Near-Field Source Localization in Nonuniform Noise: An Efficient Symmetric Matrix Factorization-Based Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Signal Model
3. Symmetric Matrix Factorization Based Near-Field Localization Approach
3.1. Problem Reformulation
3.2. Inexact Block Coordinate Descent Algorithm for Symmetric Matrix Factorization
3.3. Near-Field Localization Algorithm
3.4. Computational Complexity Analysis
| Algorithm 1 Proposed Algorithm Procedure for Near-field Localization |
Input: , K
|
4. CRB for Near-Field Sources in Nonuniform Noise
5. Simulation Results
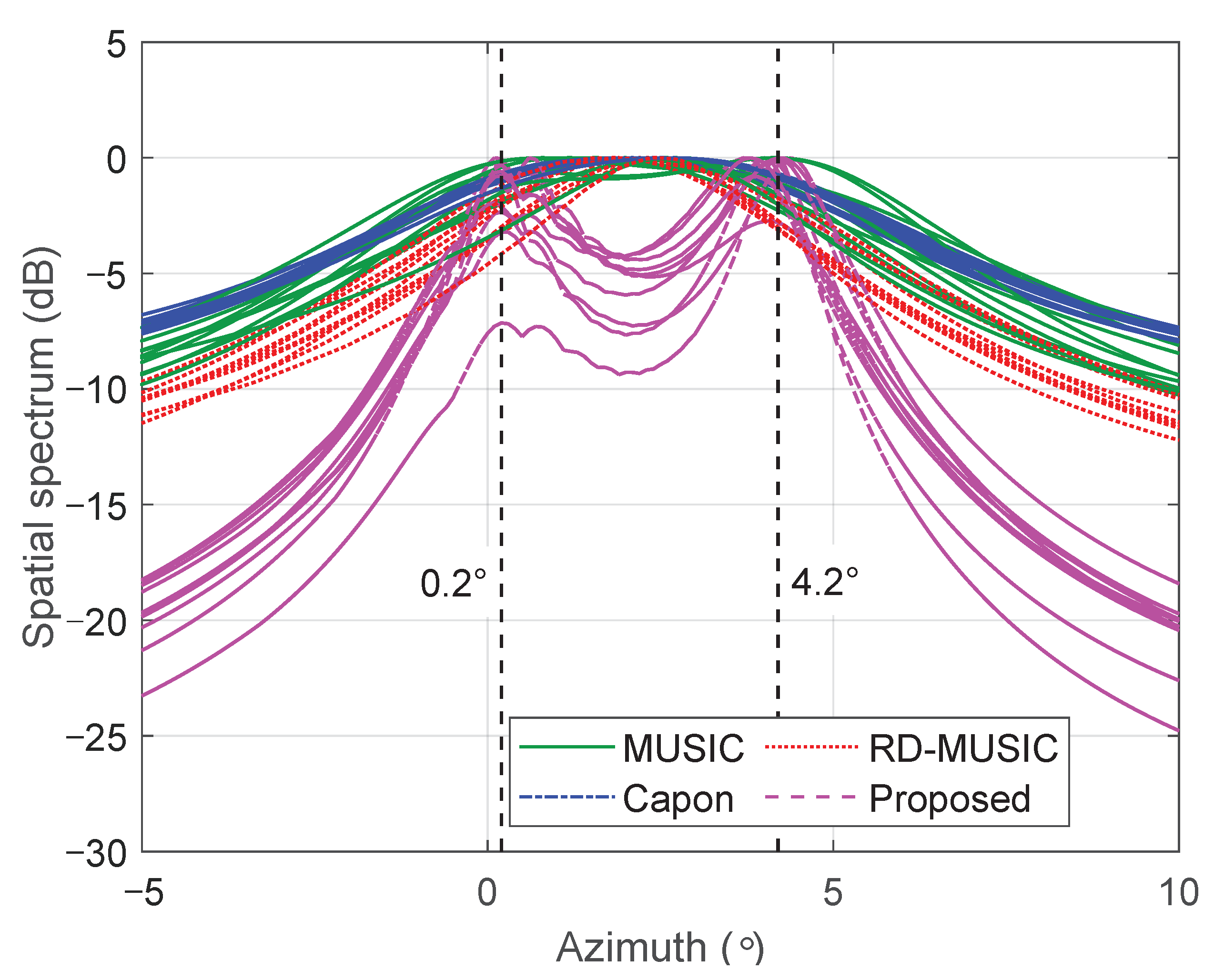
5.1. Convergence and Resolution
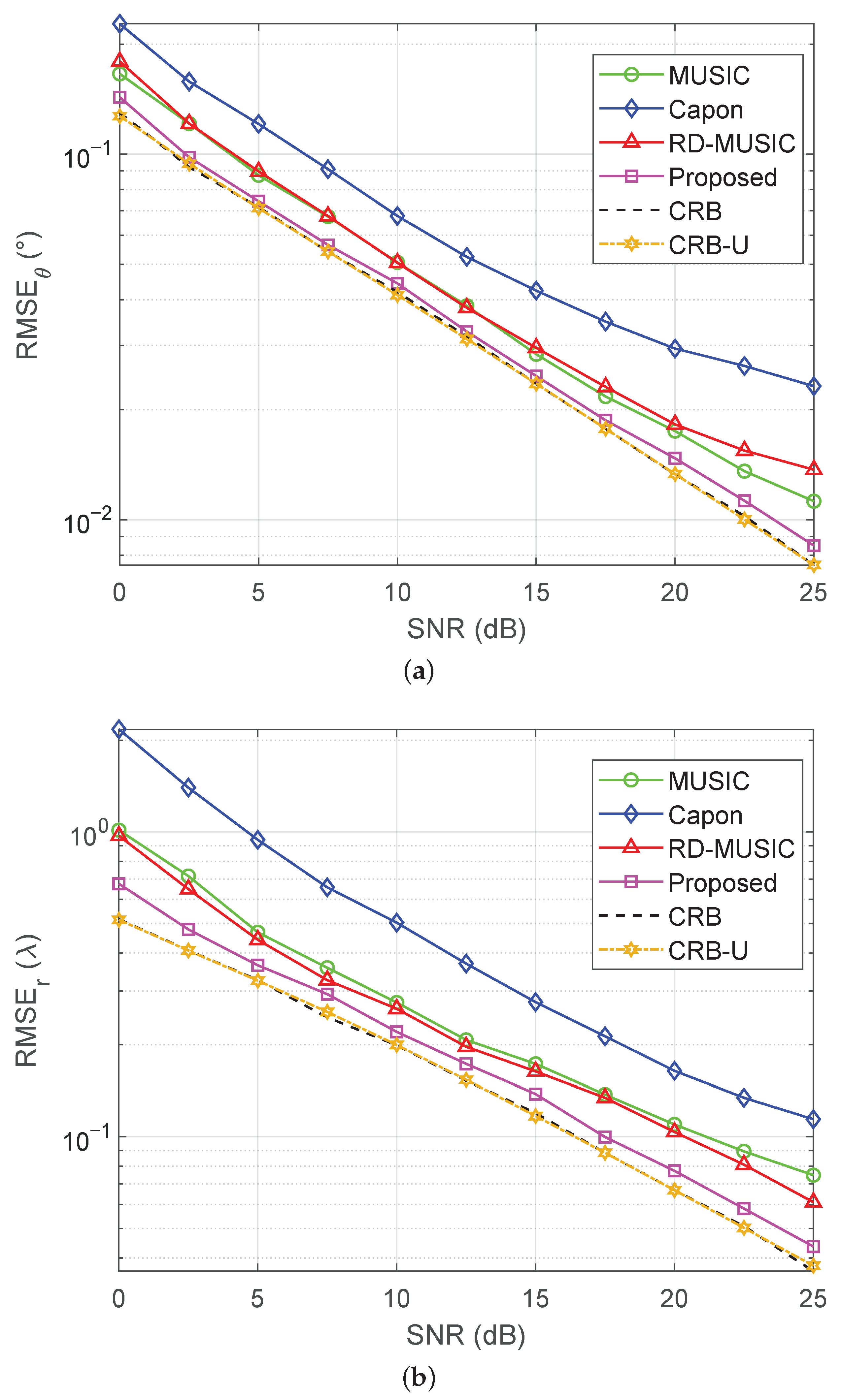
5.2. Estimation Accuracy Versus SNR
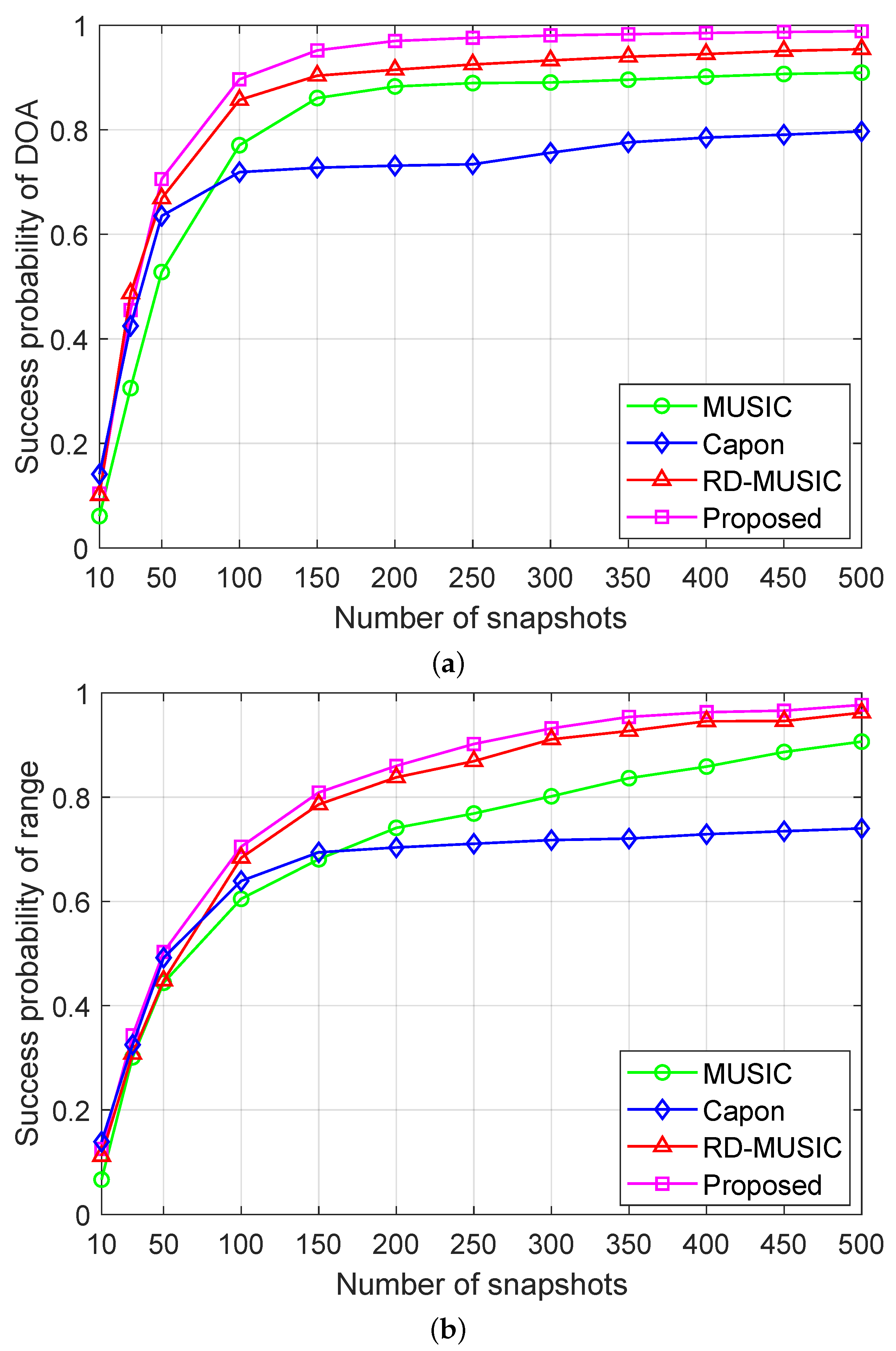
5.3. Estimation Accuracy Versus the Number of Snapshots
5.4. Estimation Accuracy Versus the Number of Sensors
5.5. Estimation Accuracy Versus WNPR
5.6. Computation Time Comparison
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krim, H.; Viberg, M. Two decades of array signal processing research: The parametric approach. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2002, 13, 67–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gao, F.; Jin, S.; Lin, H. An overview of enhanced massive MIMO with array signal processing techniques. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2019, 13, 886–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, M.; Fang, W.; Liu, Q.; Yan, G.; Yang, Q.; Lu, H. Resonant beam enabled DOA estimation in passive positioning system. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 16290–16300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weißer, F.; Turan, N.; Utschick, W. DOA-aided MMSE channel estimation for wireless communication systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Taipei, Taiwan, 6–11 April 2025; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xia, W.; Zhu, L.; Qu, C.; Zhou, J. High resolution DOA estimation of coherent distributed millimeter-wave radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2025, 61, 6098–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaei, A.M.; Fusco, V.; Abbasi, M.A.B.; Khalily, M.; Lopes, C.G.; Yurduseven, O. Efficient Active Azimuth-Elevation DOA Estimations via Massive MIMO Radar. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1986, 34, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, P.; Nehorai, A. MUSIC, maximum likelihood, and Cramer-Rao bound. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 2002, 37, 720–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Kailath, T. ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 2002, 37, 984–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swindlehurst, A.; Kailath, T. Passive direction-of-arrival and range estimation for near-field sources. In Proceedings of the Fourth Annual ASSP Workshop on Spectrum Estimation and Modeling, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–5 August 1988; Volume 123, pp. 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, M.; Wu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wei, X.; Dai, L. Near-field MIMO communications for 6G: Fundamentals, challenges, potentials, and future directions. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2022, 61, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.D.; Barkat, M. Near-field multiple source localization by passive sensor array. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2002, 39, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Hudson, R.E.; Yao, K. Maximum-likelihood source localization and unknown sensor location estimation for wideband signals in the near-field. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 50, 1843–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Xin, J.; Zheng, N.; Sano, A. Subspace-based localization of far-field and near-field signals without eigendecomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 4461–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Xin, J.; Liu, W.; Zheng, N.; Ohmori, H.; Sano, A. Localization of near-field sources based on linear prediction and oblique projection operator. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 67, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Xin, J.; Ohmori, H.; Zheng, N.; Sano, A. Subspace-based algorithms for localization and tracking of multiple near-field sources. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2019, 13, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Zheng, W.; Xia, Z.; Wang, Y. Localization of near-field sources: A reduced-dimension MUSIC algorithm. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 1422–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.Q.; Shi, Z.P.; Huang, L. Covariance sparsity-aware DOA estimation for nonuniform noise. Digit. Signal Process. 2014, 28, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesavento, M.; Gershman, A.B. Maximum-likelihood direction-of-arrival estimation in the presence of unknown nonuniform noise. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 49, 1310–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Chan, S.C.; Huang, L.; Guo, C. Iterative methods for subspace and DOA estimation in nonuniform noise. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 3008–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Xin, J.; Zheng, N.; Ohmori, H.; Sano, A. Subspace-based near-field source localization in unknown spatially nonuniform noise environment. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 4713–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razaviyayn, M.; Hong, M.; Luo, Z.Q. A unified convergence analysis of block successive minimization methods for nonsmooth optimization. SIAM J. Optim. 2013, 23, 1126–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Razaviyayn, M.; Luo, Z.Q.; Pang, J.S. A unified algorithmic framework for block-structured optimization involving big data: With applications in machine learning and signal processing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2015, 33, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed-Meraim, K.; Hua, Y.; Belouchrani, A. Second-order near-field source localization: Algorithm and performance analysis. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the Thirtieth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 3–6 November 1996; Volume 1, pp. 723–727. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.; Sun, H.; Lu, S.; Hong, M.; Razaviyayn, M. Inexact block coordinate descent methods for symmetric nonnegative matrix factorization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 5995–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.; Teboulle, M. A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2009, 2, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.J.; Huang, Y. Analysis