Research on Deep Learning-Based Human–Robot Static/Dynamic Gesture-Driven Control Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Iconic gestures: Represent concrete entities or actions through visual imagery (e.g., mimicking a “drinking” motion).
- Metaphorical gestures: Convey abstract concepts indirectly by mapping physical actions to intangible ideas (e.g., spreading hands wide to signify “freedom”).
- Deictic gestures: Point to objects, directions, or spatial relationships (e.g., extending an index finger to indicate “this one”).
- Beat gestures: Synchronize with speech rhythm to emphasize timing (e.g., finger tapping to mark syllables).
2. Methods
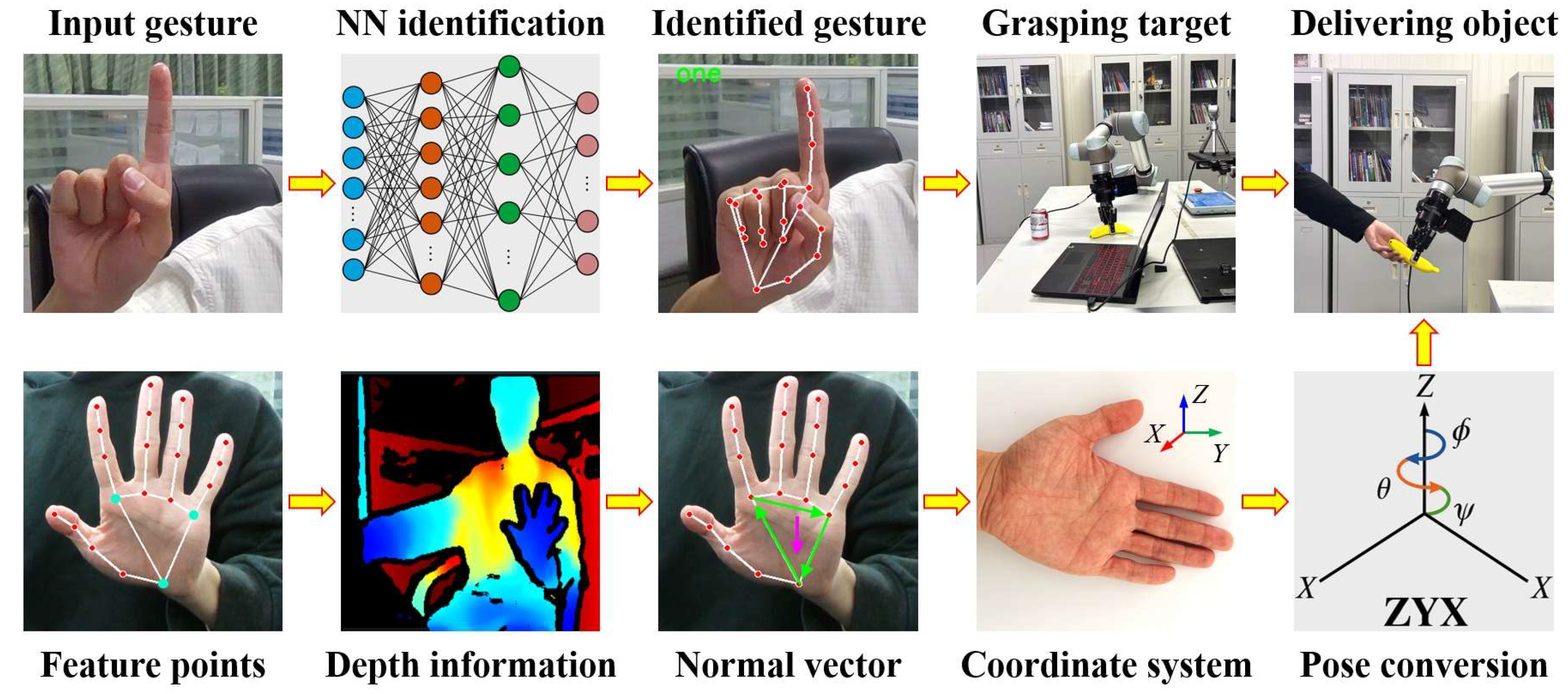
2.1. Overall Technical Workflow
2.2. Static Gesture Recognition
2.2.1. Static Gesture Dataset Collection
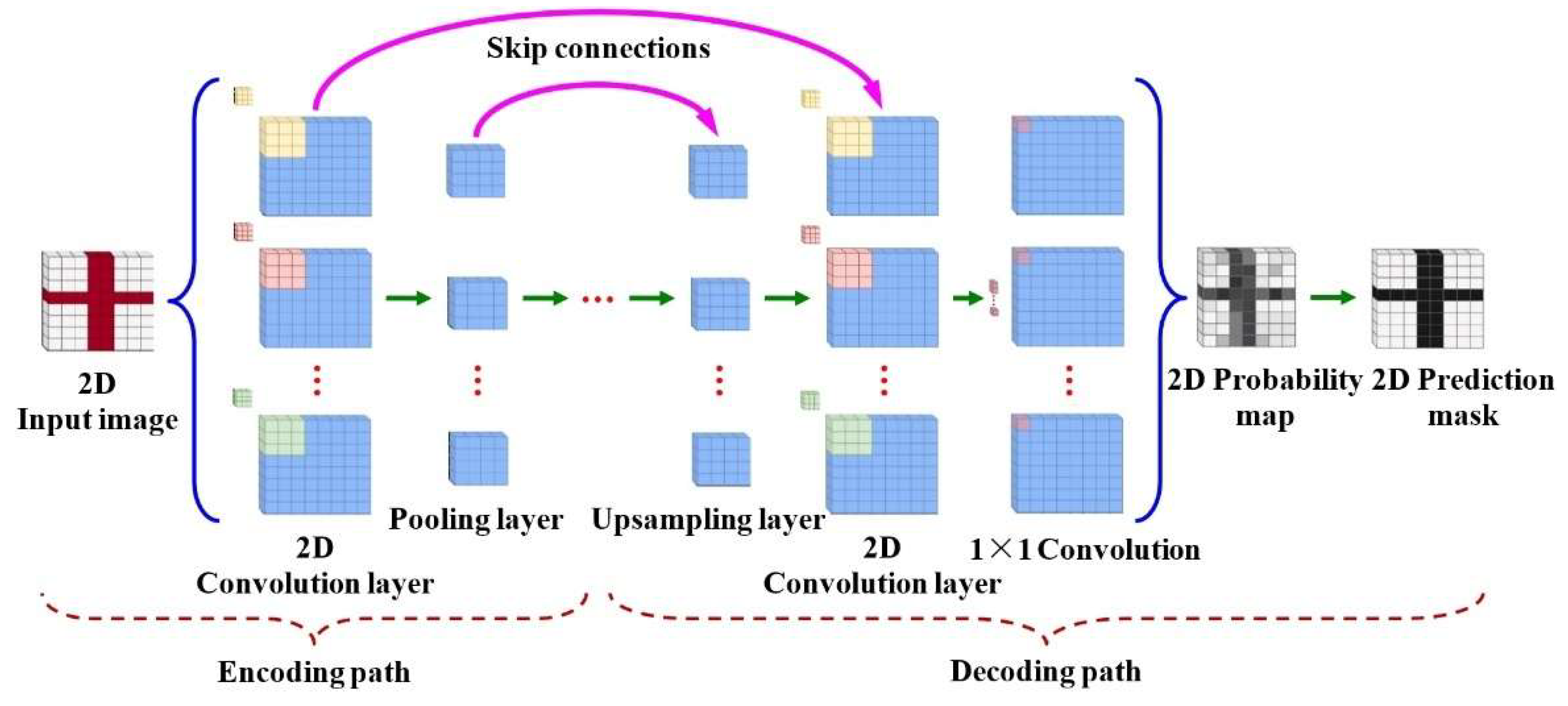
2.2.2. Static Gesture Recognition Using 2D-CNN
2.2.3. Analysis of Static Gesture Recognition
2.3. Dynamic Gesture Recognition
2.3.1. Dynamic Gesture Dataset Collection
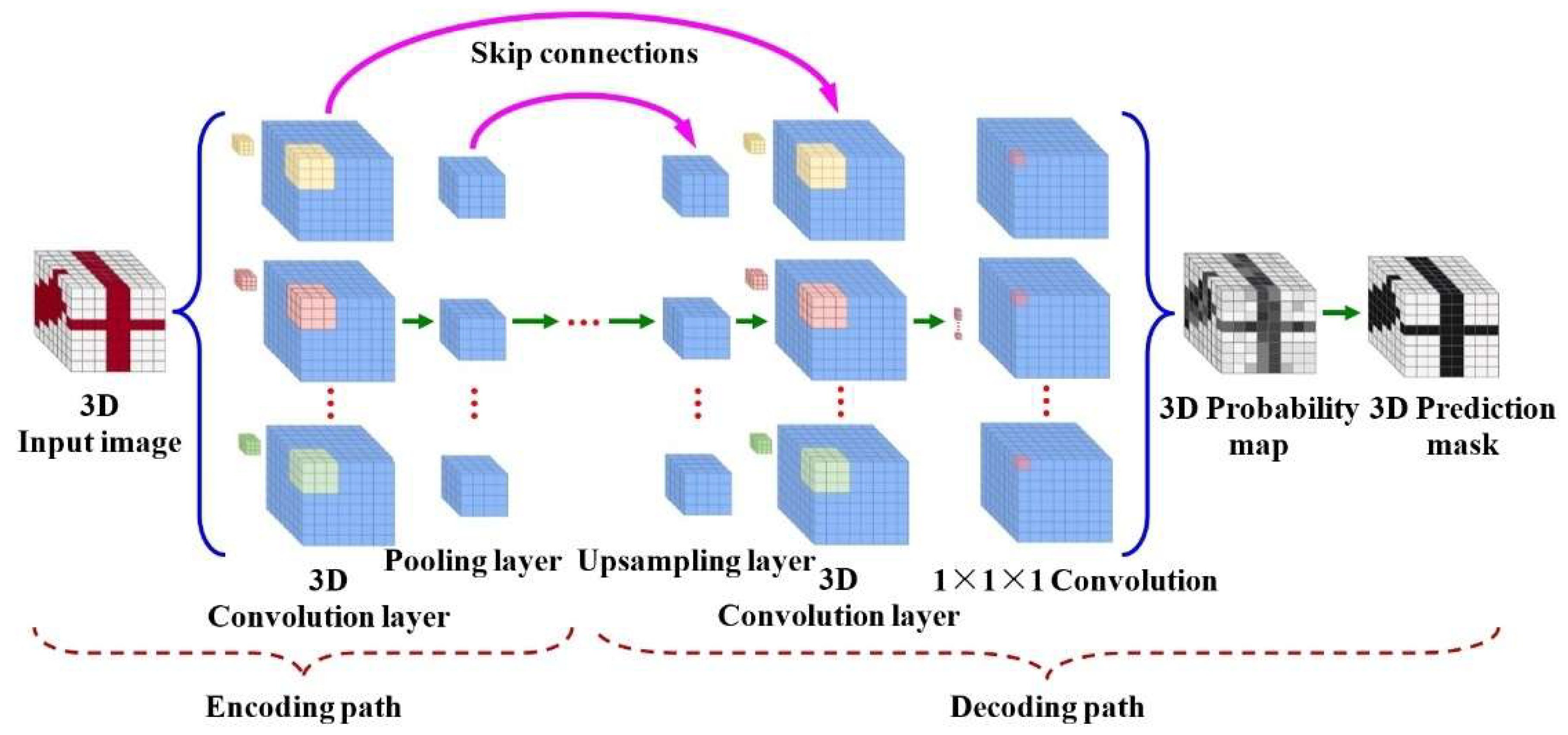
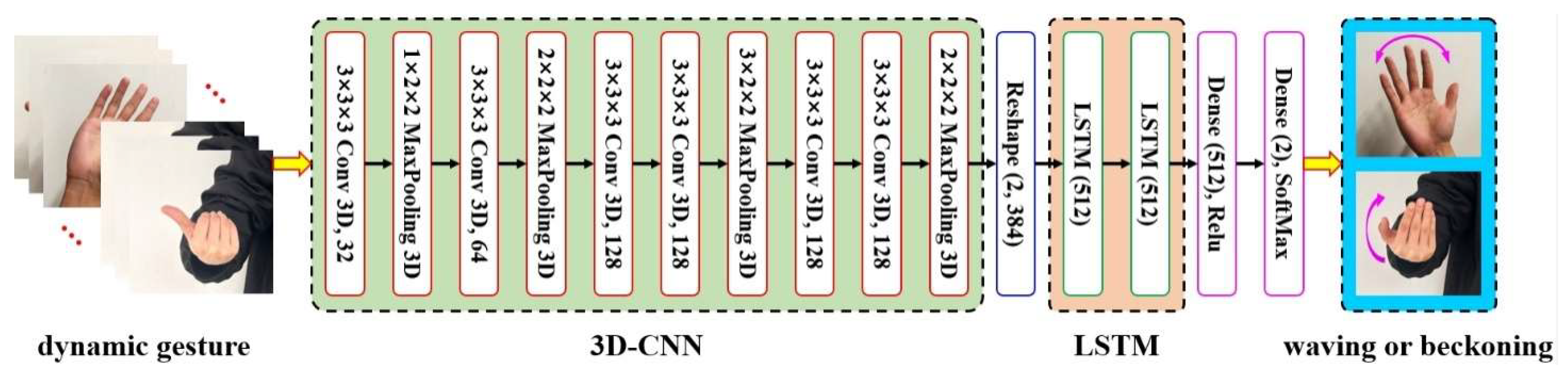
2.3.2. Dynamic Gesture Recognition via Hybrid 3D-CNN + LSTM Architecture
2.3.3. Analysis of Dynamic Gesture Recognition
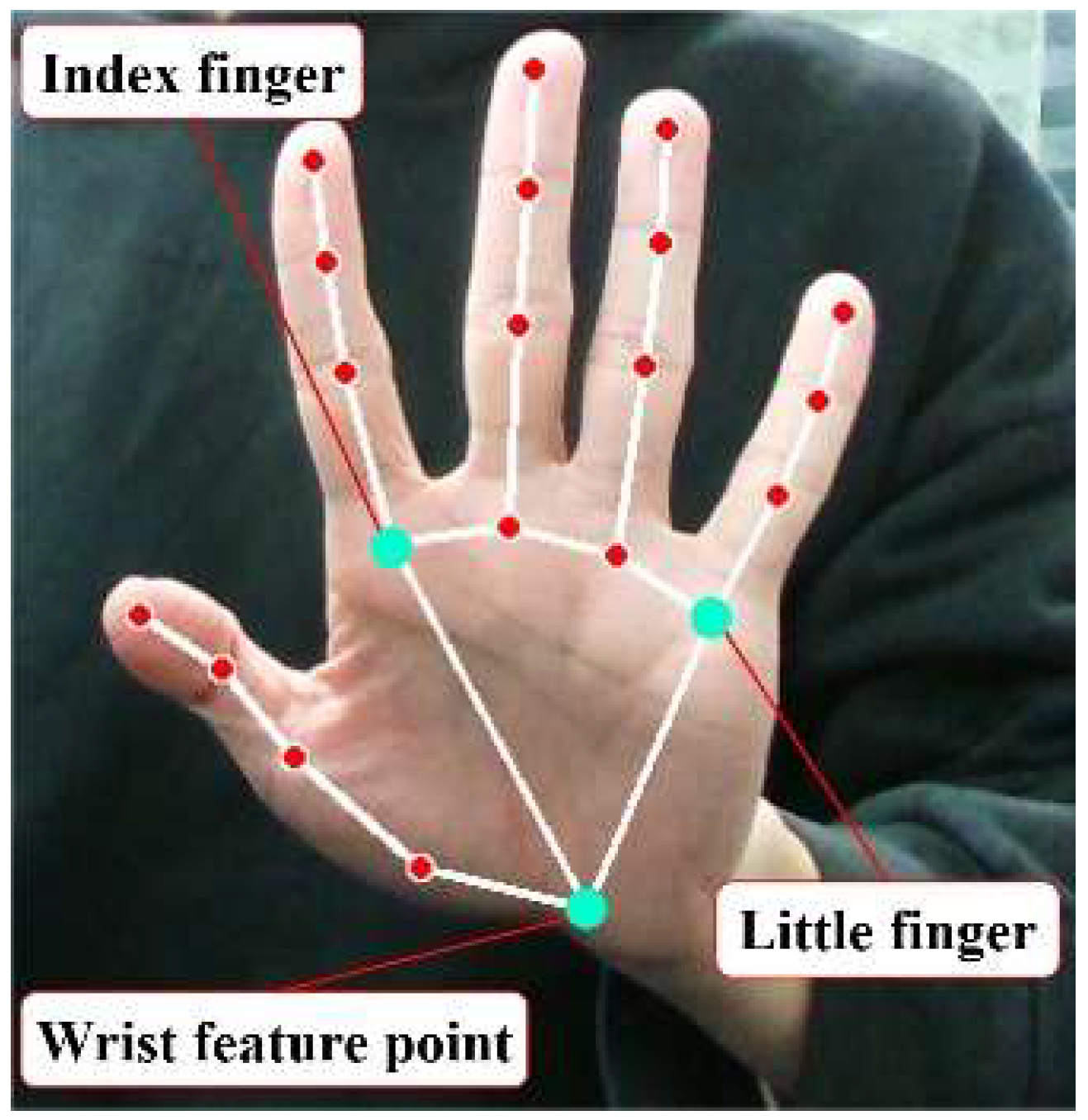
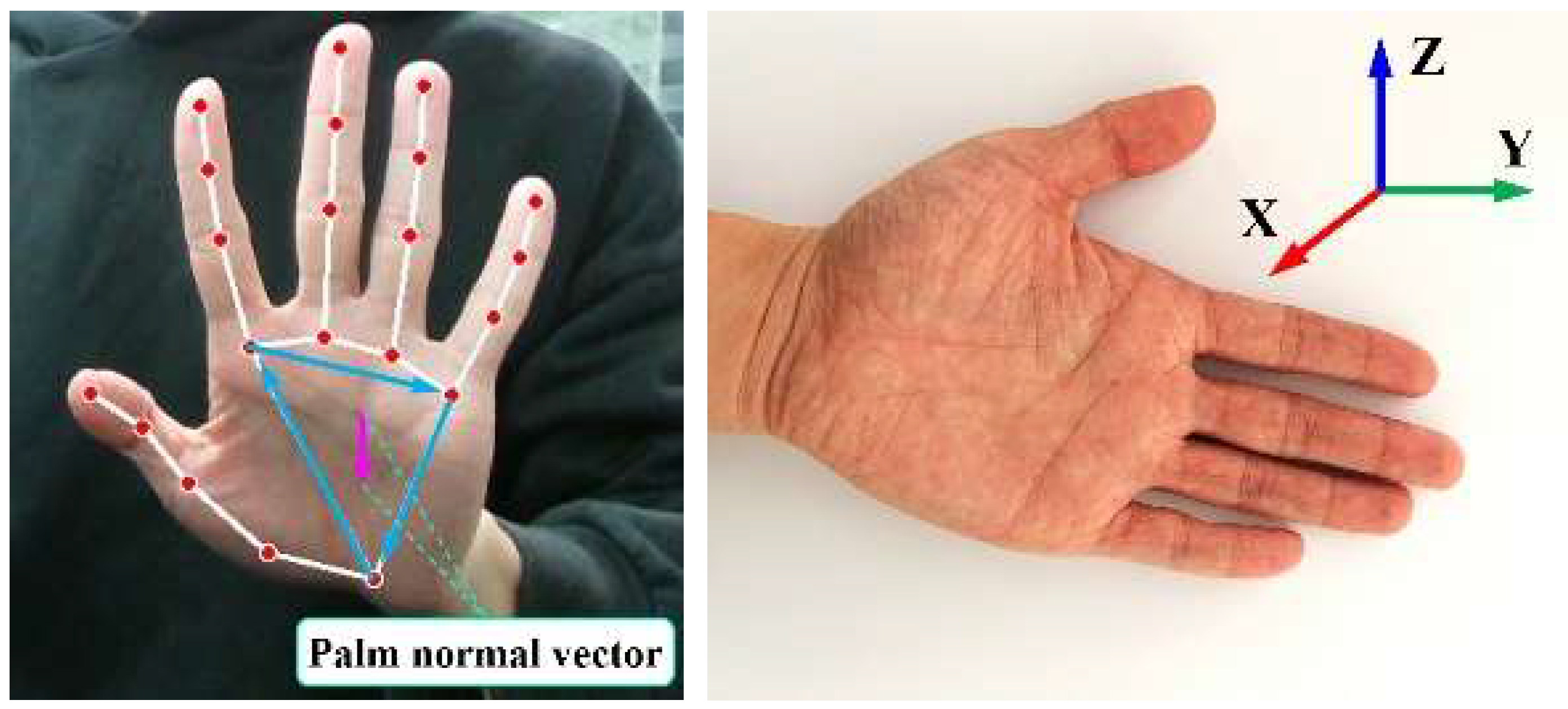
2.4. Hand Pose Estimation and Coordinate Transformation
2.4.1. Hand Pose Estimation
2.4.2. Hand–Eye Calibration and Pose Transformation
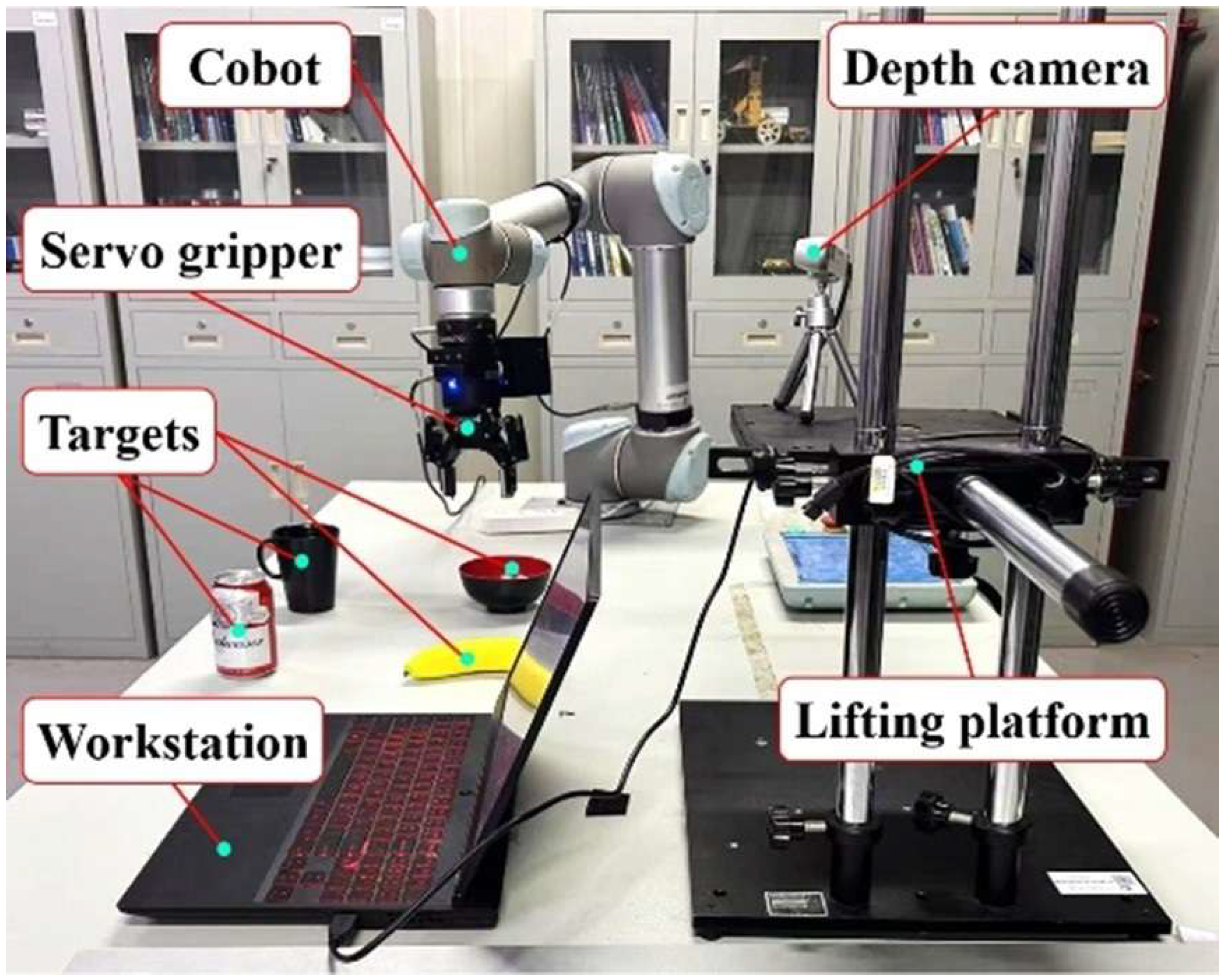
