Upper Limb Capacity, Performance, and Leisure Participation in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy
Highlights
- Children with unilateral cerebral palsy maintain high overall physical activity, despite reduced performance of the non-dominant arm.
- There are no associations between arm capacity, arm performance, and leisure participation in children with unilateral cerebral palsy.
- Effective compensatory use of the dominant arm in children with unilateral cerebral palsy may help sustain their overall activity level.
- Children with unilateral cerebral palsy may adopt effective compensation mechanisms with their dominant arm to stay active.
- Leisure participation in children with unilateral cerebral palsy is a multifaceted phenomenon that often goes beyond motor impairments.
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- To compare UL performance, measured by the intensity of UL activity, between children with uCP and TD children and between sides (dominant and non-dominant). We hypothesized that children with uCP would show reduced overall UL activity for both ULs, as well as a greater interlimb asymmetry compared to TD children.
- 2.
- To explore the associations between UL performance, UL capacity, and their participation in leisure activities outside the school setting in children with uCP. We hypothesized that higher UL capacity and UL performance would be associated with higher leisure participation.
- 1.
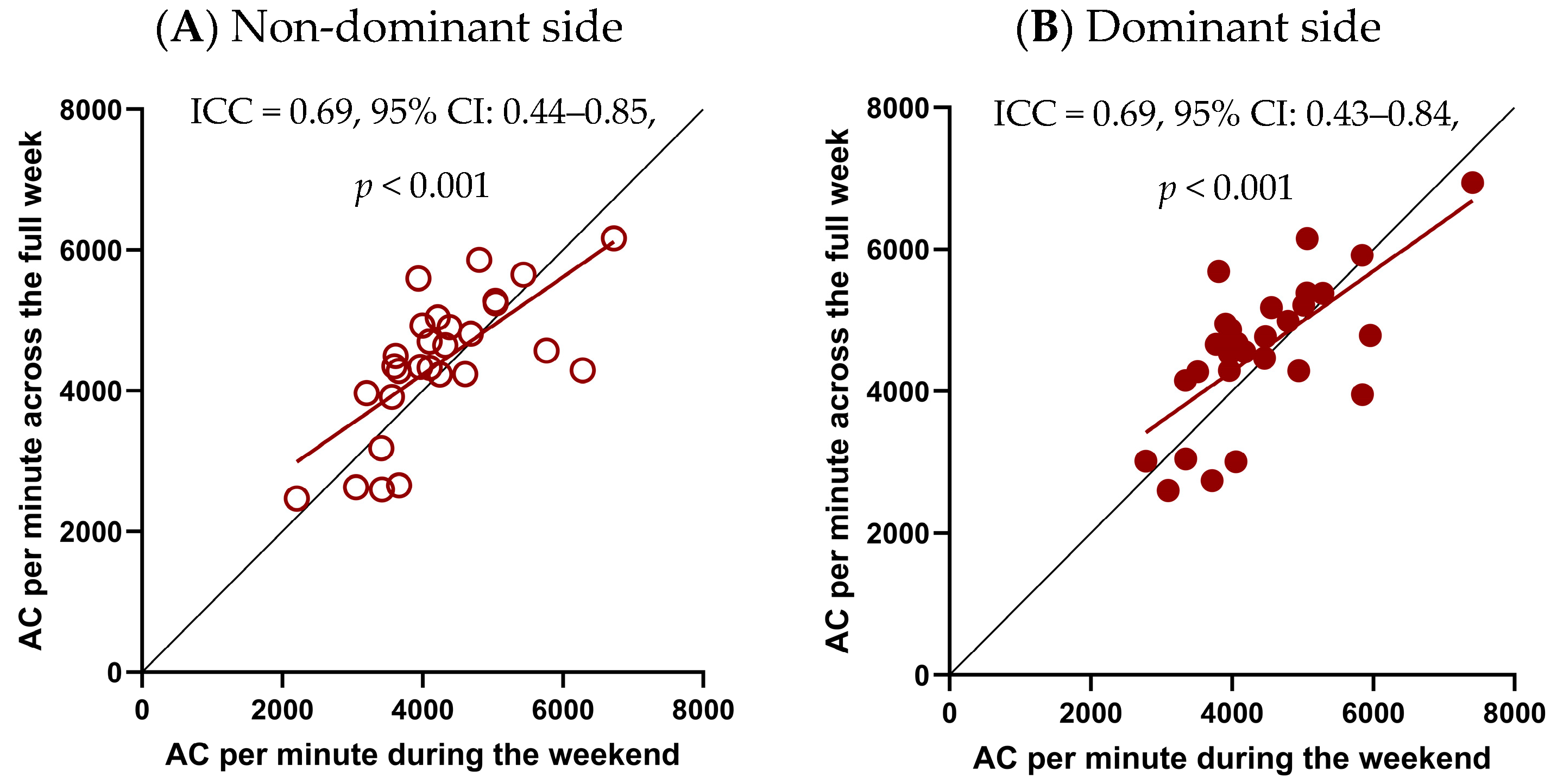
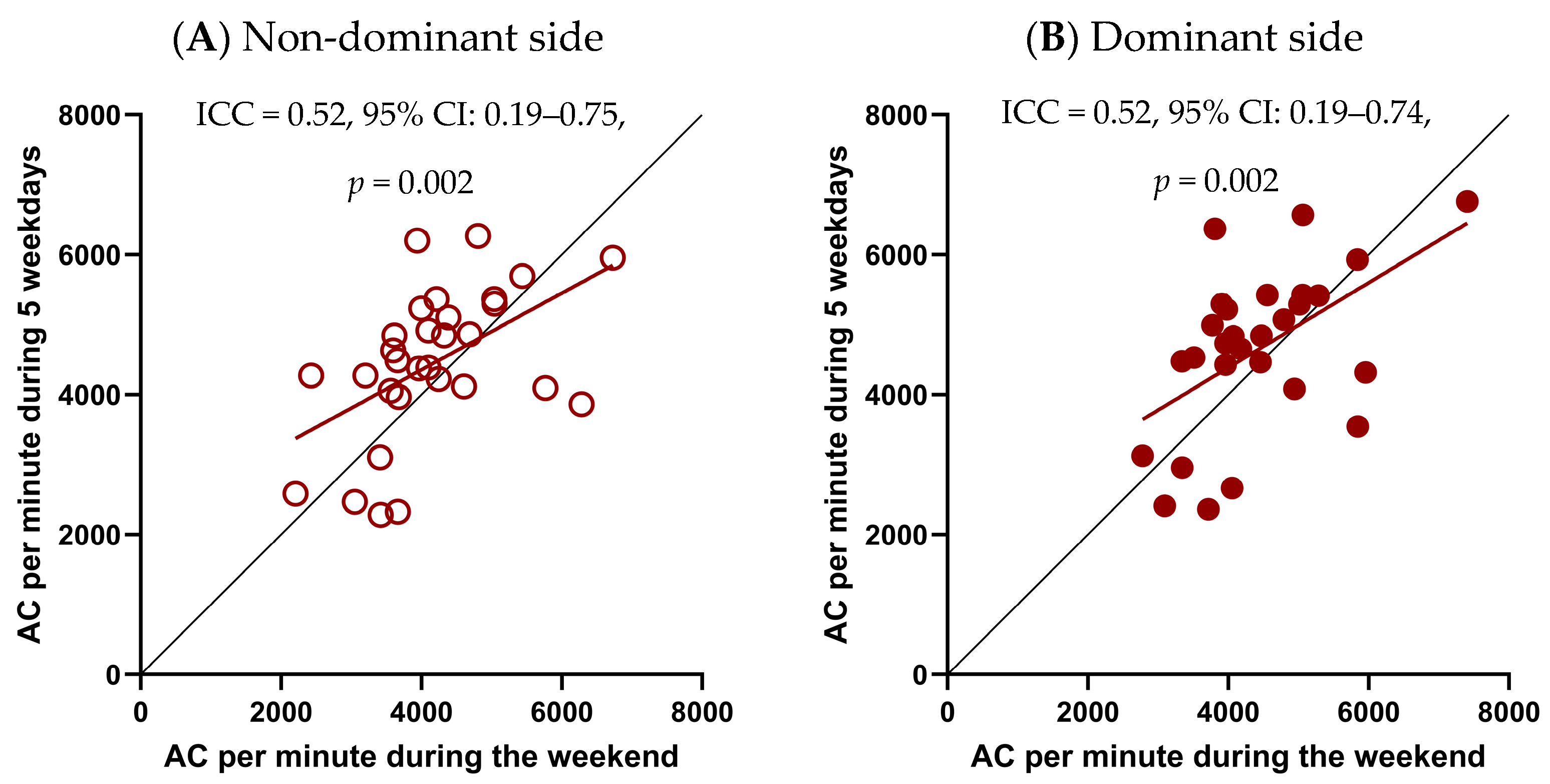
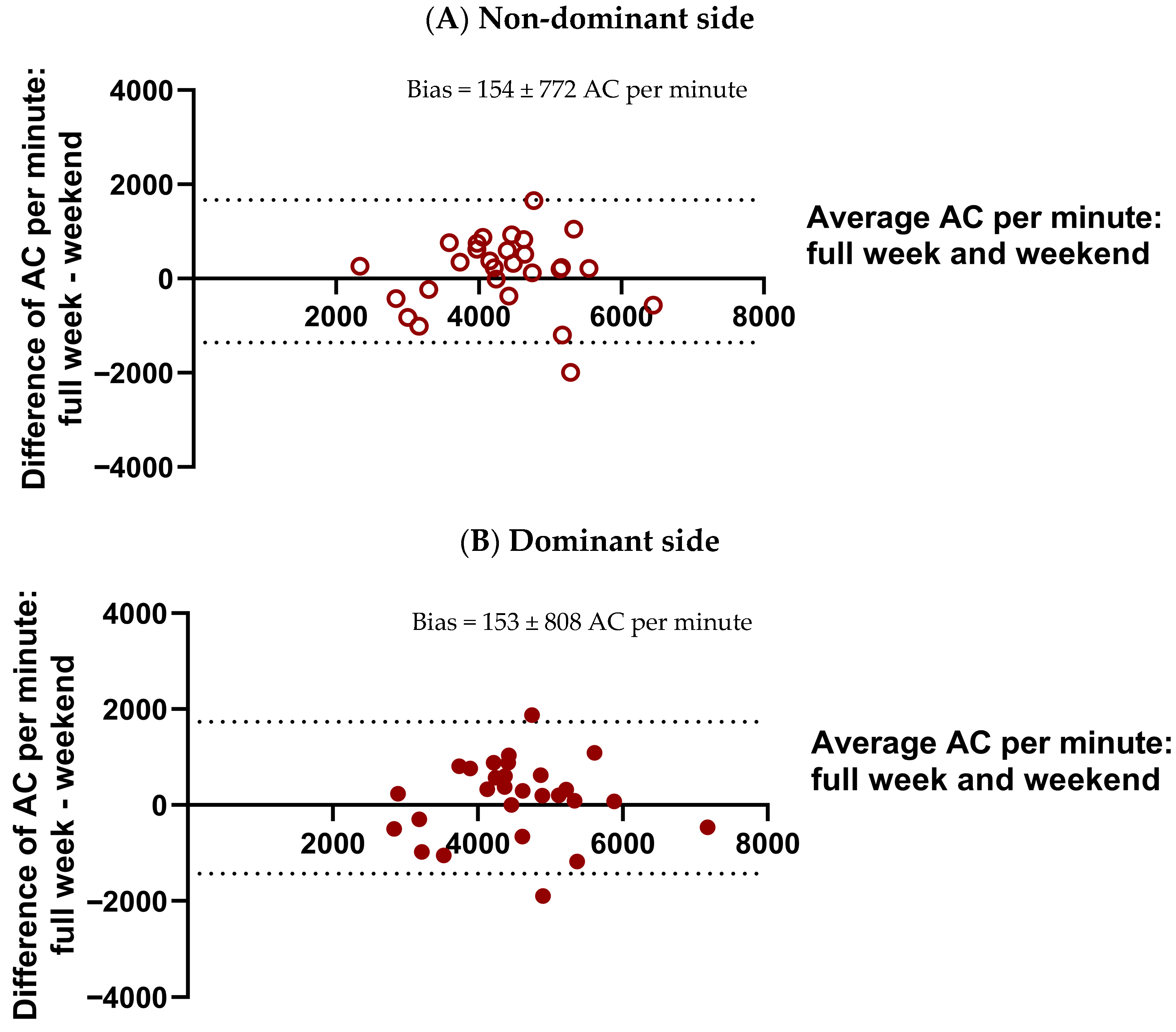
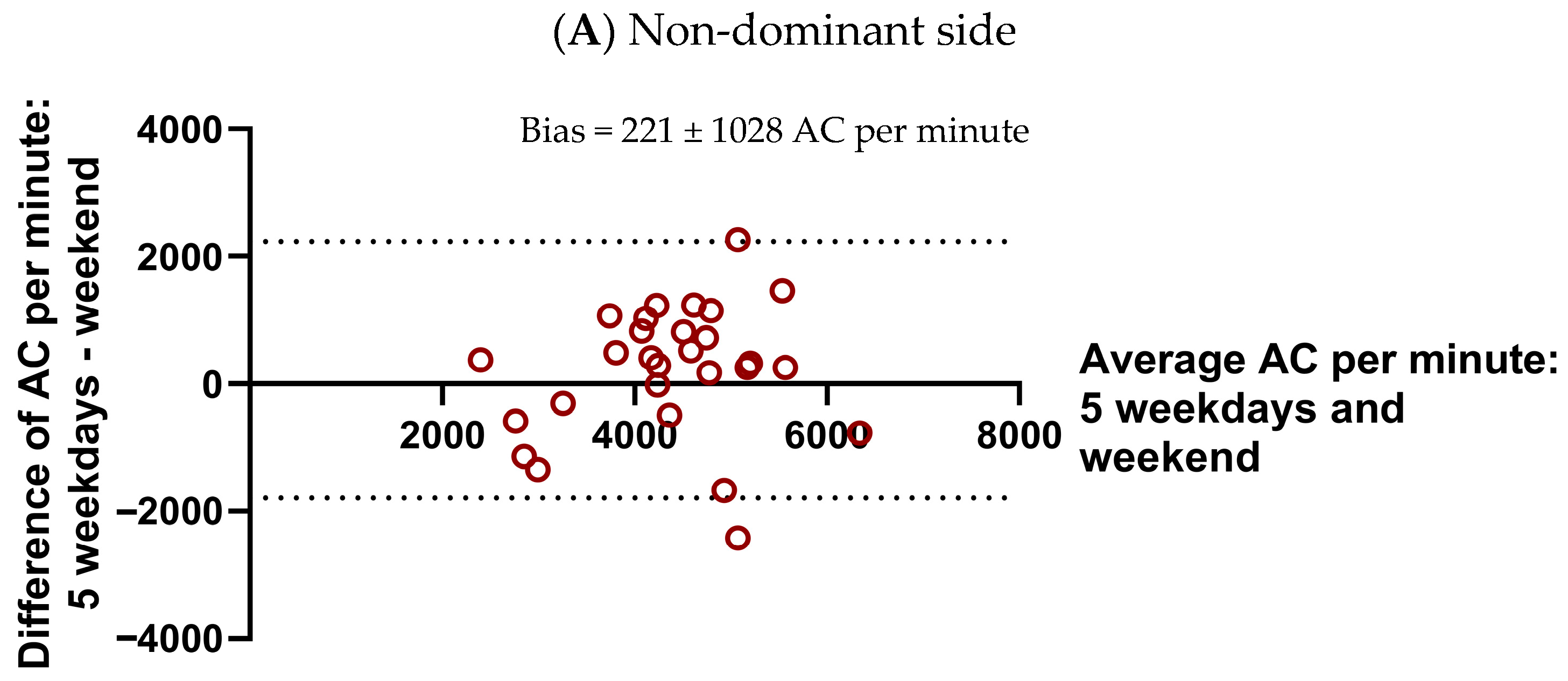
- To examine whether a 2-day (weekend) measurement period provides a reliable estimate of UL performance compared to 5-day (weekdays) and 7-day (full week) periods, and to evaluate the reproducibility of children’s activity patterns across these different recording durations. This validation was only performed within the TD group, because the data for the uCP participants were limited to the weekend recordings. This limitation was explained by their participation in a separate longitudinal study with multiple evaluations of the effects of bimanual therapy, where the use of accelerometry was limited to weekends to ease the burden on both children and their families before, during, and after the intervention.
- 2.
- To assess the effect of age on the UL performance, given the large heterogeneity in our group in terms of age.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethics
2.2. Participants
2.3. Study Protocol
2.4. Instruments
2.4.1. Accelerometry Data Collection and Processing
2.4.2. The Jebsen-Taylor Hand Function Test (JTHFT)
2.4.3. Children’s Assessment of Participation and Enjoyment (CAPE)
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Sample Description
3.2. Main Results
3.2.1. Comparison of UL Performance Between Sides and Groups
3.2.2. Correlation Between UL Performance, UL Capacity and the Participation Intensity in Leisure Activity
3.3. Results of the Secondary Objectives Focusing on Methodological Aspects
3.3.1. Reproducibility of Weekend and Longer Monitoring Periods of UL Performance
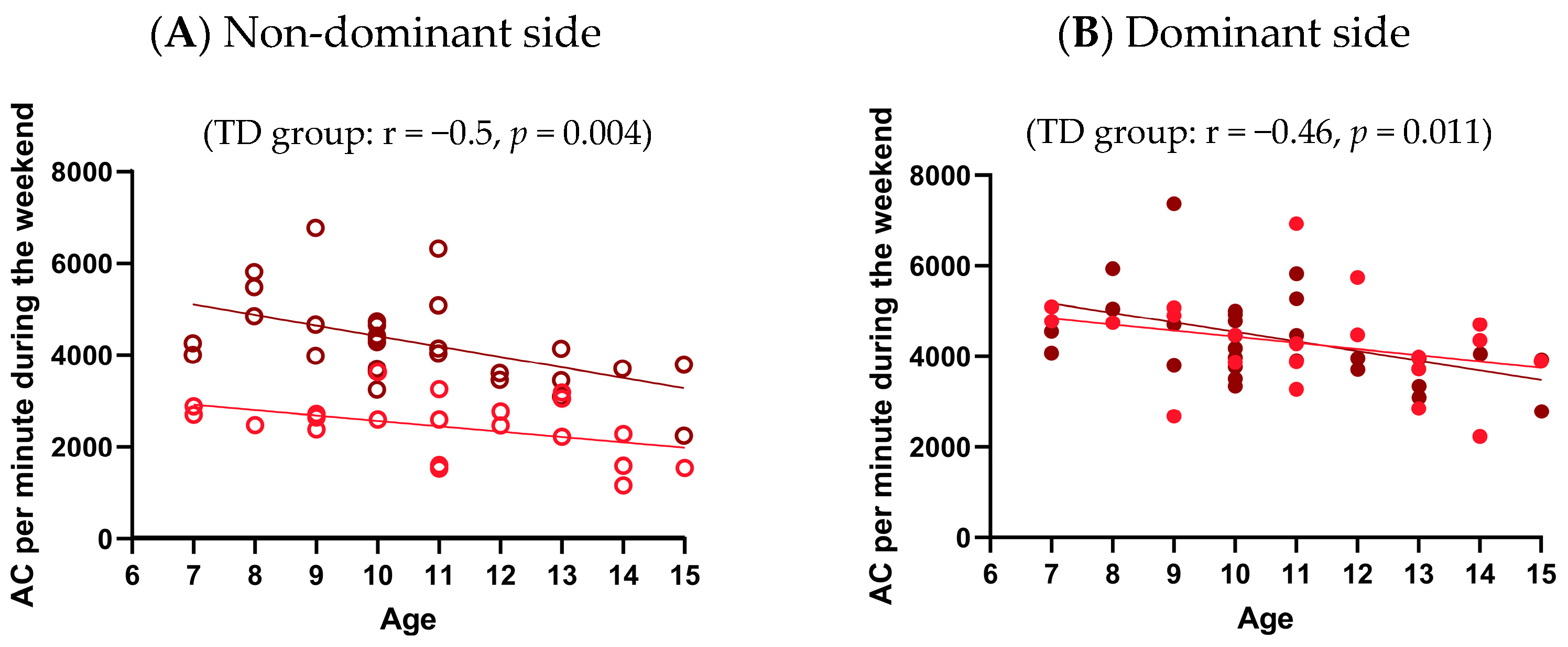
3.3.2. Effect of Age on UL Performance for Each Group
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CP | Cerebral palsy |
| uCP | Unilateral cerebral palsy |
| UL | Upper limb |
| TD | Typically developing |
| CIUSSS-CN | Centre intégré universitaire de santé et de services sociaux de la Capitale-Nationale |
