Wear Your Heart on Your Sleeve: Smart Textile ECG Wearables for Comfort, Integration, Signal Quality and Continuous Monitoring in Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
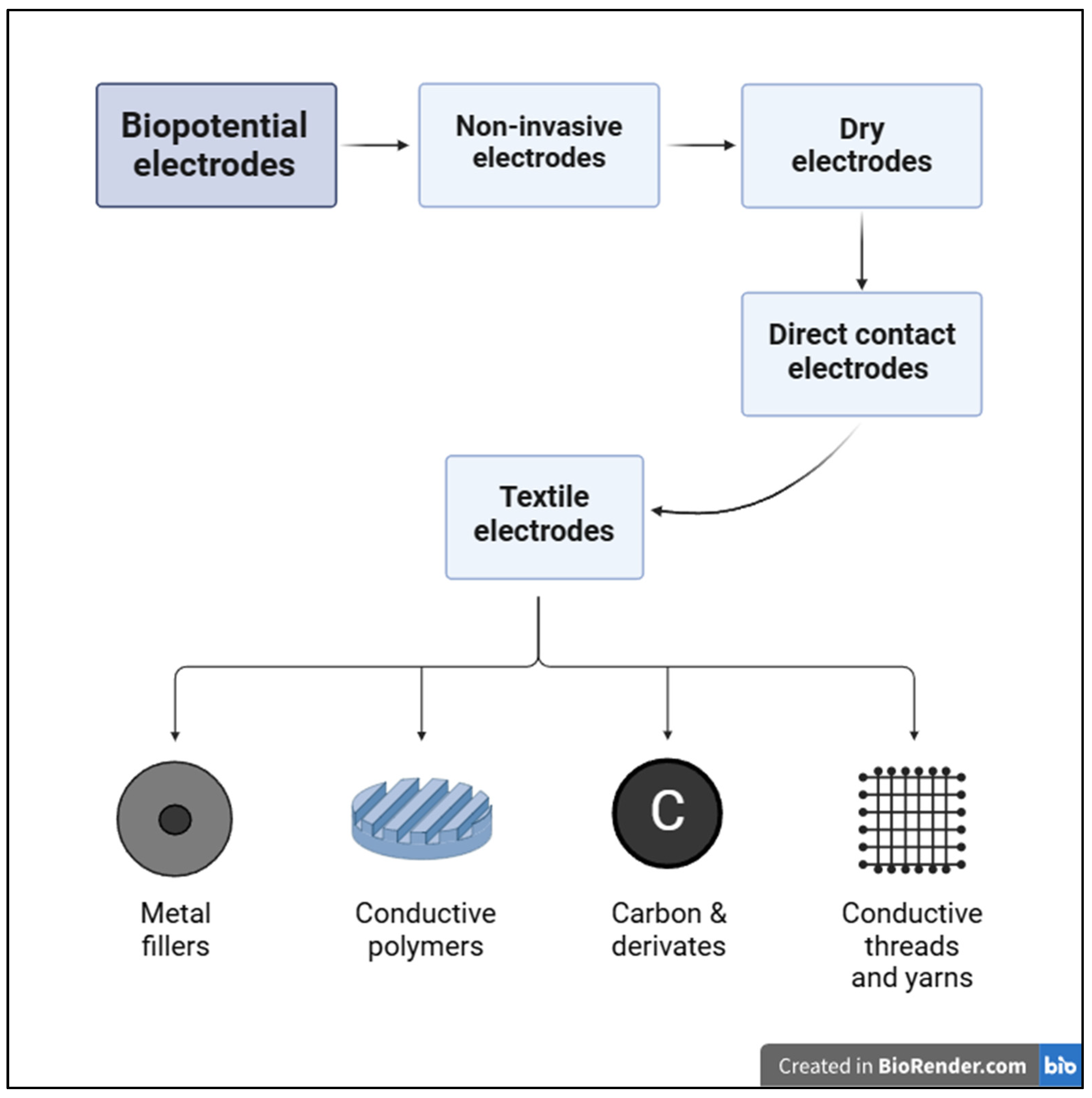
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Past and Current Developments
4. Performance and Integration
4.1. Technical and Performance Indicators
4.2. Usability and Compliance
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Cardiovascular Diseases Kill 10,000 People in the WHO European Region Every Day, with Men Dying More Frequently than Women. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/news/item/15-05-2024-cardiovascular-diseases-kill-10-000-people-in-the-who-european-region-every-day--with-men-dying-more-frequently-than-women (accessed on 16 November 2024).
