1. Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases remain a leading cause of death worldwide, showing a significant increase in the number of fatalities over the last three decades. In 2021, the mortality rate from CVD reached over 19 million globally, up from approximately 12 million in 1990. The early and accurate detection of CVDs is crucial for improving patient outcomes and reducing the burden on healthcare systems [
1]. Electrocardiograms (ECGs) are widely used for diagnosing heart-related abnormalities, as they provide a non-invasive and cost-effective way to monitor the heart’s electrical activity. However, the utility of ECG signals is often compromised by various types of noise, which can obscure critical diagnostic information.
The modern lifestyle, characterized by increased nocturnal activity, high work pressure, lack of exercise, and unhealthy dietary habits, has led to an increase in the incidence of chronic diseases, particularly heart diseases, at younger ages. Regular health check-ups have thus become crucial, and ECG serves as an effective, non-invasive tool for monitoring heart function. However, ECG signals are often weak and susceptible to various noise types, such as baseline wander (BW), muscle artifacts (MAs), electrode motion (EM) [
2], and power line interference (PLI) [
3]. This noise can significantly affect diagnostic accuracy and increase healthcare costs. Traditional signal processing techniques, such as adaptive filtering [
4,
5,
6], have been employed to mitigate noise in ECG signals. Rahman et al. [
4] proposed efficient and simplified adaptive noise cancelers for ECG signals, designed for sensor-based remote health monitoring, achieving significant noise reduction while maintaining computational efficiency. Sharma et al. [
5] introduced an adaptive filter using the LMS algorithm to effectively reduce noise in ECG signals, demonstrating its efficiency in enhancing signal clarity in real-time applications. Shaddeli et al. [
6] extended this concept by incorporating a variable step-size least mean square (LMS) algorithm optimized with evolutionary algorithms, improving adaptability to dynamic noise conditions.
However, when dealing with more complex signal structures or nonlinear dynamic systems, adaptive filtering alone may not sufficiently separate target signals from noise. To address these challenges, advanced signal decomposition techniques such as empirical mode decomposition (EMD) [
7] and wavelet transform (WT) [
8,
9] have been developed to offer more robust solutions for ECG denoising. EMD adaptively decomposes a signal into a series of Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMFs), each representing oscillatory modes at different frequency bands. An integrated EMD adaptive threshold denoising method (IEMD-ATD) [
7] has been proposed to improve decomposition quality and stability in ECG processing. This approach combines complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise (CEEMDAN) to effectively reduce noise in ECG signals. Wavelet transform-based techniques have also shown promise for ECG noise reduction. In contrast to EMD, DWT uses mathematically defined wavelet bases to decompose signals. Through multi-resolution analysis, DWT separates a signal into low-frequency and high-frequency components across different scales. Supraja et al. [
8] demonstrated the effectiveness of wavelet thresholding in enhancing ECG signal quality. Yadav et al. [
9] advanced this technique by applying non-local filtering in the wavelet transform domain, which enhances the preservation of critical ECG features during noise removal. While these methods can improve signal quality to some extent, they often rely on predefined assumptions about noise characteristics and may struggle with complex or overlapping noise sources.
Recently, deep learning approaches have shown great promise in addressing these challenges due to their ability to learn intricate patterns in data without the need for manual feature extraction. In 2008, Vincent et al. [
10] proposed an architecture based on autoencoder (AE), improved into a denoising autoencoder (DAE), which demonstrated better generalization ability than traditional digital signal processing denoising algorithms. Building on this, Peng Xiong et al. [
11] developed a DAE architecture based on Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), utilizing four fully connected layers and sigmoid activation functions in both the encoder and decoder. This architecture offered the advantage of simplicity, but its performance in high-noise scenarios was limited. Chiang et al. [
12] introduced a Fully Convolutional DAE (FCN-DAE), which replaced fully connected layers with convolutional layers, significantly reducing the parameter count and computational cost while maintaining decent denoising capabilities. Despite these advancements, the denoising performance of these architectures remained insufficient in scenarios with strong noise.
To address temporal dependencies in sequential data like ECG signals, Hochreiter et al. [
13] proposed the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural network. Building on this, Dasan et al. [
14] combined LSTM with DAE to propose the CNN-LSTM DAE, embedding an LSTM module in the encoder’s final layer. This hybrid architecture was able to learn temporal correlations within ECG signals, enabling higher-quality signal reconstruction. However, introducing the LSTM module increased the risk of overfitting in high-noise environments, which negatively impacted denoising performance. Jhang et al. [
15,
16] further presented innovations with two architectures: the Low-Memory Shortcut Connection DAE (LMSC-DAE) [
15] and the Channel-wise Average Pooling with Pixel-Shuffle DAE (CPDAE) [
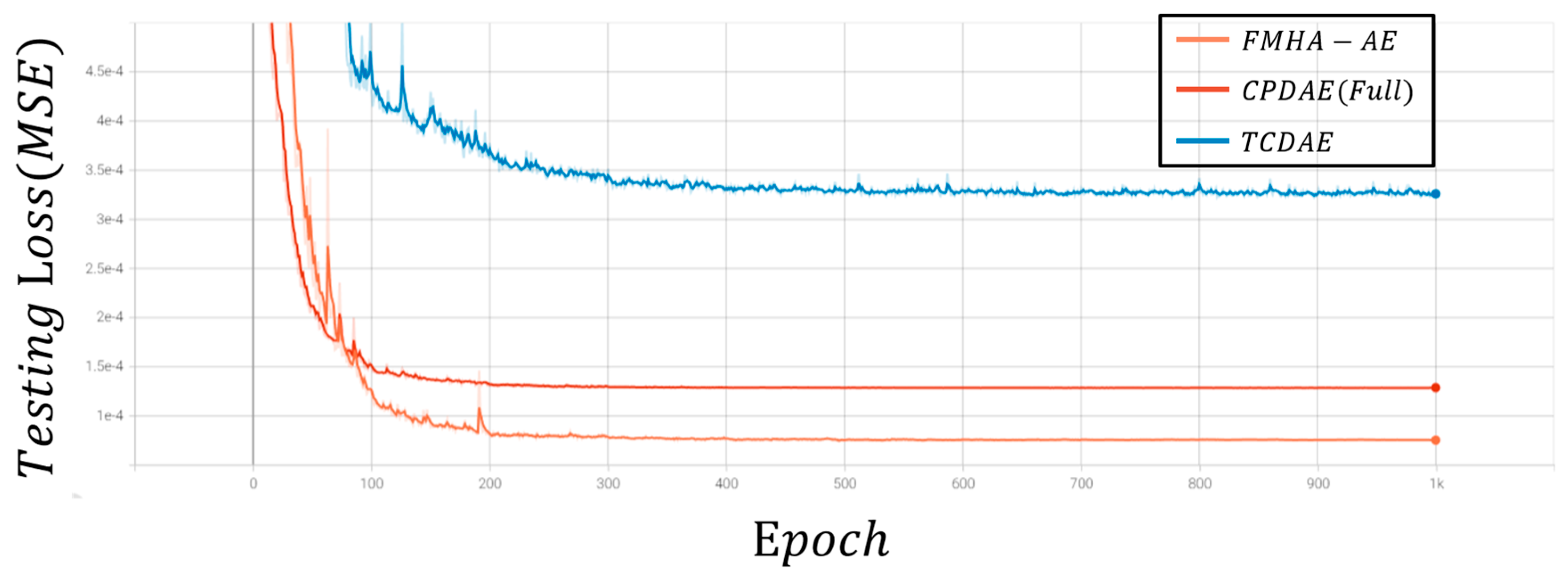
16]. Both architectures incorporated shortcut connections in the encoder and decoder, effectively reconstructing high-quality ECG signals and achieving superior denoising performance. Among existing approaches, CPDAE demonstrated the best overall results, but challenges persist in scenarios with significant noise interference.