3. Experimental Protocols
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, G.; Xu, Z.; Hou, Z.; Yang, W.; Liang, J.; Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Han, C. A systematic error compensation strategy based on an optimized recurrent neural network for collaborative robot dynamics. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.K.; Rai, V.; Singh, H.R.; Kumar, R. Analyzing body language and facial expressions using machine learning techniques. In Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Pervasive Computational Technologies (ICPCT), Greater Noida, India, 8–9 February 2025; pp. 629–633. [Google Scholar]
- Petrov, M.; Chibizov, P.; Sintsov, M.; Balashov, M.; Kapravchuk, V.; Briko, A. Multichannel surface electromyography system for prosthesis control using RNN classifier. In Proceedings of the 2023 Systems and Technologies of the Digital HealthCare (STDH), Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 4–6 October 2023; pp. 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Scheck, K.; Ren, Z.; Dombeck, T.; Sonnert, J.; Gogh, S.V.; Hou, Q.; Wand, M.; Schultz, T. Cross-speaker training and adaptation for electromyography-to-speech conversion. In Proceedings of the 2024 46th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 July 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, Y. Lightweight and high accurate RR interval compensation for signals from wearable ECG sensors. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2024, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L. A real-time recognition method of static gesture based on DSSD. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 17445–17461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Tao, H.; Li, W.; Yuan, H.; Li, T. Dynamic gesture recognition based on feature fusion network and variant ConvLSTM. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 2480–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, D. Gesture and Thought, 1st ed.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.; Kim, H.; Park, C.; Sim, Y.; Lee, S.; Jung, Y. sEMG-based hand gesture recognition using binarized neural network. Sensors 2023, 23, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agab, S.E.; Chelali, F.Z. New combined DT-CWT and HOG descriptor for static and dynamic hand gesture recognition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 26379–26409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Leu, M.C.; Yin, Z. Real-time multi-modal human–robot collaboration using gestures and speech. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2022, 144, 101007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Wen, S.; Liu, Y.; Huang, T. YOLOv8-G2F: A portable gesture recognition optimization algorithm. Neural Netw. 2025, 188, 107469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Y.; Ren, H.; Li, H.; Yuan, K.-H.; Zhu, C.-F. Static gesture recognition based on thermal imaging sensors. J. Supercomput. 