Reliability Assessment of High-Speed Train Gearbox Based on Digital Twin and WHO-WPHM
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. DT Modeling Framework and Theoretical Foundations for High-Speed Train Gearbox Systems
2.1. DT Modeling Framework
2.2. Dynamic Model Reduction Theory
2.2.1. ROM Theory
2.2.2. POD Theory
3. Reliability Assessment Modeling via WHO-Optimized WPHM
3.1. WHO Optimization Algorithm
3.1.1. Population Initialization
3.1.2. Grazing Behavior
3.1.3. Mating Behavior
3.1.4. Population Leadership
3.1.5. Exchange and Selection of Leaders
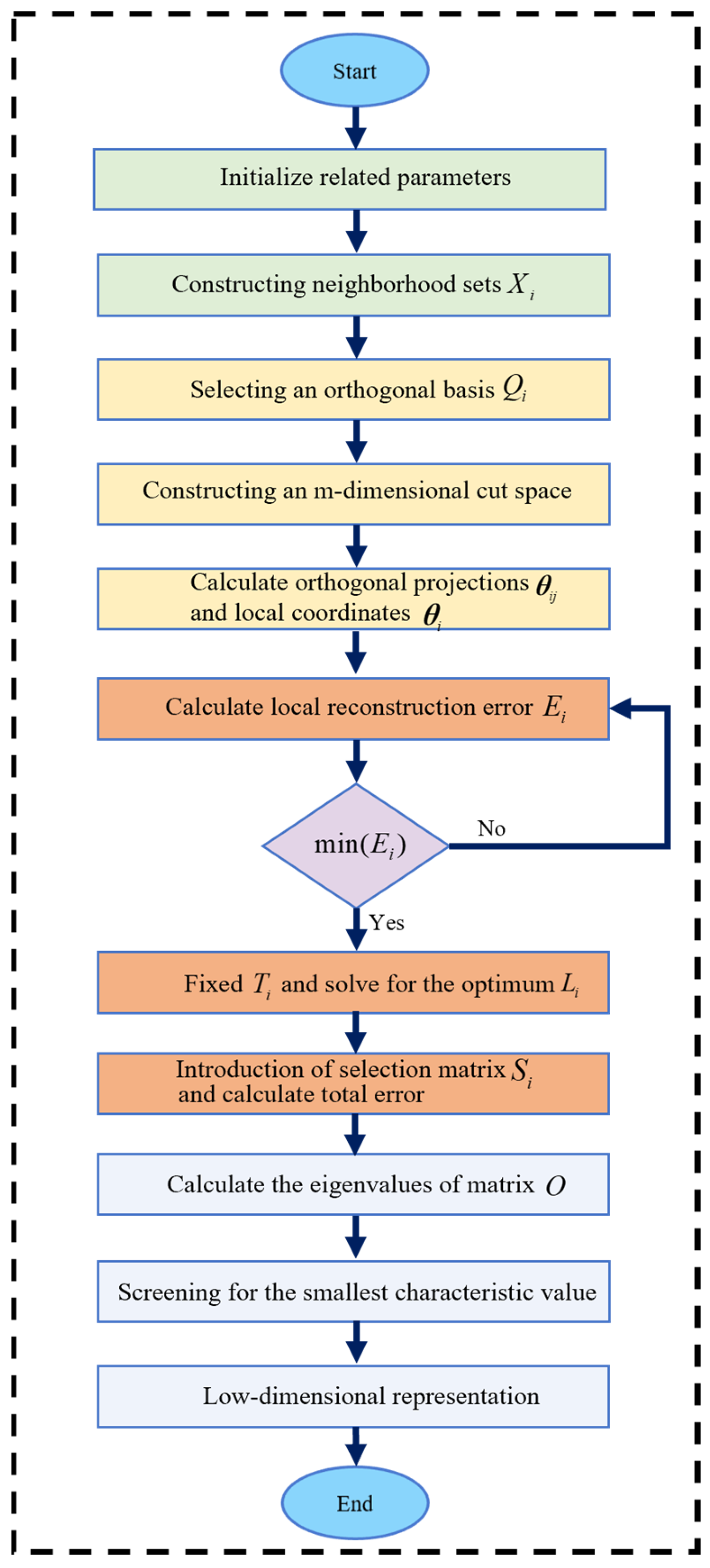
3.2. LTSA Algorithm
3.2.1. Extraction of Local Neighborhood Characteristics
3.2.2. Local Linear Fitting
3.2.3. Local Coordinate Global Arrangement
3.2.4. Determine the Low-Dimensional Global Coordinate Mapping
3.3. Estimation of WPHM Parameters
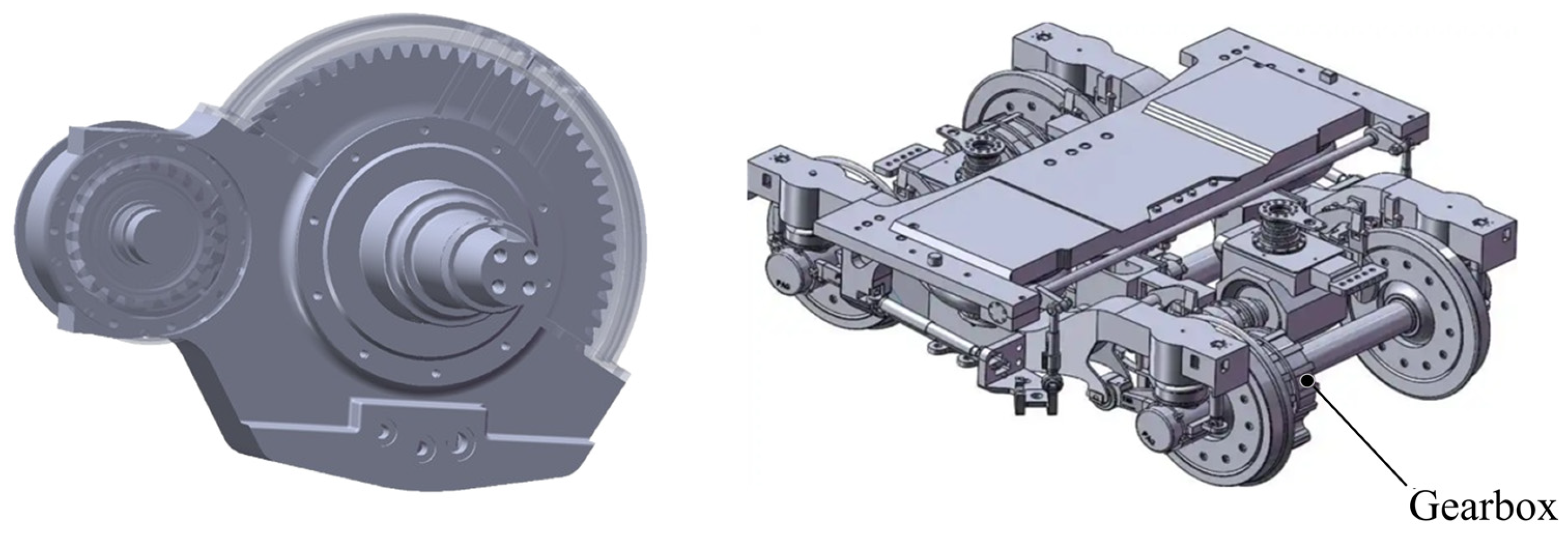
4. Construction of a DT Model for a High-Speed Train Gearbox
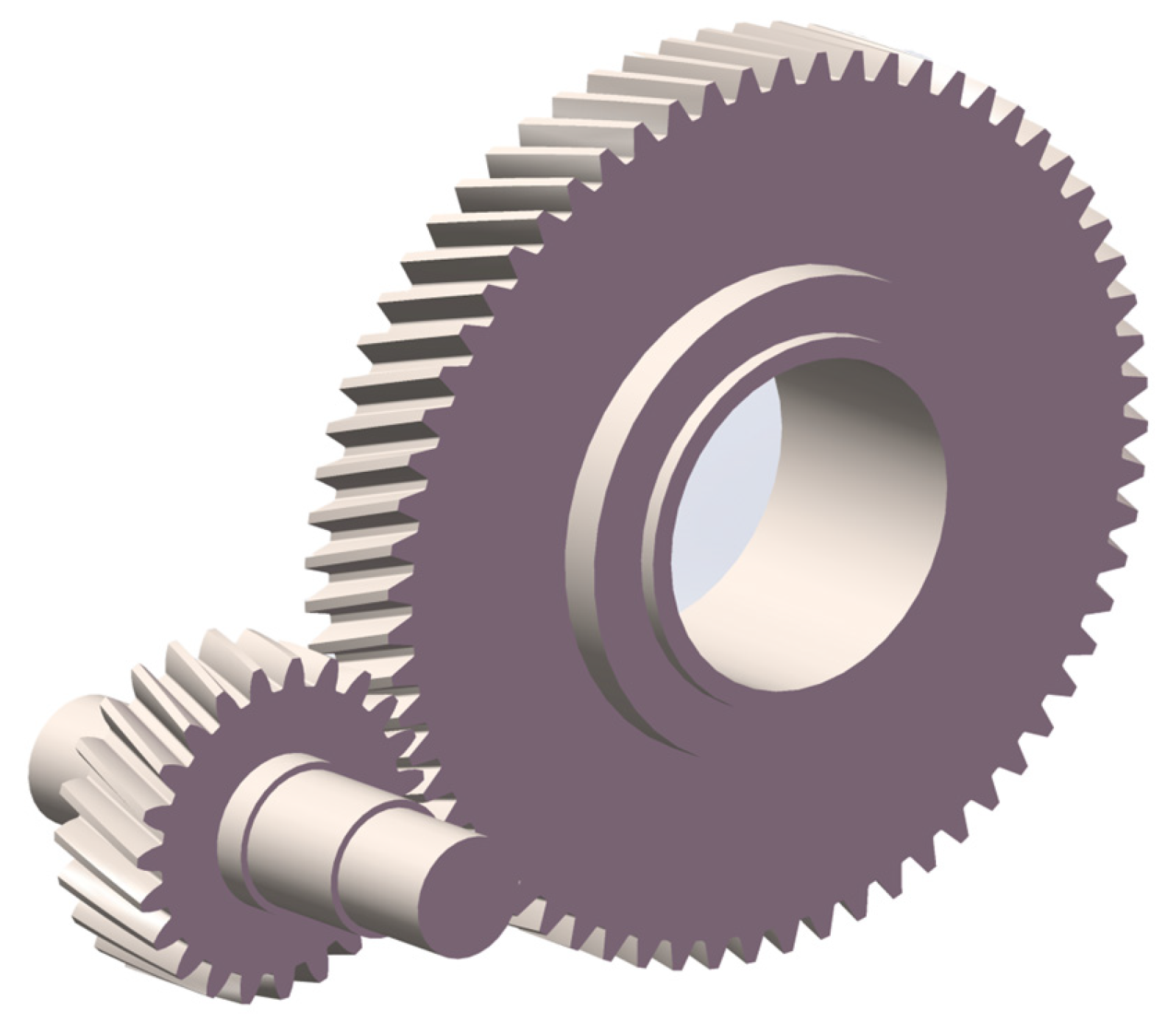
4.1. Geometric Modeling
4.2. Offline Finite Element Simulation Analysis
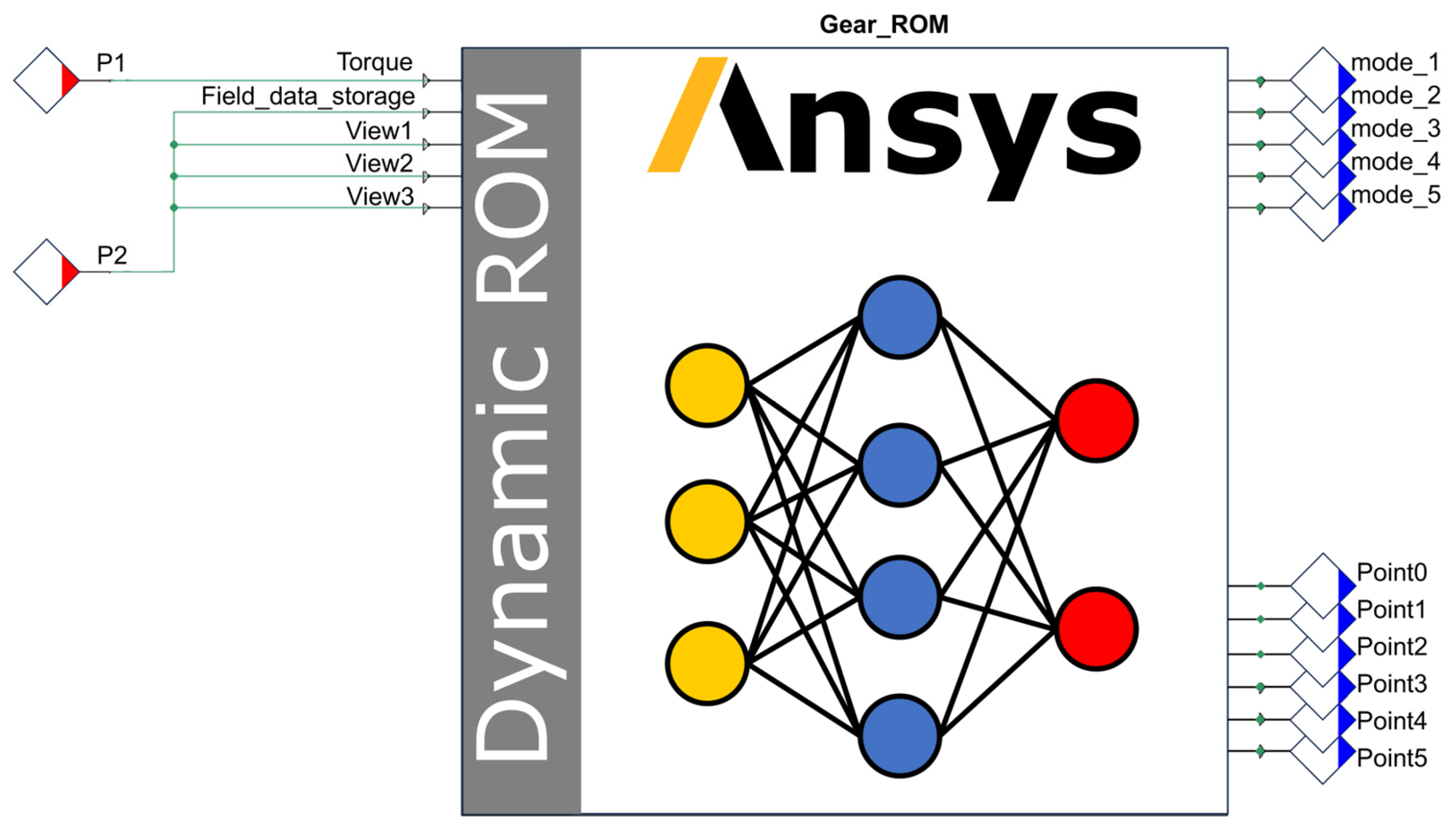
4.3. DT Model Construction
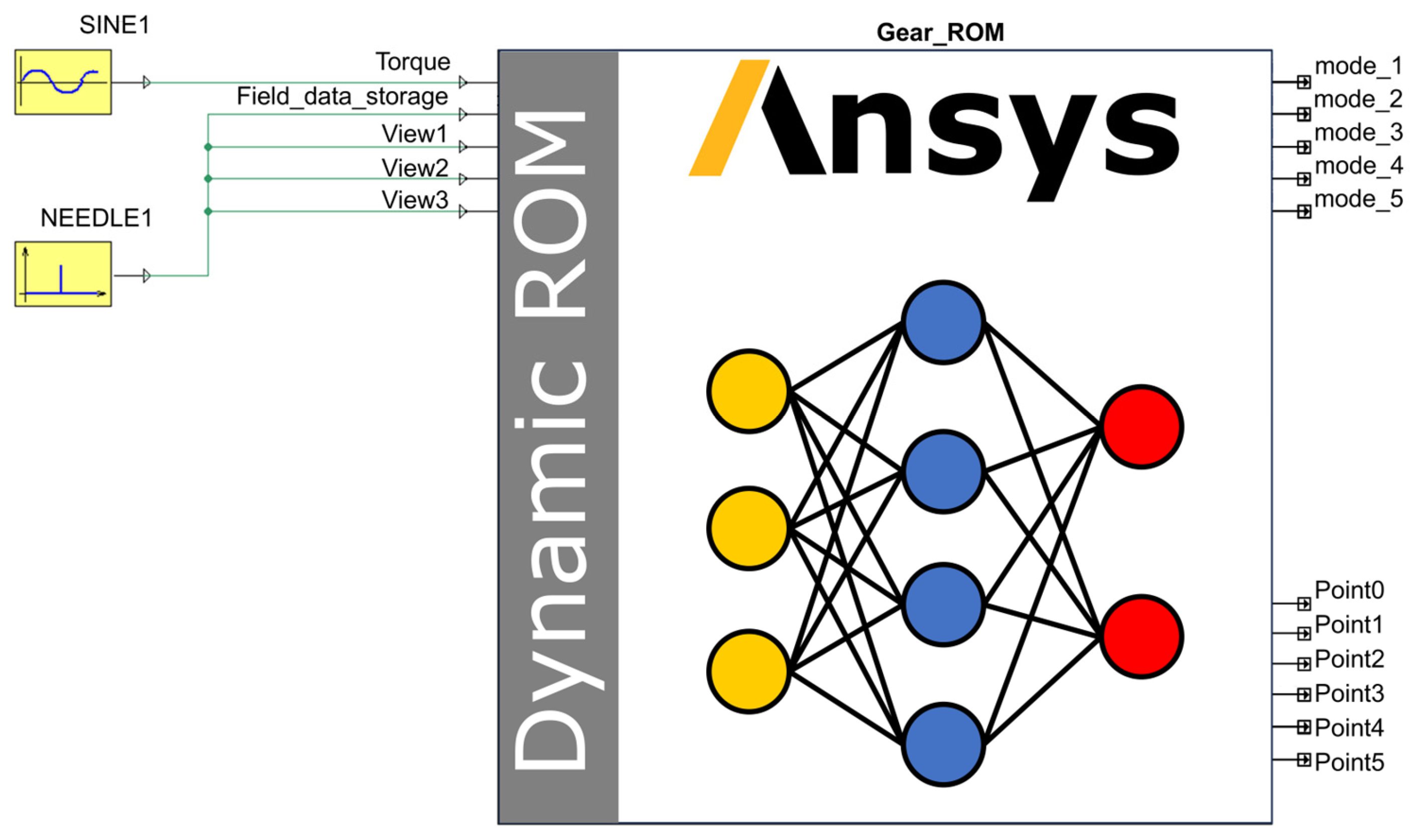
4.3.1. Generate the ROM
4.3.2. Determine the Critical Measurement Points
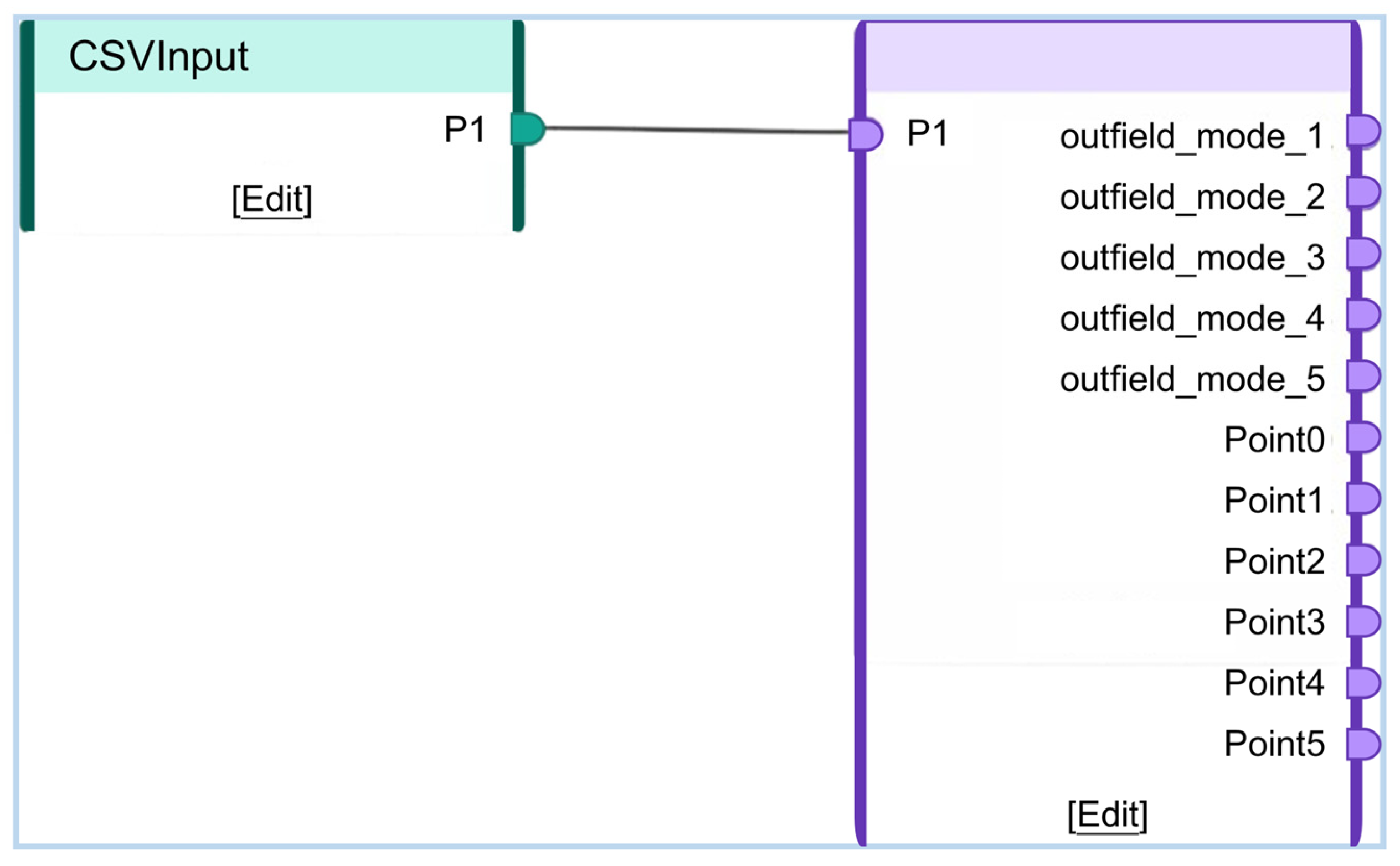
