Learning Hierarchically Consistent Disentanglement with Multi-Channel Augmentation for Public Security-Oriented Sketch Person Re-Identification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
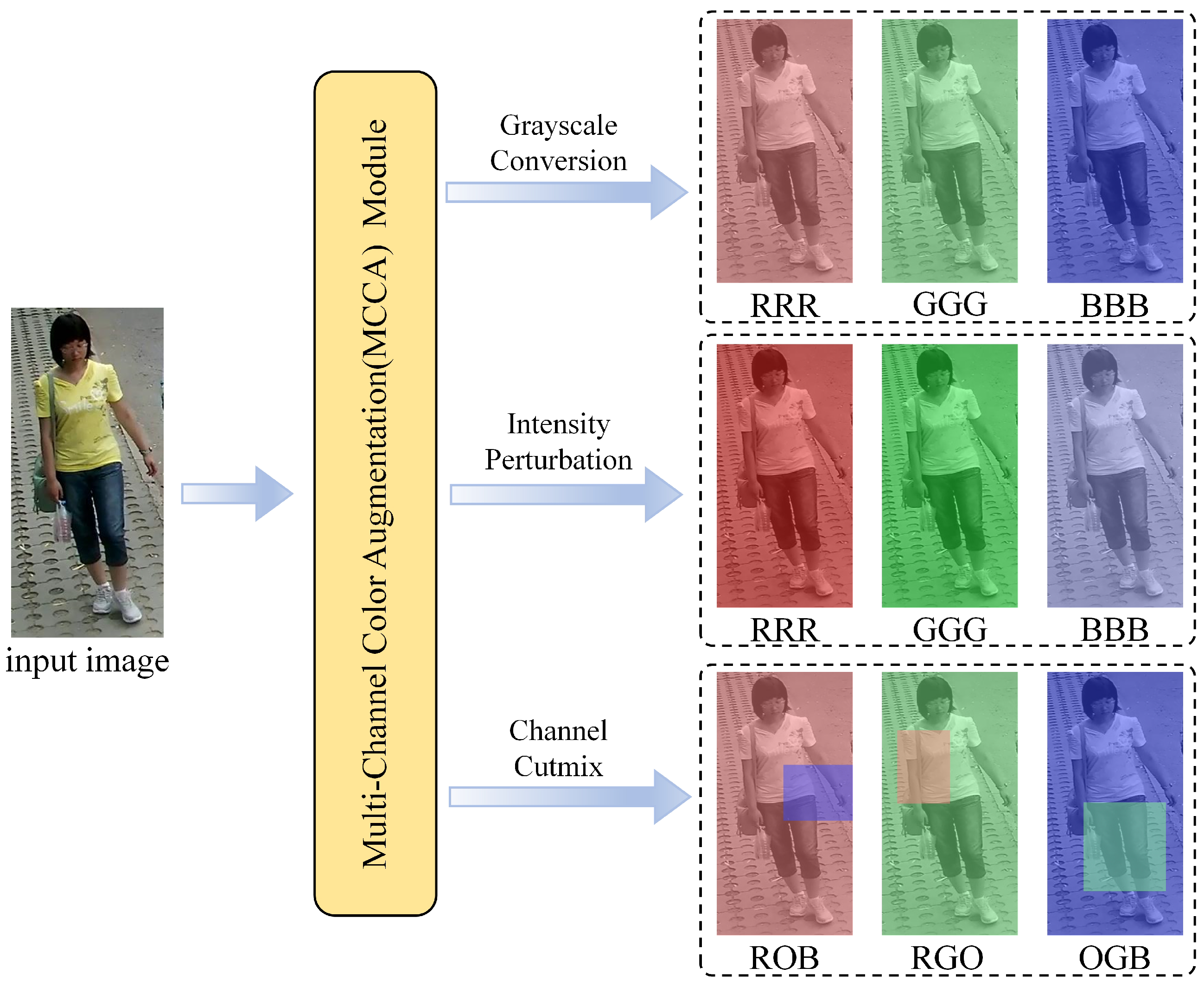
- A multi-channel color augmentation(MCCA) module is proposed to address the information asymmetry between sketch and photo modalities. By applying diverse color transformations to the input images, the network is encouraged to discover modality-invariant features beyond color cues.
