Multi-Domain CoP Feature Analysis of Functional Mobility for Parkinson’s Disease Detection Using Wearable Pressure Insoles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Datasets and Data Availability
| Algorithm 1: Dataset Curation for TUG Analysis |
| Input: Dso: WearGait-PD original dataset M: Demographic metadata (age, group labels) F: Trial identifiers for TUG tasks Output: : Subset with valid insole signals during TUG : Demographically balanced subset 1 Initialize ← ∅; ← ∅; 2 foreach participant p ∈ do 3 if p contains AND complete insole recordings then 4 Remove modalities {, , Walkway}; 5 if insole signals are valid ∧ synchronized then 6 ← ∪ {p}; 7 Demographic Balancing: 8 Compute , from ; 9 Construct such that: , with matched covariates in M; 10 return , ; |
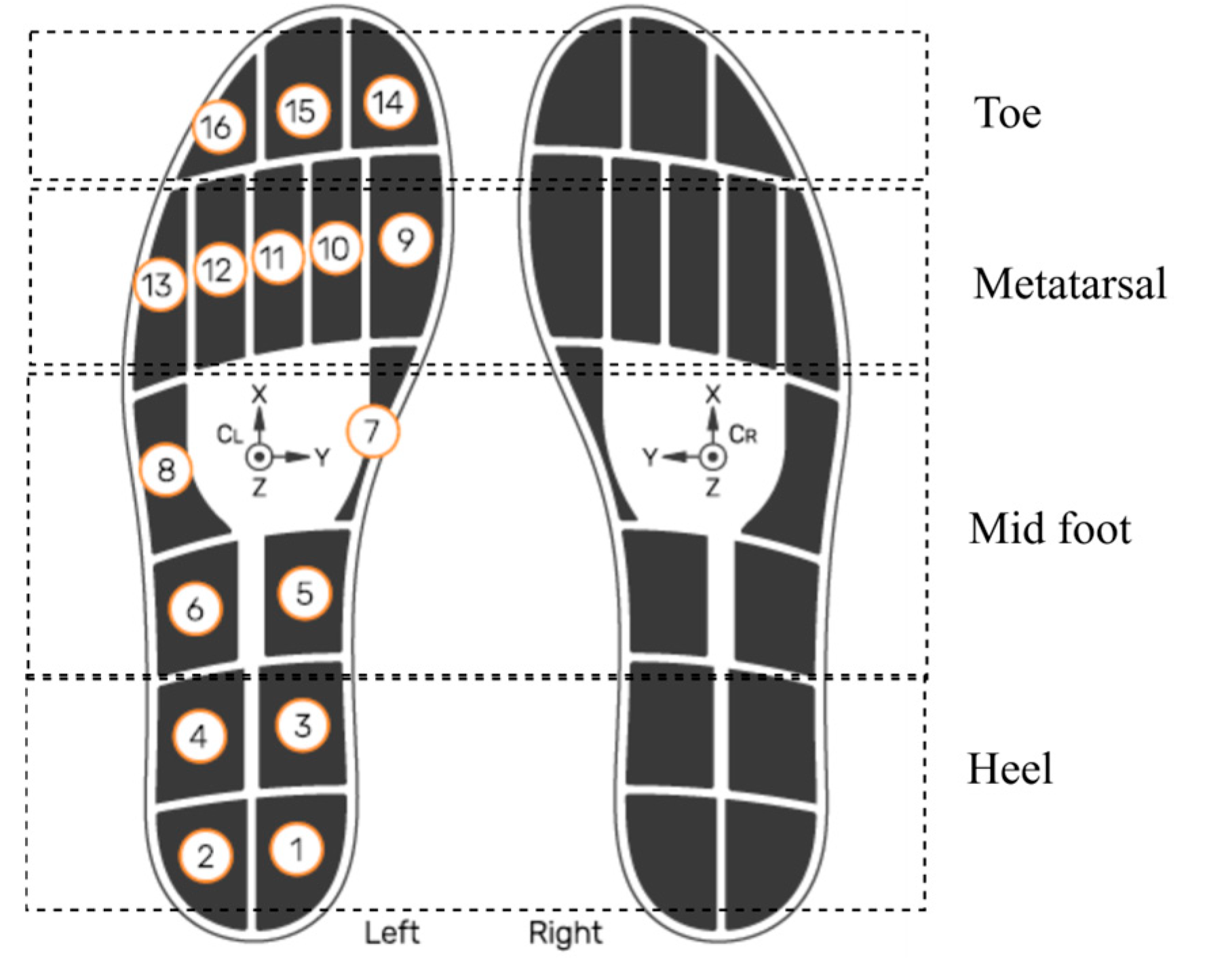
3.2. Insole-Based CoP Measurement and Data Processing
- and denote the coordinates of the ith pressure sensor along the ML and AP axes, respectively.
