HGF-MiLaG: Hierarchical Graph Fusion for Emotion Recognition in Conversation with Mid-Late Gender-Aware Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Graph Neural Network
2.2. Multi-Task Learning
2.3. Auxiliary Information Fusion
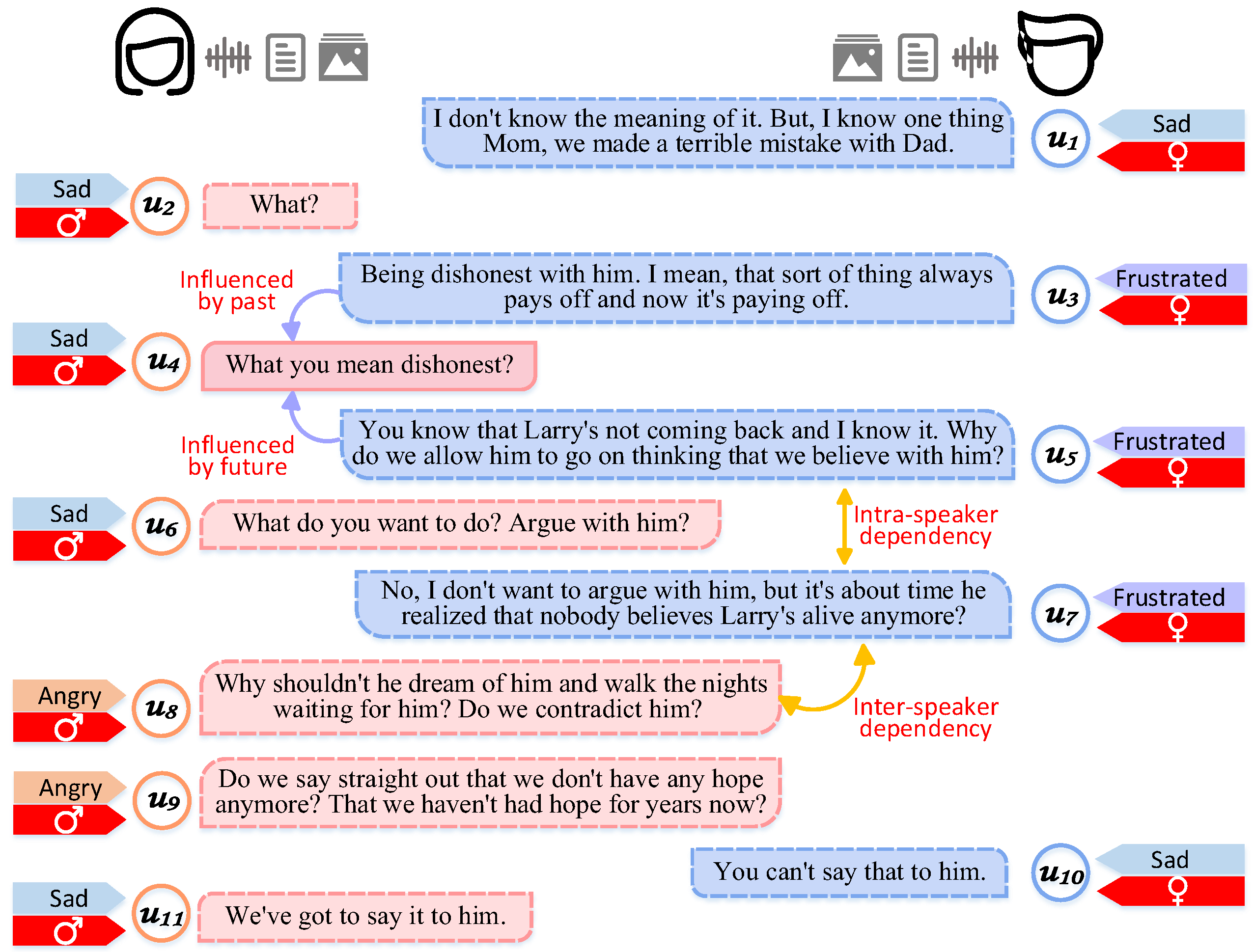
3. Method
3.1. Task Definition
3.2. Unimodal Feature Extraction
3.3. Hierarchical Graph Fusion
3.3.1. Context Encoding
3.3.2. Hierarchical Fusion Graph Construction
3.4. Mid-Late Gender-Aware Emotion Feature Classifier
3.4.1. Middle Gender-Aware Emotion Classifier
3.4.2. Late Gender-Aware Emotion Classifier
3.4.3. Loss Function
4. Experiment
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Baseline
4.3. Experiment Setup
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Comparison with Baseline Models
5.2. Ablation Study
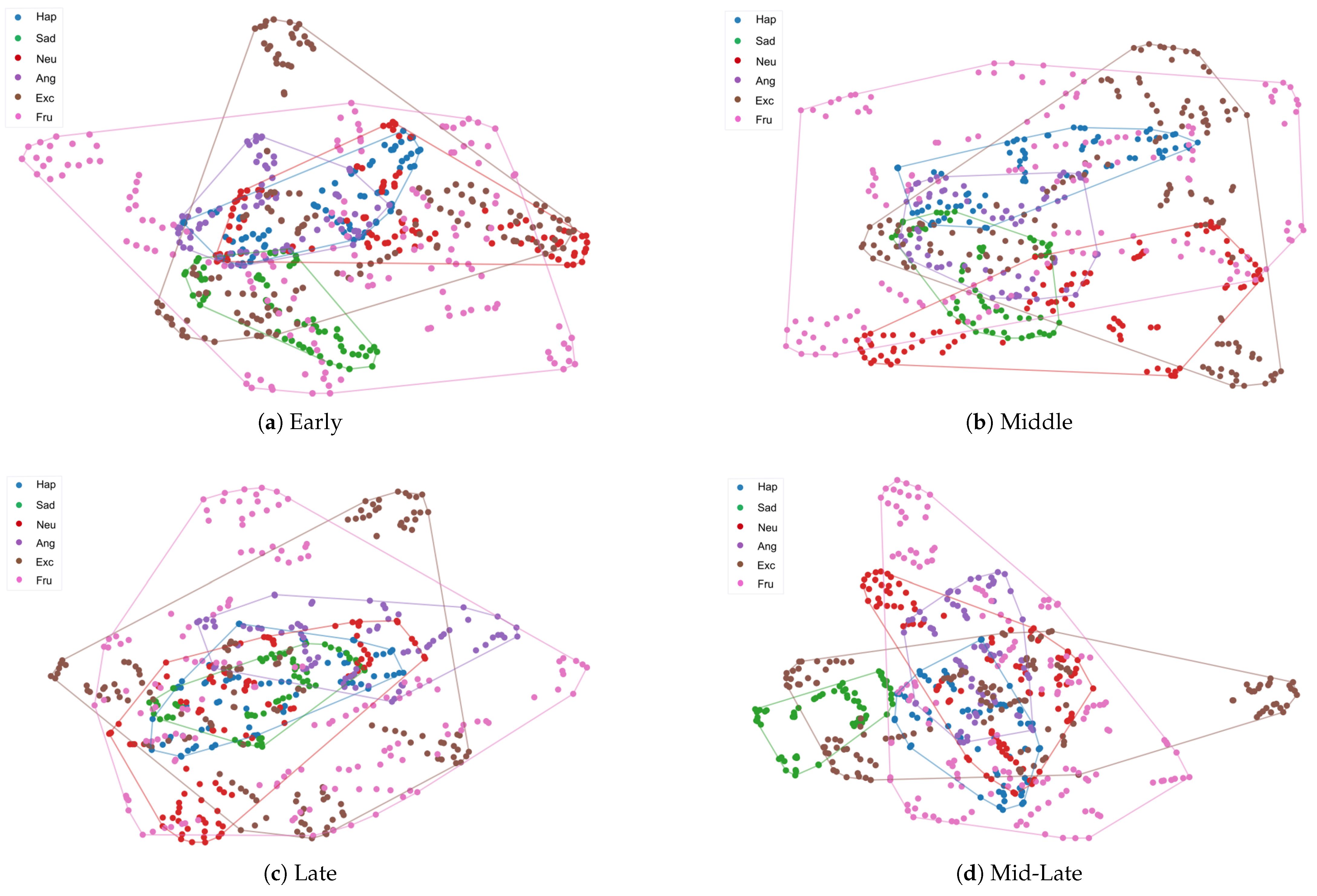
5.3. Comparison with Different Position of Gender Injection
5.4. Effect of Window Size
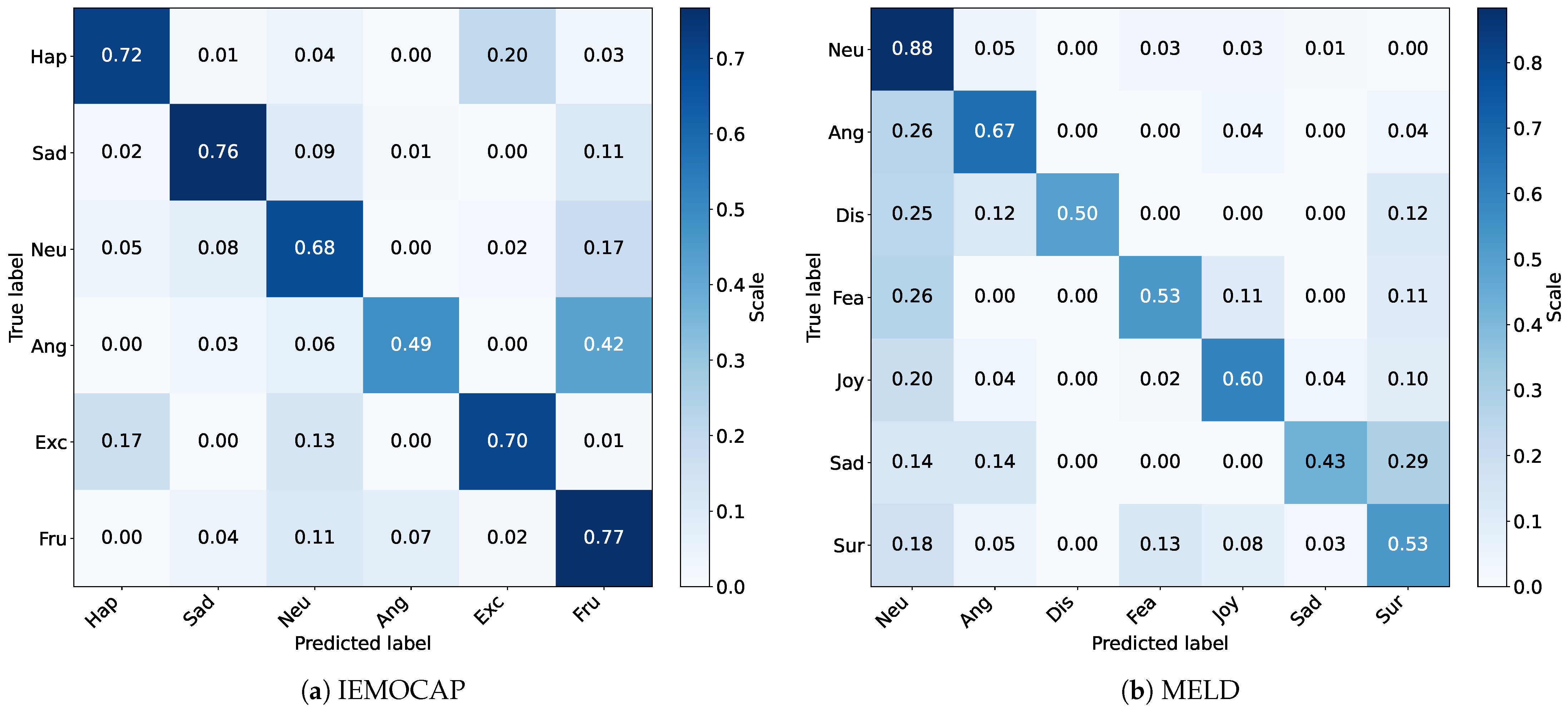
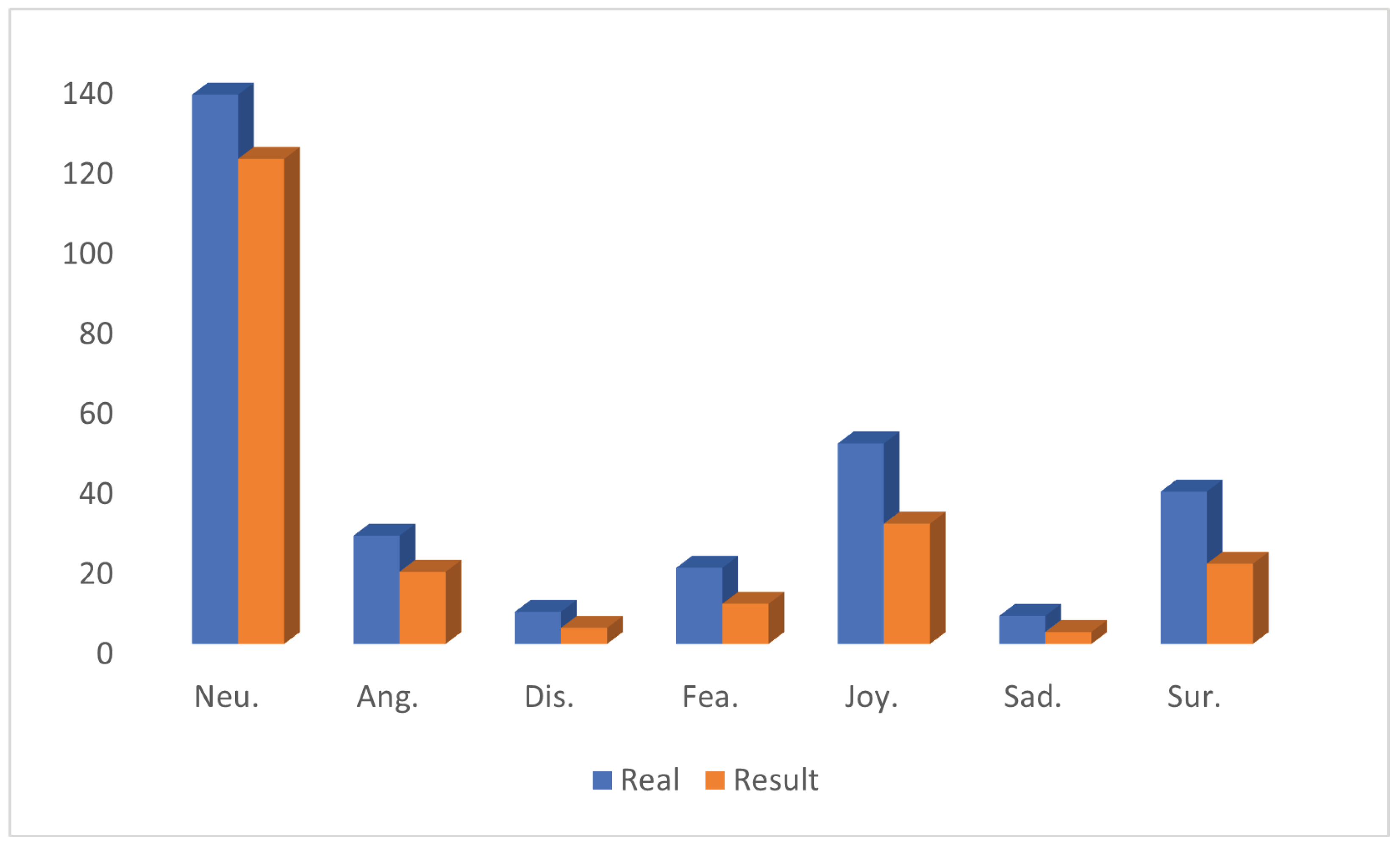
5.5. Insight from Output
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pereira, R.; Mendes, C.; Costa, N.; Frazão, L.; Fernández-Caballero, A.; Pereira, A. Human-Computer Interaction Approach with Empathic Conversational Agent and Computer Vision. In Artificial Intelligence for Neuroscience and Emotional Systems, Proceedings of the 10th International Work-Conference on the Interplay Between Natural and Artificial Computation, Olhâo, Portugal, 4–7 June 2024; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 431–440. [Google Scholar]
- Votintseva, A.; Johnson, R.; Villa, I. Emotionally Intelligent Conversational User Interfaces: Bridging Empathy and Technology in Human-Computer Interaction. In Human-Computer Interaction, Proceedings of the International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Washington DC, USA, 29 June 2024; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 404–422. [Google Scholar]