Additionally, generative adversarial networks (GANs) have also been explored for ECG denoising tasks. GAN-based methods employ a generator-discriminator framework, where the generator attempts to produce clean ECG signals from noisy inputs, and the discriminator evaluates the quality of the reconstructed signals. This adversarial training process encourages the generator to learn a robust mapping for noise removal. Seo et al. [
17] proposed an ECG-GAN framework that successfully denoised ECG signals while preserving critical waveform features. This method achieved superior performance compared to traditional denoising autoencoders and wavelet-based techniques. Wang et al. [
18] proposed an improved conditional GAN (CGAN)-based framework for ECG denoising, which features a generator composed of an optimized convolutional autoencoder and a discriminator with four convolutional layers and one fully connected layer. The results achieved an average signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) exceeding 39 dB for both single and mixed noise scenarios, and improved the classification accuracy of four cardiac diseases by over 32% under severe noise conditions.
Recently, inspired by the transformer architecture initially proposed by Vaswani et al. [
19] for natural language processing, Meng Chen et al. [
20] introduced the transformer-based convolutional denoising autoencoder (TCDAE). This architecture combined a transformer encoder with a convolutional DAE, placing the transformer module in the encoder’s final layer to better capture temporal correlations between features. Compared to CNN-LSTM DAE, TCDAE more effectively incorporated temporal dependencies, which achieves enhanced denoising and reconstruction performance for ECG signals. However, CPDAE still holds an edge in extreme noise scenarios, which indicates that there is still room for improvement in transformer-based approaches.
In summary, advancements in ECG denoising have evolved from traditional filtering techniques to deep learning-based methods, each with unique strengths and limitations. While EMD and DWT improve signal decomposition, they struggle with mode mixing and rely on predefined assumptions about noise characteristics. Deep learning approaches, such as DAEs, have shown promise but often face challenges in generalization under high-noise conditions. GAN-based frameworks improve noise removal and feature