YOLO-AR: An Improved Artificial Reef Segmentation Algorithm Based on YOLOv11
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Image Annotation and Dataset Construction
3.2. YOLO-AR Model
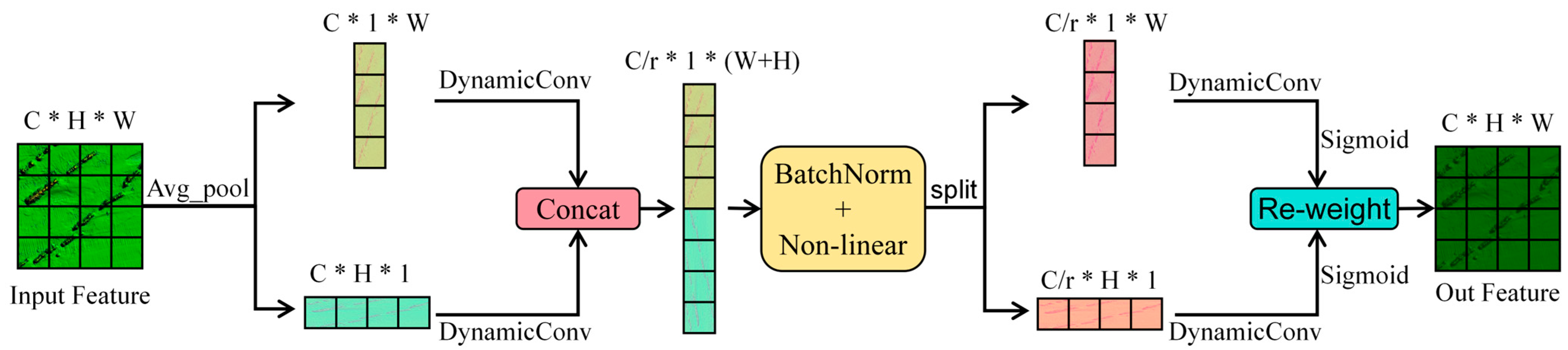
3.2.1. Improved Backbone Network with DCCA Module
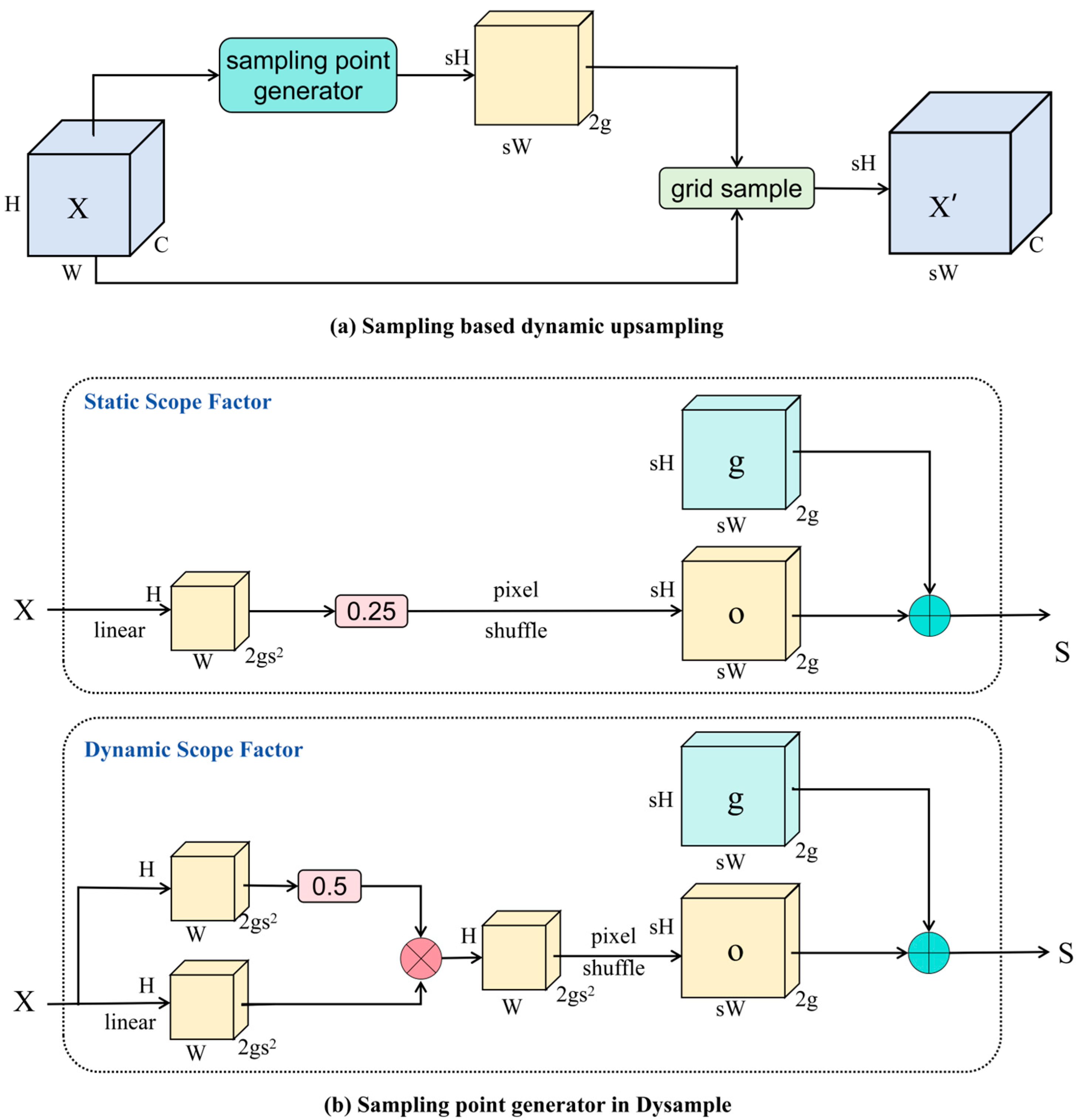
3.2.2. Small-Target Detection Neck with DySample Module
3.2.3. Reduce Network Parameters with ADown Module
4. Results
4.1. Experimental Hardware Configuration and Parameter Setting
4.2. Precision Evaluation Index
4.3. Analysis of Artificial Reef Segmentation Results
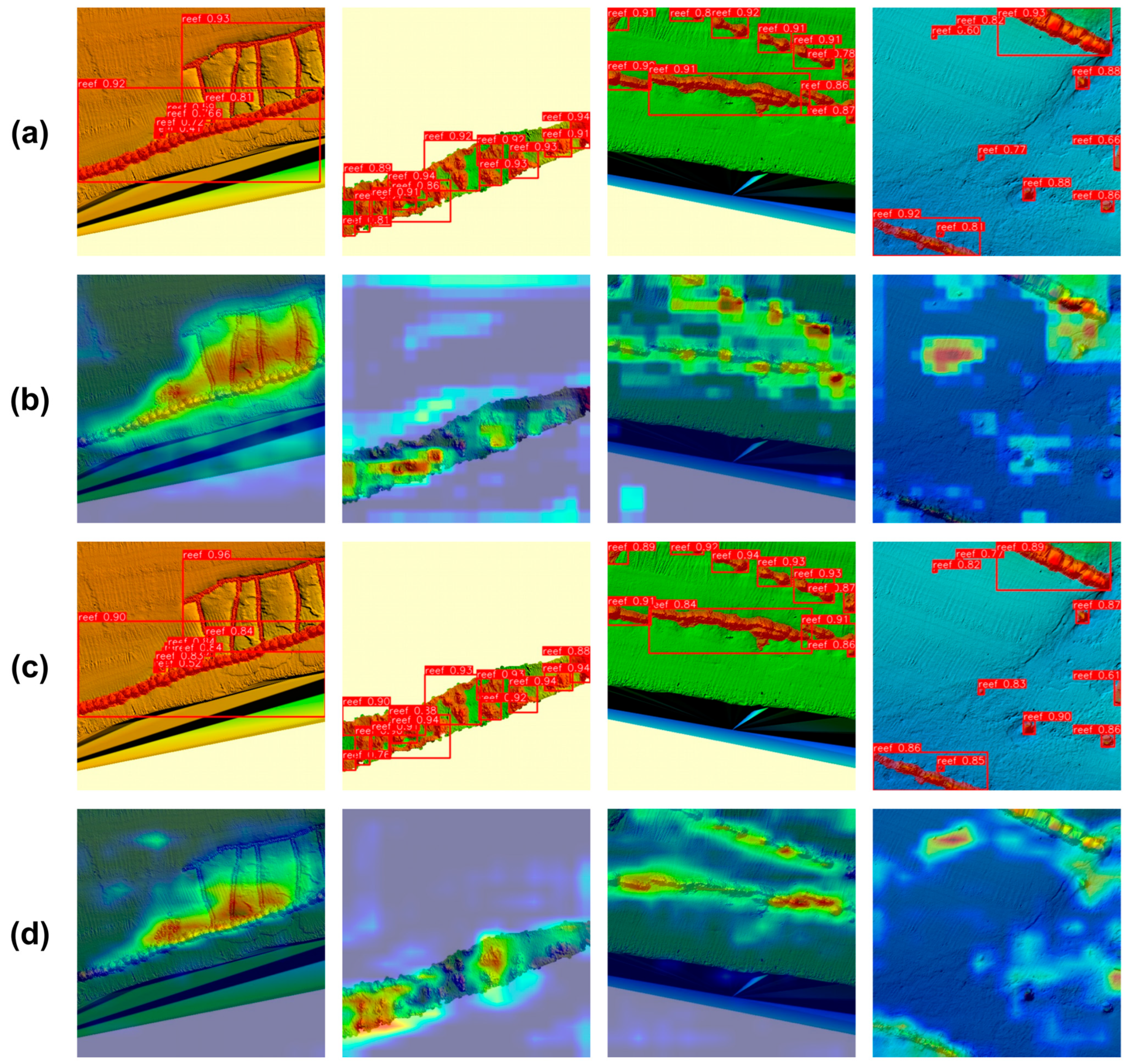
4.4. Visual Evaluation of YOLO-AR by Grad-CAM
4.5. Model Parameter Evaluation
4.6. Performance Comparison Experiment of the Mainstream Segmentation Model
5. Discussion
5.1. Ablation Experiment
5.2. Visual Evaluation of Artificial Reef Segmentation by Different Models
5.3. Research Limitations and Future Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, W.; Xu, Y.; Ni, J. Evolution of Marine Ecology-Industry Symbiosis Patterns and Ecological Security Assessment: New Evidence from Coastal Areas of China. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2024, 247, 106939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komyakova, V.; Chamberlain, D.; Jones, G.P.; Swearer, S.E. Assessing the Performance of Artificial Reefs as Substitute Habitat for Temperate Reef Fishes: Implications for Reef Design and Placement. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Wu, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Peng, S. Regional Patterns and Factors Analysis of the Sustainable Development of Benefits in China’s National-Level Marine Ranching: Based on Shellfish and Algae. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 467, 142994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, L. Evolution of Marine Ranching Policies in China: Review, Performance and Prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Feng, Y.; Ding, J.; Jiang, F. Artificial Reef Detection Method for Multibeam Sonar Imagery Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescangeli, M.; Toma, D.M.; Mendizabal, V.; Carandell, M.; Martinez, E.; Martin, D.; Mura, M.P.; Aguzzi, J.; Gil Espert, L.; Del Rio, J. Artificial Reef Based Ecosystem Design and Monitoring. Ecol. Eng. 2025, 221, 107752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Song, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Zhu, L.; Xie, W.; Liang, Z.; Jiang, Z. Improving Costal Marine Habitats in the Northern Yellow Sea: The Role of Artificial Reefs on Macrobenthic Communities and Eco-Exergy. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 971, 179027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcão, M.; Santos, M.N.; Drago, T.; Serpa, D.; Monteiro, C. Effect of Artificial Reefs (Southern Portugal) on Sediment–Water Transport of Nutrients: Importance of the Hydrodynamic Regime. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 83, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Woo, J.; Yoon, H.-S.; Na, W.-B. Efficiency, Tranquillity and Stability Indices to Evaluate Performance in the Artificial Reef Wake Region. Ocean Eng. 2016, 122, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Liang, Z.; Sun, L.; Nie, Z.; Wang, J.; Xie, W.; Jiang, Z. Numerical Study of Efficiency Indices to Evaluate the Effect of Layout Mode of Artificial Reef Unit on Flow Field. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackradt, C.W.; Félix-Hackradt, F.C.; García-Charton, J.A. Influence of Habitat Structure on Fish Assemblage of an Artificial Reef in Southern Brazil. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 72, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerry, J.T.; Bellwood, D.R. The Effect of Coral Morphology on Shelter Selection by Coral Reef Fishes. Coral Reefs 2012, 31, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaman, W. Unifying Trends and Opportunities in Global Artificial Reef Research, Including Evaluation. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2002, 59, S14–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Tweedley, J.R.; Loneragan, N.R.; Zhang, X. Artificial Reefs Can Mimic Natural Habitats for Fish and Macroinvertebrates in Temperate Coastal Waters of the Yellow Sea. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 139, 105579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Taylor, M.D.; Lowry, M.B. Monitoring of Reef Associated and Pelagic Fish Communities on Australia’s First Purpose Built Offshore Artificial Reef. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2017, 74, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, M.; Folpp, H.; Gregson, M.; Suthers, I. Comparison of Baited Remote Underwater Video (BRUV) and Underwater Visual Census (UVC) for Assessment of Artificial Reefs in Estuaries. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2012, 416–417, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zang, X.; Kondyukov, G.; Hou, Z.; Peng, G.; Pander, J.; Knott, J.; Geist, J.; Melesse, M.B.; Jacobson, P. Towards Automated and Real-Time Multi-Object Detection of Anguilliform Fish from Sonar Data Using YOLOv8 Deep Learning Algorithm. Ecol. Inform. 