- Messaoudi, C.; Guessoum, Z.; Ben Romdhane, L. Opinion mining in online social media: A survey. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2022, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Wu, B.C.; Nguyen, P.A.; Wang, H.H.; Kao, C.C.; Lee, P.C.; Rahmanti, A.R.; Hsu, J.C.; Yang, H.C.; Li, Y.C.J. Emotion recognition in doctor-patient interactions from real-world clinical video database: Initial development of artificial empathy. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2023, 233, 107480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; LiMember, W.J.; Fu, C.; Lian, C.; Shan, P. Image Encoding and Fusion of Multi-modal Data Enhance Depression Diagnosis in Parkinson’s Disease Patients. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2024, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, M.; Montazer, G.A. A survey of emotion recognition methods with emphasis on E-Learning environments. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2019, 147, 102423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poria, S.; Majumder, N.; Mihalcea, R.; Hovy, E. Emotion recognition in conversation: Research challenges, datasets, and recent advances. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 100943–100953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.; Bhat, A.; Jain, A.; Singh, A.V.; Modi, A. COGMEN: COntextualized GNN based multimodal emotion recognition. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.02455. [Google Scholar]
- Defferrard, M.; Bresson, X.; Vandergheynst, P. Convolutional Neural Networks on Graphs with Fast Localized Spectral Filtering. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, W.; Yang, H.; King, I.; Lyu, M.R. HiGRU: Hierarchical Gated Recurrent Units for Utterance-level Emotion Recognition. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.04446. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosal, D.; Majumder, N.; Poria, S.; Chhaya, N.; Gelbukh, A. DialogueGCN: A graph convolutional neural network for emotion recognition in conversation. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China, 3–7 November 2019; pp. 154–164. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jin, Q. MMGCN: Multimodal fusion via deep graph convolution network for emotion recognition in conversation. In Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics & 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), Online, 1–6 August 2021; pp. 5666–5675. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lv, G.; Zeng, Z. GA2MIF: Graph and attention based two-stage multi-source information fusion for conversational emotion detection. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2024, 15, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lv, G.; Zeng, Z. GraphCFC: A Directed Graph Based Cross-Modal Feature Complementation Approach for Multimodal Conversational Emotion Recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Ji, D.; Liu, Y. Multi-task learning with auxiliary speaker identification for conversational emotion recognition. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.01478. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Cao, B.; Guan, X.; Gu, T.; Bao, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, B.; Cao, J. Emotion recognition in conversations with emotion shift detection based on multi-task learning. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 248, 108861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Yu, J.; Xia, R.; Wang, S. A Facial Expression-Aware Multimodal Multi-task Learning Framework for Emotion Recognition in Multi-party Conversations. In Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Toronto, ON, Canada, 9–14 July 2023; pp. 15445–15459. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Li, H.; Wang, W. A study on gender differences in speech emotion recognition based on corpus. J. Nanjing Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2019, 55, 758–764. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lv, G.; Zeng, Z. GraphMFT: A graph network based multimodal fusion technique for emotion recognition in conversation. Neurocomputing 2023, 550, 126427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, Q.; Jain, D.K.; Štruc, V. A graph neural network with context filtering and feature correction for conversational emotion recognition. Inf. Sci. 2024, 658, 120017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Su, Y.; Su, K.; Liu, Y.; Shi, J.; Wu, B.; Liu, C.; Ishi, C.T.; Ishiguro, H. HAM-GNN: A hierarchical attention-based multi-dimensional edge graph neural network for dialogue act classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 261, 125459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruana, R. Multitask Learning. Mach. Learn. 