2025, 81, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Bo, Y.; Lu, Y. Improving static gesture recognition with capacitive sensor arrays by incorporating distance measurements. Measurement 2026, 257, 118697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhao, B. Gesture recognition achieved by utilizing LoRa signals and deep learning. Sensors 2025, 25, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnnane, B.; Li, J. Hand gesture controlled robot arm. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence and Intelligent Manufacturing (AIIM), Chengdu, China, 20–22 December 2024; pp. 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoodi, J.; Nezamabadi-Pour, H. Violence detection in video using statistical features of the optical flow and 2D convolutional neural network. Comput. Intell. 2025, 41, e70034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xing, X.H.; Kuai, T. Rotation-invariant 3D convolutional neural networks for 6D object pose estimation. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2025, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, W. An ensemble deep learning network based on 2D convolutional neural network and 1D LSTM with self-attention for bearing fault diagnosis. Appl. Soft Comput. 2025, 172, 112889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Li, S.; Fan, X.; Wang, M.; Lian, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M. 6D pose estimation algorithm for local feature representation. Appl. Res. Comput. 2022, 39, 3808–3814. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Ha, E.J.; Choi, J.H. Human pose estimation using MediaPipe pose and optimization method based on a humanoid model. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudeep; Sangram; Shivaprasad; Prasad, S.; Nayaka, R. Deep learning based image classification using small VGGNet architecture. In Proceedings of the 2021 1st International Conference on EMMA, Chennai, India, 24–26 December 2024; Volume 2742, pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Chen, X.; Yang, G.; Wu, Y.; Qi, C.; Di, S. Intelligent human-robot collaborative handover system for arbitrary objects based on 6D pose recognition. Chin. J. Eng. 2024, 46, 148–156. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlović, T.; Popović, T.; Čakić, S. Breast cancer detection using ResNet and DenseNet architecture. In Proceedings of the 2025 29th International Conference on Information Technology (IT), Zabljak, Montenegro, 19–22 February 2025; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Malakouti, S.M.; Menhaj, M.B.; Suratgar, A.A. The usage of 10-fold cross-validation and grid search to enhance ML methods performance in solar farm power generation prediction. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2023, 15, 100664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong-Sheng, Z.; Jie, C.; Qi-Long, L.; Bin-Quan, D.; Jie, W.; Cheng-Gong, C. Deep contrastive learning: A survey. Acta Autom. Sin. 2023, 49, 15–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shuping, L.; Yi, H.; Yingying, W. Improvement of human action recognition method based on C3D convolutional neural network. Exp. Technol. Manag. 