- (2)
- A modality-disentangled prototype(MDP) module is introduced to disentangle sketch and photo features into structural and appearance prototypes at different network layers. Moreover, a cross-layer decoupling consistency constraint is incorporated to ensure that the decoupled representations maintain coherent semantic information across different network hierarchies.
- (3)
- Experimental results on the public sketch Re-ID dataset demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our proposed method through comprehensive experiments against state-of-the-art (SOTA) approaches.
2. Relate Work
2.1. Cross-Modal Person Re-Identification
2.2. Sketch Re-Identification
2.3. Disentangled Representation Learning
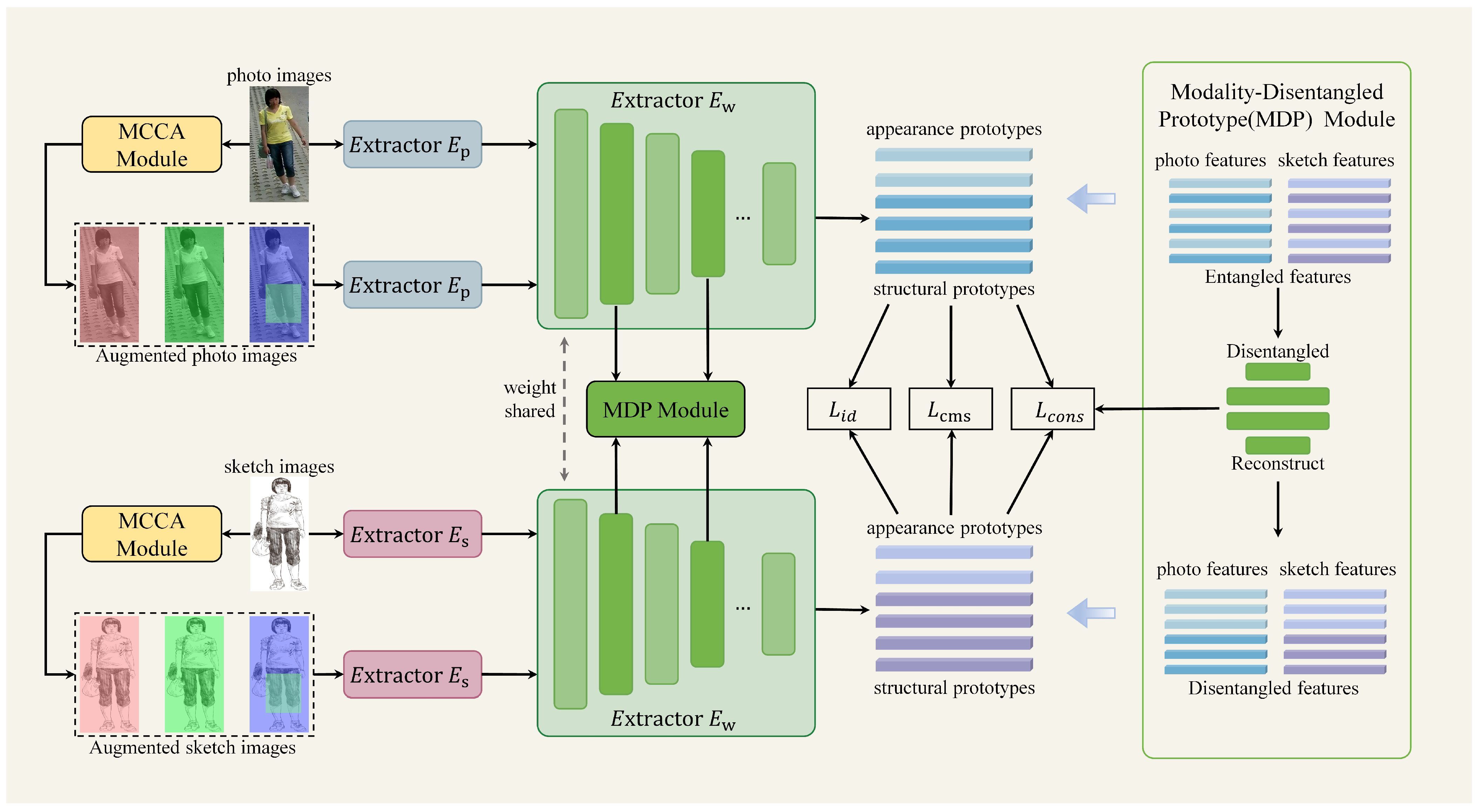
3. Method
3.1. The over All Framework
3.2. Multi-Channel Color Augmentation Module
3.3. Modality-Disentangled Prototype Module
3.4. Cross-Layer Decoupling Consistency Constraint
3.5. Overall Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Protocols
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Arts
4.4. Ablation Study
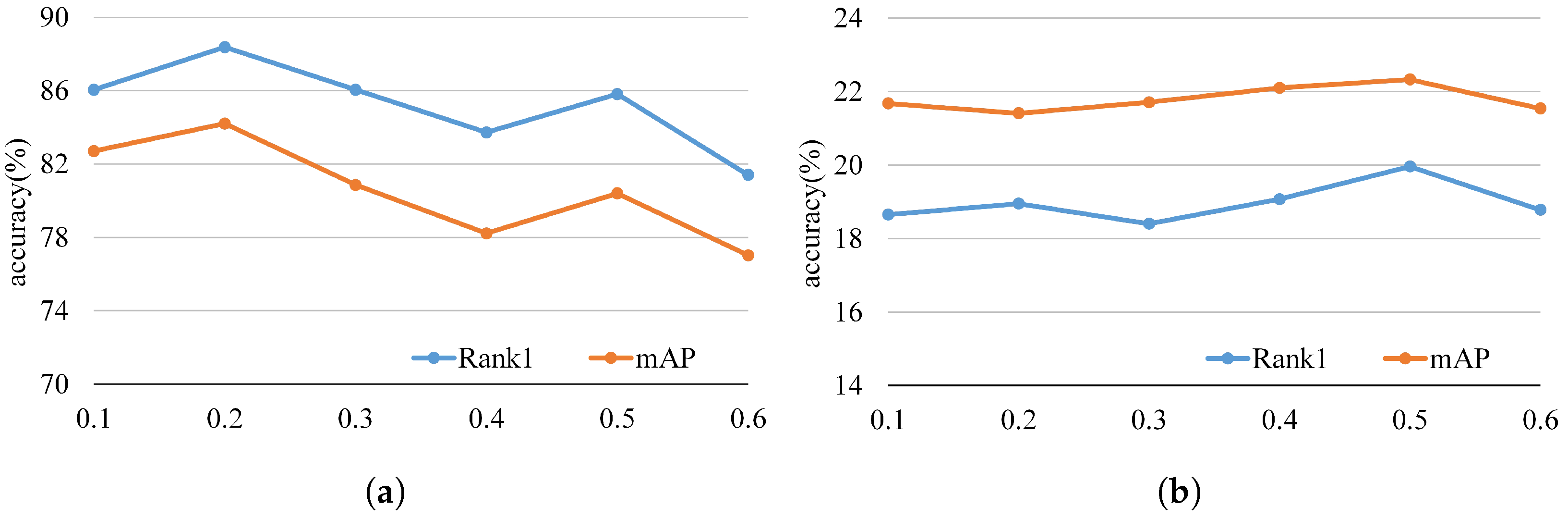
4.5. Parameter Analysis
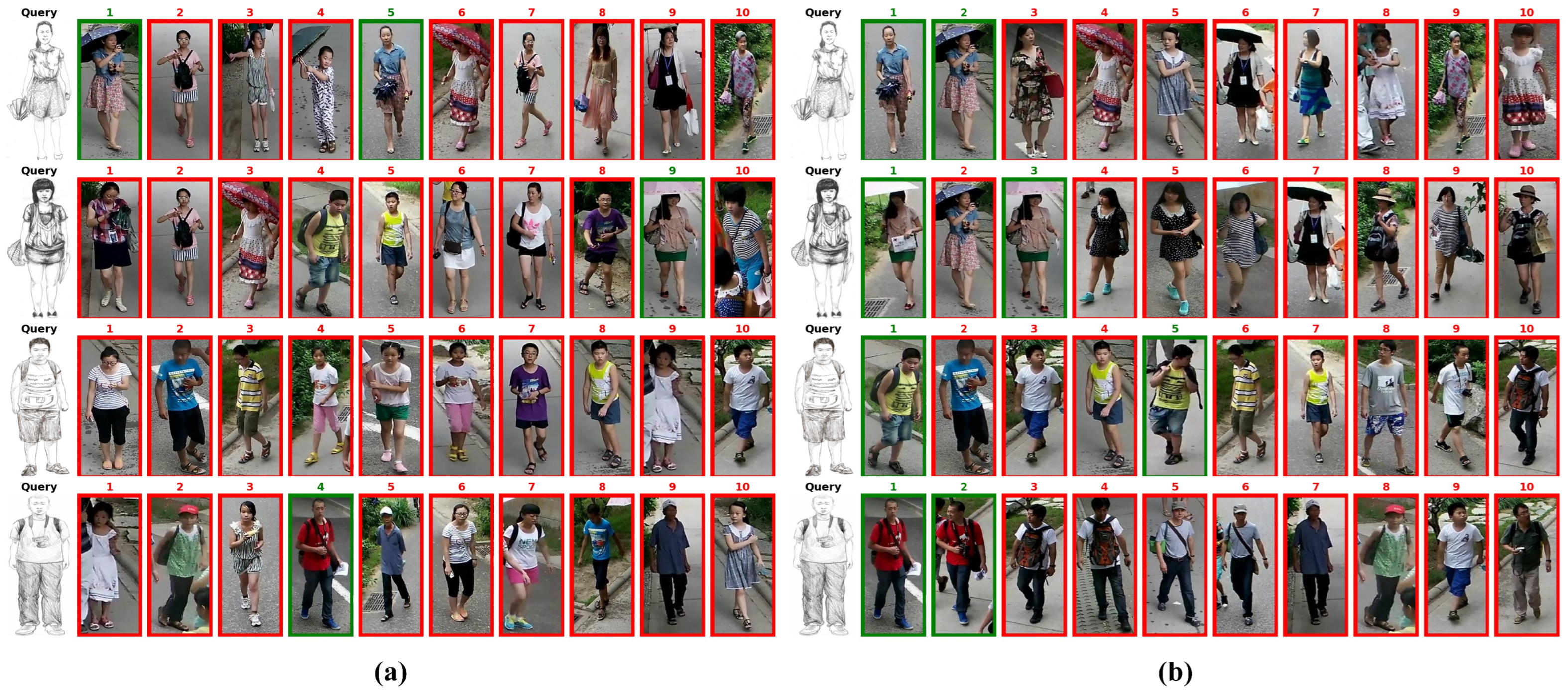
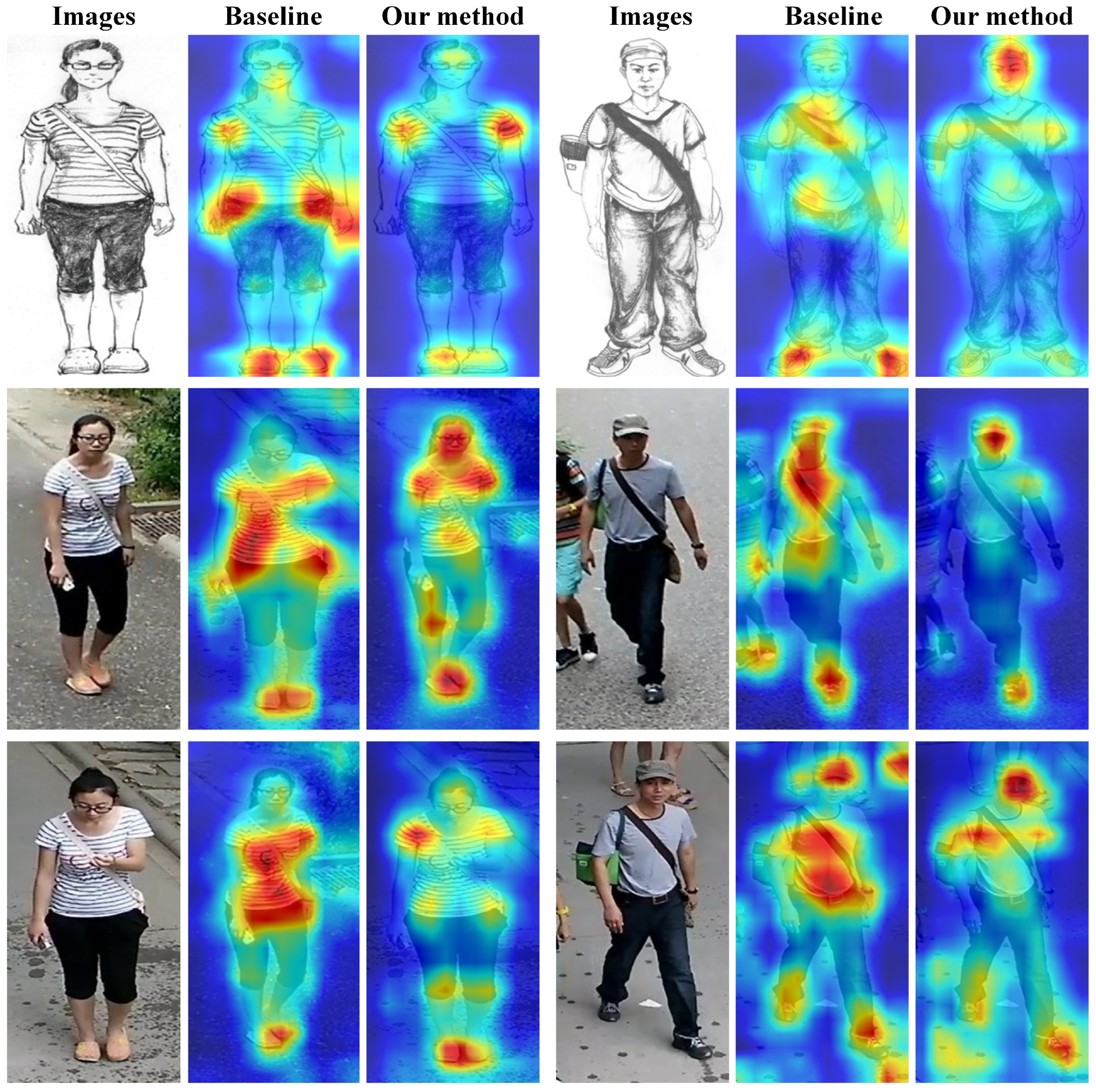
4.6. Visualization of Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, C.; Chen, J.; Fang, Q.; He, K.; Zhao, Z.; Ren, H.; Xu, G.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, Y. Rethinking Membership Inference Attacks Against Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2024, 19, 6441–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, J.; Zhu, S.; Feng, W.; He, K.; Du, R.; Xiang, Y. WAFBooster: Automatic Boosting of WAF Security Against Mutated Malicious Payloads. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2025, 22, 1118–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Jia, J.; Hu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, Y. Profit or Deceit? Mitigating Pump and Dump in DeFi via Graph and Contrastive Learning. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2025, 20, 8994–9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Gu, Y.; Liao, X.; Lai, S.; Jiang, W. Bag of Tricks and a Strong Baseline for Deep Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Shen, L.; Tian, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Tian, Q. Scalable Person Re-identification: A Benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 13–16 December 2015; pp. 