Early Detection of Dysphagia Signs in Parkinson’s Disease: An Artificial Intelligence-Based Approach Using Non-Invasive Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
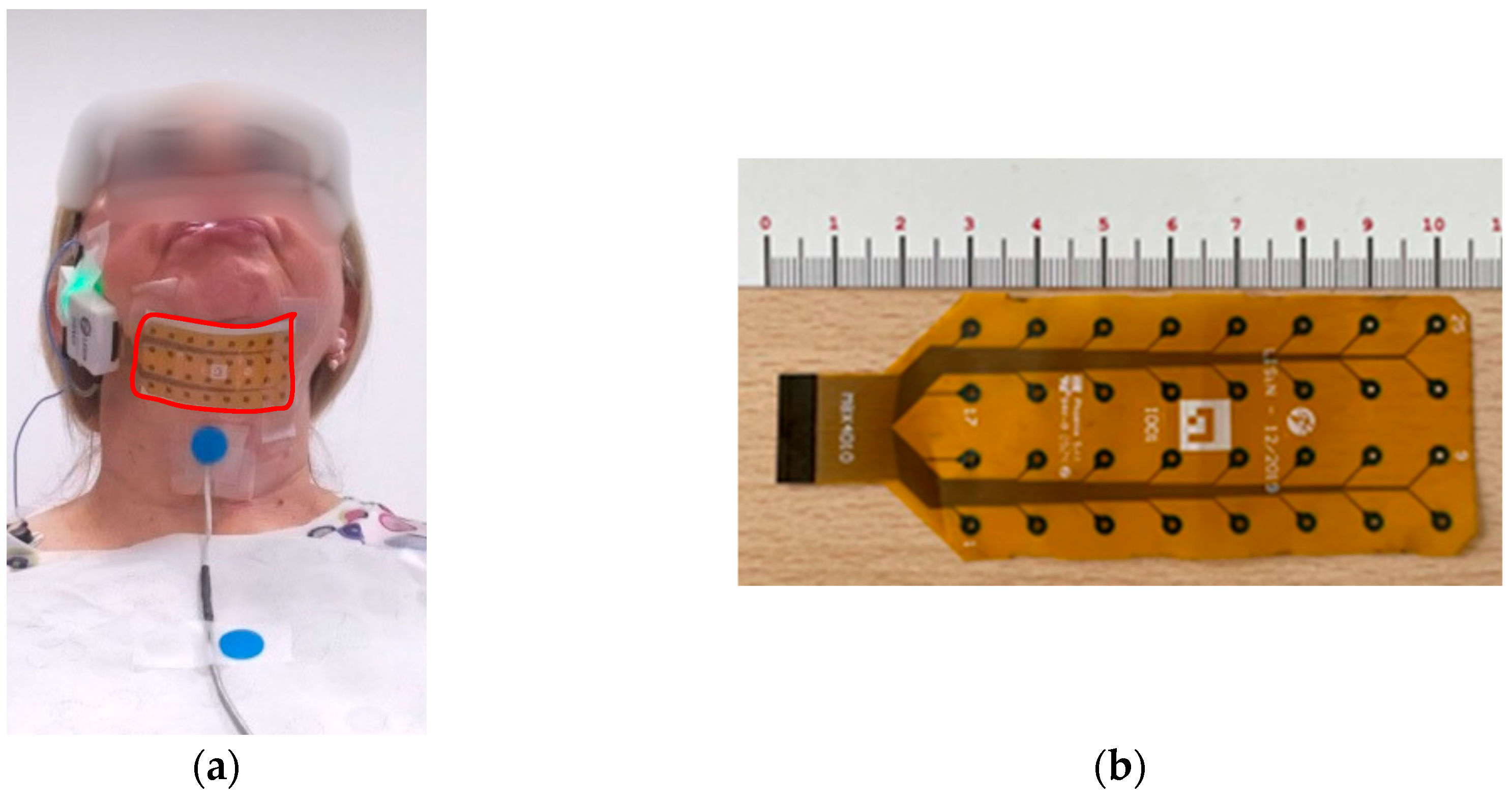
2.1. Set-Up
2.2. Participants
2.3. Experimental Protocol
2.4. Identification of the Swallowing Acts
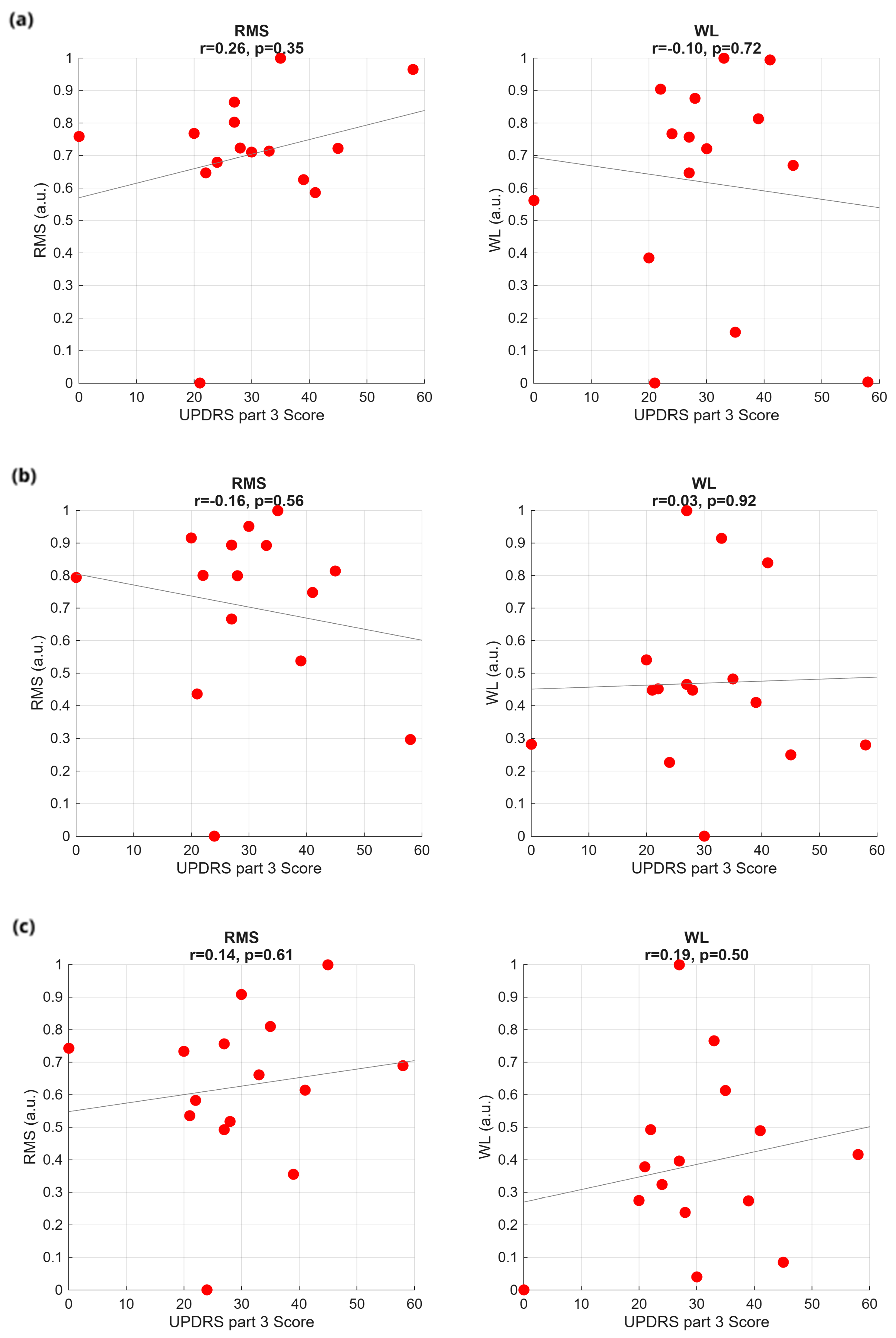
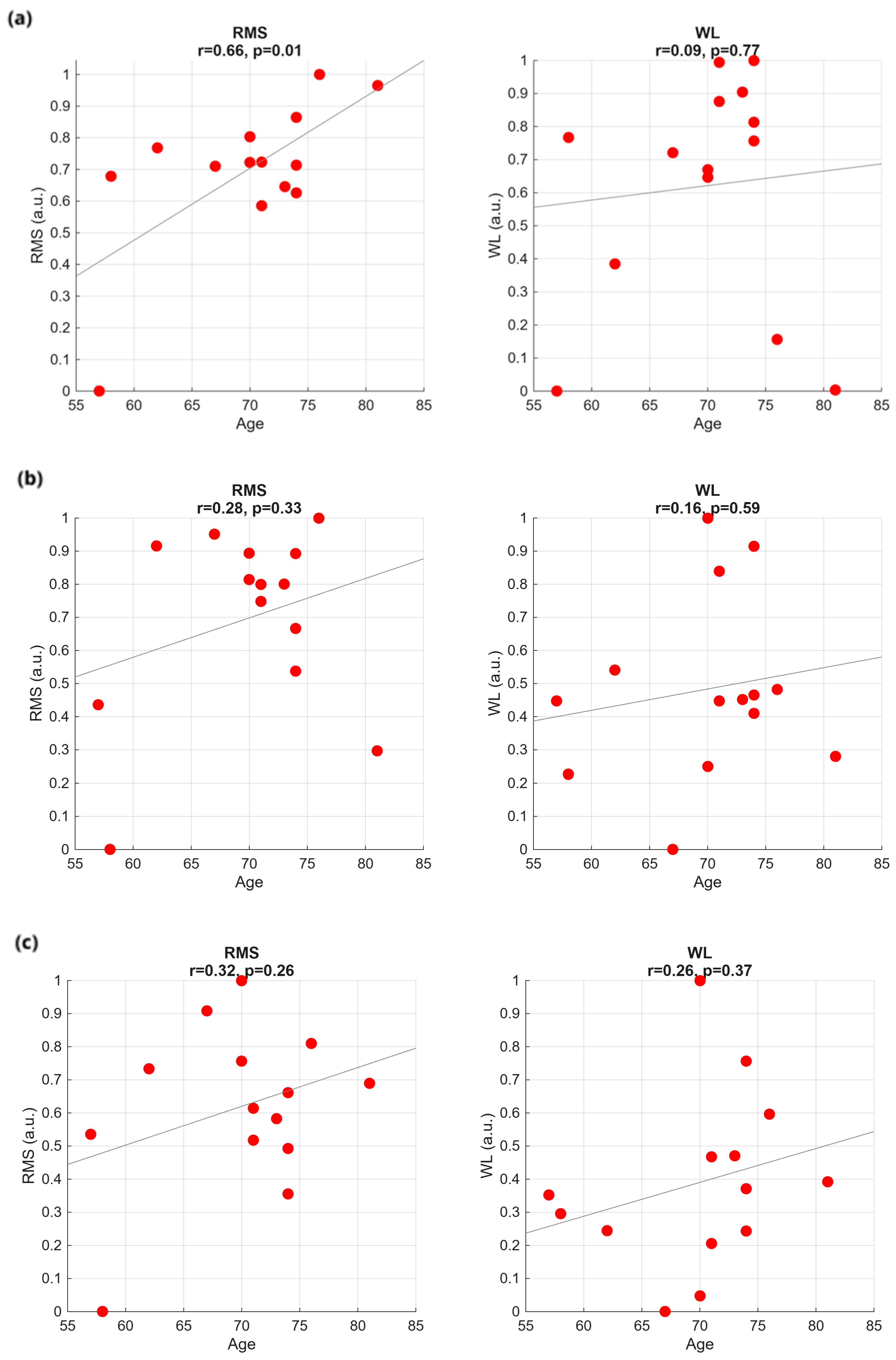
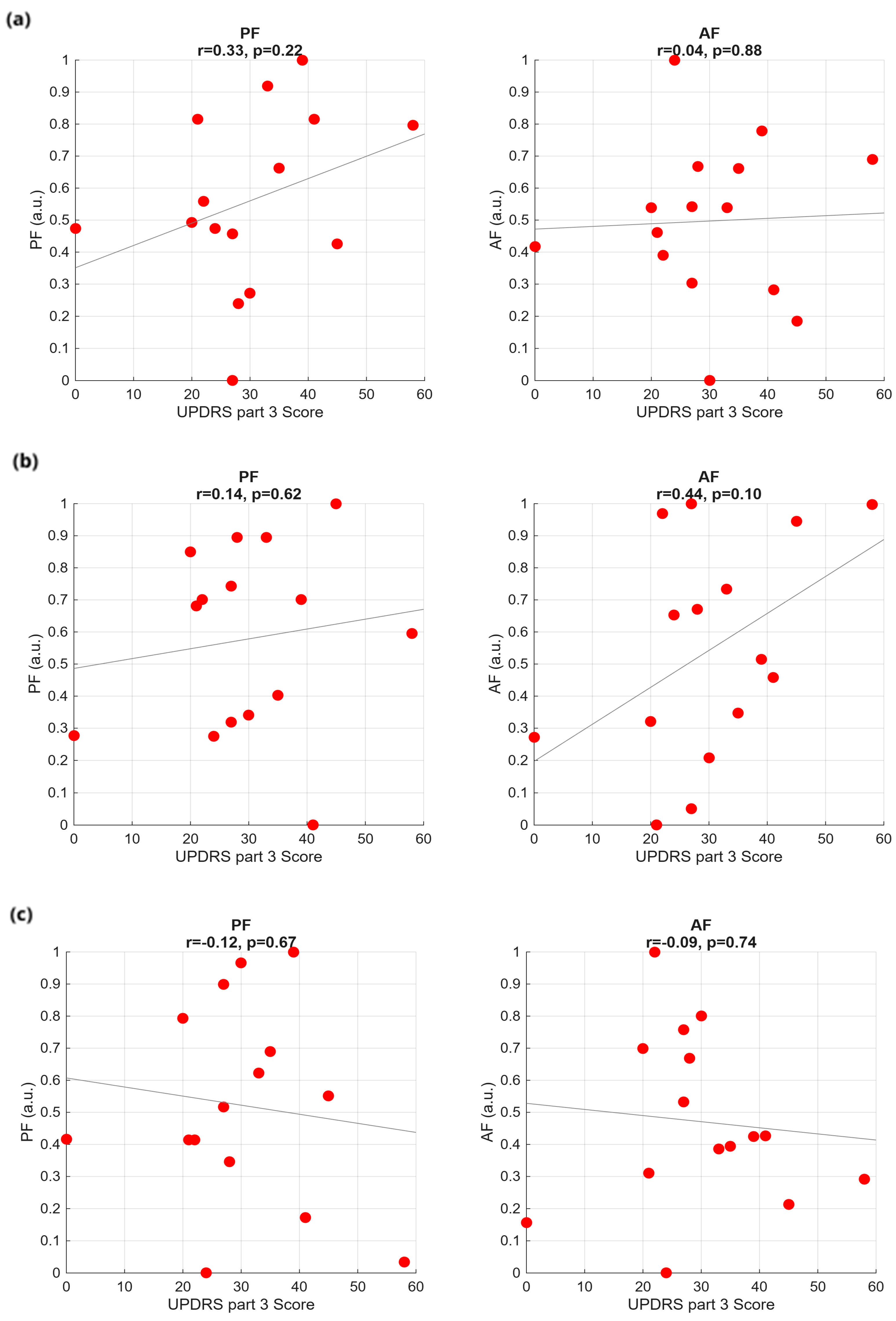
2.5. Feature Extraction and Correlations with PD Scores
2.6. Principal Component Analysis
2.7. Classification
3. Results
3.1. Time Analysis
3.2. Frequency Analysis
3.3. Principal Component Analysis

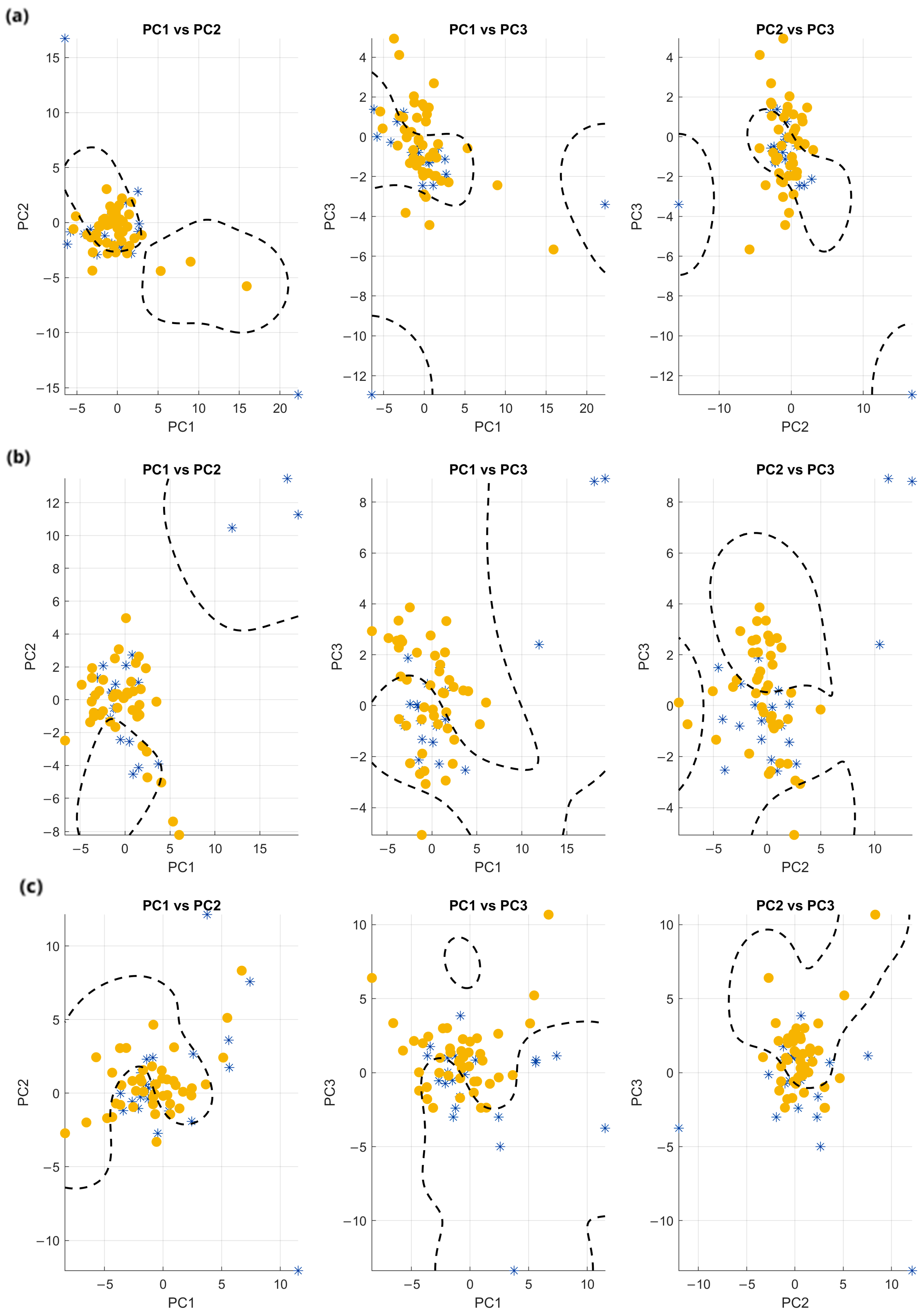
3.4. Classification
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Current Methodology and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IEIIT | Institute of Electronics, Computer and Telecommunication Engineering |
| CNR | Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche |
| HD-sEMG | High-Density surface Electromyography |
| PD | Parkinson’s Disease |
| VFSS | Videofluoroscopic swallow study |
| FEES | Fiberoptic endoscopy evaluation of swallowing |
| IMU | Inertial measurement units |
| LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis |
| HC | Healthy Controls |
| MDS | Movement Disorder Society |
| MoCA | Montreal Cognitive Assessment |
| MDS-UPDRS | Movement Disorder Society-Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale |
| FAB | Frontal Assessment Battery |
| SDQ | Swallowing Disturbance Questionnaire |
| CET | Comitato Etico Territoriale |
| LEDD | Levodopa Equivalent Daily Dose |
| WT | Water Task |
| GT | Gelled water Task |
| ST | Solid bolus Task |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| MS | Mastication start |
| ME | Mastication end |