2021, 38, 168–171. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, Y. Review of human action recognition based on deep learning. J. Front. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2021, 15, 438–455. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Ding, B.; He, Y. Multi-view fusion 3D model classification. J. Harbin Univ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 27, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, Q. Method of camera pose estimation based on feature point uncertaint. Eng. Surv. Mapp. 2023, 32, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.M.; Zhang, J.K. Study on track gauge measurement system based on laser triangulation principle. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 34, 1934–1940. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Wu, M.; Shi, J.; Miao, X. Research on improved A algorithm integrating vector cross-product and jump point search strategy. Mech. Sci. Technol. Aerosp. Eng. 2024, 43, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X. Machine Vision: Principles and Detailed Explanation of Classic Cases, 1st ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, R.Y.; Lenz, R.K. A new technique for fully autonomous and efficient 3 d robotics hand/eye calibration. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1989, 5, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
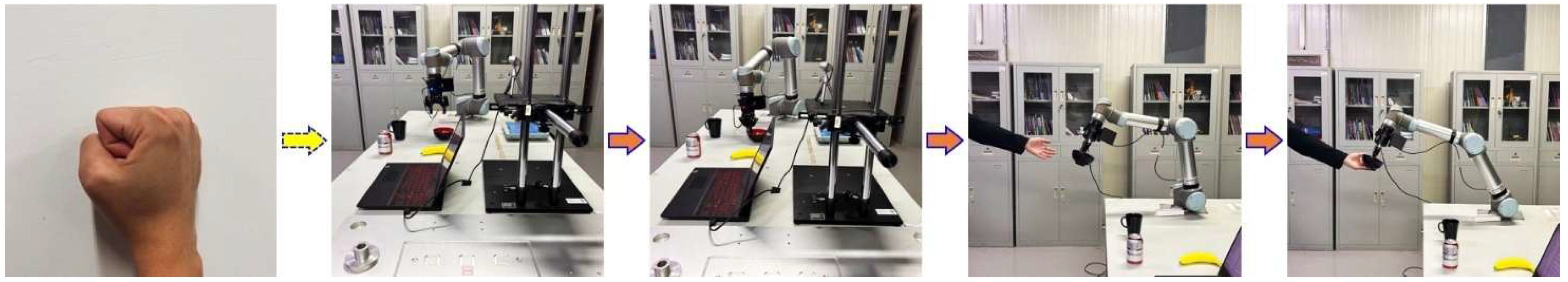
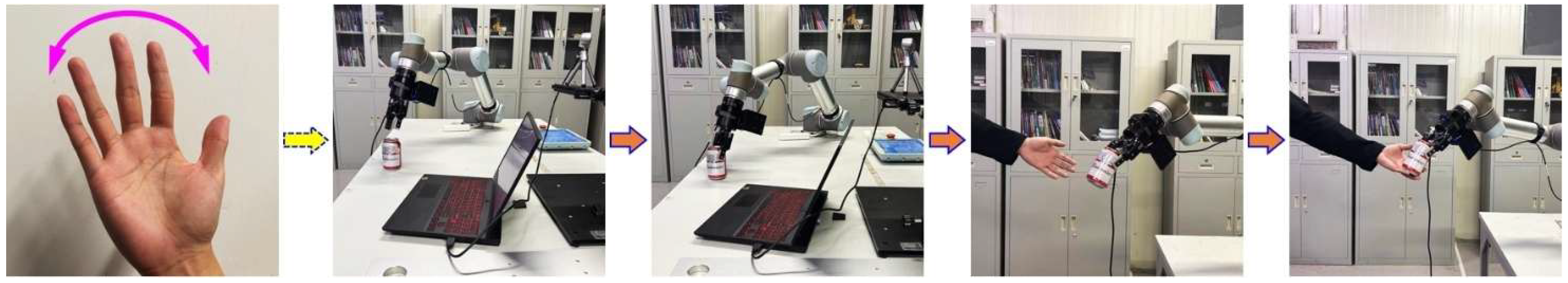
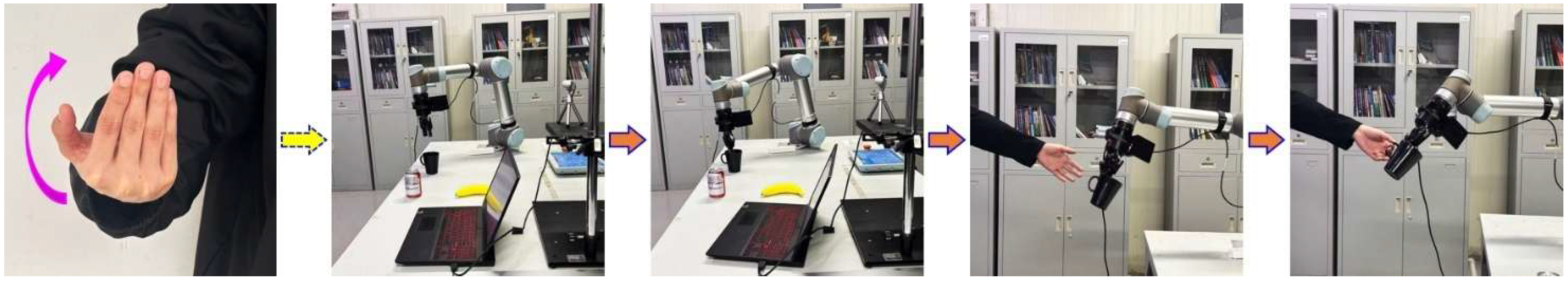





| Gesture Name | Gesture Example | Target Object | Object Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Closed fist |  | Bowl | |
| Index finger |  | Banana | |
| Gesture Name | Gesture Example | Target Object | Object Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waving side-to-side | 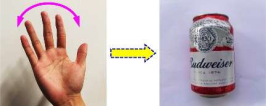 | Beverage can | |
| Backward beckoning | 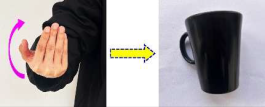 | Drinking cup | |
| Model Name | Parameter Count | Recognition Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| C3D [27] | 94,910,722 | 92.73% |
| Res3D [28] | 26,547,498 | 94.49% |
| 3D-CNN+RNN [29] | 3,688,706 | 94.85% |
| 3D-CNN+LSTM | 5,547,143 | 95.66% |
| Participants | Natural Light | Low Light | High Light | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Completion Time/s | Success Rate/% | Completion Time/s | Success Rate/% | Completion Time/s | Success Rate/% | |
| 1 | 18.18 | 98.50 | 19.22 | 95.00 | 18.93 | 97.00 |
| 2 | 18.13 | 98.00 | 18.22 | 97.00 | 18.20 | 99.50 |
| 3 | 17.28 | 99.00 | 18.55 | 96.50 | 19.69 | 94.50 |
| 4 | 16.84 | 99.00 | 17.91 | 98.00 | 16.79 | 99.00 |
| Average value | 17.60 | 98.13 | 18.43 | 96.88 | 18.39 | 97.63 |
