SWCNT/PEDOT:PSS/SA Composite Yarns with High Mechanical Strength and Flexibility via Wet Spinning for Thermoelectric Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
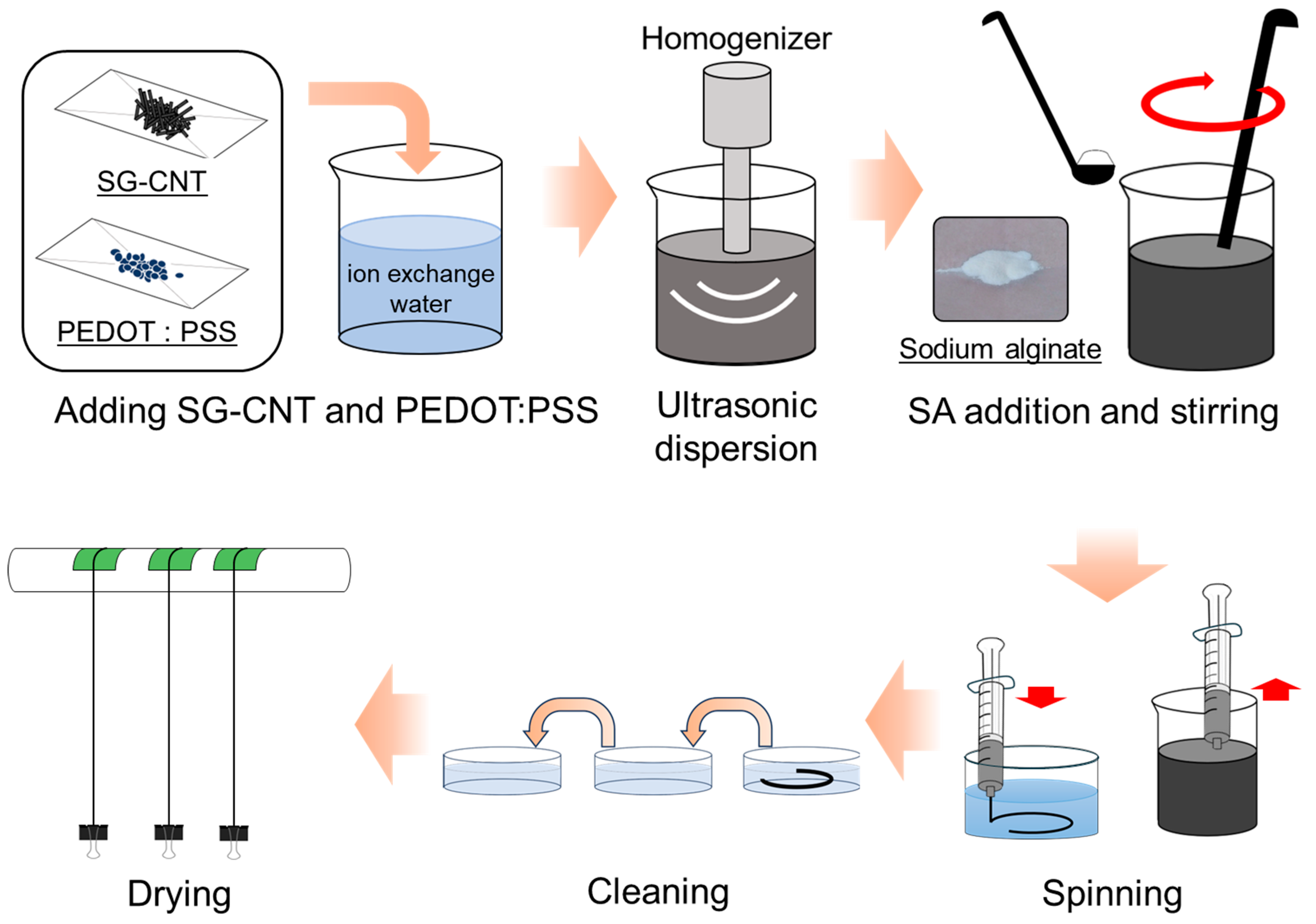
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
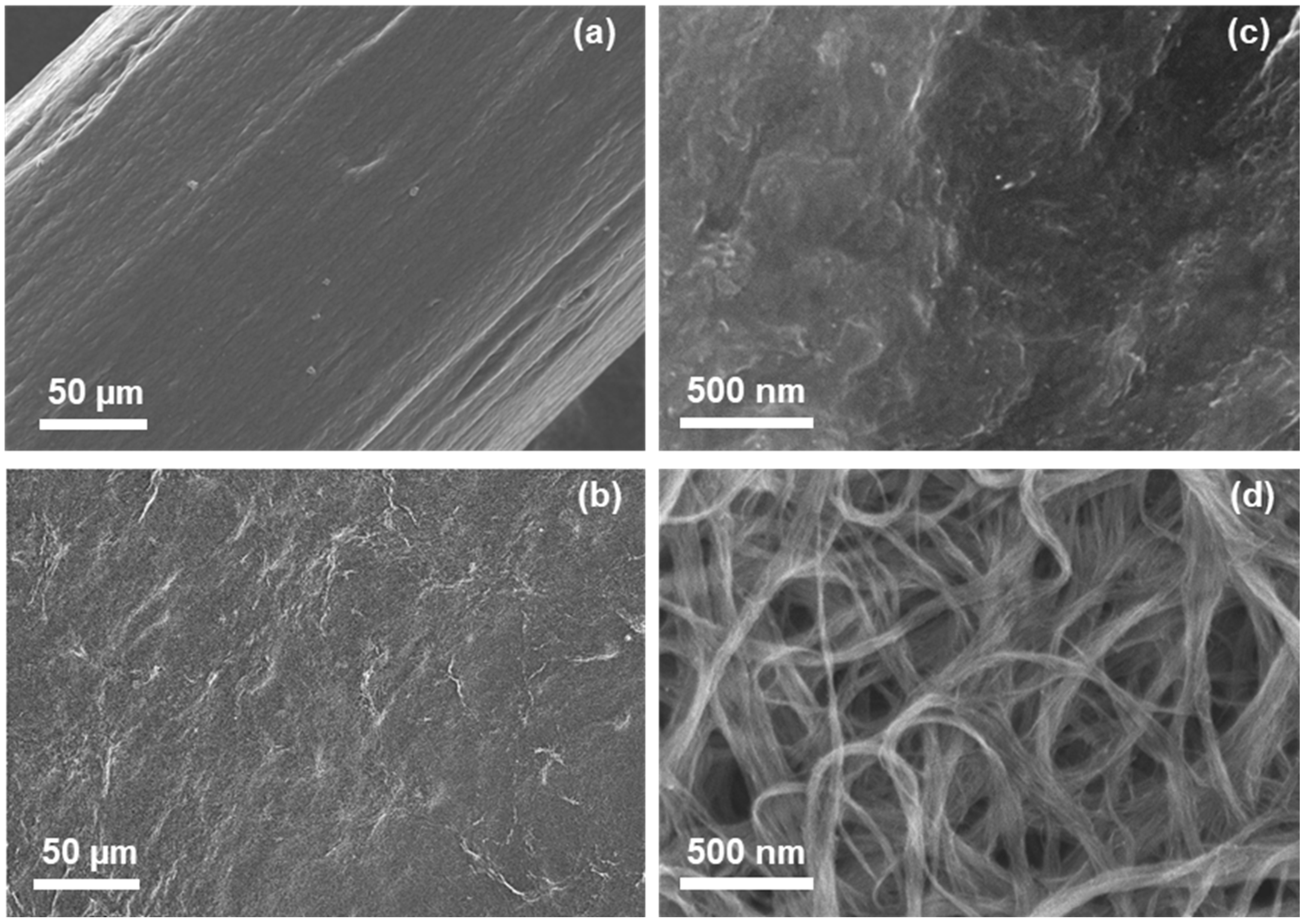
3.1. Properties of Composite Yarns
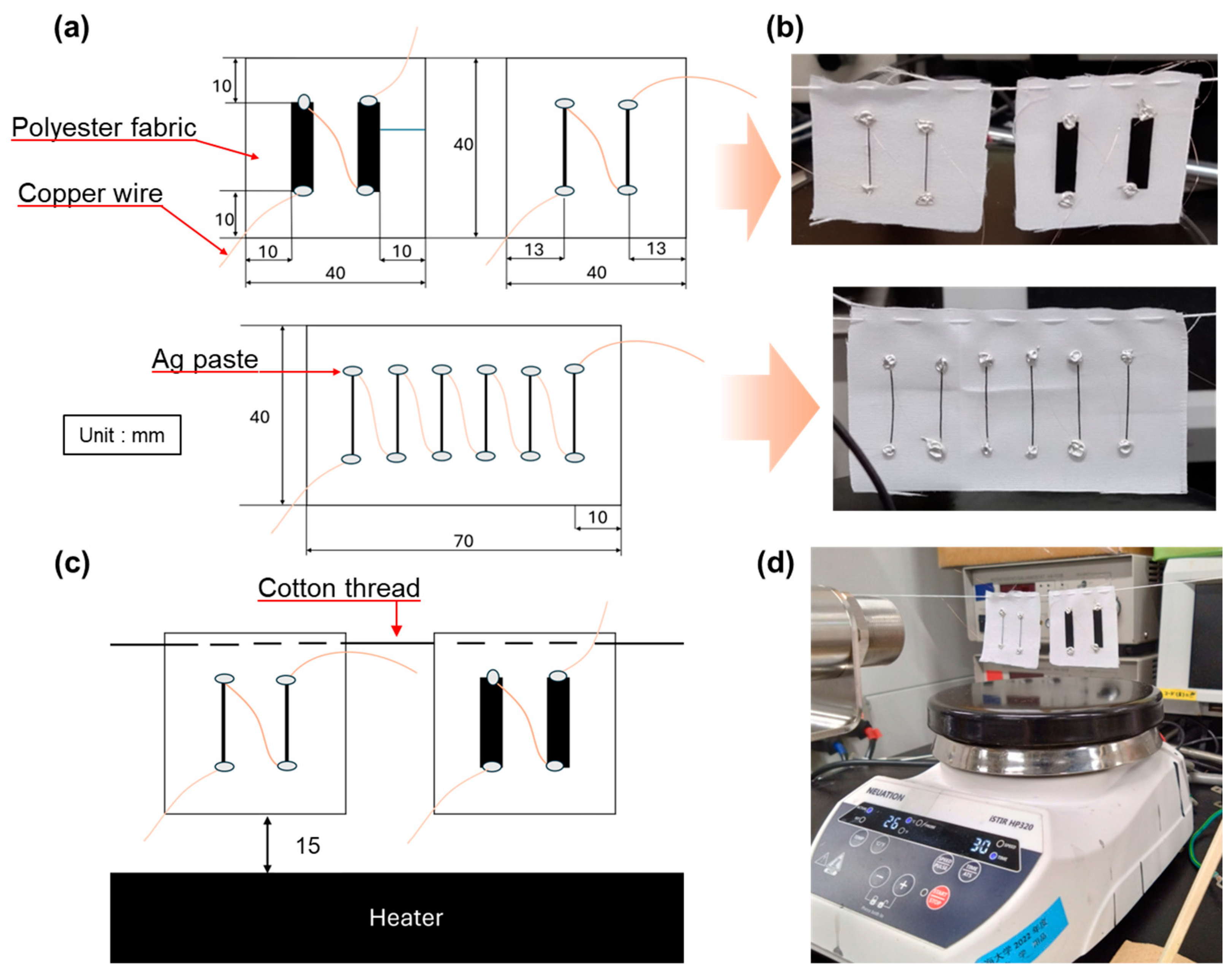
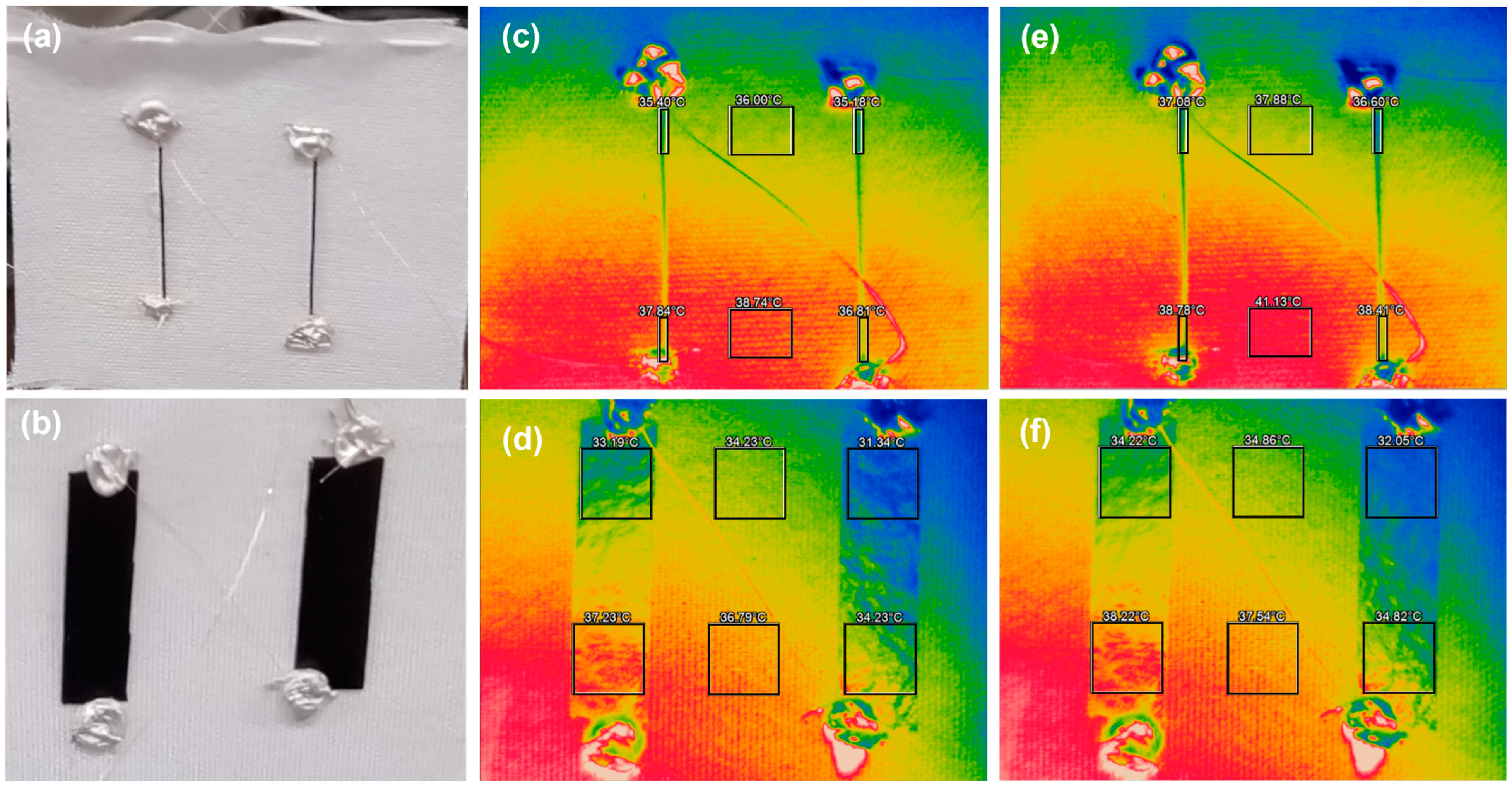
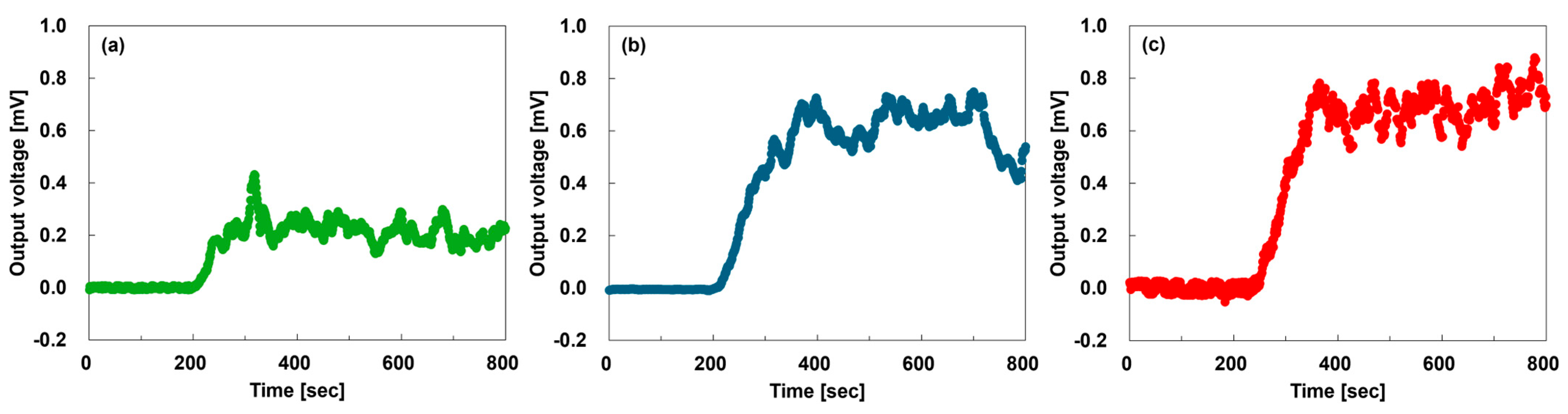
3.2. Performance of Composite-Yarn TEGs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nižetić, S.; Šolić, P.; López-de-Ipiña, D.; González-de-Artaza, D.; Patrono, L. Internet of Things (IoT): Opportunities, issues and challenges towards a smart and sustainable future. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 122877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullo, S.L.; Sinha, G.R. Advances in smart environment monitoring systems using IoT and sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, C.S.; Suryadevara, K.N.; Nag, A. Wearable sensors and systems in the IoT. Sensors 2021, 21, 7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dian, F.J.; Reza, V.; Alireza, R. Wearables and the internet of things (IoT), applications, opportunities, and challenges: A survey. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 69200–69211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuti, G.; Ricotti, L.; Menciassi, A.; Dario, P. MEMS sensor technologies for human centred applications in healthcare, physical activities, safety and environmental sensing: A review on research activities in Italy. Sensors 2015, 15, 6441–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Guo, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Lan, W.; Liao, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y. A review of recent advances in vital signals monitoring of sports and health via flexible wearable sensors. Sensors 2022, 22, 7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Antwi-Afari, M.F.; Fadaie, S.; Mi, H.; Anwer, S.; Liu, J. Self-powered wearable internet of things sensors for human-machine interfaces: A systematic literature review and science mapping analysis. Nano Energy 2024, 131, 110252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, G.; Zheng, Y.; Sawan, M. Energy solutions for wearable sensors: A review. Sensors 2021, 21, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Wang, P.; Jiang, L.; Wang, B.; Yao, Y.; Liu, S.; Chu, D.; Cheng, W.; Lu, Y. Power generation for wearable systems. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 2114–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.W.; Ismail, W.; Ko, K.; Lee, C.Y. Energy harvesting for wearable devices: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 9047–9062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Song, Y.; Han, M.; Zhang, H. Portable and wearable self-powered systems based on emerging energy harvesting technology. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2021, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargusch, M.; Liu, W.D.; Chen, Z.G. Thermoelectric generators: Alternative power supply for wearable electrocardiographic systems. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, H.; Munir, K.; Eugeni, M.; Atek, S.; Gaudenzi, P. Energy harvesting towards self-powered IoT devices. Energies 2020, 13, 5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Energy harvesting for self-powered nanosystems. Nano Res. 2008, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, T.; Amma, Y.; Takashiri, M. Heat source free water floating carbon nanotube thermoelectric generators. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanfua, J.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, H.; Liu, P.; Hu, D.; Pei, Y.; Liu, W.; Crispin, X.; Fabiano, S.; Ma, Y.; et al. Wearable thermoelectric materials and devices for self-powered electronic systems. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2102990. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Gao, H.; Lin, Z.; Zhu, W.; Ye, H. A novel self-powered wireless temperature sensor based on thermoelectric generators. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 80, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Hoshino, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Kaneko, K.; Okano, Y.; Takashiri, M. Stretchable and flexible painted thermoelectric generators on Japanese paper using inks dispersed with p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes. Sensors 2024, 24, 2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Amezawa, T.; Okano, Y.; Hoshino, K.; Ochiai, S.; Sunaga, K.; Miyake, S.; Takashiri, M. High thermal durability and thermoelectric performance with ultra-low thermal conductivity in n-type single-walled carbon nanotube films by controlling dopant concentration with cationic surfactant. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2025, 126, 063902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Fang, Y.; Lyu, X.; Peng, X.; Zhong-Zhen Luo, Z.-Z.; Zou, Z. Construction and application of thermogalvanic hydrogels. Soft Sci. 2024, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, Y.; Ochiai, S.; Okano, Y.; Okutsu, R.; Amma, Y.; Takashiri, M. Enhancing heat-source free water-floating single-walled carbon nanotube thermoelectric generators with water-absorbing paper. J. Power Sources 2025, 642, 236966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-K.; Kim, M.-S.; Lee, S.; Kim, C.; Kim, Y.-J. Wearable thermoelectric generator for harvesting human body heat energy. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 105002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyland, M.; Hunter, H.; Liu, J.; Veety, E.; Vashaee, D. Wearable thermoelectric generators for human body heat harvesting. Appl. Energy 2016, 182, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhu, R. A fully self-powered wearable monitoring system with systematically optimized flexible thermoelectric generator. Appl. Energy 2020, 271, 115250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, F.; Nozariasbmarz, A.; Vashaee, D.; Öztürk, M.C. Designing thermoelectric generators for self-powered wearable electronics. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2099–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, A.; Alam, M.M.; Middya, T.R.; Mandal, D. A pyroelectric generator as a self-powered temperature sensor for sustainable thermal energy harvesting from waste heat and human body heat. Appl. Energy 2018, 221, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norimasa, O.; Tamai, R.; Nakayama, H.; Shinozaki, Y.; Takashiri, M. Self-generated temperature gradient under uniform heating in p–i–n junction carbon nanotube thermoelectric generators. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 15956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Qiu, P.; Chen, L.; Shi, X. Recent developments in flexible thermoelectric devices. Small Sci. 2021, 1, 2100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Kim, J.; Acharya, S.; Kim, W. Review on the operation of wearable sensors through body heat harvesting based on thermoelectric devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 200501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.L.; Chen, W.Y.; Zhang, T.; Zou, J.; Chen, Z.G. Fiber-based thermoelectrics for solid, portable, and wearable electronics. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 729–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Shi, J.; Hao, Y.; He, M.; Cai, J.; Qin, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, J. Highly stretchable, durable, and breathable thermoelectric fabrics for human body energy harvesting and sensing. Carbon Energy 2022, 4, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norimasa, O.; Chiba, T.; Hase, M.; Komori, T.; Takashiri, M. Improvement of thermoelectric properties of flexible Bi2Te3 thin films in bent states during sputtering deposition and post-thermal annealing. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 898, 162889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S.; Ichihashi, T. Single-shell carbon nanotubes of 1-nm diameter. Nature 1993, 363, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, J.L.; Ferguson, A.J.; Cho, C.; Grunlan, J.C. Carbon-nanotube-based thermoelectric materials and devices. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Han, S.; Che, C. Organic thermoelectric materials for wearable electronic devices. Sensors 2024, 24, 4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Xu, W.; Zhu, D. Recent advances in organic polymer thermoelectric composites. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2017, 5, 4350–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, B. Carbon nanotube-based organic thermoelectric materials for energy harvesting. Polymers 2018, 10, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, T.; Yabuki, H.; Takashiri, M. High thermoelectric performance of flexible nanocomposite films based on Bi2Te3 nanoplates and carbon nanotubes selected using ultracentrifugation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, Y.; Takashiri, M. Freestanding bilayers of drop-cast single-walled carbon nanotubes and electropolymerized poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for thermoelectric energy harvesting. Org. Electron. 2018, 76, 105478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, L.; Armentano, I.; Lozzi, L.; Santucci, S.; Kenny, J.M. Interaction of methane with carbon nanotube thin films: Role of defects and oxygen adsorption. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2004, 4, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Park, N.; Ko, J.; Bae, E.; Park, W. Oxygen-induced p-type doping of a long individual single-walled carbon nanotube. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Huang, H.; Wang, D.; Liu, D.; Wang, L. Organic radical compound and carbon nanotube composites with enhanced electrical conductivity towards high-performance p-type and n-type thermoelectric materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 24675–24684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, S.; Chiba, T.; Seki, Y.; Takashiri, M. Origin of n-type properties in single wall carbon nanotube films with anionic surfactants investigated by experimental and theoretical analyses. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, Y.; Nagata, K.; Takashiri, M. Facile preparation of air-stable n-type thermoelectric single-wall carbon nanotube films with anionic surfactants. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, G. A convenient and highly-tunable way to n-type carbon nanotube thermoelectric composite film using common alkylammonium cationic surfactant. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 19030–19037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlie, L.; Shapter, J. Advances in carbon nanotube n-type doping: Methods, analysis and applications. Carbon 2018, 126, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khongthong, J.; Raginov, I.N.; Khabushev, M.E.; Goldt, E.A.; Kondrashov, A.V.; Russakov, M.D.; Shandakov, D.S.; Krasnikov, V.D.; Nasibulin, G.A. Aerosol doping of SWCNT films with p- and n-type dopants for optimizing thermoelectric performance. Carbon 2024, 218, 118670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amma, Y.; Miura, K.; Nagata, S.; Nishi, T.; Miyake, S.; Miyazaki, K.; Takashiri, M. Ultra-long air-stability of n-type carbon nanotube films with low thermal conductivity and all-carbon thermoelectric generators. