A Multidimensional Matrix Completion Method for 2-D DOA Estimation with L-Shaped Array
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a matrix completion method leveraging the intrinsic connection between the covariance matrix and MLT structure. It simultaneously captures the joint sparsity and the coherence between signals received by the two subarrays. An efficient alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) algorithm is further developed to reduce computational complexity. The proposed method extends the virtual aperture through an interpolation-like mechanism, thereby improving estimation accuracy and identifiability (see Section 3 and Section 4).
- Extensive simulation results demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed method in terms of identifiability and statistic estimation accuracy benchmarked by the Cramér-Rao bound (CRB). The computational efficiency gained by the ADMM implementation is also empirically verified (see Section 6).
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Basic Model
2.2. Joint Sparse Recovery Framework
3. Multidimensional Matrix Completion Method
4. Efficient Implementation via ADMM
4.1. Algorithm Framework
4.2. Closed-Form Solution of Subproblem
| Algorithm 1 ADMM for Multidimensional Matrix Completion |
| Input: and model order K Output: Initialize ,,,; for do 1: Update , via (22); 2: Update via (24); 3: Update via (25) with set as (26); 4: Calculate and via (31); 5: Reconstruct and via (30) and (20); 6: Update via (31); 7: Update via (31); 8: Update , via (22); 9: ; if then break end if end for 10: Reconstruct via and postprocess with K-order truncated eigendecomposition to obtain ; 11: Extract and pair the DOA groups using MD-ESPRIT algorithm; 12: return . |