preservation but suffer from training instability and high data requirements. Transformer-based architectures effectively capture temporal dependencies but are computationally intensive and less robust in extreme noise scenarios. To address these limitations, this paper introduces a feature-shuffle multi-head attention autoencoder (FMHA-AE), which leverages both feature-shuffling and multi-head self-attention to efficiently remove noise, particularly EM noise, from ECG signals. The proposed model improves signal reconstruction quality and provides a more accurate tool for clinical diagnosis, thus lowering medical costs and improving treatment outcomes. The principal contributions of this work can be summarized as follows:
This study introduces the feature-shuffle multi-head attention autoencoder (FMHA-AE) architecture, a cutting-edge framework designed to address the challenges of ECG signal denoising. It outperforms transformer-based architectures by achieving superior denoising performance, particularly in improving signal-to-noise ratio (SNRimp) and reducing percentage root mean square difference (PRD), which makes it highly effective for removing challenging noise types such as EM noise;
We propose a novel FMHA-AE architecture that incorporates three key components: the feature-shuffle multi-head self-attention (FMHSA) encoder, the multi-head self-attention (MHSA) shortcut, and the feature-shuffle multi-head cross-attention (FMHCA) decoder. This model effectively removes noise, while preserving critical ECG features. By leveraging multi-head attention and feature-shuffling mechanisms, the architecture ensures robust feature extraction and reconstruction, significantly enhancing signal quality for clinical diagnostics;
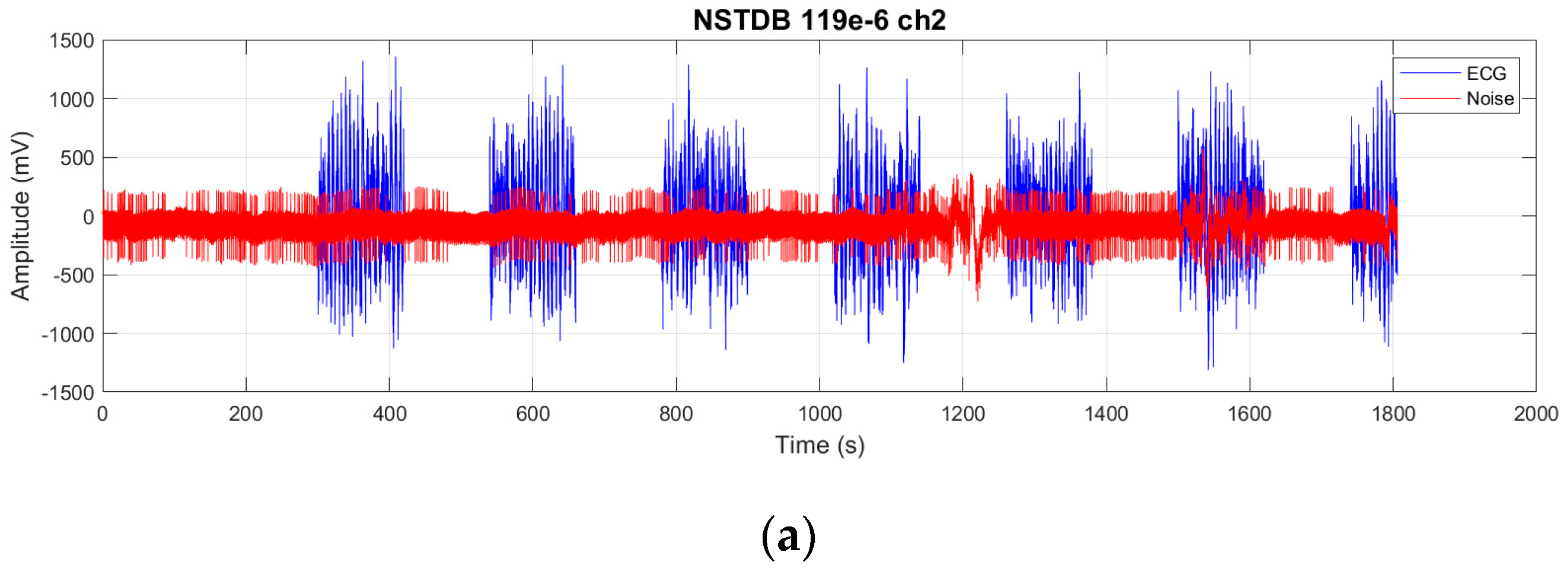
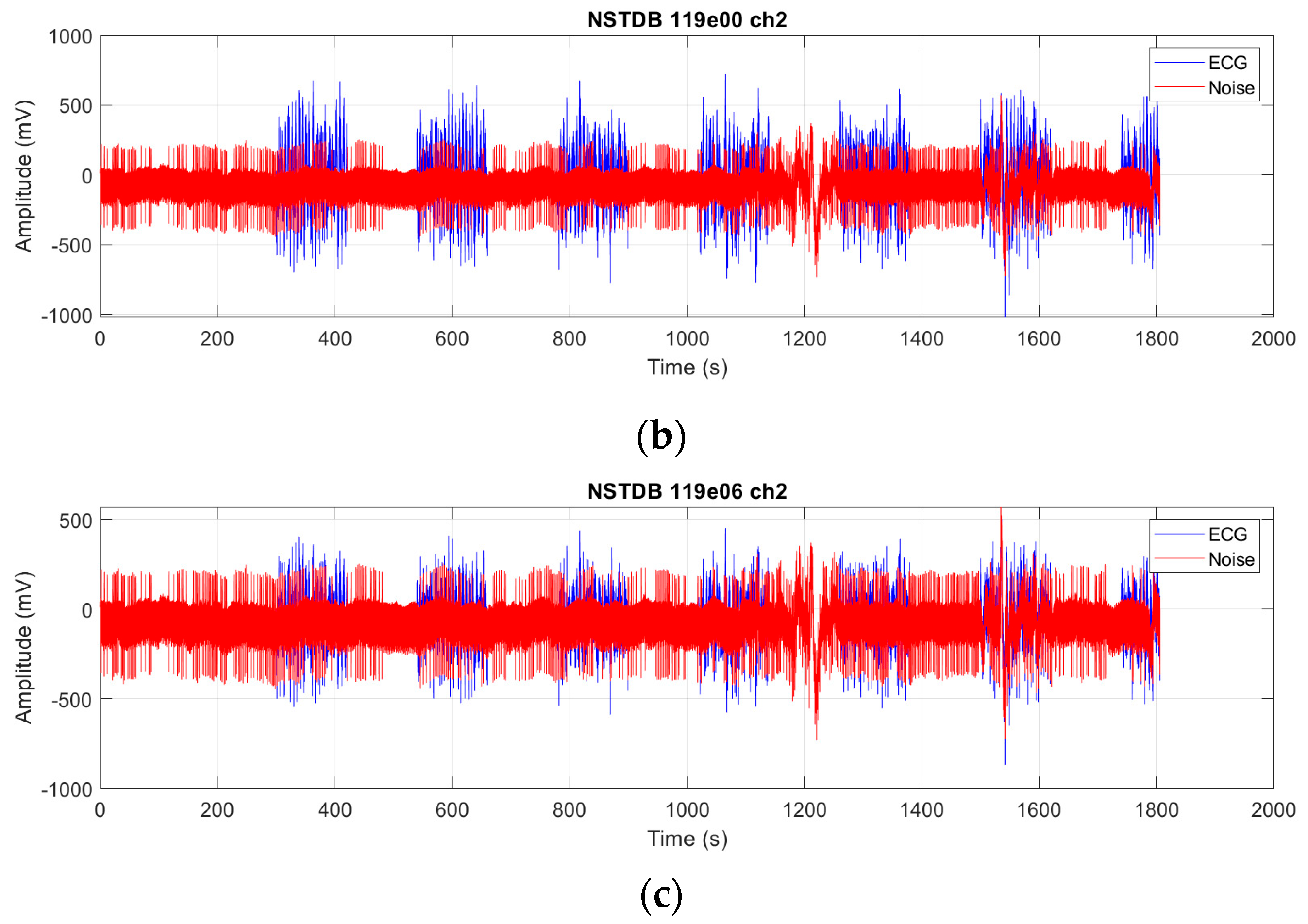
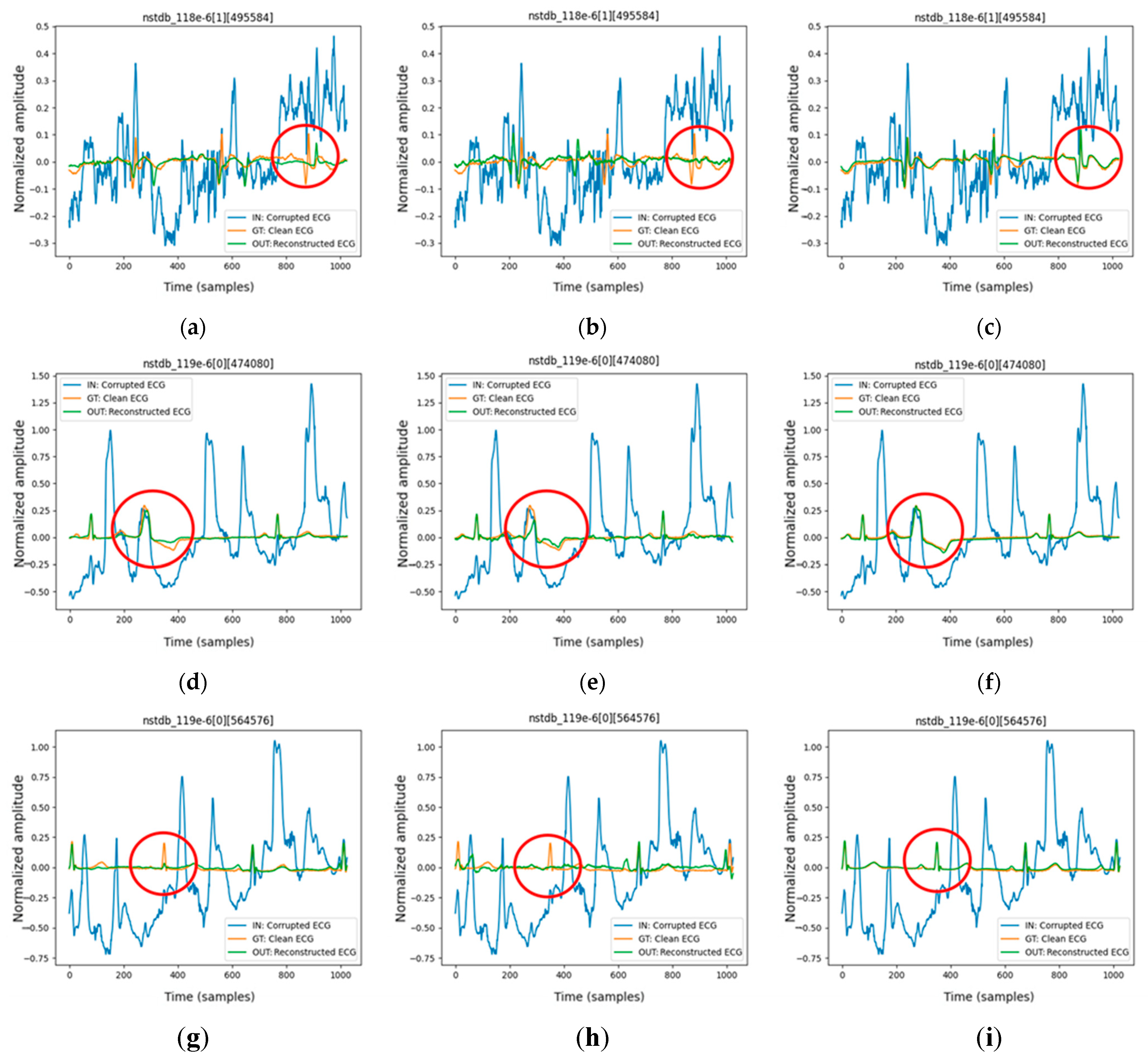
We evaluate the proposed FMHA-AE on MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database (MITDB) [
21] as the source of clean ECG signals and the MIT-BIH Noise Stress Test Database (NSTDB) [
22] for noisy signals. The experimental results demonstrate that the model exhibits exceptional denoising and signal reconstruction capabilities under extremely noisy conditions (SNR
in from −6 to 24 dB), which achieves an average SNR improvement (SNR