for Capon and MUSIC DOA estimation algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, North Charleston, SC, USA, 1–5 June 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jansson, M.; Goransson, B.; Ottersten, B. A subspace method for direction of arrival estimation of uncorrelated emitter signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 47, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, P.; Nehorai, A. Performance study of conditional and unconditional direction-of-arrival estimation. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1990, 38, 1783–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütkepohl, H. Handbook of Matrices, 1st ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, R.O. A Signal Subspace Approach to Multiple Emitter Location Spectral Estimation; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Grosicki, E.; Abed-Meraim, K.; Hua, Y. A weighted linear prediction method for near-field source localization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2005, 53, 3651–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Algorithm | Complexity |
|---|---|
| Proposed | |
| RD-MUSIC | |
| Capon | |
| MUSIC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, W.; He, Z.; Sun, G.; Feng, S. Near-Field Source Localization in Nonuniform Noise: An Efficient Symmetric Matrix Factorization-Based Approach. Sensors 2025, 25, 5684. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185684
Song W, He Z, Sun G, Feng S. Near-Field Source Localization in Nonuniform Noise: An Efficient Symmetric Matrix Factorization-Based Approach. Sensors. 2025; 25(18):5684. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185684
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Wenze, Zhenqing He, Guohao Sun, and Shou Feng. 2025. "Near-Field Source Localization in Nonuniform Noise: An Efficient Symmetric Matrix Factorization-Based Approach" Sensors 25, no. 18: 5684. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185684
APA StyleSong, W., He, Z., Sun, G., & Feng, S. (2025). Near-Field Source Localization in Nonuniform Noise: An Efficient Symmetric Matrix Factorization-Based Approach. Sensors, 25(18), 5684. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25185684