| SS | Swallowing start |
| SE | Swallowing end |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| WL | Waveform length |
| AS | Asymmetry index |
| DOS | Degree of Symmetry |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
| PF | Peak frequency |
| AF | Average frequency |
| TP | Total power |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PC1 | First principal component |
| PC2 | Second principal component |
| PC3 | Third principal component |
| mRMR | Minimum redundancy–maximum relevance |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| RBF | Radial basis function |
References
- Jean, A. Brain Stem Control of Swallowing: Neuronal Network and Cellular Mechanisms. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 929–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, E.T.; Jones, B. Anatomical and Physiological Overview. In Normal and Abnormal Swallowing: Imaging in Diagnosis and Therapy; Jones, B., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 11–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leira, J.; Maseda, A.; Lorenzo-López, L.; Cibeira, N.; López-López, R.; Lodeiro, L.; Millán-Calenti, J.C. Dysphagia and its association with other health-related risk factors in institutionalized older people: A systematic review. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2023, 110, 104991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvan, A.; Devergnas, A.; Wichmann, T. Alterations in neuronal activity in basal ganglia-thalamocortical circuits in the parkinsonian state. Front. Neuroanat. 2015, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rüb, U.; de Vos, R.A.I.; Steur, E.N.H.J.; Braak, E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttrup, I.; Warnecke, T. Dysphagia in Parkinson’s Disease. Dysphagia 2016, 31, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuh, J.