Internet of Things Node with Real-Time LoRa GEO Satellite Connectivity for Agrifood Chain Tracking in Remote Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Contributions
- The development and characterization of an IoT sensor node based on LoRa connectivity supported by GEO satellite radio access technology. The node integrates relevant sensors and a LoRa satellite modem. Although the design was tailored for cattle breeding [9], the architecture can be adapted to other use cases.
- This work extends the proof-of-concept from [10] by presenting a more mature prototype enclosed in a dedicated box suitable for field testing in realistic scenarios. The experimental characterization addresses the entire end-to-end process, from data acquisition on the field to data availability in cloud storage.
- The evaluation of real-world experimental tests with GEO connectivity, enabling a performance assessment of the proposed IoT node in terms of power consumption.
1.2. Literature Review
2. Materials and Methods
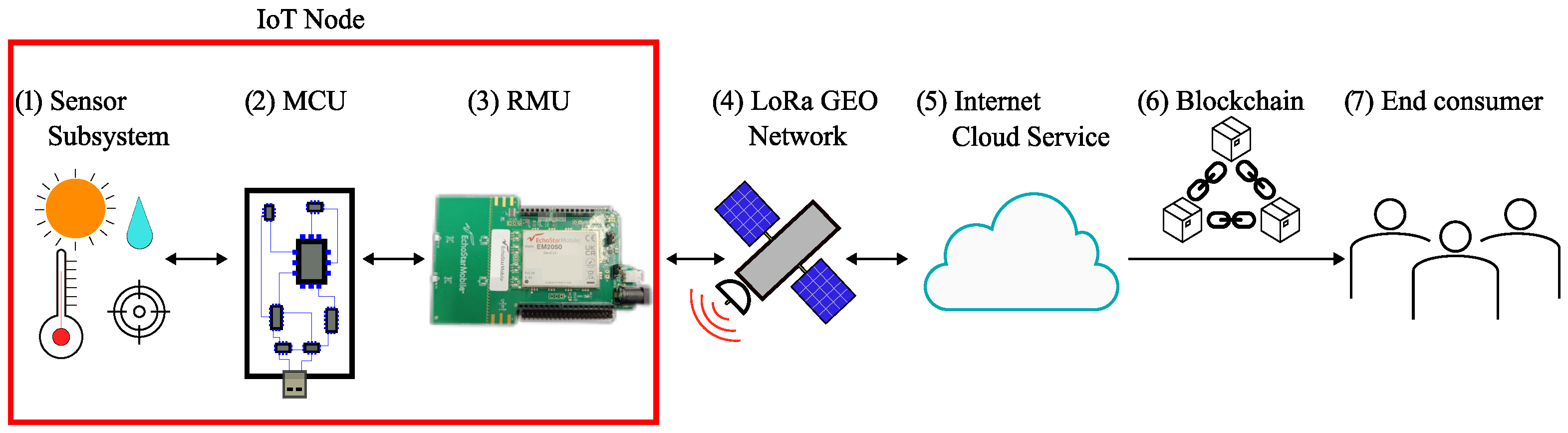
2.1. IoT Node
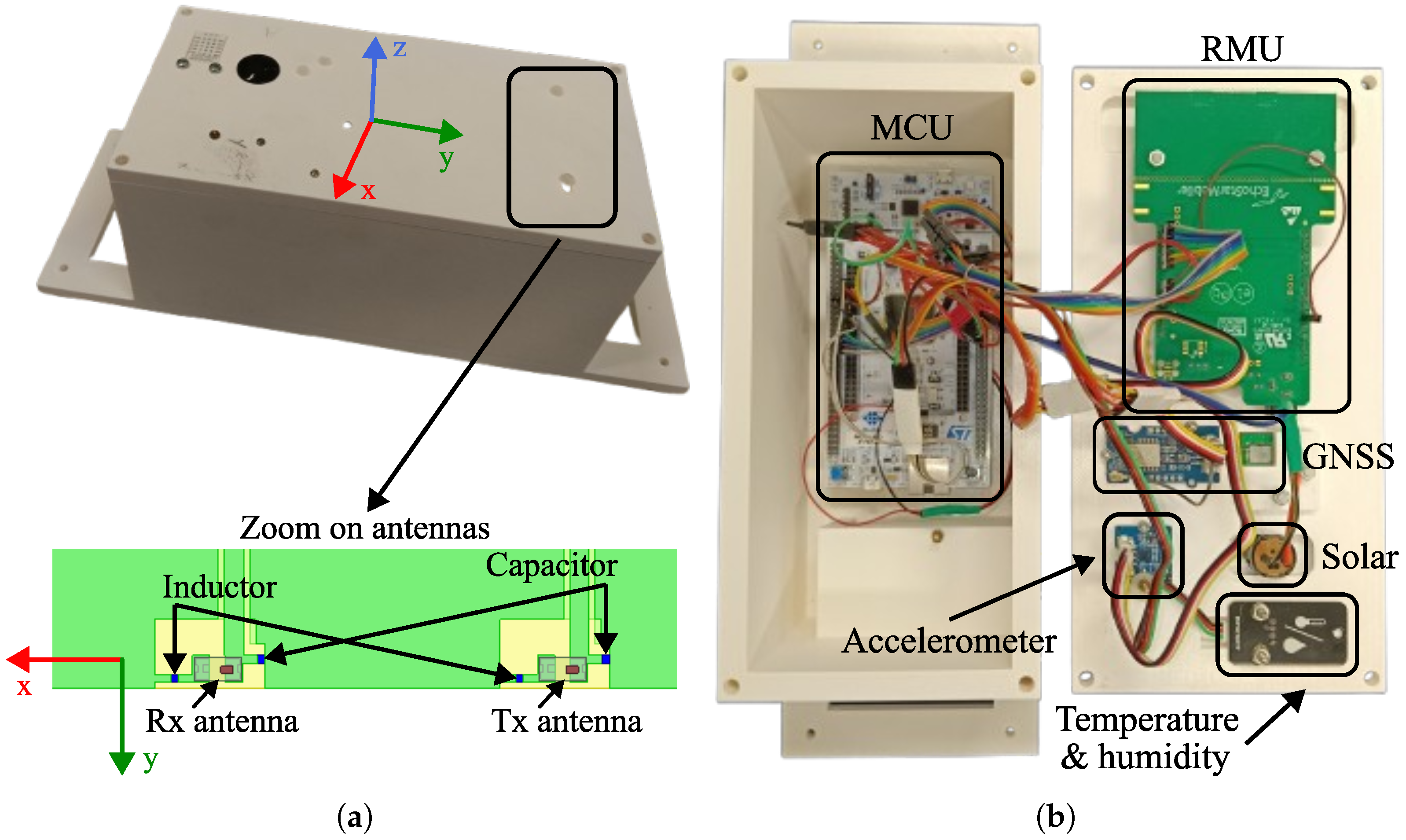
2.1.1. Hardware Components
- Sensor subsystem
- –
- GNSS module
- –
- accelerometer
- –
- temperature and humidity sensor
- –
- solar radiation intensity sensor
- –
- current probe (for monitoring purposes only)
- MCU
- LoRa RMU
GNSS Module
Accelerometer
Temperature and Humidity Sensor
Solar Radiation Intensity Sensor
Current Probe
Microcontroller Unit
LoRa Radio-Modem Unit
2.1.2. System Integration
2.1.3. Prototype Enclosure
2.2. Satellite Budget Uplink
2.3. Cloud Service and Python Application Programming Interface
- start a communication with AWS;
- read messages in the queue;
- delete messages in the queue;
- decode the messages;
- get data;
- process the data in the messages.