imp) of 25.34 dB and a percentage root mean square difference (PRD) of 10.29%, which outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in both signal quality improvement and robustness.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 reviews related works on feature-shuffle and residual blocks.
Section 3 provides a detailed explanation of the proposed FMHA-AE architecture.
Section 4 discusses the datasets, training parameters, and experimental results. Finally,
Section 5 summarizes the findings and concludes the paper.
3. Methods
The feature-shuffling multi-head attention autoencoder (FMHA-AE) is designed to enhance the process of ECG signal denoising by combining feature-shuffling and multi-head self-attention mechanisms. The architecture consists of an encoder-decoder structure where the core components of the model operate in three stages: the feature-shuffle multi-head self-attention (FMHSA) encoder, multi-head self-attention (MHSA) shortcut, and feature multi-head cross-attention (FMHCA) decoder. The model incorporates three distinctive features that contribute to its effectiveness: (1) the integration of residual blocks and feature-unshuffle in the FMHSA encoder to improve feature extraction and noise suppression, (2) the use of MHSA shortcuts to transmit critical feature information across stages, enhancing reconstruction accuracy, and (3) the employment of FMHCA in the decoder to refine the reconstruction process by leveraging cross-attention mechanisms. These features collectively enable the model to address the challenges of noisy ECG signals, as detailed in the subsequent explanation.
Noisy ECG signals are first sent to the input layer to expand the channels. The FMHSA Encoder extracts high-dimensional clean ECG features, which are then reconstructed in the FMHCA Decoder. Additionally, information from the FMHSA Encoder is transmitted to the FMHCA Decoder through the MHSA Shortcut to supplement the progressively reduced feature content, thereby enhancing the reconstruction quality. The FMHSA encoder integrates residual blocks, feature unshuffle, point-wise convolution, and MHSA to enhance noisy ECG signal feature extraction. The residual block mitigates vanishing gradient issues, while feature unshuffle transforms spatial dimensions into higher-dimensional channel representations for effective noise suppression. The MHSA block leverages multi-head mechanisms to capture temporal and spatial dependencies across features, improving robustness in denoising.
