A Hierarchical Multi-Feature Point Cloud Lithology Identification Method Based on Feature-Preserved Compressive Sampling (FPCS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
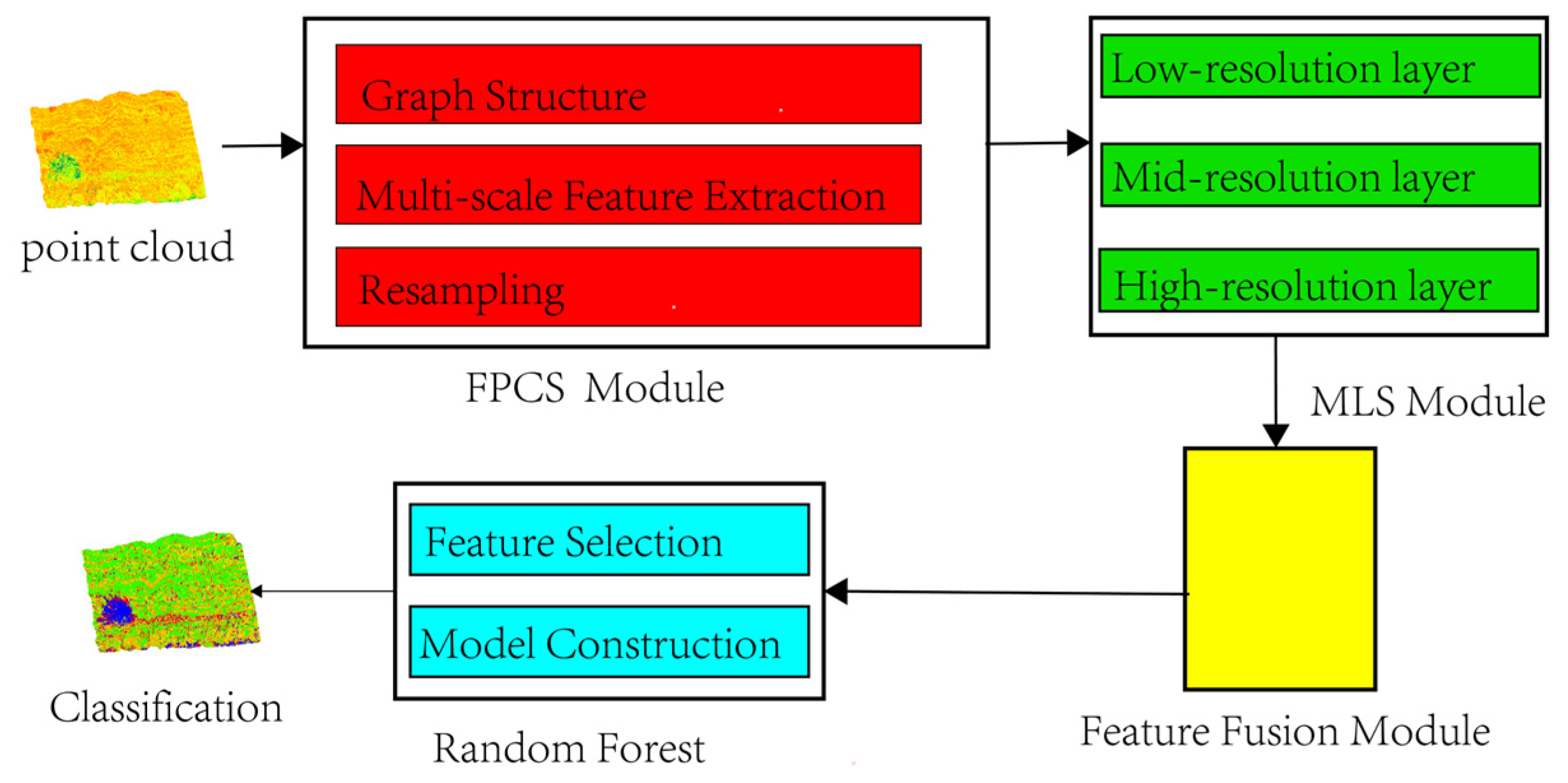
2. Methodology
2.1. FPCS-Based Point Cloud Resampling
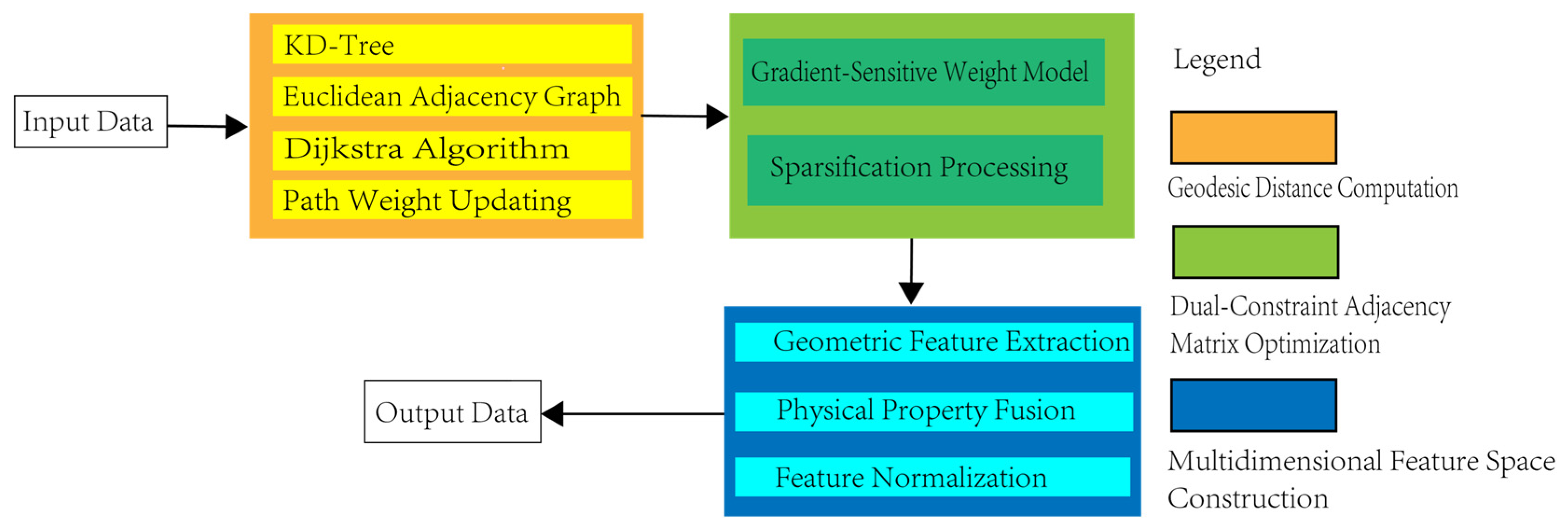
2.1.1. Graph Topology Feature Modeling
- (1)
- Neighborhood Restriction: Dijkstra’s algorithm is constrained to local neighborhoods (k = 30 nearest points) via KD-tree acceleration, reducing complexity from O(N2) to O(NlogN).