-L.; Lee, R.-C.; Wang, S.-J.; Lin, C.-H.; Wang, P.-N.; Chiang, J.-H.; Liu, H.-C. Swallowing difficulty in Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 1997, 99, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalf, J.G.; de Swart, B.J.M.; Bloem, B.R.; Munneke, M. Prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis. Park. Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, M.; Ferreira, J.J. Late-stage Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 8, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmore, S.E. Evaluation of oropharyngeal dysphagia: Which diagnostic tool is superior? Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2003, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labeit, B.; Michou, E.; Hamdy, S.; Trapl-Grundschober, M.; Suntrup-Krueger, S.; Muhle, P.; Bath, P.M.; Dziewas, R. The assessment of dysphagia after stroke: State of the art and future directions. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, P.M.; Luschei, E.S.; Jaffe, D.; McCulloch, T.M. Contributions of Individual Muscles to the Submental Surface Electromyogram During Swallowing. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1999, 42, 1378–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepp, C.E. Surface Electromyography for Speech and Swallowing Systems: Measurement, Analysis, and Interpretation. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2012, 55, 1232–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merletti, R.; Muceli, S. Tutorial. Surface EMG detection in space and time: Best practices. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2019, 49, 102363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldan-Vasco, S.; Orozco-Duque, A.; Orozco-Arroyave, J. Swallowing disorders analysis using surface EMG biomarkers and classification models. Digit. Signal Process 2022, 133, 103815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malandraki, G.A. Advances for Dysphagia in the Digital Age: Integrative Imaging and Wearable Technologies. Folia Phoniatr. Logop. 2023, 75, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, K.; Chu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J. Advancements and Challenges in Non-Invasive Sensor Technologies for Swallowing Assessment: A Review. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Patiño, L.V.; Roldan-Vasco, S.; Suarez-Escudero, J.C.; Orozco-Duque, A.; Perez-Giraldo, E. sEMG as complementary tool for VFSS: A synchronized study in patients with neurogenic oropharyngeal dysphagia. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2024, 78, 102913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Mao, L.; Lin, K.; Huang, C.; Su, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, D.; Song, J.; Chen, Z. Accurate and Noninvasive Dysphagia Assessment via a Soft High-Density sEMG Electrode Array Conformal to the Submental and Infrahyoid Muscles. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2500472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://recbioengineering.com/ (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Cerone, G.L.; Botter, A.; Gazzoni, M. A Modular, Smart, and Wearable System for High Density sEMG Detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 3371–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giangrande, A.; Viganò, M.; Carbonaro, M.; Gilardone, M.; Tropea, P.; Cerone, G.L.; Corbo, M.; Gazzoni, M.; Botter, A. Swallowing Onset Detection: Comparison of Endoscopy- and Accelerometry-Based