1997, 28, 41–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruder, S. An Overview of Multi-Task Learning in Deep Neural Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05098. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Yang, K.; Sun, C.J.; Liu, B.; Ji, Z. Knowledge-interactive network with sentiment polarity intensity-aware multi-task learning for emotion recognition in conversations. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2021, Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 16–20 November 2021; pp. 2879–2889. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, B.; Wei, D.; Shao, Y. Dynamic weighted multitask learning and contrastive learning for multimodal sentiment analysis. Electronics 2023, 12, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Liao, J.; Zheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Li, D. Sentiment classification method based on multitasking and multimodal interactive learning. In Proceedings of the 22nd China National Conference on Computational Linguistics, Harbin, China, 3–5 August 2023; pp. 315–327. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Jia, W.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, B.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Z. Personality Enhanced Emotion Generation Modeling for Dialogue Systems. Cogn. Comput. 2024, 16, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; He, Y.; Sun, L.; Lian, Z.; Liu, B.; Tao, J.; Xu, M.; Wang, K. Multimodal sentiment analysis based on recurrent neural network and multimodal attention. In Proceedings of the 2nd on Multimodal Sentiment Analysis Challenge, Online, 24 October 2021; pp. 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Gao, C.; Xiao, X.; Liu, H.; He, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, F. SKEP: Sentiment knowledge enhanced pre-training for sentiment analysis. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.05635. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, C.; Geng, B. Deep Multimodal Data Fusion. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 56, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, A.; Liang, P.P.; Poria, S.; Vij, P.; Cambria, E.; Morency, L.P. Multi-attention recurrent network for human communication comprehension. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Nagrani, A.; Yang, S.; Arnab, A.; Jansen, A.; Schmid, C.; Sun, C. Attention bottlenecks for multimodal fusion. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 14200–14213. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Li, S.; Zhou, G. Multimodal emotion recognition with auxiliary sentiment information. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao 2020, 56, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Schuller, B.; Batliner, A.; Steidl, S.; Seppi, D. Recognising realistic emotions and affect in speech: State of the art and lessons learnt from the first challenge. Speech Commun. 2011, 53, 1062–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Liu, C.; Ishi, C.T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Iio, T.; Ishiguro, H. Using an android robot to improve social connectedness by sharing recent experiences of group members in human-robot conversations. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 6670–6677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Chudasama, V.; Kar, P.; Gudmalwar, A.; Shah, N.; Wasnik, P.; Onoe, N. M2fnet: Multi-modal fusion network for emotion recognition in conversation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 4652–4661. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Liu, B.; Li, Z. Multimodal Sentiment Analysis Based on a Cross-Modal Multihead Attention Mechanism. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2024, 78, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.; Ritzert, M.; Fey, M.; Hamilton, W.L.; Lenssen, J.E.; Rattan, G.; Grohe, M. Weisfeiler and Leman go neural: Higher-order graph neural networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 29–31 January 2019; Volume 33, pp. 4602–4609. [Google Scholar]
- Foggia, P.; Greco, A.; Saggese, A.; Vento, M. Multi-task learning on the edge for effective gender, age, ethnicity and emotion recognition. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 118, 105651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampiconi, L.; Elwood, A.; Leonardi, M.; M’ohamed, A.; Rozza, A. A survey and taxonomy of loss functions in machine learning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.05579. [Google Scholar]
