High-Precision Extrinsic Calibration for Multi-LiDAR Systems with Narrow FoV via Synergistic Planar and Circular Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Contribution
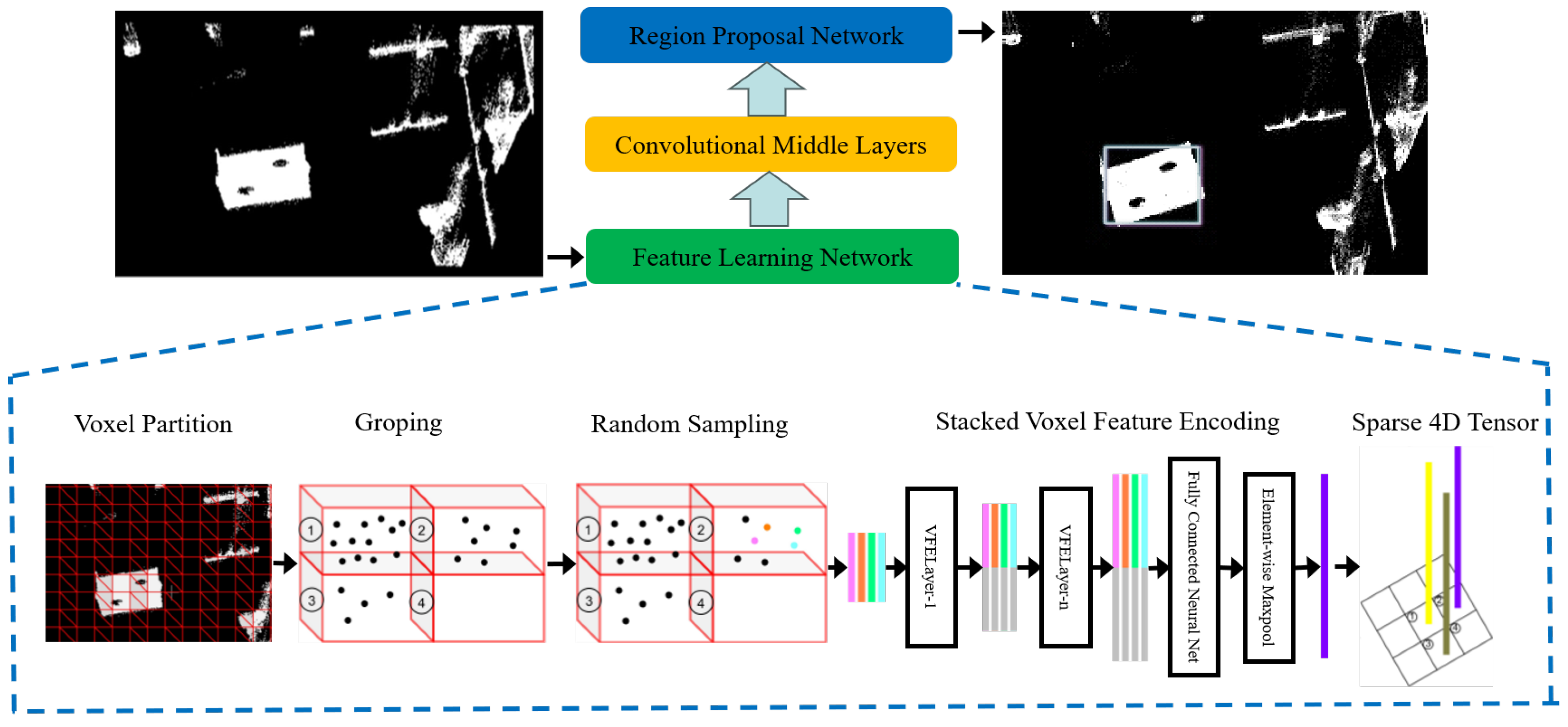
- We propose an automatic method for calibration board detection and segmentation using an improved VoxelNet, which ensures efficient and robust extraction of the board’s point cloud even in complex environments.
- We develop a planar point cloud filtering technique using the GMIF to effectively suppress noise, thereby significantly enhancing the quality of subsequent feature extraction.
- We design a nonlinear optimization framework that jointly constrains planar and circular features. This framework incorporates an innovative adaptive weighting model to balance the contributions of different geometric primitives, leading to substantially improved calibration accuracy.