- represents the force measured by that sensor.
3.3. CoP Density Mapping and Trajectory Computation
3.4. Feature Engineering from CoP Data
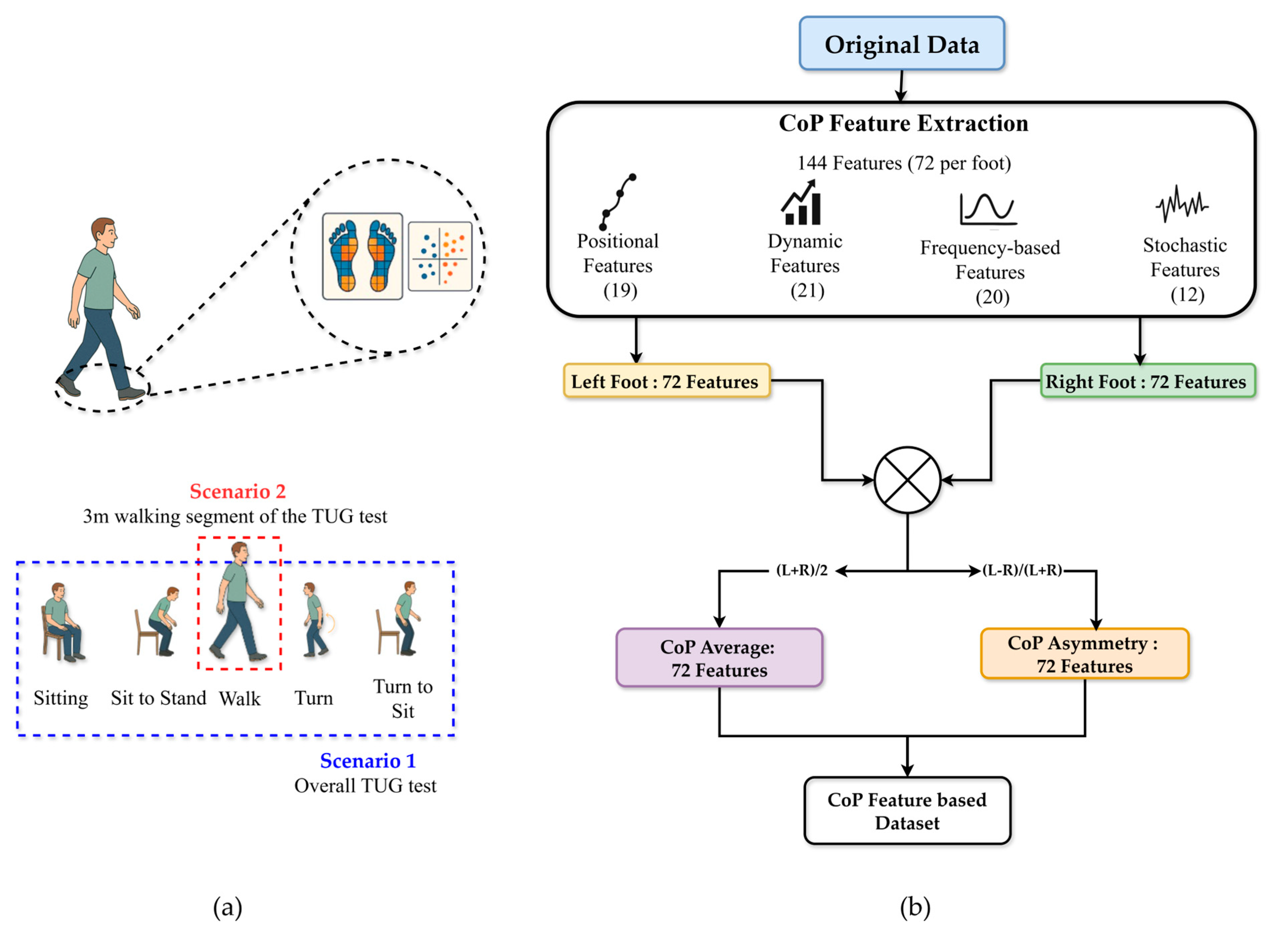
3.5. Model Development and Evaluation
4. Results and Analysis
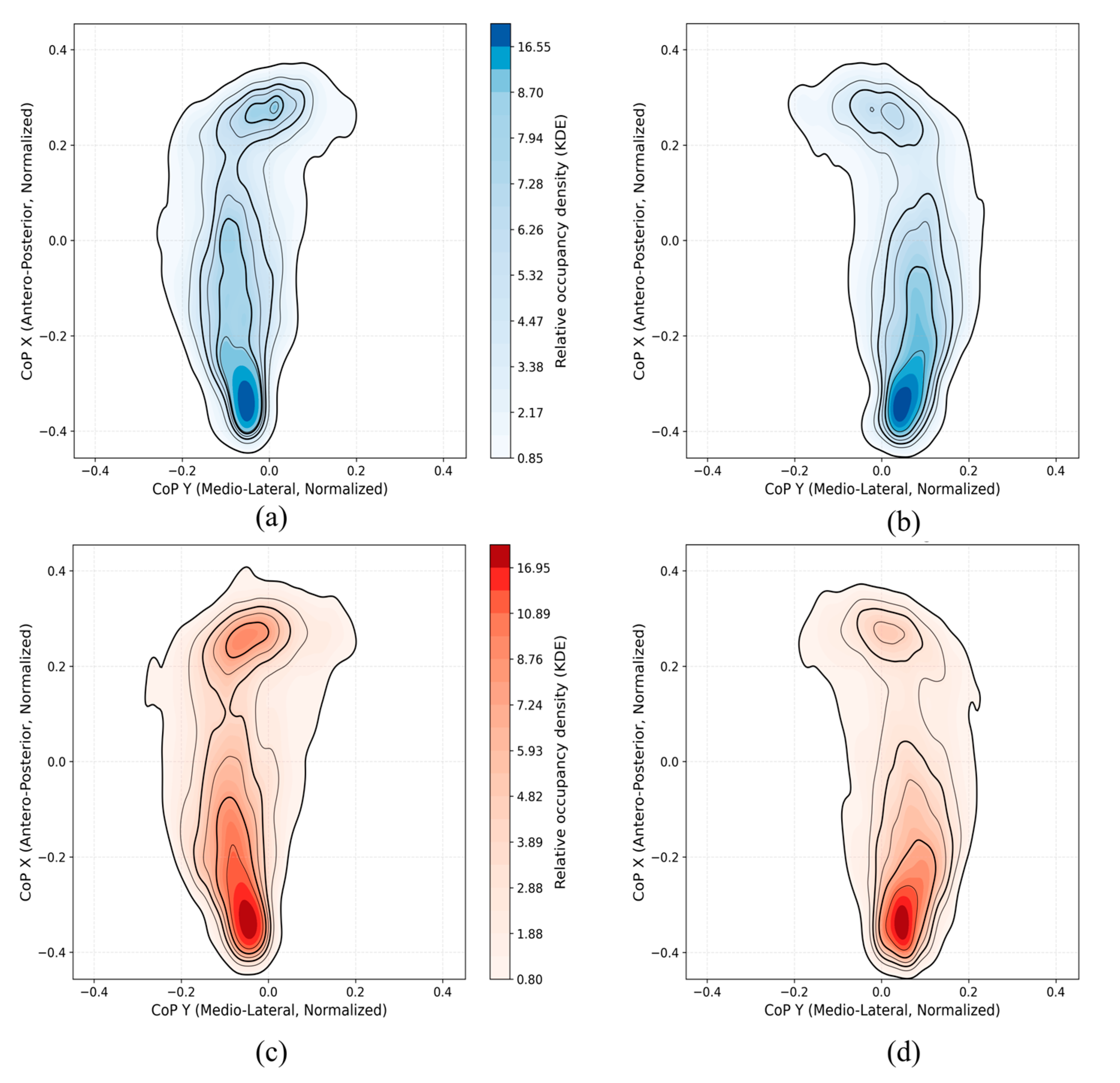
4.1. CoP Density Maps and Trajectory Maps Analysis
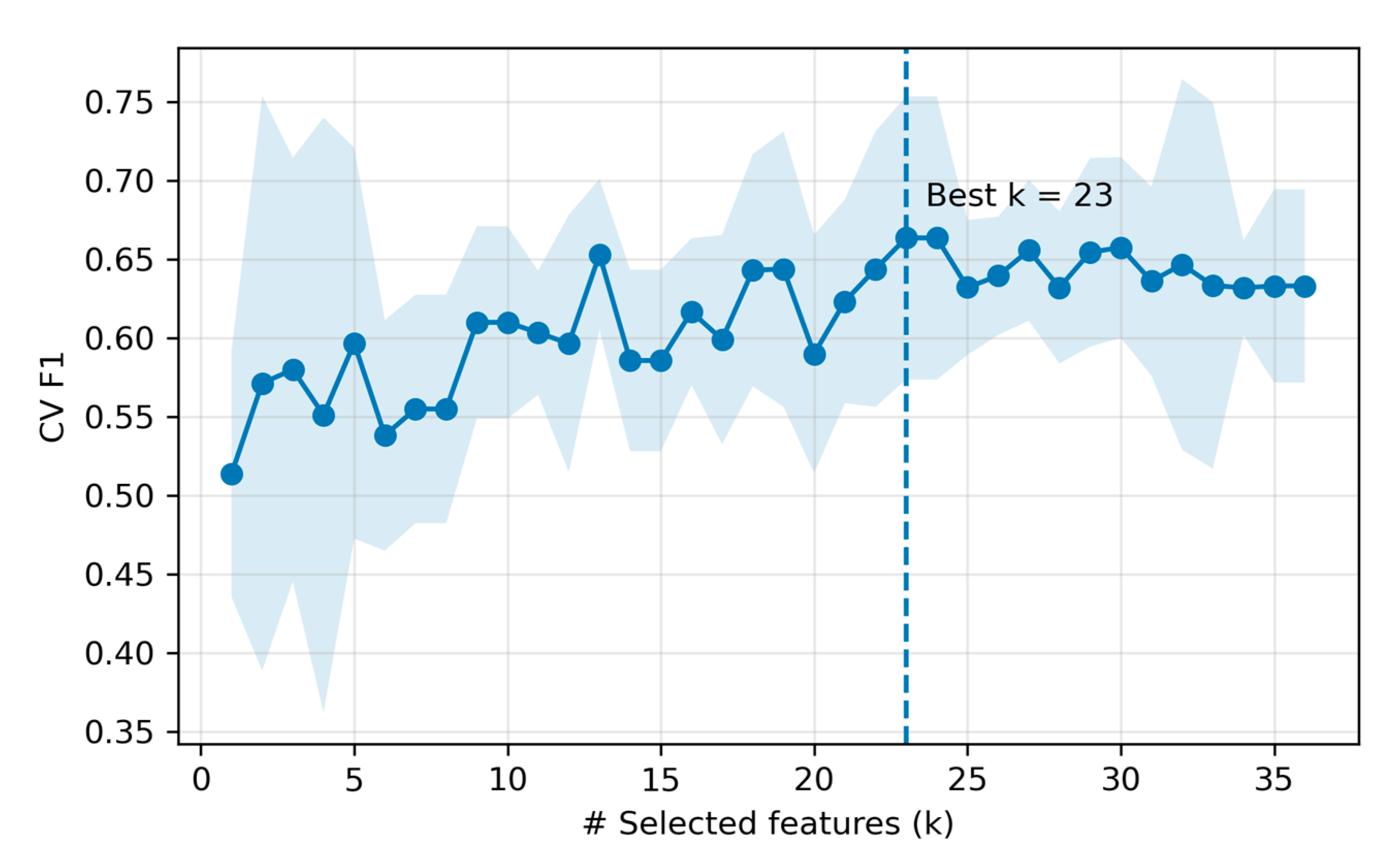
4.2. Machine Learning Classification Performance
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Student, J.; Engel, D.; Timmermann, L.; Bremmer, F.; Waldthaler, J. Visual Perturbation Suggests Increased Effort to Maintain Balance in Early Stages of Parkinson’s to Be an Effect of Age Rather Than Disease. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 762380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melendez, R.A.R.; Thompson, L.A. Investigating the Effects of Center of Gravity (CoG) Shift Due to a Simulated Exploration Extravehicular Mobility Unit (XEMU) Suit on Balance. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, S.B.; Fling, B.W.; Lee, H.; Peterson, D.S. The Assessment of Center of Mass and Center of Pressure during Quiet Stance: Current Applications and Future Directions. J. Biomech. 2021, 123, 110485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, L.V.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peskar, M.; Manganotti, P.; Marusic, U.; Gramann, K. Neurophysiological Underpinnings of Balance Control and Cognitive-Motor Interaction in Early Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 25082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, D.; Greulich, R.S.; Parola, A.; Vinehout, K.; Student, J.; Waldthaler, J.; Timmermann, L.; Bremmer, F. Sway Frequencies May Predict Postural Instability in Parkinson’s Disease: A Novel Convolutional Neural Network Approach. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2025, 22, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Bastidas, P.; Gómez, B.; Aqueveque, P.; Luarte-Martínez, S.; Cano-de-la-Cuerda, R. Instrumented Timed Up and Go Test (ITUG)—More Than Assessing Time to Predict Falls: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society® MDS-Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS). Available online: https://www.movementdisorders.org/MDS/MDS-Rating-Scales/MDS-Unified-Parkinsons-Disease-Rating-Scale-MDS-UPDRS.htm (accessed on 28 July 2025).
