A Double Extended Kalman Filter Algorithm for Weakening Non-Line-of-Sight Errors in Complex Indoor Environments Based on Ultra-Wideband Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. System Model
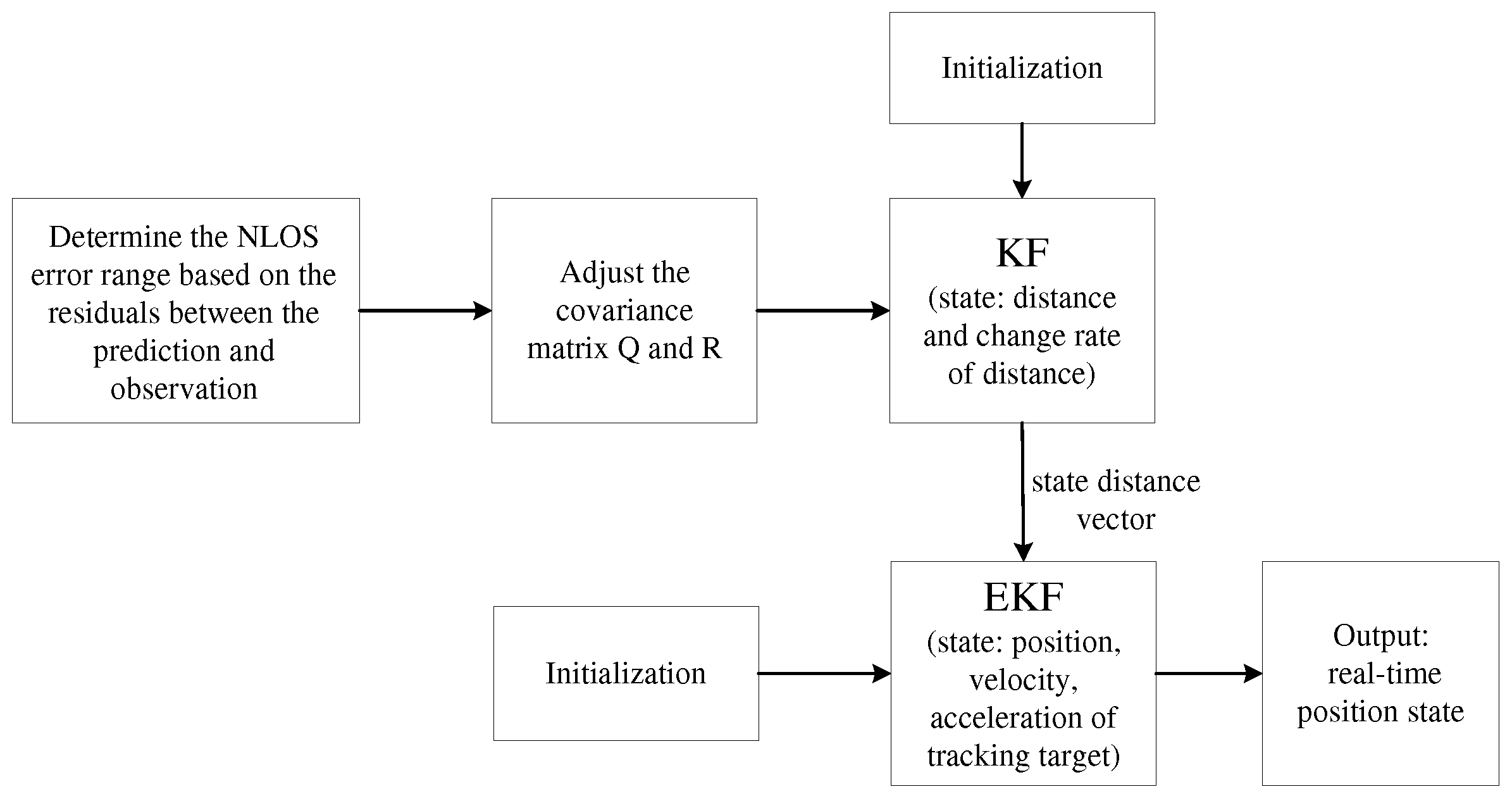
2.1. Extended Kalman Filter Modeling
2.2. Measurement Error Modeling
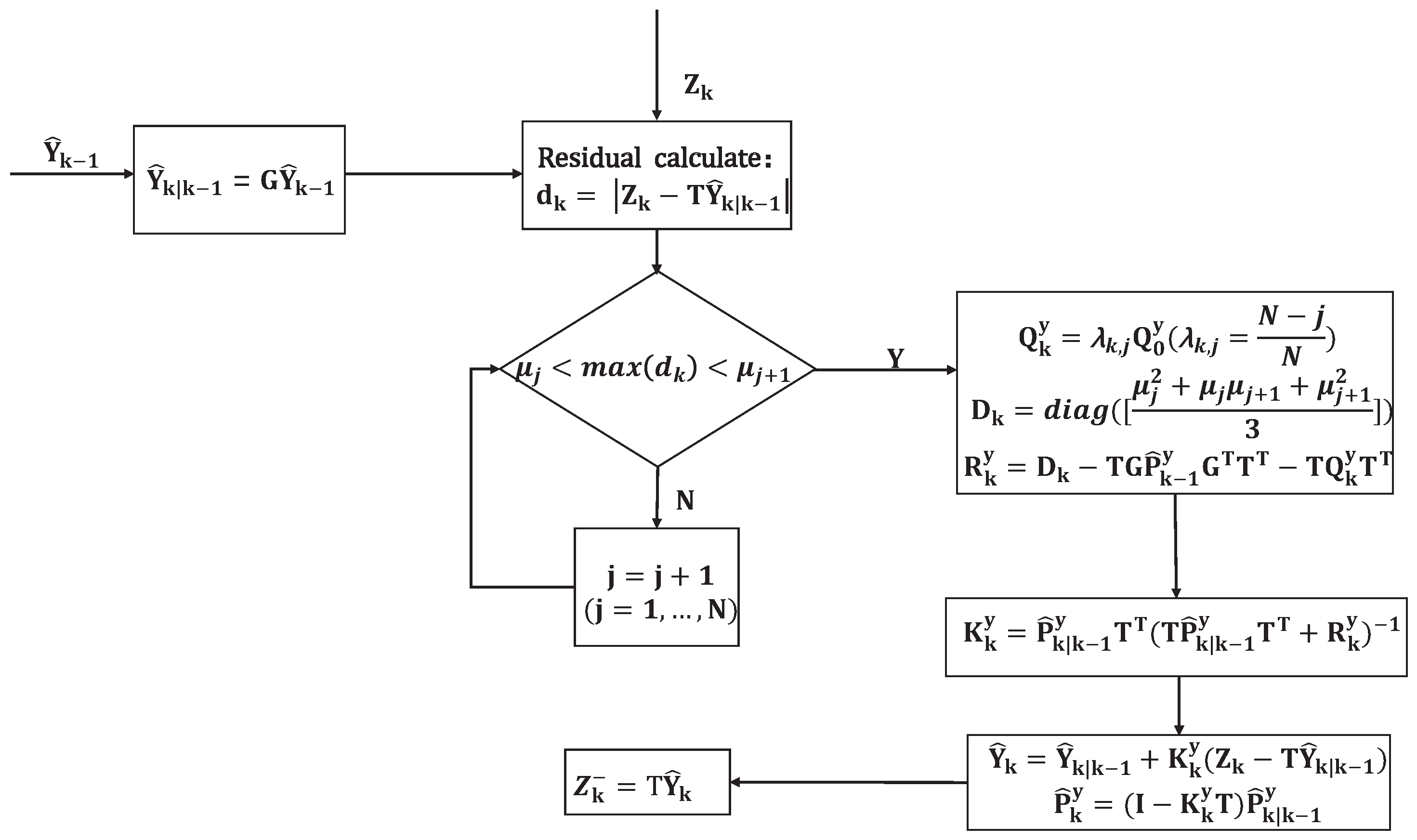
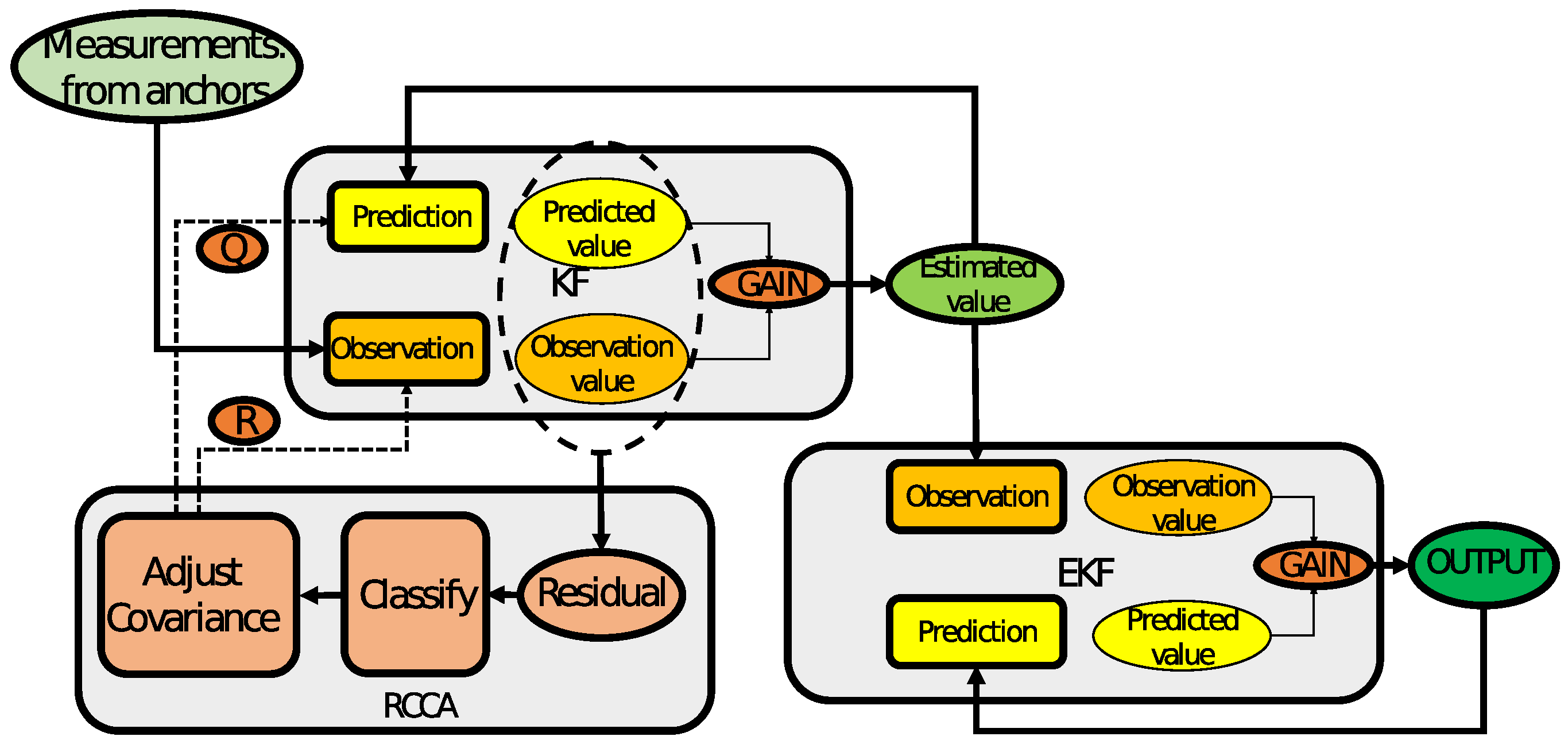
3. Residual Classification and Covariance Adjustment
4. Double Extended Kalman Filter Based on RCCA
| Algorithm 1 Double-layer extended-Kalman filter algorithm. |
|
5. Simulation Results and Experimental Verification
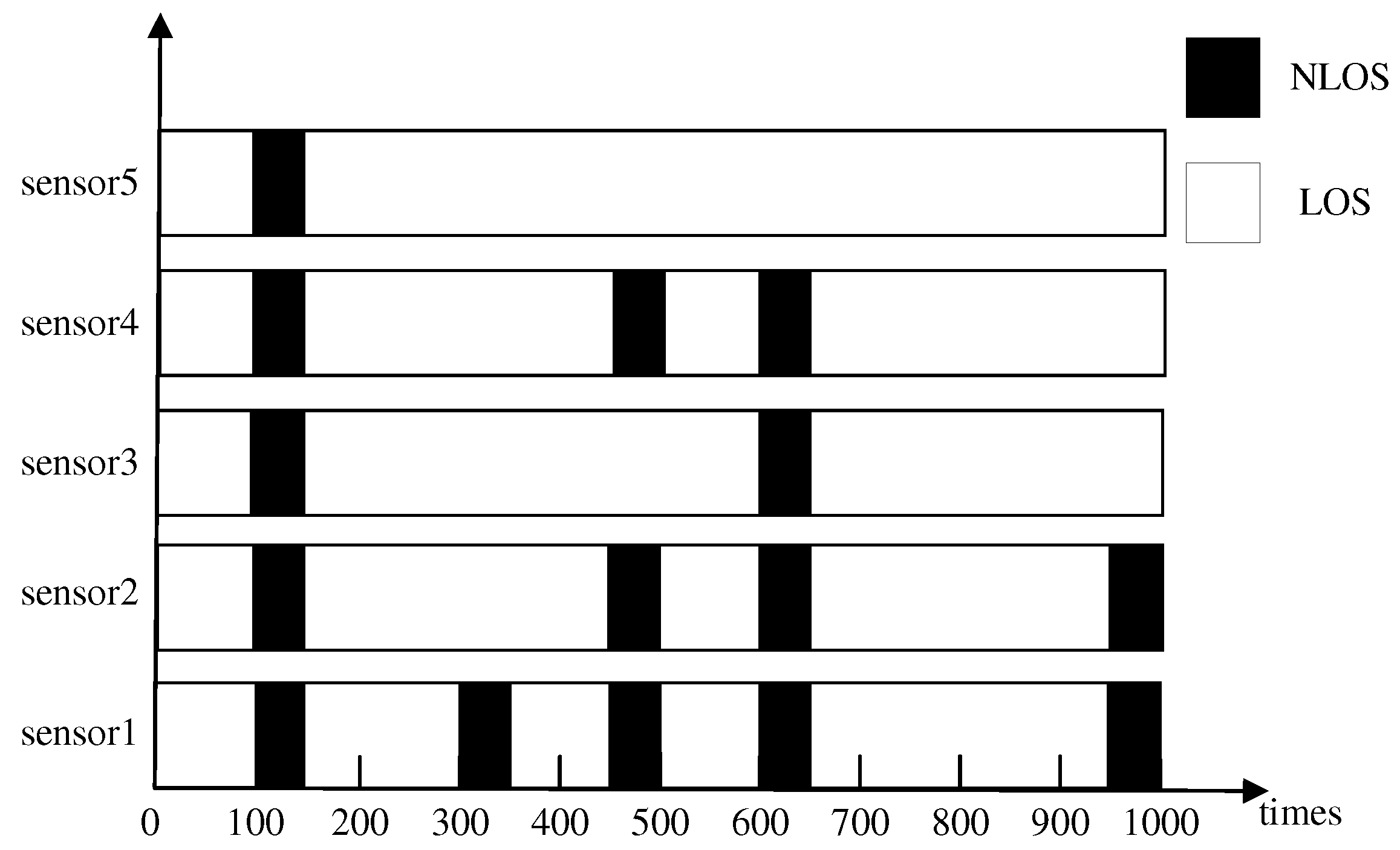
5.1. Simulation Environments and Settings
5.2. Performance Metrics
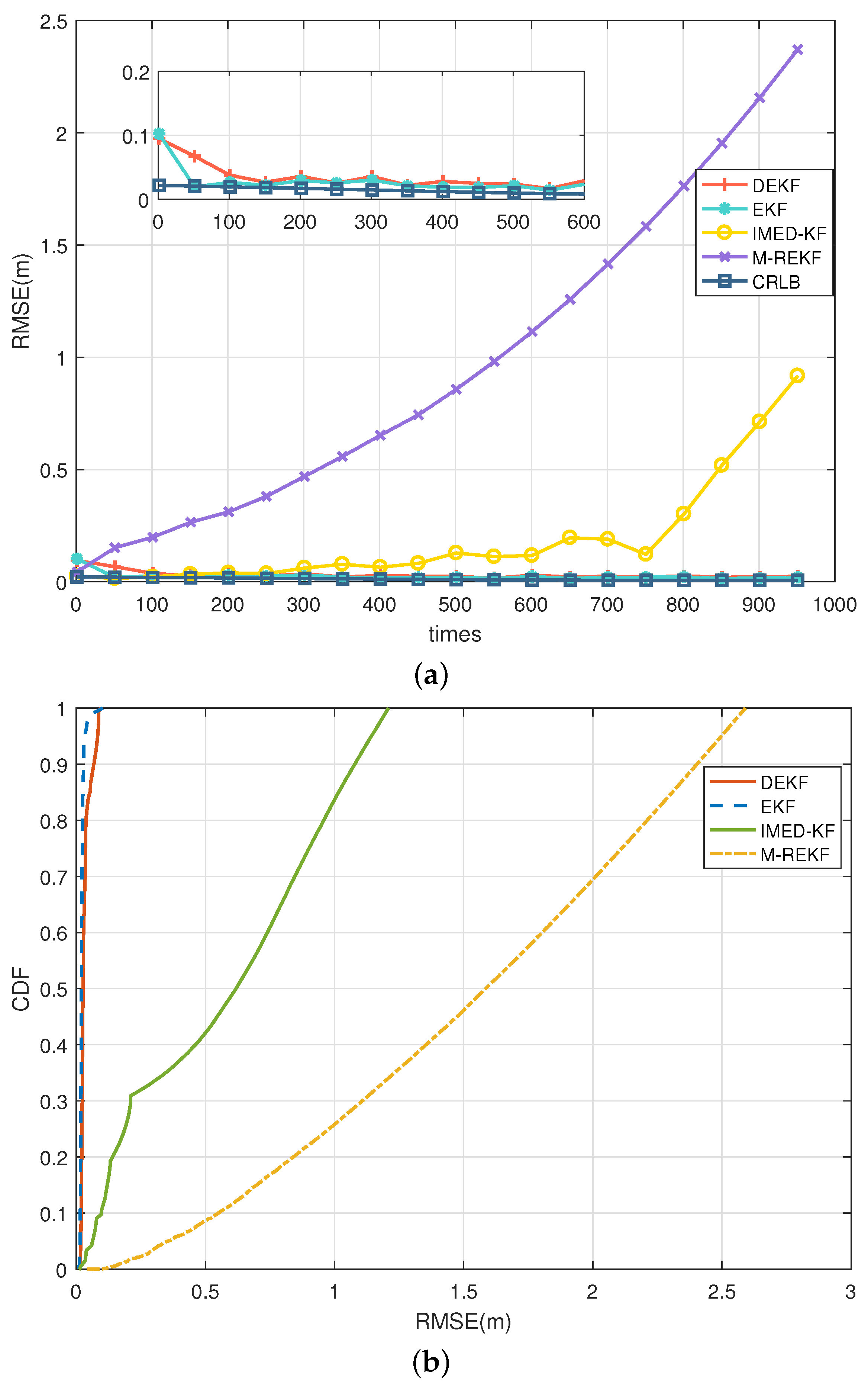
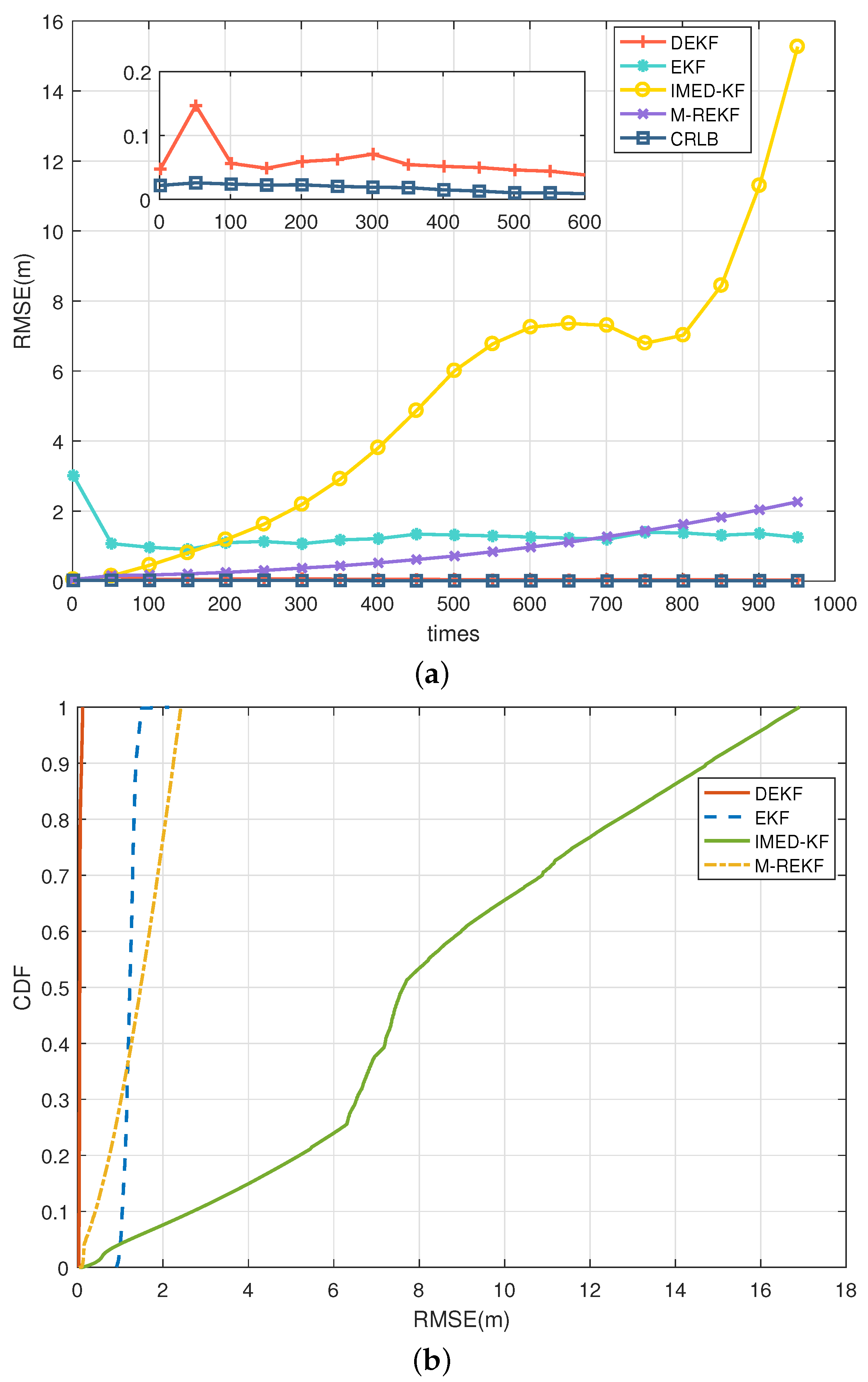
5.3. Simulation Results
- S1:
- S2:
- S3:
- S4:
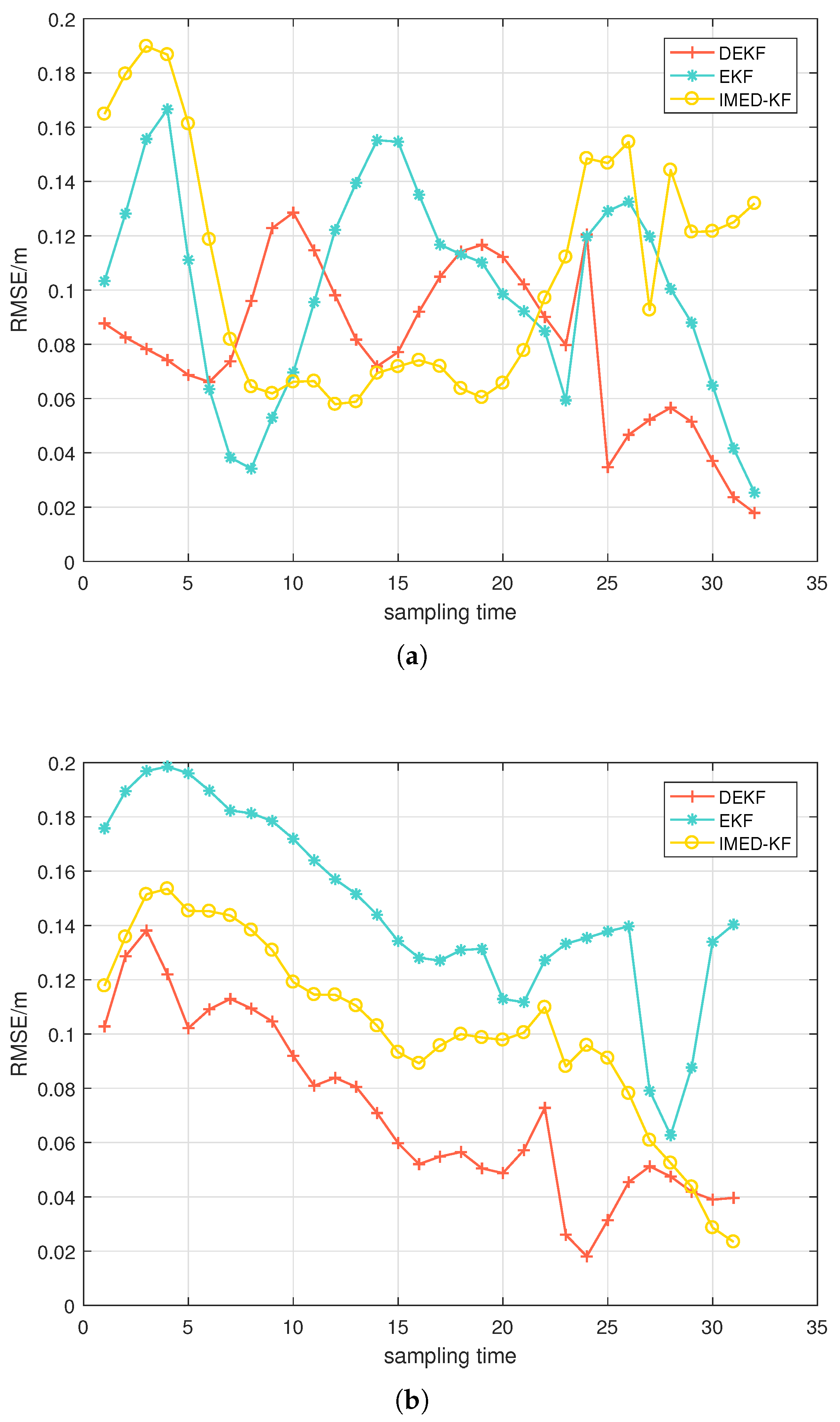
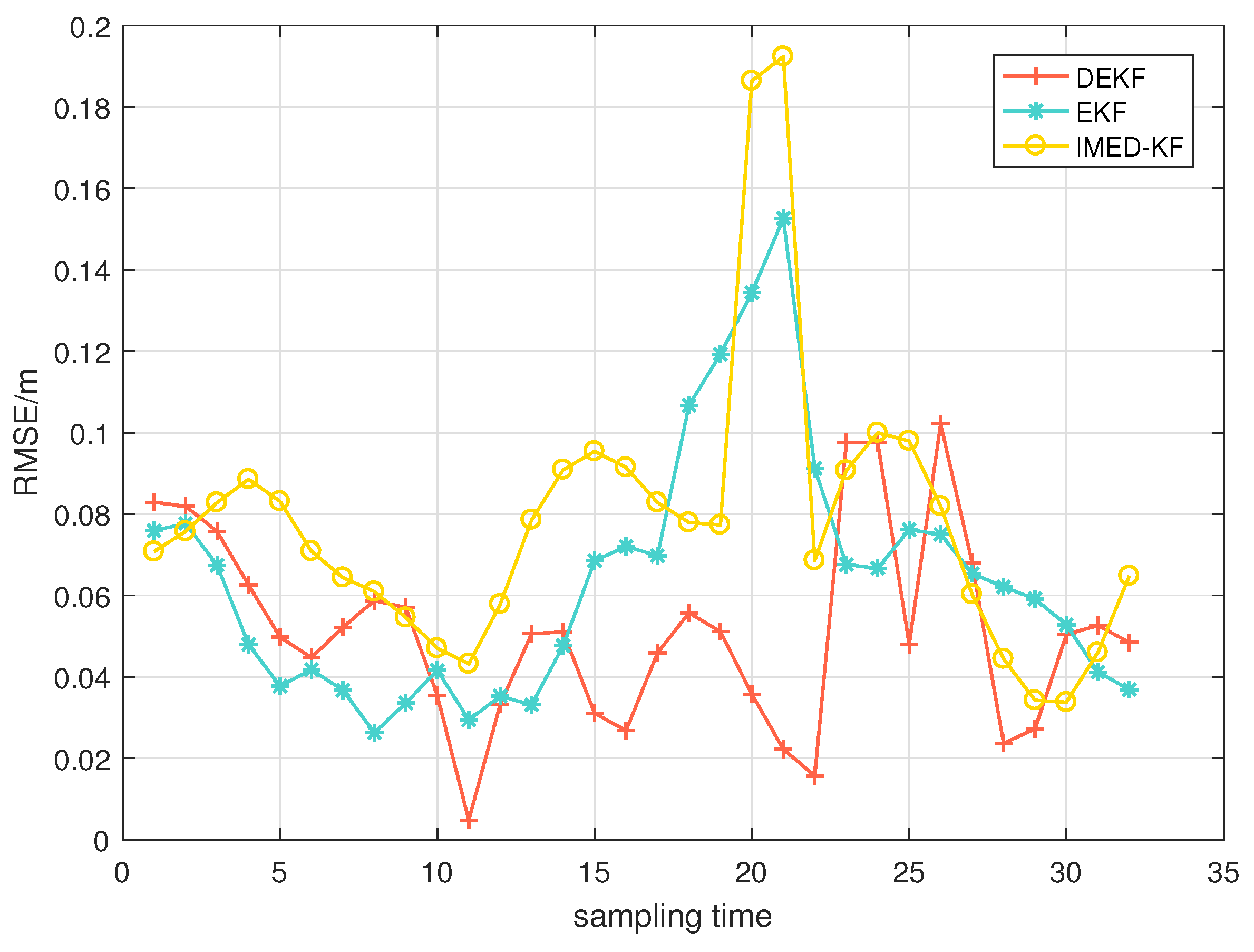
5.4. Experimental Verification of the Algorithm
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbas, R.; Michael, K.; Michael, M.G. The Regulatory Considerations and Ethical Dilemmas of Location-Based Services (LBS): A Literature Review. Inf. Technol. People 2014, 27, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Meng, W.; Han, S.; He, K.; Zhang, Z. Toward Ubiquitous LBS: Multi-Radio Localization and Seamless Positioning. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2016, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Zhu, X.; Chi, H.; Li, H. Pseudo-Location Updating System for privacy-preserving location-based services. China Commun. 