Enhanced Nanoparticle Sensing by Sagnac–Fizeau Shift in a Microcavity Based on Exceptional Surfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
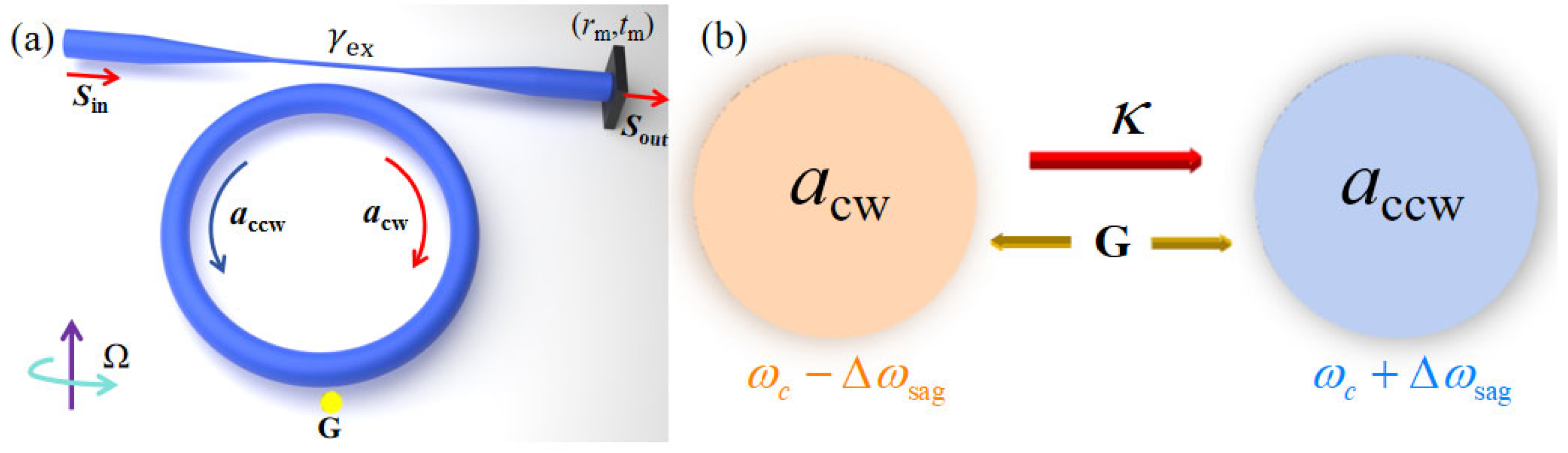
2. Theoretical Models
3. Results and Discussion
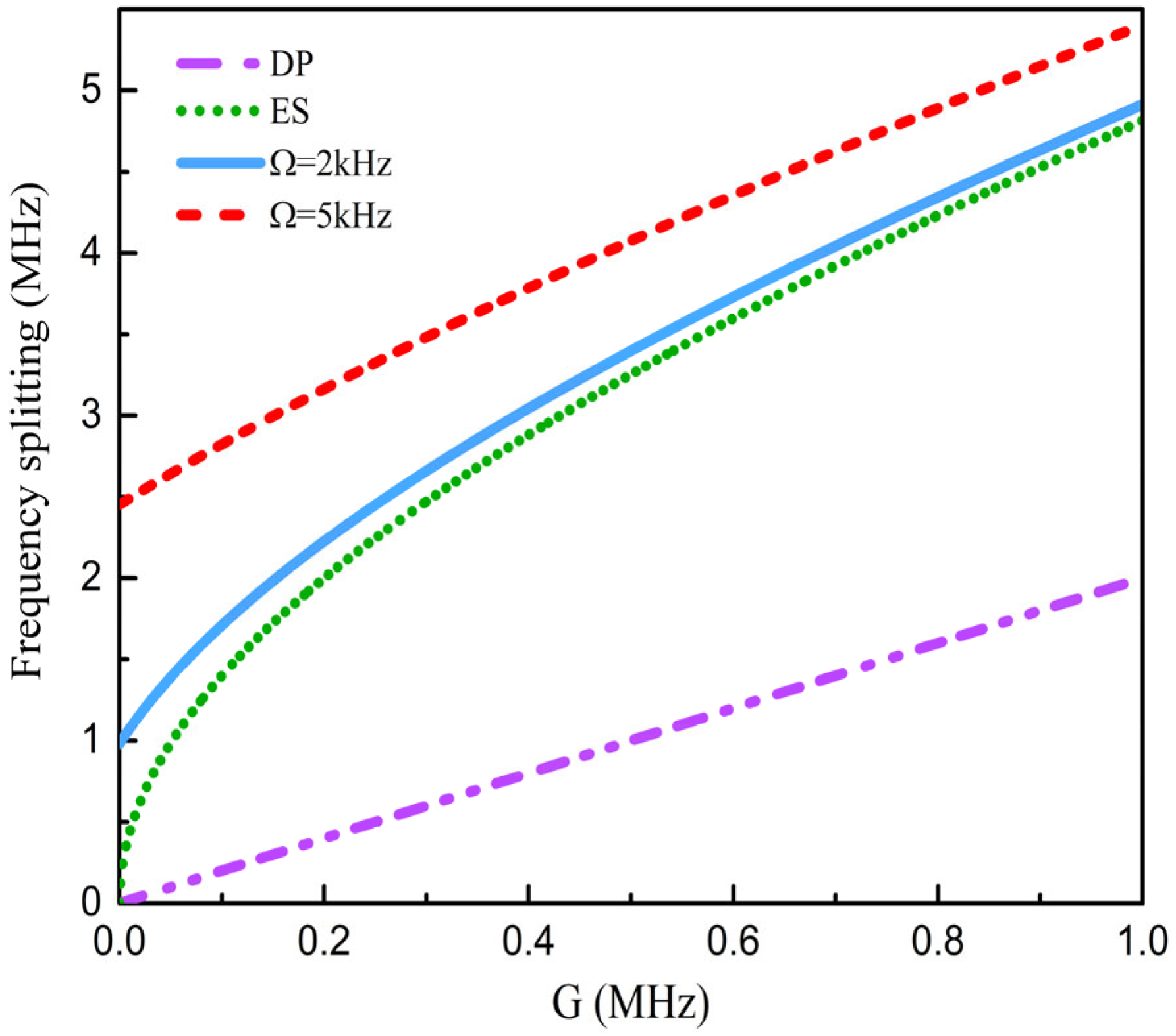
3.1. Enhanced Frequency Splitting in the ES-Based Structure
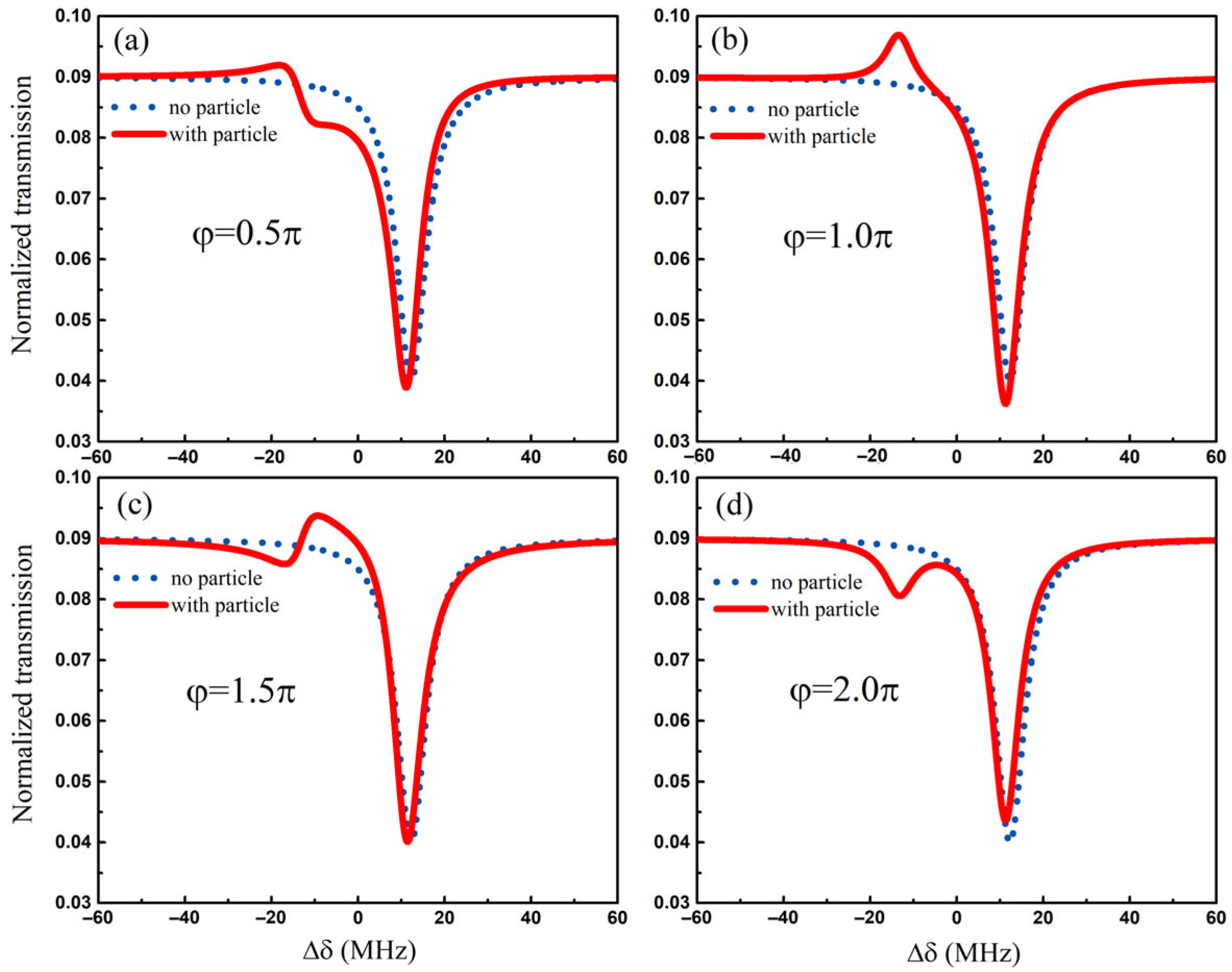
3.2. Manipulating Spectral Line Shape in the ES-Based Structure
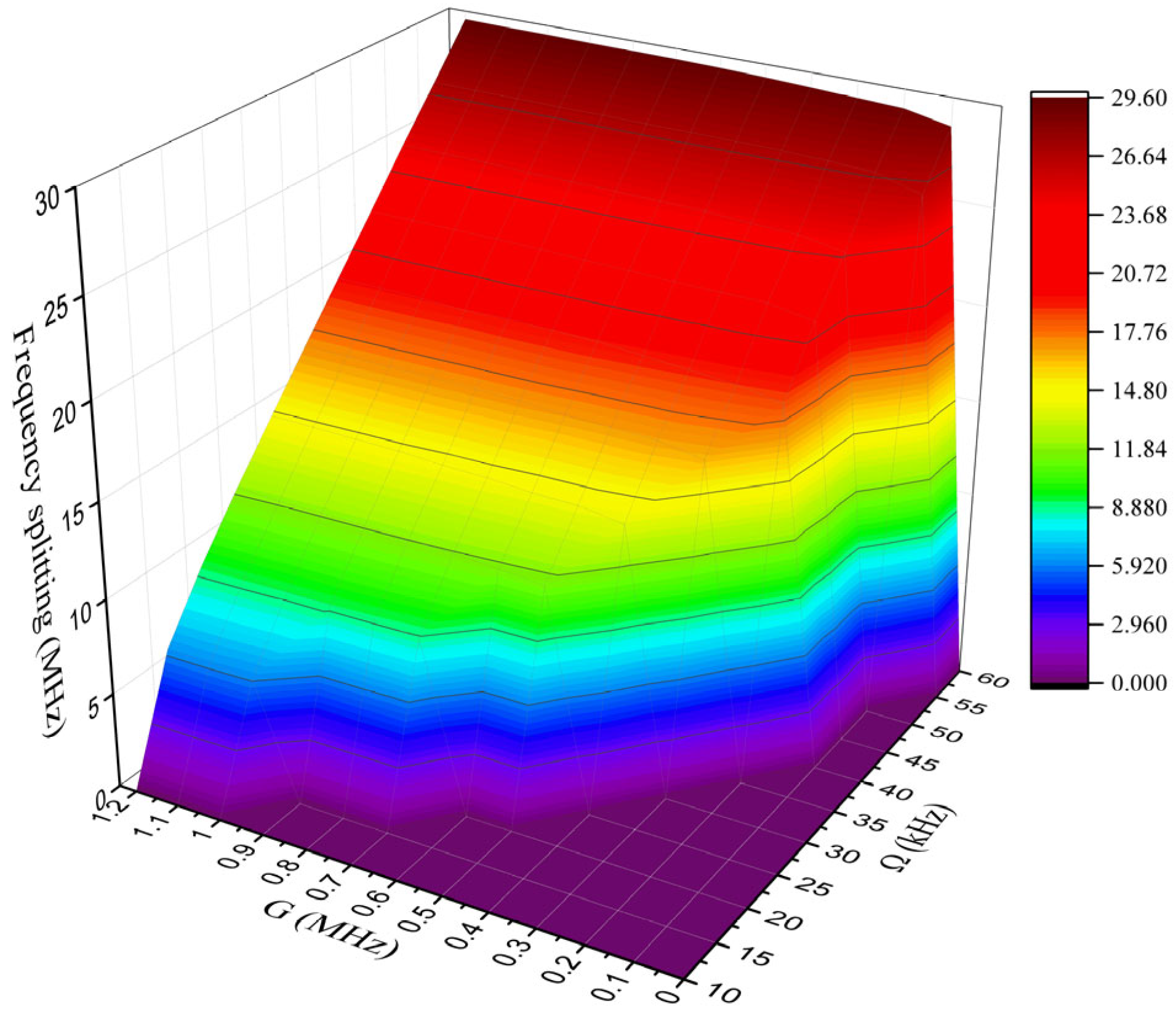
3.3. Enhancement of Frequency Splitting in the Spectrum
3.4. Improvement of the Detection Limit
3.5. Experimental Consideration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Parameters | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Diameter of the microcavity | d |
| Input light field | Sin |
| Output light field | Sout |
| Wavelength of input light | |
| Coupling coefficient | |
| Reflection coefficient of the partially reflective mirror | rm |
| Transmission coefficient of the partially reflective mirror | tm |
| Unidirectional coupling strength | |
| Angular velocity | |
| Transmission amplitude in the reflection | |
| Phase accumulation in the reflection | |
| Refractive index of the microcavity | |
| Resonant frequency of a stationary microcavity | |
| Speed of light | |
| Dispersion term | |
| Total loss of the microcavity | |
| Intrinsic loss of the microcavity | |
| Complex perturbation induced by the nanoparticle | |
| Coupling rate induced by the nanoparticle | |
| Polarizability of the nanoparticle | |
| Radius of the nanoparticle | |
| Relative permittivity of the nanoparticle | |
| Relative permittivity of the environment medium | |
| Microcavity mode function | |
| Mode volume of the microcavity | |
| Loss caused by scattering and absorption of the nanoparticle | |
| Detector noise | |
| Optical shot noise | |
| Electrical shot noise | |
| Photon energy | |
| Electron charge | |
| Detector responsivity | |
| Input power | |
| Power change in the detector |
References
