DynamicVLN: Incorporating Dynamics into Vision-and-Language Navigation Scenarios
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We introduce Dynamic Vision-and-Language Navigation (DynamicVLN), a novel task that incorporates dynamic real-world scenarios such as moving vehicles, pedestrians, fluctuating traffic signals, and varying weather conditions, addressing the limitations of traditional static VLN tasks.
- We constructed the DynamicVLN dataset, comprising 11,261 navigation instances across ten dynamic scenarios. Data collection was automated using the CARLA simulator, and captions were generated automatically by GPT-4, ensuring both realism and diversity.
- We propose DynaNav, a baseline model equipped with a Dynamic Detection Module, enabling agents to recognize dynamic elements and make context-aware decisions, such as when to execute a ‘temporal stop’.
2. Related Works
2.1. Vision-and-Language Navigation Dataset
2.2. Approach for Vision-and-Language Navigation
2.3. Large Language Model for Dataset Generation
3. DynamicVLN Dataset
3.1. Task Definition
3.2. Scenario Design
3.3. Dataset Collection
3.4. Instruction Generation
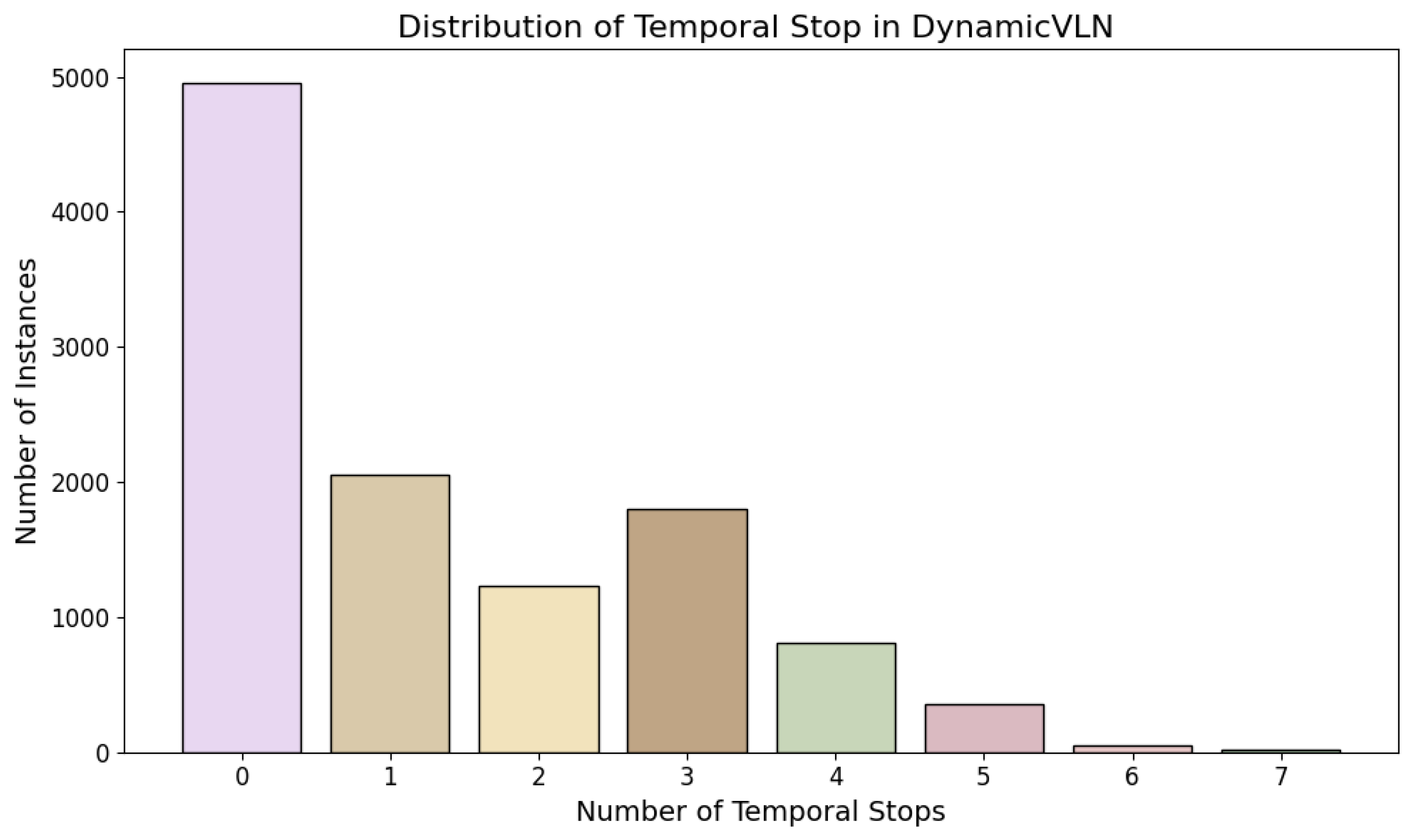
3.5. Data Statistics
4. Method
4.1. Model Details
4.2. Loss Function
5. Experiments
5.1. Implementation Details
5.2. Baseline Models
5.3. Metrics
5.4. Quantitative Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VLN | Vision-and-Language Navigation |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| GPT | Generative Pre-Trained Transformers |
| LD | Linear Dichroism |
References
- Anderson, P.; Wu, Q.; Teney, D.; Bruce, J.; Johnson, M.; Sünderhauf, N.; Reid, I.; Gould, S.; van den Hengel, A. Vision-and-Language Navigation: Interpreting visually-grounded navigation instructions in real environments. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Suhr, A.; Misra, D.; Snavely, N.; Artzi, Y. TOUCHDOWN: Natural Language Navigation and Spatial Reasoning in Visual Street Environments. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shridhar, M.; Thomason, J.; Gordon, D.; Bisk, Y.; Han, W.; Mottaghi, R.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Fox, D. ALFRED: A Benchmark for Interpreting Grounded Instructions for Everyday Tasks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Ros, G.; Codevilla, F.; Lopez, A.; Koltun, V. CARLA: An Open Urban Driving Simulator. In Proceedings of the 1st Annual Conference on Robot Learning, Mountain View, CA, USA, 13–15 November 2017; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- OpenAI; Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; et al. GPT-4 Technical Report. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, A.; Dai, A.; Funkhouser, T.; Halber, M.; Niessner, M.; Savva, M.; Song, S.; Zeng, A.; Zhang, Y. Matterport3D: Learning from RGB-D Data in Indoor Environments. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1709.06158. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, A.; Anderson, P.; Patel, R.; Ie, E.; Baldridge, J. Room-Across-Room: Multilingual Vision-and-Language Navigation with Dense Spatiotemporal Grounding. In Proceedings of the EMNLP, Online, 16–20 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, A.; Wang, X.E.; Feng, J.; Li, L.; Wang, W.Y. Cross-Lingual Vision-Language Navigation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.11301. [Google Scholar]