- University Hospital, Basel, Switzerland. Determine AF Burden With PPG Trial—Detection and Quantification of Episodes of Atrial Fibrillation Using a Cloud Analytics Service Connected to a Wearable with Photoplethysmographic (PPG) Sensor. Clinical Trial Registration NCT04563572. 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04563572 (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- ESC Guidelines for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation. Available online: https://www.escardio.org/Guidelines/Clinical-Practice-Guidelines/Atrial-Fibrillation (accessed on 16 November 2024).
- 2024 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics: A Report of US and Global Data From the American Heart Association. Available online: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/epub/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001209 (accessed on 16 November 2024).
- Fabritz, L.; Guasch, E.; Antoniades, C.; Bardinet, I.; Benninger, G.; Betts, T.R.; Brand, E.; Breithardt, G.; Bucklar-Suchankova, G.; Camm, A.J.; et al. Expert consensus document: Defining the major health modifiers causing atrial fibrillation: A roadmap to underpin personalized prevention and treatment. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganapathy, N.; Baumgärtel, D.; Deserno, T.M. Automatic Detection of Atrial Fibrillation in ECG Using Co-Occurrence Patterns of Dynamic Symbol Assignment and Machine Learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Rienstra, M.; Bunting, K.V.; Casado-Arroyo, R.; Caso, V.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; De Potter, T.J.R.; Dwight, J.; Guasti, L.; Hanke, T.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): Developed by the task force for the management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Endorsed by the European Stroke Organisation (ESO). Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3314–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiviniemi, T. Cardiovascular Research Consortium—A Randomized Prospective Trial to Assess Low Workload Concept for the Detection of Silent Atrial Fibrillation (AF) and Atrial Fibrillation Burden in Patients at High Risk of AF and Stroke. Clinical Trial Registration NCT05351775. 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05351775 (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Determine Atrial Fibrillation Burden with a Photoplethysmographic Mobile Sensor: The Atrial Fibrillation Burden Trial: Detection and Quantification of Episodes of Atrial Fibrillation Using a Cloud Analytics Service Connected to a Wearable with Photoplethysmographic Sensor. Available online: https://academic-oup-com.dbproxy.umfiasi.ro/ehjdh/article/4/5/402/7220547 (accessed on 18 November 2024).
- Steinberg, C.; Philippon, F.; Sanchez, M.; Fortier-Poisson, P.; O’hara, G.; Molin, F.; Sarrazin, J.-F.; Nault, I.; Blier, L.; Roy, K.; et al. A Novel Wearable Device for Continuous Ambulatory ECG Recording: Proof of Concept and Assessment of Signal Quality. Biosensors 2019, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machino, T.; Aonuma, K.; Komatsu, Y.; Yamasaki, H.; Igarashi, M.; Nogami, A.; Ieda, M. Dry textile electrode for ambulatory monitoring after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: A pilot study of simultaneous comparison to the Holter electrocardiogram. F1000Research 2022, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medtronic Cardiac Rhythm and Heart Failure. CRYptogenic STroke and underLying AF Trial. Clinical Trial Registration NCT00924638. 2014. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00924638 (accessed on 18 November 2024).
- Gladstone, D.D. 30-Day Cardiac Event Monitor Belt for Recording Atrial Fibrillation After a Cerebral Ischemic Event: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clinical Trial Registration NCT00846924. 2018. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00846924 (accessed on 18 November 2024).