2. Related Work
2.1. Motion-Based Methods
2.2. Feature-Based Methods
2.3. SLAM-Based Methods
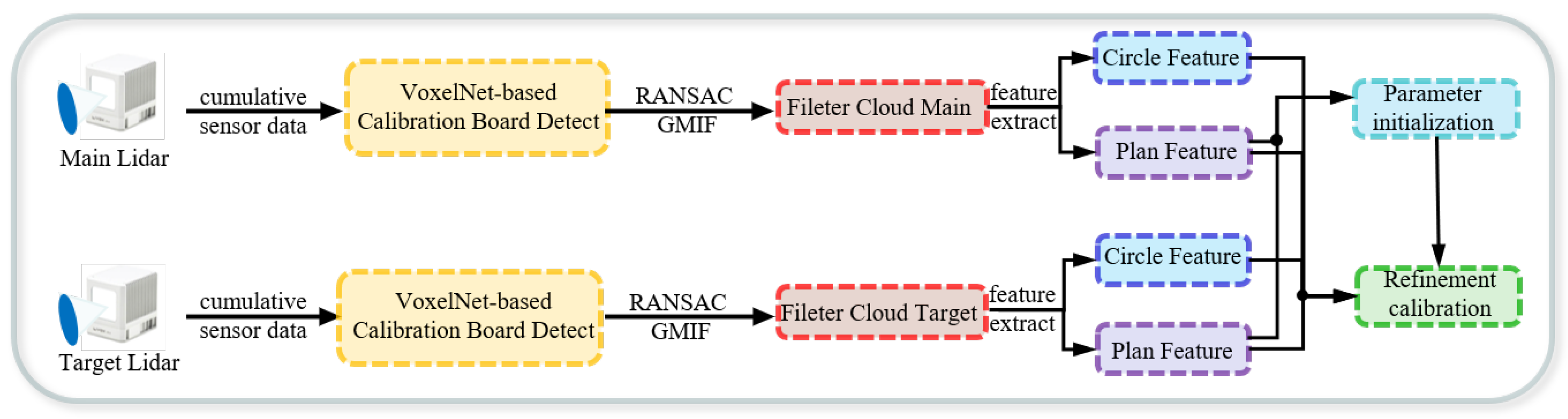
3. Methodology
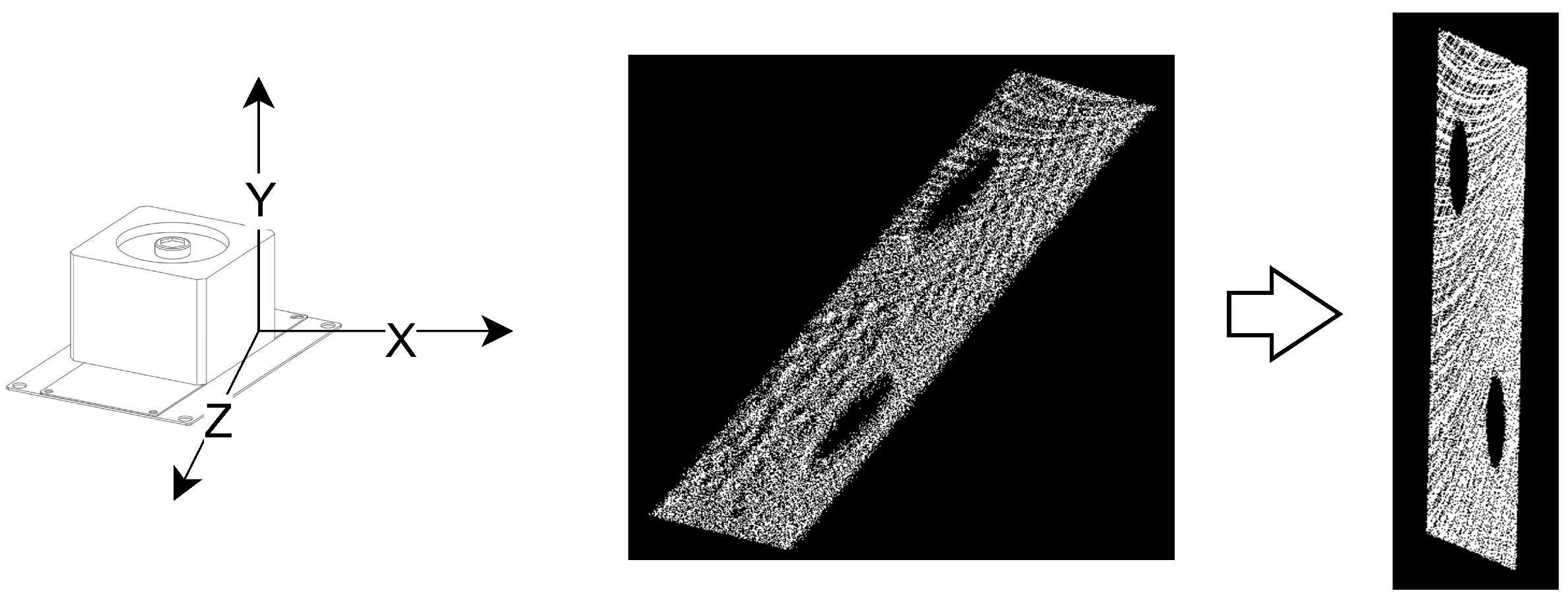
3.1. Notation
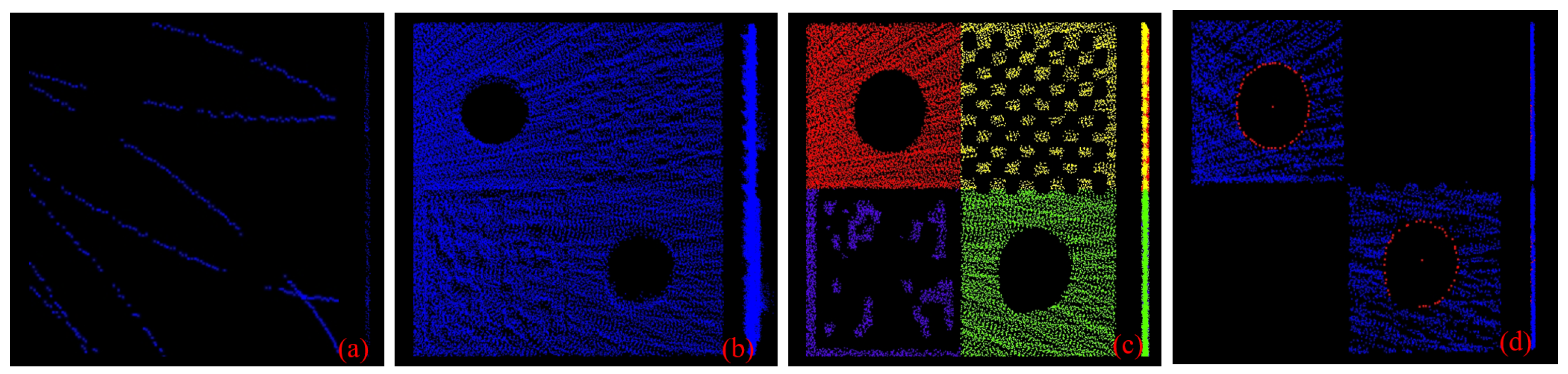
3.2. Target Detection and Extraction
3.3. Plane and Circle Feature Extraction
3.3.1. Plane Feature Extraction
| Algorithm 1: Mean Intensity filtering based on Gaussian Newton |
| Input: segmented point cloud: , , Output:
