ACGAN-Based Multi-Target Elevation Estimation with Vector Sensor Arrays in Low-SNR Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
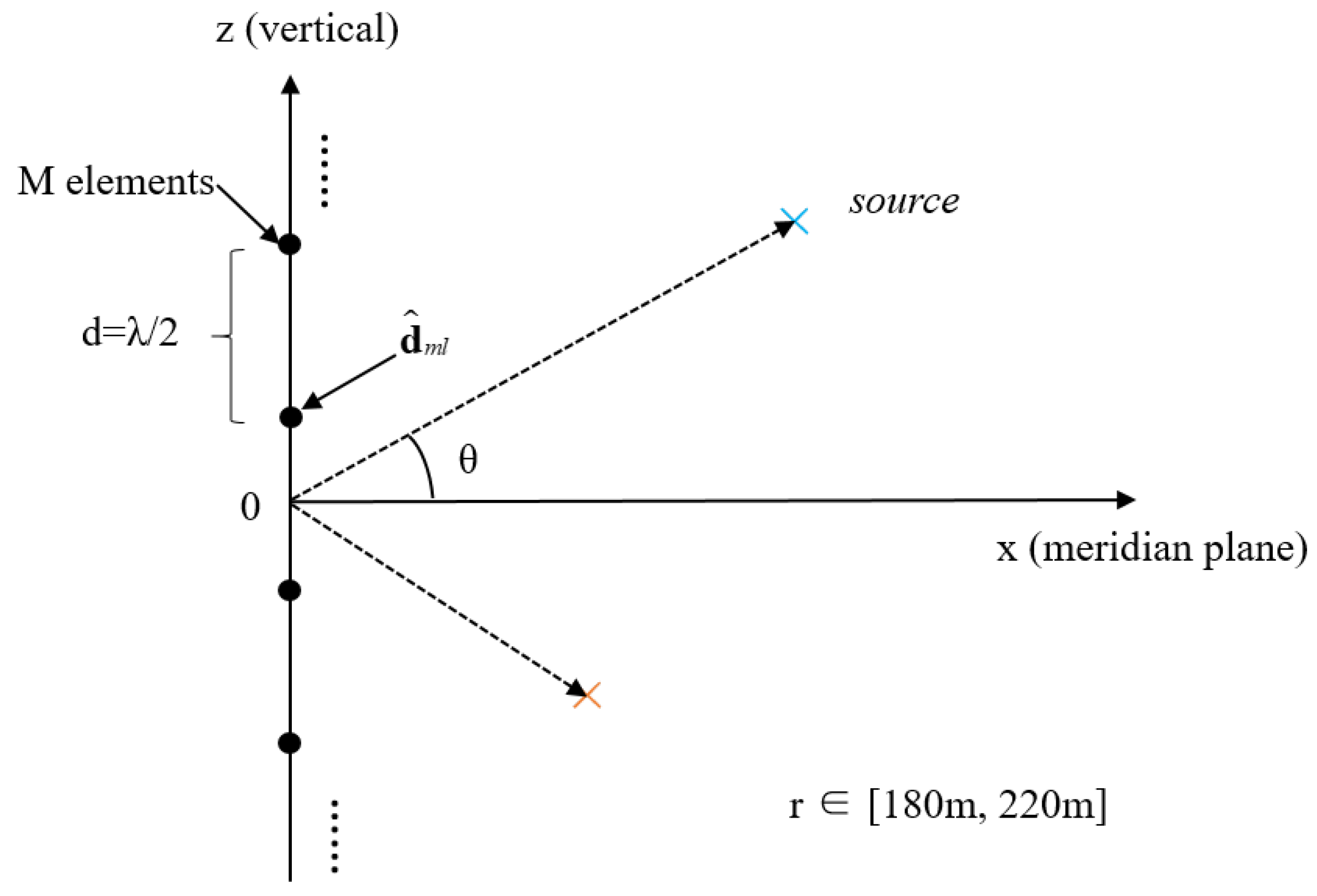
2. Signal Model
3. Network Model
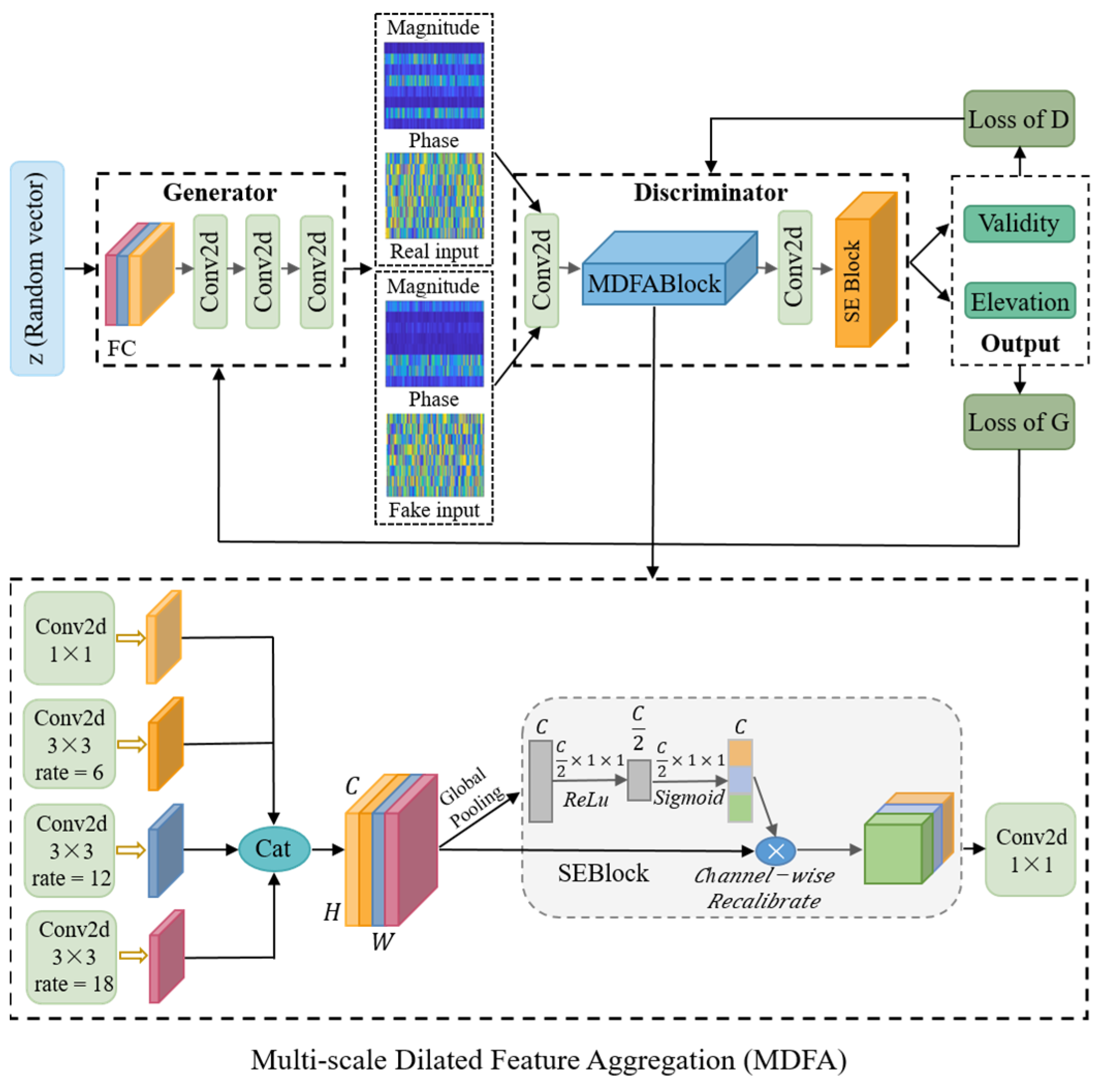
3.1. Overall Network Architecture Design
3.2. The Architecture of the Generator
3.3. The Architecture of the Discriminator
3.3.1. Summary of the Channel Attention Mechanism
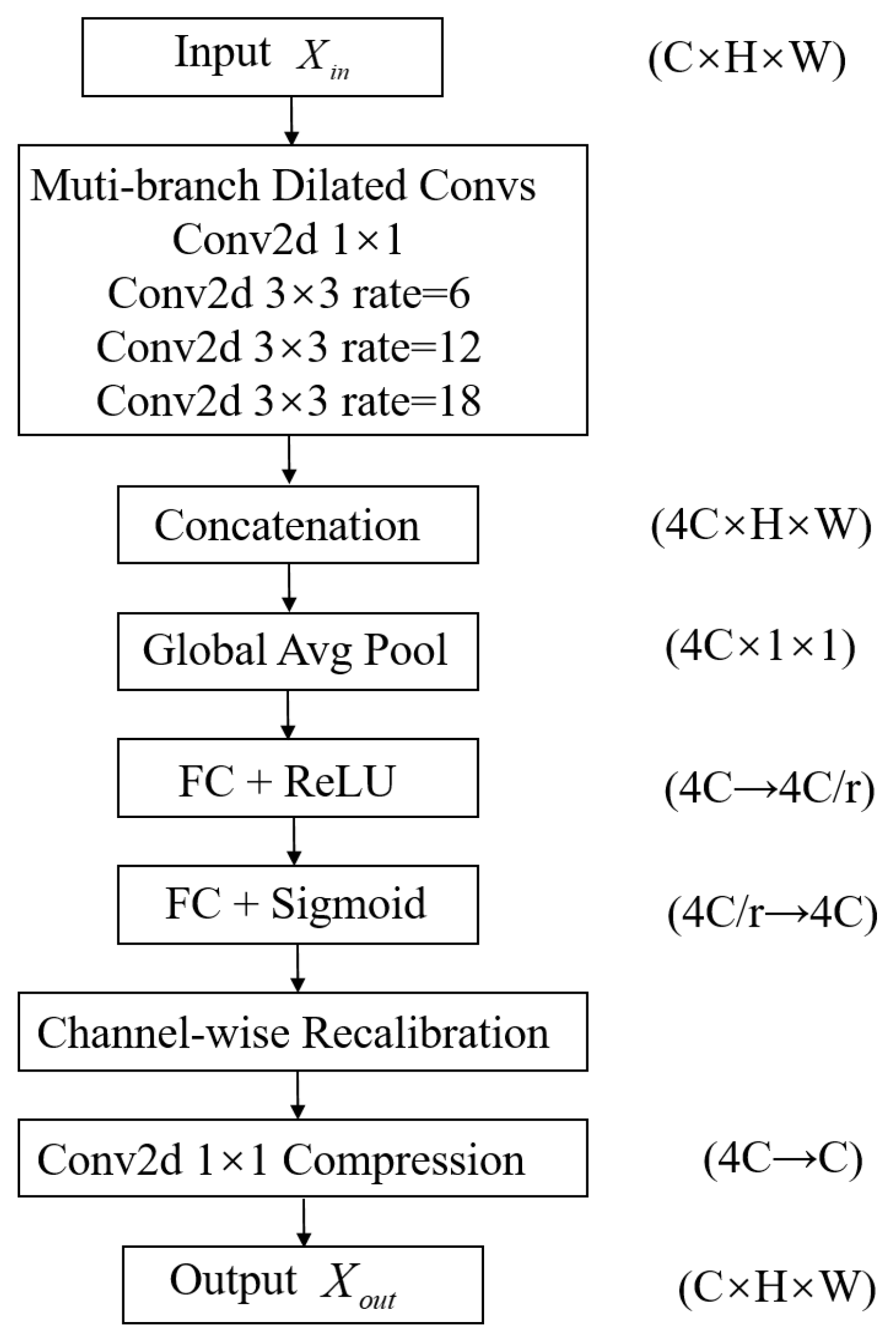
3.3.2. Structure and Principle of Multi-Scale Dilated Feature Aggregation
3.4. Loss Function Design
- (1)
- Kullback–Leibler (KL) Divergence Loss
- (2)
- Focal Loss
- (3)
- L1 Distribution Loss
- (4)
- Confidence Penalty
- (5)
- Permutation Invariant Binary Cross-Entropy (PIT-BCE)
- (6)
- Feature Consistency Loss
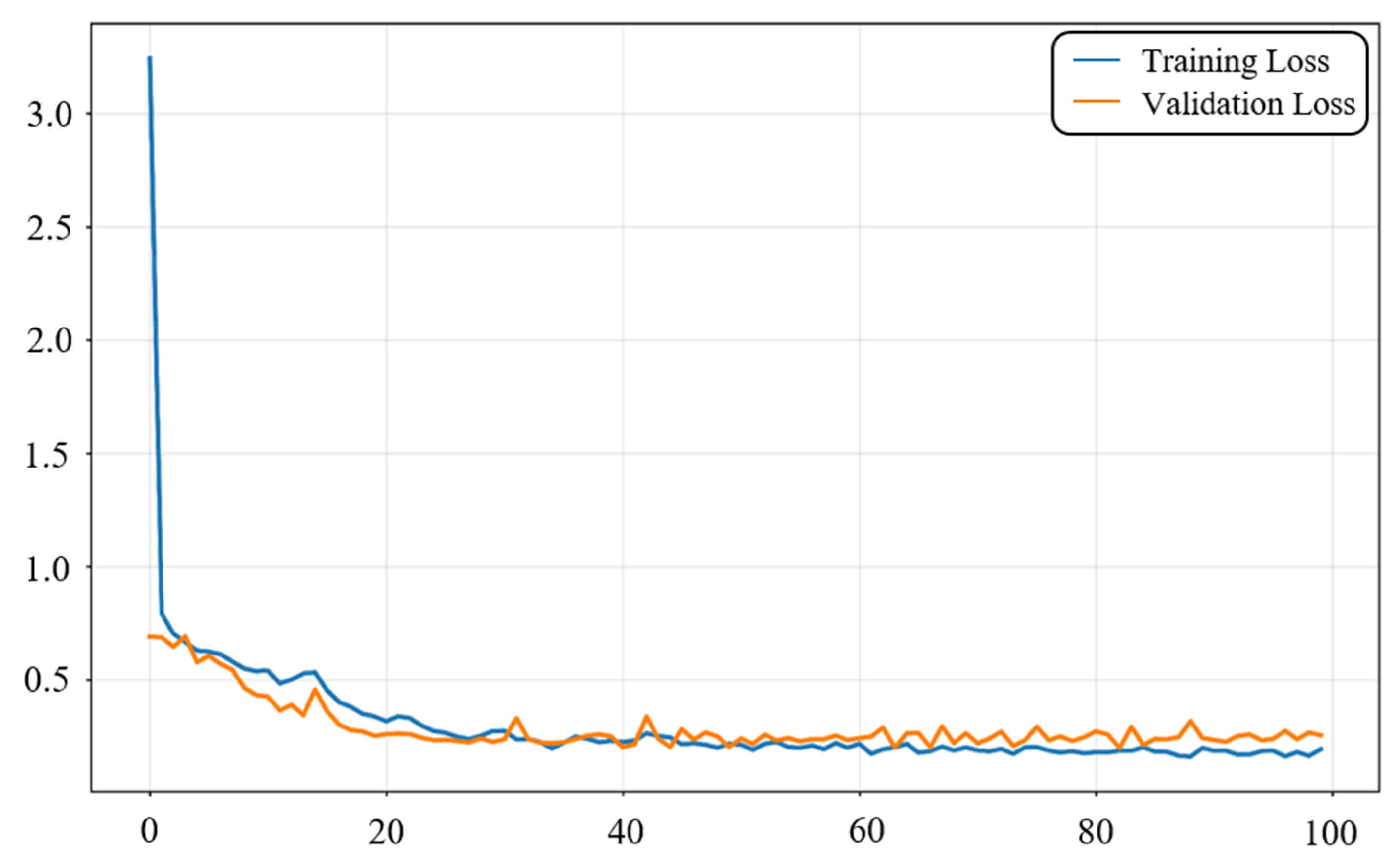
3.5. ACGAN Training
4. Experimental Results
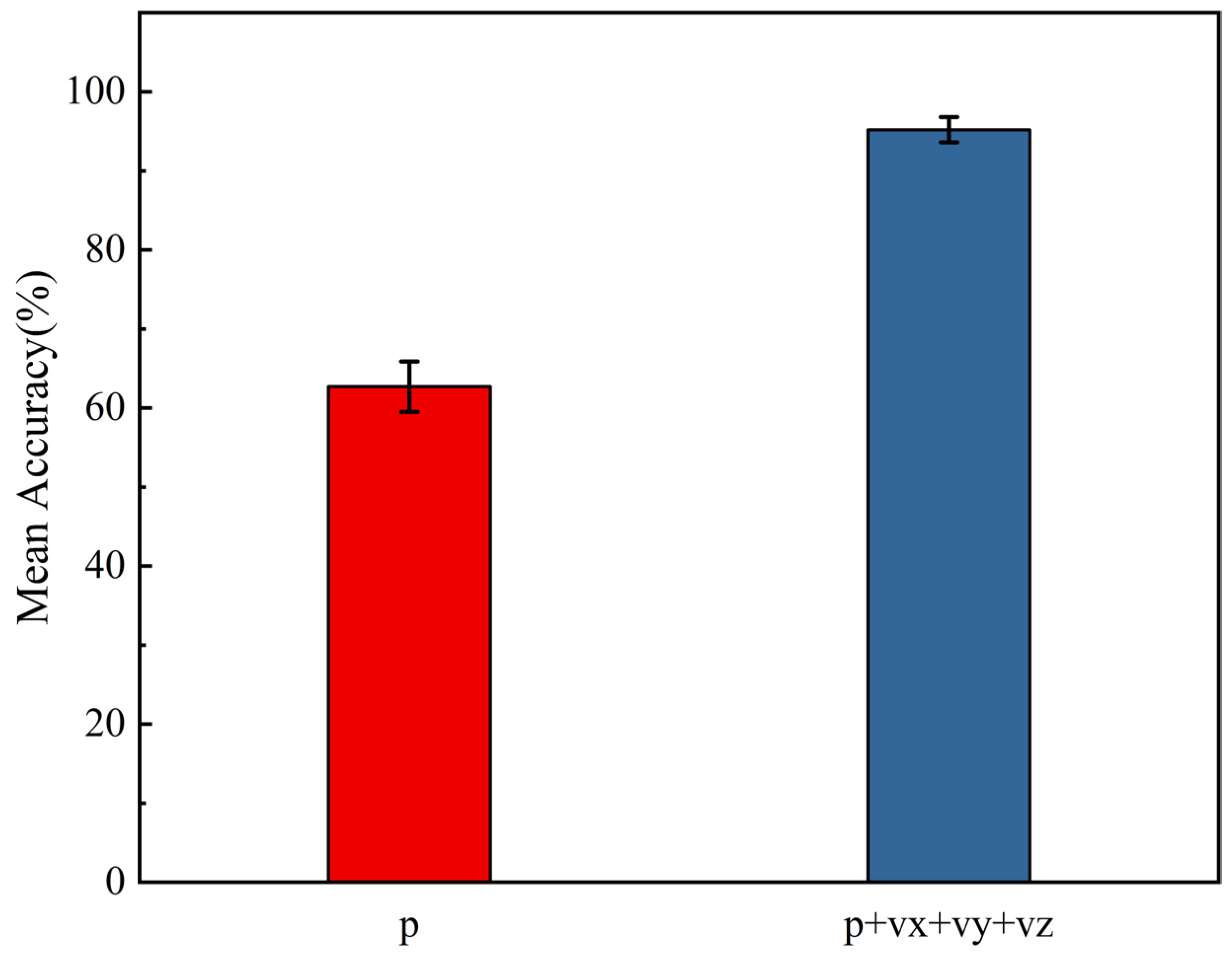
4.1. Verification of the Advantage of Vector Arrays Under Vertical Incidence
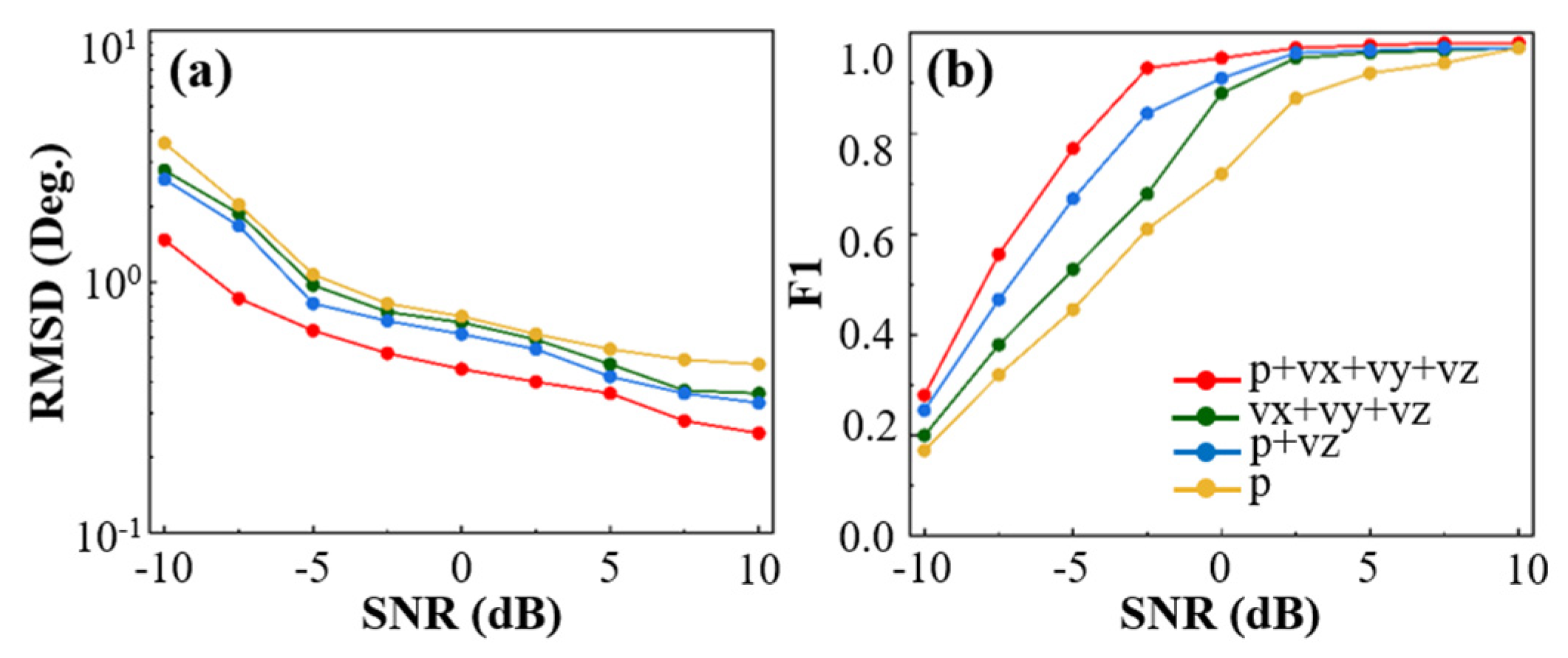
4.2. Impact of Input Channels on Elevation Angle Estimation Performance