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Okano, Y.; Uchida, K.; Kageshima, M.; Kuzumaki, T.; Miyake, S.; Takashiri, M. Phonon transports in single-walled carbon nanotube films with different structures determined by tensile tests and thermal conductivity measurements. Carbon Trends 2024, 17, 100435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M. Yarn spun from carbon nanotube forests: Production, structure, properties and applications. Particuology 2013, 11, 378–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dariyal, P.; Arya, K.A.; Singh, P.B.; Dhakate, R.S. A review on conducting carbon nanotube fibers spun via direct spinning technique. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 1087–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Davis, C.R.; Futaba, N.D.; Sakurai, S.; Kobashi, K.; Yumura, M.; Hata, K. A sweet spot for highly efficient growth of vertically aligned single-walled carbon nanotube forests enabling their unique structures and properties. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Yamashita, I. Thermoelectric cloths using carbon nanotube yarn for wearable electronics. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2024, 63, 010803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, W.; Jing, Y.; Chen, X.; Han, X.; Bao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; et al. Carbon nanotube yarn based thermoelectric textiles for harvesting thermal energy and powering electronics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 2984–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzounis, L.; Gravalidis, C.; Vassiliadou, S.; Logothetidis, S. Fiber yarns/CNT hierarchical structures as thermoelectric generators. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 7070–7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.M.; Okamoto, N.; Abe, R.; Pandey, M.; Moneim, A.A.; Nakamura, M. Gas phase doping of pre-fabricated CNT yarns for enhanced thermoelectric properties. Synth. Met. 2021, 280, 116874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culebras, M.; Ren, G.; O’Connell, S.; Vilatela, J.J.; Collins, N.M. Lignin doped carbon nanotube yarns for improved thermoelectric efficiency. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2020, 4, 2000147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, J.; Liang, L.; Deng, L.; Chen, G. A PEDOT:PSS thermoelectric fiber generator. Nano Energy 2022, 102, 107678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, W.; Kang, Y.H.; Cho, S.Y.; Jang, K.