Experimental Study on Noise-Reduced Propagation Characteristics of the Parametric Acoustic Array Field in a Neck Phantom
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
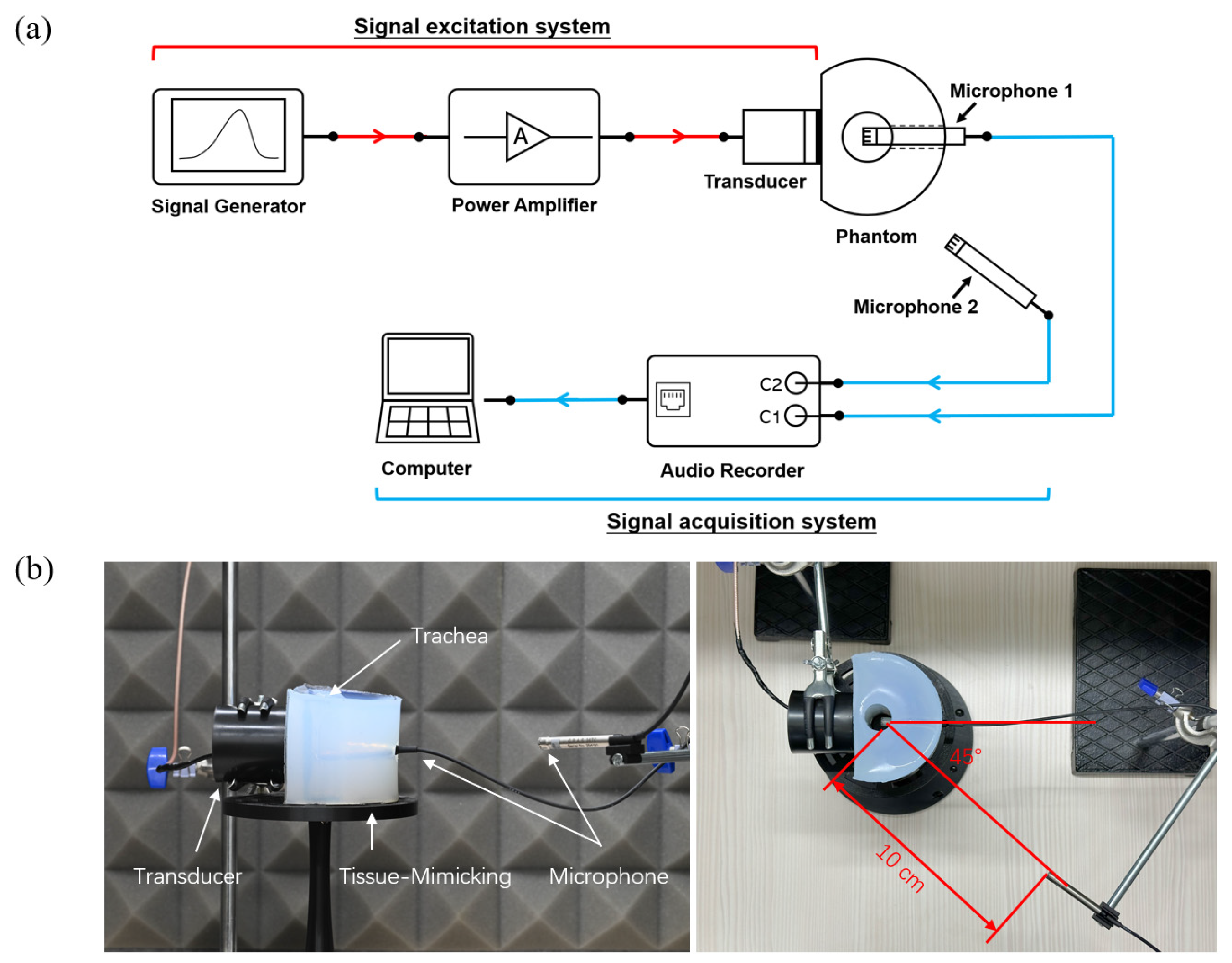
2.1. Experimental Platform
2.1.1. Human Neck Tissue-Mimicking Phantom
2.1.2. Signal Excitation System
2.2. Experimental Procedure
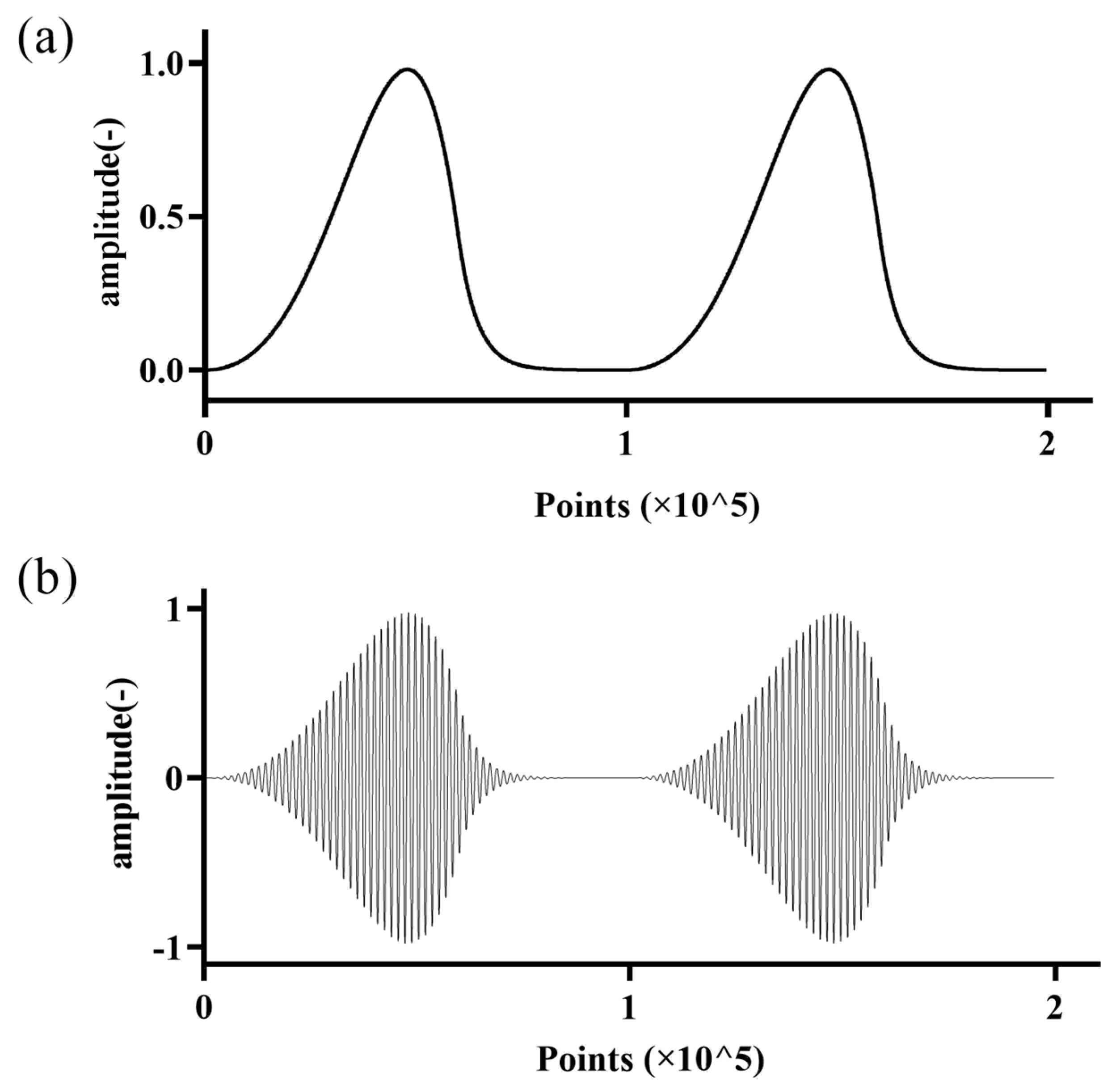
2.3. Excitation Signal
2.4. Signal Processing and Parameter Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Time-Domain Analysis
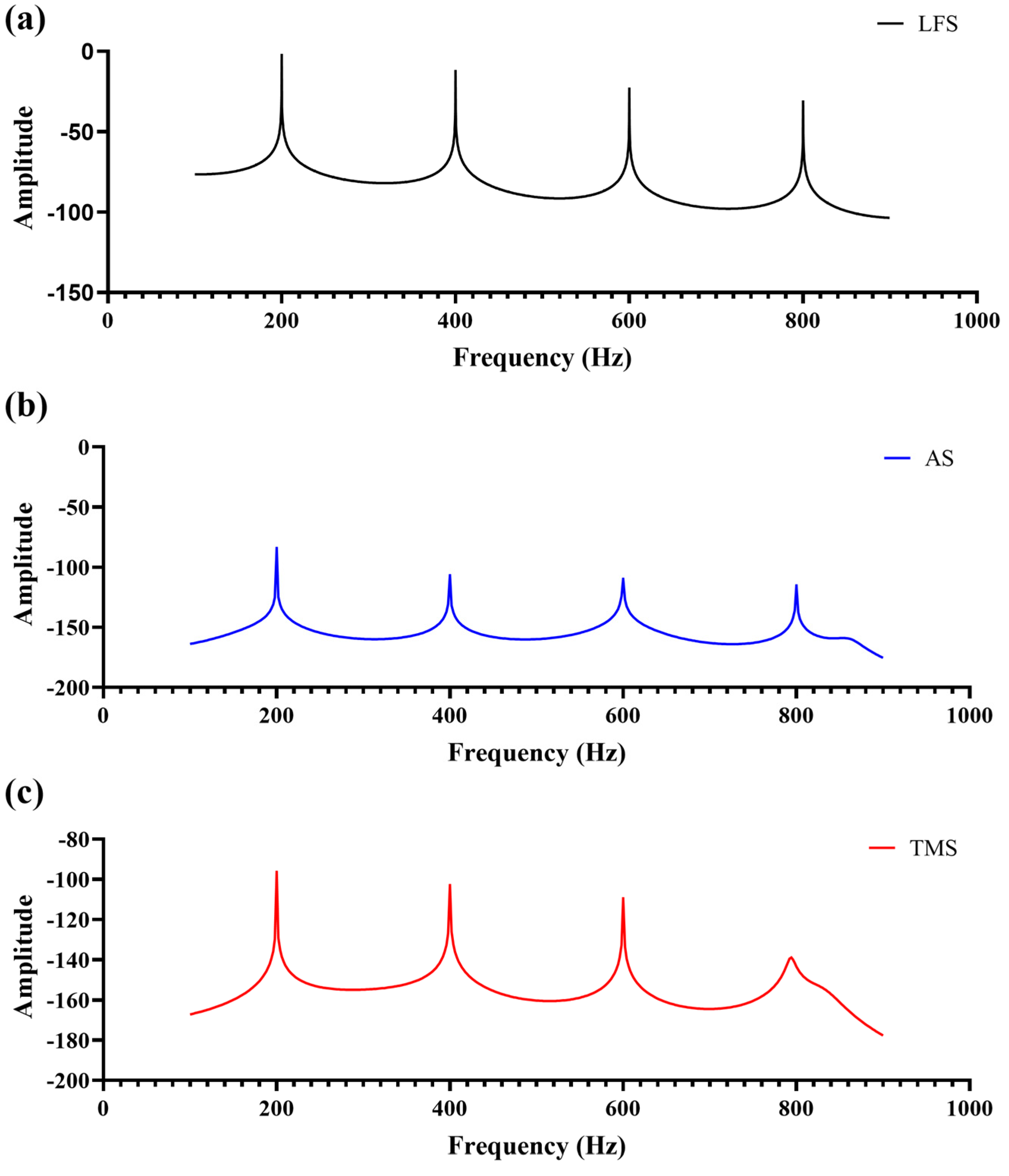
3.2. Frequency-Domain Analysis
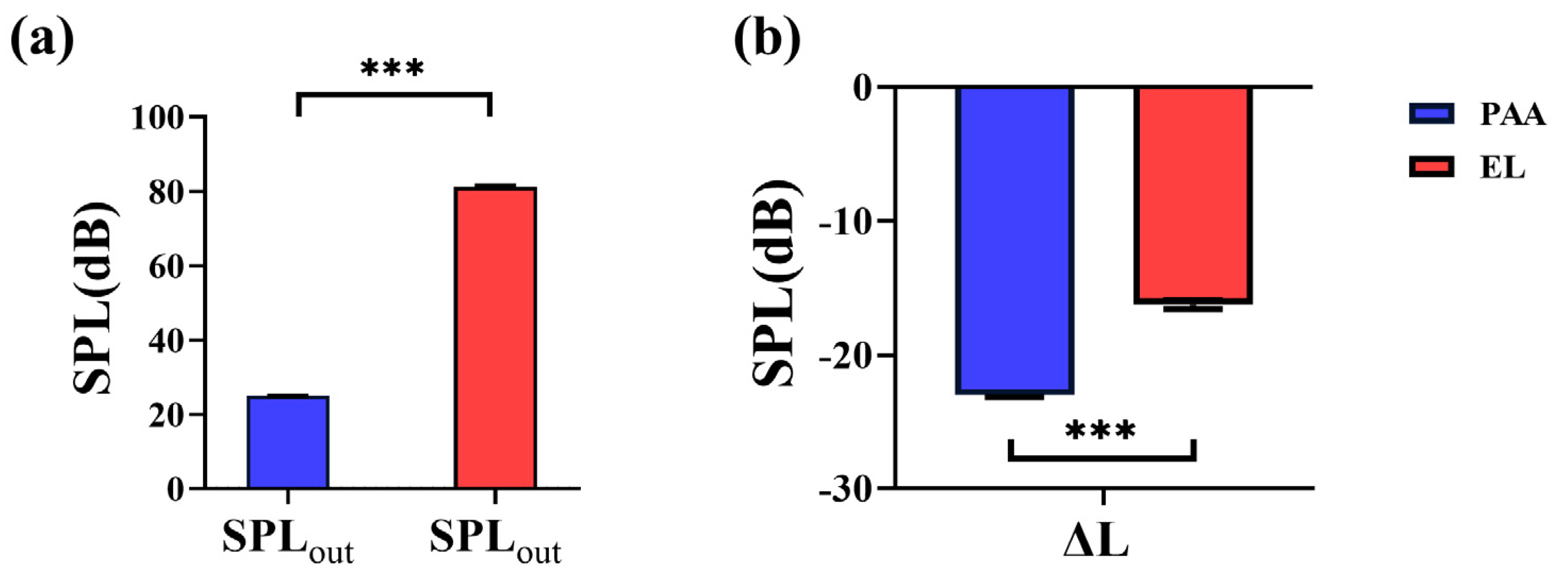
3.3. Radiation Noise Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Souza, F.G.R.; Santos, I.C.; Bergmann, A.; Thuler, L.C.S.; Freitas, A.S.; Freitas, E.Q.; Dias, F.L. Quality of Life after Total Laryngectomy: Impact of Different Vocal Rehabilitation Methods in a Middle Income Country. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2020, 18, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.A.; McCarroll, L.; Schmalbach, C.E. Voice Restoration and Quality of Life in Larynx Cancer. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 56, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendenhall, W.M.; Morris, C.G.; Stringer, S.P.; Amdur, R.J.; Hinerman, R.W.; Villaret, D.B.; Robbins, K.T. Voice Rehabilitation after Total Laryngectomy and Postoperative Radiation Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 2500–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, H.-J.; Wan, M.-X.; Wang, S.-P.; Liu, H.-J. Enhancement of Electrolarynx Speech Using Adaptive Noise Cancelling Based on Independent Component Analysis. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2003, 41, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, R.; Tang, C.G.; Sinclair, C.F. The Electrolarynx: Voice Restoration after Total Laryngectomy. Med. Devices 2017, 10, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, B.; Nolan, M.; Burke, E.; Condron, J.; Coyle, E. Intelligibility of Electrolarynx Speech Using a Novel Actuator. In Proceedings of the IET Irish Signals and Systems Conference (ISSC 2010), Cork, Ireland, 23–24 June 2010; IET: London, UK; pp. 158–162. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, R.L.; Bernstein, R.S. Improved Laboratory Prototype Electrolarynx (LAPEL): Using Inverse Filtering of the Frequency Response Function of the Human Throat. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 1993, 21, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boll, S. Suppression of Acoustic Noise in Speech Using Spectral Subtraction. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process 1979, 27, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Toda, T. Electrolaryngeal Speech Enhancement with Statistical Voice Conversion Based on CLDNN. In Proceedings of the 2018 26th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Rome, Italy, 3–7 September 2018; IEEE: Rome, Italy; pp. 2115–2119. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, D.; Sridharan, S.; Moody, M.; Geva, S. Application of Noise Reduction Techniques for Alaryngeal Speech Enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE TENCON ’97. IEEE Region 10 Annual Conference. Speech and Image Technologies for Computing and Telecommunications (Cat. No.97CH36162), Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 4 December 1997; Volume 2, pp. 491–494. [Google Scholar]