5. CRB
6. Numerical Simulations
- SPA [33]: The SPA is separately applied to the two subarrays to estimate the elevation angles and azimuth angles, and the probable pairing error is neglected in this process.
- JSR: The JSR framework is implemented as described in Corollary 1 with the regularization parameters set as [39].
- CRB: The average lower bounds for estimation separately implemented in two subarrays is denoted as CRB, which is calculated as (32).
- CRB+: The lower bounds for joint 2-D DOA estimation based on the whole covariance matrix is represented as CRB+, which is calculated as (45).
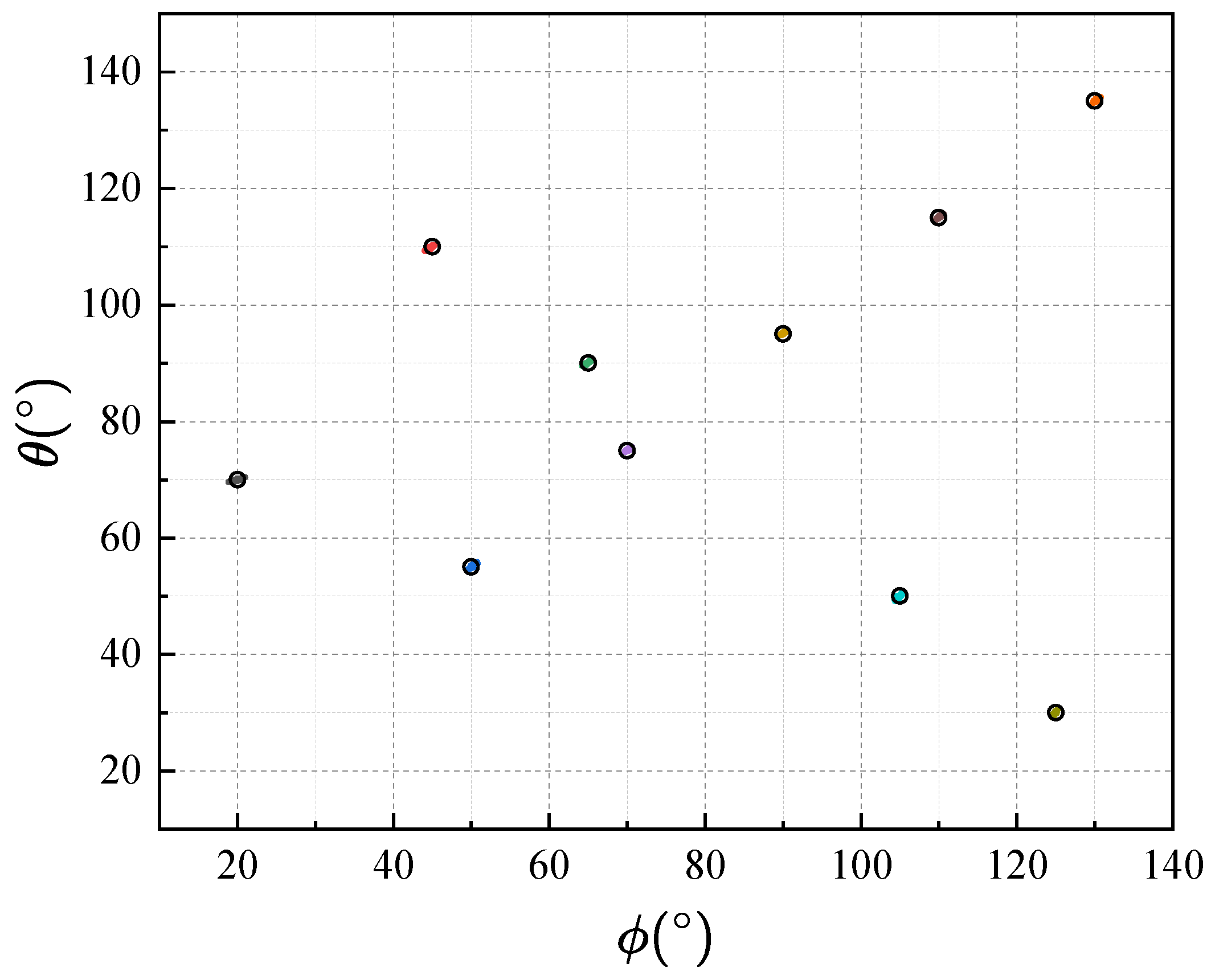
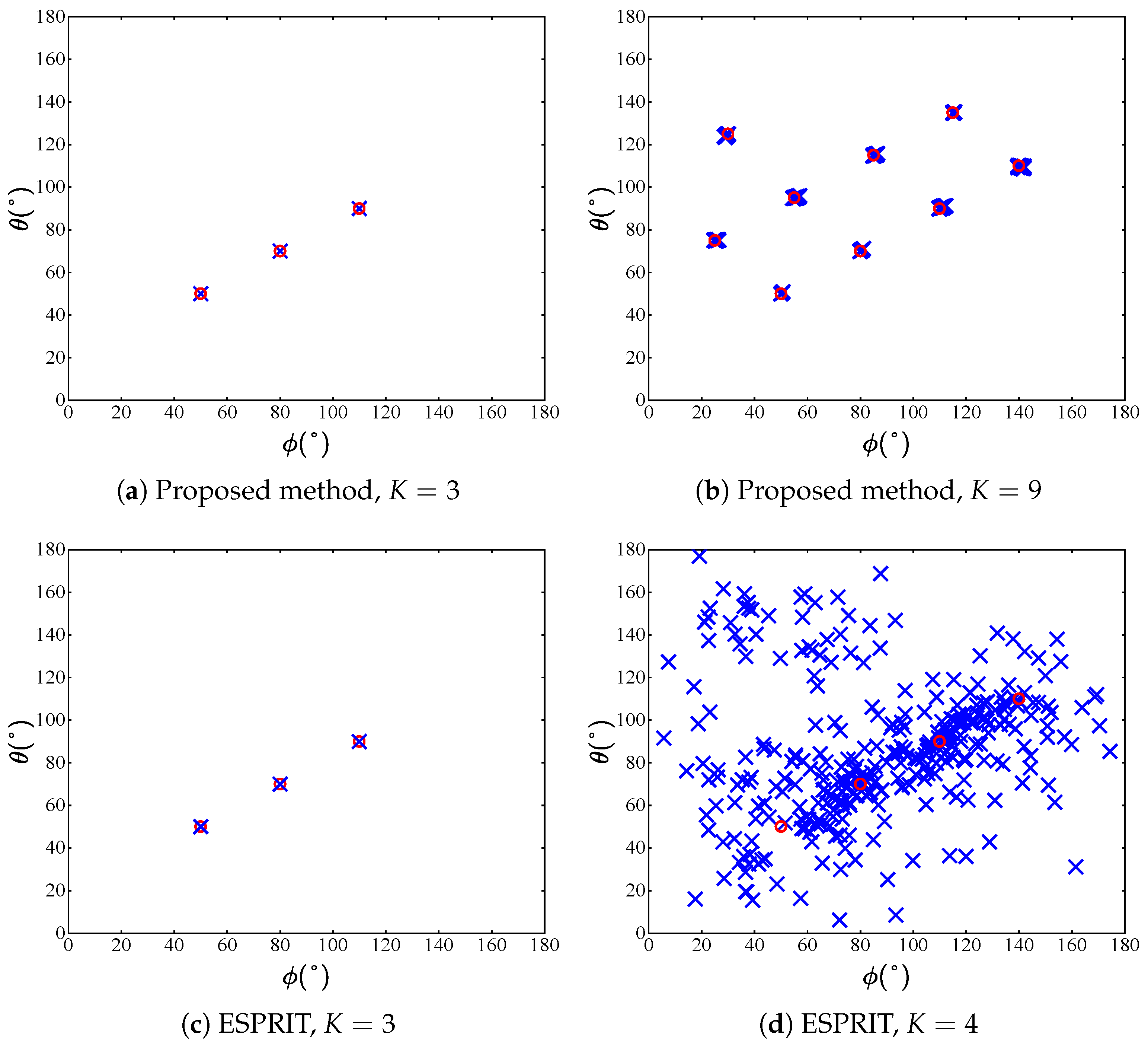
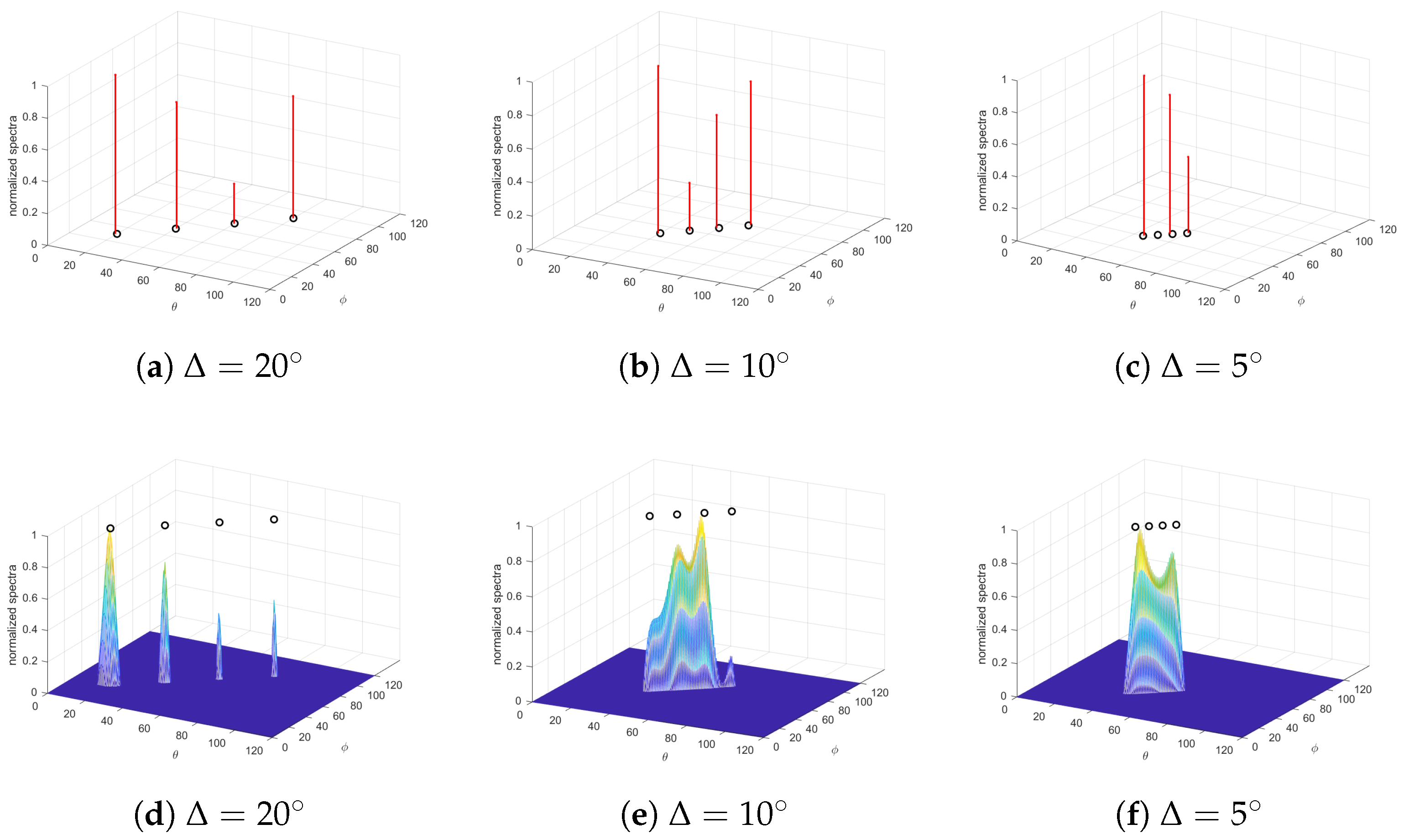
6.1. Effectiveness and Identifiability
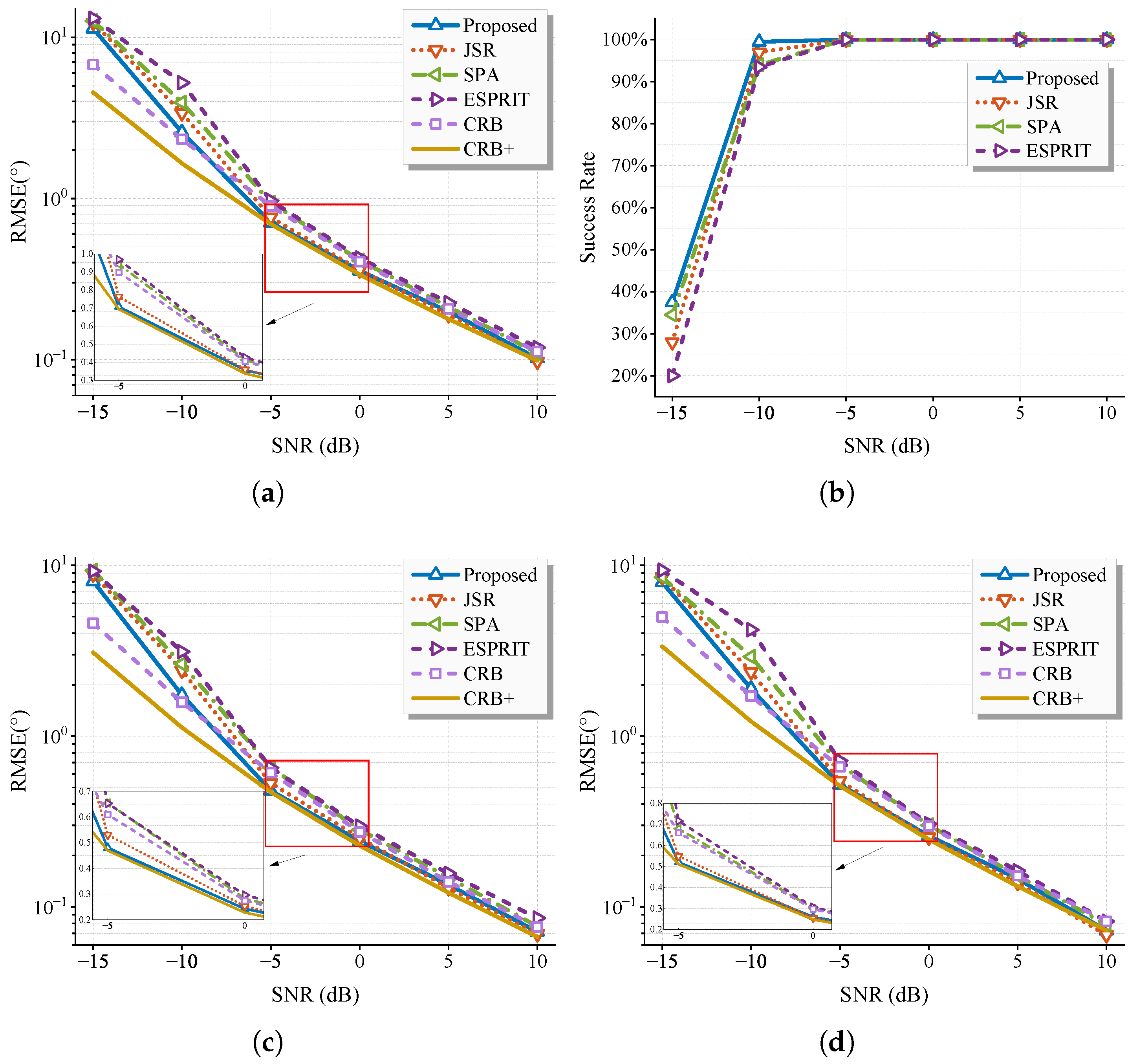
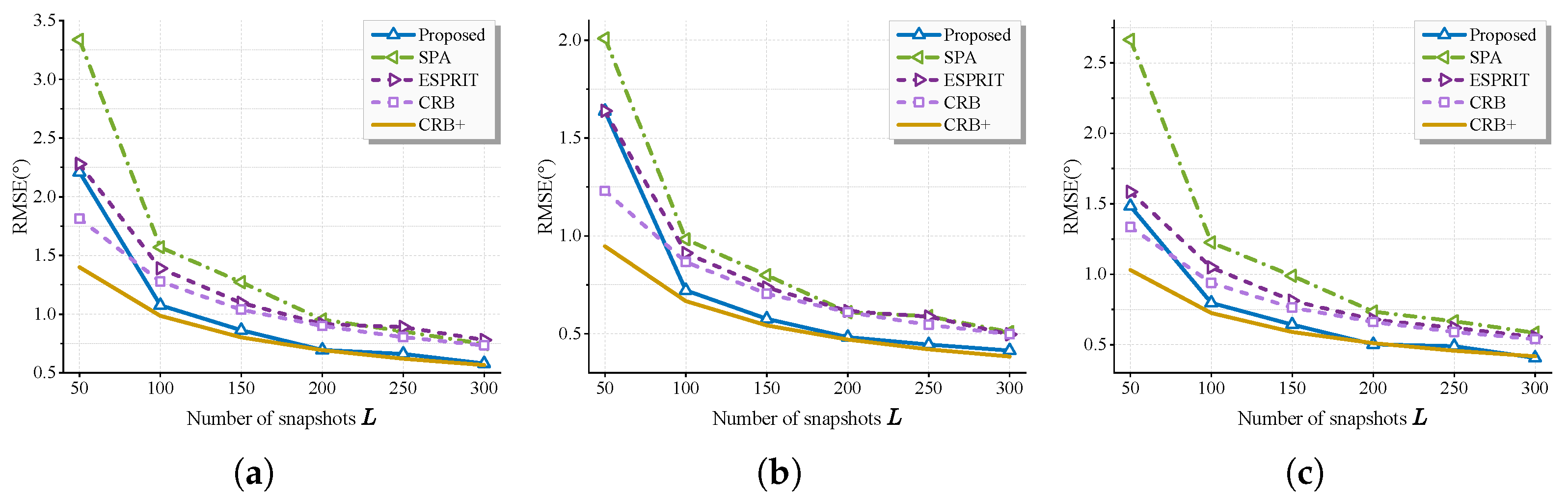
6.2. Statistic Performance Versus SNR and Snapshots
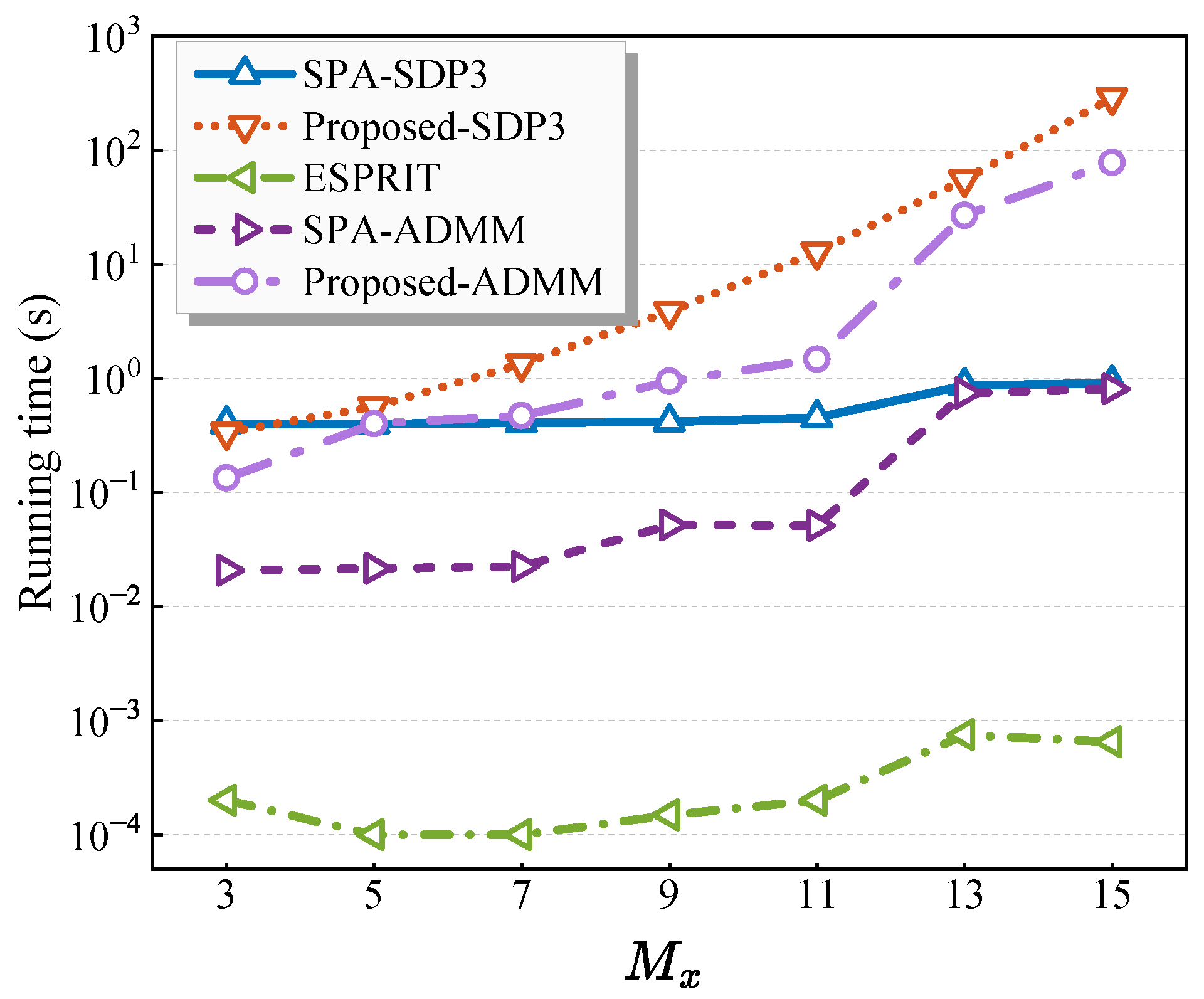
6.3. Complexity Analysis
6.4. Resolution Performance of Closely Located Targets
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Proof of Proposition 1
Appendix B. Proof of Theorem 2
References
- Yu, K.; Hudson, R.E.; Zhang, Y.D.; Yao, K.; Taylor, C.; Wang, Z. Low-Complexity 2D Direction-of-Arrival Estimation for Acoustic Sensor Arrays. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1791–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, W.; So, H.C. Joint DOD and DOA Estimation of Coherent Targets for Coprime MIMO Radar. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2023, 71, 1408–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Liu, L.; Muller, M.; Zhang, J.; Wofk, D.; Cheng, M.; Pietikainen, M. Rapid Salient Object Detection With Difference Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Hu, G.; Zhang, X.; Sun, F.; Zhou, H. Sparsity-Based Two-Dimensional DOA Estimation for Coprime Array: From Sum–Difference Coarray Viewpoint. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 5591–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Yuen, C.; Guan, Y.L.; Renzo, M.D.; Debbah, M.; Poor, H.V.; Hanzo, L. Two-Dimensional Direction-of-Arrival Estimation Using Stacked Intelligent Metasurfaces. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2024, 42, 2786–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, W.; Chen, H.; Tian, Y. Efficient 2-D DOA Estimation for Incoherently Distributed Sources with an L-shaped Array. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2025, 14, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Sarkar, T.; Weiner, D. An L-shaped Array for Estimating 2-D Directions of Wave Arrival. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1991, 39, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R. Multiple Emitter Location and Signal Parameter Estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1986, 34, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayem, N.; Kwon, H. L-Shape 2-Dimensional Arrival Angle Estimation with Propagator Method. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2005, 53, 1622–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, L.; Li, D.; Cao, H. Subspace Extension Algorithm for 2D DOA Estimation with L-shaped Sparse Array. Multidimens. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 28, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Zhang, X.; Hassan, W.U. A Higher-Order Propagator Method for 2D-DOA Estimation in Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhang, Z. Convex Optimization-Based 2-D DOA Estimation with Enhanced Virtual Aperture and Virtual Snapshots Extension for L-shaped Array. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 6473–6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Gui, G.; Gacanin, H.; Sari, H. Compressive Sampling Framework for 2D-DOA and Polarization Estimation in mmWave Polarized Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 22, 3071–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xin, J.; Zheng, N.; Sano, A. Computationally Efficient Subspace-Based Method for Two-Dimensional Direction Estimation with L-shaped Array. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 3197–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.F.; Wei, P. Joint SVD of Two Cross-Correlation Matrices to Achieve Automatic Pairing in 2-D Angle Estimation Problems. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2007, 6, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Liu, S. Decoupled 2-D Direction of Arrival Estimation in L-shaped Array. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2017, 21, 1989–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Junli, L. L-Shaped Array-Based 2-D DOA Estimation Using Parallel Factor Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2010 8th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Jinan, China, 7–9 July 2010; pp. 6949–6952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zheng, H.; Vorobyov, S.A. Tensor-Based 2-D DOA Estimation for L-shaped Nested Array. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 604–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.Y.; Dong, C.x.; Liu, W.; Chen, H.; Zhao, G.q. 2-D DOA Estimation for L-shaped Array with Array Aperture and Snapshots Extension Techniques. