Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Wheat Based on Nucleic Aptamer Chemiluminescence Sensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of AFB1 Standard Solution and AFB1-Spiked Wheat Samples
2.3. AFB1-OVA Coated
2.4. Chemiluminescence Competitive Aptamer Assay
3. Results
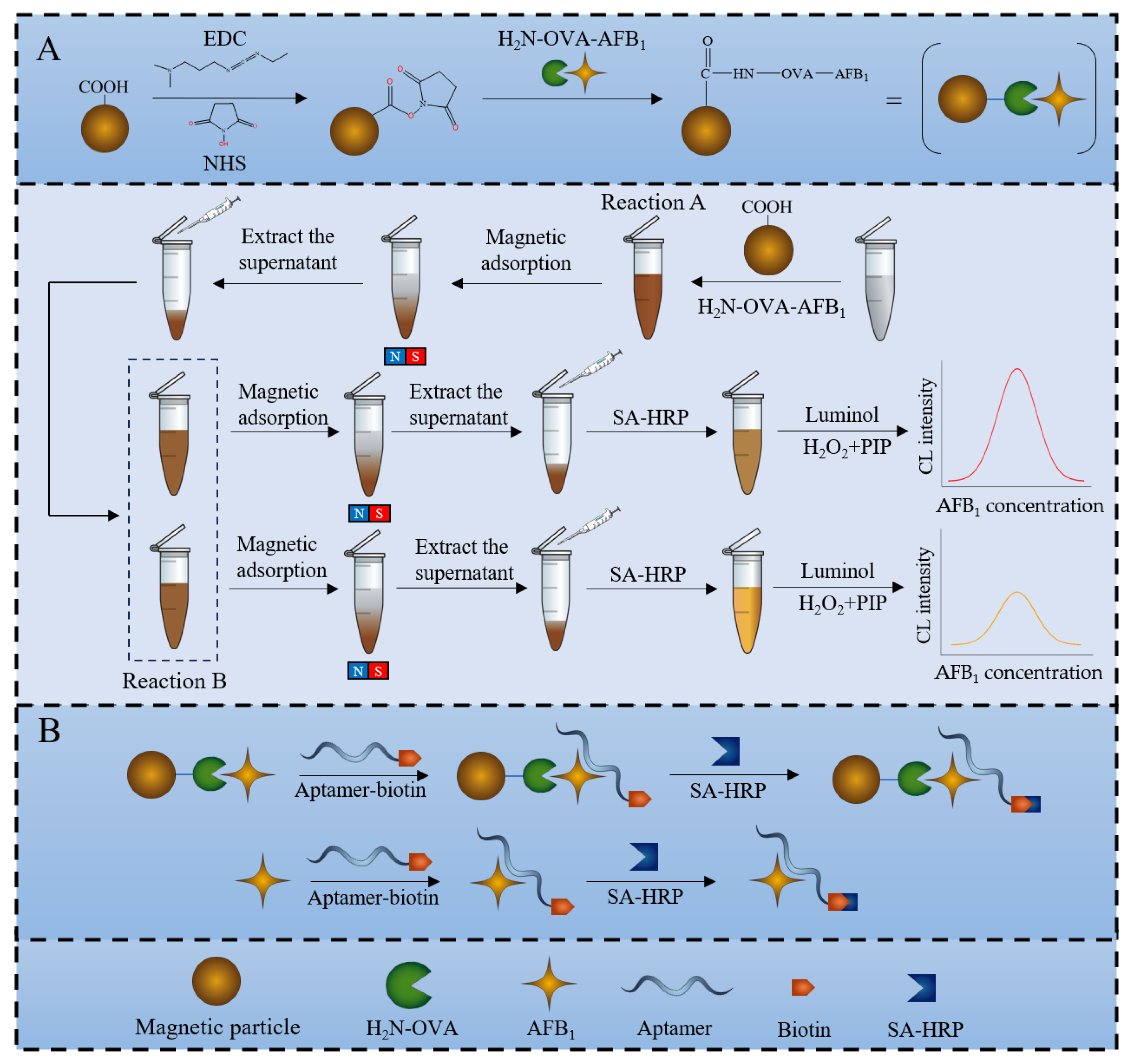
3.1. Principle of Sensor for AFB1 Detection
3.2. Sensor Workflow
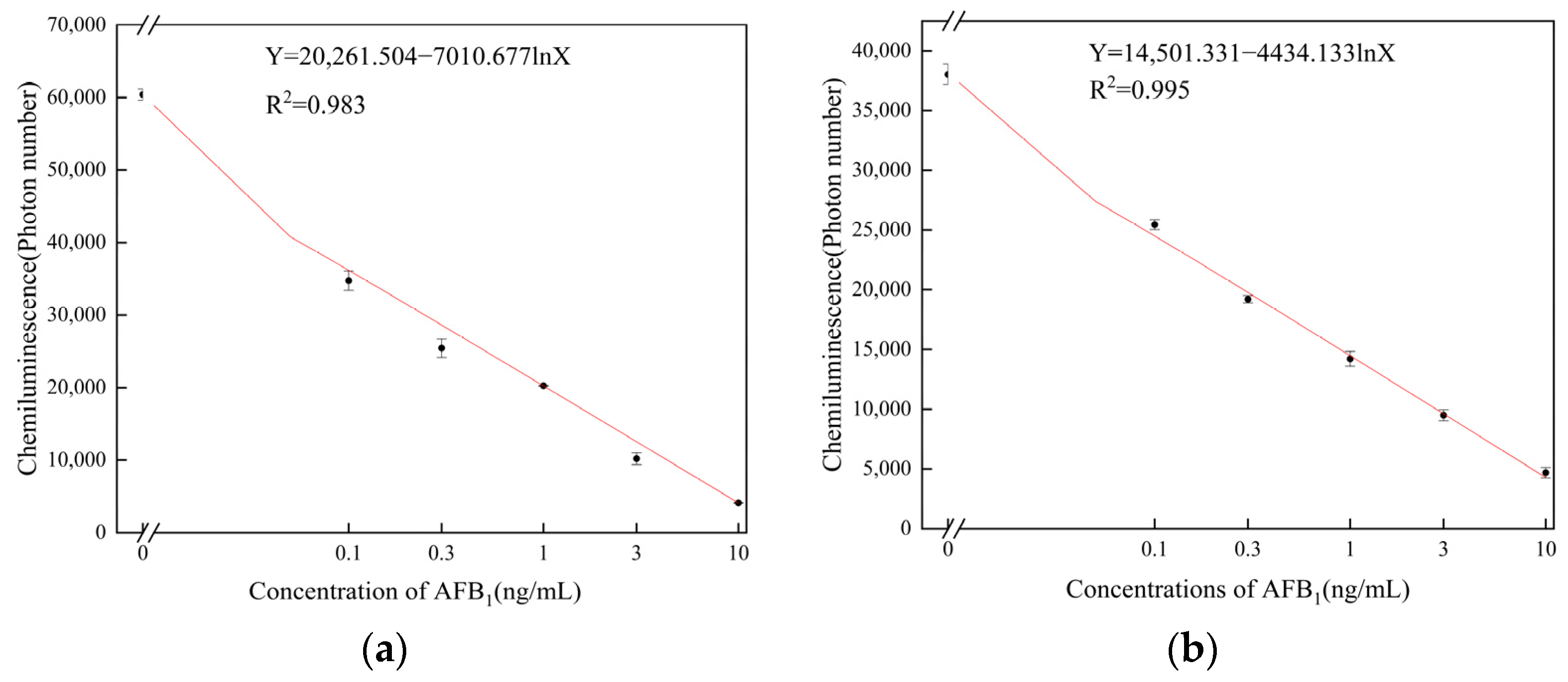
3.3. Assessment of Detection Performance for Different Coating Modes
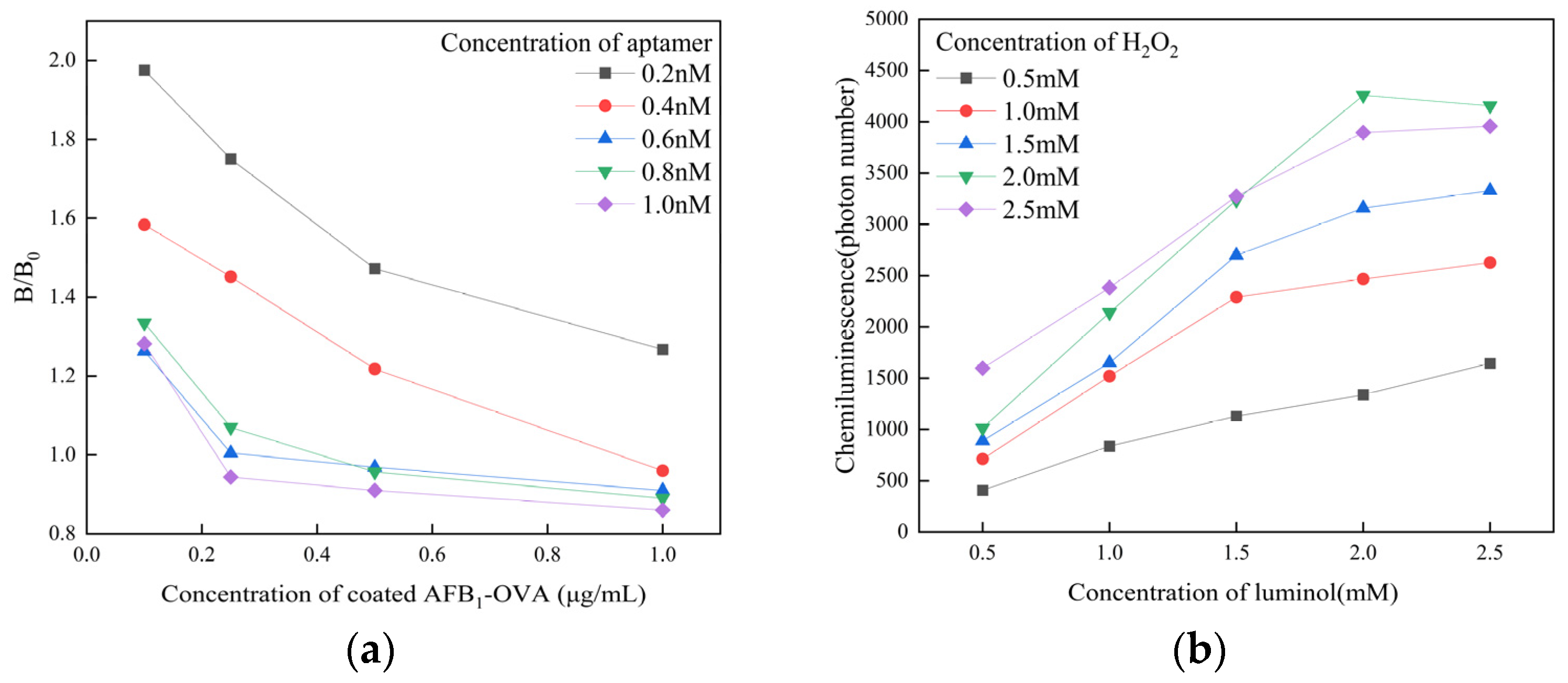
3.4. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
3.5. Detection of AFB1 by the Aptamer Sensor
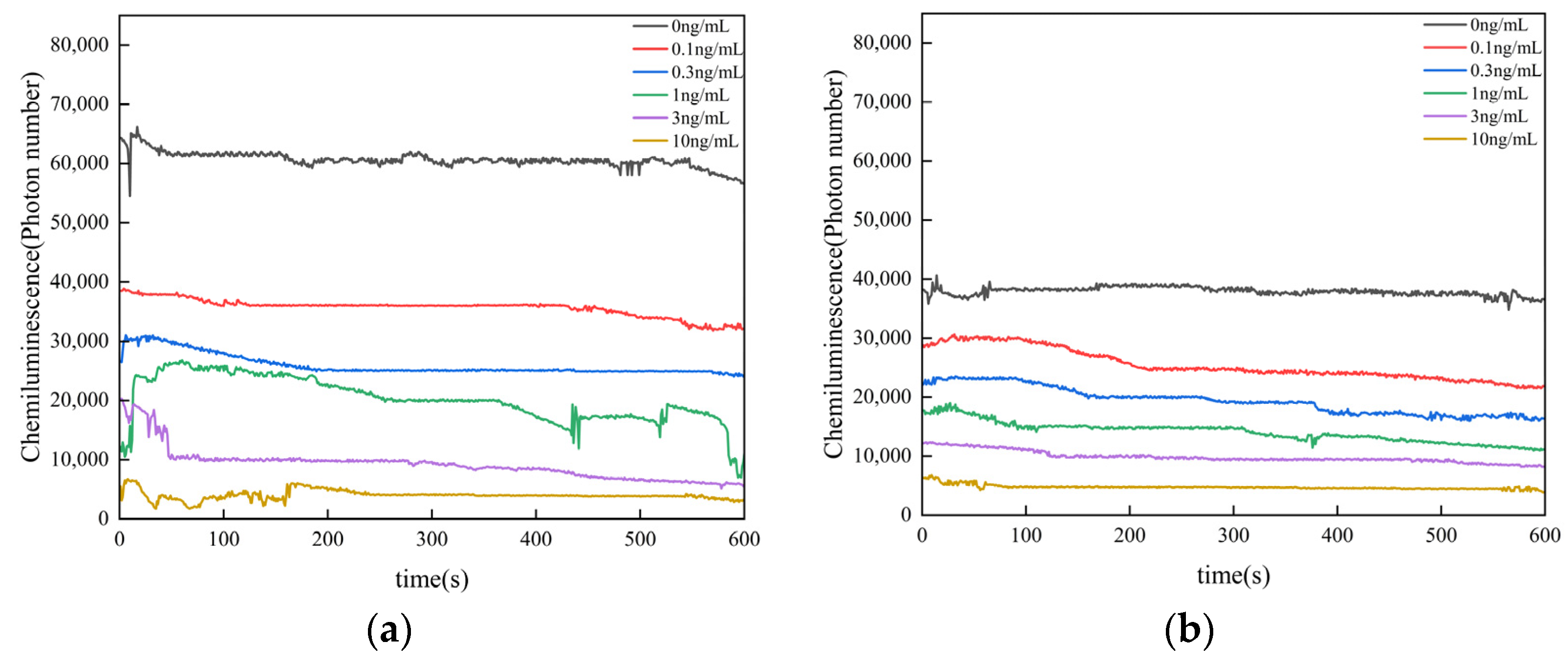
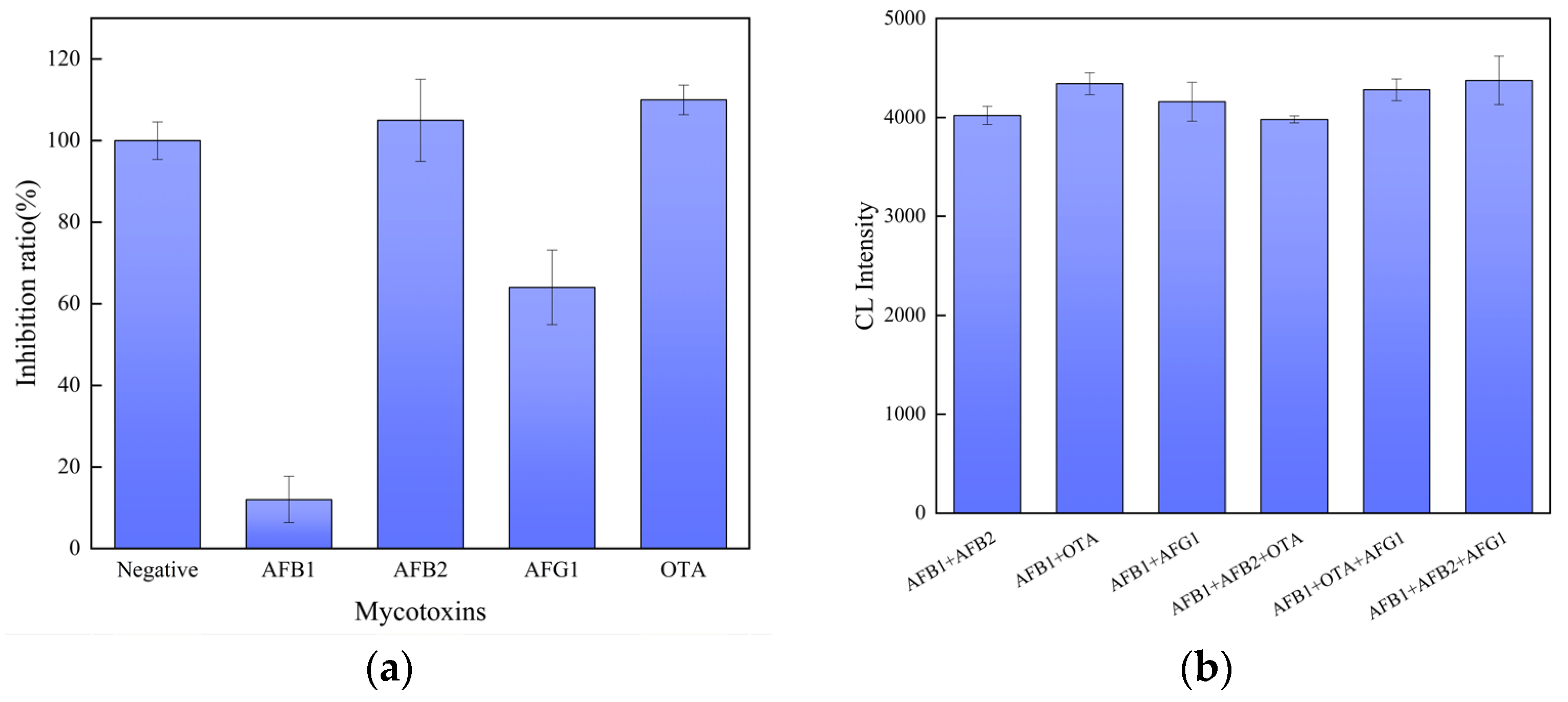
3.6. Sensor Specificity and Anti-Interference
3.7. Application of Sensor in Wheat Samples
3.8. Comparison of the Chemiluminescence Aptamer Sensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mao, L.; Liu, H.; Yao, L.; Wen, W.; Chen, M.-M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. Construction of a dual-functional CuO/BiOCl heterojunction for high-efficiently photoelectrochemical biosensing and photoelectrocatalytic degradation of aflatoxin B1. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, S.G. Determination of mycotoxins in human foods. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 2468–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Han, G.; Liu, Y.; Zou, P. A novel fluorescent aptasensor based on exonuclease-assisted triple recycling amplification for sensitive and label-free detection of aflatoxin