- Violeta, L.P.; Huang, W.-C.; Ma, D.; Yamamoto, R.; Kobayashi, K.; Toda, T. Electrolaryngeal Speech Intelligibility Enhancement through Robust Linguistic Encoders. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2024—2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–19 April 2024; pp. 10961–10965. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, H.; Nakao, M.; Kikuchi, Y.; Kaga, K. Intra-Oral Pressure–Based Voicing Control of Electrolaryngeal Speech with Intra-Oral Vibrator. J. Voice 2008, 22, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Nakao, M.; Kikuchi, Y.; Kaga, K. Alaryngeal Speech Aid Using an Intra-Oral Electrolarynx and a Miniature Fingertip Switch. Auris Nasus Larynx 2005, 32, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-Y.; Lin, B.-S.; Lien, C.-F.; Yu, W.-H.V.; Peng, Y.-Y.; Lin, B.-S. A Voice-Producing System With Naturalness and Variable Multi-Frequency Vocalization for Patients Who Have Undergone Laryngectomy. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 30619–30627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, C.; Fredrickson, J.M.; Kaiser, T.; Karzon, R. Human Speech Development for an Implantable Artificial Larynx. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1987, 96, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, F.; Feng, H.; Huang, M.; Wang, B.; Xia, J. China’s First Demonstration of Cobalt-Rich Manganese Crust Thickness Measurement in the Western Pacific with a Parametric Acoustic Probe. Sensors 2019, 19, 4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Zhu, G.; Yin, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, X. A Modulation Method of Parametric Array for Underwater Acoustic Communication. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 145, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantinelli De Carvalho, A.C.; Arnela, M.; Burbano-Escolà, R.; Vaquerizo-Serrano, J. A Study of the Ultrasonic and Audible Frequency Response of Commercial Loudspeakers for Use as Parametric Acoustic Arrays. Inter-Noise Noise-Con. Congr. Conf. Proc. 2024, 270, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.-S.; Yang, J.; Kamakura, T. A Review of Parametric Acoustic Array in Air. Appl. Acoust. 2012, 73, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogami, Y.; Nakayama, M.; Nishiura, T. Virtual Sound Source Construction Based on Radiation Direction Control Using Multiple Parametric Array Loudspeakers. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 146, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Červenka, M.; Bednařík, M. An Algebraic Correction for the Westervelt Equation to Account for the Local Nonlinear Effects in Parametric Acoustic Array. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2022, 151, 4046–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, P.; Zara, J. 3D Simulation of an Audible Ultrasonic Electrolarynx Using Difference Waves. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Pollet, A.M.A.O.; Panfilova, A.; Zhou, M.; Turco, S.; Den Toonder, J.M.J.; Mischi, M. Acoustic Characterization of Tissue-Mimicking Materials for Ultrasound Perfusion Imaging Research. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2022, 48, 124–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breatnach, E.; Abbott, G.C.; Fraser, R.G. Dimensions of the Normal Human Trachea. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1984, 142, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, S. Design of Parametric Acoustic Array Based on Inverse Control Processing. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 195, 108816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fant, G. Glottal Flow: Models and Interaction. J. Phon. 1986, 14, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Li, F.; Zhou, J.; Niu, H. Experimental Study on Noise-Reduced Propagation Characteristics of the Parametric Acoustic Array Field in a Neck Phantom. Sensors 2025, 25, 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030802
Wang L, Li F, Zhou J, Niu H. Experimental Study on Noise-Reduced Propagation Characteristics of the Parametric Acoustic Array Field in a Neck Phantom. Sensors. 2025; 25(3):802. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030802
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Li, Fengji Li, Jie Zhou, and Haijun Niu. 2025. "Experimental Study on Noise-Reduced Propagation Characteristics of the Parametric Acoustic Array Field in a Neck Phantom" Sensors 25, no. 3: 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030802
APA StyleWang, L., Li, F., Zhou, J., & Niu, H. (2025). Experimental Study on Noise-Reduced Propagation Characteristics of the Parametric Acoustic Array Field in a Neck Phantom. Sensors, 25(3), 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030802