- Kuopio University Hospital. Identification of Arrhythmias with One-Time ECG. Clinical Trial Registration NCT03753139. 2021. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03753139 (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Teferra, M.N.; Hobbs, D.A.; Clark, R.A.; Reynolds, K.J. Preliminary Analysis of a Wireless and Wearable Electronic-Textile EASI-Based Electrocardiogram. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 806726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, P.; Mohanavelu, K.; Safeer, K.; Kotresh, T.; Shakunthala, D.; Gopal, P.; Padaki, V. Smart Vest: Wearable multi-parameter remote physiological monitoring system. Med. Eng. Phys. 2008, 30, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Effectiveness of Atrial Fibrillation Identification Using Noninvasive Long-Term Electrocardiographic Monitoring System (Nomed-Af Tech). Available online: https://www.mp.pl/paim/issue/article/16450 (accessed on 11 February 2024).
- Norav Medical. Holter NR-314-P Compact Size 14 Day Holter. Available online: https://www.noravmedical.com/products/holter-nr314-p-compact-size-14-day-holter/ (accessed on 4 January 2025).
- Sanna, T.; Diener, H.C.; Passman, R.S.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Bernstein, R.A.; Morillo, C.A.; Rymer, M.M.; Thijs, V.; Rogers, T.; Beckers, F.; et al. Cryptogenic Stroke and Underlying Atrial Fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2478–2486. Available online: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1313600 (accessed on 18 November 2024). [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, C. Design of intelligent wearable equipment based on real-time dynamic ECG-monitoring system. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2023, 15, 6413. [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane Library. Smartwatch and External Holter Monitoring to Detect Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Cryptogenic Stroke. Available online: https://www.cochranelibrary.com/central/doi/10.1002/central/CN-02468898/full (accessed on 12 April 2024).
- Sun, F.M.; Yi, C.; Li, W.; Li, Y. A wearable H-shirt for exercise ECG monitoring and individual lactate threshold computing. Comput. Ind. 2017, 92–93, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Chiu, C.-W. Facile Fabrication of a Stretchable and Flexible Nanofiber Carbon Film-Sensing Electrode by Electrospinning and Its Application in Smart Clothing for ECG and EMG Monitoring. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, L.; Corazza, I.; Oberdier, M.T.; Lago, J.; Gallelli, I.; Cicero, A.F.; Diemberger, I.; Orro, A.; Beker, A.; Paolocci, N.; et al. Comparison Between a Single-Lead ECG Garment Device and a Holter Monitor: A Signal Quality Assessment. J. Med. Syst. 2024, 48, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajbhandary, P.L.; Nallathambi, G.; Selvaraj, N.; Tran, T.; Colliou, O. ECG Signal Quality Assessments of a Small Bipolar Single-Lead Wearable Patch Sensor. Cardiovasc. Eng. Tech. 2022, 13, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilnius University. Personalized Detection of Triggers and Risk Factors for Recurrence of Atrial Fibrillation and Other Atrial Arrhythmias with the Use of Long-term Monitoring. Clinical Trial Registration NCT05526170. 2024. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05526170 (accessed on 18 November 2024).
- Tao, X.; Huang, T.-H.; Shen, C.-L.; Ko, Y.-C.; Jou, G.-T.; Koncar, V. Bluetooth Low Energy-Based Washable Wearable Activity Motion and Electrocardiogram Textronic Monitoring and Communicating System. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagola, J.; Juega, J.; Francisco-Pascual, J.; Rodriguez, M.; Dorado, L.; Martinez, R.; De Lera-Alfonso, M.; Arenillas, J.F.; Cabezas, J.A.; Moniche, F.; et al. Intensive 90-day textile wearable Holter monitoring: An alternative to detect paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in selected patients with cryptogenic stroke. Heart Vessel. 2023, 38, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machino, T.; Aonuma, K.; Maruo, K.; Komatsu, Y.; Yamasaki, H.; Igarashi, M.; Nogami, A.; Ieda, M. Randomized crossover trial of 2-week Garment electrocardiogram with dry textile electrode to reveal instances of post-ablation recurrence of atrial fibrillation underdiagnosed during 24-hour Holter monitoring. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroudi, A.; Hernández, N.; Berglin, L.; Nierstrasz, V. Electrode placement in electrocardiography smart garments: A review. J. Electrocardiol. 2019, 57, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, A.; Cowie, M.R. The Role of Wearables in Heart Failure. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2020, 17, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, E.S.; Kalra, A.M.; Lowe, A.; Anand, G. Wearable Technology for Monitoring Electrocardiograms (ECGs) in Adults: A Scoping Review. Sensors 2024, 24, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botto, G.L.; Tortora, G.; Casale, M.C.; Canevese, F.L.; Brasca, F.A.M. Impact of the Pattern of Atrial Fibrillation on Stroke Risk and Mortality. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. Rev. 2021, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigusse, A.B.; Malengier, B.; Mengistie, D.A.; Maru, A.; Langenhove, L.V. Investigating Textile-Based Electrodes for ECG Monitoring in Veterinary Clinical Practice. AUTEX Res. J. 2023, 23, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arquilla, K.; Webb, A.K.; Anderson, A.P. Textile Electrocardiogram (ECG) Electrodes for Wearable Health Monitoring. Sensors 2020, 20, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhou, T.; Liang, Z.; Liu, R.; Guo, J.; Yu, X.; Cao, Z.; Yu, C.; Liu, Q.; Li, J. Electrochemical Characteristics Based on Skin-Electrode Contact Pressure for Dry Biomedical Electrodes and the Application to Wearable ECG Signal Acquisition. J. Sens. 2021, 2021, 7741881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidhya, C.M.; Maithani, Y.; Singh, J.P. Recent Advances and Challenges in Textile Electrodes for Wearable Biopotential Signal Monitoring: A Comprehensive Review. Biosensors 2023, 13, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pani, D.; Achilli, A.; Bassareo, P.P.; Cugusi, L.; Mercuro, G.; Fraboni, B.; Bonfiglio, A. Fully-textile polymer-based ECG electrodes: Overcoming the limits of metal-based textiles. In Proceedings of the 2016 Computing in Cardiology Conference (CinC), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 11–14 September 2016; pp. 373–376. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7868757 (accessed on 18 November 2024).
- Chung, C.T.S.; Roy, V.; Tse, G.; Liu, H. Chapter 4—Detection of atrial fibrillation using photoplethysmography signals: A systemic review. In Signal Processing Driven Machine Learning Techniques for Cardiovascular Data Processing; Tripathy, R.K., Pachori, R.B., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalarus, Z.; Balsam, P.; Bandosz, P.; Grodzicki, T.; Kaźmierczak, J.; Kiedrowicz, R.; Mitręga, K.; Noczyński, M.; Opolski, G.; Rewiuk, K.; et al. NOninvasive Monitoring for Early Detection of Atrial Fibrillation: Rationale and design of the NOMED-AF study. Pol. Heart J. 2018, 76, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Das, T.; Grodin, J.; Minniefield, N.; Tsai, S.; Banerjee, R.; Persen, K.; Novak, S. Clinical Validation of a Continuous Monitoring Mobile Cardiac Detection Device for Atrial Fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2023, 189, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigusse, A.B.; Mengistie, D.A.; Malengier, B.; Tseghai, G.B.; Langenhove, L.V. Wearable Smart Textiles for Long-Term Electrocardiography Monitoring—A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubitz, S.A.; Atlas, S.J.; Ashburner, J.M.; Lipsanopoulos, A.T.T.; Borowsky, L.H.; Guan, W.; Khurshid, S.; Ellinor, P.T.; Chang, Y.; McManus, D.D. Screening for Atrial Fibrillation in Older Adults at Primary Care Visits: VITAL-AF Randomized Controlled Trial. Circulation 2022, 145, 946–954. Available online: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.057014 (accessed on 4 January 2025). [CrossRef]
- PMC. Predisposing Factors for Atrial Fibrillation in the Elderly. Available online: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5460064/ (accessed on 4 January 2025).