4.3.3. Compiling and Packaging the DT Model
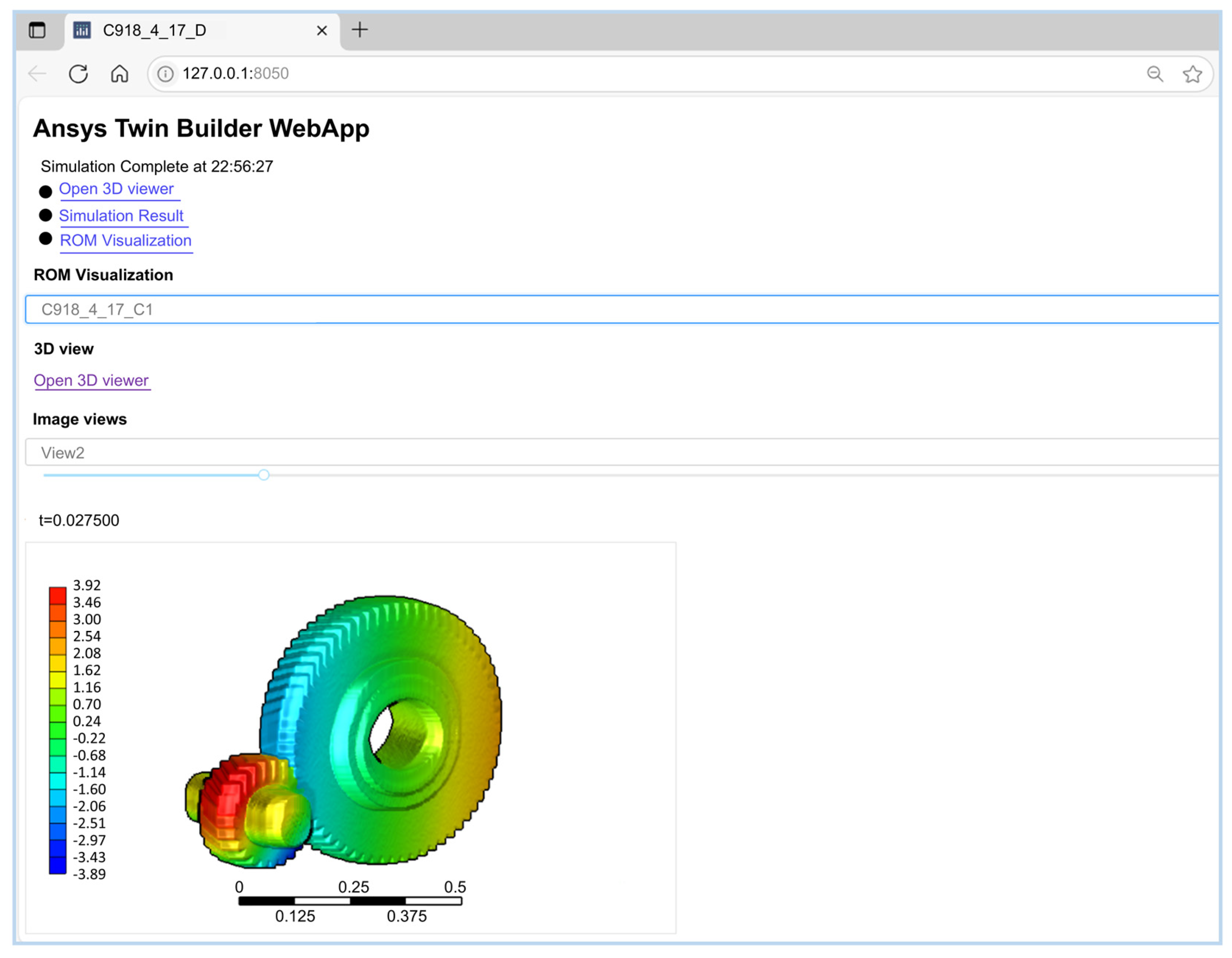
4.4. DT Model Deployment
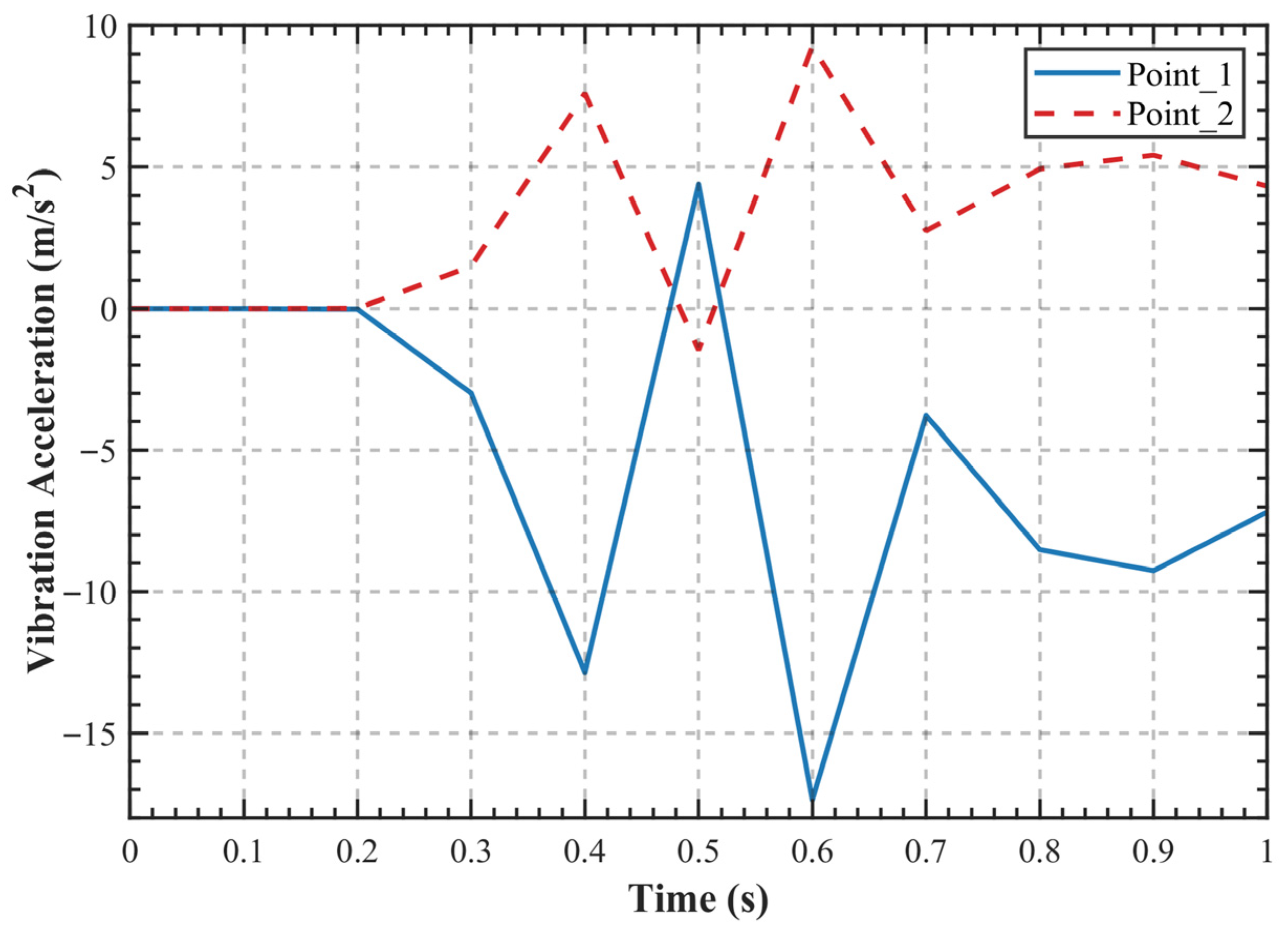
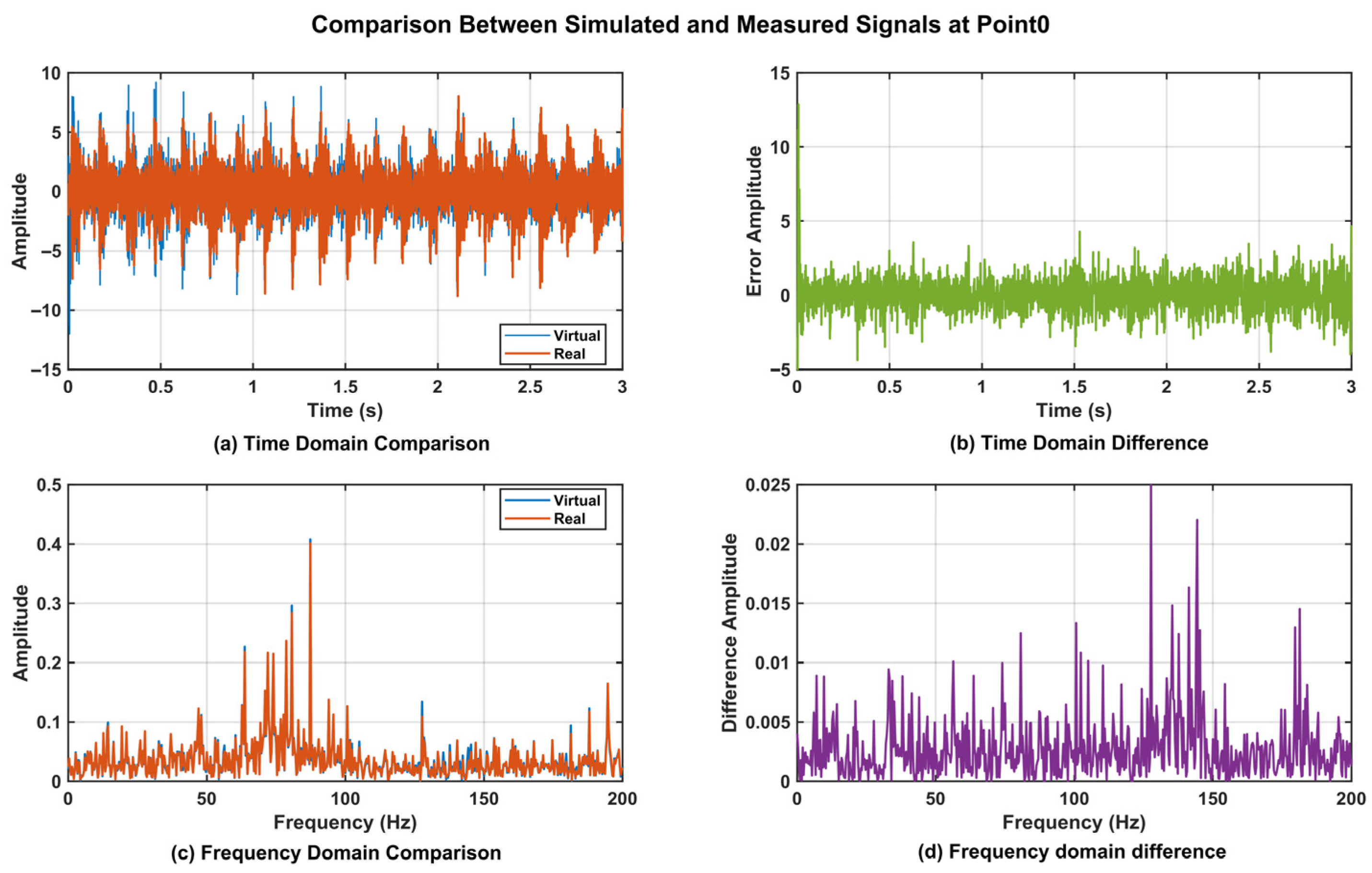
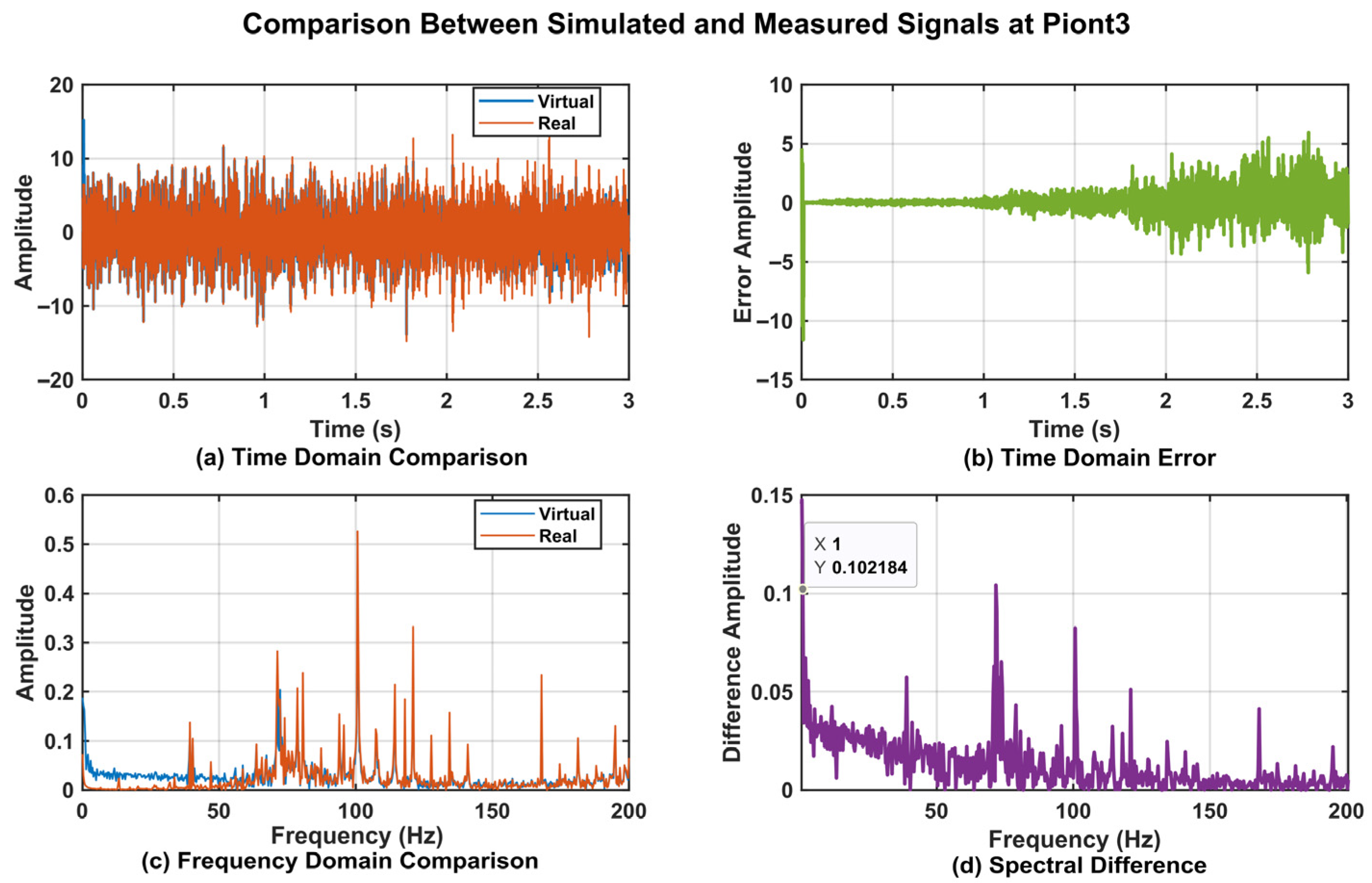
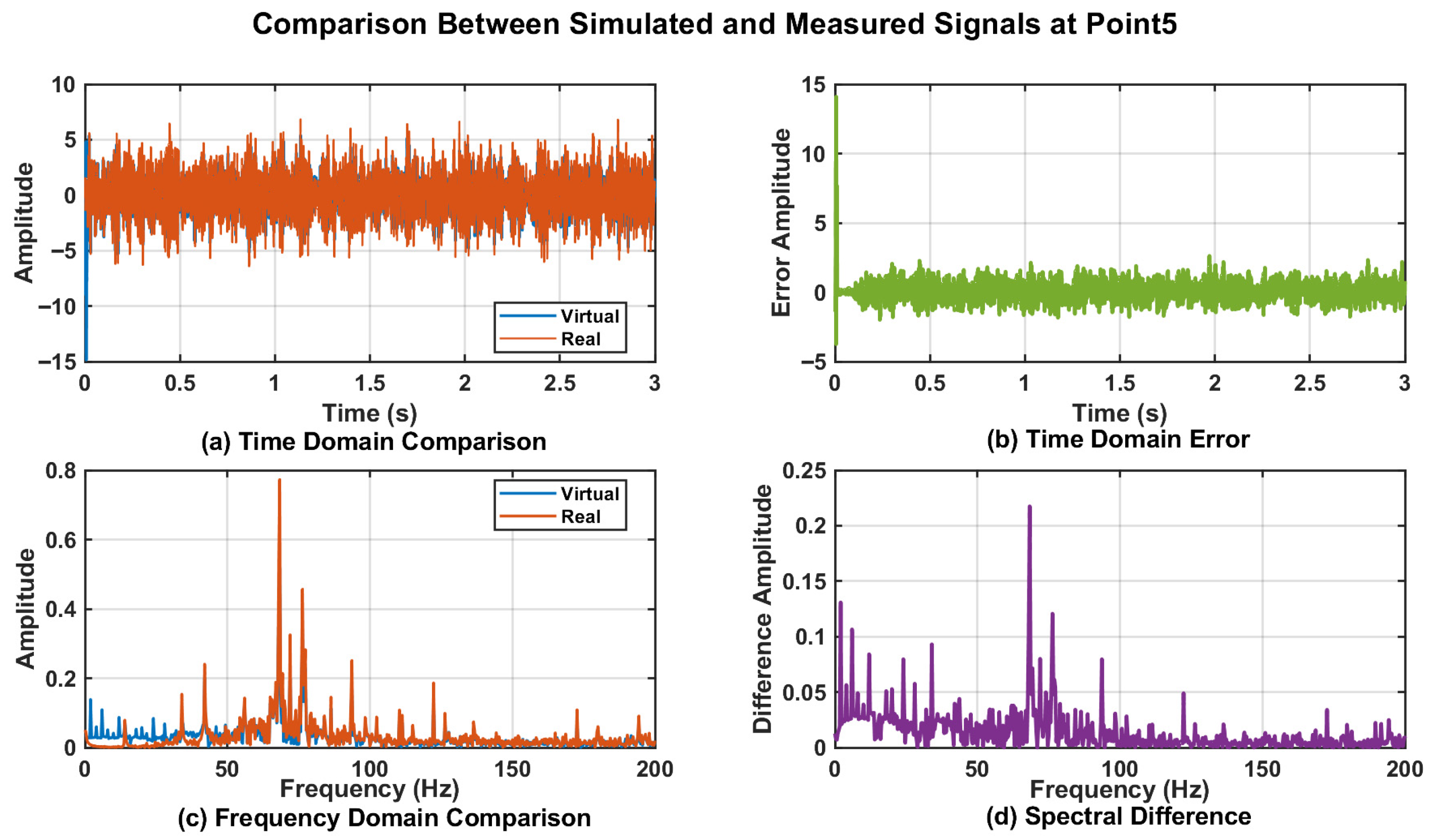
4.5. DT Data Verification
5. Reliability Assessment of High-Speed Train Gearbox
5.1. A Comparison of the Methods Used to Evaluate the Parameters of the WPHM Reliability Model
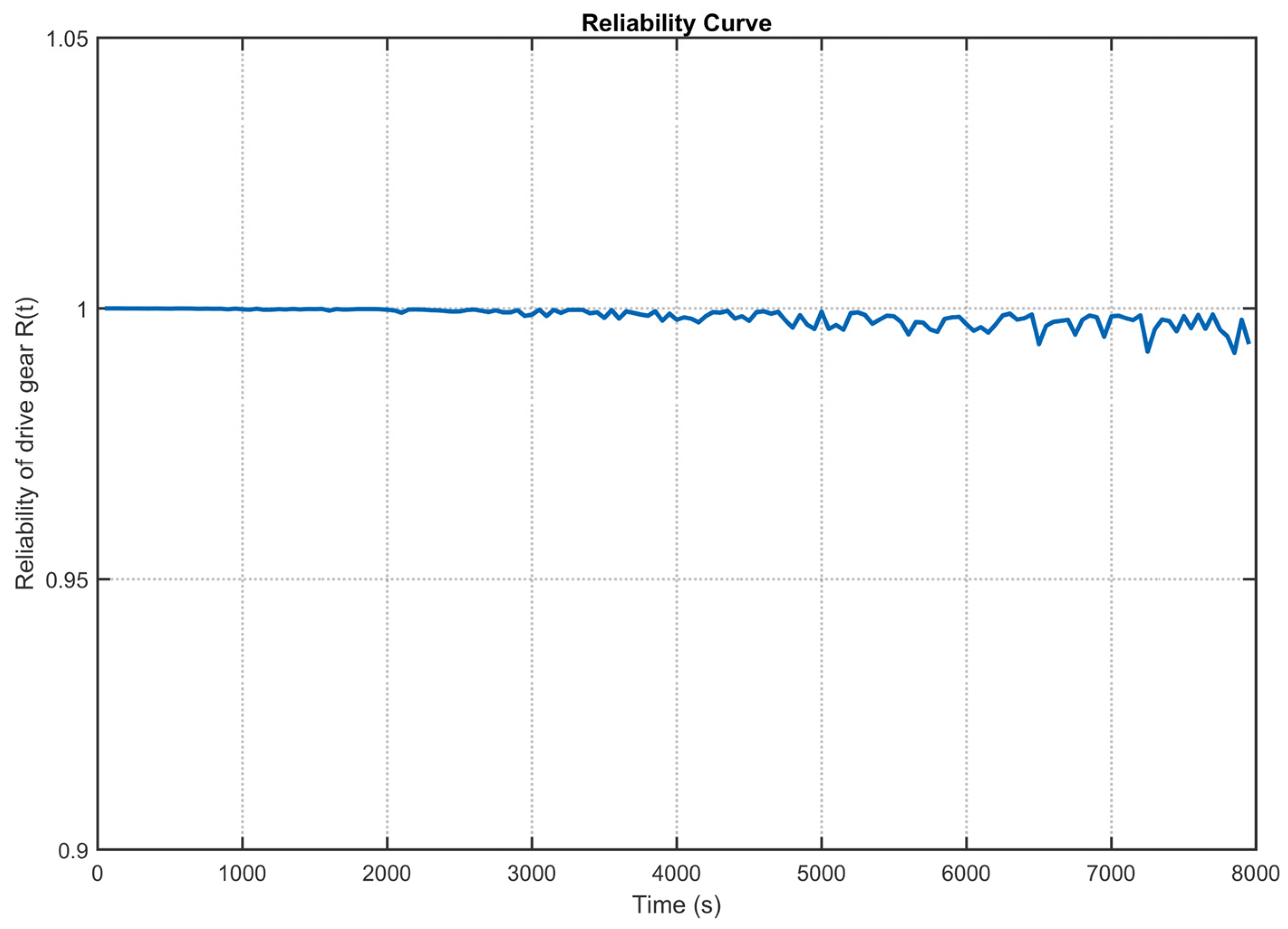
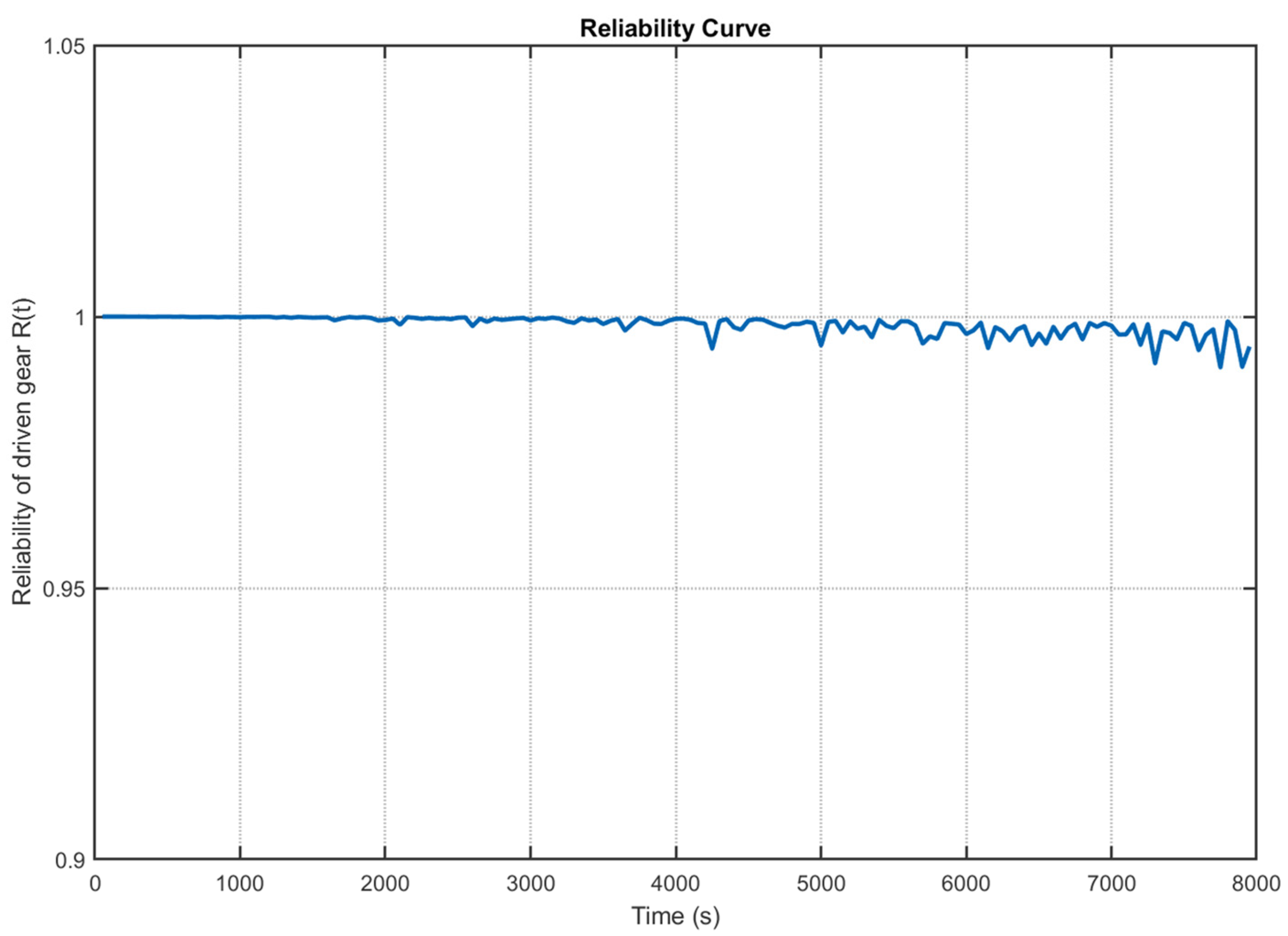
5.2. Reliability Assessment of Key Components in High-Speed Train Gearbox
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, X.; Lian, W.; Zhou, M.; Song, H.; Dong, H. A Digital Twin-Based Fault Diagnosis Framework for Bogies of High-Speed Trains. IEEE J. Radio Freq. Identif. 2023, 7, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Dong, W.; Yin, J.; Sun, K.; Li, S. Application and Practice of Digital Twin Technology in Train System Optimization and Simulation. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Algorithms, Network, and Communication Technology (ICANCT 2024); Marozzo, F., Ed.; SPIE: Wuhan, China, 2025; p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhang, C.; Yang, C.; Chu, H. Data Super-Network Fault Prediction Model and Maintenance Strategy for Mechanical Product Based on Digital Twin. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 177284–177296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Guo, R.; Wang, H.; Zhao, R.; Ning, R.; Huang, Z.; Chu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Gear-Fault Monitoring and Digital Twin Demonstration of Aircraft Engine Based on Piezoelectric Vibration Sensor for Engine Health Management. Nano Energy 2025, 133, 110448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Huang, R.; Chen, Z.; He, G.; Li, W. A Novel Digital Twin-Driven Approach Based on Physical-Virtual Data Fusion for Gearbox Fault Diagnosis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 240, 109542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Ji, J.C.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, Q.; Liu, Z.; Beer, M. Digital Twin-Driven Intelligent Assessment of Gear Surface Degradation. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 186, 109896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matania, O.; Bechhoefer, E.; Bortman, J. Digital Twin of a Gear Root Crack Prognosis. Sensors 2023, 23, 9883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, C.; Yan, R.; Chen, X. Wear State Assessment of External Gear Pump Based on System-Level Hybrid Digital Twin. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 209, 111123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ran, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Mu, Z.; Zhi, S. A Digital Twin-Driven Hybrid Approach for the Prediction of Performance Degradation in Transmission Unit of CNC Machine Tool. Rob. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2022, 73, 102230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, H. A Digital Twin-Based State Monitoring Method of Gear Test Bench. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, D.; Hou, L.; Luo, J.; Liu, F.; Qin, Y. The Meta-Defect-Detection System for Gear Pitting Based on Digital Twin. Adv. Eng. Inf. 2023, 56, 102003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Bao, S.; Jiang, R. Fault Diagnosis of Wind Turbine Planetary Gear Based on a Digital Twin. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, X.; Sun, W.; Wang, B. Intelligent Operation and Maintenance of Wind Turbines Gearboxes via Digital Twin and Multi-Source Data Fusion. Sensors 2025, 25, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wei, J.; Wu, P.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y. Dynamic Response Analysis of High-Speed Train Gearboxes Excited by Wheel out-of-Round: Experiment and Simulation. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2025, 63, 1478–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zio, E.; Zhang, C.; Dui, H.; Chen, R. Model-Guided System Operational Reliability Assessment Based on Gradient Boosting Decision Trees and Dynamic Bayesian Networks. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2025, 259, 110949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ErDong, X.; FuPing, Z.; Kun-Chieh, W.; ChunRong, W.; Hao, G. A Novel Reliability Analysis Methodology Based on IPSO-MCopula Model for Gears with Multiple Failure Modes. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2024, 16, 16878132241228194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, W.; Gao, J. Reliability Modeling of Wind Turbine Gearbox System Considering Failure Correlation under Shock–Degradation. Sensors 2025, 25, 4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T. Dynamic Reliability Modeling of Gear Transmission System Considering Multiple Failure Modes Based on Copula Functions. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2025, 39, 5131–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Dynamic Reliability Evaluation of High-Speed Train Gearbox Based on Copula Function. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 51792–51803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Reliability Assessment and Prediction of Rolling Bearings Based on Hybrid Noise Reduction and BOA-MKRVM. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 116, 105391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, B.; Huang, Q.; Gao, S. A Reliability Assessment Method for Rolling Bearings under Variable Speed and Variable Load Conditions. Measurement 2025, 253, 117571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Guo, J.; Wan, J.-L.; Wang, J.; Zan, X. A Reliability Evaluation Model of Rolling Bearings Based on WKN-BiGRU and Wiener Process. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2022, 225, 108646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y. Operational Reliability Evaluation and Prediction of Rolling Bearing Based on Isometric Mapping and NoCuSa-LSSVM. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 201, 106968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naruei, I.; Keynia, F. Wild Horse Optimizer: A New Meta-Heuristic Algorithm for Solving Engineering Optimization Problems. Eng. Comput. 2022, 38, 3025–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, T.; Lin, T. Novel Mathematical Modelling Method for Meshing Impact of Helical Gear. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 152, 103949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanović, M.; Klimenta, D.; Panić, M.; Klimenta, J.; Perović, B. An Application of Wild Horse Optimizer to Multi-Objective Energy Management in a Micro-Grid. Electr. Eng. 2022, 104, 4521–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







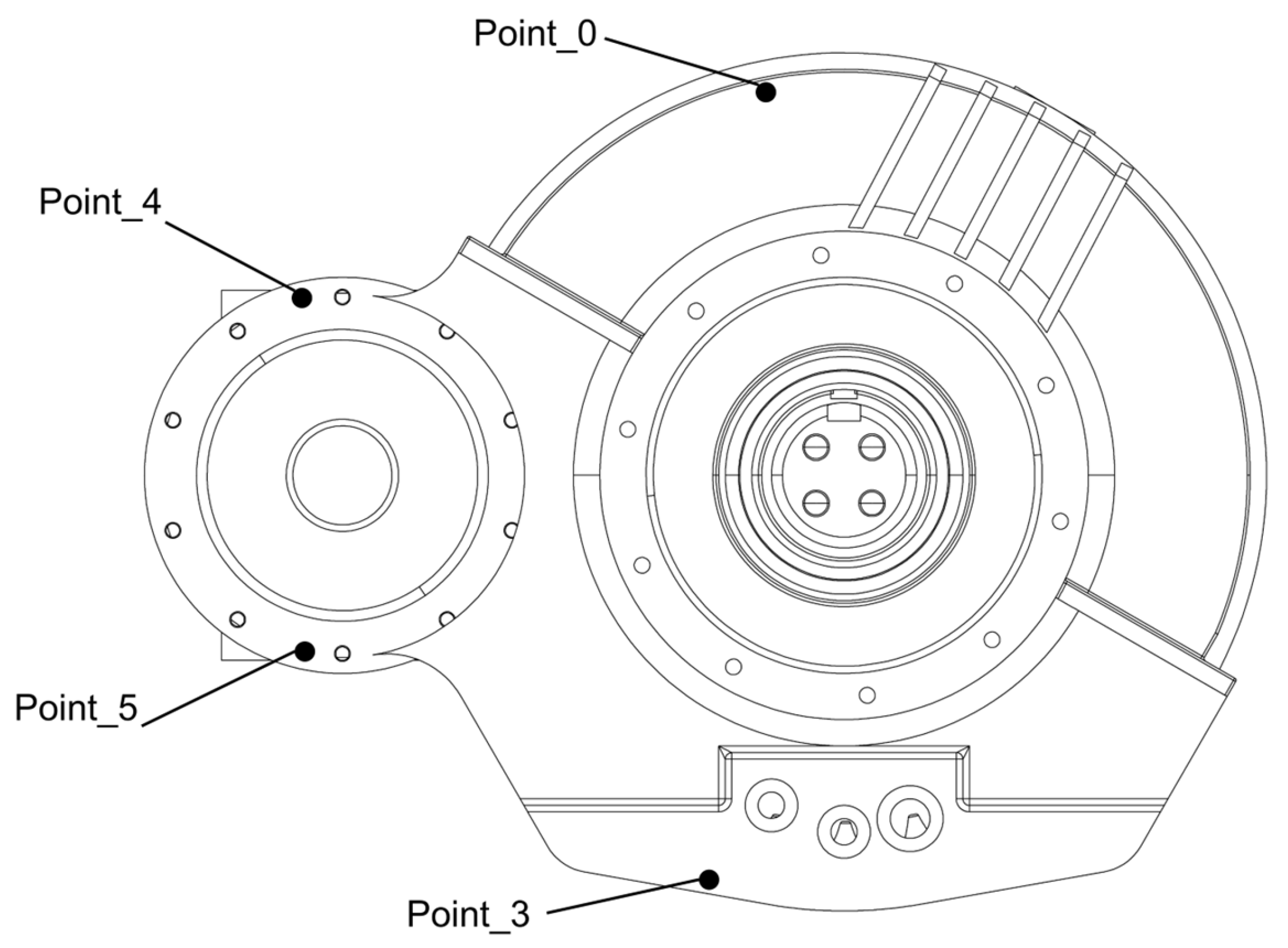



| Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of teeth on the drive gear | 23 | Number of teeth on the driven gear | 64 | Tooth top coefficient | 1 |
| Normal displacement coefficient of the drive gear | 0.45 | Normal displacement coefficient of the driven gear | −0.20 | Root coefficient | 0.25 |
| Modulus | 8 | Helix angle | 23 | Pressure angle | 20 |
| Tooth width | 70 mm | Center distance | 378 mm |
| Measurement Point | Cosine Similarity | RMSE | Cross-Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|
| Point_0 | 0.878 | 5.147% | 0.879 |
| Point_3 | 0.962 | 3.935% | 0.963 |
| Point_4 | 0.934 | 3.727% | 0.935 |
| Point_5 | 0.939 | 3.886% | 0.940 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of iterations | 100 |
| Population size | 300 |
| Crossover type | Mean |
| Crossover percentage | 0.1 |
| Stallions percentage | 0.2 |
| Algorithm Type | Fitness Value |
|---|---|
