Determination of Cenozoic Sedimentary Structures Using Integrated Geophysical Surveys: A Case Study in the Hebei Plain, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
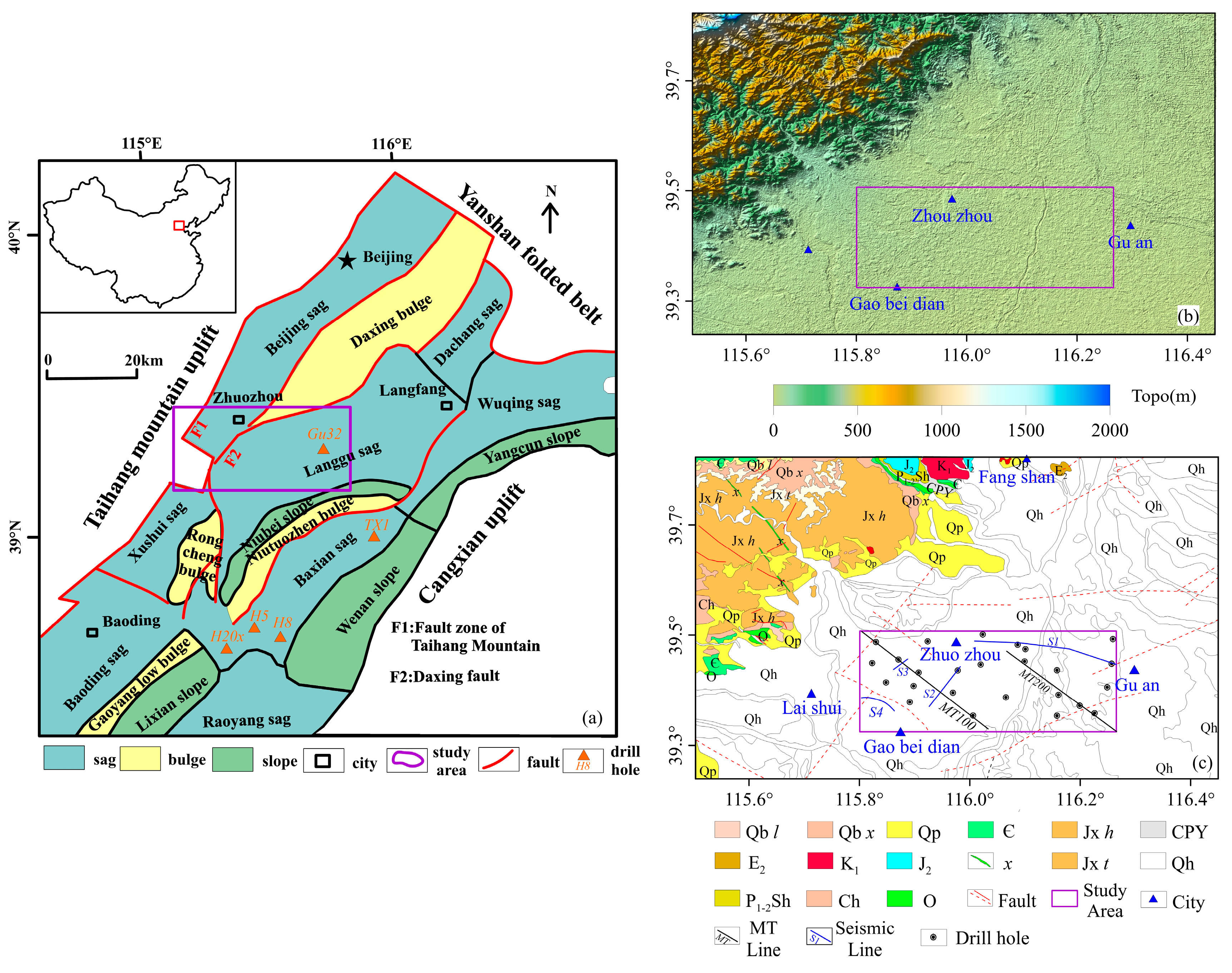
2. Geological and Geophysical Setting
2.1. Geological Background
2.2. The Physical Properties of Stratum
3. Data
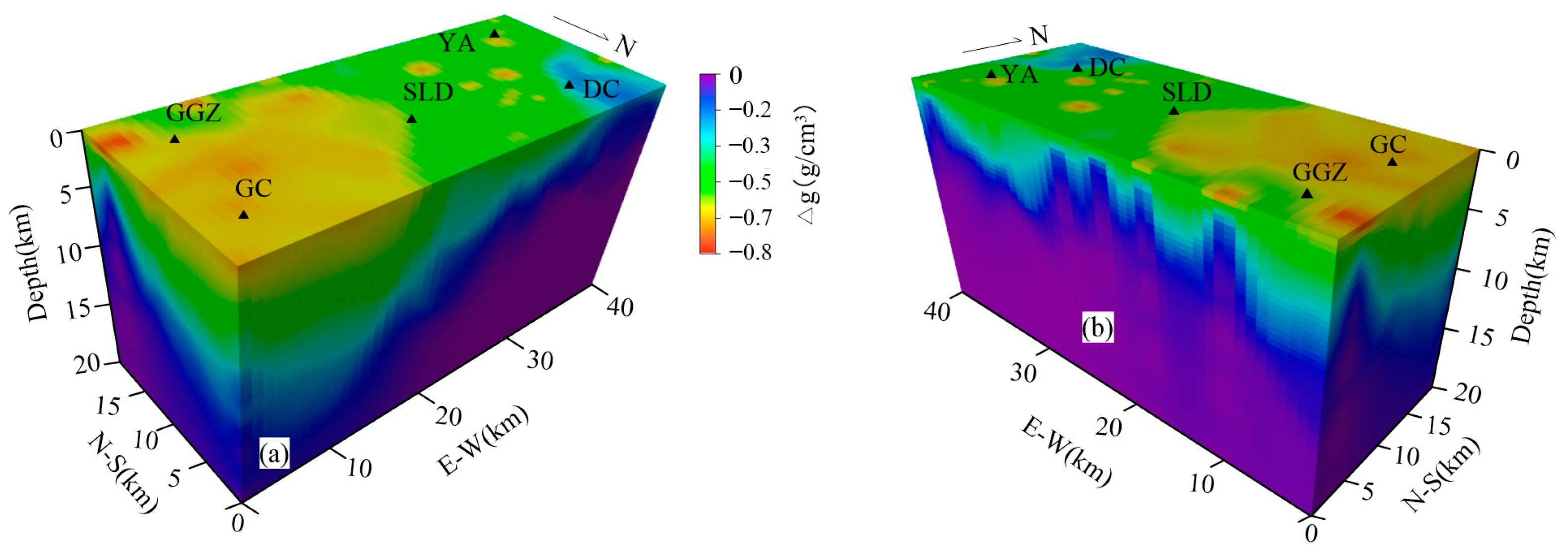
3.1. Gravity
3.2. Magnetotelluric
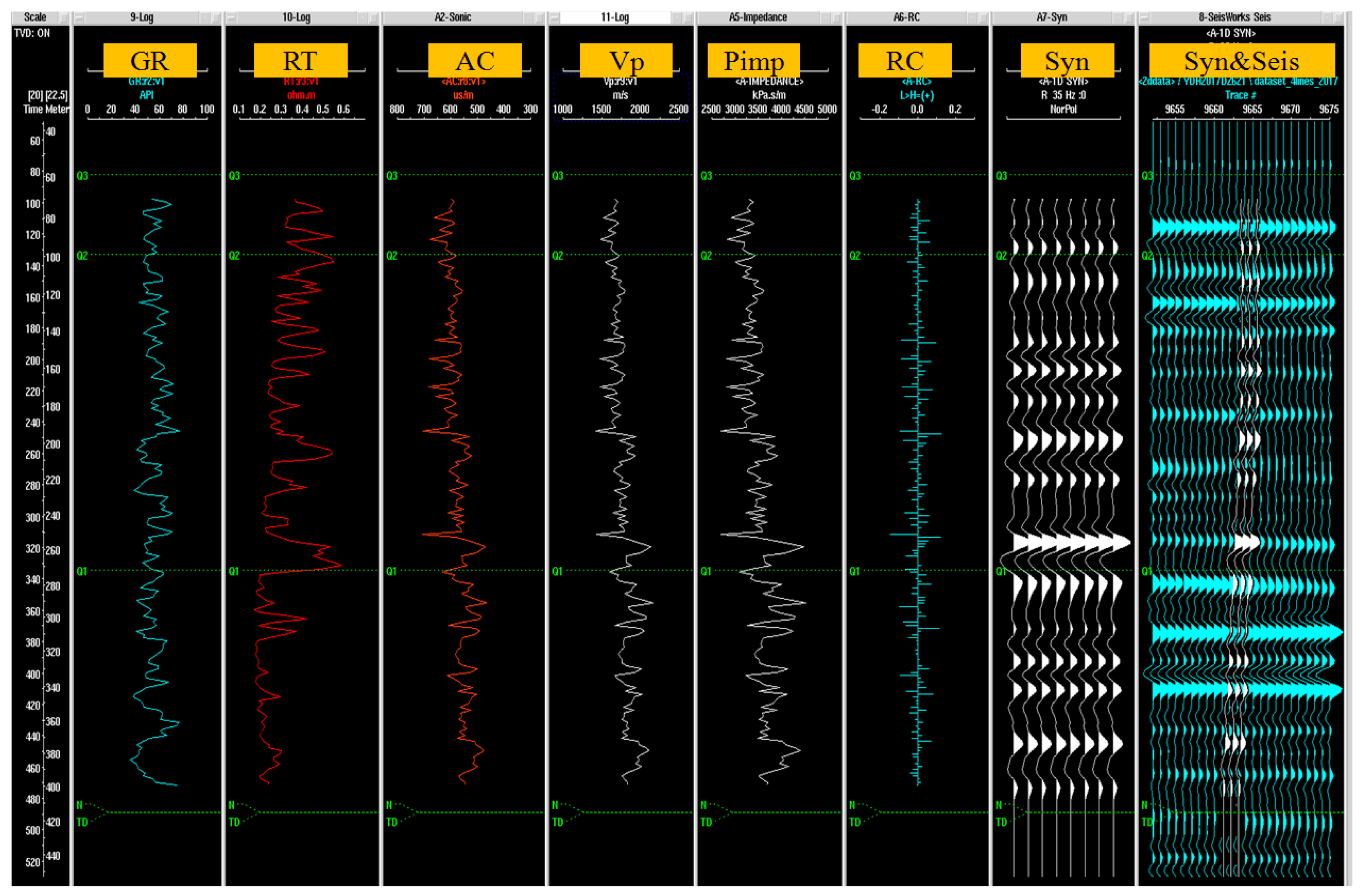
3.3. Reflection Seismic
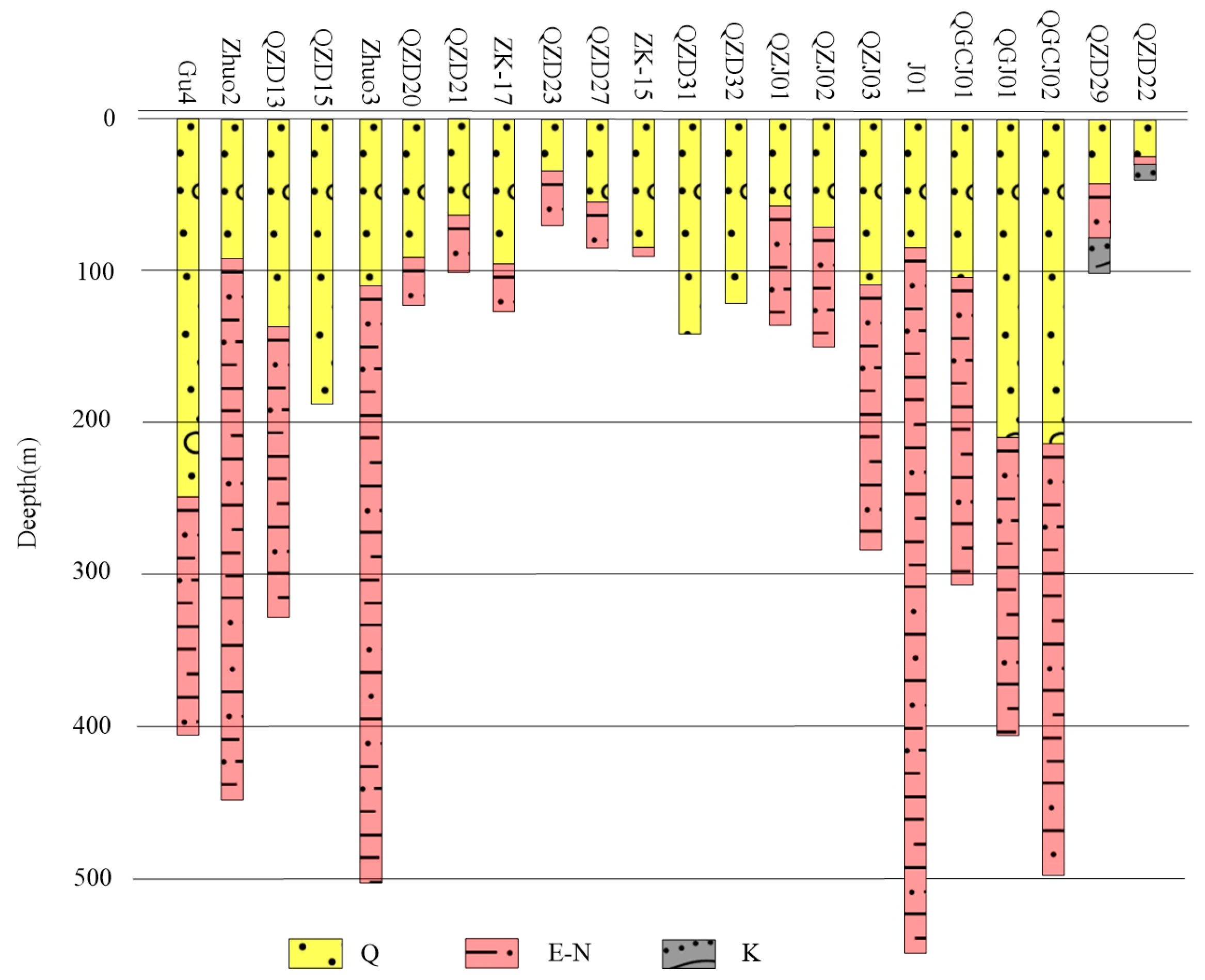
3.4. Borehole
4. Methodology and Result
4.1. Implementation Method
4.2. Establishment of Density Difference Model
4.3. Interface Estimation of Sedimentary Depth
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, X.; Wu, D. Cenozoic extensional tectonic in China. Tectonophysics 1987, 133, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; An, Z.; Han, S. The analysis of main characteristics of new neotectonic activity in Hebei plain. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 1984, 4, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, X.K.; Lin, Z.Y.; Wu, Q.J.; Zhang, Y.S. Crustal structure beneath the Xingtai earthquake area in North China and its tectonic implication. Tectonophysics 1997, 274, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, W.; Dong, S. Neotectonics of North China, interplay between far-field effect of India-Eurasia collision and Pacific subduction related deep-seated mantle upwelling. Acta Geol. Sin. 2019, 93, 971–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, M.; Li, X. Division of crustal movement of Himalayan period in Yanshan area and its expressed features. Geosciences 1995, 9, 325–326. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y. The upland morphologic surface and Neozoic tectonic movement in North China. North China Earthq. Sci. 1996, 14, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; He, J.; Bai, L.; Cai, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, T. The response relationship between the variation characteristics of deposition rate of Quaternary depression basin on the northern margin of Beijing depression and the activity of Shunyi fault. Geol. China 2016, 43, 511–519. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, R.; Lin, C.; Cui, B. Advances in the study of the styles of seimentation and the tectonic controls. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2000, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Van WJ, C.; Mitchum, R.M.; Campion, K.M.; Rahmanian, V.D. Siliciclastic Sequence Stratigraphy in Well Logs, Cores and Outcrops, Concepts for High-Resolution Correlation of Time and Facies; Methods in Exploration, Series 7; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Oruc, B.; Sertcelik, I.; Kafadar, O.; Selim, H. Structural interpretation of the Erzurum Basin, eastern Turkey, using curvature gravity gradient tensor and gravity inversion of basement relief. J. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 88, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edel, J.B.; Fluck, P. The upper Rhenish shield basement (Vosges, Upper Rhinegraben and Schwarzwald), main structural features deduced from magnetic, gravimetric and geological data. Tectonophysics 1989, 169, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandersen PB, E.; Jorgensen, F. Buried Quaternary valleys in western Denmark—Occurrence and inferred implications for groundwater resources and vulnerability. J. Appl. Geophys. 2003, 53, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J.D. A Promising Tool for Subsurface Permafrost Mapping, An Application of Airborne Geophysics from the Yukon River Basin, Alaska; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Burlington, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Koketsu, K.; Higashi, S. Three-dimensional topography of the sediment/basement interface in the Tokyo metropolitan area, central Japan. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1992, 82, 2328–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudyal, Y.R.; Yatabe, R.; Bhandary, N.P.; Dahal, R.K. Basement topography of the Kathmandu Basin using micro-tremor observation. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 62, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Z. Effect of the depression in the topography of bedrock underlying Beijing on earthquake ground motion. Acta Seismol. Sin. 1985, 7, 326–336. [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet, S.; Guillocheau, F.; Brun, J.P.; Driessche, J.V.D. Large-scale relief development related to Quaternary tectonic uplift of a Proterozoic-Paleozoic basement, the Armorican Massif, NW France. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 19273–19288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallero JL, G.; Fernandez MJ, L.; Bonvalot, S.; Fudym, O. Gravity inversion and uncertainty assessment of basement relief via particle swarm ptimization. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 139, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielik, M.; Krajnak, M.; Makarenko, I.; Legostaeva, O.; Starostenko, V.I.; Bošanský, M.; Grinč, M.; Hók, J. 3D gravity interpretation of the pretertiary basement in the intramontane depressions of the Western Carpathians, a case study from the Turiec Basin. Geol. Carpath. 2013, 64, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivochieva, S.; Chouteau, M. Integrating TDEM and MT methods for characterization and delineation of the Santa Catarina aquifer (Chalco Sub-Basin, Mexico). J. Appl. Geophys. 2003, 52, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, F.; Sandersen PB, E.; Auken, E. Imaging buried Quaternary valleys using the transient electromagnetic method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2003, 53, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, M.; Markandeyulu, A.; Chaturvedi, A.K. Mapping subtrappean sediments and delineating structure with the aid of heliborne time domain electromagnetics: Case study from Kaladgi Basin, Karnataka. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 136, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, F.; Lykke, A.H.; Sandersen, P.B.E.; Auken, E.; Nørmark, E. Geophysical investigations of buried Quaternary valleys in Denmark, an integrated application of transient electromagnetic soundings, reflection seismic surveys and exploratory drillings. J. Appl. Geophys. 2003, 53, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, B.S.; Rosenbaum, G. Structure of the Texas Orocline beneath the sedimentary cover (southeast Queensland, Australia). Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2015, 62, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschirhart, V.; Pehrsson, S.J. New insights from geophysical data on the regional structure and geometry of the southwest Thelon Basin and its basement, northwest territories, Canada. Geophysics 2016, 81, B167–B178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthi, V.; Shankar, G.B.K.; Muralidharan, D.; Harinarayana, T.; Sundararajan, N. An integrated geophysical approach for imaging subbasalt sedimentary basins, case study of Jam River Basin, India. Geophysics 2007, 72, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eirik, M.; Jan, S.R.; Geoffrey, D.C. High-resolution reflection seismics applied to mapping the Quaternary stratigraphy of the Tana delta, northern Norway. J. Appl. Geophys. 1995, 34, 137–167. [Google Scholar]
- Xavier, M.P.; Paul, G. Electrical resistivity and Ground Penetrating Radar for the characterization of the internal architecture of Quaternary sediments in the Midlands of Ireland. J. Appl. Geophys. 2011, 75, 638–647. [Google Scholar]
- Xavier, M.P.; Mario, Z.; Paul, G. Time-lapse resistivity analysis of Quaternary sediments in the Midlands of Ireland. J. Appl. Geophys. 2012, 82, 46–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lyons, R.P.; Scholz, C.A.; Buoniconti, M.R.; Martin, M.R. Late Quaternary stratigraphic analysis of the Lake Malawi Rift, East Africa, An integration of drill-core and seismic-reflection data. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2011, 303, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Liang, M.; Li, D.; Liang, M.; Ou, Y.; Jia, D.; Tang, X.; Li, X. Deep structure and geothermal resource effects of the Gonghe basin revealed by 3D magnetotelluric. Geotherm. Energy 2024, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willocks, A.J.; Simons, B.A. Geologists and geophysicists, getting them on the same planet. Explor. Geophys. 1998, 29, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, N.D.; Leys MT, C.; Macklin, T.A.; Robson, D.F. A New Era! —Collaborative Geological and Geophysical Mapping. Explor. Geophys. 1997, 28, 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J. General situation of geological mapping engineering in special area. J. Geomech. 2016, 22, 803–808. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.F.; Shan, S.Q.