3. Results
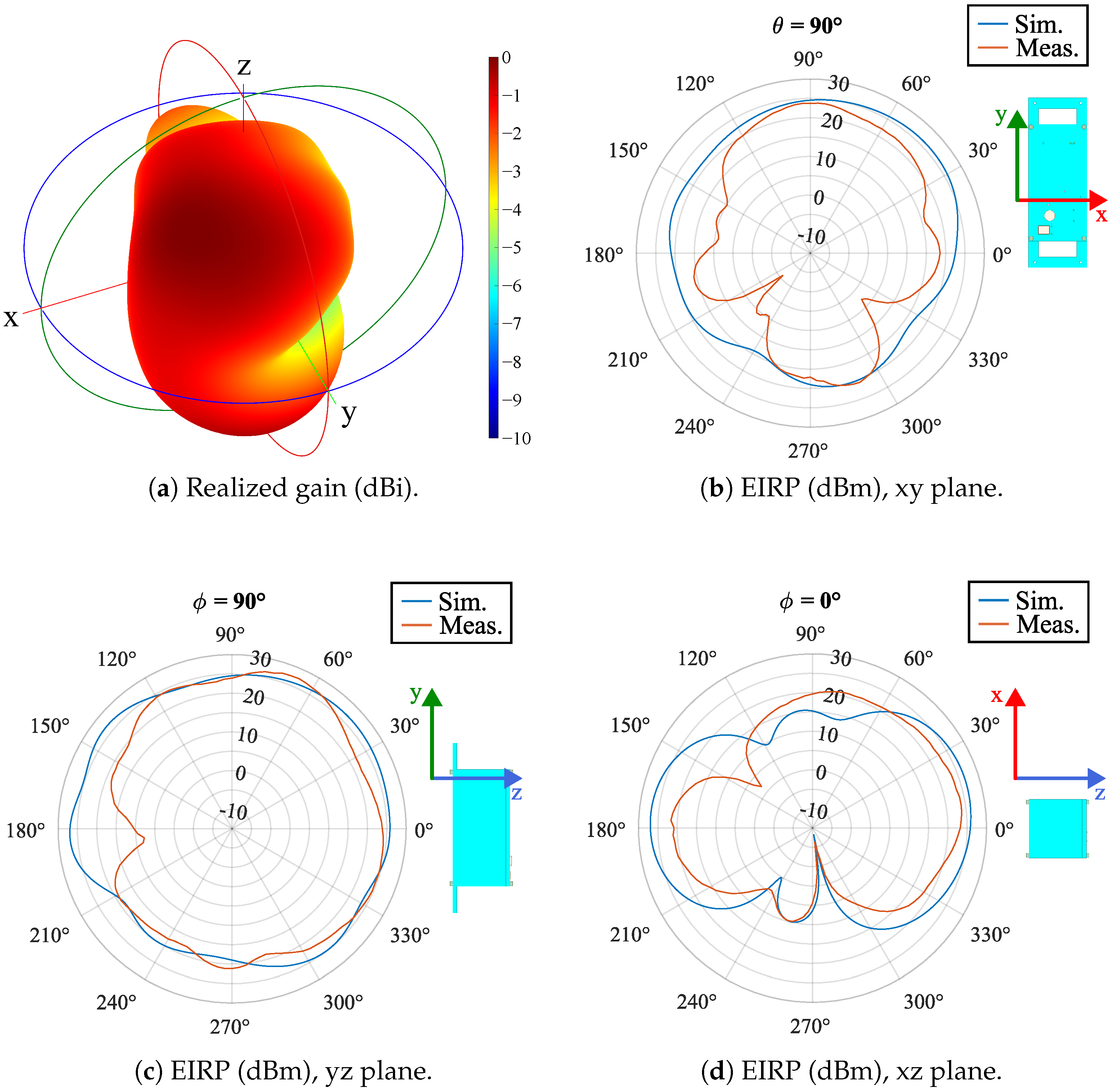
3.1. Characterization of the Antenna Transmission
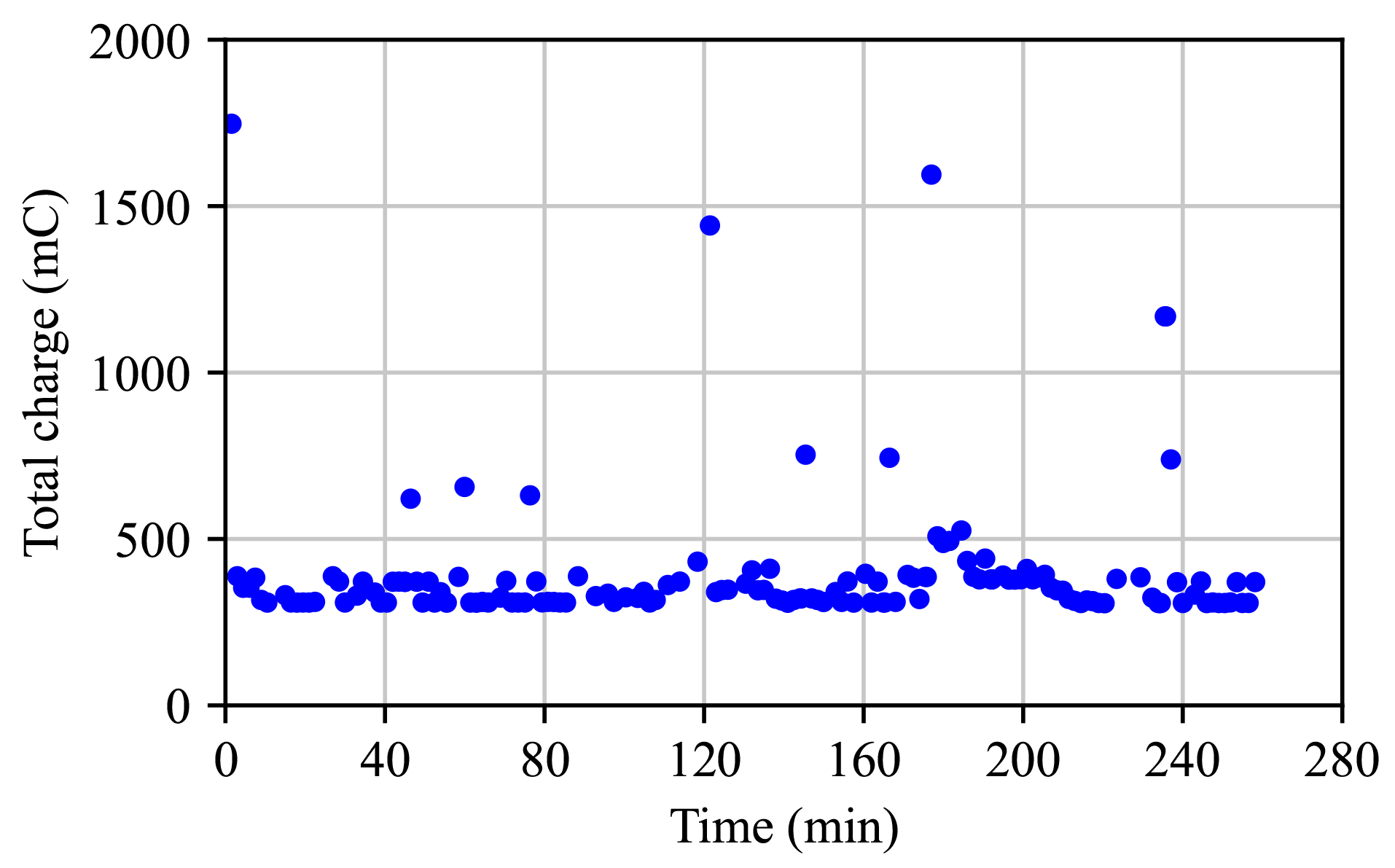
3.2. Sensor Data
3.3. Current Absorption
4. Discussion
4.1. Characterization of the Antenna Transmission
4.2. Sensor Data
4.3. Current Absorption
4.4. Network Scalability
4.5. Cost Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABS | acrylonitrile butadiene styrene |
| ACK | acknowledgement |
| AWS | Amazon Web Services |
| DtS | direct-to-satellite |
| EIRP | effective isotropic radiated power |
| GEO | geostationary Earth orbit |
| GNSS | global navigation satellite system |
| IC | integrated circuit |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| ISM | industrial, scientific and medical |
| LEO | low Earth orbit |
| LR-FHSS | long-range frequency hopping spread spectrum |
| LoRa | Long Range |
| LoRaWAN | long range wide area network |
| MCU | microcontroller unit |
| NGEU | Next Generation EU |
| NRRP | National Recovery and Resilience Plan |
| PA | precision agriculture |
| PCB | printed circuit board |
| RMU | radio-modem unit |
| SNR | signal-to-noise ratio |
References
- Singh, R.K.; Berkvens, R.; Weyn, M. AgriFusion: An architecture for IoT and emerging technologies based on a precision agriculture survey. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 136253–136283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocco, L.; Mannaro, K.; Tonelli, R.; Mariani, L.; Lodi, M.B.; Melis, A.; Simone, M.; Fanti, A. A Blockchain-Based Traceability System in Agri-Food SME: Case Study of a Traditional Bakery. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 62899–62915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Centre for Agricultural Technologies (Agritech). PNNR MUR-M4C2 (Missione 4 Componente 2) Investimento 1.4 “National Research Centre for Agricultural Technologies” Agritech CUP HUB-B63D21015240004. 2025. Available online: https://agritechcenter.it/ (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Farooq, M.S.; Riaz, S.; Abid, A.; Abid, K.; Naeem, M.A. A survey on the role of IoT in agriculture for the implementation of smart farming. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 156237–156271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foubert, B.; Mitton, N. Long-range wireless radio technologies: A survey. Futur. Internet 2020, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sanctis, M.D.; Cianca, E.; Araniti, G.; Bisio, I.; Prasad, R. Satellite communications supporting internet of remote things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2015, 3, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraire, J.A.; Céspedes, S.; Accettura, N. Direct-to-satellite IoT—A survey of the state of the art and future research perspectives. In Proceedings of the Ad-Hoc, Mobile, and Wireless Networks, Luxembourg, 1–3 October 2019; Palattella, M.R., Scanzio, S., Ergen, S.C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, Z.; Shang, L. Satellite internet of things: Challenges, solutions, and development trends. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2023, 24, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, I.; Biba, T.; Çiço, B. Design of a cattle-health-monitoring system using microservices and IoT devices. Computers 2022, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasagni, G.; Badii, M.; Collodi, G.; Righini, M.; Cidronali, A. GEO satellite Internet of Things node architecture for agrifood supply chain traceability. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 & IoT (MetroInd4.0 & IoT), Florence, Italy, 29–31 May 2024; pp. 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, N.; Maddikunta, P.K.R.; Mary, D.R.K.; Murugan, R.; Chengoden, R.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Rakesh, N.; Zhu, Y.; Paek, J. Remote sensing for agriculture in the era of industry 5.0—A survey. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 5920–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, F.K.; Karim, S.; Zeadally, S.; Nebhen, J. Recent trends in internet-of-things-enabled sensor technologies for smart agriculture. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 23583–23598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, T.; Colizzi, L.; Dimauro, G.; Guerriero, E.; Pareo, D. Crop planting layout optimization in sustainable agriculture: A constraint programming approach. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 224, 109162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhigbe, B.I.; Munir, K.; Akinade, O.; Akanbi, L.; Oyedele, L.O. IoT technologies for livestock management: A review of present status, opportunities, and future trends. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2021, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centenaro, M.; Costa, C.E.; Granelli, F.; Sacchi, C.; Vangelista, L. A survey on technologies, standards and open challenges in satellite IoT. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1693–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Peng, H.; Ji, Y.; Hong, T.; Zhang, G. Adaptive resource optimization for LoRa-enabled LEO satellite IoT system in high-dynamic environments. Sensors 2025, 25, 3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, A.; Narduzzi, C.; Peruzzi, G.; Pozzebon, A. Satellite IoT for monitoring and tracking of athletes in extreme environments. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Workshop on Sport, Technology and Research (STAR), Cavalese, Italy, 6–8 July 2022; pp. 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boquet, G.; Tuset-Peiró, P.; Adelantado, F.; Watteyne, T.; Vilajosana, X. LR-FHSS: Overview and performance analysis. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2021, 59, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, J.; Zhang, Z. Understanding Long Range-Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (LR-FHSS) with real-world packet traces. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. 2024, 20, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Yue, M.; Yang, H.; Wu, L.; Yuan, X. Integrating communication, sensing and computing in satellite internet of things: Challenges and opportunities. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2024, 31, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE. IEEE Standard Glossary of Software Engineering Terminology; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onu, P.; Mbohwa, C.; Pradhan, A. Blockchain-powered traceability solutions: Pioneering transparency to eradicate counterfeit products and revolutionize supply chain integrity. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 232, 1420–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, L.; Cancimance, C.; Asorey-Cacheda, R.; Zúñiga-Cañón, C.L.; Garcia-Sanchez, A.J.; Garcia-Haro, J. Lightweight blockchain for data integrity and traceability in IoT networks. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 81105–81117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieltz, J.M.; Okanga, S.; Allan, B.F.; Rubenstein, D.I. GPS tracking cattle as a monitoring tool for conservation and management. Afr. J. Range Forage Sci. 2017, 34, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.W.; Udal, M.C.; Larson, B.T.; Shearer, S.A. Monitoring cattle behavior and pasture use with GPS and GIS. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2000, 80, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, M.J.; Grau-Campanario, P.; Mullan, S.; Held, S.D.E.; Stokes, J.E.; Lee, M.R.F.; Cardenas, L.M. Factors affecting site use preference of grazing cattle studied from 2000 to 2020 through GPS tracking: A review. Sensors 2021, 21, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan-Vásquez, J.A.; Maroto-Molina, F.; Guerrero-Ginel, J.E. GPS tracking to monitor the spatiotemporal dynamics of cattle behavior and their relationship with feces distribution. Animals 2022, 12, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.d.S.; de Medeiros, V.W.C.; Gonçalves, G.E. Monitoring and classification of cattle behavior: A survey. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 3, 100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polsky, L.B.; Madureira, A.M.L.; Filho, E.L.D.; Soriano, S.; Sica, A.F.; Vasconcelos, J.L.M.; Cerri, R.L.A. Association between ambient temperature and humidity, vaginal temperature, and automatic activity monitoring on induced estrus in lactating cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 8590–8601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.B.; Rogers, A.R.; Schütz, K.E. Effect of solar radiation on dairy cattle behaviour, use of shade and body temperature in a pasture-based system. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2008, 109, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, B.; Montón, M.; Vilajosana, I.; Prades, J.D. The power of models: Modeling power consumption for IoT devices. IEEE Sensors J. 2015, 15, 5777–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Vital, R.; Casals, L.; Heer-Salva, B.; Vidal, R.; Gomez, C.; Garcia-Villegas, E. Energy performance of LR-FHSS: Analysis and evaluation. Sensors 2024, 24, 5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannetti, G.; Badii, M.; Lasagni, G.; Maddio, S. Gianne97/IoTnodeWithGEOconnectivity: Complementary Material for the Publication Entitled: “Internet of Things Node with Real-Time LoRa GEO Satellite Connectivity for Agrifood Chain Tracking in Remote Areas”; Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, G.; Fraire, J.A.; Hassan, K.A.; Céspedes, S.; Pesch, D. Uplink transmission policies for LoRa-based direct-to-satellite IoT. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 72687–72701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.A.; Mikhaylov, K.; Alves, H. Experiment-based models for air time and current consumption of LoRaWAN LR-FHSS. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.09954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodheli, O.; Maturo, N.; Andrenacci, S.; Chatzinotas, S.; Zimmer, F. Link budget analysis for satellite-based narrowband IoT systems. In Proceedings of the Ad-Hoc, Mobile, and Wireless Networks, Luxembourg, 1–3 October 2019; Palattella, M.R., Scanzio, S., Ergen, S.C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semtech Corporation. Application Note AN1200.64 LR-FHSS System Performance. 2025. Available online: https://www.semtech.com/lora (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Krupka, J. Microwave measurements of electromagnetic properties of materials. Materials 2021, 14, 5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.; Jiménez, J.A.; Espinosa, F. Effect of event-based sensing on IoT node power efficiency. Case study: Air quality monitoring in smart cities. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 132577–132586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, D.; Kaneko, M.; Fraire, J.A.; Guitton, A.; Iova, O.; Rivano, H. Enhancing LR-FHSS scalability through advanced sequence design and demodulator allocation. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, A.; Nguyen, H.H.; Bedeer, E.; Barton, R. D2D-aided LoRaWAN LR-FHSS in direct-to-satellite IoT networks. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.04331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, D.; Cardoso, L.S.; Fraire, J.A.; Guitton, A.; Iova, O.; Kaneko, M.; Rivano, H. Enhanced LR-FHSS receiver for headerless frame recovery in space–terrestrial integrated IoT networks. Comput. Netw. 2025, 257, 111018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| State | Symbol | Measured Current (mA) |
|---|---|---|
| Sleep | 0.030 | |
| Idle | 10 | |
| Receiving (ACK) | 70 | |
| Transmitting ( (1)) | 100 (1) | |
| Joining () | 230 |
| Parameter | Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 2.009 GHz + {453.0, 609.4, 765.6, 921.9} kHz | ||
| Operating channel width | 137 kHz | ||
| Occupied bandwidth per hop | 488 Hz | ||
| Data rate | DR8 | DR9 | |
| Code rate | 1/3 | 2/3 | |
| Physical bit rate (bit/s) | 162 | 325 | |
| Sensitivity (dBm) | −137 | −134.5 | |
| Time on air [35 byte payload size] (s) | 2.6 | 1.4 | |