|
3.3.2. Circular Feature Extraction
3.4. Nonlinear Optimization
3.4.1. Parameter Initialization
3.4.2. Refined Calibration
- (1)
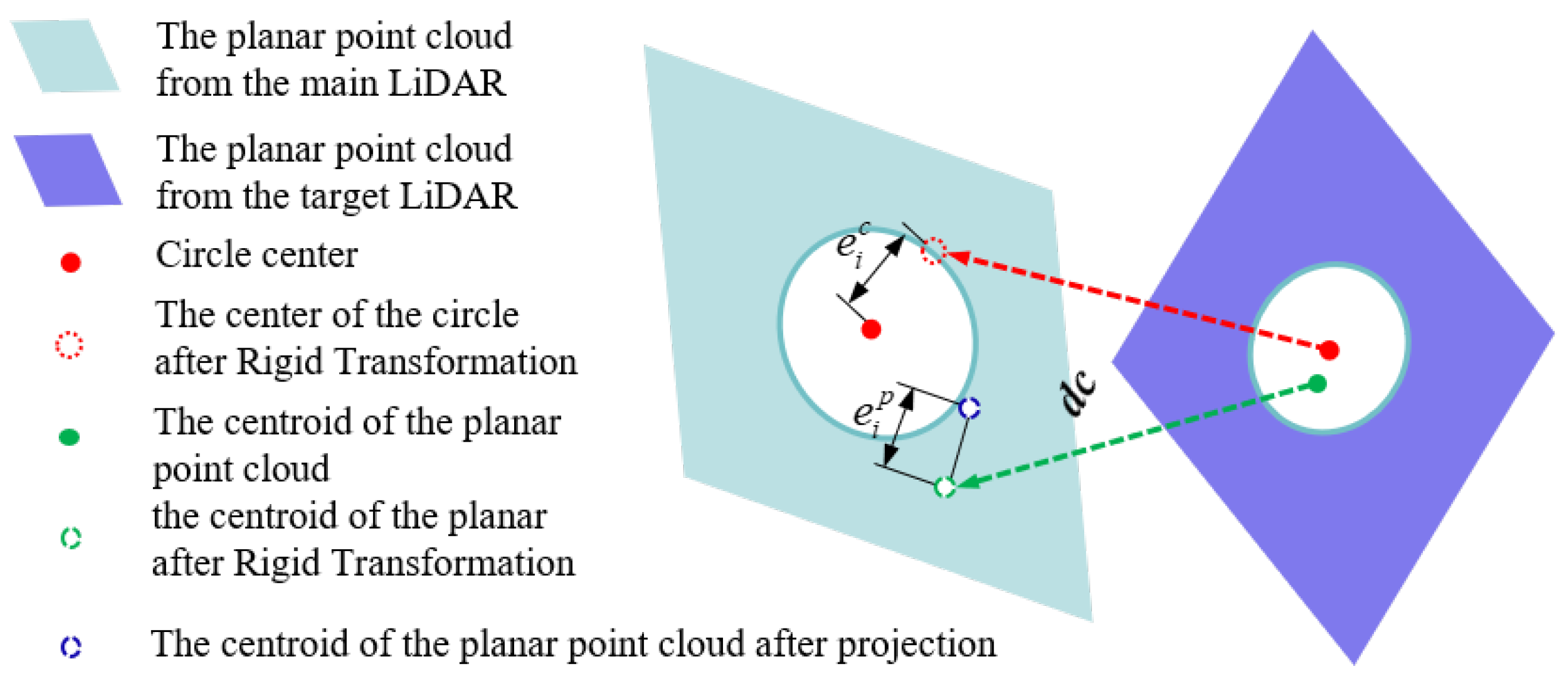
- Centroid-to-Plane Constraint
- (2)
- Center-to-Center Constraint
- (3)
- Iterative Optimization
4. Experiments
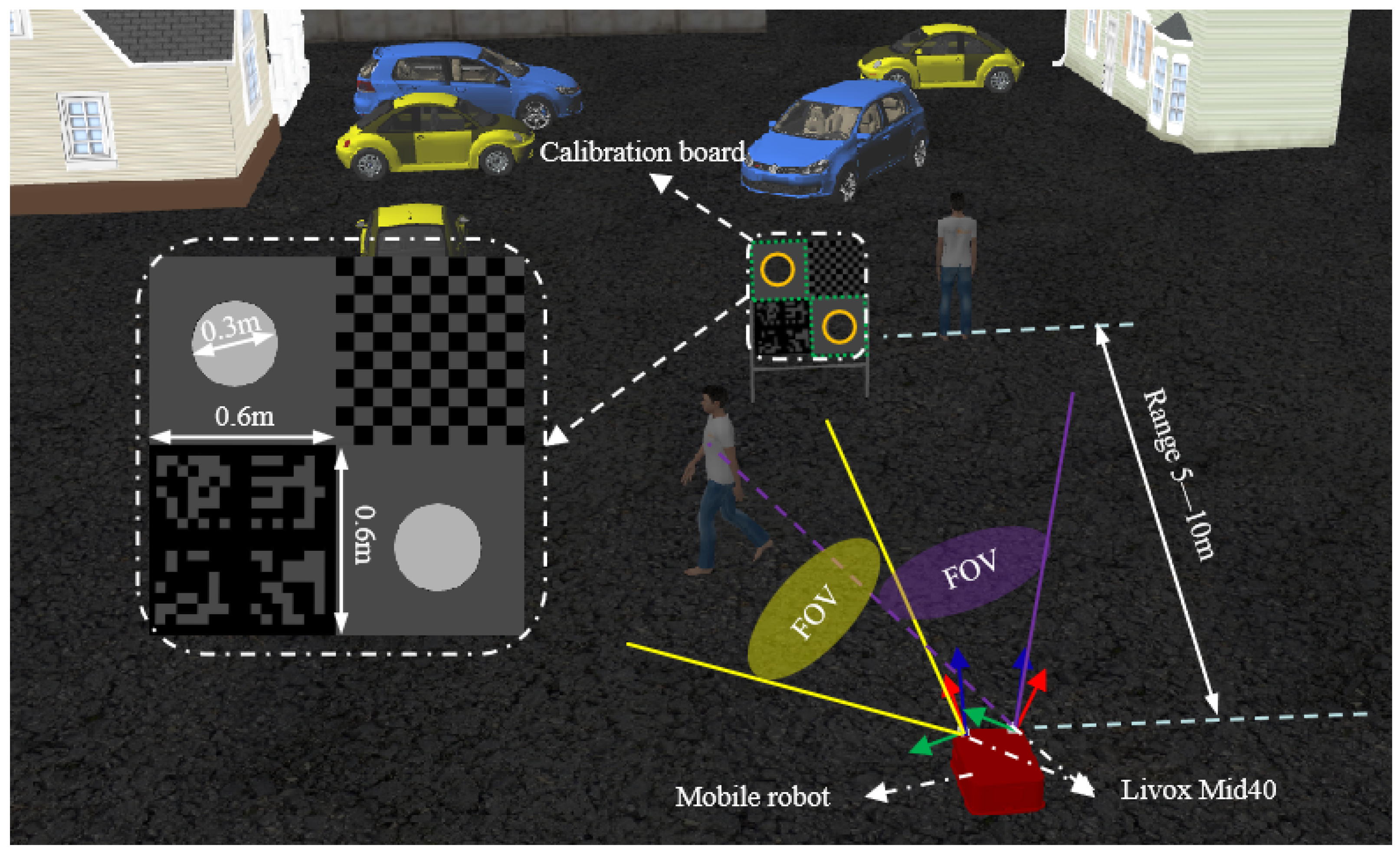
4.1. Implementation Details
4.2. Simulated Experiment
- Define the ground-truth calibration parameters.