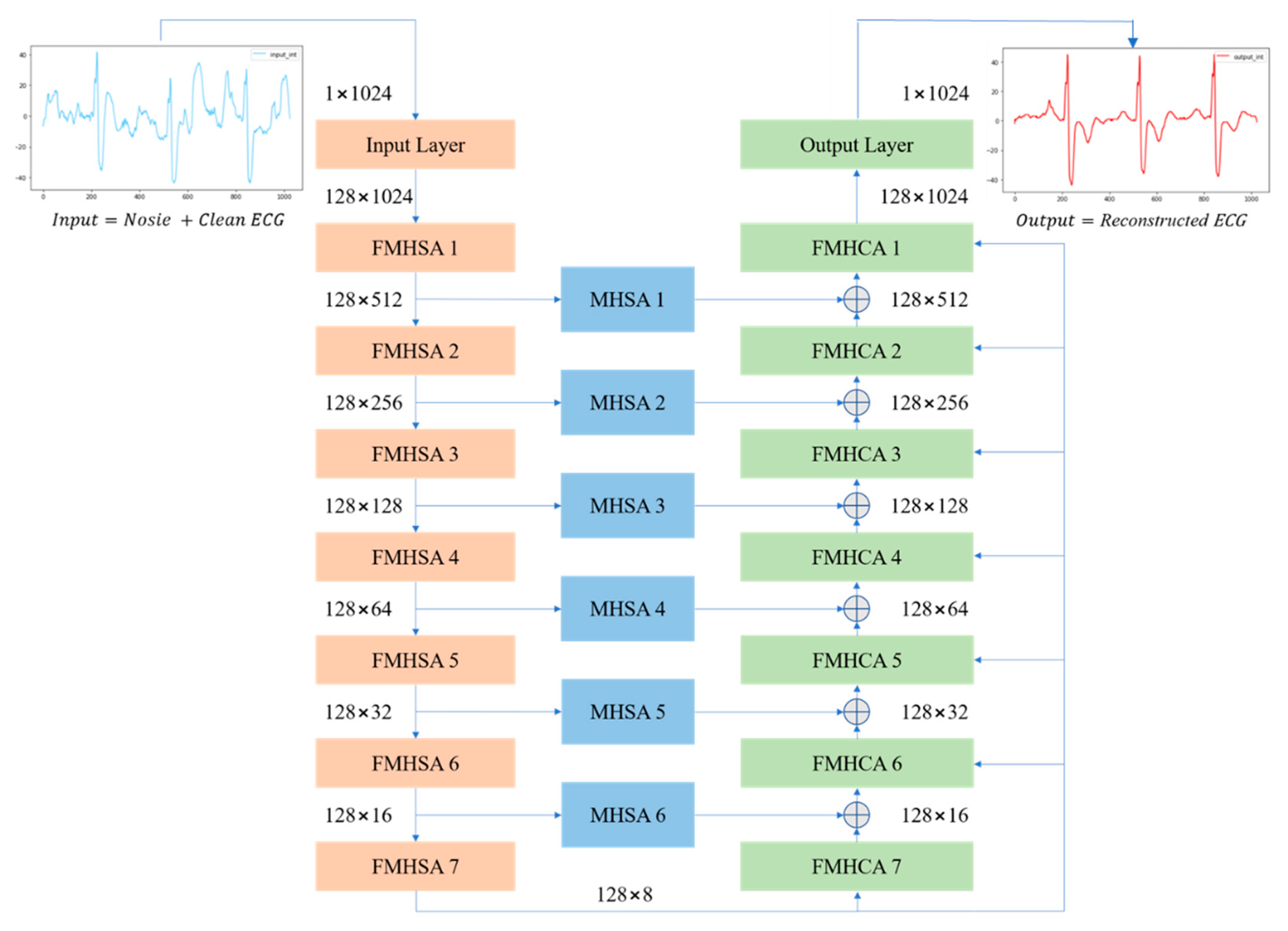
Figure 3 presents an overview of the proposed FMHA-AE model, which contains seven encoders, seven decoders, and six shortcut layers. The noisy ECG signals input size is 1 × 1024, and the feature channels has been expended to 128 through the convolutional layer. The encoder’s output channel size remains at 128, and the feature size has decreased by 50% each layer. After the 7th-layer encoder operation, the feature size is reduced from 1024 to 8. Conversely, the decoder operation process is designed to progressively upsample the feature size, which is double for each layer. After the 7th-layer decoder operation, the feature size is fully restored to its original dimension of 1024. The final output size of the decoder is 128 × 1024, which results in the reconstructed ECG signal with the same spatial resolution as the input. To further enhance the noise reduction performance of the proposed FMHA-AE, a multi-head attention operation is inserted between the encoder and decoder to transfer more feature information which is helpful for the decoder to reconstruct the noise-less ECG signals. The architecture’s design ensures robust feature extraction and reconstruction across multiple stages, as detailed in
Figure 3.
Table 1 summarizes the architecture of the proposed model, which includes the number of trainable parameters, input size, and output size for each layer. The encoder consists of an input layer followed by seven FMHSA encoder blocks, which progressively reduces the temporal dimension by a factor of 2 while maintaining the feature channel dimension at 128. Each FMHSA encoder block has 395,264 trainable parameters. The shortcut connections, which is implemented as MHSA blocks, preserve intermediate representations for multiscale reconstruction and have 198,272 trainable parameters for each block. The decoder, which consists of seven FMHCA decoder blocks, reconstructs the feature dimensions back to the original temporal size, with each block containing 395,392 parameters. The final output layer maps the reconstructed feature space back to the original single-channel signal, with 164,225 parameters. Overall, the proposed model effectively encodes and reconstructs the 1D ECG signal while leveraging hierarchical feature representations and shortcut connections for improved performance.