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Quan, Z.; Zhao, K.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Mozerov, M.G. MSIF: Multi-spectrum image fusion method for cross-modality person re-identification. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2024, 15, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ye, M.; Qi, M.; Du, B. Sketch Transformer: Asymmetrical Disentanglement Learning from Dynamic Synthesis. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 4012–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ye, M.; Qi, M.; Du, B. SketchTrans: Disentangled Prototype Learning With Transformer for Sketch-Photo Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 2950–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; Zheng, W.S.; Yu, H.X.; Gong, S.; Lai, J. RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5390–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Zheng, W.; Gong, S.; Lai, J. RGB-IR Person Re-identification by Cross-Modality Similarity Preservation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 1765–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lai, C.; Liu, J.; Huang, N.; Han, J. FMCNet: Feature-Level Modality Compensation for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 7339–7348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Shen, J. Dual-Semantic Consistency Learning for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2022, 18, 1554–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, X.; Lu, X. Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification via Partially Interactive Collaboration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 6951–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, K.; Zhang, L. Implicit Discriminative Knowledge Learning for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Ding, P.; Li, J.; Chen, M. BiFFN: Bi-Frequency Guided Feature Fusion Network for Visible–Infrared Person Re-Identification. Sensors 2025, 25, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, I.B.; Cristani, M.; Bue, A.D.; Bazzani, L.; Murino, V. Re-identification with RGB-D Sensors. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 7–13 October 2012; pp. 