Estimations. In Proceedings of the 8th European Medical and Biological Engineering Conference, Portorož, Slovenia, 29 November–3 December 2020; Jarm, T., Cvetkoska, A., Mahnič-Kalamiza, S., Miklavcic, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1053–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Cerone, G.L.; Giangrande, A.; Ghislieri, M.; Gazzoni, M.; Piitulainen, H.; Botter, A. Design and Validation of a Wireless Body Sensor Network for Integrated EEG and HD-sEMG Acquisitions. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoehn, M.M.; Yahr, M.D. Parkinsonism. Neurology 1967, 17, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, N.; Leach, L.; Murphy, K.J. A re-examination of Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) cutoff scores. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2018, 33, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, C.G.; Tilley, B.C.; Shaftman, S.R.; Stebbins, G.T.; Fahn, S.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Poewe, W.; Sampaio, C.; Stern, M.B.; Dodel, R.; et al. Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): Scale presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 2129–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, B.; Slachevsky, A.; Litvan, I.; Pillon, B. The FAB. Neurology 2000, 55, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.T.; Manor, Y. Swallowing disturbance questionnaire for detecting dysphagia. Laryngoscope 2011, 121, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitar, E.; ElSayyadi, F.; Diab, A. Duchenne muscular dystrophy detection using EMG analysis and machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 Seventh International Conference on Advances in Biomedical Engineering (ICABME), Beirut, Libanon, 12–13 October 2023; pp. 