Tracking-Based Denoising: A Trilateral Filter-Based Denoiser for Real-World Surveillance Video in Extreme Low-Light Conditions †
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A simple but efficient motion vector estimation method is put forward, which can be applied to another computer vision task.
- A motion updating filter called an amplitude-phase filter is proposed, which improves the accuracy of these motion vectors. In addition, a denoising filter, namely the trilateral filter, is proposed by considering the gradient information, and it can suppress the gradient reversal artifact of the bilateral filter.
- A tracking-based video denoising method is proposed.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Methods
2.2. Supervised Deep Learning Methods
2.3. Unsupervised Methods
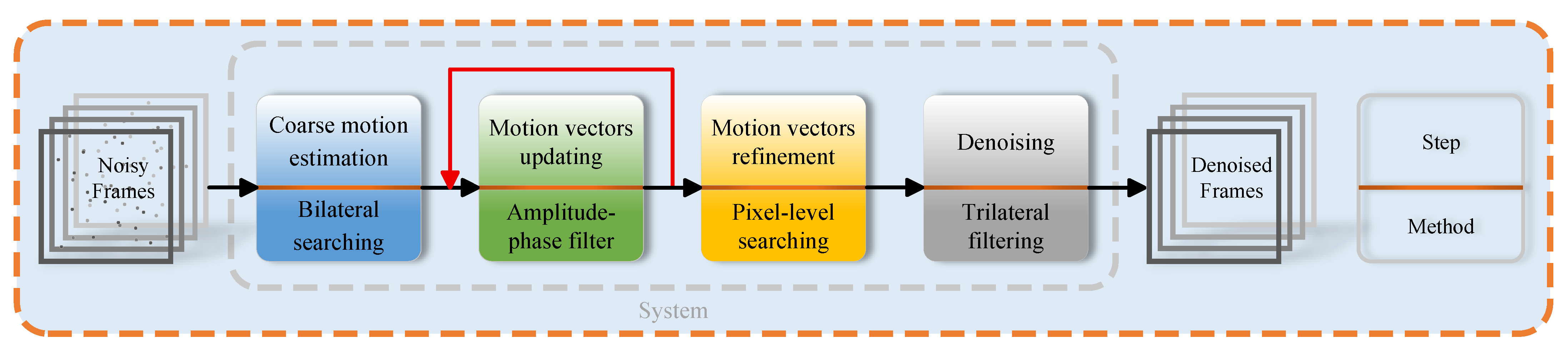
3. Methods
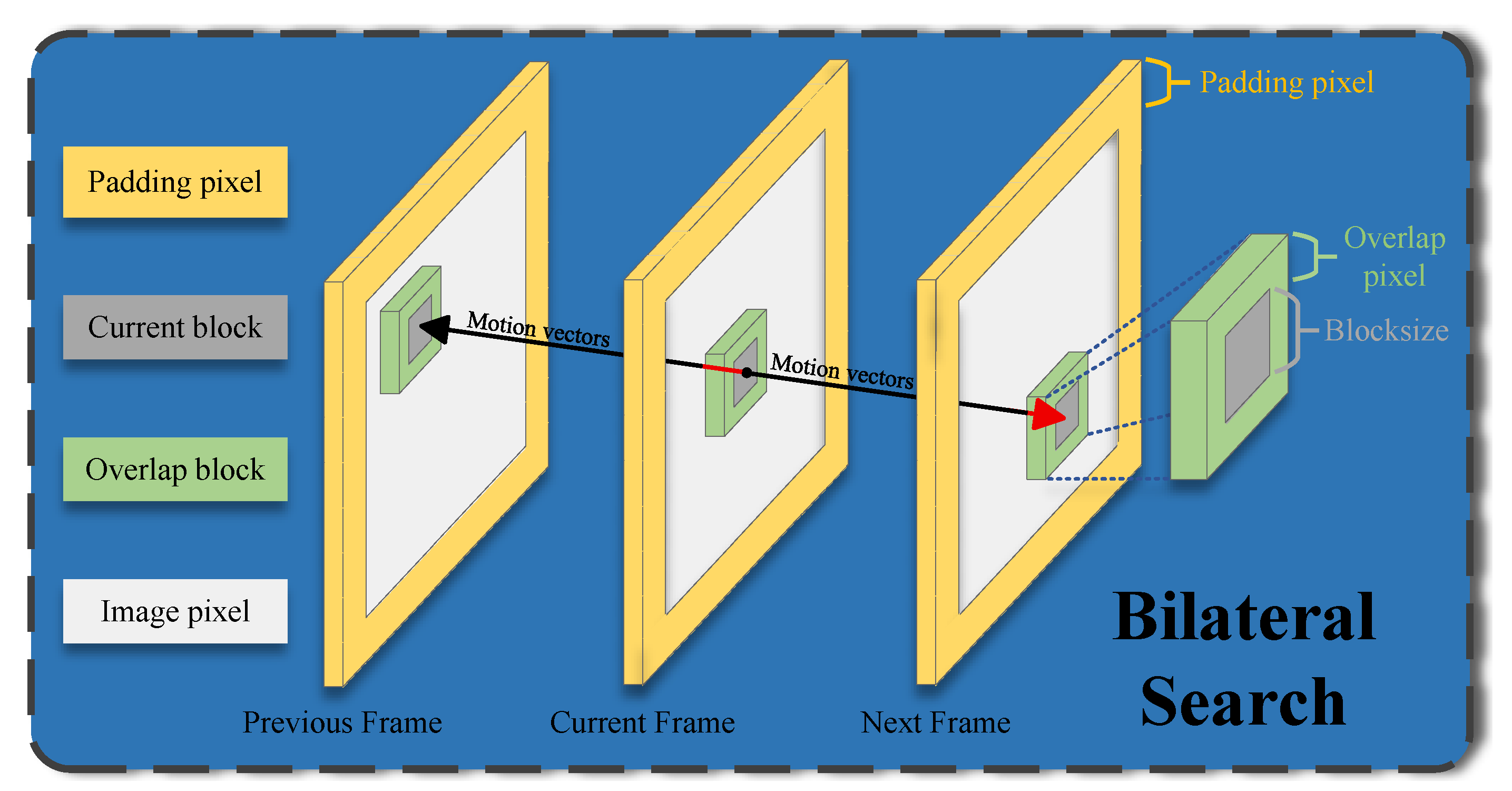
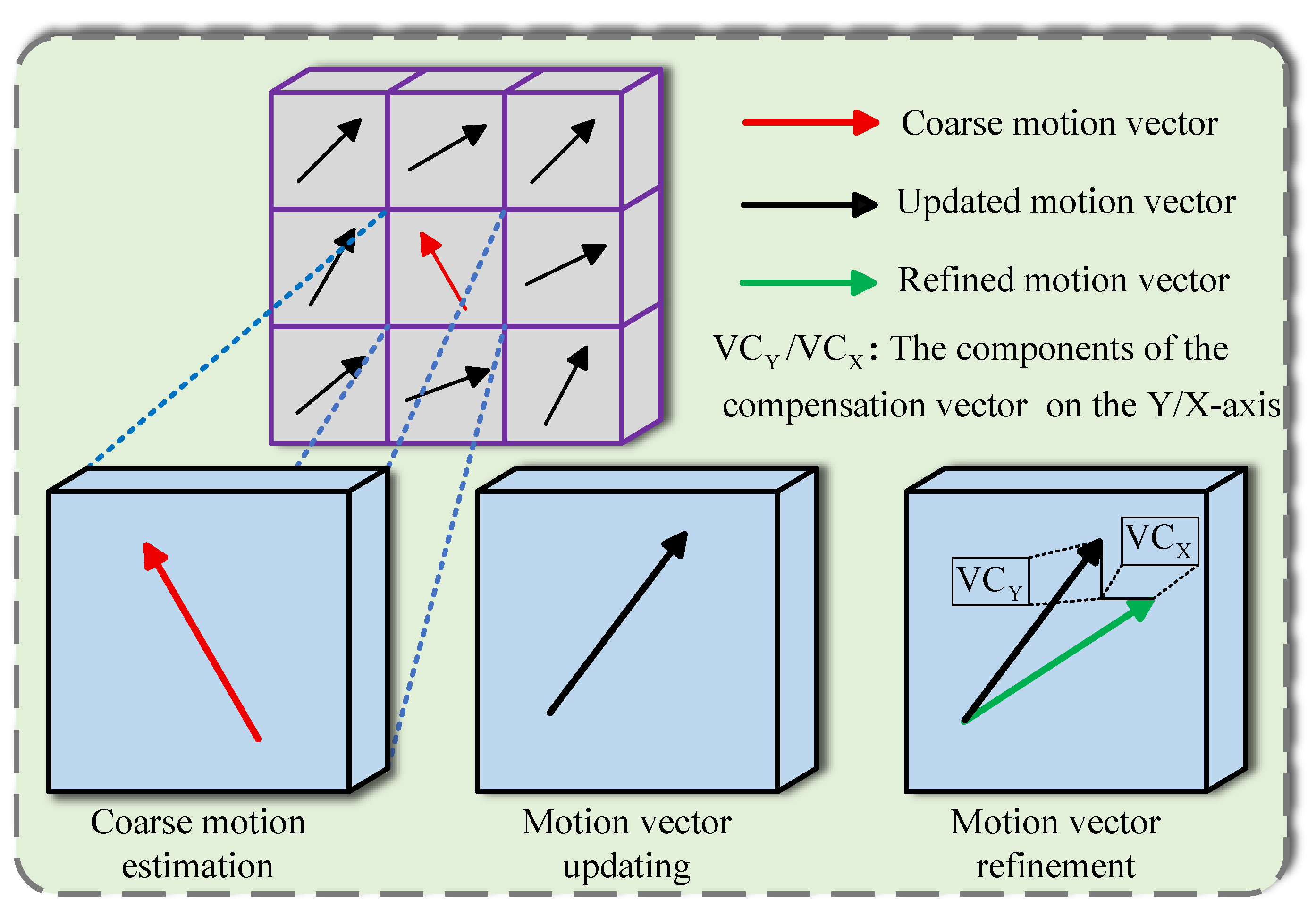
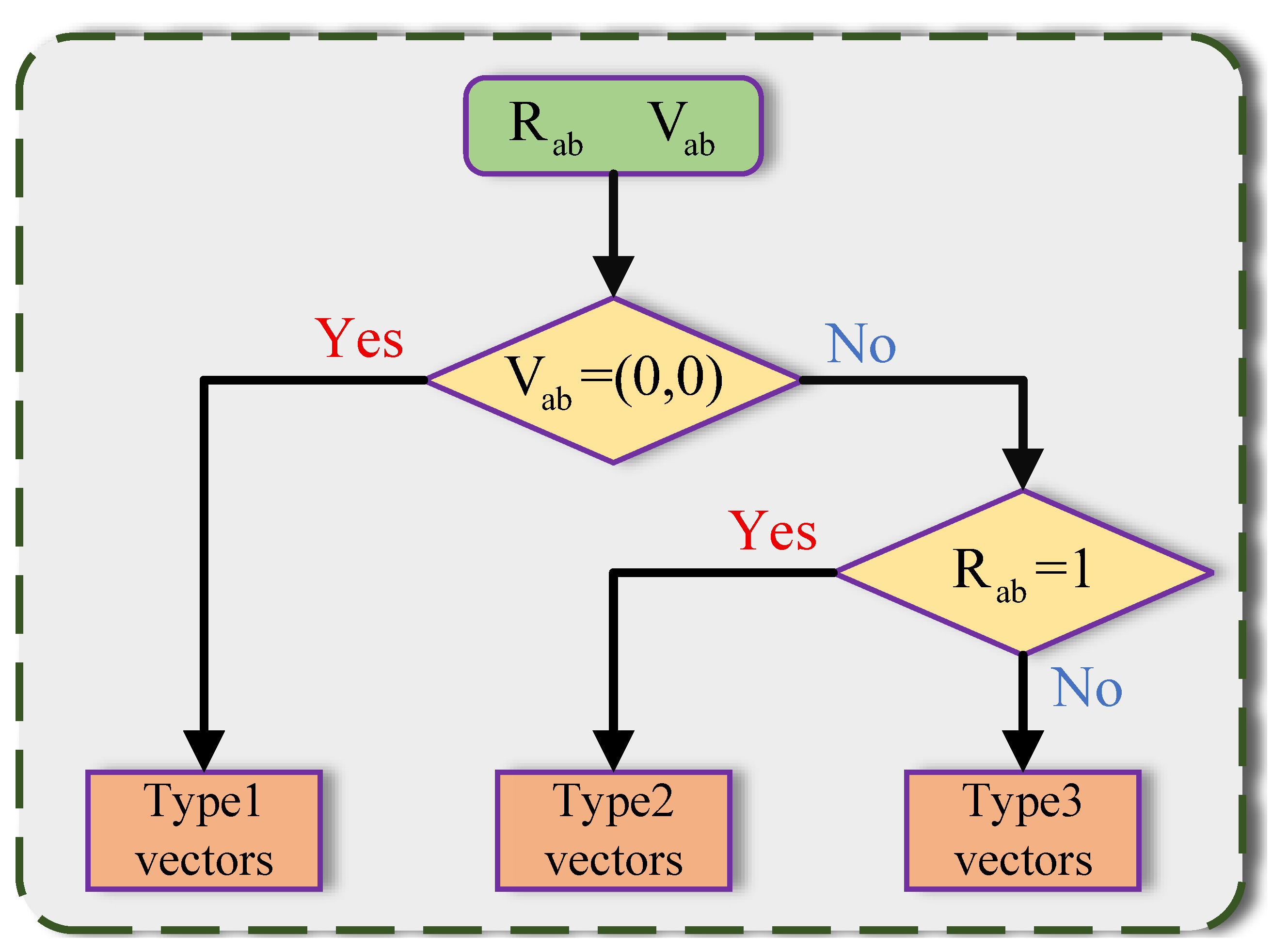
3.1. Coarse Motion Estimation
3.2. Motion Vector Updating
3.3. Motion Vector Refinement
| Algorithm 1 Motion vectors estimation, updating, and refinement. |
|
3.4. Trilateral Filter
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets for Real-World Low-Light Surveillance Video Denoising
4.2. Implementation Details
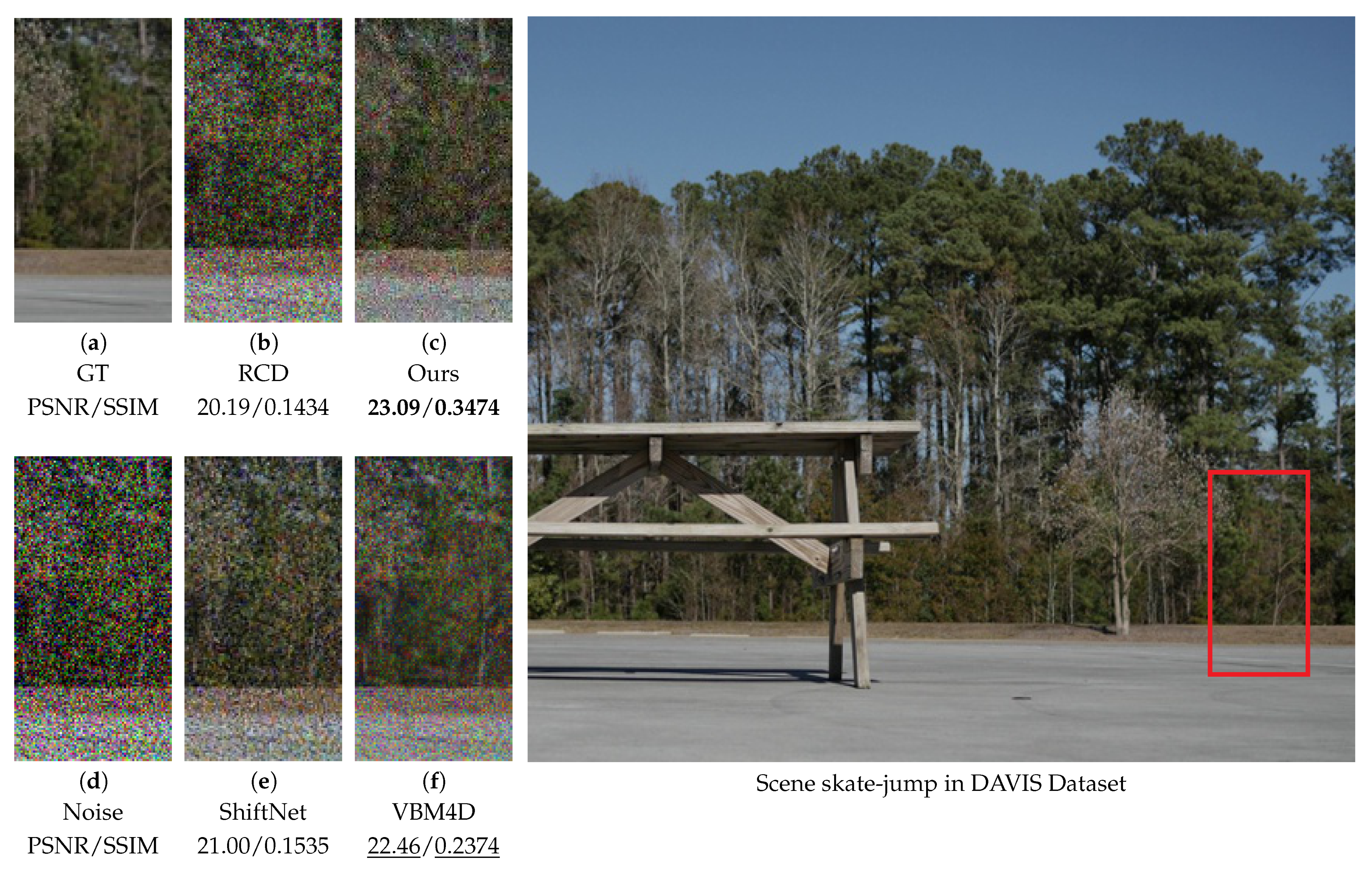
4.3. Quantitative Tests and Visual Evaluations
4.4. Speed