| Module | Max. Curr. (mA) |
|---|---|
| GNSS module | 60 |
| Accelerometer | 0.15 |
| Temperature and humidity sensor | 1.50 |
| Intensity of solar radiation sensor | 0.50 |
| RMU (joining state) | 230 |
| MCU | 500 |
| Sensor | Datum | ASCII Chars | Offset | Ex. Base-10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNSS | Latitude | 10 | 0900000000 | 0434789850 |
| Longitude | 10 | 1800000000 | 0111520182 | |
| Number of satellites | 2 | 00 | 07 | |
| Altitude | 5 | 10000 | 01802 | |
| Height | 5 | 10000 | 00452 | |
| Accel. | Acc. x | 5 | 16384 | 00064 |
| Acc. y | 5 | 16384 | −11936 | |
| Acc. z | 5 | 16384 | −10832 | |
| Temp. and hum. | Temperature | 3 | 300 | 156 |
| Humidity | 3 | 000 | 522 | |
| Solar rad. | Int. solar radiation | 5 | 00000 | 01836 |
| Parameter | Standing Test | Moving Test | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duration (min) | 258 | 63 | – |
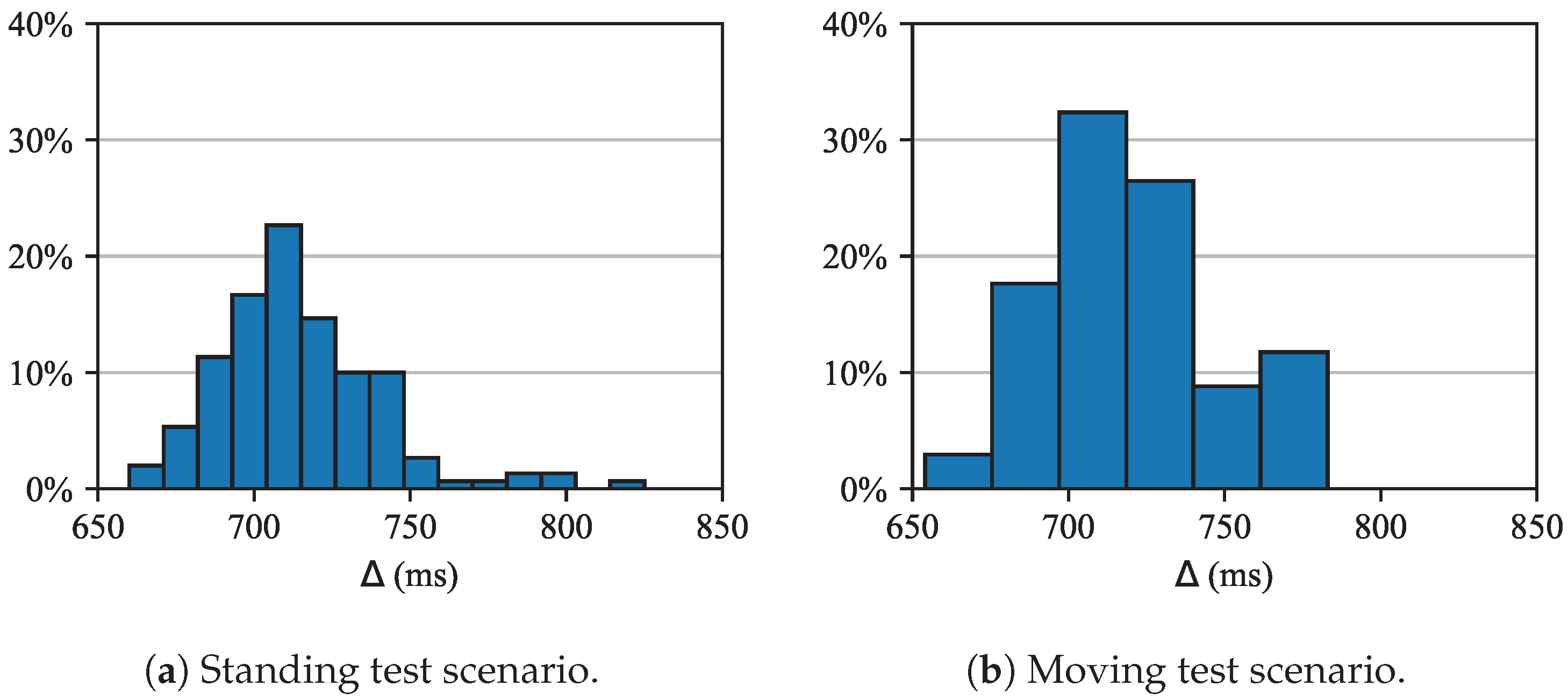
| Cycle time (s) | 38.8 | 37.6 | 38.2 |
| Gateway-cloud service delay (ms) | 714 | 719 | 717 |
| Total charge per cycle (mC) | 347 | 364 | 356 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giannetti, G.; Badii, M.; Lasagni, G.; Maddio, S.; Collodi, G.; Righini, M.; Cidronali, A. Internet of Things Node with Real-Time LoRa GEO Satellite Connectivity for Agrifood Chain Tracking in Remote Areas. Sensors 2025, 25, 6469. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206469
Giannetti G, Badii M, Lasagni G, Maddio S, Collodi G, Righini M, Cidronali A. Internet of Things Node with Real-Time LoRa GEO Satellite Connectivity for Agrifood Chain Tracking in Remote Areas. Sensors. 2025; 25(20):6469. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206469
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiannetti, Giacomo, Marco Badii, Giovanni Lasagni, Stefano Maddio, Giovanni Collodi, Monica Righini, and Alessandro Cidronali. 2025. "Internet of Things Node with Real-Time LoRa GEO Satellite Connectivity for Agrifood Chain Tracking in Remote Areas" Sensors 25, no. 20: 6469. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206469
APA StyleGiannetti, G., Badii, M., Lasagni, G., Maddio, S., Collodi, G., Righini, M., & Cidronali, A. (2025). Internet of Things Node with Real-Time LoRa GEO Satellite Connectivity for Agrifood Chain Tracking in Remote Areas. Sensors, 25(20), 6469. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206469