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himuro, K.; Uzawa, A.; Kawaguchi, N.; Kanai, T.; Isono, S.; Kuwabara, S. Quantitative Assessment of Dysphagia in Myasthenia Gravis. Intern. Med. 2025, 64, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.K.Y.; Fong, R.; Zhu, M.; Li, G.; Chan, J.Y.K.; Stewart, M.; Ku, P.K.M.; Lee, K.Y.S.; Tong, M.C.F. High-Density Surface Electromyography for Swallowing Evaluation in Post-Radiation Dysphagia. Laryngoscope 2023, 133, 2920–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascherio, A.; Schwarzschild, M.A. The epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease: Risk factors and prevention. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldan-Vasco, S.; Orozco-Duque, A.; Orozco-Arroyave, J.R. Dysphagia screening with sEMG, accelerometry and speech: Multimodal machine and deep learning approaches. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2025, 100, 107030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldan-Vasco, S.; Orozco-Duque, A.; Suarez-Escudero, J.C.; Orozco-Arroyave, J.R. Machine learning based analysis of speech dimensions in functional oropharyngeal dysphagia. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 208, 106248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Patient ID | Gender | Age (Years) | Disease Duration (Years) | MDS-UPDRS Part III | MDS-UPDRS Axial Score | SDQ | LEDD (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT01 | M | 73 | 6 | 22 | 8 | 5 | 975 |
| PT02 | M | 76 | 11 | 35 | 11 | 7 | 712 |
| PT03 | F | 62 | 4 | 20 | 9 | 6 | 750 |
| PT04 | M | 77 | 10 | 54 | 13 | 10 | 350 |
| PT05 | M | 71 | 21 | 28 | 9 | 3 | 1219 |
| PT06 | M | 58 | 5 | 24 | 7 | 3 | 600 |
| PT07 | F | 74 | 14 | 39 | 16 | 6 | 1225 |
| PT08 | F | 67 | 14 | 30 | 12 | 2 | 1092 |