4.5. Intensity Curve
4.6. Video Denoising Performance on DAVIS and CRVD Benchmarks
5. Model Analysis
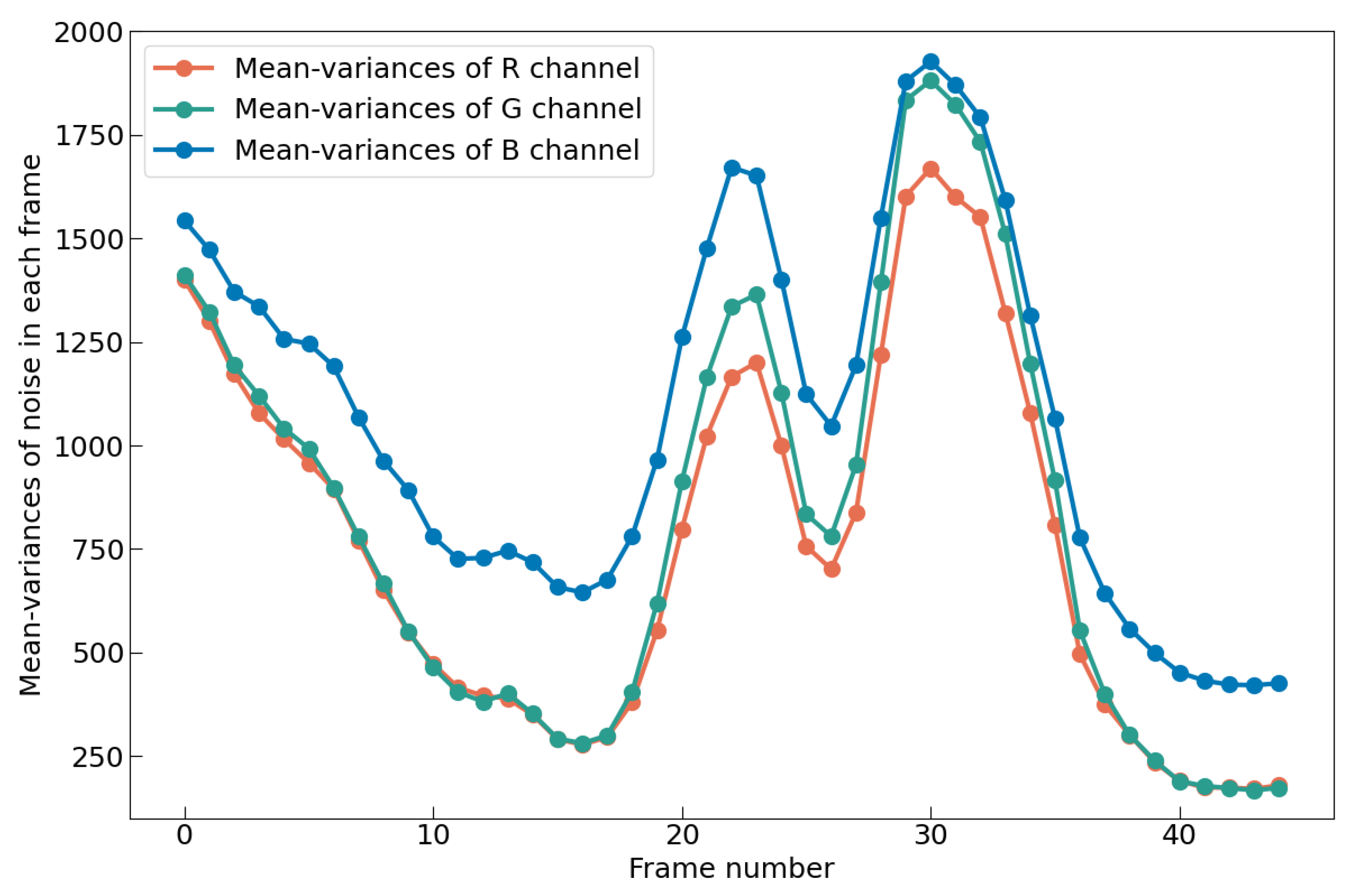
5.1. Why Low-Light Environment Is Extremely Harsh?
5.2. Why Our Model Can Work?
- Case 1: If , we set , ; thus, , and the proof ends.
- Case 2: If , a technique called mathematical induction is used, and this technique consists of three steps.
- Step 1: When number , we set , and , which meets the lemma.
- Step 2: When number , and if the lemma is satisfied, that is, , and .
- Step 3: Based on step 2, and when number , . We set and ; thus, the lemma holds when if it holds when . By the property of mathematical induction, this lemma holds for all natural numbers.