- (2)
- Parallel Batch Processing: Disjoint point clusters are processed concurrently using OpenMP (Figure 2), leveraging multicore CPU architectures.
2.1.2. Multi-Scale Feature Extraction Based on Graph Filter Banks
2.1.3. Point Cloud Resampling Distribution Optimization
- (1)
- Probability assignment: Hybrid weights for linear-varying features;
- (2)
- M-trial sampling: Conditional updates for non-replacement;
- (3)
- Geometric normalization: Centroid-zeroing, PCA rotation, and spectral scaling.
2.2. FPCS-Based Point Cloud Resampling
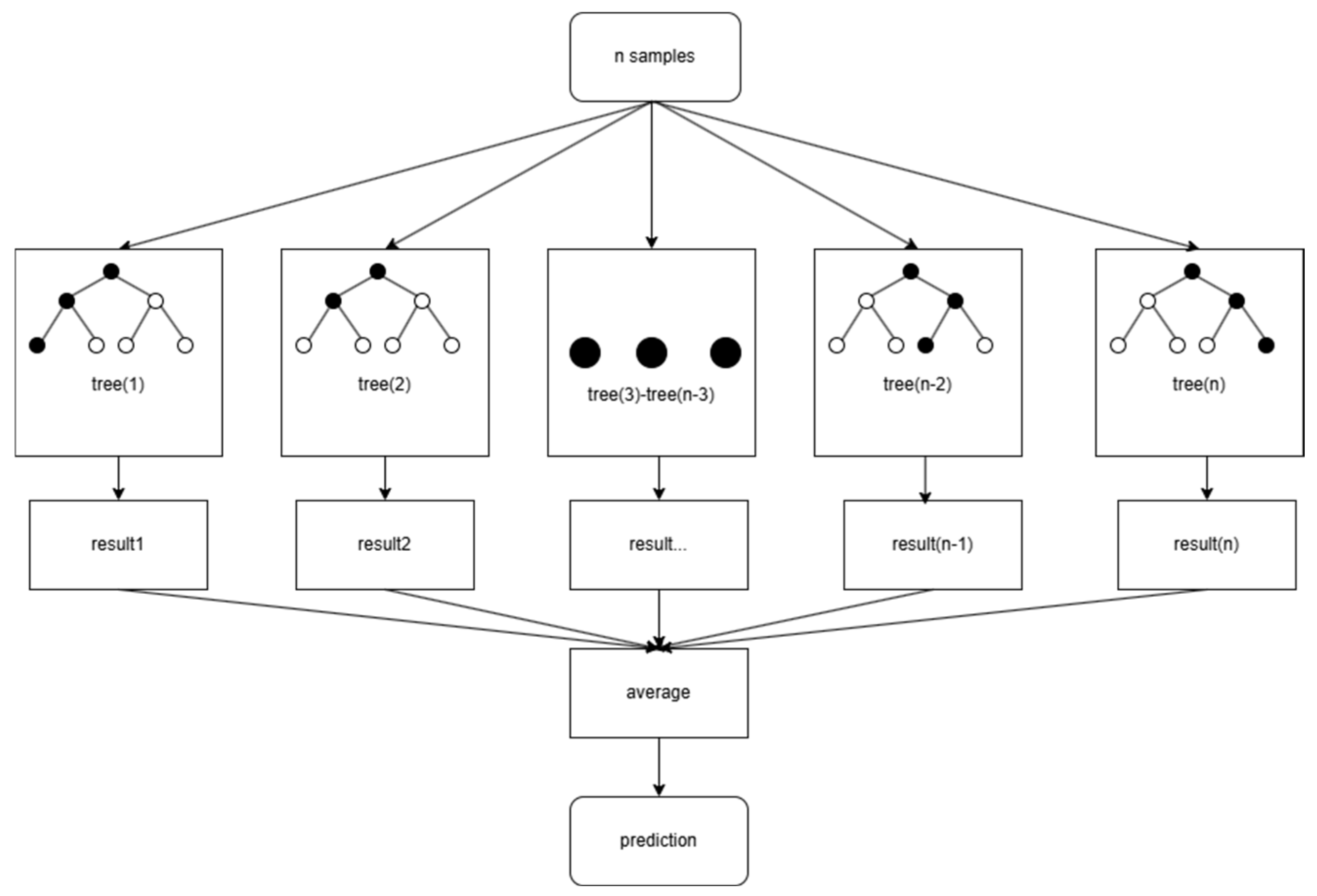
2.3. Random Forest Lithology Identification Model Construction
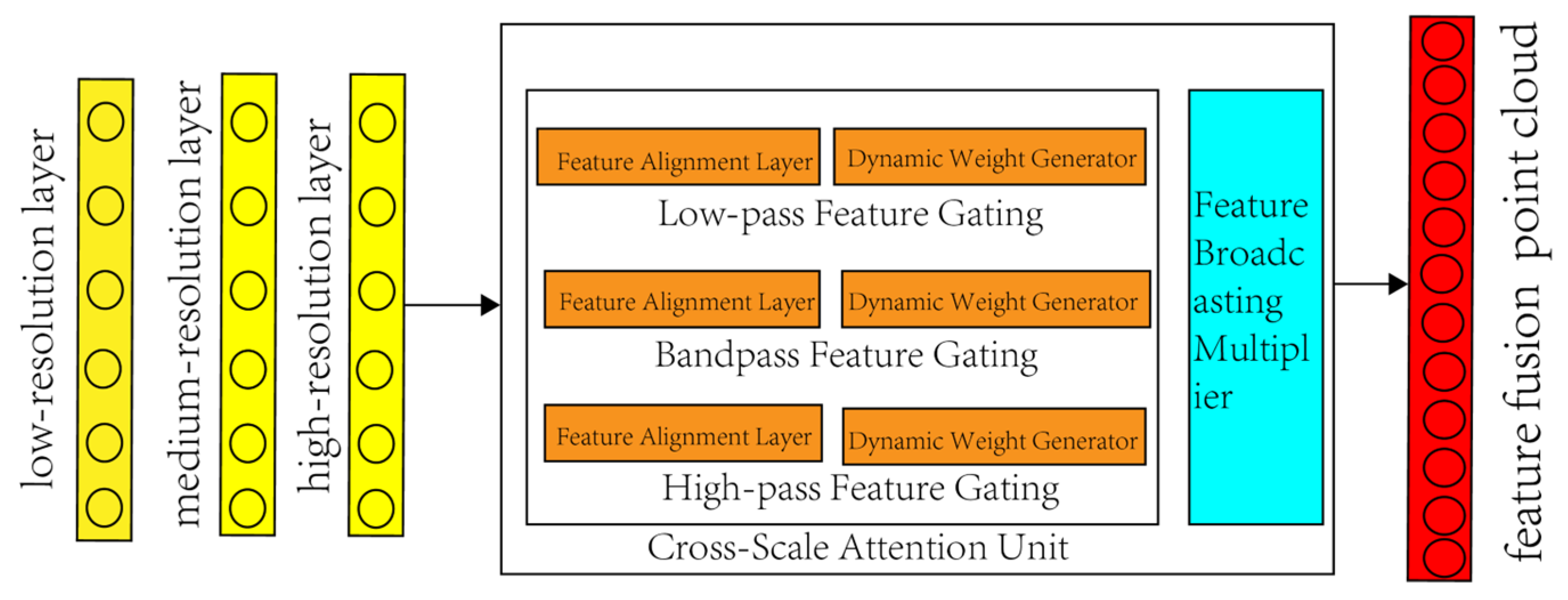
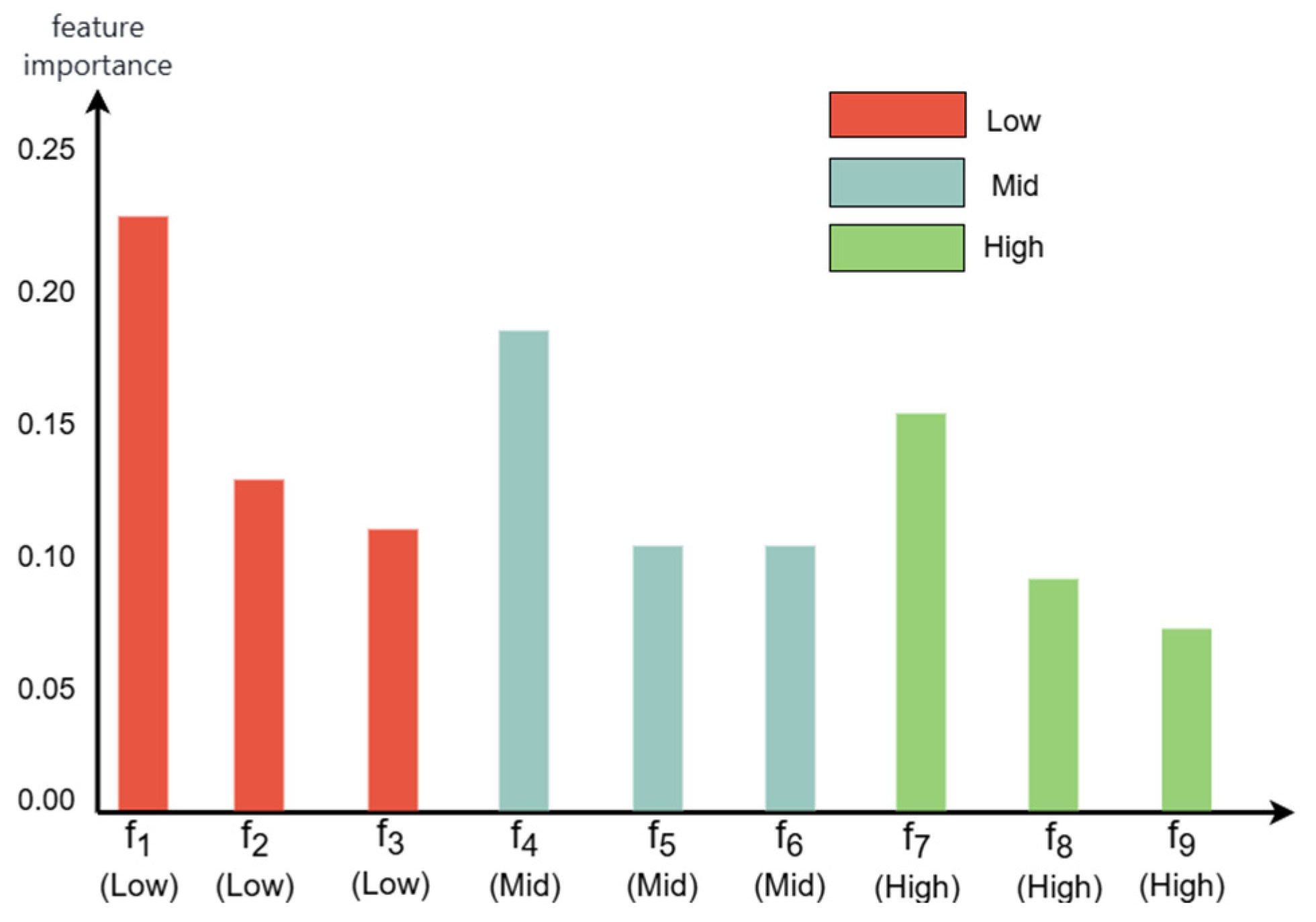
2.3.1. FPCS–MLS Feature Selection
2.3.2. Model Construction
3. Experiments and Results Analysis
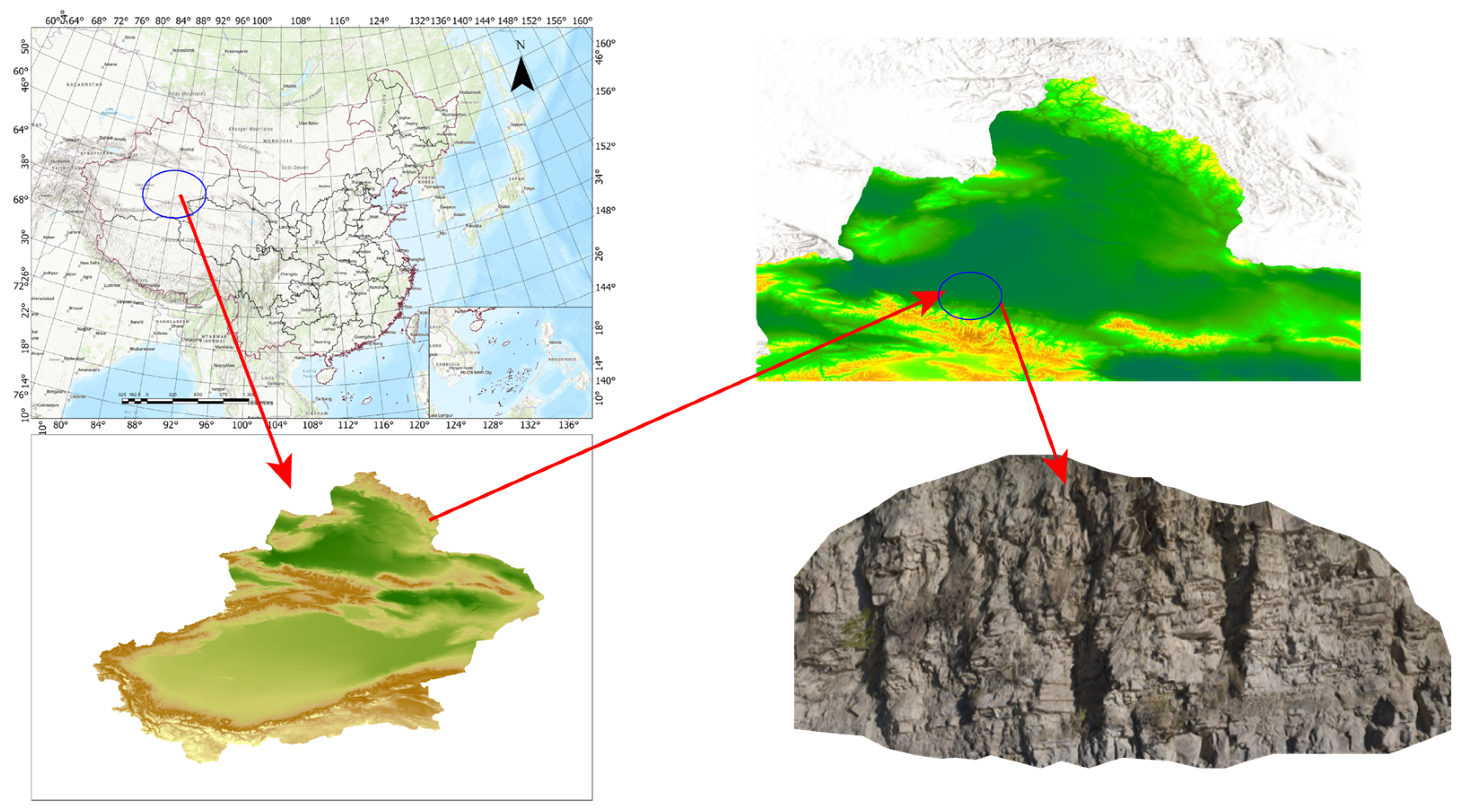
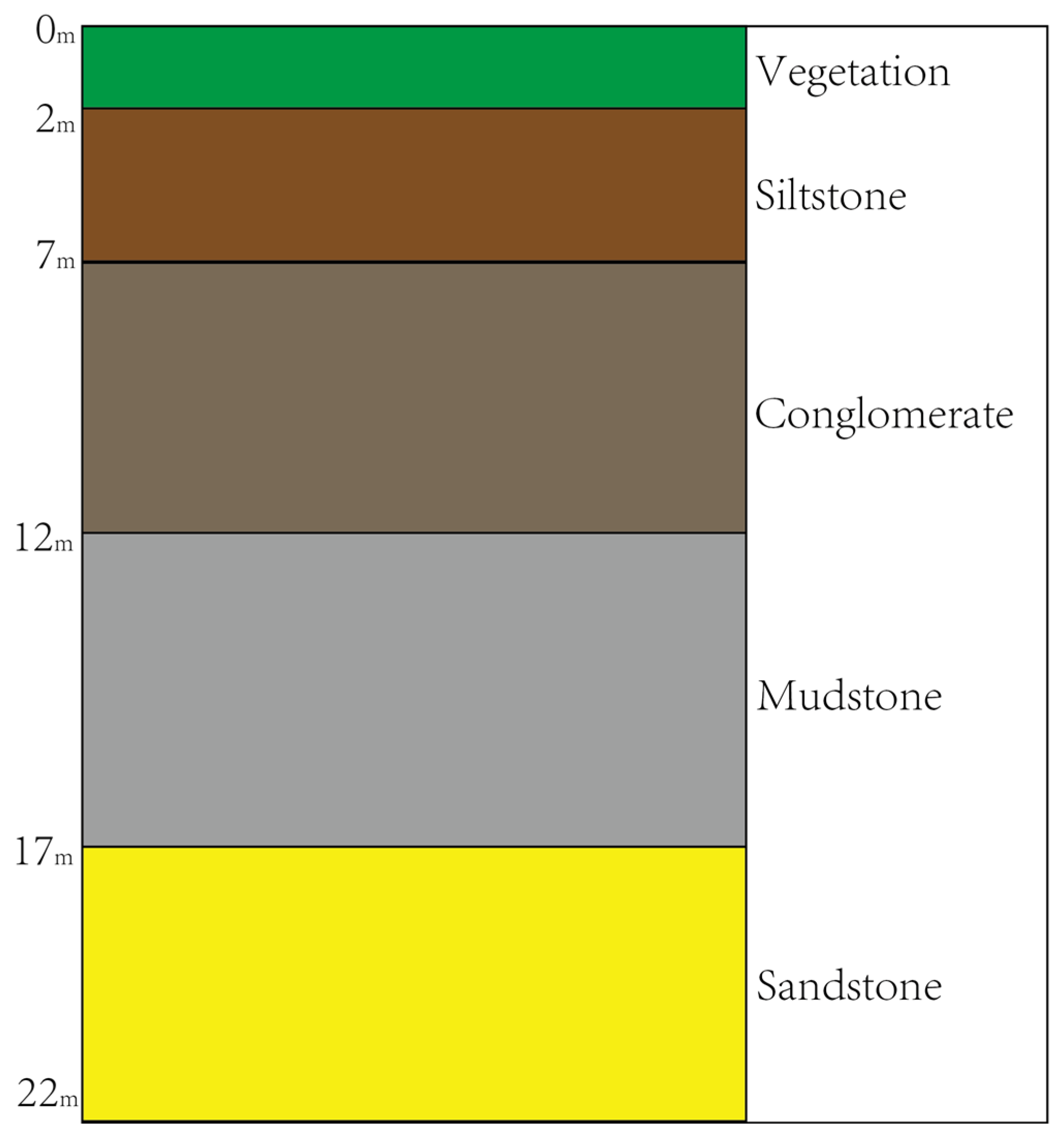
3.1. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
3.2. Sample Selection
3.3. Lithology Identification Results Analysis
3.3.1. Experimental Environment and Evaluation Metrics
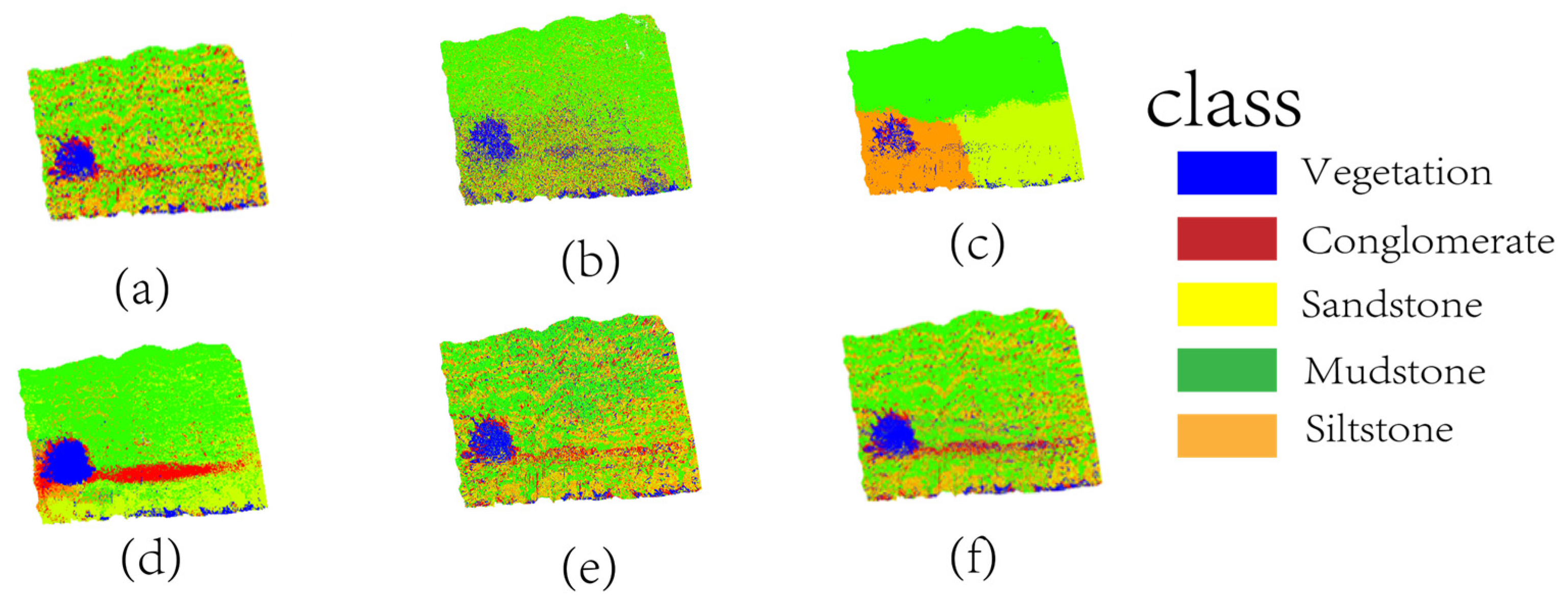
3.3.2. Ablation Experiments
3.3.3. Comparative Experimental Results Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Discussion of Sampling Methods
Comparative Analysis of Feature Preservation Capability
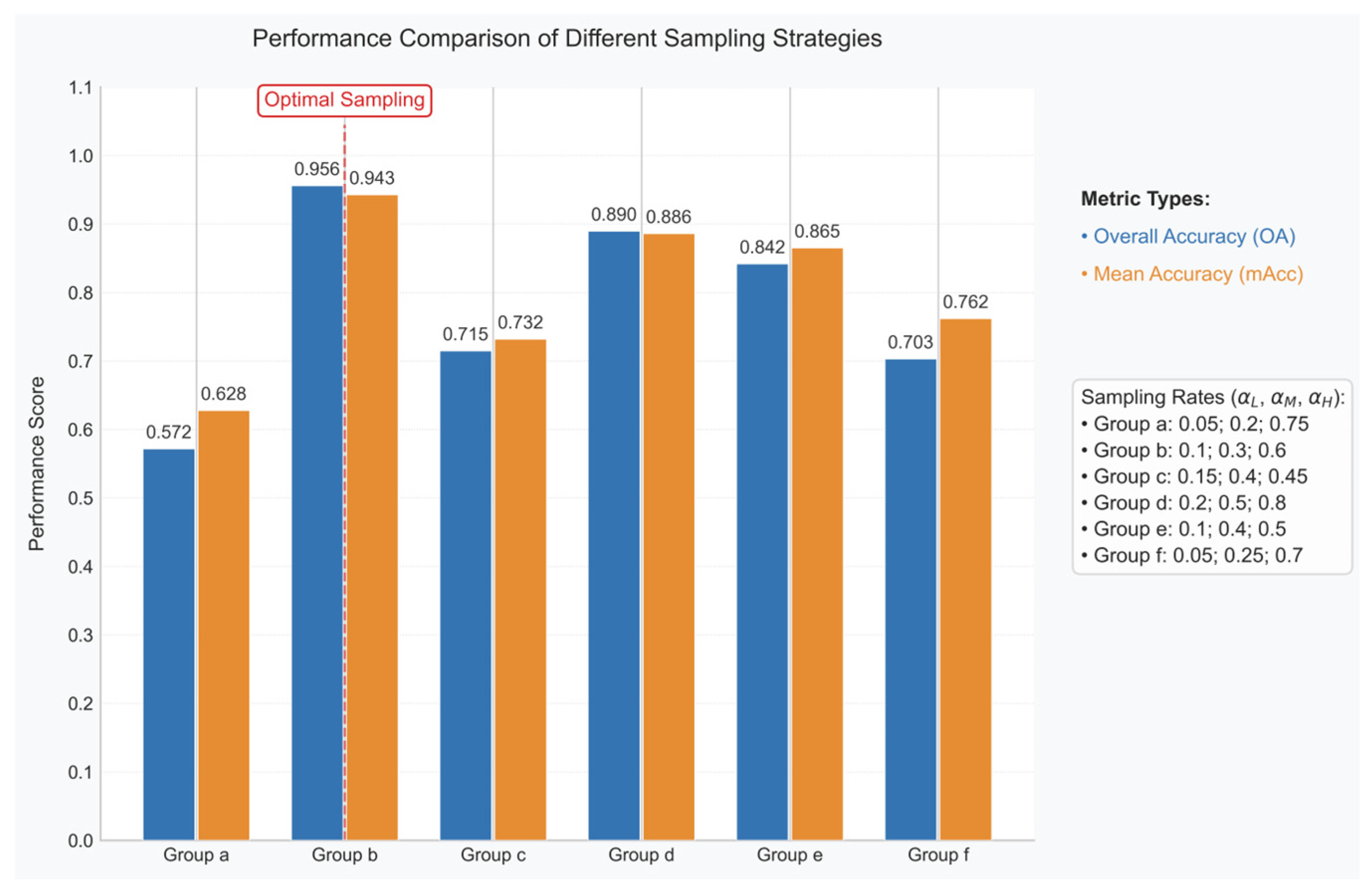
4.2. Hyperparameter Sensitivity Analysis
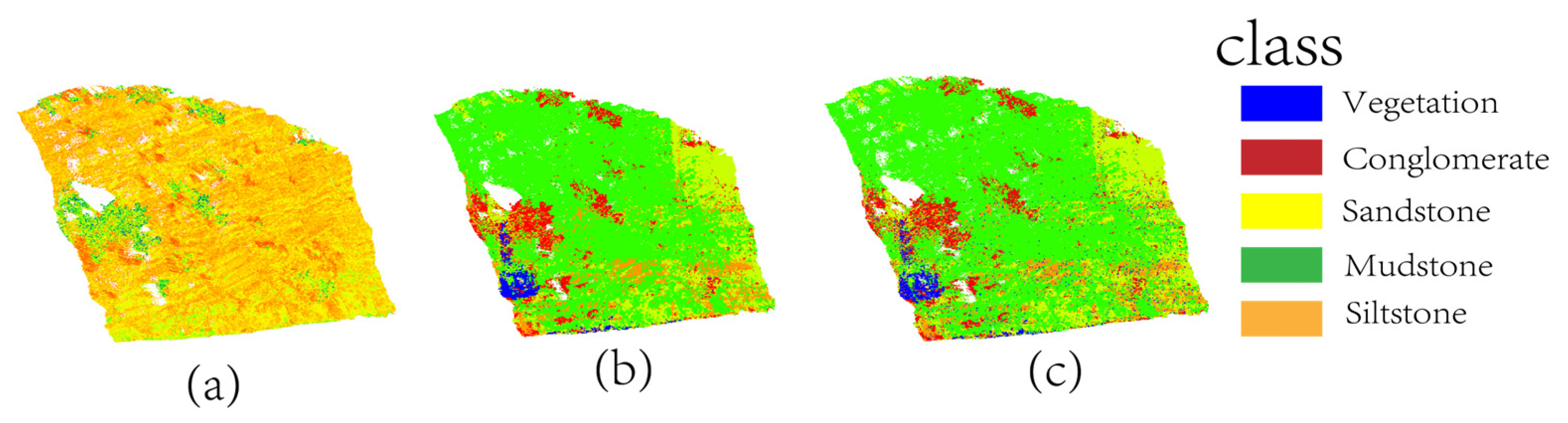
4.3. Cross-Area Generalizability Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miao, H.; Wang, G. Effects of Clay Content on the Shear Behaviors of Sliding Zone Soil Originating from Muddy Interlayers in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Eng. Geol. 2021, 294, 106380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, L.F.d.P.; Magalhães, A.P., Jr. Late Quaternary Landscape Evolution in the Atlantic Plateau (Brazilian Highlands): Tectonic and Climatic Implications of Fluvial Archives. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 207, 103228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaboyedoff, M.; Oppikofer, T.; Abellán, A.; Derron, M.