- Mirowski, P.; Grimes, M.K.; Malinowski, M.; Hermann, K.M.; Anderson, K.; Teplyashin, D.; Simonyan, K.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Zisserman, A.; Hadsell, R. Learning to Navigate in Cities Without a Map. In Proceedings of the NeurIPS, Montréal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, H.; Artzi, Y.; Baldridge, J.; Ie, E.; Mirowski, P. Retouchdown: Releasing Touchdown on StreetLearn as a Public Resource for Language Grounding Tasks in Street View. In Proceedings of the EMNLP-SpLU, Online, 16–20 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, K.; Malinowski, M.; Mirowski, P.; Banki-Horvath, A.; Anderson, K.; Hadsell, R. Learning to Follow Directions in Street View. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, A.B.; Dai, D.; Van Gool, L. Talk2Nav: Long-Range Vision-and-Language Navigation with Dual Attention and Spatial Memory. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 246–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, R.; Riezler, S. Generating Landmark Navigation Instructions from Maps as a Graph-to-Text Problem. In Proceedings of the ACL, Online, 5–10 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Padmakumar, A.; Sukhatme, G.; Bansal, M. VLN-Video: Utilizing Driving Videos for Outdoor Vision-and-Language Navigation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.03561. [Google Scholar]
- Kolve, E.; Mottaghi, R.; Han, W.; VanderBilt, E.; Weihs, L.; Herrasti, A.; Gordon, D.; Zhu, Y.; Gupta, A.; Farhadi, A. AI2-THOR: An Interactive 3D Environment for Visual AI. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.05474. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Qi, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q. AerialVLN: Vision-and-language Navigation for UAVs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.; Dey, D.; Lovett, C.; Kapoor, A. AirSim: High-Fidelity Visual and Physical Simulation for Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the Field and Service Robotics. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.05065. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, K.; Chhangani, V.; Tiwari, A.; Krishna, K.M.; Gandhi, V. Ground then Navigate: Language-guided Navigation in Dynamic Scenes. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; VanDerPloeg, B.; Bara, C.P.; Huang, Y.; Kim, E.I.; Gervits, F.; Marge, M.; Chai, J. DOROTHIE: Spoken Dialogue for Handling Unexpected Situations in Interactive Autonomous Driving Agents. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2022, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 7–11 December 2022; pp. 4800–4822. [Google Scholar]
- Krantz, J.; Wijmans, E.; Majundar, A.; Batra, D.; Lee, S. Beyond the Nav-Graph: Vision and Language Navigation in Continuous Environments. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03385. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Fried, D.; Hu, R.; Cirik, V.; Rohrbach, A.; Andreas, J.; Morency, L.P.; Berg-Kirkpatrick, T.; Saenko, K.; Klein, D.; Darrell, T. Speaker-Follower Models for Vision-and-Language Navigation. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Pan, Z.; Hong, Y.; Yang, M.; van den Hengel, A.; Wu, Q. The Road to Know-Where: An Object-and-Room Informed Sequential BERT for Indoor Vision-Language Navigation. In Proceedings of the ICCV, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 1655–1664. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Wu, Q.; Qi, Y.; Rodriguez-Opazo, C.; Gould, S. A Recurrent Vision-and-Language BERT for Navigation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2021; pp. 1643–1653. [Google Scholar]
- Moudgil, A.; Majumdar, A.; Agrawal, H.; Lee, S.; Batra, D. SOAT: A Scene- and Object-Aware Transformer for Vision-and-Language Navigation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.14143. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Aoki, Y.; Kataoka, H. Outdoor Vision-and-Language Navigation Needs Object-Level Alignment. Sensors 2023, 23, 6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Aoki, Y.; Kataoka, H. Guided by the Way: The Role of On-the-route Objects and Scene Text in Enhancing Outdoor Navigation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 13–17 May 2024; pp. 5198–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, R.; Zhu, W.; Feng, W.; Fu, T.J.; Riezler, S.; Wang, W.Y. VELMA: Verbalization Embodiment of LLM Agents for Vision and Language Navigation in Street View. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.06082. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yuan, L.P.; Wang, L.; Jiang, B.; Zeng, W. VirtuWander: Enhancing Multi-modal Interaction for Virtual Tour Guidance through Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the 2024 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI ’24), New York, NY, USA, 11–16 May 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lin, B.; Xu, R.; Chai, Z.; Liang, X.; Wong, K.Y. MapGPT: Map-Guided Prompting with Adaptive Path Planning for Vision-and-Language Navigation. In Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Bangkok, Thailand, 11–16 August 2024; pp. 9796–9810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2020; Volume 33, pp. 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Wu, F.; Guo, S.; Zhang, T.; Wang, G. Text Classification via Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.08377. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, R. Element-aware Summarization with Large Language Models: Expert-aligned Evaluation and Chain-of-Thought Method. In Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Toronto, ON, Canada, 9–14 July 2023; pp. 8640–8665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Liu, H.; Dong, Q.; Xu, J.; Huang, S.; Kong, L.; Chen, J.; Li, L. Multilingual Machine Translation with Large Language Models: Empirical Results and Analysis. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.04675. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, C.; Wu, Q.; Lee, Y.J. Visual Instruction Tuning. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Orleans, LA, USA, 10–16 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Meng, Y.; Ratner, A.; Krishna, R.; Shen, J.; Zhang, C. Large language model as attributed training data generator: A tale of diversity and bias. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS ’23), Red Hook, NY, USA, 10–16 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.; Kamar, E.; Amershi, S. Increasing Diversity While Maintaining Accuracy: Text Data Generation with Large Language Models and Human Interventions. In Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Toronto, ON, Canada, 9–14 July 2023; pp. 575–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.; Baek, J.; Thorne, J.; Hwang, S.J. Retrieval-Augmented Data Augmentation for Low-Resource Domain Tasks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.13482. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.H.; Pujara, J.; Sewak, M.; White, R.W.; Jauhar, S.K. Making Large Language Models Better Data Creators. In Proceedings of the The 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Singapore, 6–10 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.00020. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, A.; Fernández, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Bidirectional LSTM Networks for Improved Phoneme Classification and Recognition. In Proceedings of the Artificial Neural Networks: Formal Models and Their Applications—ICANN 2005, Warsaw, Poland, 11–15 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD’96), Portland, OR, USA, 2–4 August 1996; pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Schumann, R.; Riezler, S. Analyzing Generalization of Vision and Language Navigation to Unseen Outdoor Areas. In Proceedings of the ACL, Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rizi, F.S.; Schloetterer, J.; Granitzer, M. Shortest Path Distance Approximation Using Deep Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM), Barcelona, Spain, 28–31 August 2018; pp. 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, F.P.; Vandome, A.F.; McBrewster, J. Levenshtein Distance: Information Theory, Computer Science, String (Computer Science), String Metric, Damerau? Levenshtein Distance, Spell Checker, Hamming Distance; Alpha Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, V.; Magalhaes, G.; Ku, A.; Vaswani, A.; Ie, E.; Baldridge, J. Stay on the Path: Instruction Fidelity in Vision-and-Language Navigation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.12255. [Google Scholar]