| Participants | Natural Light | Low Light | High Light | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Completion Time/s | Success Rate/% | Completion Time/s | Success Rate/% | Completion Time/s | Success Rate/% | |
| 1 | 17.94 | 96.50 | 19.95 | 94.50 | 19.71 | 95.50 |
| 2 | 18.70 | 95.00 | 18.69 | 95.50 | 19.08 | 95.50 |
| 3 | 18.68 | 95.50 | 19.44 | 95.00 | 19.49 | 95.00 |
| 4 | 18.21 | 96.50 | 19.60 | 93.50 | 19.27 | 94.50 |
| Average value | 18.38 | 95.88 | 19.42 | 94.63 | 19.39 | 95.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Su, J.; Zhang, S.; Qi, J.; Hou, Z.; Lin, Q. Research on Deep Learning-Based Human–Robot Static/Dynamic Gesture-Driven Control Framework. Sensors 2025, 25, 7203. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237203
Zhang G, Su J, Zhang S, Qi J, Hou Z, Lin Q. Research on Deep Learning-Based Human–Robot Static/Dynamic Gesture-Driven Control Framework. Sensors. 2025; 25(23):7203. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237203
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Gong, Jiahong Su, Shuzhong Zhang, Jianzheng Qi, Zhicheng Hou, and Qunxu Lin. 2025. "Research on Deep Learning-Based Human–Robot Static/Dynamic Gesture-Driven Control Framework" Sensors 25, no. 23: 7203. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237203
APA StyleZhang, G., Su, J., Zhang, S., Qi, J., Hou, Z., & Lin, Q. (2025). Research on Deep Learning-Based Human–Robot Static/Dynamic Gesture-Driven Control Framework. Sensors, 25(23), 7203. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237203