| WOA | 36.484 |
| HHO | 36.523 |
| WHO | 36.459 |
| WPHM Parameters | Drive Gear | Driven Gear |
|---|---|---|
| 1.8370 | 1.8370 | |
| 42,574.116 | 44,683.941 | |
| 0.502 | 0.589 | |
| −0.170 | 1.105 | |
| 0.247 | 0.918 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Lv, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Yan, Q. Reliability Assessment of High-Speed Train Gearbox Based on Digital Twin and WHO-WPHM. Sensors 2025, 25, 6418. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206418
Wang T, Chen Y, Li S, Lv J, Liu Y, Yang J, Yan Q. Reliability Assessment of High-Speed Train Gearbox Based on Digital Twin and WHO-WPHM. Sensors. 2025; 25(20):6418. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206418
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tengfei, Yun Chen, Siying Li, Jinhe Lv, Yumei Liu, Jinyu Yang, and Qiushi Yan. 2025. "Reliability Assessment of High-Speed Train Gearbox Based on Digital Twin and WHO-WPHM" Sensors 25, no. 20: 6418. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206418
APA StyleWang, T., Chen, Y., Li, S., Lv, J., Liu, Y., Yang, J., & Yan, Q. (2025). Reliability Assessment of High-Speed Train Gearbox Based on Digital Twin and WHO-WPHM. Sensors, 25(20), 6418. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25206418