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Zheng, W.S.; Lai, J. Robust Depth-based Person Re-identification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 2588–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Zheng, A.; He, R.; Tang, J. Interact, embed, and enlarge: Boosting modality-specific representations for multi-modal person re-identification. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 22 February–1 March 2022; pp. 2633–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, W.; Sun, M.; Niu, K.; Gao, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q. A Simple andRobust Correlation Filtering Method forText-Based Person Search. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, A.; Awais, M.; Kittler, J.; Khalid, S.S. AXM-Net: Implicit Cross-Modal Feature Alignment for Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 22 February–1 March 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Ye, M. Cross-Modal Implicit Relation Reasoning and Aligning for Text-to-Image Person Retrieval. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 2787–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Huang, T.; Tian, Y. Cross-domain adversarial feature learning for sketch re-identification. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, S.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, X.; Ling, X. Learning multi-level domain invariant features for sketch re-identification. Neurocomputing 2020, 403, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ye, J. Cross-Domain Attention and Center Loss for Sketch Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2022, 17, 3421–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, Z.; Mukherjee, M. Data compensation and feature fusion for sketch based person retrieval. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2024, 104, 104287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Shen, J.; Lin, G.; Xiang, T.; Shao, L.; Hoi, S.C.H. Deep Learning for Person Re-Identification: A Survey and Outlook. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 2872–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Sakti, S.; Nakamura, S. Instance-level heterogeneous domain adaptation for limited-labeled sketch-to-photo retrieval. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2020, 23, 2347–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Tao, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, P.; Deng, Y. Enhanced Multiview attention network with random interpolation resize for few-shot surface defect detection. Multimed. Syst. 2025, 31, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Quan, Z.; Zhao, K.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y. A Cross-Modality Sketch Person Re-identification Model Based on Cross-Spectrum Image Generation. In Proceedings of the Digital TV and Wireless Multimedia Communications, Shanghai, China, 8–9 December 2022; pp. 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Satoh, S. Beyond Domain Gap: Exploiting Subjectivity in Sketch-Based Person Retrieval. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 2078–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Tang, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, W. Disentangled Representation Learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 9677–9696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatys, L.A.; Ecker, A.S.; Bethge, M. Image Style Transfer Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2414–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Tseng, H.-Y.; Mao, Q.; Huang, J.-B.; Lu, Y.-D.; Singh, M.; Yang, M.-H. DRIT++: Diverse Image-to-Image Translation via Disentangled Representations. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 2402–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, F.; Fu, Y.; Xiang, T.; Jiang, Y.G.; Xue, X. Long-Term Cloth-Changing Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 30 November–4 December 2020; pp. 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sain, A.; Bhunia, A.K.; Yang, Y.; Xiang, T.; Song, Y. StyleMeUp: Towards Style-Agnostic Sketch-Based Image Retrieval. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 8504–8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yuan, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Hu, R. Rank-in-Rank Loss for Person Re-identification. ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput. Commun. Appl. 2022, 18, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.J.; Grother, P.; Micheals, R. Evaluation Methods in Face Recognition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 551–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Imagenet: A large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Xiang, T.; Hospedales, T.M.; Loy, C.C. Sketch me that shoe. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangkloy, P.; Burnell, N.; Ham, C.; Hays, J. The sketchy database: Learning to retrieve badly drawn bunnies. ACM Trans. Graph. 2016, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, S. Cross-Compatible Embedding and Semantic Consistent Feature Construction for Sketch Re-identification. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 3347–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Shen, J.; Crandall, D.J.; Shao, L.; Luo, J. Dynamic Dual-Attentive Aggregation Learning for Visible-Infrared Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Hu, Y.; Wu, X.; Shi, H.; Mei, T.; He, R. CM-NAS: Cross-Modality Neural Architecture Search for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 11823–11832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Ruan, W.; Du, B.; Shou, M.Z. Channel Augmented Joint Learning for Visible-Infrared Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 13567–13576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Huang, Z.; Hu, P.; Li, T.; Lv, J.; Peng, X. Learning with Twin Noisy Labels for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 14288–14297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Qu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Ma, L. Not All Pixels Are Matched: Dense Contrastive Learning for Cross-Modality Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 5333–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Diverse Embedding Expansion Network and Low-Light Cross-Modality Benchmark for Visible-Infrared Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 2153–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Jin, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Feng, S.; Li, Y. Bridging the Gap: Multi-Level Cross-Modality Joint Alignment for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 2024, 34, 7683–7698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H. Towards a Unified Middle Modality Learning for Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Chengdu, China, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhay, A.; Sarkar, A.; Howlader, P.; Balasubramanian, V.N. Grad-CAM++: Generalized Gradient-Based Visual Explanations for Deep Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 839–847. [Google Scholar]





