EEG-to-EEG: Scalp-to-Intracranial EEG Translation Using a Combination of Variational Autoencoder and Generative Adversarial Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
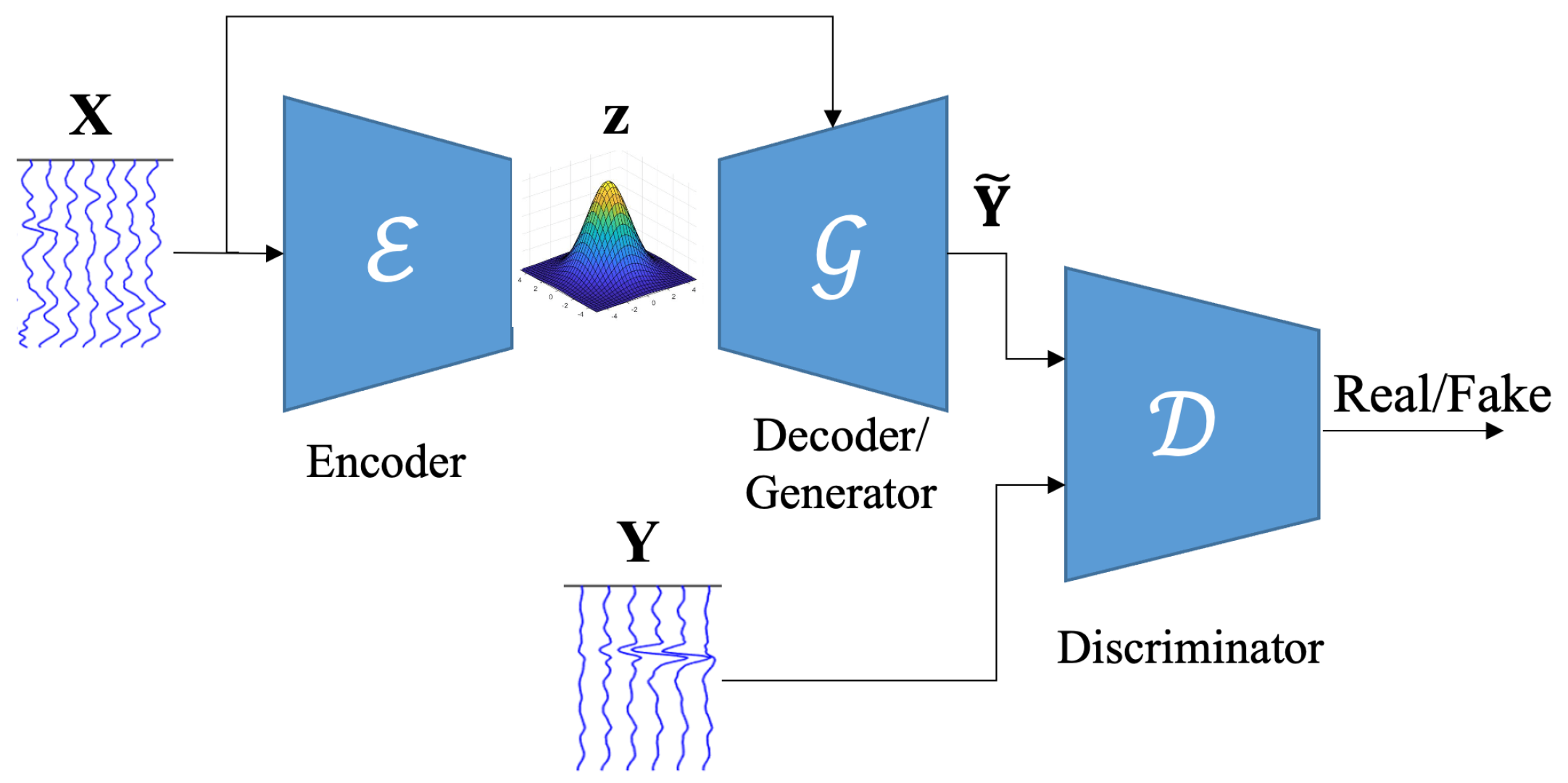
2. EEG-to-EEG Mapping Method
2.1. VAE
2.2. GAN
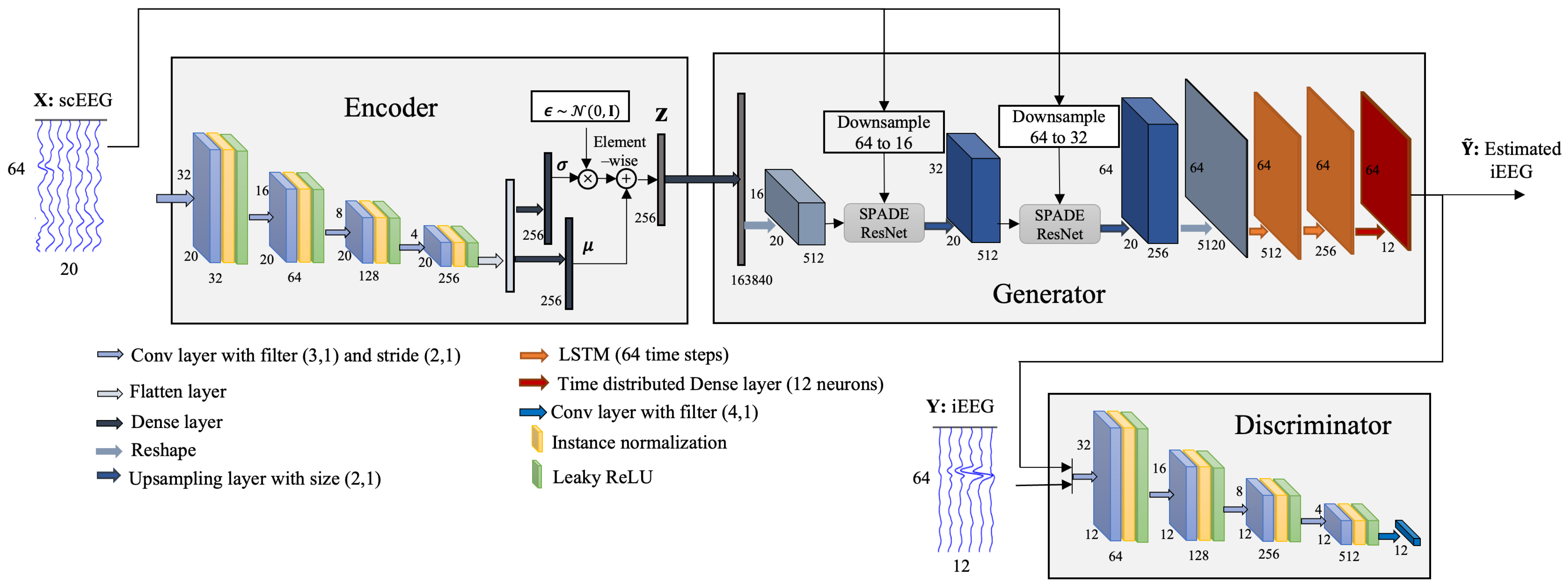
2.3. Scalp-to-Intracranial EEG Translation
2.3.1. Encoder
2.3.2. Generator
2.3.3. Discriminator
2.3.4. Optimization and Loss Function
3. Experiment
3.1. Dataset
3.2. IED Annotation and Pre-Processing
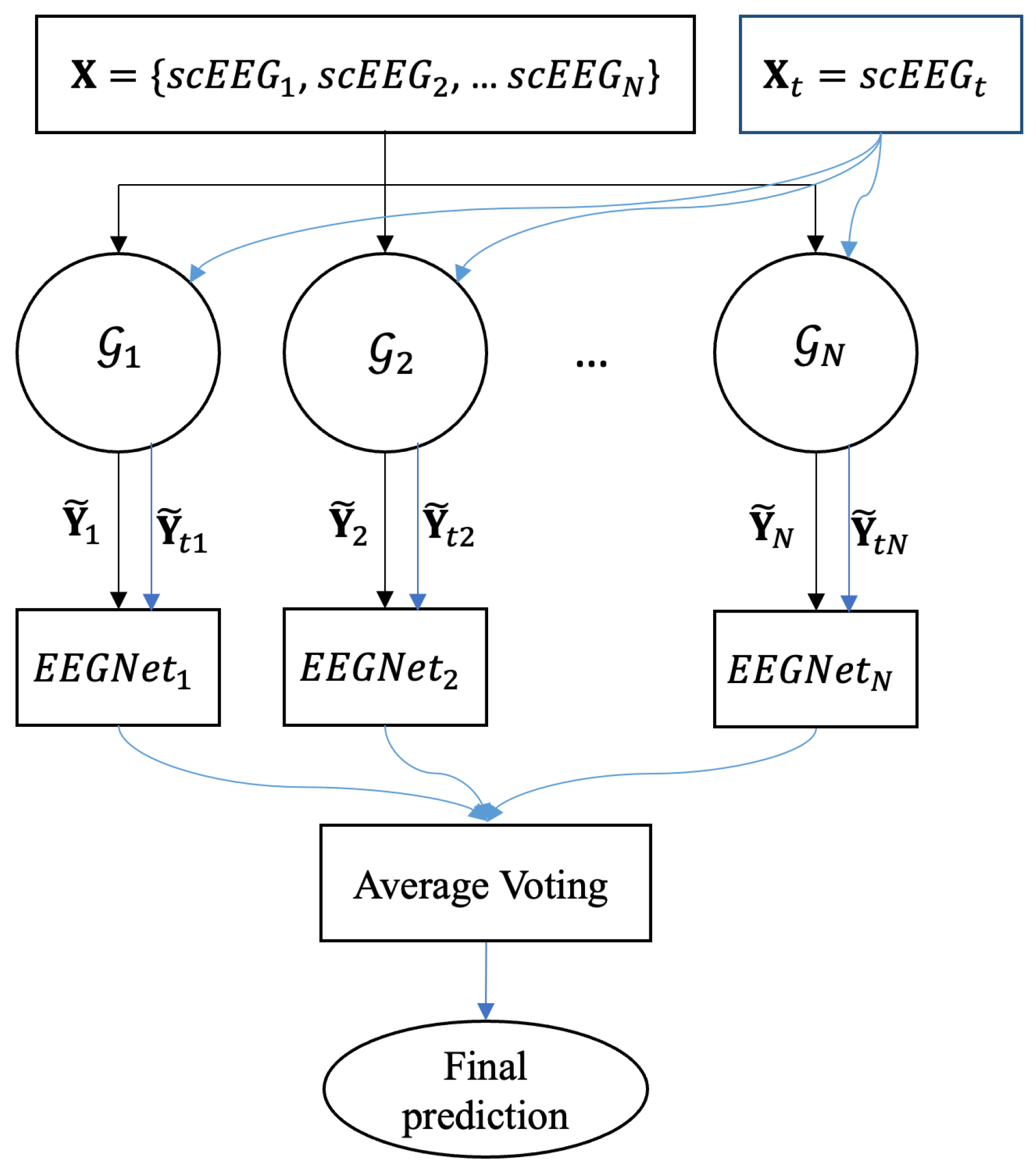
3.3. Translating/Mapping scEEG to iEEG
3.4. Classification and Cross Validation
4. Results
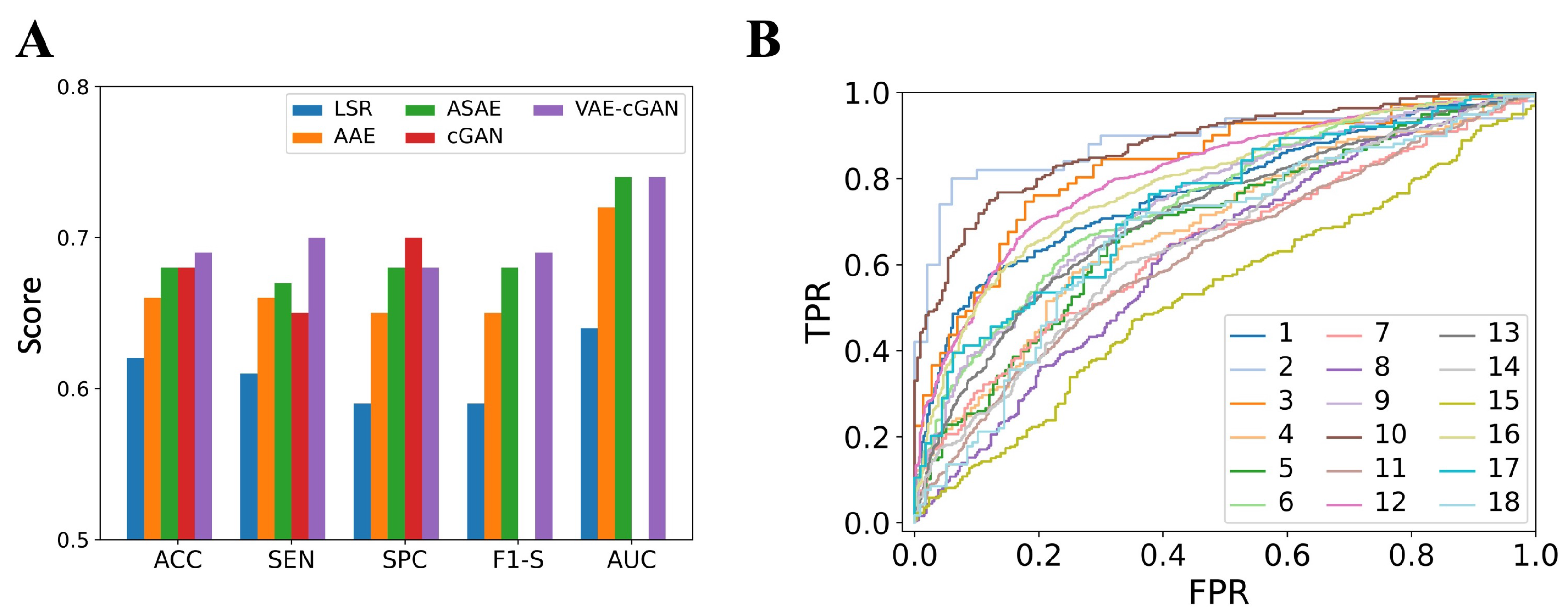
4.1. The Performance of Mapping Model
4.2. The Performance of IED Detection
4.3. Ablation Study
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAE | Asymmetric autoencoder |
| ACC | Accuracy |
| ASAE | Asymmetric–symmetric autoencoder |
| AUC | Area under ROC curve |
| cGAN | Conditional generative adversarial network |
| COSSIM | Cosine similarity |
| EEG | Electroencephalographe |
| ERP | Event-related potential |
| F1-S | F1-score |
| FO | Foramen |
| GAN | Generative adversarial network |
| IED | Interictal epileptiform discharges |
| iEEG | Intracranial electroencephalograph |
| KL | Kullback–Leibler |
| LSTM | Long short-term memory |
| LSR | Least-square regression |
| MSE | Mean squared error |
| PCORR | Pearson correlation coefficient |
| PRC | Precision |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| SEN | Sensitivity |
| scEEG | Scalp electroencephalograph |
| SPADE | Spatially-adaptive denormalization |
| SPC | Specificity |
| STD | Standard deviation |
| STN | Subthalamic nucleus |
| tanh | Hyperbolic tangent |
| VAE | Variational autoencoder |
References
- Sanei, S.; Chambers, J.A. EEG Signal Processing and Machine Learning; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Falcon-Caro, A.; Shirani, S.; Ferreira, J.F.; Bird, J.J.; Sanei, S. Formulation of Common Spatial Patterns for Multi-Task Hyperscanning BCI. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 71, 1950–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esfahani, M.M.; Najafi, M.H.; Sadati, H. Optimizing EEG Signal Classification for Motor Imagery BCIs: FilterBank CSP with Riemannian Manifolds and Ensemble Learning Models. In Proceedings of the 2023 9th International Conference on Signal Processing and Intelligent Systems (ICSPIS), Bali, Indonesia, 14–15 December 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Esfahani, M.M.; Sadati, H. Application of NSGA-II in channel selection of motor imagery EEG signals with common spatio-spectral patterns in BCI systems. In Proceedings of the 2022 8th International Conference on Control, Instrumentation and Automation (ICCIA), Tehran, Iran, 2–3 March 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shirani, S.; Abdi-Sargezeh, B.; Valentin, A.; Alarcon, G.; Jarchi, D.; Bird, J.; Sanei, S. Distributed Beamforming for Localization of Brain Seizure Sources from Intracranial EEG Array. In Proceedings of the 2024 32nd European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Lyon, France, 26–30 August 2024; pp. 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirani, S.; Abdi-Sargezeh, B.; Valentin, A.; Alarcon, G.; Bird, J.; Sanei, S. Do Interictal Epileptiform Discharges and Brain Responses to Electrical Stimulation Come From the Same Location? An Advanced Source Localization Solution. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 71, 2771–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirani, S.; Valentin, A.; Abdi-Sargezeh, B.; Alarcon, G.; Sanei, S. Localization of epileptic brain responses to single-pulse electrical stimulation by developing an adaptive iterative linearly constrained minimum variance beamformer. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2023, 33, 2350050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pondal-Sordo, M.; Diosy, D.; Téllez-Zenteno, J.F.; Sahjpaul, R.; Wiebe, S. Usefulness of intracranial EEG in the decision process for epilepsy surgery. Epilepsy Res. 2007, 74, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Collinger, J.L.; Perez, M.A.; Tyler-Kabara, E.C.; Cohen, L.G.; Birbaumer, N.; Brose, S.W.; Schwartz, A.B.; Boninger, M.L.; Weber, D.J. Neural interface technology for rehabilitation: Exploiting and promoting neuroplasticity. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. 2010, 21, 157–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirani, S.; Valentin, A.; Alarcon, G.; Kazi, F.; Sanei, S. Separating inhibitory and excitatory responses of epileptic brain to single-pulse electrical stimulation. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2023, 33, 2350008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi-Sargezeh, B.; Valentin, A.; Alarcon, G.; Sanei, S. Detection of brain interictal epileptiform discharges from intracranial EEG by exploiting their morphology in the tensor structure. In Proceedings of the 2021 29th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Dublin, Ireland, 23–27 August 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1167–1171. [Google Scholar]