- Collect a dataset of 100 calibration board point cloud instances.
- Generate subsets of varying sizes via random sampling without replacement.
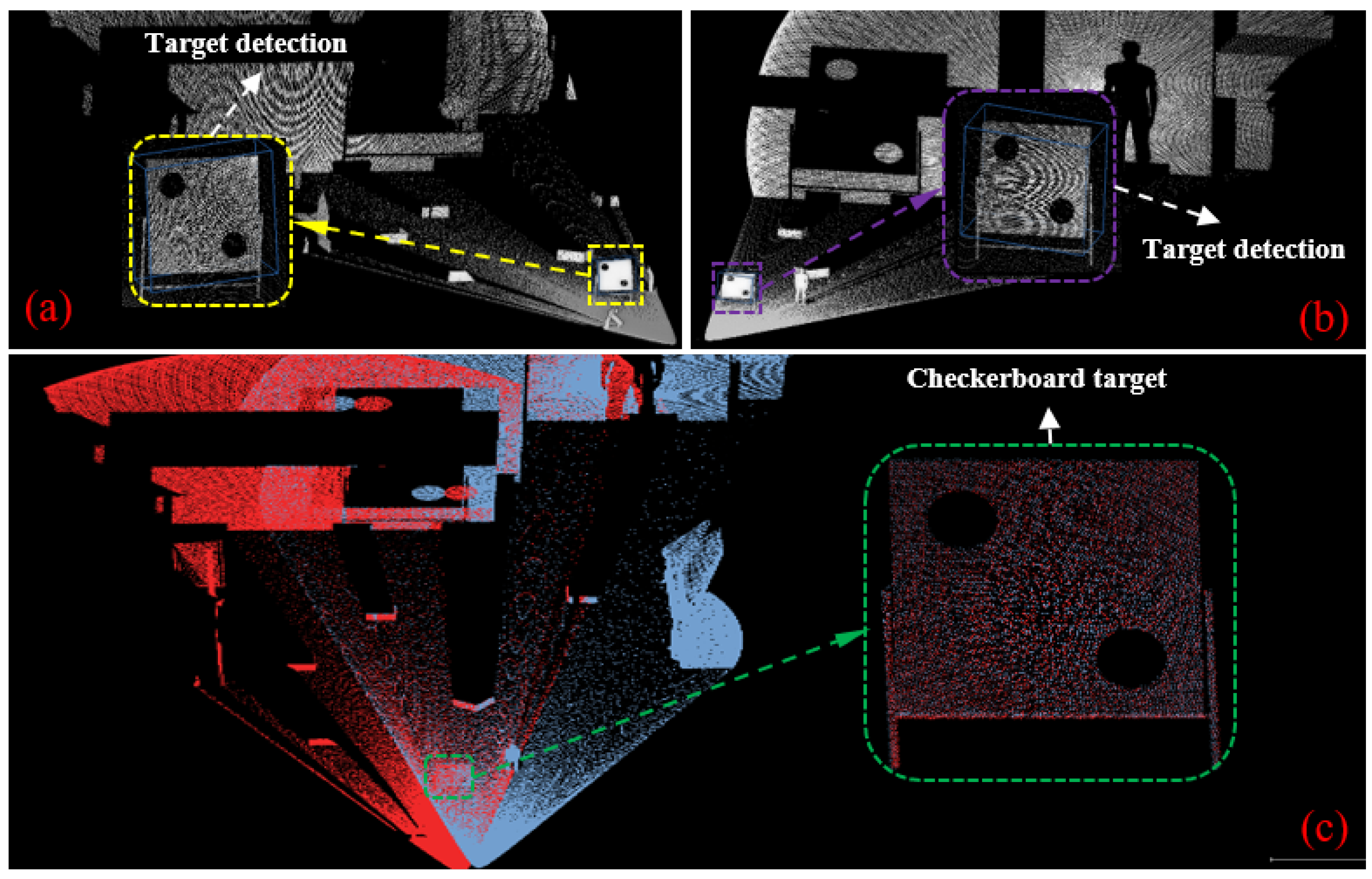
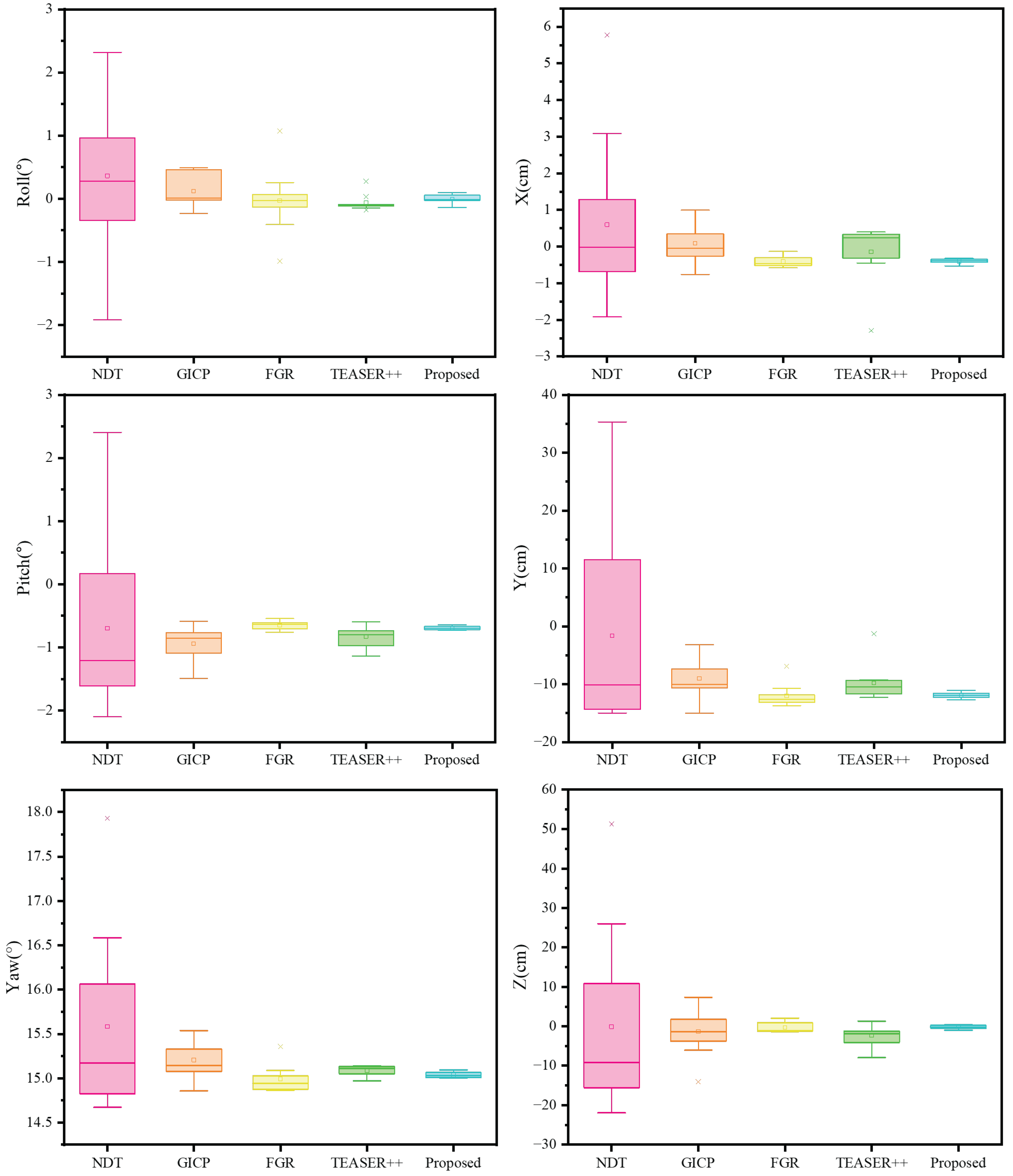
4.3. Real-World Experiments
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Ibanez-Guzman, J. Lidar for autonomous driving: The principles, challenges, and trends for automotive lidar and perception systems. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2020, 37, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Tan, X. ODLC_SAM: A novel LiDAR SLAM system towards open-air environments with loop closure. Ind. Robot 2023, 50, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, F. Fast-LIO: A fast, robust lidar-inertial odometry package by tightly-coupled iterated Kalman filter. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 3317–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Huang, S.; Qiu, S.; Zhao, L.; Yu, W.; Fang, M.; Li, R. Lidar-Link: Observability-aware probabilistic plane-based extrinsic calibration for non-overlapping solid-state lidars. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 2590–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusztai, Z.; Eichhardt, I.; Hajder, L. Accurate calibration of multi-lidar-multi-camera systems. Sensors 2018, 18, 2139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Lyu, Q.; Peng, G.; Wu, Z.; Yan, Q.; Wang, D. LB-L2L-Calib: Accurate and robust extrinsic calibration for multiple 3D LiDARs with long baseline and large viewpoint difference. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 926–932. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Li, Z.; Malekian, R.; Sotelo, M.A.; Ma, Z.; Li, W. A novel multifeature based on-site calibration method for LiDAR-IMU system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 9851–9861. [Google Scholar]
- Pentek, Q.; Kennel, P.; Allouis, T.; Fiorio, C.; Strauss, O. A flexible targetless LiDAR–GNSS/INS–camera calibration method for UAV platforms. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 166, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, R.Y.; Lenz, R.K. A new technique for fully autonomous and efficient 3D robotics hand/eye calibration. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1989, 5, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Stachniss, C. Extrinsic multi-sensor calibration for mobile robots using the Gauss-Helmert model. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 1490–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, S.; Luettel, T.; Wuensche, H.J. Odometry based online extrinsic sensor calibration. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 1287–1292. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, E.A.; Van Der Merwe, R. The unscented Kalman filter. The unscented Kalman filter. In Kalman Filtering and Neural Networks; Haykin, S., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 221–280. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, Z.; Nieto, J. Motion-based calibration of multimodal sensor extrinsics and timing offset estimation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2016, 32, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mahabadi, N.; Djikic, A.; Nassir, C.; Chatterjee, S.; Fallon, M. Extrinsic calibration and verification of multiple non-overlapping field of view lidar sensors. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 919–925. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; af Klinteberg, L.; Fallon, M.; Chatterjee, S. Observability-aware online multi-lidar extrinsic calibration. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 2860–2867. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kim, C.; Han, Y.; Kim, H.J. Automated extrinsic calibration for 3D LiDARs with range offset correction using an arbitrary planar board. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 5082–5088. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, Z.; Jia, Z.; Guo, S.; Li, J.; Han, S. Extrinsic calibration for multi-LiDAR systems involving heterogeneous laser scanning models. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 44754–44771. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Chung, W. Extrinsic calibration of multiple 3D LiDAR sensors by the use of planar objects. Sensors 2022, 22, 7234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Shi, W.; Fan, W.; Xiang, H. Automatic extrinsic calibration of dual LiDARs with adaptive surface normal estimation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 72, 1000711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Yu, P.; Yang, M.; Wang, C.; Bai, Y.; Yang, F. Extrinsic calibration of dual LiDARs based on plane features and uncertainty analysis. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 11117–11130. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, F. Extrinsic calibration of multiple lidars of small FOV in targetless environments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 2036–2043. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F. A decentralized framework for simultaneous calibration, localization and mapping with multiple LiDARs. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 4870–4877. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, J.; Ye, H.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, M. Robust odometry and map for multi-LiDAR systems with online extrinsic calibration. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 38, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L. A new PHD-SLAM method based on memory attenuation filter. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 095104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhao, X.; Gu, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Han, Y. Multi-Lidar system localization and mapping with online calibration. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Song, H. Targetless extrinsic calibration of multiple LiDARs based on pose graph optimization. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Machine Learning and Computing Applications (ICMLCA), Shenzhen, China, 23–25 February 2024; pp. 311–315. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, D.; Zhang, R.; Huang, S.; Hu, M.; Ding, R.; Qin, X. Versatile multi-lidar accurate self-calibration system based on pose graph optimization. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 4839–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tuzel, O. VoxelNet: End-to-end learning for point cloud based 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4490–4499. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chum, O.; Matas, J. Optimal randomized RANSAC. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotelling, H. Analysis of a complex of statistical variables into principal components. J. Educ. Psychol. 1933, 24, 417–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelsbrunner, H.; Mücke, E.P. Three-dimensional alpha shapes. ACM Trans. Graph. 1994, 13, 43–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biber, P.; Straßer, W. The normal distributions transform: A new approach to laser scan matching. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–31 October 2003; pp. 2743–2748. [Google Scholar]