| Datasets | IDs | Photos | Sketches | Cameras | Styles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PKU-Sketch | 200 | 400 | 200 | 2 | 5 |
| Market-Sketch-1K | 996 | 32,668 | 4763 | 6 | 6 |
| Method | Source | Rank1 | Rank5 | Rank10 | Rank20 * | mAP * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triple SN [40] | CVPR’16 | 9.00 | 26.80 | 42.20 | 65.20 | - |
| GN Siamese [41] | TOG’16 | 28.90 | 54.00 | 62.40 | 78.20 | - |
| CD-AFL [22] | MM’18 | 34.00 | 56.30 | 72.50 | 84.70 | - |
| LDMI [23] | Neuro’20 | 49.00 | 70.40 | 80.20 | 92.00 | - |
| IHDA [27] | TMM’20 | 85.00 | 94.80 | 98.00 | 100 | - |
| CDA [24] | TIFS’22 | 60.80 | 80.60 | 88.80 | 95.00 | - |
| CSIG [29] | IFTC’22 | 77.60 | 93.00 | 97.00 | 98.80 | - |
| CCSC [42] | MM’22 | 86.00 | 98.00 | 100 | - | 83.70 |
| SketchTrans [7] | MM’22 | 84.60 | 94.80 | 98.20 | 99.80 | |
| MSIF [6] | IJMLC’24 | 87.00 | 96.80 | 98.70 | 98.82 | 91.12 |
| SketchTrans+ [7] | TPAMI’24 | 85.80 | 96.00 | 99.00 | 99.30 | - |
| Ours | - | 88.37 | 95.35 | 99.80 | 100 | 84.20 |
| Method | Source | Query | Rank1 | Rank5 | Rank10 | Rank20 * | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DDAG [43] | ECCV’20 | S | 11.22 | 25.40 | 35.02 | - | 12.13 |
| CM-NAS [44] | ICCV’21 | S | 0.70 | 2.00 | 3.90 | - | 0.82 |
| CAJ [45] | ICCV’21 | S | 1.48 | 3.97 | 7.34 | - | 2.38 |
| MMN [50] | MM’21 | S | 9.32 | 21.98 | 29.58 | - | 10.41 |
| DART [46] | CVPR’22 | S | 6.58 | 16.75 | 23.42 | - | 7.77 |
| DCLNet [47] | MM’22 | S | 12.24 | 29.20 | 39.58 | - | 13.45 |
| DSCNet [12] | TIFS’22 | S | 13.84 | 30.55 | 40.34 | - | 14.73 |
| DEEN [48] | CVPR’23 | S | 12.11 | 25.44 | 30.94 | - | 12.62 |
| Subjectivity [30] | MM’23 | S | 18.10 | 38.95 | 50.75 | - | 19.61 |
| M | 24.70 | 50.40 | 63.45 | - | 24.45 | ||
| MCJA [49] | TCSVT’24 | S | 14.51 | 33.67 | 44.73 | 58.19 | 15.86 |
| M | 27.31 | 52.01 | 65.66 | 76.51 | 26.39 | ||
| Ours | - | S | 19.96 | 40.08 | 52.24 | 66.08 | 22.33 |
| M | 31.53 | 51.2 | 62.65 | 75.9 | 31.36 |
| Method | Pku-Sketch | Market-Sketch-1K | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank-1 | mAP | mINP | Rank-1 | mAP | mINP | |