- Kane, N.; Acharya, J.; Beniczky, S.; Caboclo, L.; Finnigan, S.; Kaplan, P.W.; Shibasaki, H.; Pressler, R.; van Putten, M.J. A revised glossary of terms most commonly used by clinical electroencephalographers and updated proposal for the report format of the EEG findings. Revision 2017. Clin. Neurophysiol. Pract. 2017, 2, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi-Sargezeh, B.; Sanei, S. Advances in epilepsy monitoring by detection and analysis of brain epileptiform discharges. Psychol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, D.; Valentin, A.; Alarcon, G.; Seoane, J.J.G.; Brunnhuber, F.; Juler, J.; Polkey, C.E.; Binnie, C.D. Characteristics of scalp electrical fields associated with deep medial temporal epileptiform discharges. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 1423–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, M.; Tucker, D.M.; Fujimoto, A.; Yamazoe, T.; Okanishi, T.; Yokota, T.; Enoki, H.; Yamamoto, T. Comparison of dense array EEG with simultaneous intracranial EEG for interictal spike detection and localization. Epilepsy Res. 2012, 98, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, H.; Elger, C.; Stodieck, S. The ‘foramen ovale electrode’: A new recording method for the preoperative evaluation of patients suffering from mesio-basal temporal lobe epilepsy. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1985, 61, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakis, I.; Velez-Ruiz, N.; Pathmanathan, J.S.; Sheth, S.A.; Eskandar, E.N.; Cole, A.J. Foramen ovale electrodes in the evaluation of epilepsy surgery: Conventional and unconventional uses. Epilepsy Behav. 2011, 22, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparkes, M.; Valentin, A.; Alarcon, G. Mechanisms involved in the conduction of anterior temporal epileptiform discharges to the scalp. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi-Sargezeh, B.; Shirani, S.; Sanei, S.; Took, C.C.; Geman, O.; Alarcon, G.; Valentin, A. A review of signal processing and machine learning techniques for interictal epileptiform discharge detection. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 168, 107782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi-Sargezeh, B.; Valentin, A.; Alarcon, G.; Martin-Lopez, D.; Sanei, S. Higher-order tensor decomposition based scalp-to-intracranial EEG projection for detection of interictal epileptiform discharges. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 066039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi-Sargezeh, B.; Valentin, A.; Alarcon, G.; Sanei, S. Sparse Common Feature Analysis for Detection of Interictal Epileptiform Discharges From Concurrent Scalp EEG. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 49892–49904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi-Sargezeh, B.; Valentin, A.; Alarcon, G.; Sanei, S. Incorporating Uncertainty in Data Labeling into Automatic Detection of Interictal Epileptiform Discharges from Concurrent Scalp-EEG via Multi-way Analysis. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2021, 31, 2150019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi-Sargezeh, B.; Valentin, A.; Alarcon, G.; Sanei, S. Incorporating Uncertainty In Data Labeling Into Detection of Brain Interictal Epileptiform Discharges From EEG Using Weighted optimization. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1000–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Thanh, L.T.; Dao, N.T.A.; Dung, N.V.; Trung, N.L.; Abed-Meraim, K. Multi-channel EEG epileptic spike detection by a new method of tensor decomposition. J. Neural Eng. 2020, 17, 016023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, T.; Li, M.; You, Y.; Zheng, X. Developing multi-component dictionary-based sparse representation for automatic detection of epileptic EEG spikes. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 60, 101966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Shih, J.J.; Krusienski, D.J. Empirical models of scalp-EEG responses using non-concurrent intracranial responses. J. Neural Eng. 2014, 11, 035012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Spyrou, L.; Sanei, S. Coupled dictionary learning for multimodal data: An application to concurrent intracranial and scalp EEG. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 2349–2353. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniades, A.; Spyrou, L.; Martin-Lopez, D.; Valentin, A.; Alarcon, G.; Sanei, S.; Took, C.C. Deep neural architectures for mapping scalp to intracranial EEG. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2018, 28, 1850009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2014/hash/5ca3e9b122f61f8f06494c97b1afccf3-Abstract.html (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-encoding variational bayes. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Qi, X.; Lukasiewicz, T.; Torr, P. Controllable text-to-image generation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, T.; Zhang, J.; Xu, D.; Tao, D. Mirrorgan: Learning text-to-image generation by redescription. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15 June 2019; pp. 1505–1514. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Jia, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, S.; Gao, W. Direct speech-to-image translation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2020, 14, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, S.; Bonafonte, A.; Serra, J. SEGAN: Speech enhancement generative adversarial network. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.09452. [Google Scholar]
- Abdi-Sargezeh, B.; Oswal, A.; Sanei, S. Mapping Scalp to Intracranial EEG using Generative Adversarial Networks for Automatically Detecting Interictal Epileptiform Discharges. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop (SSP), Hanoi, Vietnam, 15 May 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 710–714. [Google Scholar]
- Kebaili, A.; Lapuyade-Lahorgue, J.; Ruan, S. Deep learning approaches for data augmentation in medical imaging: A review. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Wang, F.; Luo, Y.; Kang, S.G.; Tang, J.; Lightstone, F.C.; Fang, E.F.; Cornell, W.; Nussinov, R.; Cheng, F. Deep generative molecular design reshapes drug discovery. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1784. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.C.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhu, J.Y.; Tao, A.; Kautz, J.; Catanzaro, B. High-resolution image synthesis and semantic manipulation with conditional gans. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8798–8807. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.; Liu, M.Y.; Wang, T.C.; Zhu, J.Y. Semantic image synthesis with spatially-adaptive normalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2337–2346. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Meng, L.; Yin, W.; Sigal, L. Image generation from layout. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 8584–8593. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.C.; Hwang, H.T.; Wu, Y.C.; Tsao, Y.; Wang, H.M. Voice conversion from unaligned corpora using variational autoencoding wasserstein generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.00849. [Google Scholar]