3.1. Feature-Shuffle Multi-Head Self-Attention (FMHSA) Encoder Architecture Design
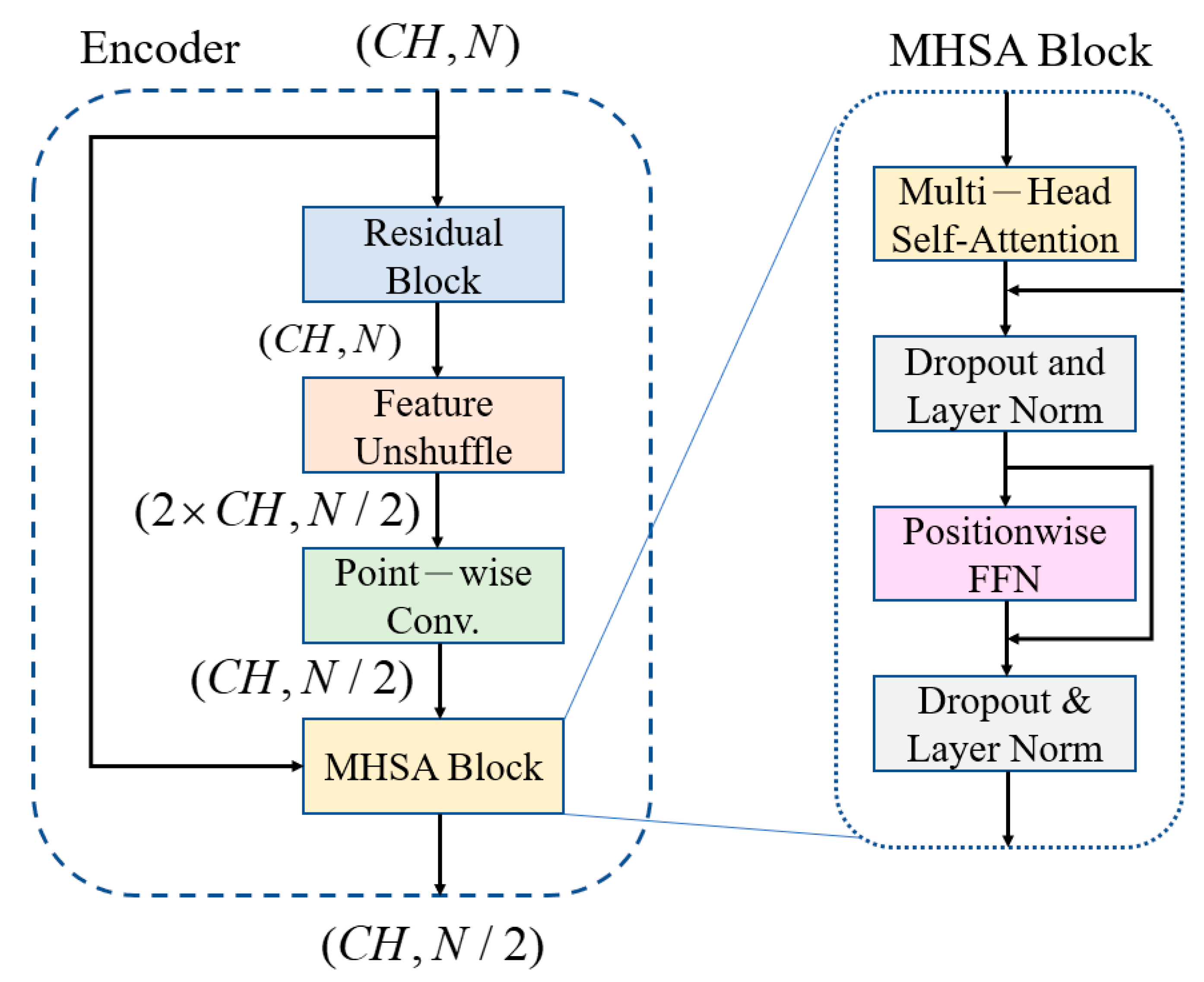
The noisy inputs are fed into an encoder comprising of a convolutional encoder and seven FMHSA encoders, as shown in
Figure 2. First, the input 1 × 1024 noisy ECG signal is fed into the input layer, where a 1 × 1 1D convolution (conv.) is used to expand the channels to 128. After passing through seven FMHSA encoders, 128 × 8 features are obtained. The FMHSA encoder architecture is shown in
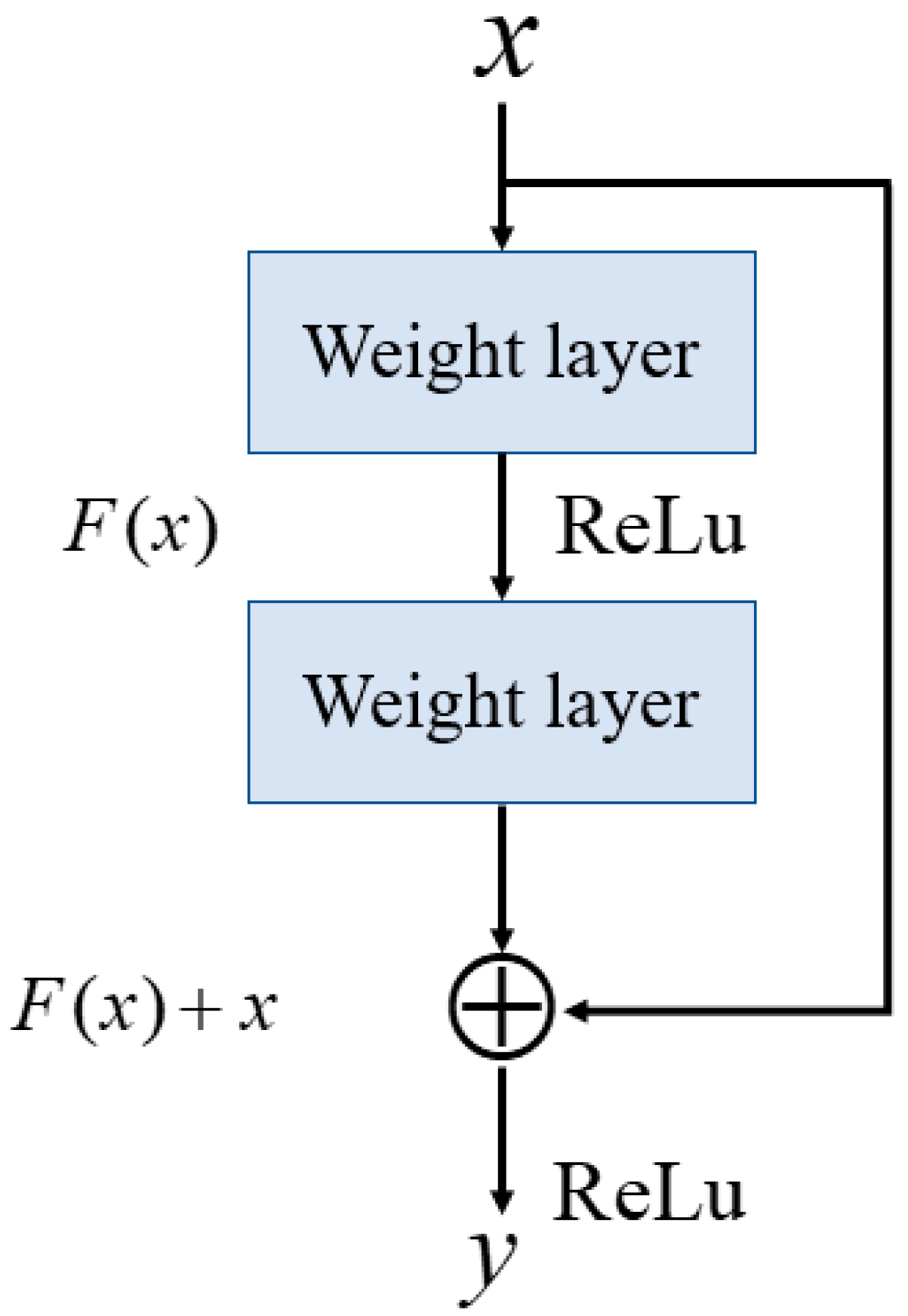
Figure 4, which includes the residual block, feature-unshuffle block, point-wise conv. block, and multi-head self-attention (MHSA) block. The residual block plays a critical role in the FMHSA encoder by addressing vanishing gradient issues and enhancing the network’s ability to train effectively for deeper layers. It introduces a shortcut connection that bypasses one or more layers, which allows the input to be directly added to the output of these layers. This design preserves essential input features while enabling deeper representations of the data. The FMHSA encoder begins with a residual block that employs a 1D convolution with a kernel size of 5 and padding of 2 to maintain
CH channels and feature dimension
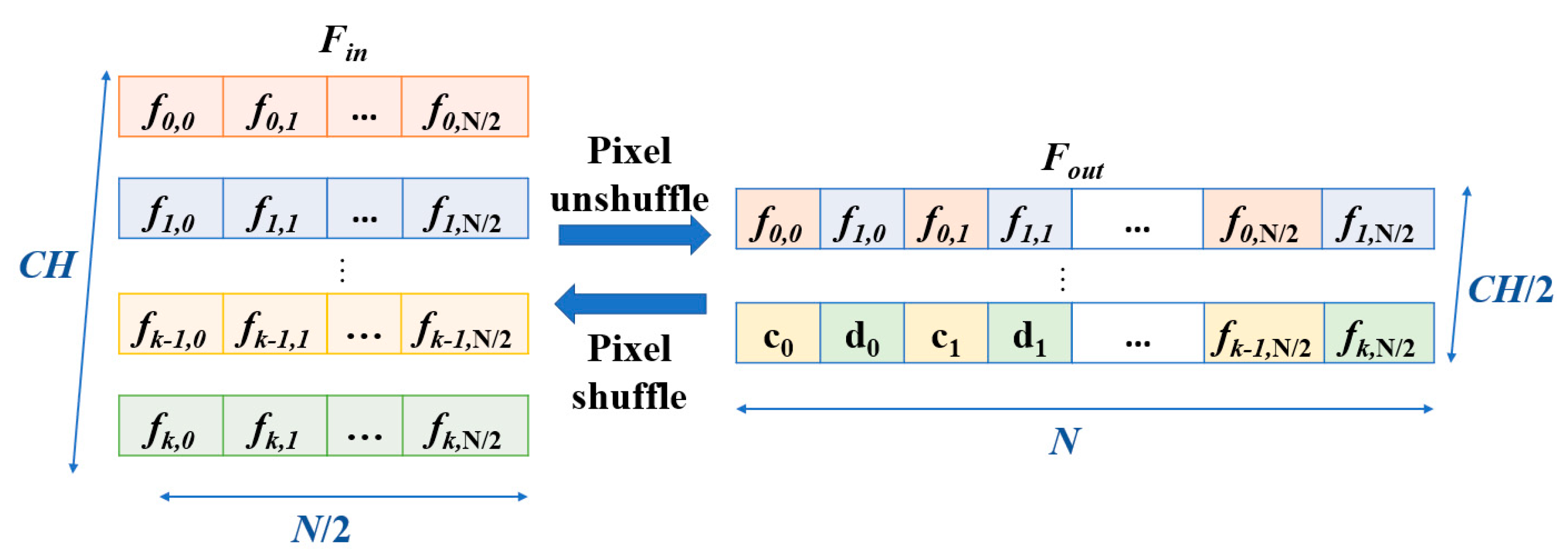
N. The input features are duplicated and processed through two sequential 1D convolutional layers, each followed by an activation function, such as ReLU, to introduce non-linearity. The outputs of these layers are summed with the original input to produce the final output of the residual block. This structure mitigates the risk of vanishing gradients in deep neural networks by maintaining feature stability across layers. Subsequently, a feature-unshuffle layer rearranges the features, which converts the spatial dimension information of the input into a higher channel dimension. Next, a point-wise convolution layer with a kernel size of 1 is applied, which reshapes the data to (
,
). This operation facilitates the mixing of information across channels without modifying the spatial dimensions. The combination of this technique with the point-wise convolution effectively reduces the feature length by half while maintaining the channel length unchanged.