-H.; Loye, A.; Metzger, R.; Pedrazzini, A. Use of LIDAR in Landslide Investigations: A Review. Nat. Hazards 2012, 61, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigli, G.; Casagli, N. Semi-Automatic Extraction of Rock Mass Structural Data from High Resolution LIDAR Point Clouds. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2011, 48, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ma, S.; Lane, M.; Chang, P.; Crompton, B.; Hagen, S.A. Laboratory Investigations into the Failure Mechanisms of New Yielding and Inflatable Rockbolts Under Axial and Shearing Loading Conditions. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2023, 56, 565–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zuo, R. Mineral Prospectivity Mapping Using a Joint Singularity-Based Weighting Method and Long Short-Term Memory Network. Comput. Geosci. 2022, 158, 104974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Tang, L.; Rao, Y.; Huang, T.; Zhou, J.; Lu, J. Point-Bert: Pre-Training 3d Point Cloud Transformers with Masked Point Modeling. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 19313–19322. [Google Scholar]
- Biosca, J.M.; Lerma, J.L. Unsupervised Robust Planar Segmentation of Terrestrial Laser Scanner Point Clouds Based on Fuzzy Clustering Methods. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ng, A.H.-M.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Du, Z.; Ge, L. Land Subsidence Modeling and Assessment in the West Pearl River Delta from Combined InSAR Time Series, Land Use and Geological Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 118, 103228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Z. SnapshotNet: Self-Supervised Feature Learning for Point Cloud Data Segmentation Using Minimal Labeled Data. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2022, 216, 103339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammoliti, E.; Di Stefano, F.; Fronzi, D.; Mancini, A.; Malinverni, E.S.; Tazioli, A. A Machine Learning Approach to Extract Rock Mass Discontinuity Orientation and Spacing, from Laser Scanner Point Clouds. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Qiu, X.; Peng, L.; Wang, W.; Lin, B.; Ding, C. A Novel Solution for Stereo Three-Dimensional Localization Combined with Geometric Semantic Constraints Based on Spaceborne SAR Data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 192, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, P.R.M.; da Costa, J.F.C.L. Automatic Variogram Model Fitting of a Variogram Map Based on the Fourier Integral Method. Comput. Geosci. 