- Razghandi, M.; Zhou, H.; Erol-Kantarci, M.; Turgut, D. Variational Autoencoder Generative Adversarial Network for Synthetic Data Generation in Smart Home. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.07387. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, A.B.L.; Sønderby, S.K.; Larochelle, H.; Winther, O. Autoencoding beyond pixels using a learned similarity metric. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 20–22 June 2016; PMLR: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1558–1566. [Google Scholar]
- Ulyanov, D.; Vedaldi, A.; Lempitsky, V. Instance normalization: The missing ingredient for fast stylization. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.08022. [Google Scholar]
- Dumoulin, V.; Shlens, J.; Kudlur, M. A learned representation for artistic style. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.07629. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Belongie, S. Arbitrary style transfer in real-time with adaptive instance normalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1501–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; PMLR: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wand, M. Precomputed real-time texture synthesis with markovian generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 702–716. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, J.; Tian, X.; Ma, J. GAN-FM: Infrared and visible image fusion using GAN with full-scale skip connection and dual Markovian discriminators. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2021, 7, 1134–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyato, T.; Kataoka, T.; Koyama, M.; Yoshida, Y. Spectral normalization for generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.05957. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Goodfellow, I.; Metaxas, D.; Odena, A. Self-attention generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; PMLR: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 7354–7363. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, J.; Xie, Y. Enhanced pix2pix dehazing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 8160–8168.