| MACS | Manual Ability Classification Scale |
| JTHFT | Jebsen-Taylor Hand Function Test |
| CAPE | Children’s Assessment of Participation and Enjoyment |
| AC | Activity counts |
| ICC | Intraclass correlation coefficients |
Appendix A
| Sides | AC per Minute During Weekend (Mean ± SD, AC/min) | AC per Minute During Full Week (Mean ± SD, AC/min) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-dominant | 4252 ± 986 | 4405 ± 985 | 0.302 |
| Dominant | 4436 ± 1014 | 4589 ± 1037 | 0.327 |
| Sides | AC per Minute During Weekend (Mean ± SD, AC/min) | AC per Minute During 5 Weekdays (Mean ± SD, AC/min) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-dominant | 4252 ± 986 | 4473 ± 1116 | 0.265 |
| Dominant | 4436 ± 1014 | 4650 ± 1175 | 0.302 |
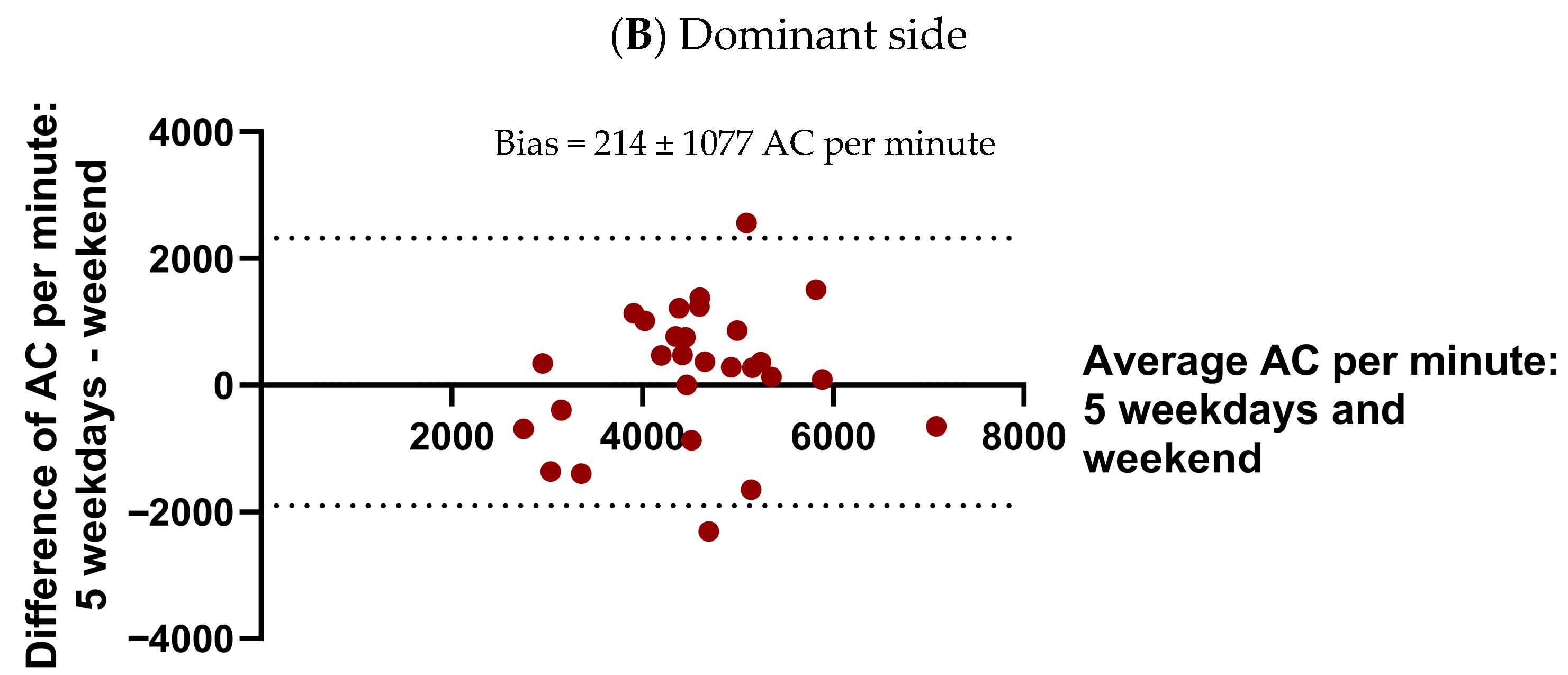
Appendix B
References
- Dan, B.; Rosenbaum, P.; Carr, L.; Gough, M.; Coughlan, J.; Nweke, N. Proposed Updated Description of Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2025, 67, e16274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowska, M.; Sarecka-Hujar, B.; Kopyta, I. Cerebral Palsy: Current Opinions on Definition, Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification and Treatment Options. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmelmann, K.; Uvebrant, P. The Panorama of Cerebral Palsy in Sweden Part XII Shows That Patterns Changed in the Birth Years 2007–2010. Acta Paediatr. 2018, 107, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingels, K.; Demeyere, I.; Jaspers, E.; De Cock, P.; Molenaers, G.; Boyd, R.; Feys, H. Upper Limb Impairments and Their Impact on Activity Measures in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2012, 16, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaebler-Spira, D. Overview of Sensorimotor Dysfunction in Cerebral Palsy. Top. Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2011, 17, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacioppo, M.; Lempereur, M.; Marin, A.; Rauscent, H.; Crétual, A.; Brochard, S.; Bonan, I. Motor Patterns of the Impaired Upper Limb in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy Performing Bimanual Tasks. Clin. Biomech. 2022, 97, 105710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houwink, A.; Aarts, P.B.M.; Geurts, A.C.H.; Steenbergen, B. A Neurocognitive Perspective on Developmental Disregard in Children with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (Ed.) International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health: ICF; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001; 299p. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, P.C.; Chang, C.H.; Granlund, M.; Hwang, A.W. The Relationships Between Capacity and Performance in Youths with Cerebral Palsy Differ for GMFCS Levels. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2017, 29, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcreff, L.; Gerber, C.N.; Paraschiv-Ionescu, A.; De Coulon, G.; Newman, C.J.; Aminian, K.; Armand, S. Comparison of Gait Characteristics Between Clinical and Daily Life Settings in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, A.C.; Nickerson, P.; Wright, K.L. Structured Leisure Activities in Middle Childhood: Links to Well-Being. J. Community Psychol. 