- Ilharco, G.; Jain, V.; Ku, A.; Ie, E.; Baldridge, J. General Evaluation for Instruction Conditioned Navigation using Dynamic Time Warping. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.05446. [Google Scholar]





| Dataset | Environment | Data Source | Dynamic Elements | Automatic Annotation | Emergent Adaptation | Complex Navigation Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Room-to-Room [1] | indoor | Matterport3D | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Structured, static |
| Room-Across-Room [7] | indoor | Matterport3D | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Structured, static |
| VLN-CE [20] | indoor | Matterport3D | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | Continuous navigation |
| ALFRED [3] | indoor | AI2-THOR 2.0 | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | Object interactions |
| Touchdown [2] | outdoor | Google Street View | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Urban navigation |
| map2seq [13] | outdoor | Google Street View | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | Urban navigation |
| AerialVLN [16] | outdoor | AirSim | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | Aerial navigation |
| CARLA-NAV [18] | outdoor | CARLA | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | Grounded navigation |
| DOROTHIE [19] | outdoor | CARLA | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | Dialogue-based navigation |
| VLN-VIDEO [14] | outdoor | Google Street View | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | Urban navigation |
| DynamicVLN (our) | outdoor | CARLA | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Emergent adaptation |
| Dynamic Element | Trigger Condition | Decision Logic | Including Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle | Obstacle appears in agent’s path | Temporal stop | Vehicle stops abruptly ahead |
| Potential collision risk detected | Temporal stop or not | Vehicle approaches from side lane | |
| Priority vehicle detected | Temporal stop | Ambulance or fire engine approaches | |
| Lane change detected | Temporal stop or not | Vehicle changes lanes abruptly | |
| Pedestrian | Pedestrian enters agent’s intended path | Temporal stop | Pedestrian crosses at crosswalk |
| Sudden pedestrian movement detected | Temporal stop | Child runs across road | |
| Traffic Condition | Change in traffic signal state | Temporal stop or not | Traffic light turns red |
| Regulatory signs encountered | Temporal stop or not | Stop sign detected | |
| Weather | Visibility reduced due to weather conditions | Temporal stop | Heavy fog or rain obscures view |
| Road condition compromised | Temporal stop | Slippery road detected |
| Method | TC ↑ | SPD ↓ | SED ↑ | CLS ↑ | nDTW ↑ | sDTW ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORAR | 1.65 | 24.02 | 1.08 | 16.35 | 4.15 | 1.05 |
| DynaVLN | 2.74 | 23.65 | 1.41 | 15.07 | 3.26 | 2.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Aoki, Y. DynamicVLN: Incorporating Dynamics into Vision-and-Language Navigation Scenarios. Sensors 2025, 25, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020364
Sun Y, Qiu Y, Aoki Y. DynamicVLN: Incorporating Dynamics into Vision-and-Language Navigation Scenarios. Sensors. 2025; 25(2):364. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020364
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yanjun, Yue Qiu, and Yoshimitsu Aoki. 2025. "DynamicVLN: Incorporating Dynamics into Vision-and-Language Navigation Scenarios" Sensors 25, no. 2: 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020364
APA StyleSun, Y., Qiu, Y., & Aoki, Y. (2025). DynamicVLN: Incorporating Dynamics into Vision-and-Language Navigation Scenarios. Sensors, 25(2), 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25020364







