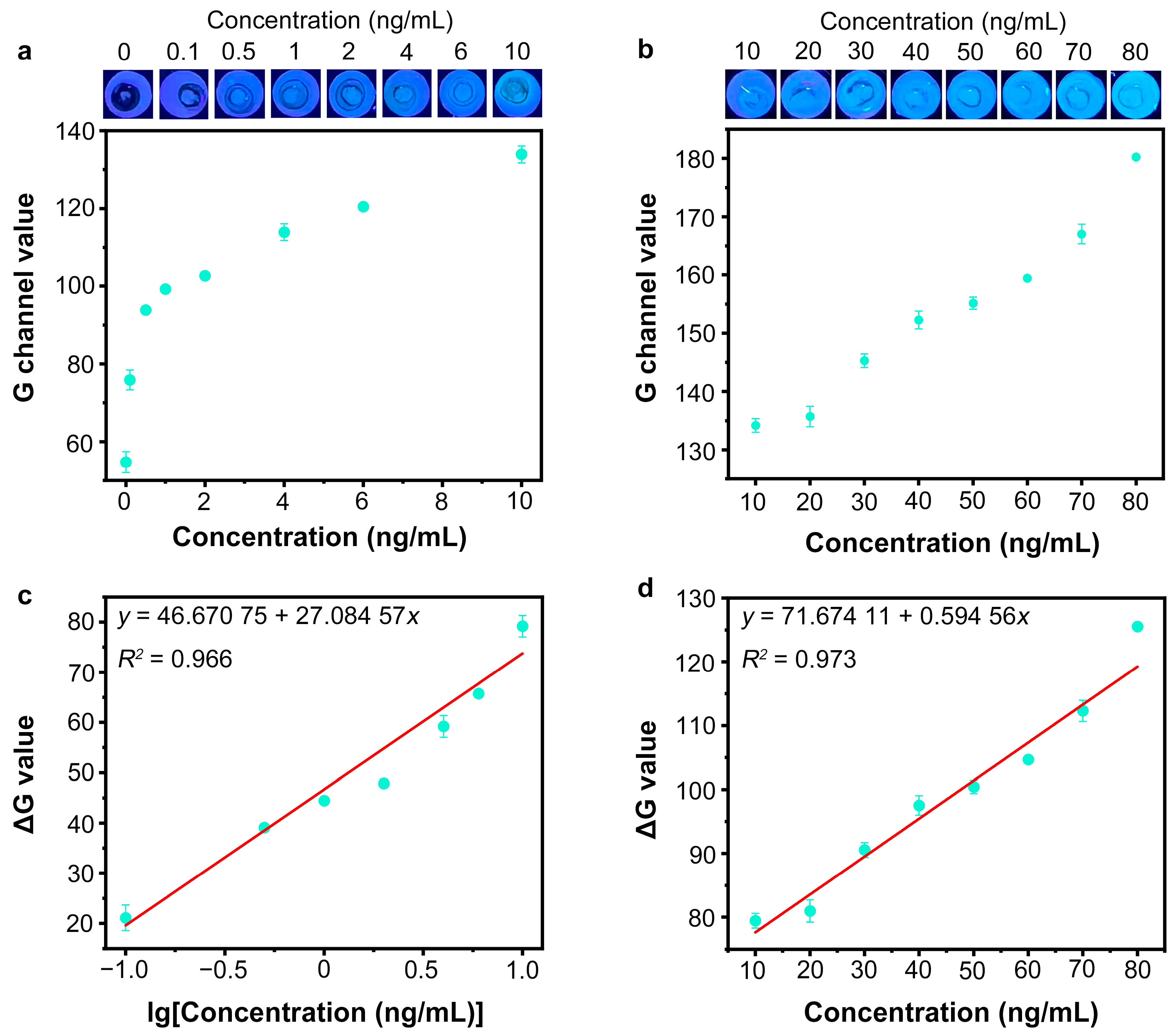
3.6. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein by Nb2C MXene/G-CDs@Apt Paper Sensor
3.7. Application in Actual Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fukana, N.; Park, J.; Silva Junior, G.J.; Malsick, L.E.; Gallichotte, E.N.; Ebel, G.D.; Geiss, B.J.; Dandy, D.S.; Bertotti, M.; Nacapricha, D.; et al. Magnetophoretic slider assay for electrochemical detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein in nasal swab samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 271, 117048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Guo, C.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. From Lab to Home: Ultrasensitive Rapid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 with a Cascade CRISPR/Cas13a-Cas12a System Based Lateral Flow Assay. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 14197–14204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pang, S.; Wang, M.; Yu, H.; Ma, P.; Dong, T.; Zheng, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, A. An ultrasensitive ELISA to assay femtomolar level SARS-CoV-2 antigen based on specific peptide and tyramine signal amplification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 387, 133746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drobysh, M.; Ratautaite, V.; Brazys, E.; Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Molecularly imprinted composite-based biosensor for the determination of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 251, 116043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhou, N.; Peng, J.; Zeng, X.; Du, L.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, X. Sensitivity-improved SERS detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein by Au NPs/COFs integrated with catalytic-hairpin-assembly amplification technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1318, 342924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, D.; Deng, J.; Guo, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yang, S.; Ji, J.S.; Luo, H.; Bai, J.; et al. Persistent pollution of genetic materials in a typical laboratory environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 470, 134201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracquemond, D.; Muriaux, D. Betacoronavirus Assembly: Clues and Perspectives for Elucidating SARS-CoV-2 Particle Formation and Egress. mBio 2021, 12, e0237121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, M.G.; Chen, W.-H.; Sankhala, R.S.; Hajduczki, A.; Thomas, P.V.; Choe, M.; Martinez, E.J.; Chang, W.C.; Peterson, C.E.; Morrison, E.B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 ferritin nanoparticle vaccines elicit broad SARS coronavirus immunogenicity. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 110143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Kwon, H.J.; Cachau, R.; Chen, C.Z.; Butay, K.J.; Duan, Z.; Li, D.; Ren, H.; Liang, T.; Zhu, J.; et al. Dromedary camel nanobodies broadly neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2201433119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitjar, J.; Liao, J.-D.; Lee, H.; Tsai, H.-P.; Wang, J.-R.; Chen, C.-H.; Wang, H.; Liu, B.H. Detection of live SARS-CoV-2 virus and its variants by specially designed SERS-active substrates and spectroscopic analyses. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1256, 341151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proal, A.D.; VanElzakker, M.B.; Aleman, S.; Bach, K.; Boribong, B.P.; Buggert, M.; Cherry, S.; Chertow, D.S.; Davies, H.E.; Dupont, C.L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 reservoir in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC). Nat. Immunol. 2023, 24, 1616–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swank, Z.; Senussi, Y.; Manickas-Hill, Z.; Yu, X.G.; Li, J.Z.; Alter, G.; Walt, D.R. Persistent Circulating Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Spike Is Associated With Post-acute Coronavirus Disease 2019 Sequelae. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, e487–e490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Bian, S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Bi, W.; Zhu, P.; Sawan, M. Rapid Optical Biosensing of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Proteins in Artificial Samples. Sensors 2022, 22, 3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, M.; Tomaiuolo, G.; Villella, V.R.; Esposito, S.; Liboà, A.; D’Angelo, P.; Marasso, S.L.; Cocuzza, M.; Bertana, V.; Camilli, E.; et al. Organic Electrochemical Transistor Immuno-Sensors for Spike Protein Early Detection. Biosensors 2023, 13, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, C.Y.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Brennan, J.D. A Paper Sensor Printed with Multifunctional Bio/Nano Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4549–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Jia, F.; Yang, N. Divalent Aptamer-Functionalized Nanochannels for Facile Detection of Cancer Cell-Derived Exosomes. Sensors 2023, 23, 9139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Alkhamis, O.; Canoura, J.; Yu, H.; Xiao, Y. Rapid Nuclease-Assisted Selection of High-Affinity Small-Molecule Aptamers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 21296–21307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Bie, L.; Saleh, L.; Frey, K.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Rapid and sensitive multiplex detection of COVID-19 antigens and antibody using electrochemical immunosensor-/aptasensor-enabled biochips. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 7285–7288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.-T.; Bao, J.-Y.; Kang, J.-W.; Wang, A.-J.; Yuan, P.-X.; Feng, J.-J. Hydrogen-Bond-Induced Melem Assemblies to Resist Aggregation-Caused Quenching for Ultrasensitive ECL Detection of COVID-19 Antigen. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 19038–19046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shao, F.; Wu, J.; Liu, M.; Cao, G.; Zhao, Z.; Bai, J.; Gao, Z. Ultrasensitive Ochratoxin A Detection in Cereal Products Using a Fluorescent Aptasensor Based on RecJf Exonuclease-Assisted Target Recycling. Foods 2024, 13, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Penning, S.; Murphy, M.P.; Kingston, T.A.; Nilsen-Hamilton, M.; Shrotriya, P. Influence of crosslinker on aptamer immobilization and aptasensor sensing response for non-metallic surfaces. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 270, 116933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Yang, L.; Zeng, L.; Feng, C.; Yang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, W.; He, J.; Zhang, C. Visualizing cancer resistance via nano-quenching and recovery detector of CD44. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhao, J.; Wu, T.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lian, Z.; Cai, S.; Yang, R. Dual ligand-induced photoelectrochemical sensing by integrating Pt/MoS2 heterostructure and Au polyhedra for sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 376, 132970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Song, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Li, N.; Song, L.; Li, X. A novel Nb2C MXene based aptasensor for rapid and sensitive multi-mode detection of AFB1. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 242, 115725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Song, J.; Liu, Q.; Song, L.; Fei, X.; Li, X. A novel multimode biosensor for sensitive detection of AFB1 in food based on Mxenes nano enzymes. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhou, X. A colorimetric sandwich-type bioassay for SARS-CoV-2 using a hACE2-based affinity peptide pair. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.R.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Jeon, M.S.; Choi, Y.