- Davidson, J.B.; Larson, D.J.; Li, J.X.; Fischer, S.L. Validating Force-Estimating Insoles for Calculating Centre of Pressure and Vertical Ground Reaction Forces during Occupational Tasks. Ergonomics 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, T.; Guruge, K.; Malekroodi, H.S.; Madusanka, N.; Yi, M.; Lee, B. IoMT-Based Smart Insole System for Comprehensive Gait Analysis: Plantar Pressure and Foot Dynamics Assessment. J. Korea Multimed. Soc. 2025, 28, 807–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakanikas, V.; Ntanis, A.; Rigas, G.; Androutsos, C.; Boucharas, D.; Tachos, N.; Skaramagkas, V.; Chatzaki, C.; Kefalopoulou, Z.; Tsiknakis, M.; et al. Evaluating Gait Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease from Instrumented Insole and IMU Sensor Data. Sensors 2023, 23, 3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada-Illa, C.; Pegueroles, J.; Claramunt-Molet, M.; Pi-Cervera, A.; Heras-Delgado, A.; Gascón-Fontal, J.; Idelsohn-Zielonka, S.; Rico, M.; Vidal, N.; Martín-Aguilar, L.; et al. Digital Biomechanical Assessment of Gait in Patients with Peripheral Neuropathies. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2025, 22, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, Â.; Coelho, T.; Vitória, A.; Ferreira, A.; Santos, R.; Rocha, N.; Fernandes, L.; Tavares, J.M.R.S. Standing Balance in Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease during Single and Dual-Task Conditions. Gait Posture 2015, 42, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terra, M.B.; Da Silva, R.A.; Bueno, M.E.B.; Ferraz, H.B.; Smaili, S.M. Center of Pressure-Based Balance Evaluation in Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease: A Reliability Study. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2020, 36, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamieniarz, A.; Michalska, J.; Marszałek, W.; Stania, M.; Słomka, K.J.; Gorzkowska, A.; Juras, G.; Okun, M.S.; Christou, E.A. Detection of Postural Control in Early Parkinson’s Disease: Clinical Testing vs. Modulation of Center of Pressure. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbers, C.; Zhang, R.; Erdman, A.; Johnson, M.D. Distinguishing Features of Parkinson’s Disease Fallers Based on Wireless Insole Plantar Pressure Monitoring. NPJ Park. Dis. 2024, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalin, G.; Pardoel, S.; Lemaire, E.D.; Nantel, J.; Kofman, J. Prediction and Detection of Freezing of Gait in Parkinson’s Disease from Plantar Pressure Data Using Long Short-Term Memory Neural-Networks. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho Costa, E.; Santinelli, F.B.; Moretto, G.F.; Figueiredo, C.; von Ah Morano, A.E.; Barela, J.A.; Barbieri, F.A. A Multiple Domain Postural Control Assessment in People with Parkinson’s Disease: Traditional, Non-Linear, and Rambling and Trembling Trajectories Analysis. Gait Posture 2022, 97, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayot, M.; Delval, A.; Moreau, C.; Defebvre, L.; Hansen, C.; Maetzler, W.; Schlenstedt, C. Initial Center of Pressure Position Prior to Anticipatory Postural Adjustments during Gait Initiation in People with Parkinson’s Disease with Freezing of Gait. Park. Relat. Disord. 2021, 84, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudejko, T.; Button, K.; Al-Amri, M. Wireless Pressure Insoles for Measuring Ground Reaction Forces and Trajectories of the Centre of Pressure during Functional Activities. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, O.; Khandelwal, P.; Gavas, R.; Sinha, A. Assessment of Insole Based Gait Feature Variation with Progression of Parkinson’s Disease. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE SENSORS, New Delhi, India, 28–31 October 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tsakanikas, V.D.; Dimopoulos, D.G.; Tachos, N.S.; Chatzaki, C.; Skaramagkas, V.; Christodoulakis, G.; Tsiknakis, M.; Fotiadis, D.I. Gait and Balance Patterns Related to Free-Walking and TUG Tests in Parkinson’s Disease Based on Plantar Pressure Data. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Virtual, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 236–239. [Google Scholar]