- Busso, C.; Bulut, M.; Lee, C.C.; Kazemzadeh, A.; Mower, E.; Kim, S.; Chang, J.N.; Lee, S.; Narayanan, S.S. IEMOCAP: Interactive emotional dyadic motion capture database. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2008, 42, 335–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poria, S.; Hazarika, D.; Majumder, N.; Naik, G.; Cambria, E.; Mihalcea, R. MELD: A Multimodal Multi-Party Dataset for Emotion Recognition in Conversations. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019; Association for Computational Linguistics: Florence, Italy, 2019; pp. 527–536. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.; Wei, L.; Huai, X. DialogueCRN: Contextual Reasoning Networks for Emotion Recognition in Conversations. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.01978. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, G. Multi-modal graph context extraction and consensus-aware learning for emotion recognition in conversation. Knowl. Based Syst. 2024, 298, 111954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Qian, F.; Su, K.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, C.; Ishi, C.T. HiMul-LGG: A hierarchical decision fusion-based local–global graph neural network for multimodal emotion recognition in conversation. Neural Netw. 2025, 181, 106764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Model | IEMOCAP | MELD | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Happy | Sad | Neutral | Angry | Excited | Frustrated | Acc. | Wa-F1 | Acc. | Wa-F1 | |
| F1 | F1 | F1 | F1 | F1 | F1 | |||||
| DiagueGCN | 41.28 | 82.52 | 64.33 | 65.18 | 73.18 | 64.46 | 66.85 | 66.78 | 59.58 | 58.17 |
| DiagueCRN | 53.23 | 83.37 | 62.96 | 66.09 | 75.40 | 66.07 | 67.16 | 67.21 | 61.11 | 58.67 |
| MMGCN | 37.61 | 79.84 | 62.26 | 74.29 | 75.00 | 63.68 | 67.28 | 66.67 | 61.07 | 57.33 |
| COGMEN | 51.90 | 81.70 | 68.60 | 66.00 | 75.30 | 58.20 | 68.20 | 67.60 | - | - |
| GraphCFC | 43.08 | 84.99 | 64.70 | 71.35 | 78.86 | 63.70 | 69.13 | 68.91 | 61.42 | 58.86 |