- Segal, A.; Haehnel, D.; Thrun, S. Generalized-ICP. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), Seattle, WA, USA, 28 June–1 July 2009; pp. 435–442. [Google Scholar]
- Mints, M.O.; Abayev, R.; Theisen, N.; Paulus, D.; von Gladiss, A. Online calibration of extrinsic parameters for solid-state LiDAR systems. Sensors 2024, 24, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Shi, J.; Carlone, L. TEASER: Fast and certifiable point cloud registration. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 37, 314–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

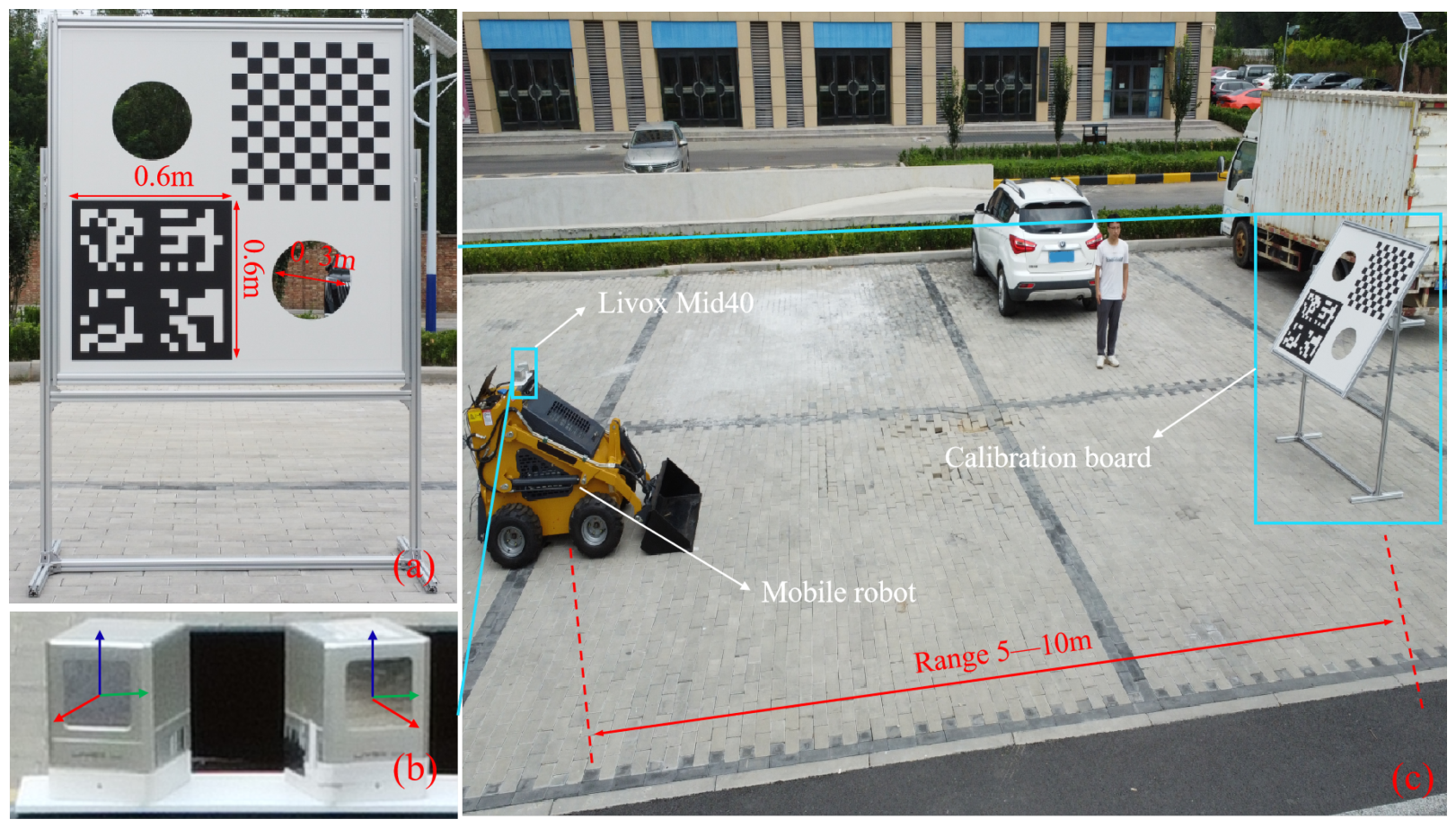
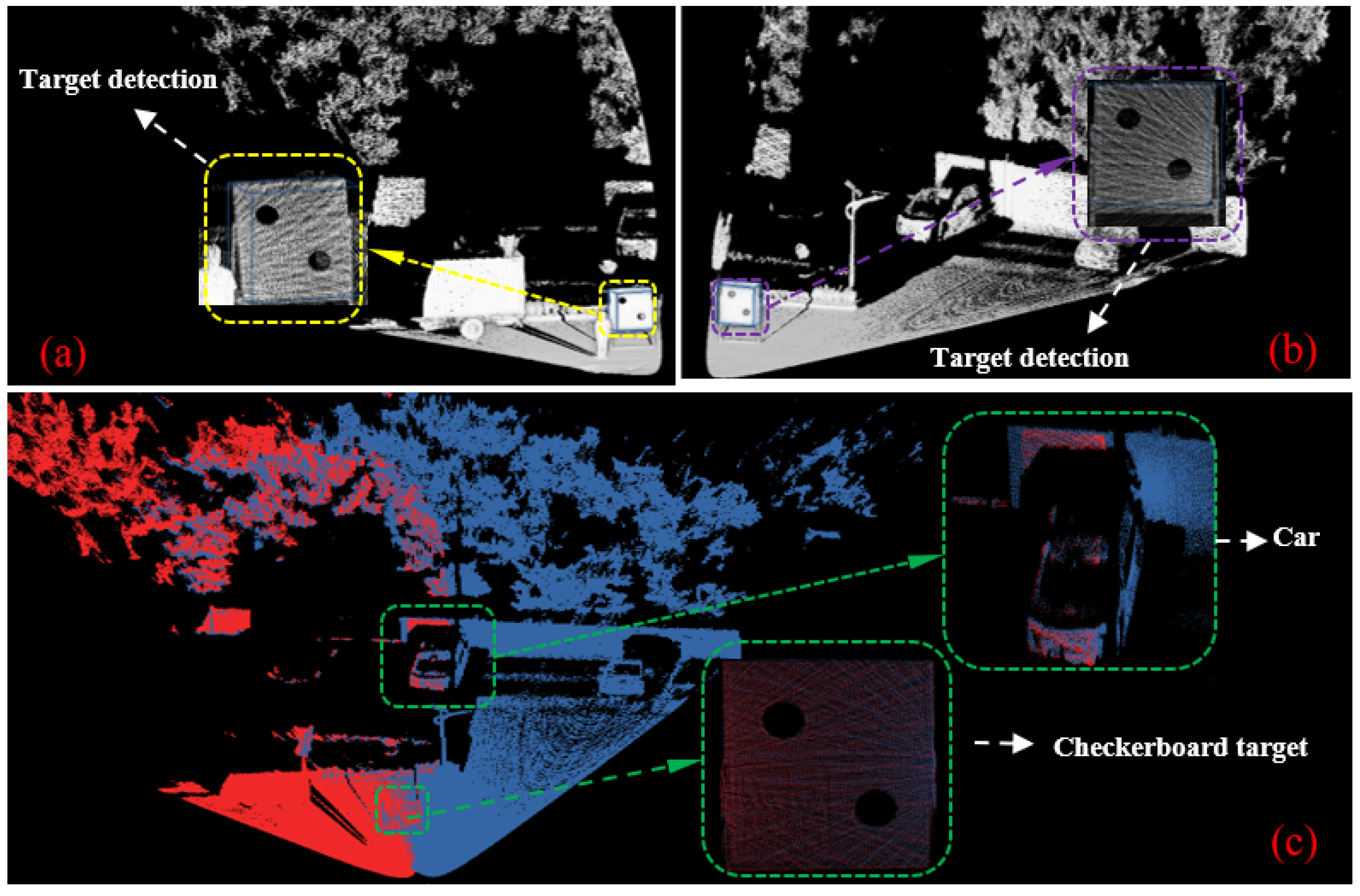
| Method | Key Approaches | Auxiliary Sensor Dependency | Automation Level | Robustness Under FoV Limitations | Drawbacks | Main Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motion-based | Multimodal And Temporal Calibration [13] | LiDAR + GNSS + camera | Fully automatic | Medium | Depends on high-quality motion data | Probabilistic and fully automatic calibration without initialization |
| Observability-aware Calibration [15] | LiDAR + GNSS + IMU | Fully automatic | Medium | Not applicable in indoor environments | Online and continuous optimization | |
| Feature-based | Heterogeneous LiDAR Calibration [17] | LiDAR | Requires manual initialization | Medium | Depends on well-structured scenes | Handles calibration between heterogeneous LiDARs |
| Adaptive Surface Normal Calibration [19] | LiDAR | Requires manual initialization | High | Not applicable in indoor environments | Robust calibration in sparse and poorly structured point clouds | |
| SLAM-based | Pose Graph Calibration [26] | LiDAR | Fully automatic | Low | Unsuitable for high-speed or degenerate scenarios | Achieves globally consistent calibration |
| Versatile Self-Calibration [27] | LiDAR | Fully automatic | Low | Unsuitable for high-speed or degenerate scenarios | Pose graph-based optimization for robust and consistent calibration | |
| Ours | - | LiDAR | Fully automatic | High | Requires a dedicated calibration target | Circle-plane joint optimization enhances calibration in challenging environments |
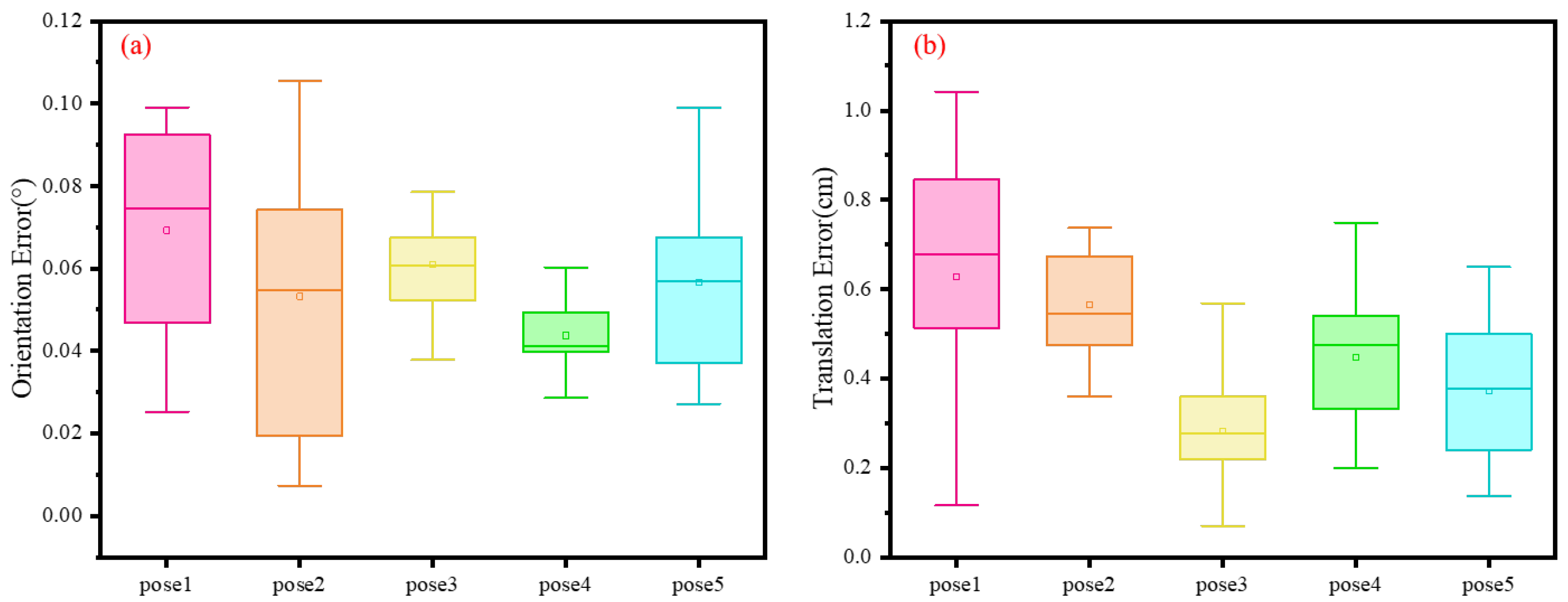
| LiDAR Position | Roll (°) | Pitch (°) | Yaw (°) | X (cm) | Y (cm) | Z (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pose1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 0 |
| pose2 | 0 | 0 | -5 | 0 | 40 | 0 |
| pose3 | 4 | −4 | −4 | 0 | 40 | 0 |