- Ayena, J.C.; Otis, M.J.-D. Dimensional Reduction of Balance Parameters in Risk of Falling Evaluation Using a Minimal Number of Force-Sensitive Resistors. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2022, 28, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.; Yoo, D.; Kim, J.; Ahn, T.-B.; Mun, K.-R. Identifying Parkinson’s Disease and Its Stages Using Static Standing Balance. NPJ Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, S.; Takamura, Y.; Ikuno, K.; Morioka, S.; Kawashima, N. A Comprehensive Multivariate Analysis of the Center of Pressure during Quiet Standing in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2024, 21, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.J.; Eguren, D.; Gonzalez, M.A.; Khan, N.; Watkinson, S.; Caiola, M.; Hirczy, S.S.; Zabetian, C.P.; Mills, K.; Moukheiber, E.; et al. WearGait-PD: An Open-Access Wearables Dataset for Gait in Parkinson’s Disease and Age-Matched Controls. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moticon OpenGo. Available online: https://moticon.com/opengo/sensor-insoles (accessed on 14 June 2025).
- Morin, P.; Muller, A.; Pontonnier, C.; Dumont, G. Evaluation of the Foot Center of Pressure Estimation from Pressure Insoles during Sidestep Cuts, Runs and Walks. Sensors 2022, 22, 5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkinson, S.A.; Anderson, A.; Caiola, M.; Eguren, D.; Gonzalez, M.; Velazquez, L.M.; Dehak, N.; Motley, C.; Moukheiber, E.; Mills, K.; et al. Concurrent Validity of Instrumented Insoles Measuring Gait and Balance Metrics in Parkinson’s Disease. In Proceedings of the 2024 46th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 July 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, L.-W.; Shen, J.-H.; Lin, H.-T.; Yang, Y.-T.; Hu, W.-P. A Study on the Influence of Number/Distribution of Sensing Points of the Smart Insoles on the Center of Pressure Estimation for the Internet of Things Applications. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quijoux, F.; Nicolaï, A.; Chairi, I.; Bargiotas, I.; Ricard, D.; Yelnik, A.; Oudre, L.; Bertin-Hugault, F.; Vidal, P.; Vayatis, N.; et al. A Review of Center of Pressure (COP) Variables to Quantify Standing Balance in Elderly People: Algorithms and Open-access Code. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e15067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Zhang, J.; Dong, E.; Du, S. Severity Classification of Parkinson’s Disease Based on Permutation-Variable Importance and Persistent Entropy. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Youm, C.; Park, H.; Kim, B.; Choi, H.; Cheon, S.-M. Machine Learning for Early Detection and Severity Classification in People with Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arco, L.; Wang, H.; Zheng, H. Assessing Impact of Sensors and Feature Selection in Smart-Insole-Based Human Activity Recognition. Methods Protoc. 2022, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafaar, S.; Ghazwan, A. Gait Asymmetry According to Limb Dominance. In Proceedings of the Fourth Scientific Conference for Electrical Engineering Techniques Research (EETR2022), Baghdad, Iraq, 15–16 June 2022; Volume 2804, p. 040017. [Google Scholar]




| Study | Year | CoP Features Used | TUG Test Used | Data Collection Method | Machine Learning Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fernandes et al. [13] | 2015 | ✔ | ✘ | Pressure platform | ✘ |
| Terra et al. [14] | 2020 | ✔ | ✘ | Force platform | ✘ |
| Kamieniarz et al. [15] | 2021 | ✔ | ✔ | Force platform | ✘ |
| Costa et al. [18] | 2024 | ✔ | ✘ | Force platform | ✘ |
| Bayot et al. [19] | 2022 | ✔ | ✘ | Force platform | ✘ |
| Engel et al. [6] | 2025 | ✔ | ✘ | Balance board (Force platform) | ✔ |
| Jung et al. [24] | 2024 | ✔ | ✘ | Pressure-sensing treadmill | ✔ |
| Fujii et al. [25] | 2025 | ✔ | ✘ | Force platform | ✔ |
| Herbers et al. [16] | 2024 | ✔ | ✘ | Smart Insole | ✔ |
| Ayena & Otis [23] | 2022 | ✔ | ✔ | Smart Insole | ✘ |
| Tsakanikas et al. [22] | 2021 | ✔ | ✔ | Smart Insole | ✘ |
| Shalin et al. [17] | 2021 | ✔ | ✘ | Smart Insole | ✔ |
| Mazumder et al. [21] | 2018 | ✔ | ✔ | Smart Insole | ✘ |
| PD | Control | |
|---|---|---|
| Sample size | 39 | 38 |
| Age (Years) | 69.03 ± 5.3 | 73.58 ± 4.6 |
| Gender (Male/Female) | 25/14 | 16/22 |
| Years with PD | 7.3 ± 6.0 | Not applicable |
| Weight (kg) | 76.83 ± 16.7 | 80.20 ± 16.9 |
| Height (cm) | 173 ± 9.4 | 168 ± 9.7 |
| Model | Hyperparameters |
|---|---|
| SVM-RBF | , class weight = “balanced”, probability = True, random state = 42 |