Subsequently, the features are input into the MHSA block. MHSA is a core component that can integrate relative positions in different spatial dimensions, as shown in
Figure 5. The feature signal
is used as query (Q), key (K), and value (V). They pass through three different linear layers
,
,
, where
,
,
,
, to obtain the weight matrices. The feature channels are evenly divided into multiple heads, each with its
,
,
matrices. This allows the feature to focus on different aspects of information in different spatial dimensions. Using a single attention function with
dimensional queries, keys, and values can be improved by linearly projecting the queries, keys, and values
times through different learned linear projections to
,
,
. Equations (4) and (5) show this process, where
,
,
and
represents of head number.
Each head’s relative position weight output matrix is calculated by scaling the dot product of
and
with
, then applying the softmax function to get the attention weight matrix, and finally multiplying with
to get the final output matrix, as shown in Equation (6), where
. The outputs of all heads are concatenated together and projected back to the original dimension using a linear layer, as shown in Equation (7), where
. The final result is
. The overall process is illustrated in
Figure 6 and
Figure 7.
Since the operations performed by MHSA are linear transformations, its ability to learn complex feature relationships is not as strong as that of nonlinear transformations. Therefore, after the MHSA, we input the features into a feed-forward network (FFN). The formula is shown in Equation (8).
W1 and
W2 are weight matrices of the two fully connected layers, and
b1 and
b2 are respective biases. The operation
applies a ReLU activation function. By employing these nonlinear activation functions, we can significantly enhance the model’s expressive power, which enables it to capture and learn more complex and detailed feature relationships. This step not only enriches the feature representations but also improves the overall network’s denoising and reconstruction performance.