2013, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Dong, M.; Chu, B.; Ao, M.; Chen, C.; Gu, S. Multi-Level High Precision LBS Architecture Based on GNSS CORS Network, A Case Study of HNCORS. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 185042–185054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, N.; Matam, R.; Mukherjee, M.; Lloret, J. LBS: A Beacon Synchronization Scheme with Higher Schedulability for IEEE 802.15.4 Cluster-Tree-Based IoT Applications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 8883–8896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Yang, B.; Long, Z.; Dai, C. A Method of Indoor Positioning by Signal Fitting and PDDA Algorithm Using BLE AOA Device. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 7877–7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Chen, R.; Guo, G.; Peng, X.; Liu, Z.; Huang, L. A Low-Cost Single-Anchor Solution for Indoor Positioning Using BLE and Inertial Sensor Data. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 162439–162453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, R.; Chen, L.; Zheng, X.; Wu, D.; Li, W.; Wu, Y. A Novel 3-D Indoor Localization Algorithm Based on BLE and Multiple Sensors. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 9359–9372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Sun, W.; Yu, H.; Tang, H.; Lin, A.; Zhang, X.; Zimmermann, R. Locate the Mobile Device by Enhancing the WiFi-Based Indoor Localization Model. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 8792–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Feng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Han, J. Joint Activity Recognition and Indoor Localization with WiFi Fingerprints. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 80058–80068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Own, C.M.; Hou, J.; Tao, W. Signal Fuse Learning Method with Dual Bands WiFi Signal Measurements in Indoor Positioning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 131805–131817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Lee, L.H.; Ho, C.C.; Wu, L.L.; Lai, Z.H. Real-Time RFID Indoor Positioning System Based on Kalman-Filter Drift Removal and Heron-Bilateration Location Estimation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.Y.; Chen, J.J.; Hsiang, T.R. Design and Implementation of a Real-Time Object Location System Based on Passive RFID Tags. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 5015–5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherhäufl, M.; Pichler, M.; Stelzer, A. UHF RFID Localization Based on Evaluation of Backscattered Tag Signals. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 2889–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, K.T. Robust Detection of Presence of Individuals in an Indoor Environment Using IR-UWB Radar. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 108133–108147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottigliero, S.; Milanesio, D.; Saccani, M.; Maggiora, R. A Low-Cost Indoor Real-Time Locating System Based on TDOA Estimation of UWB Pulse Sequences. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 5502211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.; Hancke, G.P. IR-UWB-Based Non-Line-of-Sight Identification in Harsh Environments: Principles and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 12, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Law, C.L. Indoor Positioning Using UWB-IR Signals in the Presence of Dense Multipath with Path Overlapping. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2012, 11, 3734–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Razul, S.G.; Lin, Z.; See, C.M. Target Tracking in Mixed LOS/NLOS Environments Based on Individual Measurement Estimation and LOS Detection. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2014, 13, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, G. Vehicle Localization During GPS Outages with Extended Kalman Filter and Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 7503410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiancheng, F.; Sheng, Y. Study on Innovation Adaptive EKF for In-Flight Alignment of Airborne POS. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2011, 60, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chambers, J. A Novel Adaptive Kalman Filter with Unknown Probability of Measurement Loss. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2019, 26, 1862–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangcai, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, T. M-M Estimation-Based Robust Cubature Kalman Filter for INS/GPS Integrated Navigation System. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, J.M.; Ahn, C.K.; Shmaliy, Y.S.; Lim, M.T. Improving Reliability of Particle Filter-Based Localization in Wireless Sensor Networks via Hybrid Particle/FIR Filtering. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2015, 11, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahwiadi, M.; Wang, W. An Adaptive Particle Filter Technique for System State Estimation and Prognosis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 6756–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisch, A.T.M.; Eckley, I.A.; Fearnhead, P. Innovative and Additive Outlier Robust Kalman Filtering with a Robust Particle Filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Shen, Y.; Su, X.; Esposito, C.; Choi, C. A Localization Based on Unscented Kalman Filter and Particle Filter Localization Algorithms. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 2233–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Li, B.; Dang, X. An improved Kalman filter positioning method in NLOS environment. China Commun. 2019, 16, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Wu, L. Mobile Location with NLOS Identification and Mitigation Based on Modified Kalman Filtering. Sensors 2011, 11, 1641–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.J. Robust Localization in Cellular Networks via Reinforced Iterative M-Estimation and Fuzzy Adaptation. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 4269–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejniczak, A.; Blaszkiewicz, O.; Cwalina, K.K.; Rajchowski, P.; Sadowski, J. LOS and NLOS identification in real indoor environment using deep learning approach. Digit. Netw. 2023, 10, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, S.; Cheng, P.; Vucetic, B.; Li, Y. ToF-Based NLoS Indoor Tracking with Adaptive Ranging Error Mitigation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2024, 72, 4855–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Shen, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, D.; Bo, Y. UWB NLOS/LOS Classification Using Deep Learning Method. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 2226–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarchan, P. Progress in Astronautics and Aeronautics: Fundamentals of Kalman Filtering: A Practical Approach; Aiaa: Reston, VA, USA, 2005; Volume 208. [Google Scholar]
- Reif, K.; Unbehauen, R. The extended Kalman filter as an exponential observer for nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1999, 47, 2324–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Meng, W. Robust Mobile Location Estimation in NLOS Environment Using GMM, IMM, and EKF. IEEE Syst. J. 2019, 13, 3490–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Razul, S.G.; Lin, Z.; See, C.M. Target tracking in mixed LOS/NLOS environments based on individual TOA measurement detection. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop, Jerusalem, Israel, 4–7 October 2010; pp. 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Wang, S.; Ge, S.; Ma, X.; Liu, W. A Novel Mobile Target Localization Approach for Complicate Underground Environment in Mixed LOS/NLOS Scenarios. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 96347–96362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flueratoru, L.; Wehrli, S.; Magno, M.; Lohan, E.S.; Niculescu, D. High-Accuracy Ranging and Localization with Ultrawideband Communications for Energy-Constrained Devices. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 7463–7480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikur, B.Y.; Weber, T. Posterior CRLB for tracking a mobile station in NLOS multipath environments. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; pp. 5175–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wan, Q. The CRLB for WSNs location estimation in NLOS environments. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Communications, Circuits and Systems (ICCCAS), Chengdu, China, 28–30 July 2010; pp. 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Fan, X.; Xu, C.Z.; Li, X. ER-CRLB: An Extended Recursive Cramér–Rao Lower Bound Fundamental Analysis Method for Indoor Localization Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 1605–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.09 |
| 0.25 | 0.02 | 0.06 |
| 0.5 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| 0.75 | 0.06 | 0.02 |
| Noise Situation | Tracking Results: Average RMSE/m | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEKF | EKF | IMED-KF | M-REKF | |
| LOS | 0.022 | 0.017 | 0.181 | 2.227 |
| S1 | 0.023 | 0.228 | 0.232 | 2.245 |