| RF | , class weight = “balanced”, random state = 42 |
| LR | solver = “lbfgs”, max_iter = 2000, class weight = “balanced, random state = 42 |
| k-NN | Defaults: n neighbors = 5, weights = ‘uniform’, metric = ‘minkowski’, p = 2 |
| Gaussian NB | Defaults: var smoothing = 1 × 10−9 |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | ROC-AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM-RBF | 0.813 | 0.778 | 0.875 | 0.824 | 0.859 |
| LR | 0.875 | 1.000 | 0.750 | 0.857 | 0.922 |
| RF | 0.813 | 0.778 | 0.875 | 0.824 | 0.906 |
| k-NN | 0.750 | 0.833 | 0.625 | 0.714 | 0.781 |
| Gaussian NB | 0.625 | 0.583 | 0.875 | 0.700 | 0.797 |
| CoP Features | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Name | Selection Models | No. of Models Selected | Category |
| 1 | Maximal distance (Radius)—Average | SVM, RF, LR, KNN, GNB | 5 | Positional |
| 2 | Centroidal frequency (Power Spectrum Density) ML—Asymmetry | SVM, RF, LR, GNB | 4 | Frequency |
| 3 | Energy content below 0.5 Hz (Power Spectrum Density) ML—Asymmetry | SVM, RF, KNN, GNB | 4 | Frequency |
| 4 | Mean positive peak velocity AP—Asymmetry | RF, LR, KNN, GNB | 4 | Dynamic |
| 5 | Principal sway direction—Asymmetry | SVM, RF, LR, GNB | 4 | Positional |
| 6 | Frequency Quotient Power Spectrum Density ML—Average | RF, LR, KNN, GNB | 4 | Frequency |
| 7 | Maximal distance AP—Average | SVM, LR, KNN, GNB | 4 | Positional |
| 8 | Mean Velocity AP—Average | SVM, RF, LR, KNN | 4 | Dynamic |
| 9 | Mean Velocity ML-AP—Average | SVM, RF, LR, KNN | 4 | Dynamic |
| 10 | Mean positive peak velocity ML—Average | SVM, LR, KNN, GNB | 4 | Dynamic |
| 11 | 95% confidence ellipse area—Asymmetry | RF, LR, KNN | 3 | Positional |
| 12 | Mean Velocity ML-AP—Asymmetry | LR, KNN, GNB | 3 | Dynamic |
| 13 | Mean positive peak velocity ML—Asymmetry | SVM, LR, KNN | 3 | Dynamic |
| 14 | Range ML—Asymmetry | SVM, KNN, GNB | 3 | Positional |
| 15 | Centroidal frequency (Power Spectrum Density) ML—Average | SVM, LR, KNN | 3 | Frequency |
| 16 | Energy content below 0.5 Hz (Power Spectrum Density) AP—Average | SVM, RF, KNN | 3 | Frequency |
| 17 | Mode of Power Spectrum Density ML—Average | SVM, LR, GNB | 3 | Frequency |