2003, 31, 641–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, L.L.; Rose-Krasnor, L.; Shapira, M.; Coplan, R.J. Parental Beliefs About Young Children’s Leisure Activity Involvement. J. Leis. Res. 2020, 51, 469–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikako-Thomas, K.; Shevell, M.; Lach, L.; Law, M.; Schmitz, N.; Poulin, C.; Majnemer, A. Picture Me Playing—A Portrait of Participation and Enjoyment of Leisure Activities in Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2013, 34, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlon, S.L.; Taylor, N.F.; Dodd, K.J.; Shields, N. Differences in Habitual Physical Activity Levels of Young People with Cerebral Palsy and Their Typically Developing Peers: A Systematic Review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2013, 35, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikako-Thomas, K.; Majnemer, A.; Law, M.; Lach, L. Determinants of Participation in Leisure Activities in Children and Youth with Cerebral Palsy: Systematic Review. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2008, 28, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vila-Nova, F.; Dos Santos Cardoso de Sá, C.; Oliveira, R.; Cordovil, R. Differences in Leisure Physical Activity Participation in Children with Typical Development and Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Neurorehabilit. 2021, 24, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Kemp, J.; Ketelaar, M.; Gorter, J.W. Environmental Factors Associated with Participation and Its Related Concepts Among Children and Youth with Cerebral Palsy: A Rapid Review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2021, 44, 1571–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Cherni, Y.; Batcho, C.S.; Traverse, E.; Lavoie, M.D.; Mercier, C. Facilitators and Barriers to Participation in Physical Activities in Children and Adolescents Living with Cerebral Palsy: A Scoping Review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2023, 45, 4322–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holsbeeke, L.; Ketelaar, M.; Schoemaker, M.M.; Gorter, J.W. Capacity, Capability, and Performance: Different Constructs or Three of a Kind? Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2009, 90, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.E.; Waddell, K.J.; Klaesner, J.W.; Bland, M.D. A Method for Quantifying Upper Limb Performance in Daily Life Using Accelerometers. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 122, e55673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker-Bolt, P.; Connelly, J.; Seo, N.J.; Hoover, R.; Downey, R.; Shelton, D. Quantifying Real-World Activity and Upper-Limb Use in Children with Cerebral Palsy Using Accelerometers. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2016, 70 (Suppl. 1), 7011500060p1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beani, E.; De’ Cavalieri, M.F.; Filogna, S.; Barzacchi, V.; Cianchetti, M.; Maselli, M.; Martini, G.; Menici, V.; Prencipe, G.; Sicola, E.; et al. Wearable Sensors for Measuring Spontaneous Upper Limb Use in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy and Typical Development. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2025, 22, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedberg-Graff, J.; Bezuidenhout, L.; Krumlinde-Sundholm, L.; Hallgren, J.; Moulaee Conradsson, D.; Hagströmer, M. Association Between Upper Limb Clinical Tests and Accelerometry Metrics for Arm Use in Daily Life in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Disabil. Rehabil. 2024, 47, 2436–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Amonkar, N.; Kumavor, P.D.; Bubela, D. Measuring Upper Extremity Activity of Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy Using Wrist-Worn Accelerometers: A Pilot Study. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2024, 78, 7802180050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Yi, S.-H.; Park, E.S.; Shim, D.; Choi, T.Y.; Rha, D.-W. Relationship Between the More-Affected Upper Limb Function and Daily Activity Performance in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, E.; Regalado, I.C.R.; Galvão, E.R.V.P.; Ferreira, H.N.C.; Badia, M.; Baz, B.O. I Want to Play: Children with Cerebral Palsy Talk About Their Experiences on Barriers and Facilitators to Participation in Leisure Activities. Pediatr. Phys. Ther. 2020, 32, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Meeteren, J.; Roebroeck, M.E.; Celen, E.; Donkervoort, M.; Stam, H.J.; Transition Research Group South West. Functional Activities of the Upper Extremity of Young Adults with Cerebral Palsy: A Limiting Factor for Participation? Disabil. Rehabil. 2008, 30, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornson, K.F.; Zhou, C.; Stevenson, R.; Christakis, D.A. Capacity to Participation in Cerebral Palsy: Evidence of an Indirect Path via Performance. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, C.N.; Carcreff, L.; Paraschiv-Ionescu, A.; Armand, S.; Newman, C.J. Reliability of Single-Day Walking Performance and Physical Activity Measures Using Inertial Sensors in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 64, 101250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, D.S. Equivalence of Activity Outcomes Derived from Three Research-Grade Accelerometers Worn Simultaneously on Each Wrist. J. Sports Sci. 2022, 40, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitras, I.; Clouâtre, J.; Bouyer, L.J.; Routhier, F.; Mercier, C.; Campeau-Lecours, A. Development and Validation of Open-Source Activity Intensity Count and Activity Intensity Classification Algorithms from Raw Acceleration Signals of Wearable Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 6767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulst, R.Y.; Gorter, J.W.; Obeid, J.; Voorman, J.M.; Van Rijssen, I.M.; Gerritsen, A.; Visser-Meily, J.M.A.; Pillen, S.; Verschuren, O. Accelerometer-Measured Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, and Sleep in Children with Cerebral Palsy and Their Adherence to the 24-Hour Activity Guidelines. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2023, 65, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebsen, R.H.; Taylor, N.; Trieschmann, R.B.; Trotter, M.J.; Howard, L.A. An Objective and Standardized Test of Hand Function. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1969, 50, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tofani, M.; Castelli, E.; Sabbadini, M.; Berardi, A.; Murgia, M.; Servadio, A.; Galeoto, G. Examining Reliability and Validity of the Jebsen-Taylor Hand Function Test Among Children with Cerebral Palsy. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2020, 127, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imms, C. Review of the Children’s Assessment of Participation and Enjoyment and the Preferences for Activity of Children. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2008, 28, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakzewski, L.; Boyd, R.; Ziviani, J. Clinimetric Properties of Participation Measures for 5- to 13-Year-Old Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007, 49, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.; Law, M.; King, S.; Hurley, P.; Hanna, S.; Kertoy, M.; Rosenbaum, P.; Young, N. Children’s Assessment of Participation and Enjoyment (CAPE) and Preferences for Activities of Children (PAC); Harcourt Assessment, Inc.: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, J.T.E. Eta Squared and Partial Eta Squared as Measures of Effect Size in Educational Research. Educ. Res. Rev. 2011, 6, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, G. Effect Size Guidelines for Individual and Group Differences in Physiotherapy. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2025, in press. [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokal, B.; Uswatte, G.; Vogtle, L.; Byrom, E.; Barman, J. Everyday Movement and Use of the Arms: Relationship in Children with Hemiparesis Differs from Adults. J. Pediatr. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 8, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyt, C.R.; Brown, S.K.; Sherman, S.K.; Wood-Smith, M.; Van, A.N.; Ortega, M.; Nguyen, A.L.; Lang, C.E.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Dosenbach, N.U. Using Accelerometry for Measurement of Motor Behavior in Children: Relationship of Real-World Movement to Standardized Evaluation. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2020, 96, 103546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocker, M.D.; MacKay-Lyons, M.; McDonnell, E. Forced Use of the Upper Extremity in Cerebral Palsy: A Single-Case Design. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 1997, 51, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitts, P.M.; Posner, M.I. Human Performance; Greenwood Press: Westport, CT, USA, 1979; 162p. [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca, S.C.; Echols, K.; Law, C.R.; Ramey, S.L. Intensive Pediatric Constraint-Induced Therapy for Children with Cerebral Palsy: Randomized, Controlled, Crossover Trial. J. Child Neurol. 2006, 21, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.M.; Charles, J.; Wolf, S.L. Efficacy of Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy on Involved Upper-Extremity Use in Children with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy Is Not Age-Dependent. Pediatrics 2006, 117, e363–e373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, A.M.; Hung, Y.-C.; Brandao, M.; Ferre, C.L.; Kuo, H.-C.; Friel, K.; Petra, E.; Chinnan, A.; Charles, J.R. Bimanual Training and Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy in Children with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy: A Randomized Trial. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2011, 25, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezér, M.; Gresits, O.; Engh, M.A.; Szabó, B.; Molnár, Z.; Hegyi, P.; Terebessy, T. Effectiveness of Video-Game-Based Therapy to Improve Hand Function in Children with Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinos Cisneros, T.V.; Brons, A.; Kröse, B.; Schouten, B.; Ludden, G. Playfulness and New Technologies in Hand Therapy for Children with Cerebral Palsy: Scoping Review. JMIR Ser. Games 2023, 11, e44904. Available online: https://preprints.jmir.org/preprint/44904 (accessed on 2 September 2025). [CrossRef]