3.2. Multi-Head Self-Attention (MHSA) Shortcut Architecture
As the encoder extracts features layer by layer, some subtle but indispensable features may vanish with the deepening of the network layers. This can result in the reconstructed signal not fully approximating the clean signal [
27]. To address this issue, an MHSA shortcut is added between the encoder and the decoder, which allows the decoder to receive more information from the encoder during signal reconstruction, thereby enhances the reconstruction quality. The FMHSA encoder in this paper focuses on learning correlations between different time steps. The MHSA shortcut also utilizes the MHSA block, but unlike the FMHSA encoder, the MHSA shortcut aims to learn correlations between different channels. This approach allows the decoder to not only leverage the features across time steps but also more effectively integrate crucial information from different channels, thereby further improving the performance in denoising and reconstruction. The MHSA architecture is illustrated in
Figure 4.
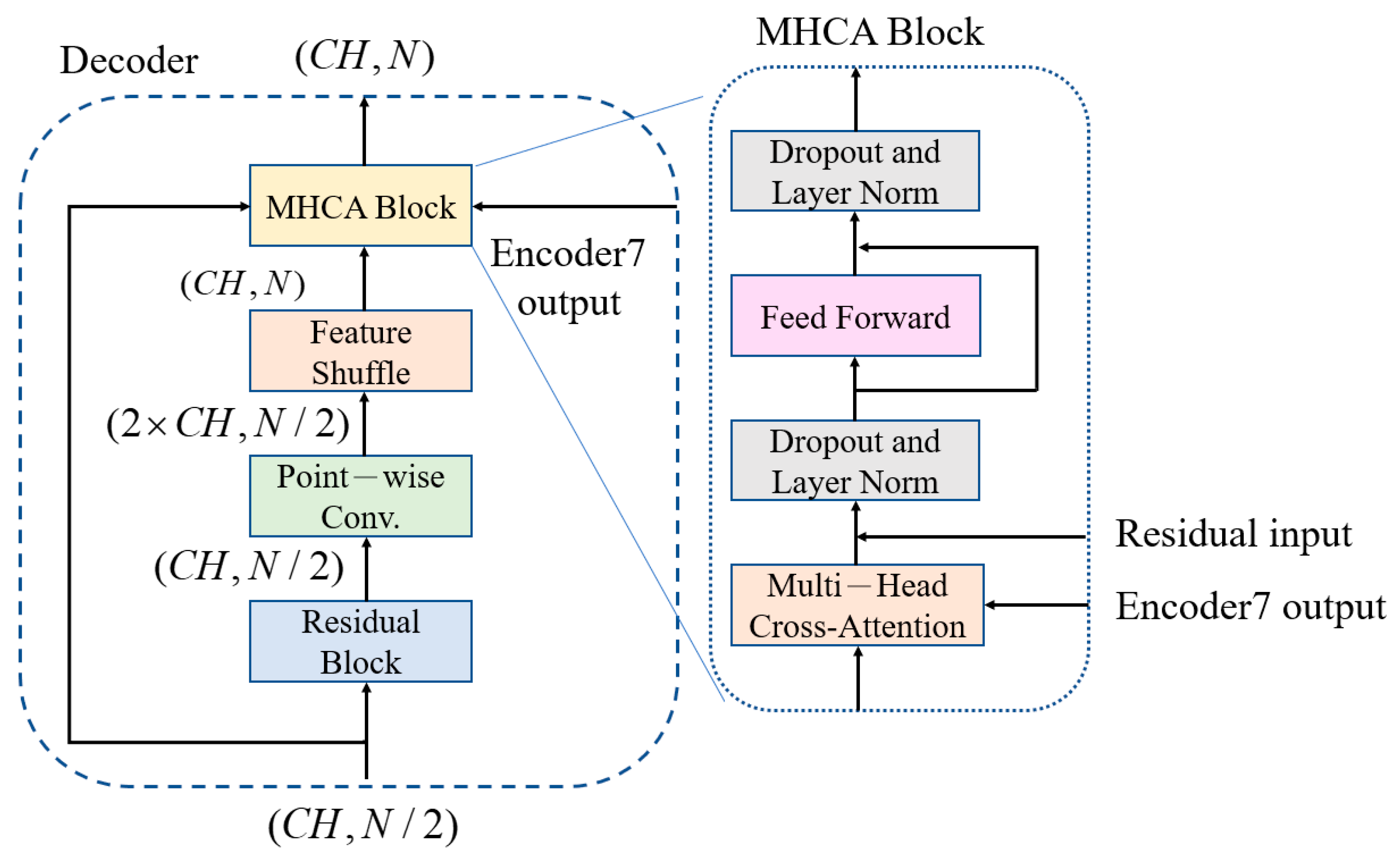
3.3. Feature-Shuffle Multi-Head Cross-Attention (FMHCA) Decoder Architecture Design
The architecture of the FMHCA decoder is shown in
Figure 5. The input signal first undergoes preliminary extraction through a residual block. Next, the signal passes through a point-wise conv., which doubles the number of channels to increase the feature representation capacity. Following this, the signal enters the feature-shuffle block, which converts high-dimensional channel features into low-dimensional spatial features, as illustrated in
Figure 2. These two modules enable the sequence length to double while keeping the number of channels unchanged, which achieves an upsampling effect. This series of operations not only assists in the layer-by-layer reconstruction of the signal but also effectively enhances the quality of the reconstructed signal, which makes it closer to the original clean ECG signal.
Next, the features are input into the multi-head cross-attention (MHCA) block, as illustrated in
Figure 5. The MHCA module has two inputs: one is the output from the feature shuffle, denoted as
, and the other is the output from the seventh layer of the MHSA encoder, denoted as
.
passes through the linear multi-head weight matrix
to form multiple heads of
, while
passes through the linear multi-head weight matrices
,
to obtain
,
, as shown in Equation (9). Next,
,
,
are used to compute the attention weight matrix as shown in Equation (10). Finally, all head output matrices are concatenated and projected back to the original dimension using the linear weight matrix
, as shown in Equation (11). The significance of this lies in that the output of the final layer of the decoder includes the high-dimensional features of the entire ECG signal. These features help the decoder better understand the comprehensive characteristics and structure of the signal. When these high-dimensional features are input into each layer of the MHCA module of the decoder, the decoder can reference these comprehensive features during each step of signal reconstruction, which results in a more accurate signal restoration.
Similarly, each MHCA block is followed by a feed-forward network to improve the learning capacity of the nonlinear components. After processing through seven layers of MHCA decoders, a 1 × 1 conv. layer is applied to restore the signal back to the original signal dimensions, which ensures that the final reconstructed ECG signal is consistent with the initial signal.