| 18 | Frequency Quotient Power Spectrum Density AP—Average | RF, KNN, GNB | 3 | Frequency |
| 19 | Mean frequency ML-AP—Average | SVM, RF, KNN | 3 | Dynamic |
| 20 | Mean Velocity ML—Average | SVM, LR, GNB | 3 | Dynamic |
| 21 | Mean positive peak velocity AP—Average | SVM, LR, GNB | 3 | Dynamic |
| 22 | 50% Power Frequency ML—Average | SVM, LR, KNN | 3 | Frequency |
| 23 | Short-term diffusion coefficient AP—Average | SVM, RF, KNN | 3 | Stochastic |
| 24 | Sway area per second ML-AP—Average | LR, KNN, GNB | 3 | Dynamic |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | ROC-AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM-RBF | 0.625 | 0.625 | 0.625 | 0.625 | 0.656 |
| LR | 0.625 | 0.583 | 0.875 | 0.700 | 0.500 |
| RF | 0.563 | 0.545 | 0.750 | 0.632 | 0.602 |
| k-NN | 0.688 | 0.800 | 0.500 | 0.615 | 0.734 |
| Gaussian NB | 0.625 | 0.583 | 0.875 | 0.700 | 0.484 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nanayakkara, T.; Herath, H.M.K.K.M.B.; Malekroodi, H.S.; Madusanka, N.; Yi, M.; Lee, B.-i. Multi-Domain CoP Feature Analysis of Functional Mobility for Parkinson’s Disease Detection Using Wearable Pressure Insoles. Sensors 2025, 25, 5859. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185859
Nanayakkara T, Herath HMKKMB, Malekroodi HS, Madusanka N, Yi M, Lee B-i. Multi-Domain CoP Feature Analysis of Functional Mobility for Parkinson’s Disease Detection Using Wearable Pressure Insoles. Sensors. 2025; 25(18):5859. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185859
Chicago/Turabian StyleNanayakkara, Thathsara, H. M. K. K. M. B. Herath, Hadi Sedigh Malekroodi, Nuwan Madusanka, Myunggi Yi, and Byeong-il Lee. 2025. "Multi-Domain CoP Feature Analysis of Functional Mobility for Parkinson’s Disease Detection Using Wearable Pressure Insoles" Sensors 25, no. 18: 5859. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185859
APA StyleNanayakkara, T., Herath, H. M. K. K. M. B., Malekroodi, H. S., Madusanka, N., Yi, M., & Lee, B.-i. (2025). Multi-Domain CoP Feature Analysis of Functional Mobility for Parkinson’s Disease Detection Using Wearable Pressure Insoles. Sensors, 25(18), 5859. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185859