-S. Wet-spinning and post-treatment of CNT/PEDOT:PSS composites for use in organic fiber-based thermoelectric generators. Carbon 2018, 133, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabia-Riquelme, R.; Noble, L.E.; Espejo, P.A.; Ke, Z.; Graham, K.R.; Mei, J.; Paterson, A.F.; Weisenberger, M.C. Highly conductive n-type polymer fibers from the wet-spinning of n-doped PBDF and their application in thermoelectric textiles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2311379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, J.; Lekakou, C. Thermoelectric polymer composite yarns and an energy harvesting wearable textile. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 095006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lund, A.; Noh, H.; Hofmann, A.I.; Craighero, M.; Darabi, S.; Zokaei, S.; Park, J.I.; Yoon, M.-H.; Müller, C. Robust PEDOT:PSS wet-spun fibers for thermoelectric textiles. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 1900749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, K. Direct wet-spun single-walled carbon nanotubes-based p-n segmented filaments toward wearable thermoelectric textiles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 44704–44712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, N.; Zeo, X.; Zhou, J.; Sun, C.; Chen, C.; Jiang, D.; Xu, H.; Wang, W.; Pan, L.; Fan, Z. Boosting thermoelectric performance of wet-spun PEDOT:PSS-based organic/inorganic composite fibers via a dual-interfacial engineering approach. Small 2025, 21, 2500866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Li, P.; Zhang, H.; He, C. Enhanced thermoelectric properties of carbon nanotubes/polyaniline fibers through engineering doping level and orientation. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2024, 253, 110660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Wang, M.; Bo, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, F.; Liang, J.; Huang, Y.; Ma, R.; et al. Highly stretchable carbon nanotubes/polymer thermoelectric fibers. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cao, X.; Wen, M.; Chen, C.; Wen, Q.; Fu, Q.; Deng, H. Highly electrical conductive PEDOT:PSS/SWCNT flexible thermoelectric films fabricated by a high-velocity non-solvent turbulent secondary doping approach. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 10947–10957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, P.; Zhang, C.; He, C. Wet-spun flexible carbon nanotubes/polyaniline fibers for wearable thermoelectric energy harvesting. Compos. Part A 2023, 166, 107386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Mo, J.-H.; Kang, Y.H.; Cho, S.Y.; Jang, K.