| Baseline | 65.43 | 64.03 | 53.16 | 6.41 | 9.09 | 4.15 |
| Baseline + MCCA(only RGB) | 74.67 | 75.58 | 62.71 | 11.52 | 13.18 | 6.40 |
| Baseline + MCCA | 82.22 | 79.50 | 64.18 | 17.69 | 18.08 | 8.79 |
| Baseline + MDP | 78.26 | 75.01 | 63.17 | 11.05 | 13.14 | 6.34 |
| Baseline + MDP + | 80.89 | 76.54 | 68.05 | 11.43 | 13.33 | 6.63 |
| Our Method | 88.37 | 84.20 | 77.34 | 19.96 | 22.33 | 15.50 |
| Method | Rank-1 | Rank-5 | Rank-10 | Rank-20 | mAP | mINP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 65.43 | 88.04 | 93.91 | 99.78 | 64.03 | 53.16 |
| Baseline + GC | 75.87 | 93.70 | 98.04 | 100 | 70.22 | 58.11 |
| Baseline + IP | 72.39 | 96.52 | 99.20 | 100 | 67.63 | 54.78 |
| Baseline + CCM | 71.74 | 90.43 | 98.26 | 99.57 | 68.41 | 57.24 |
| Our Method | 88.37 | 95.35 | 99.80 | 100 | 84.20 | 77.34 |
| Sketch Style | Pku-Sketch | Market-Sketch-1K | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank-1 | mAP | Rank-1 | mAP | |
| Style_1 | 82.14 | 69.10 | 30.51 | 27.88 |
| Style_2 | 100.00 | 93.67 | 12.50 | 15.96 |
| Style_3 | 94.96 | 89.23 | 21.21 | 23.02 |
| Style_4 | 77.50 | 57.91 | 12.75 | 17.75 |
| Style_5 | 82.33 | 82.99 | 11.50 | 13.75 |
| Style_6 | - | - | 22.04 | 21.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chen, J. Learning Hierarchically Consistent Disentanglement with Multi-Channel Augmentation for Public Security-Oriented Sketch Person Re-Identification. Sensors 2025, 25, 6155. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196155
Ye Y, Sun Z, Chen J. Learning Hierarchically Consistent Disentanglement with Multi-Channel Augmentation for Public Security-Oriented Sketch Person Re-Identification. Sensors. 2025; 25(19):6155. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196155
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Yu, Zhihong Sun, and Jun Chen. 2025. "Learning Hierarchically Consistent Disentanglement with Multi-Channel Augmentation for Public Security-Oriented Sketch Person Re-Identification" Sensors 25, no. 19: 6155. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196155
APA StyleYe, Y., Sun, Z., & Chen, J. (2025). Learning Hierarchically Consistent Disentanglement with Multi-Channel Augmentation for Public Security-Oriented Sketch Person Re-Identification. Sensors, 25(19), 6155. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196155






