Weld Seam ROI Detection and Segmentation Method Based on Active–Passive Vision Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
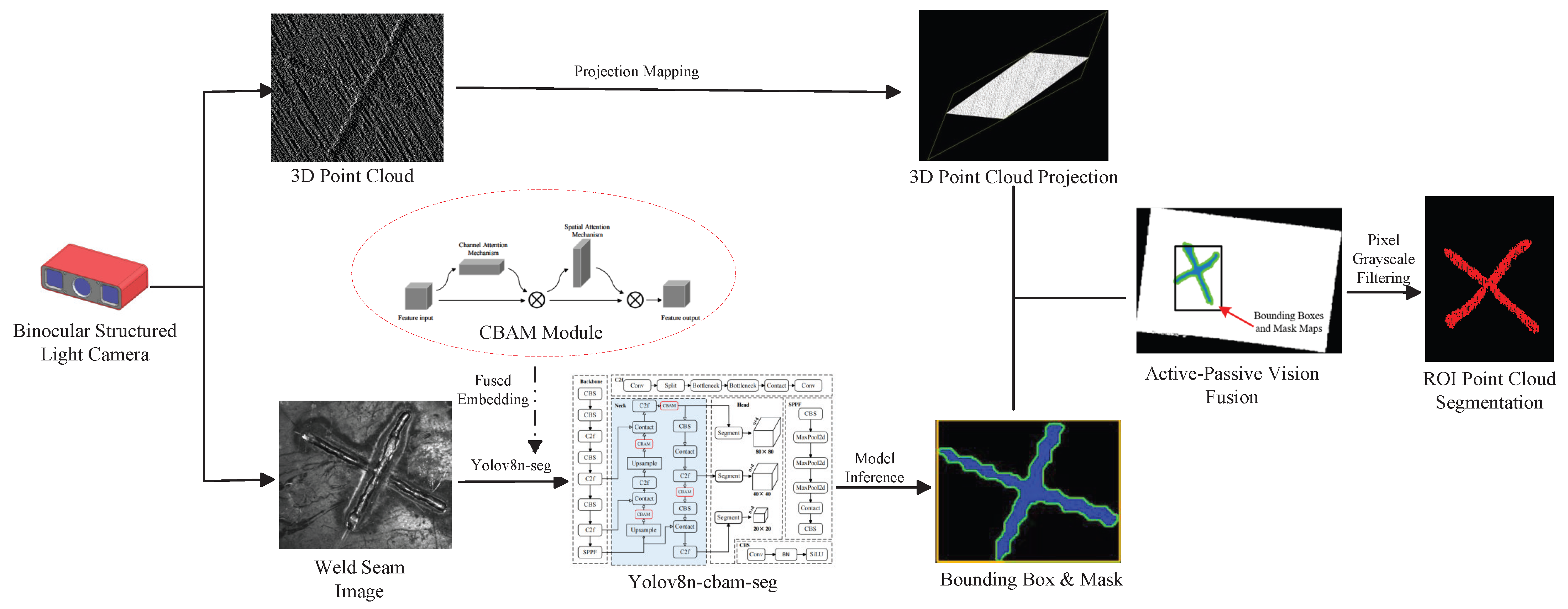
2. The Proposed Method
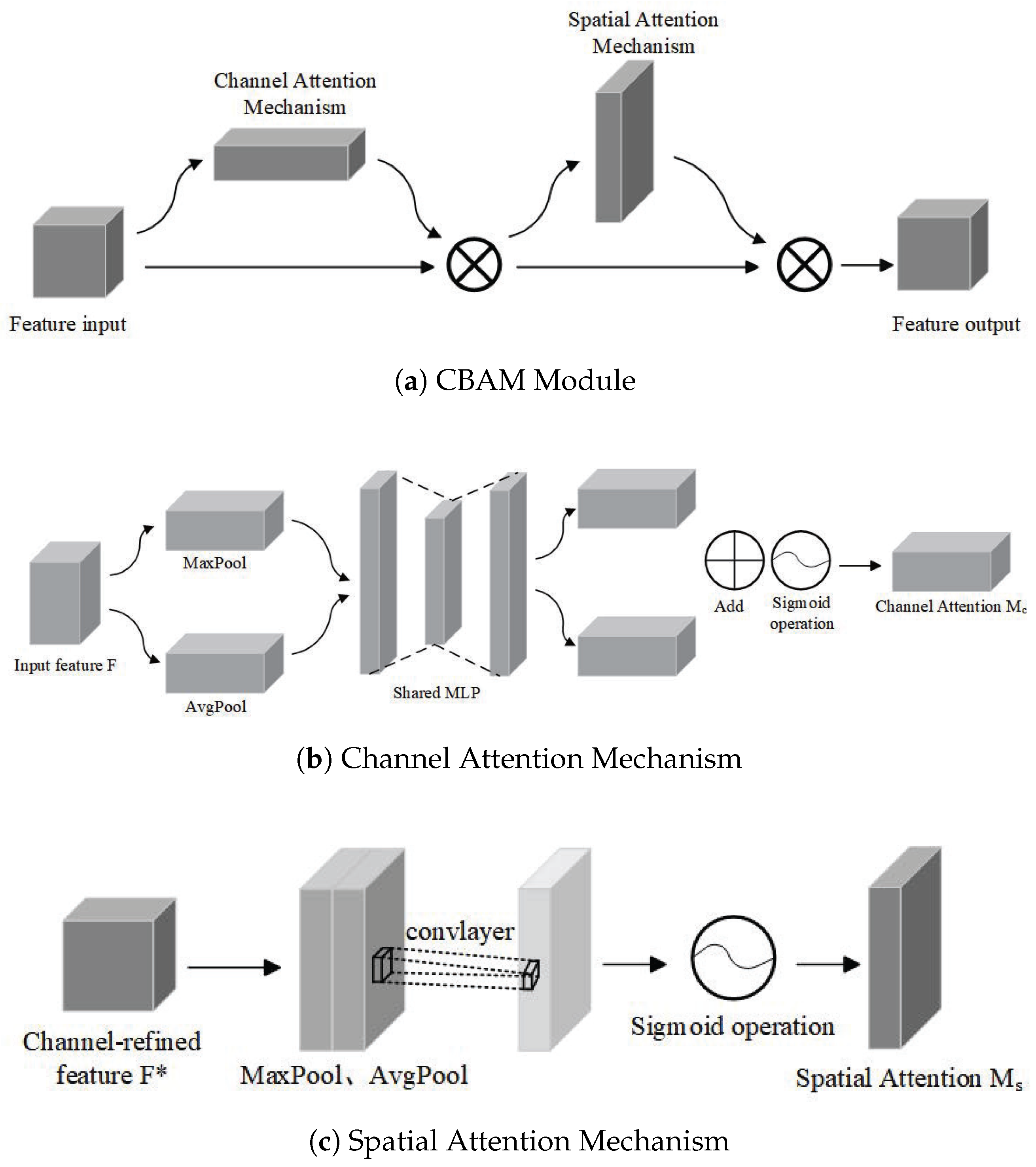
2.1. Instance Segmentation of Weld Seam Images
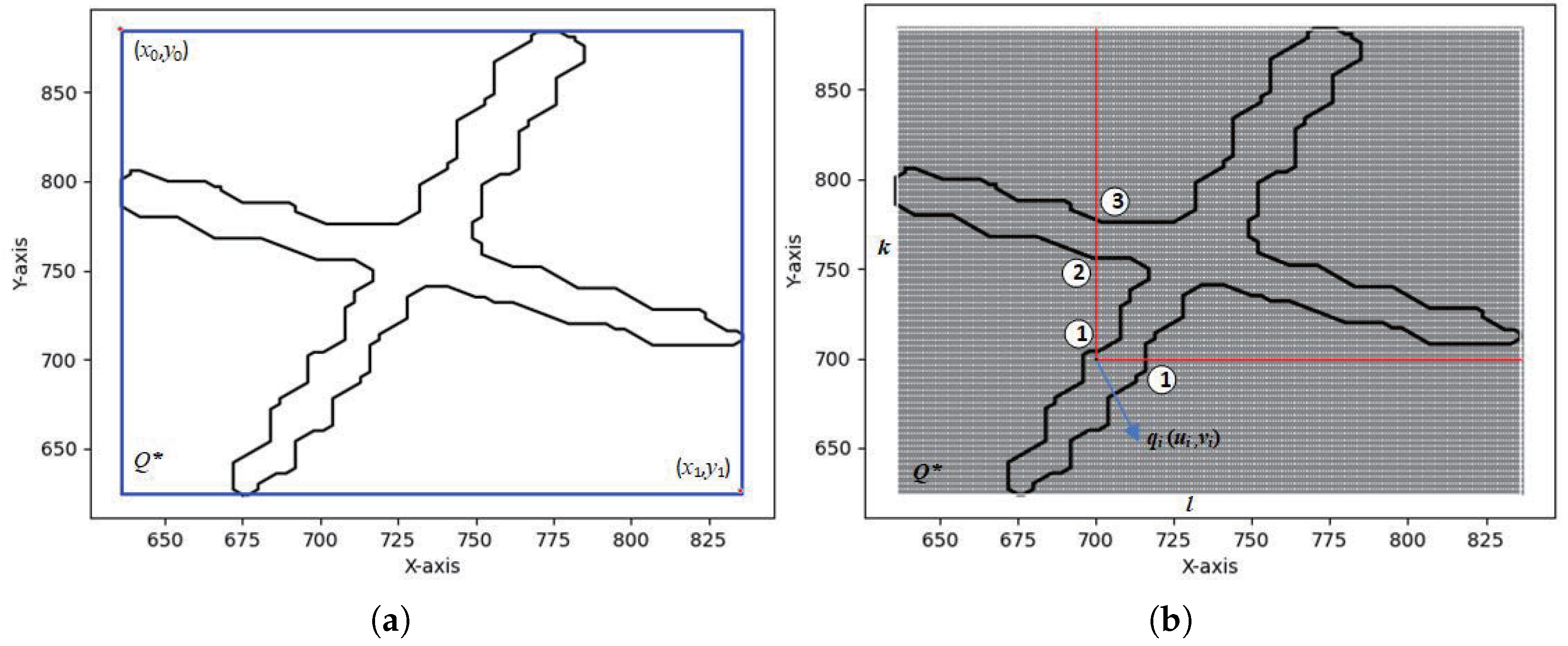
2.2. Weld ROI Point Cloud Segmentation
3. Experimental Analysis
3.1. Data Collection and Processing
3.2. Data Collection and Processing
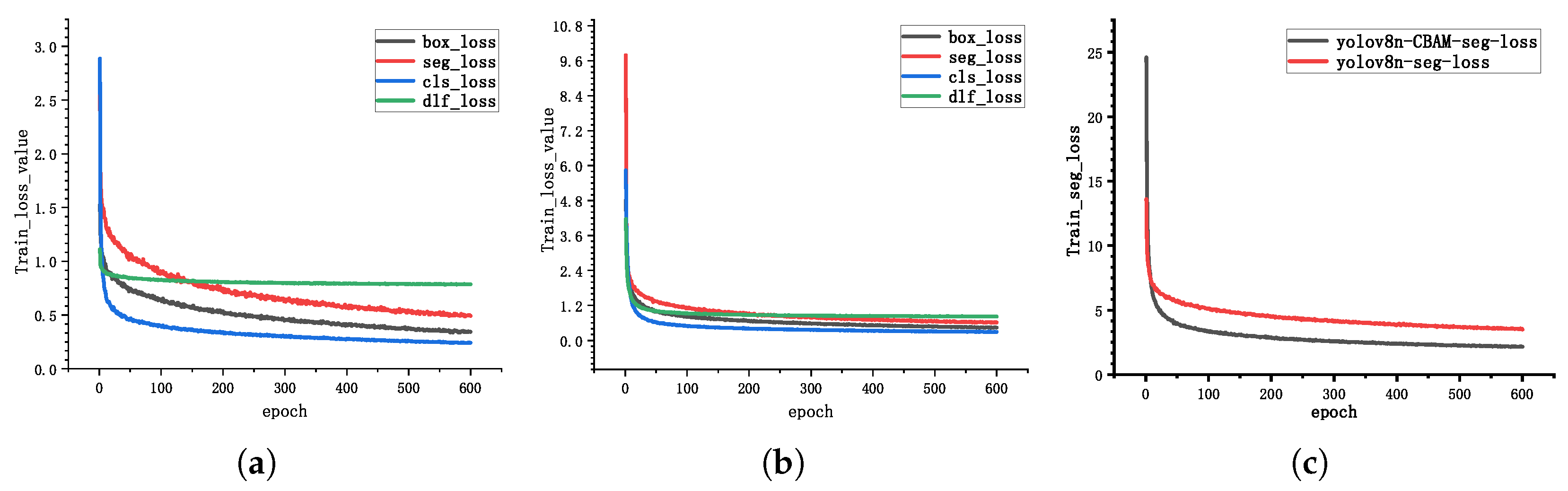
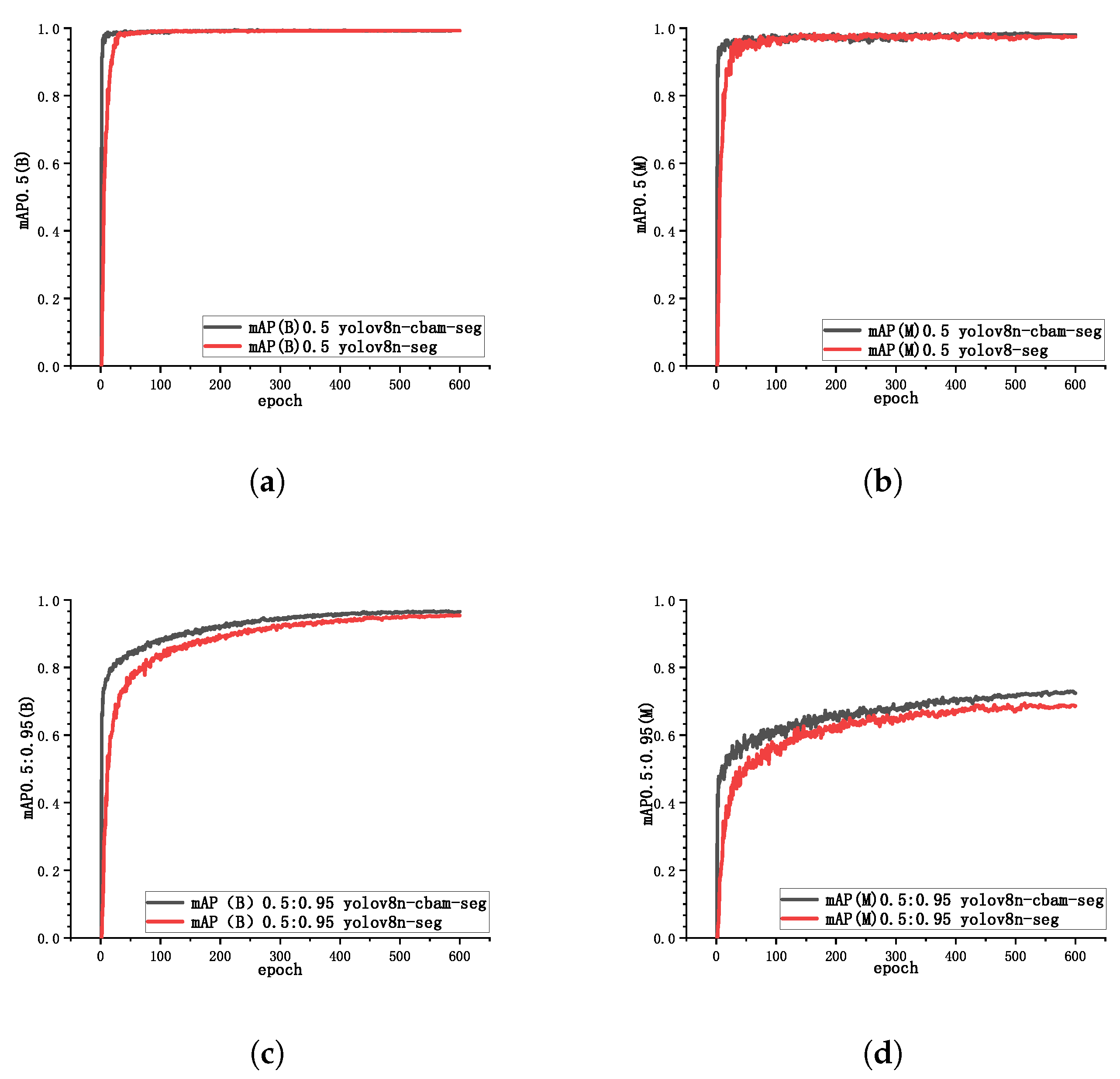
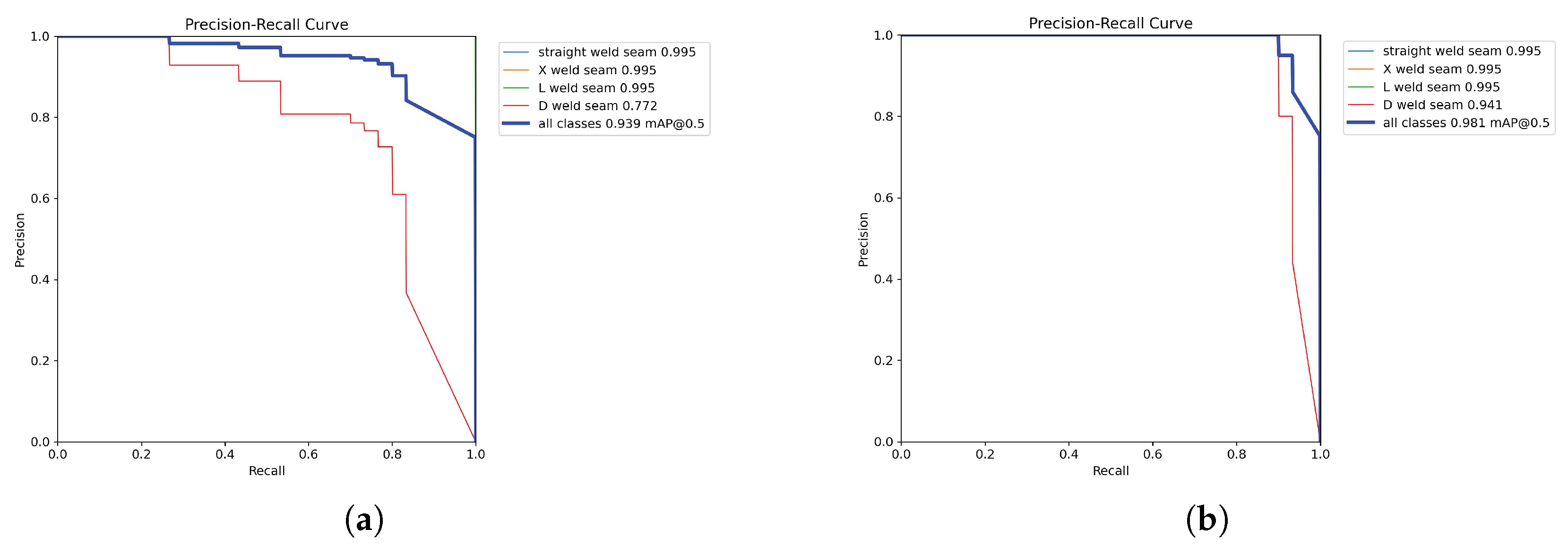
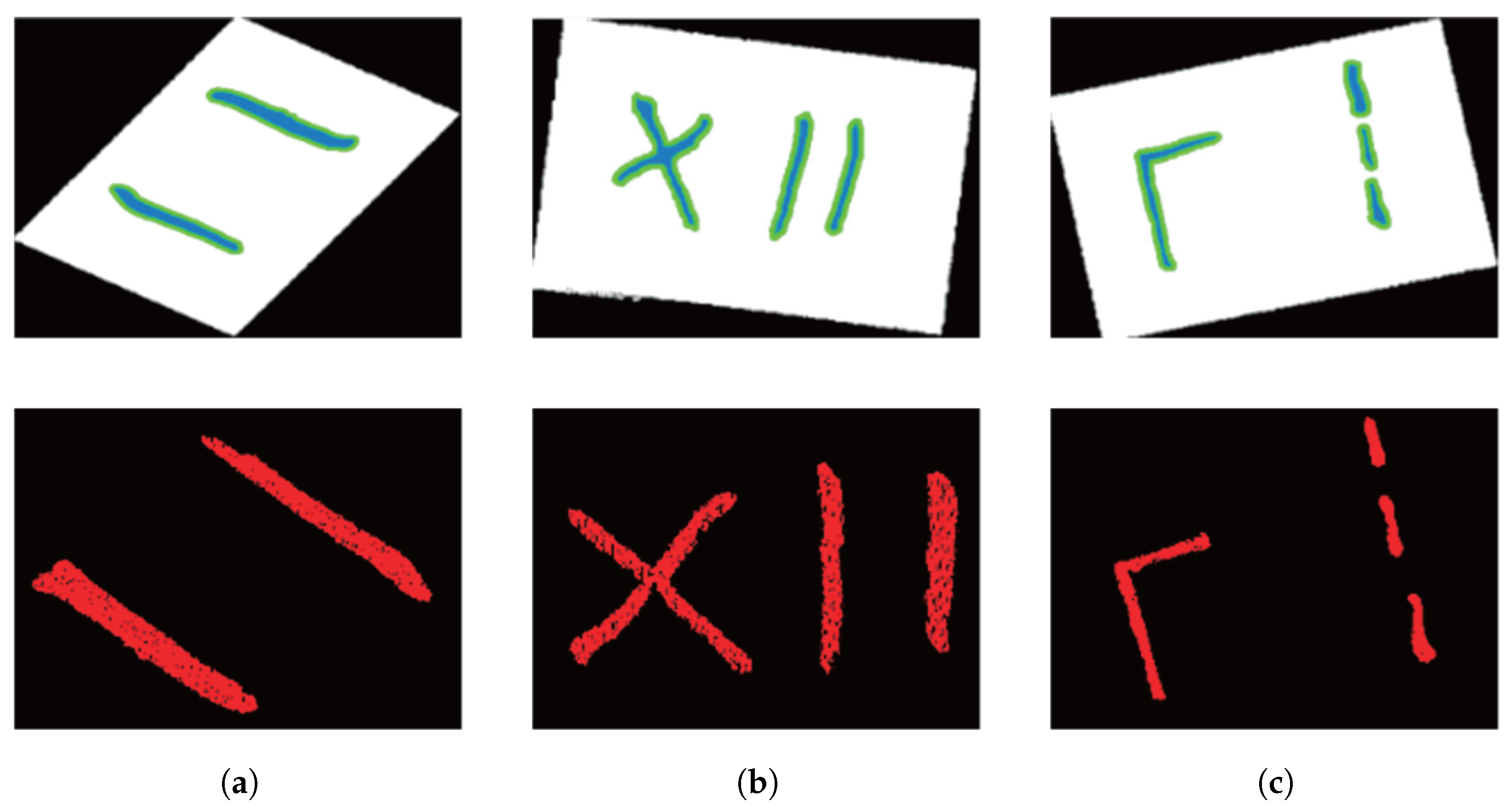
3.2.1. Model Training Results
3.2.2. Ablation Studies and Analysis
3.3. Weld ROI Point Cloud Segmentation Results
3.4. Robot Weld Grinding Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huynh, H.N.; Assadi, H.; Rivière-Lorphèvre, E.; Verlinden, O.; Ahmadi, K. Modelling the dynamics of industrial robots for milling operations. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2020, 61, 101852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Huang, X.; Qi, B.; Ren, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, X. Vision-guided path planning and joint configuration optimization for robot grinding of spatial surface weld beads via point cloud. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2024, 61, 102465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhong, K.; Shi, X.; Zhang, X. A robust weld seam recognition method under heavy noise based on structured-light vision. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2020, 61, 101821–101829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Dong, Z.; Wang, J.; Fei, Y. Weld bead segmentation using RealSense depth camera based on 3D global features and texture features of subregions. Signal Image Video Process. 2023, 17, 2369–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, B.; Dong, L.; Wang, X.; Tian, M. Weld seam identification and tracking of inspection robot based on deep learning network. Drones 2022, 6, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yao, J.; Liu, X.; Du, Y.; Liu, M.; Su, Y.; Lu, D. Weld Detection and Tracking Algorithm for Inspection Robot Based on Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Electronic Engineering and Information Systems (EEISS), Chania, Greece, 29–31 May 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, T.-J.; Al-Hussein, M.; Martinez, P. Vision-Based Guiding System for Autonomous Robotic Corner Cleaning of Window Frames. Buildings 2023, 13, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natan, O.; Putri, D.U.K.; Dharmawan, A. Deep learning-based weld spot segmentation using modified UNet with various convolutional blocks. ICIC Express Lett. Part B Appl. 2021, 12, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Haffner, O.; Kučera, E.; Kozák, Š. Weld segmentation for diagnostic and evaluation method. In Proceedings of the 2016 Cybernetics & Informatics (K&I), Levoca, Slovakia, 2–5 February 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Malarvel, M.; Sethumadhavan, G.; Bhagi, P.C.R.; Kar, S.; Thangavel, S. An improved version of Otsu’s method for segmentation of weld defects on X-radiography images. Optik 2017, 142, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Kong, J.; Shi, Y. Image Binarization Method of Equal-thickness Butt Welds Based on Regional Optimization. China Mech. Eng. 2019, 30, 1756. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Ge, S.S.; Khyam, M.O.; Luo, C. Automatic welding seam tracking and identification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 