5.3. Why Is Our Model Fast?
6. Ablation Study
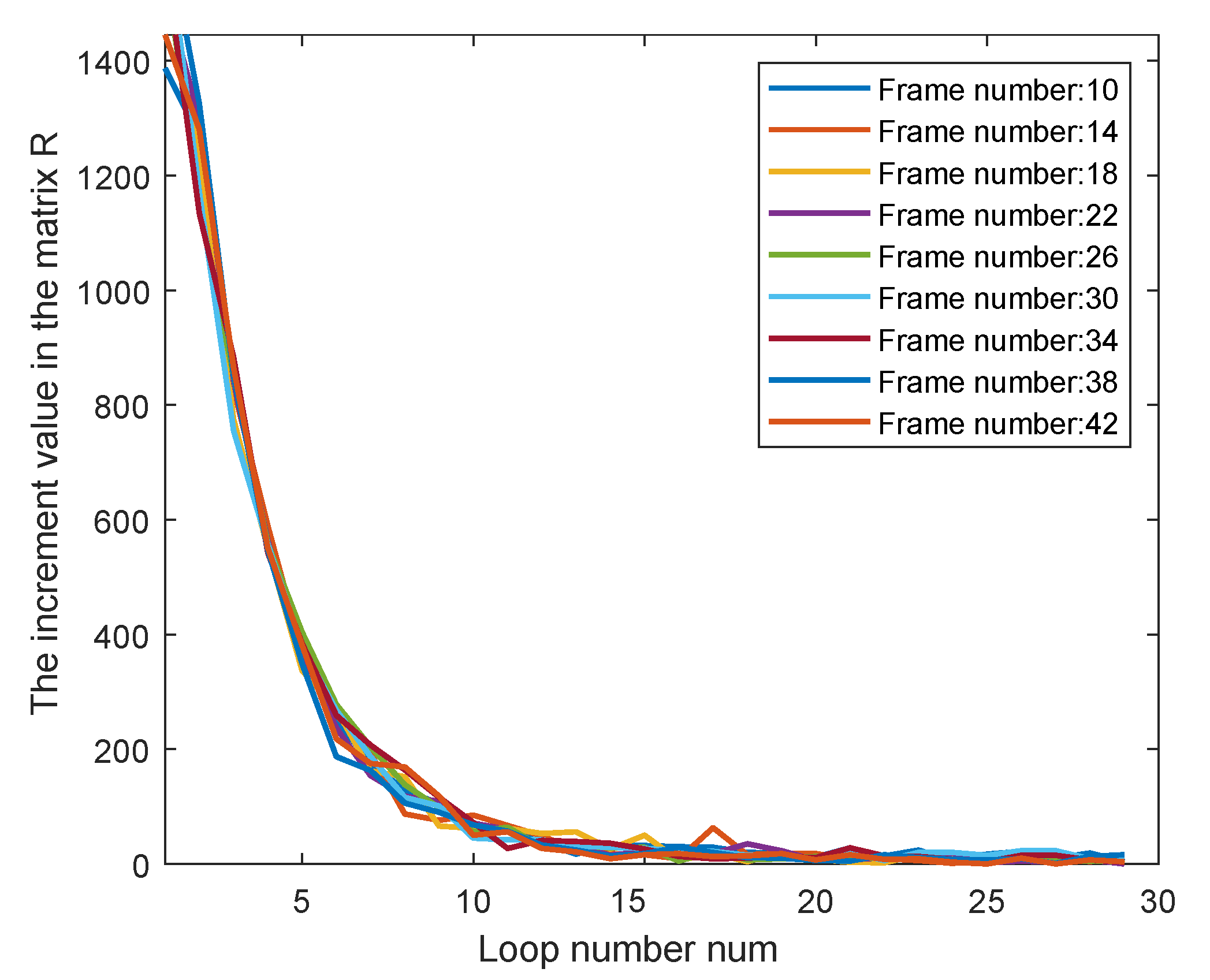
6.1. Ablation on the Loop Count as the Stopping Criterion
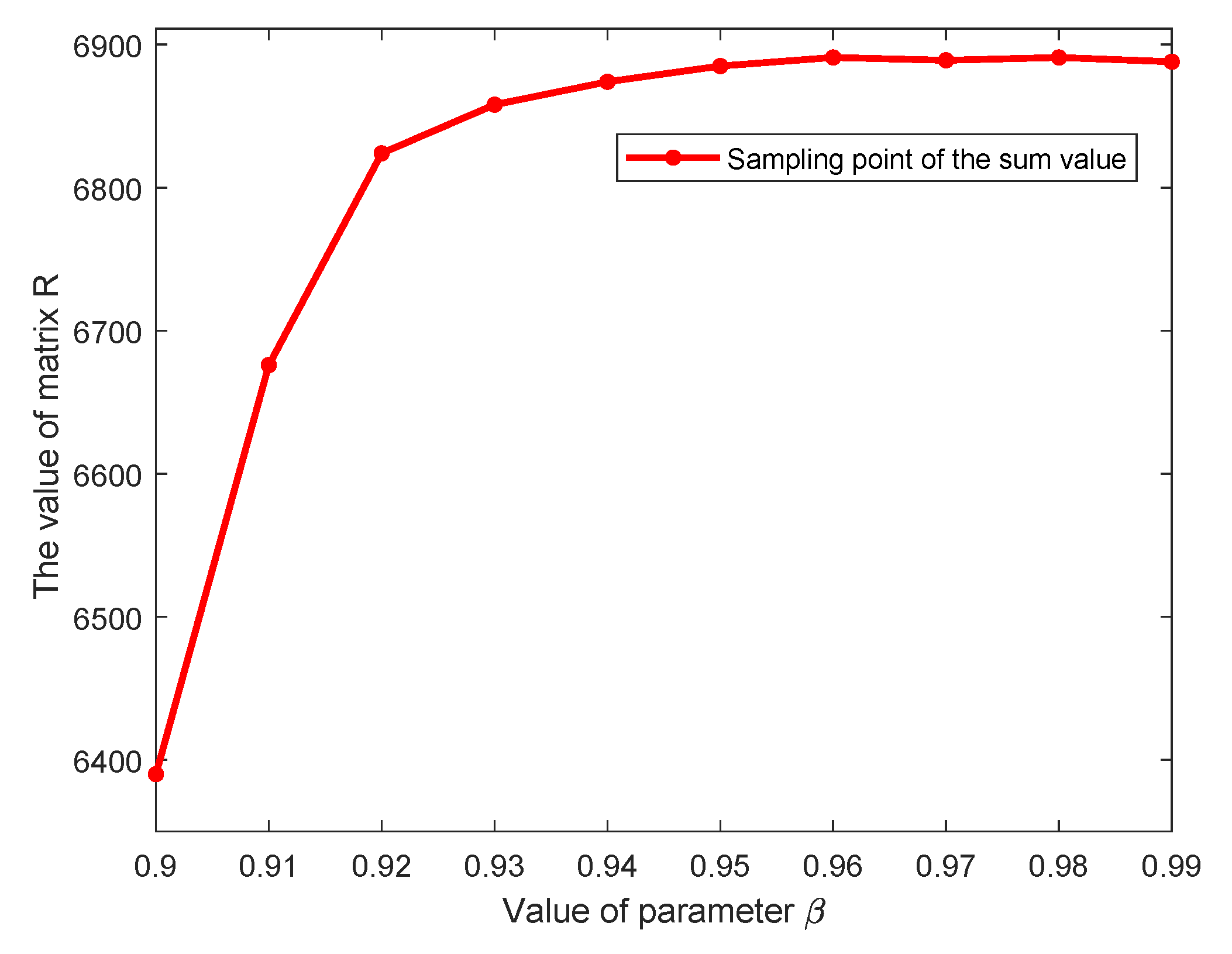
6.2. Ablation on , the Proportion of Reasonable Vectors for Stopping
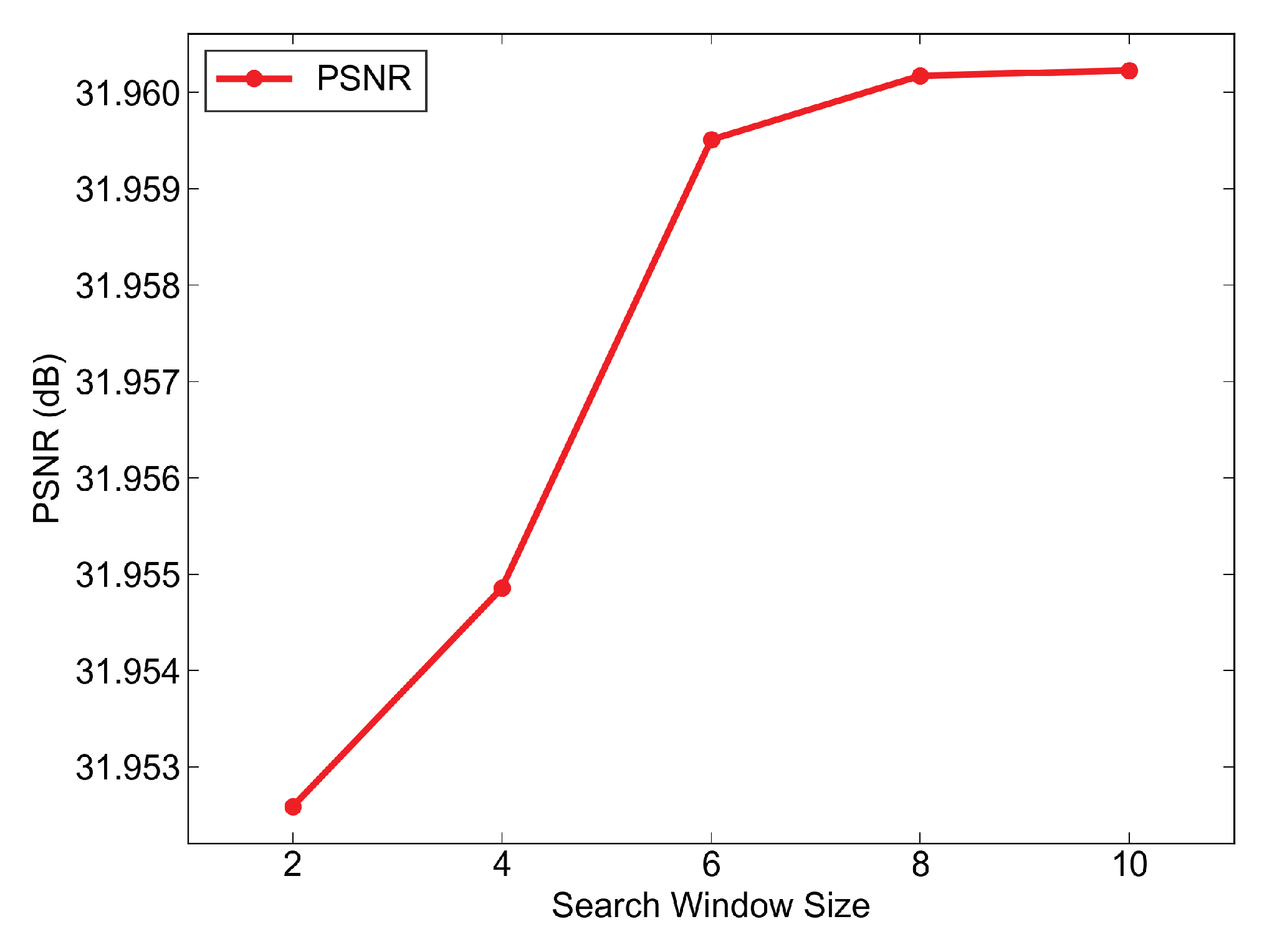
6.3. Ablation on Search Window Size for Search Scope
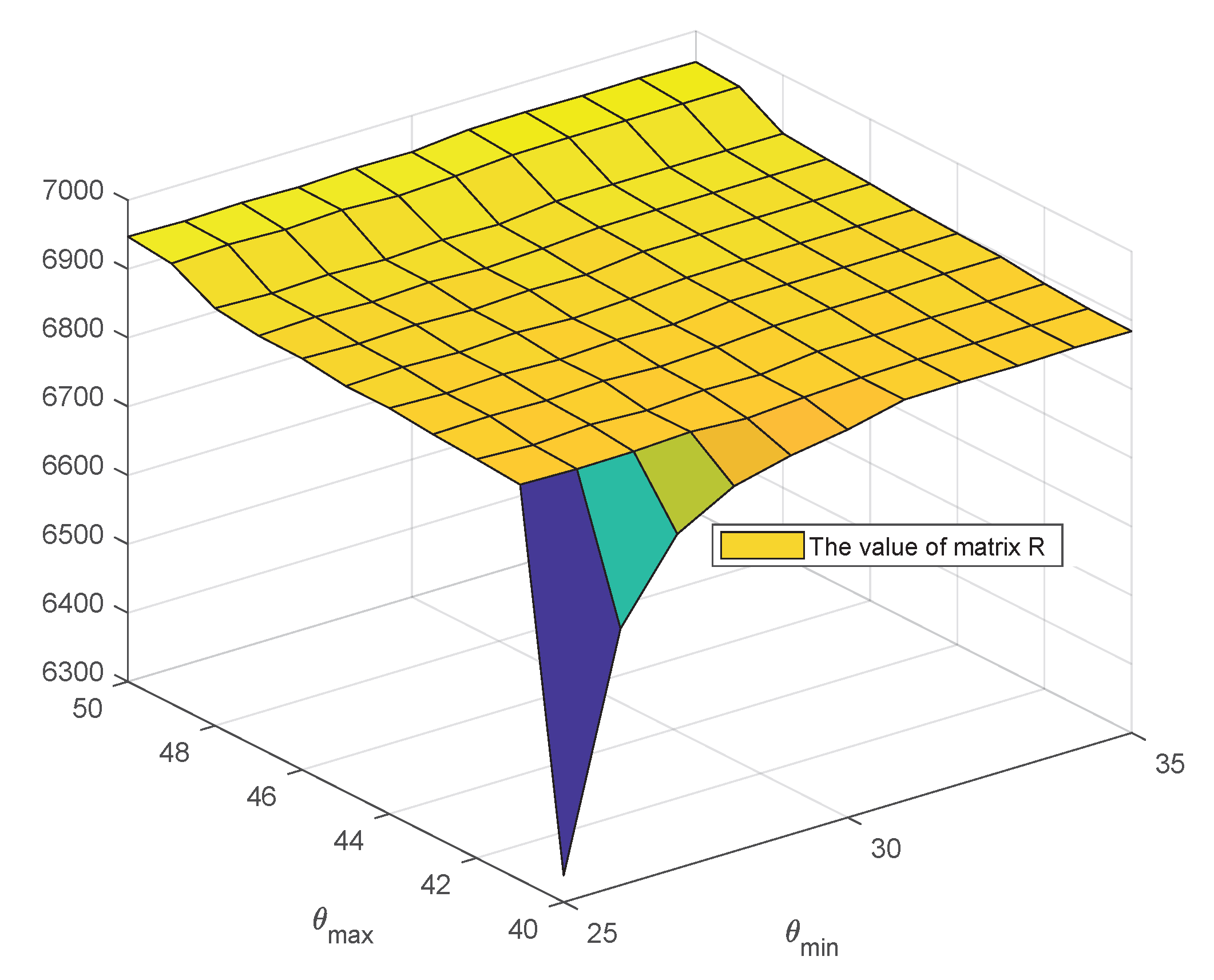
6.4. Ablation on and Used as Phase Clamping Thresholds in Amplitude Phase Filter
6.5. Ablation on Comparing Motion Estimation Methods Used for Denoising
6.6. Ablation on How Component Changes Affect Speed
7. Limitations
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malyugina, A.; Anantrasirichai, N.; Bull, D. Wavelet-based topological loss for low-light image denoising. Sensors 2025, 25, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Q. Guided filter-inspired network for low-light RAW image enhancement. Sensors 2025, 25, 2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Rhee, C.E. Motion estimation-assisted denoising for an efficient combination with an HEVC encoder. Sensors 2019, 19, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J. Low-light raw video denoising with a high-quality realistic motion dataset. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2023, 25, 8119–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, Y.; Pak, J.; Na, S.; Park, J.; Ryu, J.; Moon, S.; Koo, B.; Kang, S.-J. Supervised denoising for extreme low-light raw videos. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Anami, S.; Matsuoka, R. Optimizing dynamic mode decomposition for video denoising via plug-and-play alternating direction method of multipliers. Signals 2024, 5, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image Denoising with Block-Matching and 3D Filtering. In Proceedings of the SPIE Electronic Imaging 2006: Image Processing, San Jose, CA, USA, 15–19 January 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Guided image filtering. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.W.; Au, O.C.; Chong, T.S.; Chau, W.S. A Novel Content-Adaptive Video Denoising Filter. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 18–23 March 2005; pp. 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selesnick, I.W.; Li, K.Y. Video denoising using 2D and 3D dual-tree complex wavelet transforms. In Proceedings of the Wavelets: Applications in Signal and Image Processing X, San Diego, CA, USA, 13 November 2003; pp. 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanov, L.; Pizurica, A.; Schulte, S.; Schelkens, P.; Munteanu, A.; Kerre, E.; Philips, W. Combined Wavelet-Domain and Motion-Compensated Video Denoising Based on Video Codec Motion Estimation Methods. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2009, 19, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugad, R.; Ahuja, N. Video Denoising by Combining Kalman and Wiener Estimates. In Proceedings of the 1999 International Conference on Image Processing, Kobe, Japan, 24–28 October 1999; pp. 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buades, A.; Lisani, J.-L.; Miladinovic, M. Patch-Based Video Denoising with Optical Flow Estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 2573–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image Restoration by Sparse 3D Transform-Domain Collaborative Filtering. In Proceedings of the SPIE Electronic Imaging 2008: Image Processing: Algorithms and Systems VI, San Jose, CA, USA, 27–31 January 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, M.; Boracchi, G.; Foi, A.; Egiazarian, K. Video Denoising, Deblocking, and Enhancement Through Separable 4-D Nonlocal Spatiotemporal Transforms. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 3952–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, P.; Morel, J.-M. Video Denoising via Empirical Bayesian Estimation of Space-Time Patches. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2017, 60, 70–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaksman, G.; Elad, M.; Milanfar, P. Patch Craft: Video Denoising by Deep Modeling and Patch Matching. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 2137–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy, A.; Ehret, T.; Morel, J.-M.; Arias, P.; Facciolo, G. A Non-Local CNN for Video Denoising. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 2409–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy, A.; Ehret, T.; Morel, J.-M.; Arias, P.; Facciolo, G. Video Denoising by Combining Patch Search and CNNs. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2020, 63, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, S.; Xu, W.; Li, Q. Recursive Video Denoising Algorithm for Low Light Surveillance Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 14th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics, Shanghai, China, 22–24 October 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Park, D.; Han, D.; Ko, H. A Novel Approach for Denoising and Enhancement of Extremely Low-Light Video. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2015, 61, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassano, M.; Delon, J.; Veit, T. DVDNET: A Fast Network for Deep Video Denoising. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 1805–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassano, M.; Delon, J.; Veit, T. FastDVDnet: Towards real-time deep video denoising without flow estimation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, D.Y.; Mohan, S.; Vincent, J.L.; Manzorro, R.; Crozier, P.A.; Khapra, M.M.; Simoncelli, E.P.; Fernandez-Granda, C. Unsupervised Deep Video Denoising. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, Q. Real-time Streaming Video Denoising with Bidirectional Buffers. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisbon, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 2758–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Shao, W.; Wang, X.; Luo, P.; Lin, K.; Gu, J. Real-Time Controllable Denoising for Image and Video. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 14028–14038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cheung, K.C.; See, S.; Wang, X.; Qin, H.; Li, H. A Simple Baseline for Video Restoration with Grouped Spatial-Temporal Shift. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 9822–9832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Huang, Z.; Bian, W.; Li, D.; Zhang, M.; Cheung, K.C.; See, S.; Qin, H.; Dai, J.; Li, H. VideoFlow: Exploiting Temporal Cues for Multi-frame Optical Flow Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 12435–12446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jiang, T.; Hu, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Wang, H. Spatiotemporal Blind-Spot Network with Calibrated Flow Alignment for Self-Supervised Video Denoising. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 25 February–4 March 2025; pp. 2411–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chan, K.C.K.; Yu, K.; Dong, C.; Loy, C.C. EDVR: Video Restoration With Enhanced Deformable Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, X.; Niu, Z.; Zuo, W. Unidirectional Video Denoising by Mimicking Backward Recurrent Modules with Look-Ahead Forward Ones. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 592–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Song, L.; Yang, X. Deep RNNs for Video Denoising. In Proceedings of the Applications of Digital Image Processing XXXIX, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bai, X. Versatile recurrent neural network for wide types of video restoration. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 138, 109360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggioni, M.; Huang, Y.; Li, C.; Xiao, S.; Fu, Z.; Song, F. Efficient Multi-Stage Video Denoising with Recurrent Spatio-Temporal Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 3465–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Fan, Y.; Xiang, X.; Ranjan, R.; Ilg, E.; Green, S.; Cao, J.; Zhang, K.; Timofte, R.; Van Gool, L. Recurrent video restoration transformer with guided deformable attention. In Proceedings of the 36th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022; pp. 378–393. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, H.; Cao, C.; Liao, L.; Yang, J. RViDeformer: Efficient Raw Video Denoising Transformer with a Larger Benchmark Dataset. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiyetigbo, M.; Ravichandran, D.; Chalhoub, R.; Kalivas, P.; Luo, F.; Li, N. Unsupervised Coordinate-Based Video Denoising. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 27–30 October 2024; pp. 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Guo, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wen, B. Temporal As a Plugin: Unsupervised Video Denoising with Pre-trained Image Denoisers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; pp. 349–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Pang, T.; Ji, H. Unsupervised Deep Video Denoising with Untrained Network. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Seventh AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; pp. 3651–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, S.; Karras, T.; Lehtinen, J.; Aila, T. High-Quality Self-Supervised Deep Image Denoising. In Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 6966–6976. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemabadi, A.; Janjua, M.K.; Salameh, M.; Niu, D. Learning Truncated Causal History Model for Video Restoration. In Proceedings of the 38th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–15 December 2024; pp. 27584–27615. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, R.; Chen, H.; Gu, Y.; Ling, P.; Chen, E. Masked Video Pretraining Advances Real-World Video Denoising. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2025, 27, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewil, V.; Anger, J.; Davy, A.; Ehret, T.; Facciolo, G.; Arias, P. Self-supervised Training for Blind Multi-Frame Video Denoising. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 2723–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Cho, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.H. Restore from Restored: Video Restoration with Pseudo Clean Video. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 3536–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zheng, P.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Geng, Y.; Gao, J.; Jiang, H. Denoising Real-World Low Light Surveillance Videos Based on Trilateral Filter. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Internet of Things, Communication and Intelligent Technology, Xuzhou, China, 22–24 September 2023; Dong, J., Zhang, L., Cheng, D., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering. Springer: Singapore, 2024; Volume 1197, pp. 602–615. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, B.T.; Lee, S.H.; Ko, S.J. New Frame Rate Up-Conversion Using Bi-Directional Motion Estimation. IEEE Trans. Consumer Electron. 2000, 46, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Lu, Z. Motion-Compensated Frame Interpolation with Weighted Motion Estimation and Hierarchical Vector Refinement. Neurocomputing 2016, 181, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, C.; Manduchi, R. Bilateral Filtering for Gray and Color Images. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Computer Vision, Bombay, India, 4–7 January 1998; pp. 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, S.; Durand, F. A Fast Approximation of the Bilateral Filter Using a Signal Processing Approach. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2007, 81, 24–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Ardabilian, M.; Chen, L. Depth Edge Based Trilateral Filter Method for Stereo Matching. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015; pp. 2280–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, M.; Volz, S.; Bruhn, A. Joint Trilateral Filtering for Multiframe Optical Flow. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 15–18 September 2013; pp. 3845–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pont-Tuset, J.; Perazzi, F.; Caelles, S.; Arbeláez, P.; Sorkine-Hornung, A.; Van Gool, L. The 2017 DAVIS Challenge on Video Object Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.00675. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, H.; Cao, C.; Liao, L.; Chu, R.; Yang, J. Supervised Raw Video Denoising With a Benchmark Dataset on Dynamic Scenes. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2298–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Zheng, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Ma, H. Dancing in the Dark: A Benchmark towards General Low-light Video Enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 12831–12840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinh, T.Q.; Kim, Y.-C.; Hong, S.-H. Frame Rate Up-Conversion Using Forward-Backward Jointing Motion Estimation and Spatio-Temporal Motion Vector Smoothing. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Computer Engineering & Systems, Cairo, Egypt, 14–16 December 2009; pp. 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Yoo, S.; Kim, Y.H. Dual Motion Estimation for Frame Rate Up-Conversion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2010, 20, 1909–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.G.; Kang, S.J.; Kim, Y.H. Direction-Select Motion Estimation for Motion-Compensated Frame Rate Up-Conversion. J. Display Technol. 2013, 9, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, L.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, X. Frame Rate Up-Conversion Using Linear Quadratic Motion Estimation and Trilateral Filtering Motion Smoothing. J. Display Technol. 2015, 12, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


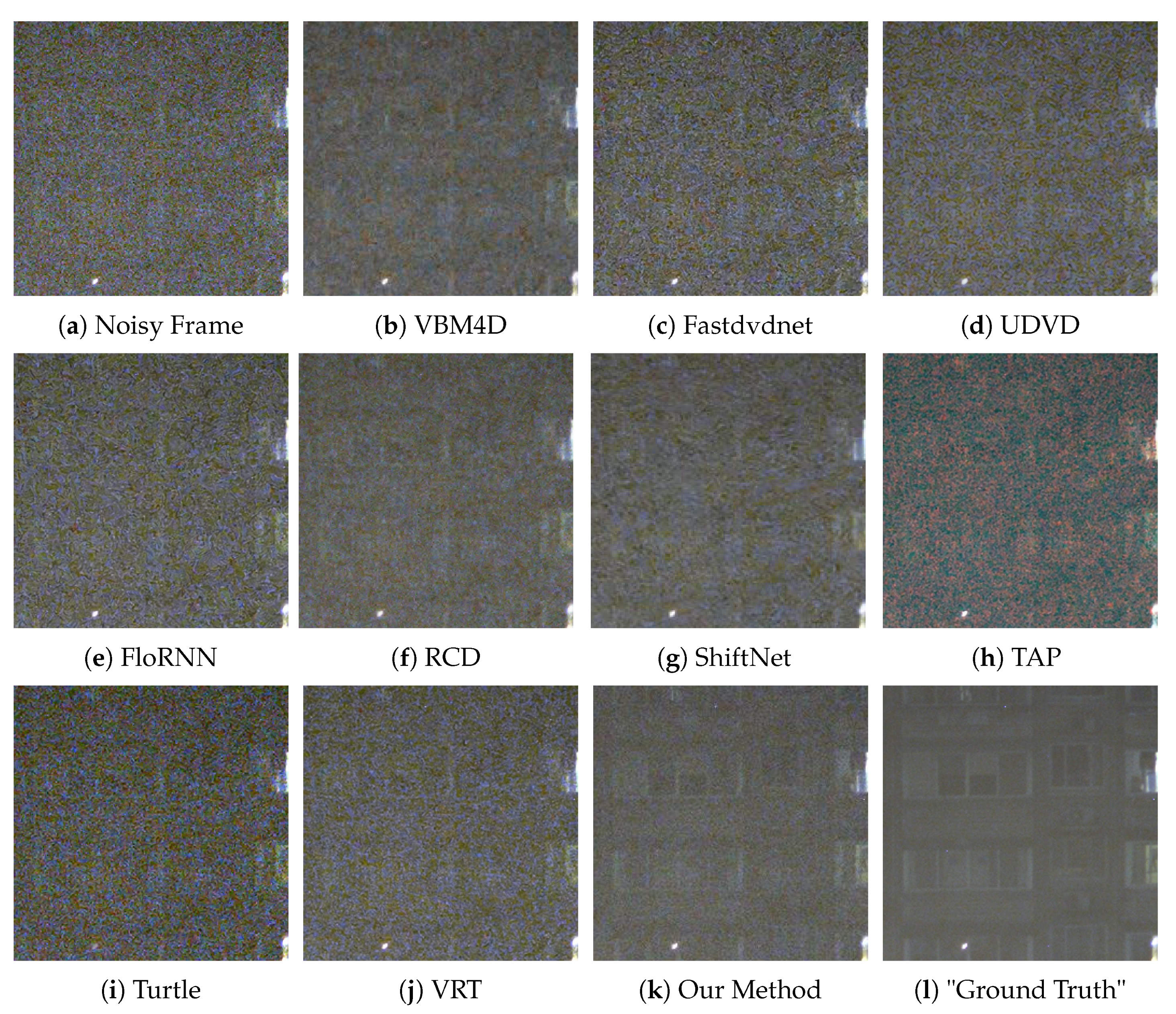



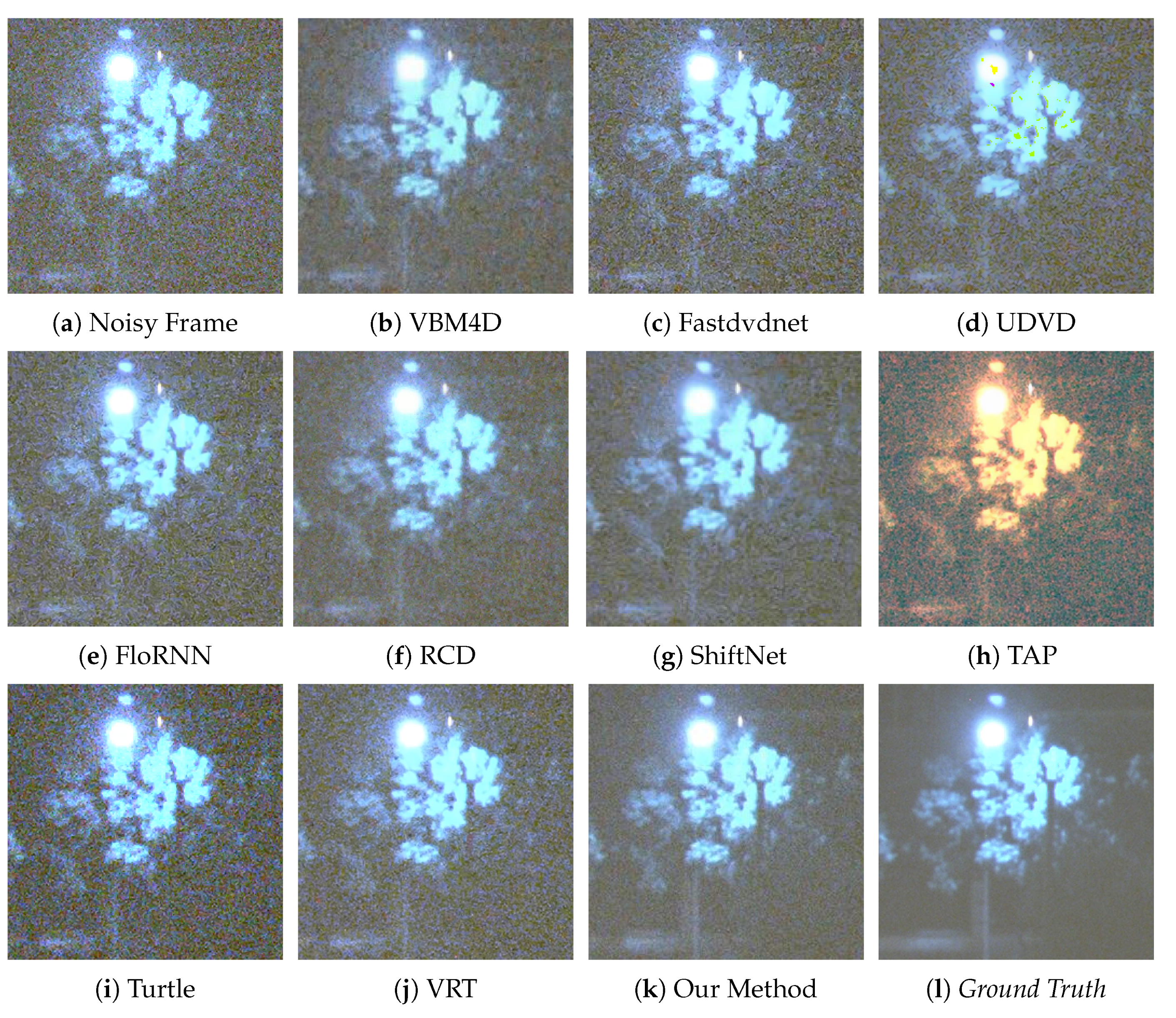







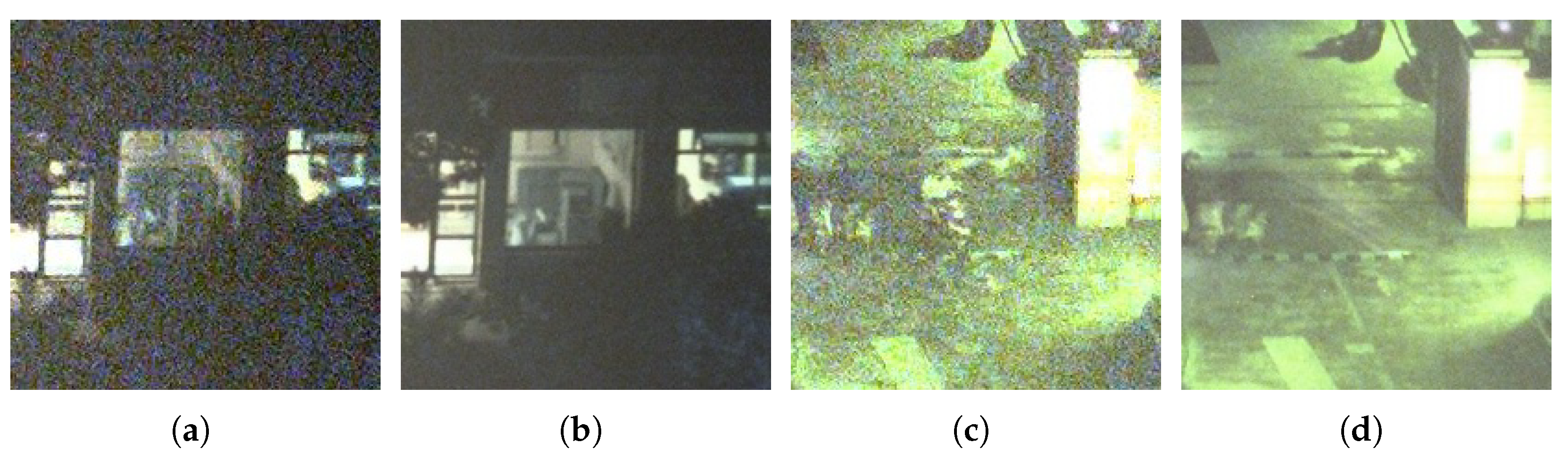
| Methods’ Names | Video 1 PSNR/SSIM | Video 2 PSNR/SSIM | Video 3 PSNR/SSIM | Video 4 PSNR/SSIM | Video 5 PSNR/SSIM | Video 6 PSNR/SSIM | Video 7 PSNR/SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VBM4D [15] | 28.01/0.6650 | 27.04/ 0.5716 | 27.51/0.5931 | 28.97/ 0.6164 | 26.38/ 0.5874 | 28.87/0.6438 | 29.15/0.6197 |
| FastdvdNet [24] | 24.37/0.4629 | 23.30/0.2848 | 23.63/0.3474 | 24.46/0.3801 | 23.01/0.3221 | 24.54/0.3860 | 24.52/0.3778 |
| UDVD [25] | 26.15/0.5615 | 25.42/0.4109 | 25.93/0.4766 | 26.92/0.4871 | 25.11/0.4532 | 26.82/0.4895 | 27.14/0.4932 |
| FloRNN [32] | 24.82/0.4851 | 23.66/0.3044 | 24.04/0.3693 | 25.02/0.4049 | 23.44/0.3474 | 25.04/0.4119 | 25.09/0.4031 |
| RCD [27] | 28.22/0.6540 | 26.52/0.5160 | 27.44/0.5692 | 28.78/0.5892 | 26.11/0.5454 | 28.66/0.6065 | 28.90/0.5886 |
| ShiftNet [28] | 25.68/0.6548 | 26.73/ 0.5286 | 27.56/0.6079 | 28.69/ 0.6154 | 26.21/0.5744 | 27.34/0.6340 | 29.04/0.6188 |
| TAP [39] | 24.95/0.4969 | 23.99/0.3405 | 24.43/0.3916 | 24.80/0.4263 | 23.34/0.3775 | 25.54/0.4361 | 24.64/0.4287 |
| Turtle [42] | 23.30/0.4652 | 20.26/0.2581 | 21.99/0.3393 | 22.23/0.3640 | 20.87/0.3044 | 23.44/0.3902 | 22.01/0.3556 |
| VRT [27] | 25.84/0.5293 | 24.67/0.3614 | 25.08/0.4198 | 26.20/0.4518 | 24.29/0.3966 | 26.14/0.4612 | 26.29/0.4500 |
| Our method | 31.14/0.7687 | 29.81/0.6524 | 30.28/0.7038 | 31.62/0.7131 | 29.03/0.6772 | 31.50/0.7220 | 31.75/0.7143 |
| Methods’ Names | Video 8 PSNR/SSIM | Video 9 PSNR/SSIM | Video 10 PSNR/SSIM | Video 11 PSNR/SSIM | Video 12 PSNR/SSIM | Video 13 PSNR/SSIM | Video 14 PSNR/SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VBM4D [15] | 29.79/0.7318 | 27.71/0.7250 | 24.01/0.7035 | 30.98/0.7483 | 28.94/0.7485 | 32.86/0.7899 | 28.02/0.7599 |