- Spyrou, L.; Martín-Lopez, D.; Valentín, A.; Alarcón, G.; Sanei, S. Detection of intracranial signatures of interictal epileptiform discharges from concurrent scalp EEG. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2016, 26, 1650016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.P.; Humphries, C.; Lee, T.W.; Makeig, S.; McKeown, M.; Iragui, V.; Sejnowski, T.J. Extended ICA Removes Artifacts from Electroencephalographic Recordings. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/1997/hash/674bfc5f6b72706fb769f5e93667bd23-Abstract.html (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- De Clercq, W.; Vergult, A.; Vanrumste, B.; Van Paesschen, W.; Van Huffel, S. Canonical correlation analysis applied to remove muscle artifacts from the electroencephalogram. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 2583–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi-Sargezeh, B.; Foodeh, R.; Shalchyan, V.; Daliri, M.R. EEG artifact rejection by extracting spatial and spatio-spectral common components. J. Neurosci. Methods 2021, 358, 109182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawhern, V.J.; Solon, A.J.; Waytowich, N.R.; Gordon, S.M.; Hung, C.P.; Lance, B.J. EEGNet: A compact convolutional neural network for EEG-based brain–computer interfaces. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 056013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waytowich, N.; Lawhern, V.J.; Garcia, J.O.; Cummings, J.; Faller, J.; Sajda, P.; Vettel, J.M. Compact convolutional neural networks for classification of asynchronous steady-state visual evoked potentials. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 066031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.X.; Le, T.T.; Dinh, V.V.; Tran, Q.L.; Nguyen, L.T.; Nguyen, D.T. Deep learning for epileptic spike detection. VNU J. Sci. Comput. Sci. Commun. Eng. 2018, 33, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fukumori, K.; Yoshida, N.; Sugano, H.; Nakajima, M.; Tanaka, T. Epileptic spike detection by recurrent neural networks with self-attention mechanism. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 7–13 May 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1406–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Abdi-Sargezeh, B.; Valentin, A.; Alarcon, G.; Sanei, S. Online Detection of Scalp-Invisible Mesial-Temporal Brain Interictal Epileptiform Discharges from EEG. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022–2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 7–13 May 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1416–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Celesia, G.; Chen, R. Parameters of spikes in human epilepsy. Dis. Nerv. Syst. 1976, 37, 277–281. [Google Scholar]
- van Donselaar, C.A.; Schimsheimer, R.J.; Geerts, A.T.; Declerck, A.C. Value of the electroencephalogram in adult patients with untreated idiopathic first seizures. Arch. Neurol. 1992, 49, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidel, S.; Pablik, E.; Aull-Watschinger, S.; Seidl, B.; Pataraia, E. Incidental epileptiform discharges in patients of a tertiary centre. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velisar, A.; Syrkin-Nikolau, J.; Blumenfeld, Z.; Trager, M.; Afzal, M.; Prabhakar, V.; Bronte-Stewart, H. Dual threshold neural closed loop deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease patients. Brain Stimul. 2019, 12, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi-Sargezeh, B.; Shirani, S.; Sharma, A.; Green, A.; Akram, H.; Zrinzo, L.; Limousin, P.; Foltynie, T.; Denison, T.; Tan, H.; et al. Prediction of pathological subthalamic nucleus beta burst occurrence in Parkinson’s disease. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sub. | No. of IEDs | No. of Scalp-Visible IEDs (Their Percentage from All IEDs) |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | 342 | 129 (37.7%) |