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2017, 24, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.Q. A Tensor-Based Approach to L-shaped Arrays Processing with Enhanced Degrees of Freedom. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhu, W.P. On Efficient Gridless Methods for 2-D DOA Estimation with Uniform and Sparse L-shaped Arrays. Signal Process. 2022, 191, 108351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Ye, K.; Qi, J.; Hong, S.; Feng, Z. 2-D DOA Estimation Based on Discrete Fractional Fourier Transform for L-shaped Nested Array. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2024, 187, 155565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Ye, K.; Zhang, X. Two-Dimensional Direction Finding for L-shaped Coprime Array via Minimization of the Ratio of the Nuclear Norm and the Frobenius Norm. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, B.N.; Tang, G.; Recht, B. Atomic Norm Denoising with Applications to Line Spectral Estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 5987–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, F.; Carlsson, M.; Tourneret, J.Y.; Wendt, H. A New Frequency Estimation Method for Equally and Unequally Spaced Data. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 5761–5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Stoica, P.; Xie, L. Sparse Methods for Direction-of-Arrival Estimation. In Academic Press Library in Signal Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 509–581. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Yang, Z.; Xu, Z. Multichannel Frequency Estimation in Challenging Scenarios via Structured Matrix Embedding and Recovery (StruMER). IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2023, 71, 3242–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huo, X. Theoretical