2021, 156, 104891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malehmir, A.; Heinonen, S.; Dehghannejad, M.; Heino, P.; Maries, G.; Karell, F.; Suikkanen, M.; Salo, A. Landstreamer Seismics and Physical Property Measurements in the Siilinjärvi Open-Pit Apatite (Phosphate) Mine, Central Finland. Geophysics 2017, 82, B29–B48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Labrador, C.; Chhatkuli, A.; Paudel, D.P.; Guerrero, J.J.; Demonceaux, C.; Gool, L.V. Unsupervised Learning of Category-Specific Symmetric 3D Keypoints from Point Sets. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2020; Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12370, pp. 546–563. ISBN 978-3-030-58594-5. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Wong, W.-F.; He, B. Optimizing the Number of Clusters for Billion-Scale Quantization-Based Nearest Neighbor Search. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2024, 36, 6786–6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trani, L.; Koymans, M.; Atkinson, M.; Sleeman, R.; Filgueira, R. Corrigendum to “WFCatalog: A Catalogue for Seismological Waveform Data” [Comput. Geosci. 106 (2017) 101–108]. Comput. Geosci. 2018, 119, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhong, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, A.; Lu, X. Urban Road Mapping Based on an End-to-End Road Vectorization Mapping Network Framework. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 178, 345–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G. A High-Performance Temporal-Spatial Discretization Method for the Parallel Computing of River Basins. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 58, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-X.; Zhou, X.-P. Three-Dimensional Reliability Analysis of Seismic Slopes Using the Copula-Based Sampling Method. Eng. Geol. 2018, 242, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, B.-S.; Pham, Q.-H.; Nguyen, D.T.; Tran, M.-K.; Yu, L.-F.; Yeung, S.-K. Scenenn: A Scene Meshes Dataset with Annotations. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Gurram, P.; Kwon, H.; Davidson, C. Shapely Value Based Random Subspace Selection for Hyperspectral Image Classification. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 4975–4978. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, S.; Marfurt, K.J. Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir Characterization; Society of Exploration Geophysicists and European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers: Houston, TX, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-1-56080-141-2. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, A. Curvature Attributes and Their Application to 3 D Interpreted Horizons. First Break 2001, 19, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, S.; Marfurt, K. Seismic Curvature Attributes for Mapping Faults/Fractures, and Other Stratigraphic. CSEG Rec. 2007, 32, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Tang, S. Investigating the Toppling Failure of Anti-Dip Rock Slopes Containing Non-Persistent Cross-Joints via a Strength-Based Fracture Method. Eng. Geol. 2024, 333, 107491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wen, Y.; Chen, M.; Yuan, S.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhang, L.; Dong, R.; Fu, H. Open-Set Domain Adaptation for Scene Classification Using Multi-Adversarial Learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2024, 208, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejani, A.S.; Klontzas, M.E.; Gatti, A.A.; Mongan, J.; Moy, L.; Park, S.H.; Kahn, C.E., Jr. Updating the Checklist for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging (CLAIM) for Reporting AI Research. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2023, 5, 950–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Huang, B. Point Cloud Self-Supervised Learning for Machining Feature Recognition. J. Manuf. Syst. 2024, 77, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, R.Q.; Su, H.; Kaichun, M.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; You, J.; Liu, C.; Zheng, S.; Lu, Z.; Wang, T.; Zheng, N.; Shao, B. Overcoming the Barrier of Orbital-Free Density Functional Theory for Molecular Systems Using Deep Learning. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2024, 4, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mémoli, F.; Sapiro, G. A Theoretical and Computational Framework for Isometry Invariant Recognition of Point Cloud Data. Found. Comput. Math. 2005, 5, 313–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froyland, G.; Koltai, P. Detecting the Birth and Death of Finite-time Coherent Sets. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 2023, 76, 3642–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Curran Associates, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; Li, F.; Wang, Q.; Bai, Z.; Xu, Y. A Hierarchical Sampling Based Triplet Network for Fine-Grained Image Classification. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 115, 107889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, R.; Khalilian-Gourtani, A.; Yu, L.; Dugan, P.; Friedman, D.; Doyle, W.; Devinsky, O.; Wang, Y.; Flinker, A. A Neural Speech Decoding Framework Leveraging Deep Learning and Speech Synthesis. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2024, 6, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sarma, S.E.; Bronstein, M.M.; Solomon, J.M. Dynamic Graph CNN for Learning on Point Clouds. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1801.07829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Kuo, C.-H.; Chiang, H.-T. CNN-Based Classification for Point Cloud Object with Bearing Angle Image. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 22, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilaki, D.I.; Stamos, A.A. TanDEM-X DEM: Comparative Performance Review Employing LIDAR Data and DSMs. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 160, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Ren, P.; Xu, P.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Hauptmann, A. A Comprehensive Survey of Scene Graphs: Generation and Application. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 45, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Yan, F.; Liu, X.; Liu, D.; Liu, P.; Liu, B. Novel Smart Card SoC Memory Architecture Based on Embedded STT-MRAM. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 13th International Conference on ASIC (ASICON), Chongqing, China, 29 October–1 November 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhong, R.; Chen, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Chen, S. Hierarchical Aggregated Deep Features for ALS Point Cloud Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 1686–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep Learning | Nature. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/nature14539 (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Wendel, A.; Underwood, J. Illumination Compensation in Ground Based Hyperspectral Imaging. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 129, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3D Point Cloud Lithology Identification Based on Stratigraphically Constrained Continuous Clustering|Research Square. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-7045774/v1 (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Lu, S.; Han, C.; Yang, H. Efficient Large-Scale Point Cloud Geometry Compression. Sensors 2025, 25, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jiang, L.; Jia, J.; Torr, P.H.S.; Koltun, V. Point Transformer. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 16259–16268. [Google Scholar]

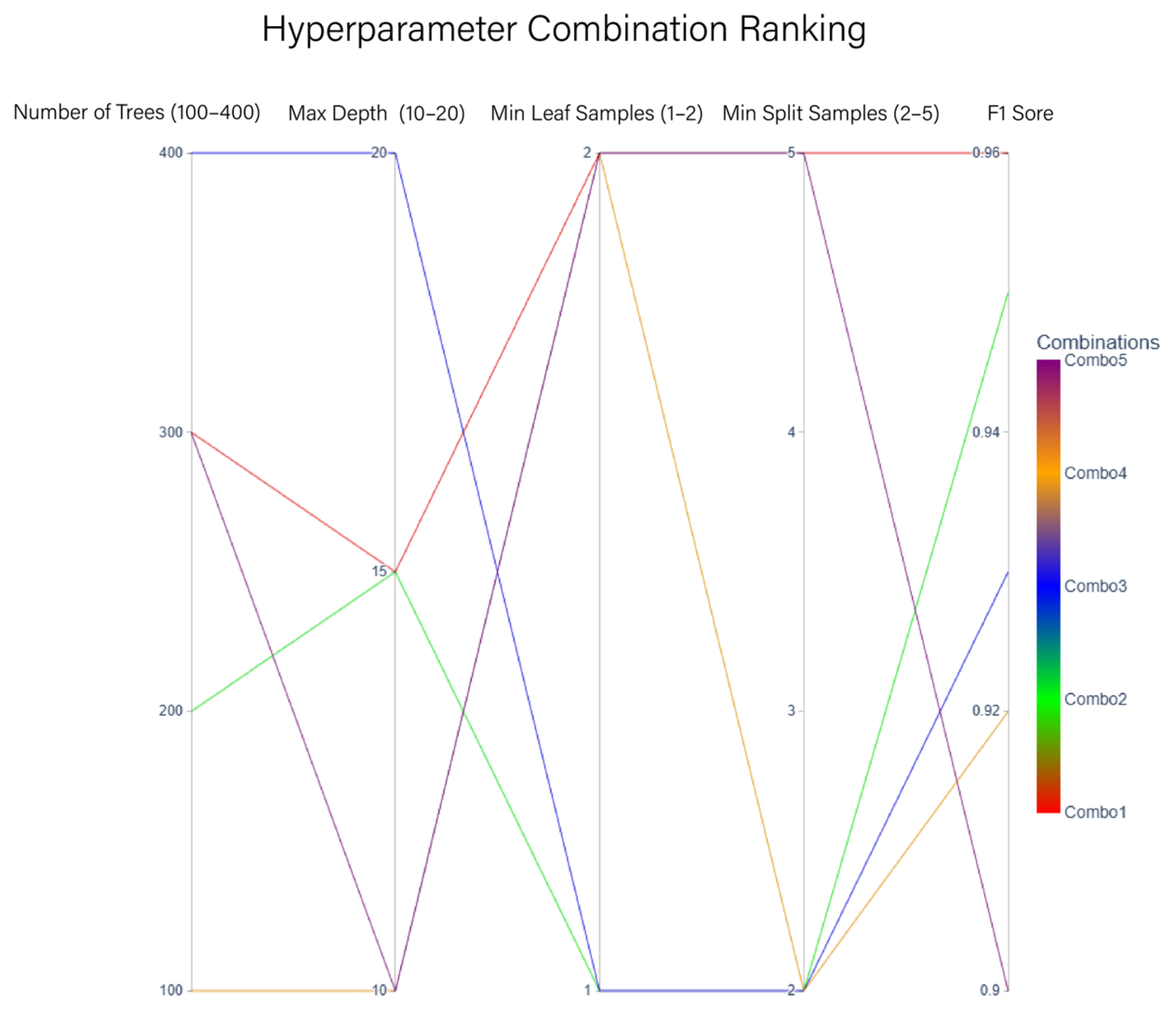


| Hyperparameter Name | Parameter Combination | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n_estimators | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | ||
| max_depth | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | ||
| min_samples_leaf | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| min_samples_split | 2 | 5 | 10 | |||
| Model | Pulse Frequency (KHz) | Acquisition Speed (Points/s) | Scan Speed (Lines/s) | Field of View (°) | Distance Accuracy (mm/m) | Angular Resolution (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIGEL VZ400 | 1200 | 500,000 | <100 | 360 × 100 | ±5/50 | <0.001 |
| Data Category | Training Set | Testing Set |
|---|---|---|
| Overall | 31,118 | 13,411 |
| Siltstone | 11,969 | 5129 |
| Conglomerate | 2477 | 1062 |
| Mudstone | 6092 | 2696 |
| Sandstone | 10,580 | 4524 |
| OA(%) | mAcc(%) | F1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| without FPCS and MLS | 0.572 | 0.628 | 0.544 |
| without feature selection | 0.842 | 0.865 | 0.782 |
| without FPCS, only MLS | 0.715 | 0.732 | 0.651 |
| without MLS, only FPCS | 0.8897 | 0.886 | 0.815 |
| proposed model group | 0.956 | 0.943 | 0.874 |