B1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Song, J.; Liu, Q.; Song, L.; Fei, X.; Li, X. A novel multimode biosensor for sensitive detection of AFB1 in food based on Mxenes nano enzymes. Food Chem. 2023, 426, 136645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Li, Y.; Gao, G.; Zhang, X. Application of Aptamer Biosensor in Detection of Aflatoxin B1. Fenxi Ceshi Xuebao (J. Instrum. Anal.) 2023, 42, 368–374. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M. Construction of Aflatoxin B1 Smart Hydrogel Detection Sensor and Screening of Its Precursor Aptamer. Master’s Thesis, Henan University of Technology, Zhengzhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Nataša, H.; Martina, M.; Dušan, Ž.; Janez, K.; Andrea, J.; Aaron, D.; James, L.; Walsh, U. Cold atmospheric pressure plasma-assisted removal of aflatoxin B1 from contaminated corn kernels. Plasma Process. Polym. 2020, 18, 2000163. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. Research on the harmful effect of aflatoxin B1 on animals. Chin. Livest. Poult. Breed. 2022, 18, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Su, J. Research Progress on the effect of related metabolic enzymes on the metabolism of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1). World J. Tumor 2007, 6, 277–281+299. [Google Scholar]
- GB 2761-2017; National Food Safety Standards, Limit of Fungal Toxins in Food. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the PRC, China Food and Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Xuan, Z.; Liu, H.; Ye, J.; Li, L.; Tian, W.; Wang, S. Reliable and disposable quantum dot–based electrochemical immunosensor for aflatoxin B1 simplified analysis with automated magneto-controlled pretreatment system. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 7615–7625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Liu, H.; Ye, J.; Ni, B.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S. Target-responsive aptamer-cross-linked hydrogel sensors for the visual quantitative detection of aflatoxin B1 using exonuclease I-Triggered target cyclic amplification. Food Chem. X 2022, 15, 100395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daradimos, E.; Marcaki, P.; Koupparis, M. Evaluation and validation of two fluorometric HPLC methods for the determination of aflatoxin B1 in olive oil. Food Addit. Contam. 2000, 17, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zou, P. Target-triggered and T7 exonuclease-assisted cascade recycling amplification strategy for label-free and ultrasensitive fluorescence detection of aflatoxin B1. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 321, 128599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Yang, L.; Yao, L.; Xu, J.; Yao, B.; Liu, G.; Chen, W. Ingenious electrochemiluminescence bioaptasensor based on synergistic effects and enzyme-driven programmable 3D DNA nanoflowers for ultrasensitive detection of aflatoxin B1. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 14122–14129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Xue, X.; Xu, X.; Wen, W.; Chen, M.M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. Heterostructured CuO-g-C3N4 nanocomposites as a highly efficient photocathode for photoelectrochemical aflatoxin B1 sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Sun, D.W.; Pu, H.; Huang, L. Bridging Fe3O4@ Au nanoflowers and Au@ Ag nanospheres with aptamer for ultrasensitive SERS detection of aflatoxin B1. Food Chem. 2020, 324, 126832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Singh, R.; Li, M.; Li, G.; Min, R.; Marques, C.; Zhang, B.; Kumar, S. Plasmonic Sensor Based on Offset-Splicing and Waist-Expanded Taper Using Multicore Fiber for Detection of Aflatoxins B1 in Critical Sectors. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 4783–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, L. Research progress of aptasensors for the detection of aflatoxins. Food Ferment. Ind. 2024, 50, 323–331. [Google Scholar]
- Ruscito, A.; DeRosa, M. Small-molecule binding aptamers: Selection strategies, characterization, and applications. Front. Chem. 2016, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Song, Y.; Li, C.; Zou, Y.; Zhu, L.; An, Y.; Yang, C.J. Monoclonal surface display SELEX for simple, rapid, efficient, and cost-effective aptamer enrichment and identification. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5881–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Han, M.; Wu, Y. Progress on Detection Method of AFB1 in Cereal and Application of Aptamer. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2024, 13, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, Z. Magnetic particle-based DNA hybridization assay with chemiluminescence and chemiluminescent imaging detection. Analyst 2009, 134, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, W.; Mun, H.; Joung, H.; Ofori, J.; Chung, D.; Kim, G. Chemiluminescence competitive aptamer assay