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Lu, R.; Zhang, R.; Cui, Y. 3-D geologic architecture of Xiong’an New Area, Constraints from seismic reflection data. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 48, 1207–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.S. Study on the Formation Mechanism of Ground Fissures in North China Epicontinental Basin; Chang’an University: Xi’an, China, 2012; pp. 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D. Geology and structural characteristics of BoHai Bay, China. Acta Pet. Sinaca 1980, 1, 6–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, Q.H. Jizhong Depression, China—Its geologic framework, evolutionary history, and distribution of hydrocarbons. AAPG Bull. 1984, 68, 983–992. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Sun, M.; Wilde, S.A.; Li, S. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton, Key issues revisited. Precambrian Res. 2005, 136, 177–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, F.; He, B.; Yan, D.; Zhang, W. 3D fine geological structure of Langfang-Gu’an fault-sag in Bohaiwan Gulf Basin, China. Chin. J. Geol. 2011, 46, 787–797. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, S.Q.; He, D.F.; Zhang, Y.Y. Tectono-stratigraphic sequence and basin evolution of Baoding sag in the western Bohai Bay Basin. Chin. J. Geol. 2016, 51, 402–414. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Cui, Y.Q.; Song, J.M.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, S.; Liang, W. Application of gravity seismic joint modeling forward technology in buried hill exploration in SH area. Oil Geophys. Prospect. 2016, 51, 152–161. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Yang, B.Y.; Zhao, H.G. Extensional Structures of the Paleogene in the Central Hebei Basin, China. Geol. Rev. 2002, 48, 58–67. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.R.; Zheng, C.J.; Wu, W.L.; Li, J.H. Techniques and systems for Larger-depth and Multi-function electromagnetic survey. Geol. Surv. China 2015, 2, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Egbert, G.D.; Booker, J.R. Robust estimation of geomagnetic transfer function. Geophys. J. Int. 1986, 87, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chave, A.D.; Tomason, D.J. Bounded influence magnetotelluric response function estimation. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 157, 988–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.T.; Chen, X.B.; Zhao, G.Z. Refined techniques for data processing and tow-dimensional inversion in magnetotelluric I, tensor decomposition and dimensionality analysis. Chin. J. Geophys. 2010, 53, 2516–2526. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.Z.; Wang, L. Controllable Source Audio Frequency Magnetotelluric Method, New Progress of Electrical Exploration; Geological Press: Beijing, China, 1996; pp. 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Bostick, J.F.X. A Simple and Almost Exact Method of MT Analysis, Presented at the Workshop on Electrical Methods in Geothermal Exploration; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Rodi, W.; Mackie, R.L. Nonlinear conjugate gradients algorithm for 2-D magnetotelluric inversion. Geophysics 2001, 1, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.S.; He, Z.H.; Cao, Z.L.; Shi, L.; Zhou, H. Well-to-Seismic Calibration Method with Multiple Seismic Geological Information Integrated. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2009, 20, 254–257. [Google Scholar]
- Bott, M.H.P. The use of rapid digital computing methods for direct gravity interpre-tation of sedimentary basins Geophys, J. Int. 1960, 3, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Oldenburg, D.W. The inversion and interpretation of gravity anomalies. Geophysics 1974, 39, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leao, J.W.D.; Menezes, P.T.L.; Beltrao, J.F.; Silva, J.B.C. Gravity inversion of basement relief constrained by the knowledge of depth at isolated points. Geophysics 1996, 61, 1702–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa VC, F.; Silva JB, C.; Medeiros, W.E. Gravity inversion of basement relief using approximate equality constraints on depths. Geophysics 1997, 62, 1745–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordell, L. Gravity analysis using an exponential density-depth function-San Jacinto Graben, California. Geophysics 1973, 38, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Hinze, W.J. Gravity inversion of an interface above which the density contrast varies exponentially