- Burahmah, E.; Shanmugam, S.; Stansfield, B. The Accumulation of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour in Children with Cerebral Palsy and Their Typically Developing Peers Aged 6–12 Years. Gait Posture 2024, 113, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamoudi, N.A.; Algabbani, M.F.; Al-Heizan, M.O.; Alhusaini, A.A. Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior Among Ambulatory Children with Cerebral Palsy Using Accelerometer: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Pediatr. 2024, 12, 1463288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.M.; Forde, C.; Hussey, J.M.; Gormley, J. Comparison of Patterns of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior Between Children with Cerebral Palsy and Children with Typical Development. Phys. Ther. 2015, 95, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, J.; Balemans, A.C.J.; Noorduyn, S.G.; Gorter, J.W.; Timmons, B.W. Objectively Measured Sedentary Time in Youth with Cerebral Palsy Compared with Age-, Sex-, and Season-Matched Youth Who Are Developing Typically: An Explorative Study. Phys. Ther. 2014, 94, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janzen, L.; Toomey, C.M.; Brunton, L.K.; Condliffe, E.G.; Esau, S.; Kirton, A.; Emery, C.A.; Kuntze, G. Physical Activity Levels and Adiposity in Ambulant Children and Adolescents with Cerebral Palsy Compared with Their Typically Developing Peers. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2023, 35, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staudt, M. Reorganization After Pre- and Perinatal Brain Lesions. J. Anat. 2010, 217, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, A.M.; Bleyenheuft, Y.; Steenbergen, B. Pathophysiology of Impaired Hand Function in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2013, 55, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrechts, C.; Kalkantzi, A.; Decraene, L.; Kleeren, L.; Crotti, M.; Klingels, K.; Ortibus, E.; Feys, H.; Mailleux, L. The Relation Between Bimanual Coordination, Lesion Timing, and Corticospinal Tract Wiring Pattern in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Gait Posture 2023, 106, S110–S111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingol, H.; Fidan, H.; Asena Sel, S.; Burc, E.; Gunel, M.K. Causal Pathways of Potential Factors Affecting Participation Level of Individuals with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Br. J. Occup. Ther. 2024, 87, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palisano, R.J.; Chiarello, L.A.; Orlin, M.; Oeffinger, D.; Polansky, M.; Maggs, J.; Bagley, A.; Gorton, G.; The Children’s Activity and Participation Group. Determinants of Intensity of Participation in Leisure and Recreational Activities by Children with Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2011, 53, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné-Pelletier, L.; Poitras, I.; Roig, M.; Mercier, C. Factors Associated with Upper Extremity Use After Stroke: A Scoping Review of Accelerometry Studies. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2025, 22, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, N.H.; Ng, S.S.M. Contribution of Perceived Upper Limb Function to the Participation and Activity Levels Among Community-Dwelling People with Chronic Stroke. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2025, 49, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vier, C.; Mochizuki, L.; Gomes, R.P.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Demartino, A.M.; Michaelsen, S.M. Bilateral Capacity Is Related to Bilateral Upper Limb Use After Stroke: A Study by Behavioral Maps, Accelerometers and Perceived Amount of Use. Disabil. Rehabil. 