for the detection of aflatoxin B1 in corn samples. Food Control 2014, 36, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, F. Development of a chemiluminescent aptasensor for ultrasensitive and selective detection of aflatoxin B1 in peanut and milk. Talanta 2019, 201, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Wu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, K. Design of optical fiber detection system for aflatoxin B1. Electron. Meas. Technol. 2022, 45, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.; Chen, R.; Ren, S.; Gao, Z.; Liang, J. Detection of aflatoxin B1 in vegetable protein meat based on surface enhanced Raman spectral aptamer sensor. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2023, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, S.; Wei, J.; Jiao, T.; Chen, Q.; Oyama, M.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X. Screening-capture-integrated Electrochemiluminescent aptasensor based on mesoporous silica nanochannels for the ultrasensitive detection of deoxynivalenol in wheat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 12052–12060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhao, Z. Quantitative determination of aflatoxin B1 in wheat by quantum dot fluorescence microsphere immunoassay. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2024, 15, 208–216. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, W. Preparation and Analytical Application of Chemiluminescence Functionalized Magnetic Microbeads and Study on Single Particle Chemiluminescence Imaging. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wu, C. Plastic Optical Fiber Functionalized with Polyaniline for the Detection of Aflatoxin B1 Concentration. Semiconductoroptoelectronics 2024, 45, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Wen, F.; Li, M.; Guo, X.; Li, S.; Zheng, N.; Wang, J. A simple aptamer-based fluorescent assay for the detection of Aflatoxin B1 in infant rice cereal. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhou, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J. A metal-organic framework/aptamer system as a fluorescent biosensor for determination of aflatoxin B1 in food samples. Talanta 2020, 219, 121342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kuang, X.; Fan, D.; Sun, X.; Ren, X.; Wei, Q. 1, 1, 2, 2-tetra (4-carboxylphenyl) ethylene-based metal–organic gel as aggregation-induced electrochemiluminescence emitter for the detection of aflatoxin B1 based on nanosurface energy transfer. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 12593–12597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhao, Q. Direct fluorescence anisotropy approach for aflatoxin B1 detection and affinity binding study by using single tetramethylrhodamine labeled aptamer. Talanta 2018, 189, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Added AFB1/(μg/kg) | Found AFB1/(μg/kg) | Recovery/% |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | <LOD | - |
| 0.5 | 0.396 ± 0.050 | 79.19 ± 10.01 |
| 1 | 0.985 ± 0.127 | 98.53 ± 12.69 |
| 2 | 2.264 ± 0.106 | 113.21 ± 5.31 |
| 5 | 4.628 ± 0.351 | 92.56 ± 7.02 |
| 10 | 10.929 ± 0.429 | 109.29 ± 4.29 |