| Methods | OA | mAcc | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| K-means | 0.428 | 0.486 | 0.342 |
| SVM | 0.522 | 0.592 | 0.436 |
| PointNet | 0.703 | 0.762 | 0.725 |
| PointTransformer | 0.845 | 0.817 | 0.786 |
| Proposed model | 0.956 | 0.943 | 0.874 |
| Lithology | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conglomerate | 0.961 | 0.942 | 0.951 |
| Sandstone | 0.938 | 0.963 | 0.950 |
| Siltstone | 0.921 | 0.895 | 0.908 |
| Mudstone | 0.927 | 0.897 | 0.912 |
| Sampling Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Random Sampling | 0.62 | 0.41 | 0.18 |
| FPS | 0.83 | 0.56 | 0.29 |
| Voxel-based Sampling | 0.81 | 0.67 | 0.35 |
| FPCS | 0.93 | 0.85 | 0.79 |
| Method | Time (Million Points/s) | Memory Peak (GB) |
|---|---|---|
| Random Sampling | 5.1 | 1.2 |
| FPS | 1.3 | 3.8 |
| Voxel-based Sampling | 1.3 | 5.6 |
| FPCS | 4.2 | 2.1 |
| Methods | OA | mAcc | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed model | 0.932 | 0.917 | 0.841 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, X.; Jing, R.; Shao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gan, B.; Li, P.; Li, L. A Hierarchical Multi-Feature Point Cloud Lithology Identification Method Based on Feature-Preserved Compressive Sampling (FPCS). Sensors 2025, 25, 5549. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175549
Duan X, Jing R, Shao Y, Liu Y, Gan B, Li P, Li L. A Hierarchical Multi-Feature Point Cloud Lithology Identification Method Based on Feature-Preserved Compressive Sampling (FPCS). Sensors. 2025; 25(17):5549. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175549
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Xiaolei, Ran Jing, Yanlin Shao, Yuangang Liu, Binqing Gan, Peijin Li, and Longfan Li. 2025. "A Hierarchical Multi-Feature Point Cloud Lithology Identification Method Based on Feature-Preserved Compressive Sampling (FPCS)" Sensors 25, no. 17: 5549. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175549
APA StyleDuan, X., Jing, R., Shao, Y., Liu, Y., Gan, B., Li, P., & Li, L. (2025). A Hierarchical Multi-Feature Point Cloud Lithology Identification Method Based on Feature-Preserved Compressive Sampling (FPCS). Sensors, 25(17), 5549. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175549