2022, 44, 2258–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banjai, R.M.; Freitas, S.M.S.F.D.; Silva, F.P.D.; Alouche, S.R. Individuals’ Perception About Upper Limb Influence on Participation After Stroke: An Observational Study. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2018, 25, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.E.; Eng, J.J. Paretic Upper-Limb Strength Best Explains Arm Activity in People with Stroke. Phys. Ther. 2007, 87, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, J.W. Motor Learning: Its Relevance to Stroke Recovery and Neurorehabilitation. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2006, 19, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, G.; Law, M.; King, S.; Rosenbaum, P.; Kertoy, M.K.; Young, N.L. A Conceptual Model of the Factors Affecting the Recreation and Leisure Participation of Children with Disabilities. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 2003, 23, 63–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodman, P.; Riazi, A.; Pereira, C.; Jones, F. Social Participation Post-Stroke: A Meta-Ethnographic Review of the Experiences and Views of Community-Dwelling Stroke Survivors. Disabil. Rehabil. 2014, 36, 2031–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, G.; Kalkantzi, A.; Mailleux, L.; Palomo-Carrión, R.; Feys, H.; Boyd, R.N.; Beani, E.; Cianchetti, M.; Filogna, S.; Prencipe, G.; et al. A Holistic Approach Towards Evaluating Upper Limb Function in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy: A Narrative Review of Clinical Tools and Promising Technologies for Comprehensive Assessment. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, J.; Liu, X.; Jacobson, J.S.; Rundle, A. New Insights into Activity Patterns in Children, Found Using Functional Data Analyses. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braito, I.; Maselli, M.; Sgandurra, G.; Inguaggiato, E.; Beani, E.; Cecchi, F.; Cioni, G.; Boyd, R. Assessment of Upper Limb Use in Children with Typical Development and Neurodevelopmental Disorders by Inertial Sensors: A Systematic Review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heye, A.L.; Kersting, C.; Kneer, M.; Barzel, A. Suitability of Accelerometry as an Objective Measure for Upper Extremity Use in Stroke Patients. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.I.; Jung, H.T.; Park, J.; Jeong, J.; Ryu, T.; Kim, Y.; dos Santos, V.S.; Miranda, J.G.V.; Daneault, J.-F. Towards the Ambulatory Assessment of Movement Quality in Stroke Survivors Using a Wrist-Worn Inertial Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; IEEE: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2018; pp. 2825–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashakori, A.; Jiang, Z.; Servati, A.; Soltanian, S.; Narayana, H.; Le, K.; Nakayama, C.; Yang, C.-L.; Wang, Z.J.; Eng, J.J.; et al. Capturing Complex Hand Movements and Object Interactions Using Machine Learning-Powered Stretchable Smart Textile Gloves. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2024, 6, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demers, M.; Cain, A.; Bishop, L.; Gunby, T.; Rowe, J.B.; Zondervan, D.K.; Winstein, C.J. Understanding Stroke Survivors’ Preferences Regarding Wearable Sensor Feedback on Functional Movement: A Mixed-Methods Study. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2023, 20, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
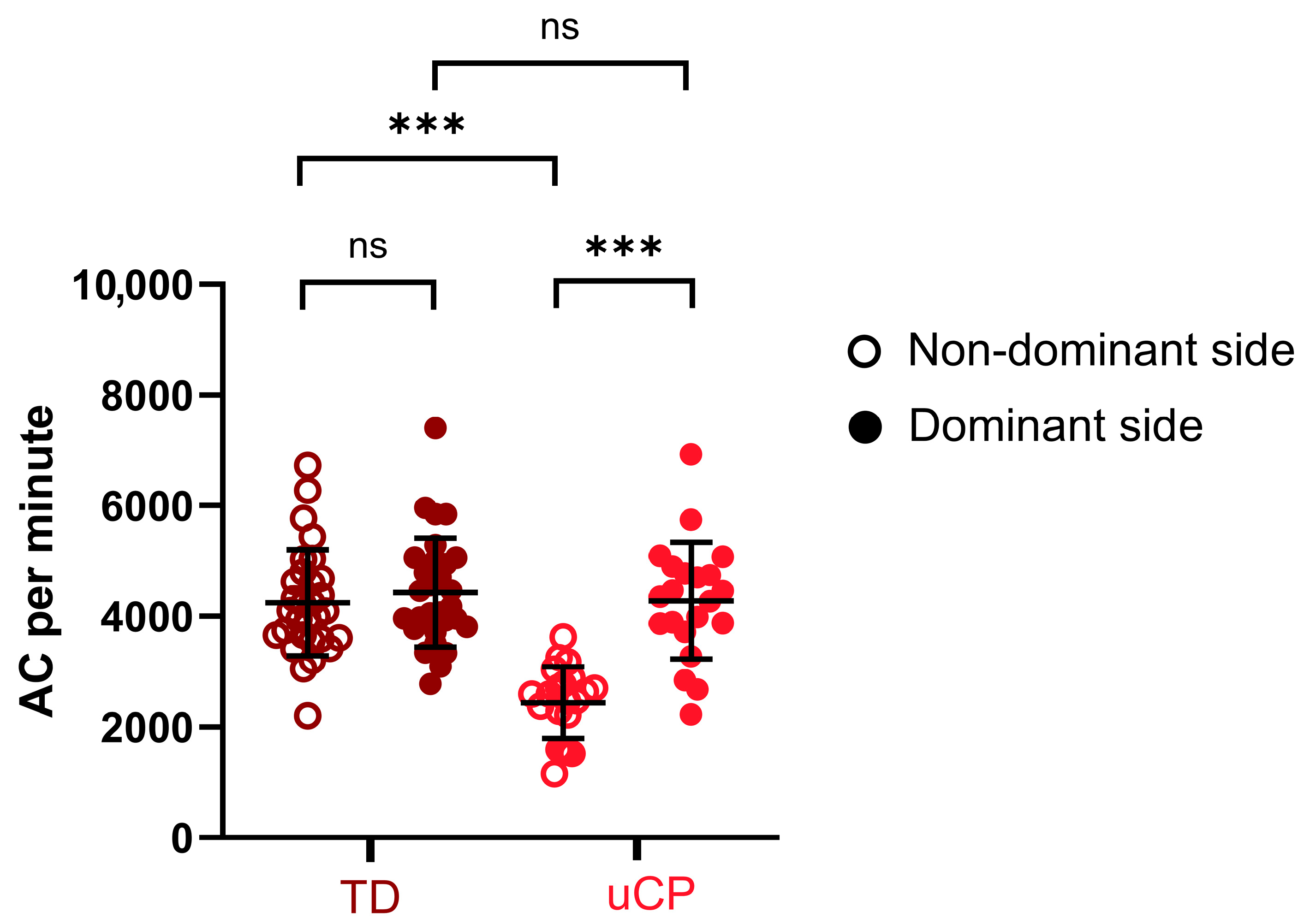
| Subject | Age (Years) | Sex | Affected Side | MACS Level | Device Used | Mean Wear Time (Hours/Day) | AC per Minute | JTHFT Scores (s) | CAPE Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ND | D | ND | D | ||||||||