| PR02 | F | 74 | 3 | 27 | 4 | 13 | 300 |
| PR03 | M | 81 | 23 | 58 | 20 | 15 | 655 |
| PR04 | M | 70 | 15 | 45 | 16 | 9 | 1468 |
| PR05 | M | 57 | 7 | 21 | 5 | 3 | 832 |
| PR06 | M | 71 | 8 | 41 | 11 | 3 | 900 |
| PR07 | M | 74 | 16 | 33 | 11 | 9 | 1200 |
| PR08 | M | 58 | 13 | 28 | 16 | 4 | 1610 |
| Patient ID | Gender | Age (Years) | SDQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| HC01 | F | 65 | 1 |
| HC02 | M | 65 | 2 |
| HC03 | F | 62 | 6 |
| HC04 | M | 65 | 4 |
| HC05 | M | 74 | 1 |
| HC06 | F | 68 | 2 |
| HC07 | F | 60 | 3 |
| N° | Features |
|---|---|
| 1 | Slope Sign Changes |
| 2 | Hjorth Complexity |
| 3 | Variance |
| 4 | Multiplied Power and Peak Amplitude |
| 5 | Singular Value Decomposition Entropy |
| 6 | Zero Crossings |
| 7 | Ratio of Mean Frequency to Median Frequency |
| 8 | Variance of Central Frequency |
| 9 | Median Frequency |
| 10 | Spectral Concentration Measure |
| 11 | Standard Deviation |
| 12 | Difference in Moments (4th–2nd) |
| 13 | Instantaneous Median Frequency |
| 14 | Mean Power Ratio |
| 15 | Mean Absolute Value |
| Task | PCA Plane | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 1–2 | 74.24 | 93.75 | 66.67 | 77.92 |
| WT | 1–3 | 77.27 | 89.47 | 75.56 | 81.93 |
| WT | 2–3 | 72.73 | 96.55 | 62.22 | 75.68 |
| GT | 1–2 | 61.54 | 91.30 | 47.73 | 62.69 |
| GT | 1–3 | 81.54 | 90.00 | 81.82 | 85.71 |
| GT | 2–3 | 73.85 | 90.91 | 68.18 | 77.92 |
| ST | 1–2 | 83.33 | 85.42 | 91.11 | 88.17 |
| ST | 1–3 | 84.85 | 90.70 | 86.67 | 88.64 |
| ST | 2–3 | 68.18 | 81.58 | 68.89 | 74.70 |
| Metrics | Best Value (%) Seed (151) | Average on 500 Trials (%) | STD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 83.3 | 67.56 | 5.47 |
| Precision | 79.0 | 66.22 | 5.36 |
| Recall | 90.7 | 71.77 | 8.19 |