Results on Sparse Representations of Multiple-Measurement Vectors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 4634–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, P.; Babu, P.; Li, J. SPICE: A Sparse Covariance-Based Estimation Method for Array Processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, P.; Babu, P. SPICE and LIKES: Two Hyperparameter-Free Methods for Sparse-Parameter Estimation. Signal Process. 2012, 92, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, Z.; Stoica, P.; Xu, Z. Maximum Likelihood Line Spectral Estimation in the Signal Domain: A Rank-Constrained Structured Matrix Recovery Approach. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2022, 70, 4156–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Li, J.; Shen, Y.; Li, H.; Li, S. Super-Resolution Compressed Sensing: An Iterative Reweighted Algorithm for Joint Parameter Learning and Sparse Signal Recovery. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2014, 21, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, L.; Zhang, C. A Discretization-Free Sparse and Parametric Approach for Linear Array Signal Processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 4959–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedighi, S.; Rao, B.S.M.R.; Ottersten, B. An Asymptotically Efficient Weighted Least Squares Estimator for Co-Array-Based DoA Estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Chen, Y. Compressive Two-Dimensional Harmonic Retrieval via Atomic Norm Minimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 1030–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, L.; Stoica, P. Vandermonde Decomposition of Multilevel Toeplitz Matrices with Application to Multidimensional Super-Resolution. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2016, 62, 3685–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Z. Efficient Two-Dimensional Line Spectrum Estimation Based on Decoupled Atomic Norm Minimization. Signal Process. 2019, 163, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, L. Exact Joint Sparse Frequency Recovery via Optimization Methods. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 5145–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Liu, T.; Shi, J.; Guan, D.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Generalized Gridless Formulation of Reweighted ℓ2,1 Minimization for DoA Estimation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 61, 2295–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottersten, B.; Stoica, P.; Roy, R. Covariance Matching Estimation Techniques for Array Signal Processing Applications. Digit. Signal Process. 1998, 8, 185–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinli, C.; Hong, G.; Weimin, S. Angle Estimation Using ESPRIT without Pairing in MIMO Radar. Electron. Lett. 2008, 44, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, L. On Gridless Sparse Methods for Multi-Snapshot Direction of Arrival Estimation. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 36, 3370–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, L. Enhancing Sparsity and Resolution via Reweighted Atomic Norm Minimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.; Parikh, N.; Chu, E.; Peleato, B.; Eckstein, J. Distributed Optimization and Statistical Learning via the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2010, 3, 1–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, P.; Nehorai, A. Performance Study of Conditional and Unconditional Direction-of-Arrival Estimation. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech, Signal Process. 1990, 38, 1783–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Nehorai, A. Maximum Likelihood Direction Finding in Spatially Colored Noise Fields Using Sparse Sensor Arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 1048–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, K.C.; Todd, M.J.; Tütüncü, R.H. SDPT3—A Matlab Software Package for Semidefinite Programming, Version 1.3. Optim. Methods Softw. 1999, 11, 545–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seber, G.A.F. A Matrix Handbook for Statisticians, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Optimization | DOA Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| ESPRIT | - | |
| SPA | ||
| Proposed method |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Shi, S. A Multidimensional Matrix Completion Method for 2-D DOA Estimation with L-Shaped Array. Sensors 2025, 25, 5583. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175583
Zhang H, Shi J, Li Z, Shi S. A Multidimensional Matrix Completion Method for 2-D DOA Estimation with L-Shaped Array. Sensors. 2025; 25(17):5583. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175583
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haoyue, Junpeng Shi, Zhihui Li, and Shuyun Shi. 2025. "A Multidimensional Matrix Completion Method for 2-D DOA Estimation with L-Shaped Array" Sensors 25, no. 17: 5583. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175583
APA StyleZhang, H., Shi, J., Li, Z., & Shi, S. (2025). A Multidimensional Matrix Completion Method for 2-D DOA Estimation with L-Shaped Array. Sensors, 25(17), 5583. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175583