| S1 | 11 | F | R | 2 | ActiGraph | 11.58 | 1596 | 4274 | 215 | 31 | 2.8 |
| S2 | 14 | M | R | 2 | ActiGraph | 13.97 | 1158 | 2230 | 46 | 26 | 1.6 |
| S3 | 11 | F | L | 3 | ActiGraph | 13.18 | 3254 | 6929 | 549 | 36 | 2.4 |
| S4 | 14 | M | L | 2 | ActiGraph | 7.10 | 2283 | 4351 | 83 | 34 | 2.2 |
| S5 | 12 | M | R | 3 | ActiGraph | 11.73 | 2769 | 5743 | 510 | 26 | 1.7 |
| S6 | 9 | F | L | 2 | ActiGraph | 10.88 | 2641 | 4902 | 385 | 33 | 2 |
| S7 | 9 | M | R | 1 | ActiGraph | 12.09 | 2381 | 2676 | 47 | 44 | 1.9 |
| S8 | 13 | M | L | 1 | ActiGraph | 12.22 | 2221 | 2848 | 37 | 24 | 2.3 |
| S9 | 11 | M | L | 2 | ActiGraph | 10.22 | 2598 | 3883 | 96 | 32 | 2.7 |
| S10 | 7 | F | L | 3 | ActiGraph | 9.64 | 2886 | 5098 | 273 | 42 | 3.2 |
| S11 | 9 | F | R | 3 | ActiGraph | 10.90 | 2719 | 5077 | 528 | 43 | 2.7 |
| S12 | 13 | M | L | 1 | ActiGraph | 10.66 | 3047 | 3725 | 37 | 32 | 2.4 |
| S13 | 10 | F | L | 1 | ActiGraph | 12.56 | 2594 | 3869 | 87 | 45 | 2.6 |
| S14 | 11 | F | R | 3 | ActiGraph | 10.10 | 1522 | 3278 | 576 | 33 | 2.9 |
| S15 | 8 | M | R | 3 | Axivity | 13.61 | 2479 | 4744 | 590 | 38 | 3.3 |
| S16 | 12 | F | L | 1 | Axivity | 7.17 | 2472 | 4471 | 92 | 42 | 3.4 |
| S17 | 7 | M | R | 1 | Axivity | 12.43 | 2702 | 4775 | 125 | 41 | 3.3 |
| S18 | 15 | M | L | 3 | ActiGraph | 11.80 | 1534 | 3899 | 604 | 166 | 1.8 |
| S19 | 13 | M | R | 2 | ActiGraph | 10.17 | 3181 | 3986 | 318 | 30 | 2.1 |
| S20 | 14 | F | R | 3 | Axivity | 11.15 | 1582 | 4702 | 720 | 35 | 1.3 |
| S21 | 10 | F | L | 3 | Axivity | 11.62 | 3633 | 4466 | 540 | 102 | 3.7 |
| Mean (SD)/% | 11.1 (2.4) | F: 47.6% | L: 52.38% | I: 28.6%; II: 28.6%; III: 42.9% | Axivity: 23.8% | 11.18 (1.77) | 2441 (647) | 4282 (1055) | 308 (238) | 45 (32) | 2.5 (0.7) |
| Correlation Tested | Side | r | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance (AC/min) ↔ Capacity (JTHFT) | ND | 0.058 | 0.801 |
| D | 0.198 | 0.39 | |
| Performance (AC/min) ↔ Participation intensity (CAPE) | ND | 0.315 | 0.164 |
| D | 0.211 | 0.36 | |
| Capacity (JTHFT) ↔ Participation intensity (CAPE) | ND | 0.051 | 0.826 |
| D | 0.349 | 0.121 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abid, M.; Poitras, I.; Gagné-Pelletier, L.; Rigourd, C.; Sèbiyo Batcho, C.; Mercier, C. Upper Limb Capacity, Performance, and Leisure Participation in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Sensors 2025, 25, 7120. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237120
Abid M, Poitras I, Gagné-Pelletier L, Rigourd C, Sèbiyo Batcho C, Mercier C. Upper Limb Capacity, Performance, and Leisure Participation in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Sensors. 2025; 25(23):7120. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237120
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbid, Manel, Isabelle Poitras, Léandre Gagné-Pelletier, Carole Rigourd, Charles Sèbiyo Batcho, and Catherine Mercier. 2025. "Upper Limb Capacity, Performance, and Leisure Participation in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy" Sensors 25, no. 23: 7120. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237120
APA StyleAbid, M., Poitras, I., Gagné-Pelletier, L., Rigourd, C., Sèbiyo Batcho, C., & Mercier, C. (2025). Upper Limb Capacity, Performance, and Leisure Participation in Children with Unilateral Cerebral Palsy. Sensors, 25(23), 7120. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25237120