-S. Thermoelectric fibers from well-dispersed carbon nanotube/poly(vinylidene fluoride) pastes for fiber-based thermoelectric generators. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 19766–19773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Yang, S.; Li, P.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Liu, Z. Wet-spun PEDOT:PSS/CNT composite fibers for wearable thermoelectric energy harvesting. Compos. Commun. 2022, 32, 101179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guo, X.; Liu, W.; Lee, C. Recent progress in the energy harvesting technology—From self-powered sensors to self-sustained IoT, and new applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okano, Y.; Ochiai, S.; Nakayama, H.; Nagai, K.; Takashiri, M. Optimization of Ultrasonic Dispersion of Single-Walled SWCNT Inks for Improvement of Thermoelectric Performance in SWCNT Films Using Heat Source-Free Water-Floating SWCNT Thermoelectric Generators. Materials 2025, 18, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Deng, H.; Fu, Q. Recent progress on PEDOT:PSS based polymer blends and composites for flexible electronics and thermoelectric devices. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 3130–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemata, A.T.; Zheng, Y.; Kyaw, K.K.A.; Wang, X.; Song, J.; Chin, S.W.; Xu, J. Modulation of the doping level of PEDOT:PSS film by treatment with hydrazine to improve the Seebeck coefficient. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 1786–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Ma, Y.; Yan, X. Preparation and characterization of coaxial multiwalled carbon nanotubes/polyaniline tubular nanocomposites for electrochemical energy storage in the presence of sodium alginate. Synth. Met. 2014, 193, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Shi, X.-L.; Liu, W.-D.; Li, M.; Yue, F.; Huang, P.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Z.-G. High thermoelectric performance and flexibility in rationally treated PEDOT:PSS fiber bundles. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2024, 6, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behabtu, N.; Young, C.C.; Tsentalovich, D.E.; Kleinerman, O.; Wang, X.; Ma, A.W.K.; Bengio, E.A.; Ter Waarbeek, R.F.; De Jong, J.J.; Hoogerwerf, R.E.; et al. Strong, light, multifunctional fibers of carbon nanotubes with ultrahigh conductivity. Science 2013, 339, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Kong, D.; Tao, J.; Kong, N.; Mota-Santiago, P.; Lynch, P.A.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, J. Wet twisting in spinning for rapid and cost-effective fabrication of superior carbon nanotube yarns. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2400197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Coates, N.E.; Segalman, R.A.; Cahill, D.G. Thermal conductivity and elastic constants of PEDOT:PSS with high electrical conductivity. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami, M.; Ganji, D.D. Natural convection of sodium alginate (SA) non-Newtonian nanofluid flow between two vertical flat plates by analytical and numerical methods. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2014, 2, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Amezawa, T.; Tanaka, S.; Takashiri, M. Improved heat dissipation of dip-coated SWCNT/mesh sheets with high flexibility and free-standing strength for thermoelectric generators. Coatings 2024, 14, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Gao, C.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Deng, T.; Zhu, J. Wet spinning enabled advanced PEDOT:PSS composite fibers for smart devices. Acc. Mater. Res. 2025, 6, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
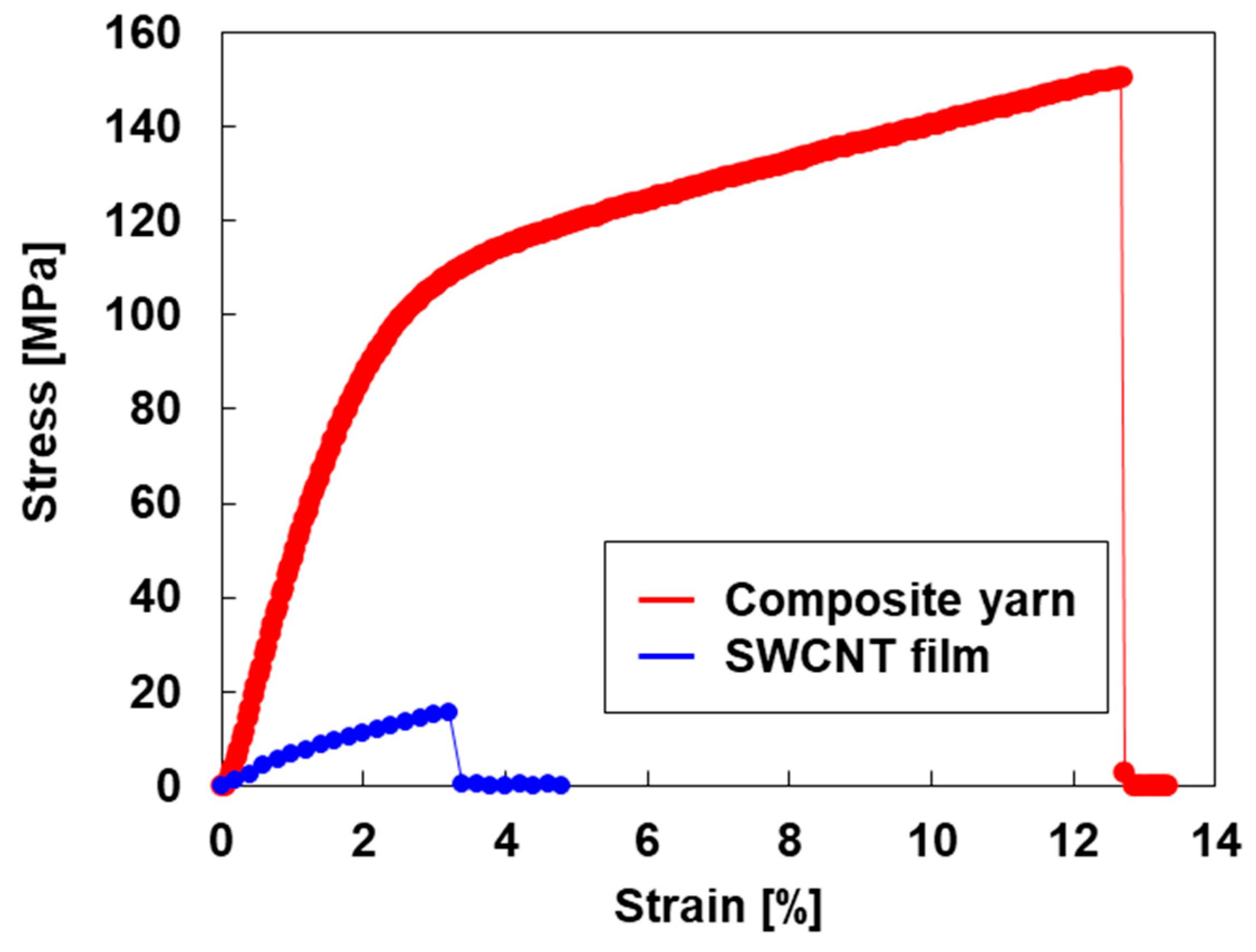
| Sample | Tensile Strength | Breaking Strain | Young’s Modulus | Mass Density | Longitudinal Sound Velocity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composite yarn | 151 MPa | 12.7% | 0.26 GPa | 1.36 g/cm3 | 437 m/s |
| SWCNT film | 16 MPa | 3.6% | 0.70 GPa | 0.42 g/cm3 | 1289 m/s |
| Sample | Seebeck Coefficient | Electrical Conductivity | Power Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Composite yarn | 29.4 μV/K | 15.3 S/cm | 1.3 μW/(m·K2) |
| SWCNT film | 55.5 μV/K | 29.0 S/cm | 8.9 μW/(m·K2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uchida, K.; Shinozaki, Y.; Nakayama, H.; Ochiai, S.; Nakazawa, Y.; Takashiri, M. SWCNT/PEDOT:PSS/SA Composite Yarns with High Mechanical Strength and Flexibility via Wet Spinning for Thermoelectric Applications. Sensors 2025, 25, 6202. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196202
Uchida K, Shinozaki Y, Nakayama H, Ochiai S, Nakazawa Y, Takashiri M. SWCNT/PEDOT:PSS/SA Composite Yarns with High Mechanical Strength and Flexibility via Wet Spinning for Thermoelectric Applications. Sensors. 2025; 25(19):6202. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196202
Chicago/Turabian StyleUchida, Keisuke, Yoshiyuki Shinozaki, Hiroto Nakayama, Shuya Ochiai, Yuto Nakazawa, and Masayuki Takashiri. 2025. "SWCNT/PEDOT:PSS/SA Composite Yarns with High Mechanical Strength and Flexibility via Wet Spinning for Thermoelectric Applications" Sensors 25, no. 19: 6202. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196202
APA StyleUchida, K., Shinozaki, Y., Nakayama, H., Ochiai, S., Nakazawa, Y., & Takashiri, M. (2025). SWCNT/PEDOT:PSS/SA Composite Yarns with High Mechanical Strength and Flexibility via Wet Spinning for Thermoelectric Applications. Sensors, 25(19), 6202. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196202