- Bender, C.M.; Boettcher, S. Real spectra in non-Hermitian Hamiltonians having PT symmetry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüter, C.E.; Makris, K.G.; El-Ganainy, R.; Christodoulides, D.N.; Segev, M.; Kip, D. Observation of parity-time symmetry in optics. Nat. Phys. 2010, 6, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein, H.; Miri, M.-A.; Heinrich, M.; Demetrios, N. Parity-time-symmetric microring lasers. Science 2014, 346, 975–978. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; El-Ganainy, R.; Ge, L. Non-Hermitian photonics based on parity-time symmetry. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Kaya Özdemir, Ş.; Zhao, G.; Wiersig, J.; Yang, L. Exceptional points enhance sensing in an optical microcavity. Nature 2017, 548, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, Ş.K.; Rotter, S.; Nori, F.; Yang, L. Parity-time symmetry and exceptional points in photonics. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 783–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Wei, H.; Cotrufo, M.; Chen, W.; Mann, S.; Ni, X.; Xu, B.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Fan, S.; et al. Exceptional points and non-Hermitian photonics at the nanoscale. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2023, 18, 706–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Qin, G.-Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, B.-Y.; Long, D.; Li, G.-Q.; Long, G.-L. Enhanced sensing mechanism based on shifting an exceptional point. Research 2023, 6, 0260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hokmabadi, M.P.; Schumer, A.; Christodoulides, D.N.; Khajavikhan, M. Non-Hermitian ring laser gyroscopes with enhanced Sagnac sensitivity. Nature 2019, 576, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.-H.; Lu, Y.-K.; Suh, M.-G.; Yuan, Z.; Vahala, K. Observation of the exceptional-point-enhanced Sagnac effect. Nature 2019, 576, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Hodaei, H.; Harari, G.; Hassan, A.U.; Chow, W.; Soltani, M.; Christodoulides, D.; Khajavikhan, M. Ultrasensitive micro-scale parity-time-symmetric ring laser gyroscope. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 1556–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carlo, M.; De Leonardis, F.; Lamberti, L.; Passaro, V.M. High-sensitivity real-splitting anti-PT-symmetric microscale optical gyroscope. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 3956–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Chang, X.; Li, W.; Han, P.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, A.; Xiao, Z. On-chip high sensitivity rotation sensing based on higher-order exceptional points. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2019, 36, 2618–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, P.; Sheng, L.; Xie, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Lin, X. Gas sensing near exceptional points. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2021, 54, 254001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Shen, D. Sensing enhancement at an exceptional point in a nonreciprocal fiber ring cavity. J. Lightwave Technol. 2020, 38, 2511–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Tang, Y.; Xu, A.-N.; Liu, Y.-C. Observation of exceptional points in thermal atomic ensembles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2023, 130, 263601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononchuk, R.; Kottos, T. Orientation-sensed optomechanical accelerometers based on exceptional points. Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 023252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Peng, B.; Özdemir, Ş.K.; Fan, X.; Yang, L. Parity-time-symmetric whispering-gallery mode nanoparticle sensor. Photon. Res. 2018, 6, A23–A30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, R.; Zhang, S.-D.; Li, Y.; Qiu, C.-W.; Nori, F.; Jing, H. Breaking anti-PT symmetry by spinning a resonator. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 7594–7599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Han, P.; Chang, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, A.; Xiao, Z. Real frequency splitting indirectly coupled anti-parity-time symmetric nanoparticle sensor. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 134503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiersig, J. Enhancing the sensitivity of frequency and energy splitting detection by using exceptional points: Application to microcavity sensors for single-particle detection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 203901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Ren, J.; Khajavikhan, M.; Christodoulides, D.N.; Özdemir, Ş.K.; El-Ganainy, R. Sensing with exceptional surfaces in order to combine sensitivity with robustness. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 153902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Mao, X.; Qin, G.-Q.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Ruan, D.; Long, G.-L. Scalable higher-order exceptional surface with passive resonators. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 4025–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carlo, M.; De Leonardis, F.; Soref, R.A.; Passaro, V.M. Design of a Trap-Assisted Exceptional-Surface-Enhanced Silicon-on-Insulator Particle Sensor. J. Lightwave Technol. 2022, 40, 6021–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Xie, R.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, G.; Xu, H.; Lei, F.; Ruan, D.; Long, G. Experimental realization of sensitivity enhancement and suppression with exceptional surfaces. Laser Photonics Rev. 2021, 15, 2000569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Huang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Huang, A.; Xiao, Z. Experimental realization of exceptional surfaces enhanced displacement sensing with robustness. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 123, 201106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Huang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Huang, A.; Xiao, Z. Enhanced detection limit in an exceptional surface-based fiber resonator by manipulating Fano interference. Opt. Lett. 2024, 49, 3954–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, H.; Lu, H.; Ozdemir, S.K.; Carmon, T.; Nori, F. Nanoparticle sensing with a spinning resonator. Optica 2018, 5, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Xiao, Z.; Li, W.; Chen, T.; Li, J.; Huang, A.; Zhang, H. Enhanced nanoparticle sensing by mode intensity in a non-reciprocally coupled microcavity. J. Appl. Phys. 2022, 131, 103106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maayani, S.; Dahan, R.; Kligerman, Y.; Moses, E.; Hassan, A.U.; Jing, H.; Nori, F.; Christodoulides, D.N.; Carmon, T. Flying couplers above spinning resonators generate irreversible refraction. Nature 2018, 558, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Yin, Y.; Ding, M. Sensing and induced transparency with a synthetic anti-PT symmetric optical resonator. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 5463–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, H.K.; Clerk, A.A. Fundamental limits and non-reciprocal approaches in non-Hermitian quantum sensing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, M.J.; Digonnet, M.J.F. Rotation sensitivity and shot-noise-limited detection in an exceptional-point coupled-ring gyroscope. Opt. let. 2021, 46, 2936–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Chen, P.; Hu, T.; Jiang, S. Enhanced Nanoparticle Sensing by Sagnac–Fizeau Shift in a Microcavity Based on Exceptional Surfaces. Sensors 2025, 25, 6055. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196055
Yang Q, Chen P, Hu T, Jiang S. Enhanced Nanoparticle Sensing by Sagnac–Fizeau Shift in a Microcavity Based on Exceptional Surfaces. Sensors. 2025; 25(19):6055. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196055
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qingde, Peixin Chen, Tonghua Hu, and Shuo Jiang. 2025. "Enhanced Nanoparticle Sensing by Sagnac–Fizeau Shift in a Microcavity Based on Exceptional Surfaces" Sensors 25, no. 19: 6055. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196055
APA StyleYang, Q., Chen, P., Hu, T., & Jiang, S. (2025). Enhanced Nanoparticle Sensing by Sagnac–Fizeau Shift in a Microcavity Based on Exceptional Surfaces. Sensors, 25(19), 6055. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25196055