| GA2MIF | 46.15 | 84.50 | 68.38 | 70.29 | 75.99 | 66.49 | 69.75 | 70.00 | 61.65 | 58.94 |
| GraphMFT | 45.99 | 83.12 | 63.08 | 70.30 | 76.92 | 63.84 | 67.90 | 68.07 | 61.30 | 58.37 |
| GCCL | 54.05 | 81.10 | 70.28 | 68.21 | 72.17 | 64.00 | 69.87 | 69.29 | 62.82 | 60.28 |
| AVL COLD Fusion | 43.70 | 60.20 | 48.90 | 58.40 | 61.60 | 57.90 | 82.70 | 55.10 | - | - |
| HiMul-LGG | 53.95 | 79.92 | 71.66 | 67.56 | 72.00 | 68.46 | 70.12 | 70.22 | 66.21 | 65.18 |
| HGF-MiLaG | 59.16 | 83.94 | 70.60 | 68.60 | 74.20 | 66.21 | 70.98 | 71.02 | 66.22 | 65.26 |
| Method | IEMOCAP | MELD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc. | Wa-F1 | Acc. | Wa-F1 | |
| HGF-MiLaG | 70.98 | 71.02 | 66.22 | 65.26 |
| w/o MiLaG | 69.87 | 70.01 | 65.91 | 64.91 |
| w/o MG | 65.43 | 65.45 | 65.64 | 64.89 |
| w/o UG | 69.01 | 69.09 | 66.03 | 64.75 |
| Position | IEMOCAP | |
|---|---|---|
| Acc. | Wa-F1 | |
| Early | 69.50 | 69.69 |
| Middle | 69.38 | 69.64 |
| Late | 69.25 | 69.21 |
| Mid-Late | 70.98 | 71.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Hao, R.; Li, Z.; Kuang, X.; Dong, J.; Zhang, Q.; Qian, F.; Fu, C. HGF-MiLaG: Hierarchical Graph Fusion for Emotion Recognition in Conversation with Mid-Late Gender-Aware Strategy. Sensors 2025, 25, 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25041182
Wang Y, Hao R, Li Z, Kuang X, Dong J, Zhang Q, Qian F, Fu C. HGF-MiLaG: Hierarchical Graph Fusion for Emotion Recognition in Conversation with Mid-Late Gender-Aware Strategy. Sensors. 2025; 25(4):1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25041182
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yihan, Rongrong Hao, Ziheng Li, Xinhe Kuang, Jiacheng Dong, Qi Zhang, Fengkui Qian, and Changzeng Fu. 2025. "HGF-MiLaG: Hierarchical Graph Fusion for Emotion Recognition in Conversation with Mid-Late Gender-Aware Strategy" Sensors 25, no. 4: 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25041182
APA StyleWang, Y., Hao, R., Li, Z., Kuang, X., Dong, J., Zhang, Q., Qian, F., & Fu, C. (2025). HGF-MiLaG: Hierarchical Graph Fusion for Emotion Recognition in Conversation with Mid-Late Gender-Aware Strategy. Sensors, 25(4), 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25041182