| pose4 | 4 | −4 | −10 | 0 | 40 | 0 |
| pose5 | 8 | −8 | −12 | 0 | 40 | 0 |
| LiDAR Position | No. of Trials | Orientation Error (°) [Median±SD] | Translation Error (cm) [Median±SD] |
|---|---|---|---|
| pose1 | 10 | 0.07458 ± 0.02487 | 0.67825 ± 0.31342 |
| pose2 | 10 | 0.05483 ± 0.03298 | 0.54427 ± 0.12831 |
| pose3 | 10 | 0.06078 ± 0.01236 | 0.27693 ± 0.1427 |
| pose4 | 10 | 0.04111 ± 0.00934 | 0.47408 ± 0.15487 |
| pose5 | 10 | 0.05693 ± 0.02088 | 0.37655 ± 0.17177 |
| Method | NDT | GICP | FGR | TEASER++ | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of Trials | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Avg. Time (s) | 1.193 | 7.002 | 10.701 | 15.606 | 10.062 |
| Roll (°) [Median ± SD] | 0.280 ± 1.184 | 0.012 ± 0.273 | −0.026 ± 0.514 | −0.101 ± 0.131 | −0.011 ± 0.074 |
| Pitch (°) [Median ± SD] | −1.212 ± 1.431 | −0.857 ± 0.264 | −0.631 ± 0.070 | −0.804 ± 0.164 | −0.697 ± 0.033 |
| Yaw (°) [Median ± SD] | 15.174 ± 1.037 | 15.147 ± 0.222 | 14.943 ± 0.149 | 15.108 ± 0.058 | 15.030 ± 0.033 |
| X (°) [Median ± SD] | −0.019 ± 2.314 | −0.050 ± 0.578 | −0.470 ± 0.159 | −0.446 ± 1.123 | −0.386 ± 0.070 |
| Y (°) [Median ± SD] | −10.076 ± 16.836 | −10.056 ± 3.778 | −12.588 ± 2.005 | −10.493 ± 3.141 | −11.878 ± 0.466 |
| Z (°) [Median ± SD] | −9.207 ± 23.233 | −1.336 ± 6.255 | −1.045 ± 1.207 | −1.830 ± 2.700 | −0.195 ± 0.468 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, S.; Liu, J. High-Precision Extrinsic Calibration for Multi-LiDAR Systems with Narrow FoV via Synergistic Planar and Circular Features. Sensors 2025, 25, 6432. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206432
Sun X, Zhang Z, Xu S, Liu J. High-Precision Extrinsic Calibration for Multi-LiDAR Systems with Narrow FoV via Synergistic Planar and Circular Features. Sensors. 2025; 25(20):6432. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206432
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Xinbao, Zhi Zhang, Shuo Xu, and Jinyue Liu. 2025. "High-Precision Extrinsic Calibration for Multi-LiDAR Systems with Narrow FoV via Synergistic Planar and Circular Features" Sensors 25, no. 20: 6432. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206432
APA StyleSun, X., Zhang, Z., Xu, S., & Liu, J. (2025). High-Precision Extrinsic Calibration for Multi-LiDAR Systems with Narrow FoV via Synergistic Planar and Circular Features. Sensors, 25(20), 6432. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206432