with depth. Geophysics 1988, 53, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.B. Analysis of gravity anomalies of sedimentary basins by an asymmetrical trapezoidal model with quadratic density function. Geophysics 1990, 55, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthi, V.; Raghuram, H.M.; Singh, S.B. 3-D forward gravity modeling of basement interfaces above which the density contrast varies continuously with depth. Comput. Geosci. 2002, 28, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H. Moho depths inversion of Qinghai-Tibet plateau with variable density model. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2006, 31, 289–292. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Silva, J.B.C.; Oliveira, F.S.; Barbosa, V.C.F.; Velho, H.F.C. Apparent-density mapping using entropic regularization. Geophysics 2007, 72, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Shi, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.S.; Han, C.W. 3D interface inversion of gravity data in the frequency domain using a parabolic density-depth function the application in Sichuan-Yunnan region China. J. Geophys. 2015, 58, 556–565. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.L.; Yuan, B.Q.; Li, Y.H. Three dimensional variable density gravity inversion of Weihe basin basement. Pet. Geophys. Explor. 2019, 54, 461–471. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.L. Gravity Field and Gravity Exploration; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2005. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.K.; Wang, X.W.; Chen, J. Geological evidence of the Cenozoic tectonic uplifting in Taihang Mountains-Apatite fission track evidence from Well Qincan 1. J. Guilin Univ. Technol. 2015, 35, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, S.Y.; Dong, G.R. The origin and source of magma in the Taihangshan tectono-magmatic-belt. Geol. Rev. 1995, 41, 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Tian, W.; Zhai, M.G.; Arakawa, Y. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of the magmatism in the Taihang Mountains and other places of the North China craton, with implications for petrogenesis and geodynamic setting. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2005, 21, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Li, S.; Xu, L.; Guo, L.; Liu, L.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Dai, L. Mesozoic–Cenozoic evolution and mechanism of tectonic geomor-phology in the central North China Block, Constraint from apatite fission track thermochronology. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 114, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.S.; Liu, C.Y.; Yang, M.H.; Du, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R. Study on Complex Extensional Structures Middle Jizhong Depression in the Bohai Bay Basin. Geol. Rev. 2004, 50, 484–491. [Google Scholar]
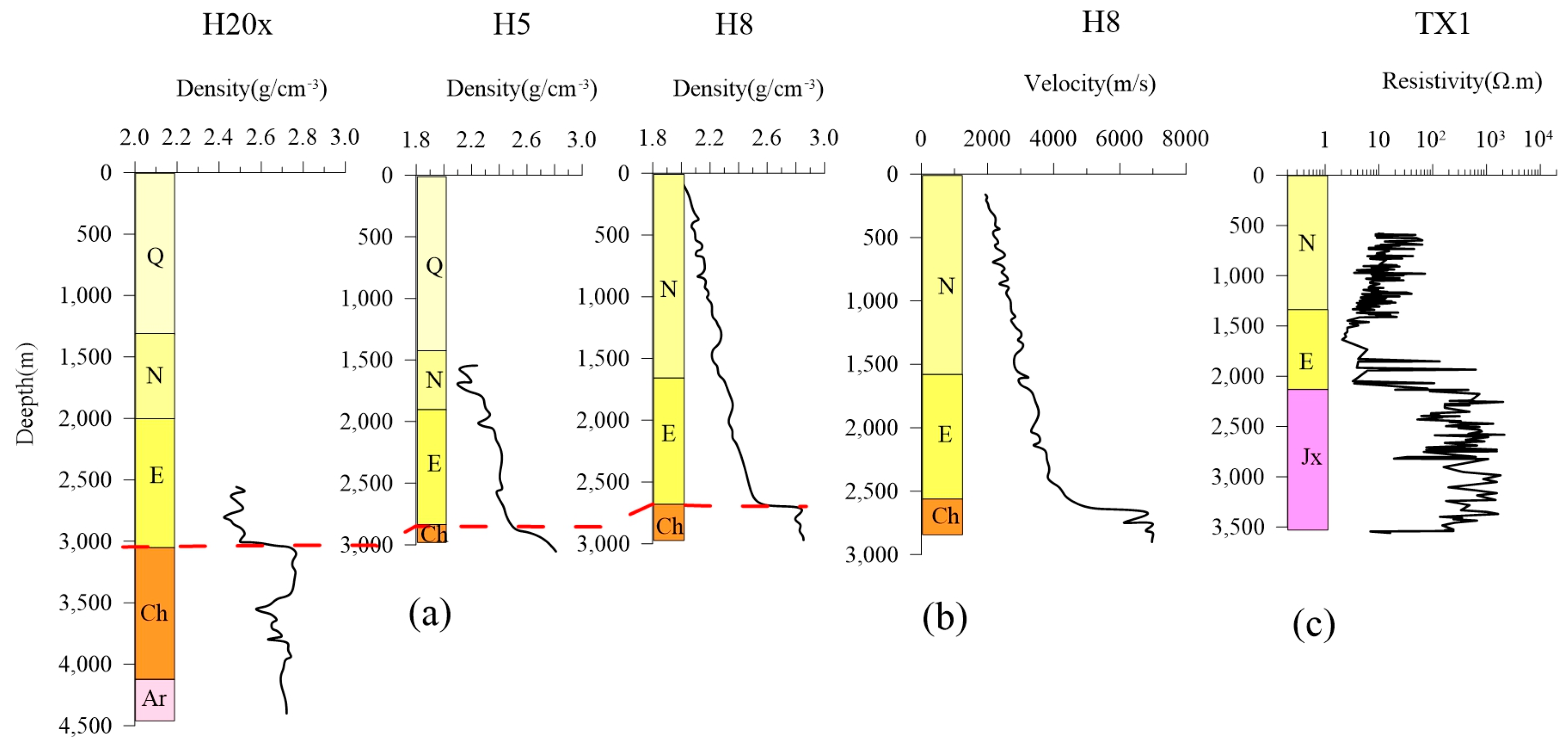



| Age | ) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Average | ||
| Quaternary | Q | 1.133–2.332 | 1.94 |
| Neogene | Ng | 2.237–2.283 | 2.25 |
| Paleogene | Ed-Es1 | 2.220–2.350 | 2.31 |
| Es2-Es3 | 2.250–2.500 | 2.38 | |
| Es4-Ek | 2.330–2.550 | 2.44 | |
| Proterozoic | Jxw, Chg, Pt | 2.610–2.800 | 2.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Zhi, Q.; Hao, G.; Li, J.; Deng, X. Determination of Cenozoic Sedimentary Structures Using Integrated Geophysical Surveys: A Case Study in the Hebei Plain, China. Sensors 2025, 25, 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020486
Yang Y, Zhang J, Wu J, Li P, Wang X, Zhi Q, Hao G, Li J, Deng X. Determination of Cenozoic Sedimentary Structures Using Integrated Geophysical Surveys: A Case Study in the Hebei Plain, China. Sensors. 2025; 25(2):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020486
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yi, Jie Zhang, Junjie Wu, Pei Li, Xingchun Wang, Qingquan Zhi, Guojiang Hao, Jianhua Li, and Xiaohong Deng. 2025. "Determination of Cenozoic Sedimentary Structures Using Integrated Geophysical Surveys: A Case Study in the Hebei Plain, China" Sensors 25, no. 2: 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020486
APA StyleYang, Y., Zhang, J., Wu, J., Li, P., Wang, X., Zhi, Q., Hao, G., Li, J., & Deng, X. (2025). Determination of Cenozoic Sedimentary Structures Using Integrated Geophysical Surveys: A Case Study in the Hebei Plain, China. Sensors, 25(2), 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020486