| Study | Score | Q1 * | Q2 * | Q3 * | Q4 * | Q5 * | Q6 * | Q7 * | Q8 * | Q9 * | Q10 * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [17] | 16.00 | 2 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| [29] | 15.50 | 2 | 1.5 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| [30] | 15.00 | 2 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| [11] | 15.00 | 2 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Ref. | [11] | [30] | [29] | [17] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients (n) | 18 | 67 * | 163 | 3014 |
| Sex (m) | 14 | 53 | 102 | 1535 |
| Age (years) | 66 ± 11 | 63.1 ± 10.6 | 74 ± 3.5 | 77.5 ± 7.9 |
| Paroxysmal AF (n) | 8 | 46 | 64 | 192 |
| Main inclusion criteria | Admitted for catheter ablation | Post-first catheter ablation for AF | Cryptogenic stroke diagnosis | Geriatric patients |
| Ref. | [11,41] | [30] | [29] | [17] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Smart bra-type device | Garment ECG device (a stretchy fabric used for sportswear) | Textile wearable Holter elastic vest | Mobile long-term ECG vest |
| Conductive material | PEDOT-PSS | Elastomeric polymers | N/A | |
| Features | Woven nanofibers coated with PEDOT-PSS; an insulated electroconductive lead ribbon connected between the electrodes and a connector terminal for signal transmission | Lead wires pre-installed on the wearable device; | The ECG signal is stored in a digital memory card inserted into a signal recorder | Exchangeable recorders fixed to the vest, a docking station acting as a charger, a GSM transmitter and a patient monitoring platform for data analysis and storage |
| No. of ECG Leads | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Wireless communication protocol | Bluetooth | N/A | 3G, WiFi, LAN | |
| Total analysis time (hours) | 3.05–3.85 | 218.4–292.8 | 1642 | 357.6–693.6 |
| Energy supply autonomy (hours) | N/A | 336 | 22 | >24 |
| Patient modules | Simultaneous positioning of textile and gel electrodes | Polyester nanofiber fabric coated with a dielectric polymer | High-quality and comfortable elastic fabric without adhesives | Two recorders to maintain continuous ECG acquisition (during charging) |
| Manufacturer | Toray Industries Inc. (Tokyo, Japan) and Cardyrode-P®, SUZUKEN Co., Ltd. (Nagoya, Japan) | Toray Industries, Inc. (Tokyo, Japan) | Nuubo® (Madrid, Spain) | Comarch Healthcare (Krakow, Poland) |
| Ref. | [11] | [30] | [29] | [17] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total analysis time (hours) | 3.05–3.85 | 218.4–292.8 | 1642 | 357.6–693.6 |
| SNR | Lower | Lower | N/A | Higher |
| Signal stability | N/A | 82.4 | N/A | 95.8 |
| Sensitivity to detect AF (%) | N/A | N/A | 89.6 | 93 |
| Specificity to detect AF (%) | N/A | N/A | 27.59 | 85 |
| Ref. | [11] | [30] | [29] | [17] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| User state | Resting and walking | Resting, walking, exercising | ||
| Discomfort during resting/physical activities | Mild | |||
| Patients with no adverse effects | 94.44% | 97.6% | N/A | 79.3% |
| Redness | 0.0% | 2.3% | N/A | 9.4% |
| Rash | 0.0% | 0.0% | N/A | 3.7% |
| Skin chafing | 0.0% | 0.0% | N/A | 3.3% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avanu, A.E.; Dodi, G. Wear Your Heart on Your Sleeve: Smart Textile ECG Wearables for Comfort, Integration, Signal Quality and Continuous Monitoring in Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. Sensors 2025, 25, 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030676
Avanu AE, Dodi G. Wear Your Heart on Your Sleeve: Smart Textile ECG Wearables for Comfort, Integration, Signal Quality and Continuous Monitoring in Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. Sensors. 2025; 25(3):676. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030676
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvanu, Alexandra E., and Gianina Dodi. 2025. "Wear Your Heart on Your Sleeve: Smart Textile ECG Wearables for Comfort, Integration, Signal Quality and Continuous Monitoring in Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation" Sensors 25, no. 3: 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030676
APA StyleAvanu, A. E., & Dodi, G. (2025). Wear Your Heart on Your Sleeve: Smart Textile ECG Wearables for Comfort, Integration, Signal Quality and Continuous Monitoring in Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation. Sensors, 25(3), 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25030676