| F1-score | 84.5 | 68.68 | 5.62 |
| Cohen’s kappa | 0.67 | 0.35 | 0.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gazzanti Pugliese di Cotrone, M.A.; Akhtar, N.F.; Patera, M.; Gallo, S.; Mosca, U.; Ghislieri, M.; Ferraris, C.; Suppa, A.; Artusi, C.A.; Zampogna, A.; et al. Early Detection of Dysphagia Signs in Parkinson’s Disease: An Artificial Intelligence-Based Approach Using Non-Invasive Sensors. Sensors 2025, 25, 6834. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226834
Gazzanti Pugliese di Cotrone MA, Akhtar NF, Patera M, Gallo S, Mosca U, Ghislieri M, Ferraris C, Suppa A, Artusi CA, Zampogna A, et al. Early Detection of Dysphagia Signs in Parkinson’s Disease: An Artificial Intelligence-Based Approach Using Non-Invasive Sensors. Sensors. 2025; 25(22):6834. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226834
Chicago/Turabian StyleGazzanti Pugliese di Cotrone, Michele Antonio, Nidà Farooq Akhtar, Martina Patera, Silvia Gallo, Umberto Mosca, Marco Ghislieri, Claudia Ferraris, Antonio Suppa, Carlo Alberto Artusi, Alessandro Zampogna, and et al. 2025. "Early Detection of Dysphagia Signs in Parkinson’s Disease: An Artificial Intelligence-Based Approach Using Non-Invasive Sensors" Sensors 25, no. 22: 6834. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226834
APA StyleGazzanti Pugliese di Cotrone, M. A., Akhtar, N. F., Patera, M., Gallo, S., Mosca, U., Ghislieri, M., Ferraris, C., Suppa, A., Artusi, C. A., Zampogna, A., Amprimo, G., Imbalzano, G., Cerfoglio, S., Cimolin, V., Borzì, L., Olmo, G., & Irrera, F. (2025). Early Detection of Dysphagia Signs in Parkinson’s Disease: An Artificial Intelligence-Based Approach Using Non-Invasive Sensors. Sensors, 25(22), 6834. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25226834
