-E. In Vivo Monitoring of Intracellular Metabolite in a Microalgal Cell Using an Aptamer/Graphene Oxide Nanosheet Complex. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 5080–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Fan, J.; Cui, L.; Ke, W.; Zheng, F.; Zhao, Y. Fluorometric nanoprobes for simultaneous aptamer-based detection of carcinoembryonic antigen and prostate specific antigen. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Hong, J.; Wu, Y.-X.; Cao, Y.; Wu, D.; Hu, F.; Gan, N. A Multicolor Fluorescence Nanoprobe Platform Using Two-Dimensional Metal Organic Framework Nanosheets and Double Stirring Bar Assisted Target Replacement for Multiple Bioanalytical Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 41506–41515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, Q.; Pan, F.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Z. Ultrathin Cellulose Nanofiber Assisted Ambient-Pressure-Dried, Ultralight, Mechanically Robust, Multifunctional MXene Aerogels. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Chopada, R.; Singh, A.; Kumar, N.; Misra, M.; Kim, K.-H. The potential of MXene-based materials in fluorescence-based sensing/biosensing of ionic and organic contaminants in environment and food samples: Recent advancements and challenges. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 332, 103264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Majhi, S.M.; Siddig, L.A.; Deshmukh, A.H.; Wen, H.; Qamhieh, N.N.; Greish, Y.E.; Mahmoud, S.T. Recent Advancements in MXene-Based Biosensors for Health and Environmental Applications—A Review. Biosensors 2024, 14, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, R.; Shen, C.; Li, M.; Zhao, Z.; Lv, M.; Sun, S.; Sun, X.; Ying, B. MXene-Based Aptameric Fluorosensor for Sensitive and Rapid Detection of COVID-19. Small 2023, 19, 2301146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Xie, H.; Li, T.; Gan, N. A turn-on–type fluorescence resonance energy transfer aptasensor for vibrio detection using aptamer-modified polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-perovskite quantum dots/Ti3C2 MXenes composite probes. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Fu, X.; Yang, L.; Xing, S.; Wang, X.-F. 2D titanium carbide nanosheets based fluorescent aptasensor for sensitive detection of thrombin. Talanta 2021, 228, 122219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.-N.; Zhou, L.-J.; Li, P.; Sui, Q.; Gao, E.-Q. Space-confined indicator displacement assay inside a metal–organic framework for fluorescence turn-on sensing. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 3307–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, F.; Xu, W.; Li, B.; Zhu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Cao, H.; He, Q.; Cheng, J. In Situ Turn-On Room Temperature Phosphorescence and Vapor Ultra-sensitivity at Lifetime Mode. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 5190–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yu, T.; Dai, Z.; Wei, Q. Aptamer-Based Fluorescent Sensor Array for Multiplexed Detection of Cyanotoxins on a Smartphone. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10448–10457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, C.; Tong, X.; Duan, N.; Wang, Z.; Wu, S. A portable paper-based aptasensor for simultaneous visual detection of two mycotoxins in corn flour using dual-color upconversion nanoparticles and Cu-TCPP nanosheets. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudan, B.K.; Matthew, S.R.; Xu, C.; Héctor, A.G.; Marien, I.O.; Shudong, J.; Tayyaba, H.; Marvin, M.D.; Brian, W.P. Combined dual-channel fluorescence depth sensing of indocyanine green and protoporphyrin IX kinetics in subcutaneous murine tumors. J. Biomed. Opt. 2024, 30, S13709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.; Wang, Y.; Cordero, J.; Watson, C.; Molestina, R.; Rashid, S.; Bradford, R. Development and validation of a rapid and easy-to-perform point-of-care lateral flow immunoassay (lfia) for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1111644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, M.; Sobhanie, E.; Salehnia, F.; Xu, G.; Rabbani, H.; Sheikholeslami, M.N.; Firoozbakhtian, A.; Sadeghi, N.; Farajollah, M.H.; Ganjali, M.R.; et al. Development of sandwich electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for COVID-19 diagnosis by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein detection based on au@bsa-luminol nanocomposites. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 147, 108161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, L.; Saroglia, M.; Galatà, G.; De Santis, R.; Fillo, S.; Luca, V.; Faggioni, G.; D’Amore, N.; Regalbuto, E.; Salvatori, P.; et al. Magnetic beads combined with carbon black-based screen-printed electrodes for COVID-19: A reliable and miniaturized electrochemical immunosensor for SARS-CoV-2 detection in saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Yong, W.; Jin, Y.; Dong, Y. Development of aptamer-based lateral flow devices for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 s protein and uncertainty assessment. Talanta 2025, 281, 126825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.W.; Zhao, T.T.; Li, C.M.; Li, Y.F.; Huang, C.Z. 2D mof-based photoelectrochemical aptasensor for SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein detection. ACS Appl. Materials. Interfaces 2021, 13, 49754–49761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrego-Martinez, J.C.; Jafari, M.; Chergui, S.; Pavel, C.; Che, D.; Siaj, M. Aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2: Nanoscale electrode-aptamer-SARS-CoV-2 imaging by photo-induced force microscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 195, 113595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, K.G.; Levy, J.I.; Gauld, J.; Rigby, J.; Kanjerwa, O.; Uzzell, C.B.; Chilupsya, C.; Anscombe, C.; Tomkins-Tinch, C.; Mbeti, O.; et al. Utilizing river and wastewater as a SARS-CoV-2 surveillance tool in settings with limited formal sewage systems. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ahmed, W.; Metcalfe, S.; Smith, W.J.M.; Tscharke, B.; Lynch, P.; Sherman, P.; Vo, P.H.N.; Kaserzon, S.L.; Simpson, S.L.; et al. Monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 in sewersheds with low COVID-19 cases using a passive sampling technique. Water Res. 2022, 218, 118481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherchan, S.P.; Thakali, O.; Ikner, L.A.; Gerba, C.; Haramoto, E. Survivability of Delta and Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater. Water Res. 2023, 246, 120644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Samples | Added (ng/mL) | Determined (ng/mL) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| River water from Haihe River | 0 | Nd | / | / |
| 10 | 9.09 ± 0.31 | 90.87 | 3.41 | |
| 50 | 48.98 ± 0.73 | 95.96 | 1.52 | |
| 80 | 80.44 ± 1.63 | 100.55 | 2.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, T.; Bai, J. Aptamer Paper-Based Fluorescent Sensor for Determination of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Sensors 2025, 25, 1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061637
Yang J, Zhao Z, Ma T, Bai J. Aptamer Paper-Based Fluorescent Sensor for Determination of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Sensors. 2025; 25(6):1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061637
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jincai, Zunquan Zhao, Tianyi Ma, and Jialei Bai. 2025. "Aptamer Paper-Based Fluorescent Sensor for Determination of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein" Sensors 25, no. 6: 1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061637
APA StyleYang, J., Zhao, Z., Ma, T., & Bai, J. (2025). Aptamer Paper-Based Fluorescent Sensor for Determination of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Sensors, 25(6), 1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25061637