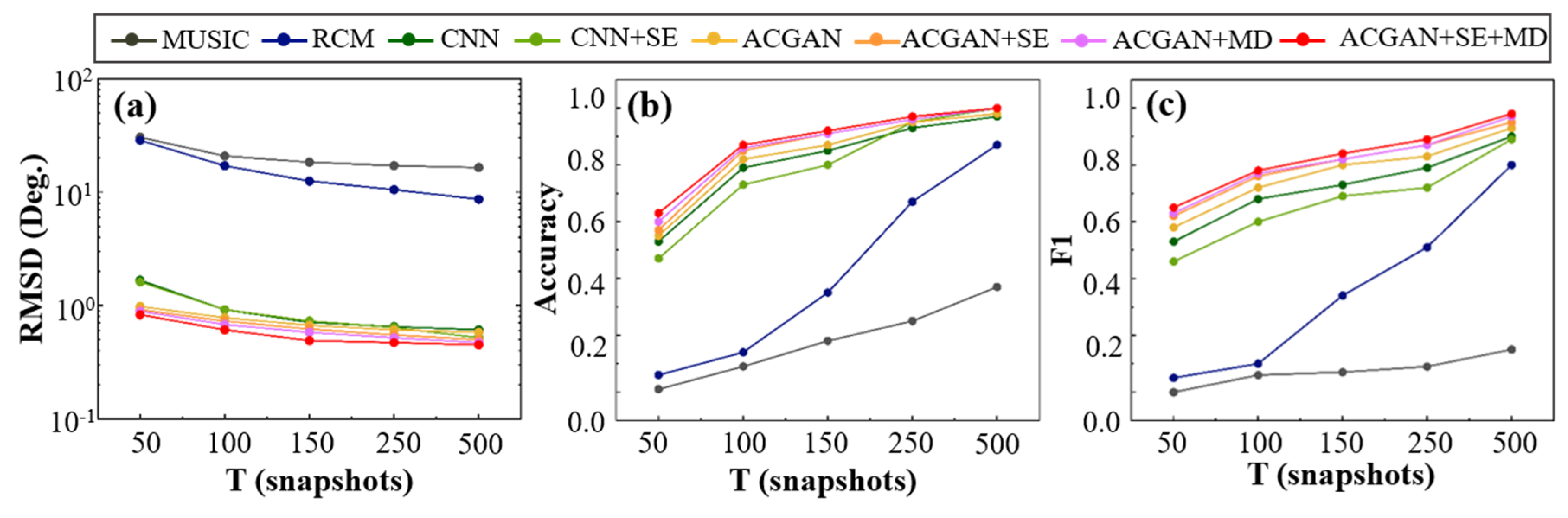
4.3. Performance Comparison of Different Algorithms for Elevation Angle Estimation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bi, H.; Yang, H.; Li, L.; Shen, M.; Yang, S. Deconvolved Improved Differential Beamforming for High-Resolution DOA Estimation. Ocean Eng. 2025, 336, 121736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R. Multiple Emitter Location and Signal Parameter Estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 1986, 34, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Kailath, T. ESPRIT-Estimation of Signal Parameters via Rotational Invariance Techniques. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1989, 37, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kaveh, M. Coherent Signal-Subspace Processing for the Detection and Estimation of Angles of Arrival of Multiple Wide-Band Sources. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1985, 33, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Stoica, P.; Wang, Z. On Robust Capon Beamforming and Diagonal Loading. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2003, 51, 1702–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, W.-Q.; So, H.C. Direction-of-Arrival Estimation of Coherent Signals via Coprime Array Interpolation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Gu, Y.; Fan, X.; Shi, Z.; Mao, G.; Zhang, Y.D. Direction-of-Arrival Estimation for Coprime Array via Virtual Array Interpolation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 5956–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhou, C.; Shi, Z.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Y.D. Coarray Tensor Direction-of-Arrival Estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2023, 71, 1128–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Lan, X. Co-Prime Array Interpolation for DOA Estimation Using Deep Matrix Iterative Network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 2533912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-M.; Zhang, C.; Yu, P.S. Direction-of-Arrival Estimation Based on Deep Neural Networks with Robustness to Array Imperfections. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2018, 66, 7315–7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, G.; Sellathurai, M.; Eldar, Y. Deep Networks for Direction-of-Arrival Estimation in Low SNR. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 3714–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, B. DOA Estimation Based on CNN for Underwater Acoustic Array. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 172, 107594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbir, A.M. DeepMUSIC: Multiple Signal Classification via Deep Learning. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2020, 4, 7001004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, Z.-M.; Huang, Z.-T. Deep Convolution Network for Direction of Arrival Estimation with Sparse Prior. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2019, 26, 1688–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Lee, K. Deep Learning-Aided Coherent Direction-of-Arrival Estimation with the FTMR Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 1118–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, W.; Chen, H.; Dong, Z. Vehicle Positioning with Deep-Learning-Based Direction-of-Arrival Estimation of Incoherently Distributed Sources. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 20083–20095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusrus, J.; Shirmohammadi, S.; Bouchard, M. Characterization of Moving Sound Sources Direction-of-Arrival Estimation Using Different Deep Learning Architectures. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 2505914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhou, M.; Hao, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Kong, A.; Qi, J. Gridless Underdetermined DOA Estimation for Mobile Agents with Limited Snapshots Based on Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. SDOA-Net: An Efficient Deep-Learning-Based DOA Estimation Network for Imperfect Array. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 8503512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zhong, G.; Yu, H. A Review on the Attention Mechanism of Deep Learning. Neurocomputing 2021, 452, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Ma, J. Attention Based DOA Estimation in the Presence of Unknown Nonuniform Noise. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 211, 109506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wei, Z. Remote Sensing Image Classification Based on a Cross-Attention Mechanism and Graph Convolution. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 8002005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, K.; Xu, F.; Guo, H.; Tian, X.; Li, M.; Bao, Z.; Li, Y. An Improved YOLOv5 Model Based on Visual Attention Mechanism: Application to Recognition of Tomato Virus Disease. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 194, 106780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; You, Z.; Feng, Y.; Lu, W. A Detection Method for Pavement Cracks Combining Object Detection and Attention Mechanism. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transport. Syst. 2022, 23, 22179–22189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D. Facial Expression Recognition in the Wild Using Multi-Level Features and Attention Mechanisms. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2023, 14, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; He, S.; Xu, E.; Zhou, Z. Semi-Supervised Meta-Learning Networks with Squeeze-and-Excitation Attention for Few-Shot Fault Diagnosis. ISA Trans. 2022, 120, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Lv, Z.; Pei, S.; Niu, M. Csenet: Complex Squeeze-and-Excitation Network for Speech Depression Level Prediction. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 546–550. [Google Scholar]
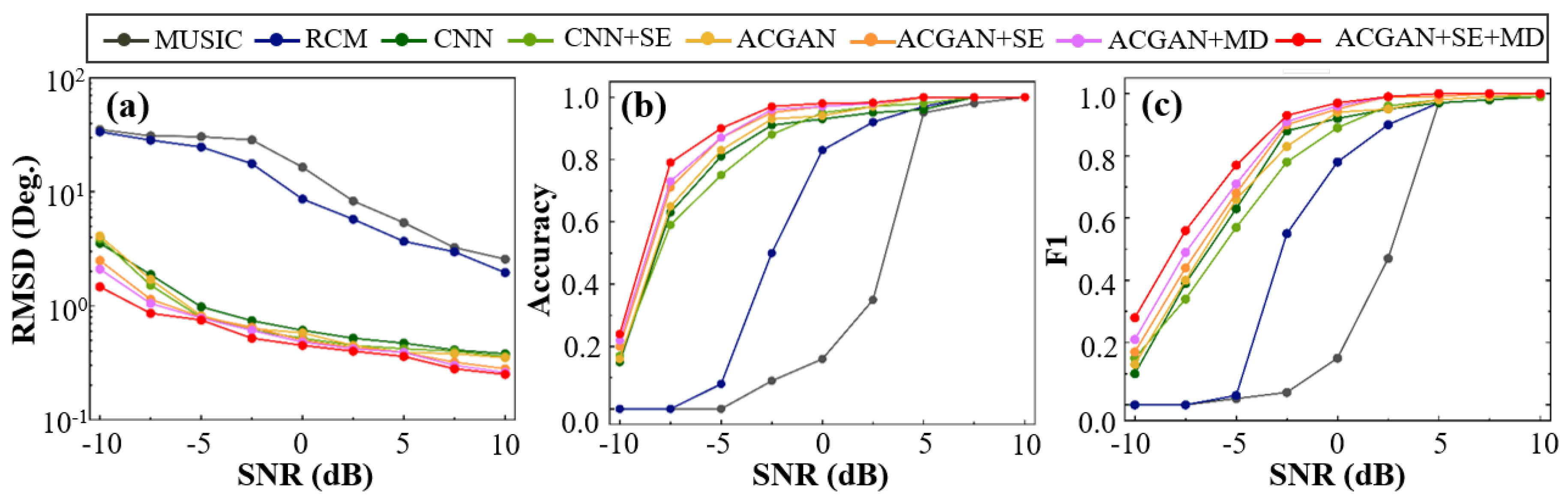
| SNR (dB) | MUSIC | RCM | CNN | CNN + SE | ACGAN | ACGAN + SE | ACGAN + MD | ACGAN + SE + MD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −10 | 35.23 | 33.67 | 3.54 | 3.9 | 4.1 | 2.5 | 2.1 | 1.47 |
| −7.5 | 31.02 | 28.47 | 1.88 | 1.52 | 1.71 | 1.14 | 1.05 | 0.86 |
| −5 | 30.52 | 24.76 | 0.98 | 0.79 | 0.82 | 0.8 | 0.78 | 0.75 |
| −2.5 | 28.59 | 17.68 | 0.74 | 0.61 | 0.63 | 0.65 | 0.61 | 0.52 |
| 0 | 16.5 | 8.66 | 0.61 | 0.52 | 0.58 | 0.5 | 0.48 | 0.45 |
| 2.5 | 8.34 | 5.76 | 0.52 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.43 | 0.42 | 0.4 |
| 5 | 5.37 | 3.68 | 0.47 | 0.42 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.36 |
| 7.5 | 3.25 | 2.98 | 0.41 | 0.4 | 0.38 | 0.32 | 0.3 | 0.28 |
| 10 | 2.57 | 1.96 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 0.35 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Shi, N.; Xie, Y. ACGAN-Based Multi-Target Elevation Estimation with Vector Sensor Arrays in Low-SNR Environments. Sensors 2025, 25, 6581. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25216581
Wang B, Shi N, Xie Y. ACGAN-Based Multi-Target Elevation Estimation with Vector Sensor Arrays in Low-SNR Environments. Sensors. 2025; 25(21):6581. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25216581
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Biao, Ning Shi, and Yangyang Xie. 2025. "ACGAN-Based Multi-Target Elevation Estimation with Vector Sensor Arrays in Low-SNR Environments" Sensors 25, no. 21: 6581. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25216581
APA StyleWang, B., Shi, N., & Xie, Y. (2025). ACGAN-Based Multi-Target Elevation Estimation with Vector Sensor Arrays in Low-SNR Environments. Sensors, 25(21), 6581. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25216581