| S2 | 50 | 17 (34.0%) |
| S3 | 71 | 9 (12.7%) |
| S4 | 165 | 60 (36.4%) |
| S5 | 158 | 19 (12.0%) |
| S6 | 472 | 77 (16.3%) |
| S7 | 199 | 45 (22.6%) |
| S8 | 317 | 143 (45.1%) |
| S9 | 341 | 46 (13.5%) |
| S10 | 224 | 86 (38.4%) |
| S11 | 848 | 90 (10.6%) |
| S12 | 953 | 12 (1.3%) |
| S13 | 829 | 35 (4.2%) |
| S14 | 536 | 74 (13.8%) |
| S15 | 260 | 28 (10.8%) |
| S16 | 606 | 11 (1.8%) |
| S17 | 114 | 28 (24.6%) |
| S18 | 118 | 5 (4.2%) |
| Mean | 366.8 | 50.8 (18.8%) |
| Subject | MSE | PCORR | COSSIM |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.012 | 0.48 | 0.47 |
| S2 | 0.012 | 0.46 | 0.45 |
| S3 | 0.017 | 0.21 | 0.21 |
| S4 | 0.013 | 0.32 | 0.32 |
| S5 | 0.014 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| S6 | 0.014 | 0.31 | 0.31 |
| S7 | 0.017 | 0.22 | 0.21 |
| S8 | 0.022 | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| S9 | 0.013 | 0.38 | 0.37 |
| S10 | 0.013 | 0.32 | 0.32 |
| S11 | 0.015 | 0.33 | 0.32 |
| S12 | 0.012 | 0.53 | 0.53 |
| S13 | 0.014 | 0.36 | 0.35 |
| S14 | 0.013 | 0.42 | 0.41 |
| S15 | 0.015 | 0.23 | 0.23 |
| S16 | 0.012 | 0.46 | 0.45 |
| S17 | 0.013 | 0.28 | 0.28 |
| S18 | 0.015 | 0.22 | 0.21 |
| Mean | 0.014 | 0.35 | 0.34 |
| Subject | LSR [26] | AAE [28] | ASAE [28] | cGAN [35] | VAE-cGAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 65 (72) | 85 (80) | 87 (78) | 67 (78) | 71 (80) |
| S2 | 86 (81) | 92 (82) | 94 (88) | 83 (95) | 87 (95) |
| S3 | 65 (69) | 72 (72) | 69 (82) | 74 (90) | 77 (78) |
| S4 | 58 (62) | 58 (71) | 59 (77) | 66 (81) | 64 (74) |
| S5 | 55 (55) | 64 (64) | 65 (75) | 67 (73 | 67 (74) |
| S6 | 61 (59) | 70 (60) | 71 (63) | 68 (68) | 70 (74) |
| S7 | 59 (64) | 54 (62) | 67 (72) | 64 (67) | 62 (68) |
| S8 | 55 (66) | 55 (62) | 57 (68) | 63 (72) | 61 (72) |
| S9 | 63 (65) | 61 (74) | 62 (68) | 61 (71) | 68 (77) |
| S10 | 66 (70) | 71 (65) | 74 (77) | 75 (91) | 82 (90) |
| S11 | 63 (64) | 65 (67) | 65 (68) | 61 (62) | 60 (63) |
| S12 | 73 (79) | 75 (84) | 77 (84) | 79 (84) | 75 (84) |
| S13 | 62 (71) | 62 (72) | 64 (71) | 63 (74) | 67 (75) |
| S14 | 59 (62) | 66 (71) | 67 (65) | 63 (69) | 60 (72) |
| S15 | 50 (46) | 50 (53) | 50 (52) | 55 (59) | 55 (60) |
| S16 | 51 (55) | 67 (77) | 68 (72) | 75 (77) | 73 (86) |
| S17 | 54 (62) | 59 (54) | 62 (71) | 66 (78) | 69 (86) |
| S18 | 66 (64) | 61 (53) | 67 (75) | 65 (72) | 67 (67) |
| Mean | 62 (65) | 66 (68) | 68 (73) | 68 (76) | 69 (77) |
| Ablation | ACC | MSE | PCORR | COSSIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No-Encoder | 70 | 0.15 | 0.32 | 0.32 |
| No-SPADE-ResNet | 64 | 0.17 | 0.26 | 0.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdi-Sargezeh, B.; Shirani, S.; Valentin, A.; Alarcon, G.; Sanei, S. EEG-to-EEG: Scalp-to-Intracranial EEG Translation Using a Combination of Variational Autoencoder and Generative Adversarial Networks. Sensors 2025, 25, 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020494
Abdi-Sargezeh B, Shirani S, Valentin A, Alarcon G, Sanei S. EEG-to-EEG: Scalp-to-Intracranial EEG Translation Using a Combination of Variational Autoencoder and Generative Adversarial Networks. Sensors. 2025; 25(2):494. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020494
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdi-Sargezeh, Bahman, Sepehr Shirani, Antonio Valentin, Gonzalo Alarcon, and Saeid Sanei. 2025. "EEG-to-EEG: Scalp-to-Intracranial EEG Translation Using a Combination of Variational Autoencoder and Generative Adversarial Networks" Sensors 25, no. 2: 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020494
APA StyleAbdi-Sargezeh, B., Shirani, S., Valentin, A., Alarcon, G., & Sanei, S. (2025). EEG-to-EEG: Scalp-to-Intracranial EEG Translation Using a Combination of Variational Autoencoder and Generative Adversarial Networks. Sensors, 25(2), 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020494