| Methods | LOD | Linear (L)/Dynamic (D) Range | Tested Samples | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemiluminescence | Aptamer | 0.09 ng/mL | (D) 0.1–10 ng/mL | Wheat | This work |
| Chemiluminescence | Aptamer | 0.20 ng/mL | (L) 0.5–40 ng/mL | Peanut and milk | [25] |
| Chemiluminescence | Antibody | 0.53 ng/mL | (D) 0.1–10 ng/mL | Wheat | [31] |
| Fluorescent | Aptamer | 1.6 ng/mL | (L) 5–100 ng/mL | Rice cereal | [32] |
| Fluorescent | Aptamer | 0.35 ng/mL | (L) 0–180 ng/mL | Corn, milk, and rice | [33] |
| Fluorescent | Aptamer | 0.62 ng/mL | (D) 0.62–312.27 ng/mL | Serum, urine, wine, and beer | [34] |
| Electrochemiluminescence | Aptamer | 0.17 ng/mL | (L) 0.50–200.00 ng/mL | Corn | [35] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhao, Z. Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Wheat Based on Nucleic Aptamer Chemiluminescence Sensor. Sensors 2025, 25, 988. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25040988
Zhang Z, Wu C, Zhao Z. Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Wheat Based on Nucleic Aptamer Chemiluminescence Sensor. Sensors. 2025; 25(4):988. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25040988
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zebing, Caizhang Wu, and Zhike Zhao. 2025. "Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Wheat Based on Nucleic Aptamer Chemiluminescence Sensor" Sensors 25, no. 4: 988. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25040988
APA StyleZhang, Z., Wu, C., & Zhao, Z. (2025). Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Wheat Based on Nucleic Aptamer Chemiluminescence Sensor. Sensors, 25(4), 988. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25040988