| FastdvdNet [24] | 28.57/0.7010 | 26.62/0.6927 | 23.37/0.6745 | 29.22/0.6840 | 26.85/0.6292 | 30.95/0.6985 | 25.93/0.5812 |
| UDVD [26] | 28.96/0.7169 | 27.16/0.7187 | 23.81/0.6990 | 29.70/0.7053 | 27.50/0.6703 | 30.85/0.6919 | 26.39/0.6136 |
| FloRNN [32] | 28.52/0.6968 | 26.63/0.6922 | 23.36/0.6740 | 29.21/0.6834 | 26.90/0.6327 | 30.85/0.6948 | 25.96/0.5830 |
| RCD [27] | 30.31/0.7704 | 28.01/0.7597 | 24.17/0.7351 | 31.70/0.7890 | 29.16/0.7807 | 33.85/0.8285 | 28.01/0.7809 |
| ShiftNet [28] | 29.25/0.6977 | 27.21/0.6752 | 23.62/0.6442 | 30.26/0.7044 | 28.91/0.7335 | 32.62/0.7927 | 28.21/0.7748 |
| TAP [39] | 28.28/0.6982 | 26.37/0.6919 | 23.35/0.6743 | 28.86/0.6975 | 26.66/0.6671 | 31.20/0.7293 | 26.12/0.6415 |
| Turtle [42] | 27.39/0.6644 | 25.76/0.6652 | 22.91/0.6494 | 27.92/0.6520 | 25.84/0.6037 | 29.54/0.6394 | 25.12/0.5420 |
| VRT [27] | 29.48/0.7463 | 27.27/0.7353 | 23.64/0.7092 | 30.40/0.7406 | 27.75/0.6917 | 32.21/0.7562 | 26.67/0.6475 |
| Our method | 31.85/0.8467 | 29.50/0.8409 | 25.53/0.8112 | 33.02/0.8544 | 30.39/0.8306 | 34.69/0.8581 | 28.90/0.7925 |
| Method | Speed (FPS) | Device | Method | Speed (FPS) | Device |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VBM4D [15] | 2.20 | CPU | FastdvdNet [24] | 129.87 | GPU |
| UDVD [25] | 20.58 | GPU | FloRNN [32] | 37.31 | GPU |
| RCD [27] | 67.56 | GPU | ShiftNet [28] | 0.33 | GPU |
| TAP [39] | 15.75 | GPU | Turtle [42] | 8.44 | GPU |
| VRT [27] | 1.05 | GPU | Our method | 1.17 | CPU |
| Dataset | BME [46] | FBJME [55] | DME [56] | DSME [57] | LQME [58] | Our Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akiyo | 44.26/0.9926 | 45.76/0.9950 | 47.20/0.9961 | 47.39/0.9962 | 46.61/0.9960 | 47.14/0.9956 |
| Paris | 34.24/0.9745 | 35.35/0.9795 | 36.42/0.9834 | 36.80/0.9847 | 36.14/0.9830 | 36.15/0.9822 |
| Silent | 34.54/0.9518 | 35.35/0.9795 | 35.88/0.9636 | 36.11/0.9656 | 36.13/0.9645 | |
| Crew | 28.46/0.8328 | 31.15/0.8962 | 31.05/0.8938 | 31.59/0.9067 | 31.91/0.9074 | |
| Foreman | 28.65/0.8636 | 31.72/0.8991 | 32.64/0.8939 | 33.15/0.9042 | 32.64/0.9049 | 33.70/0.9334 |
| Football | 22.58/0.6981 | 23.16/0.7125 | 22.49/0.6803 | 22.86/0.7046 | 22.96/0.6689 | 23.90/0.7549 |
| Mobile | 20.63/0.7095 | 27.61/0.9383 | 28.31/0.9435 | 28.63/0.9602 | 27.71/0.9438 | 29.68/0.9558 |
| Soccer | 23.48/0.7552 | 25.30/0.8154 | 24.32/0.7808 | 24.89/0.8071 | 26.70/0.8487 | |
| Average | 29.61/0.8473 | 31.93/0.9019 | 32.28/0.8919 | 32.68/0.9036 | 33.16/0.9178 |
| Case | Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 | Step 4 | Speed/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | ✓ | × | × | ✓ | |
| Case 2 | ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Case 3 | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ | |
| Case 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, H.; Wu, P.; Zheng, Z.; Gu, H.; Yi, F.; Cui, W.; Lv, C. Tracking-Based Denoising: A Trilateral Filter-Based Denoiser for Real-World Surveillance Video in Extreme Low-Light Conditions. Sensors 2025, 25, 5567. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175567
Jiang H, Wu P, Zheng Z, Gu H, Yi F, Cui W, Lv C. Tracking-Based Denoising: A Trilateral Filter-Based Denoiser for Real-World Surveillance Video in Extreme Low-Light Conditions. Sensors. 2025; 25(17):5567. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175567
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, He, Peilin Wu, Zhou Zheng, Hao Gu, Fudi Yi, Wen Cui, and Chen Lv. 2025. "Tracking-Based Denoising: A Trilateral Filter-Based Denoiser for Real-World Surveillance Video in Extreme Low-Light Conditions" Sensors 25, no. 17: 5567. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175567
APA StyleJiang, H., Wu, P., Zheng, Z., Gu, H., Yi, F., Cui, W., & Lv, C. (2025). Tracking-Based Denoising: A Trilateral Filter-Based Denoiser for Real-World Surveillance Video in Extreme Low-Light Conditions. Sensors, 25(17), 5567. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175567