| S2 | 0.027 | 0.926 | 3.385 | 2.327 |
| S3 | 0.052 | 1.453 | 8.647 | 2.408 |
| S4 | 0.054 | 1.868 | 11.934 | 2.467 |
| NLOS Number | Tracking Results/m | |
|---|---|---|
| DEKF | EKF | |
| LOS | tracking | tracking |
| 1-NLOS | tracking | tracking |
| 2-NLOS | tracking | tracking |
| 3-NLOS | tracking | tracking |
| 4-NLOS | tracking | tracking |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Liu, Q.; Lin, M.; Wang, Q.; Chen, K. A Double Extended Kalman Filter Algorithm for Weakening Non-Line-of-Sight Errors in Complex Indoor Environments Based on Ultra-Wideband Technology. Sensors 2025, 25, 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030740
Xu S, Liu Q, Lin M, Wang Q, Chen K. A Double Extended Kalman Filter Algorithm for Weakening Non-Line-of-Sight Errors in Complex Indoor Environments Based on Ultra-Wideband Technology. Sensors. 2025; 25(3):740. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030740
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Sheng, Qianyun Liu, Min Lin, Qing Wang, and Kaile Chen. 2025. "A Double Extended Kalman Filter Algorithm for Weakening Non-Line-of-Sight Errors in Complex Indoor Environments Based on Ultra-Wideband Technology" Sensors 25, no. 3: 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030740
APA StyleXu, S., Liu, Q., Lin, M., Wang, Q., & Chen, K. (2025). A Double Extended Kalman Filter Algorithm for Weakening Non-Line-of-Sight Errors in Complex Indoor Environments Based on Ultra-Wideband Technology. Sensors, 25(3), 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030740