7261–7271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golodov, V.A.; Maltseva, A.A. Approach to weld segmentation and defect classification in radiographic images of pipe welds. NDT E Int. 2022, 127, 102597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, B.; Yang, W.; Chen, W.-M.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Ma, T.; Hu, X.; Ma, L. Comprehensive review of deep learning-based 3d point cloud completion processing and analysis. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 22862–22883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ren, X.; Li, L.; Feng, H.; He, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, X. Point cloud 3D parent surface reconstruction and weld seam feature extraction for robotic grinding path planning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 107, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, O.; Lai, Z.; Qinghong, W.; Xin, L.; Yingjie, L. Weld-seam identification and model reconstruction of remanufacturing blade based on three-dimensional vision. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 49, 101300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Piya, C.; Shin, Y.C.; Zhao, F.; Ramani, K. Remanufacturing of turbine blades by laser direct deposition with its energy and environmental impact analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 80, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Deng, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Lv, L.; Liu, T. Robot welding seam online grinding system based on laser vision guidance. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 116, 1737–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Deng, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, T.; Zhang, H.; Nie, J. An efficient system based on model segmentation for weld seam grinding robot. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 121, 7627–7641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Tang, Q.; Tian, X. A novel path planning method of robotic grinding for free-form weld seam based on 3D point cloud. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 131, 5155–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Pang, G.; Tong, Q. Research on point cloud processing and grinding trajectory planning of steel helmet based on 3D scanner. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 123456–123467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Bennamoun, M. Deep learning for 3d point clouds: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 4338–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yang, H.; Lv, H. Intelligent control for a robot belt grinding system. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2012, 21, 716–724. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, S.; Qian, K.; Liu, Y.; Gong, Y. Weld Seam Segmentation in RGB-D Data using Attention-based Hierarchical Feature Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2022 China Automation Congress (CAC), Xiamen, China, 25–27 November 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1337–1342. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Shi, T.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, X.; Liu, C. 1D Segmentation Network for 3D Seam Weld Grinding. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1924, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, R.; Sambath, M. YOLOv8: A Novel Object Detection Algorithm with Enhanced Performance and Robustness. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Advances in Data Engineering and Intelligent Computing Systems (ADICS), Chennai, India, 18–19 April 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Stoken, A.; Borovec, J.; Kwon, Y.; Michael, K.; Fang, J.; Wong, C.; Yifu, Z.; Montes, D.; et al. ultralytics/yolov5: V6. 2-yolov5 classification models, apple m1, reproducibility, clearml and deci. ai integrations. Zenodo 2022, 10, 5281. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.C.; Wu, E.H. A New Method for Deciding Whether a Point is in a Polygon or a Polyhedron. J. Softw. 2000, 11, 1614–1619. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Li, X.; Ge, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Trajectory planning for spray painting robot based on point cloud slicing technique. Electronics 2020, 9, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Training Epochs | 600 | Optimizer | AdamW |
| Initial Learning Rate | 0.01 | Input Size | 1920 × 1200 |
| Batch Size | 16 | Decay Coefficient | 0.0005 |
| Model | Params (M) | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n-seg (Baseline) | 3.25 | 12.0 | 156 |
| YOLOv8n-CBAM-seg (Ours) | 3.42 | 14.1 | 148 |
| Model | CAM | SAM | BBox mAP (%) | Mask mAP (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| @0.5 | @0.5:0.95 | @0.5 | @0.5:0.95 | |||
| A: Baseline | – | – | 96.2 | 68.5 | 95.8 | 67.1 |
| B: Baseline + CAM | ✓ | – | 96.8 | 70.1 | 96.3 | 68.9 |
| C: Baseline + SAM | – | ✓ | 97.1 | 71.3 | 96.7 | 70.2 |
| D: Baseline + CBAM (Ours) | ✓ | ✓ | 97.5 | 72.6 | 97.2 | 71.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, M.; Hu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhan, H. Weld Seam ROI Detection and Segmentation Method Based on Active–Passive Vision Fusion. Sensors 2025, 25, 7530. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247530
Hu M, Hu X, Zhao J, Zhan H. Weld Seam ROI Detection and Segmentation Method Based on Active–Passive Vision Fusion. Sensors. 2025; 25(24):7530. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247530
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Ming, Xiangtao Hu, Jiuzhou Zhao, and Honghui Zhan. 2025. "Weld Seam ROI Detection and Segmentation Method Based on Active–Passive Vision Fusion" Sensors 25, no. 24: 7530. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247530
APA StyleHu, M., Hu, X., Zhao, J., & Zhan, H. (2025). Weld Seam ROI Detection and Segmentation Method Based on Active–Passive Vision Fusion. Sensors, 25(24), 7530. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25247530