2025, 91, 103381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiao, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Cao, M. A Lightweight Detector for Small Targets Using Forward-Looking Sonar in Underwater Search Scenarios. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 290, 128373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.A.; Chuah, L.F.; Zakariya, R.; Syed, A.; Hasan, R.C.; Mahmud, S.M.; Elgorban, A.M.; Bokhari, A.; Akhtar, M.S.; AL-Shwaiman, H.A. Evaluating Climate Change Impacts on Reef Environments via Multibeam Echosounder and Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler Technology. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Walree, P.A.; Tęgowski, J.; Laban, C.; Simons, D.G. Acoustic Seafloor Discrimination with Echo Shape Parameters: A Comparison with the Ground Truth. Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 2273–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonigle, C.; Collier, J.S. Interlinking Backscatter, Grain Size and Benthic Community Structure. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 147, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, W.; Xing, C.; Li, Y. Underwater Moving Target Detection and Tracking Based on Enhanced You Only Look Once and Deep Simple Online and Realtime Tracking Strategy. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 143, 109982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pan, H.; Jing, Z.; Ling, K.; Peng, P.; Song, B. UUVDNet: An Efficient Unmanned Underwater Vehicle Target Detection Network for Multibeam Forward-Looking Sonar. Ocean. Eng. 2025, 315, 119820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šiaulys, A.; Vaičiukynas, E.; Medelytė, S.; Buškus, K. Coverage Estimation of Benthic Habitat Features by Semantic Segmentation of Underwater Imagery from South-Eastern Baltic Reefs Using Deep Learning Models. Oceanologia 2024, 66, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marre, G.; De Almeida Braga, C.; Ienco, D.; Luque, S.; Holon, F.; Deter, J. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks to Monitor Coralligenous Reefs: Operationalizing Biodiversity and Ecological Assessment. Ecol. Inform. 2020, 59, 101110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Lightweight Deep Learning Model for Underwater Waste Segmentation Based on Sonar Images. Waste Manag. 2024, 190, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Y.; Yue, C.; Xu, G.; Wang, H.; Feng, X. Real-Time Underwater Target Detection for AUV Using Side Scan Sonar Images Based on Deep Learning. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2023, 138, 103630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; He, Q.; Zhu, S.; Li, X.; Fan, X.; Xin, Y. Multi-Scale Fusion and Efficient Feature Extraction for Enhanced Sonar Image Object Detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 256, 124958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.S.; Liu, D.; Wang, F.; Zhou, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W. Improved YOLOv7 Model for Underwater Sonar Image Object Detection. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2024, 100, 104124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Pan, Y.; Chen, J.-J. A Teacher-Student Framework Leveraging Large Vision Model for Data Pre-Annotation and YOLO for Tunnel Lining Multiple Defects Instance Segmentation. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2025, 44, 100790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Lin, M.; Chang, W.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhuang, Z.; Liang, Y. MSTA-YOLO: A Novel Retinal Ganglion Cell Instance Segmentation Method Using a Task-Aligned Coupled Head and Efficient Multi-Scale Attention for Glaucoma Analysis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2025, 106, 107695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silpalatha, G.; Jayadeva, T.S. Accelerating Fast and Accurate Instantaneous Segmentation with YOLO-v8 for Remote Sensing Image Analysis. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2025, 37, 101502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, M.Y.; Elmessery, W.M.; Oraiath, A.A.T.; Elbeltagi, A.; Salem, A.; Kumar, P.; El-Messery, T.M.; El-Hafeez, T.A.; Abdelshafie, M.F.; Abd El-Wahhab, G.G.; et al. Automated On-Site Broiler Live Weight Estimation through YOLO-Based Segmentation. Smart Agric. Technol. 2025, 10, 100828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Shen, M.; Xu, D. Multi-Scale Adaptive YOLO for Instance Segmentation of Grape Pedicels. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 229, 109712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xie, W.; Hu, P. YOLO-LOGO: A Transformer-Based YOLO Segmentation Model for Breast Mass Detection and Segmentation in Digital Mammograms. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 221, 106903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Jiang, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Bo, Y. Coal-Rock Interface Real-Time Recognition Based on the Improved YOLO Detection and Bilateral Segmentation Network. Undergr. Space 2025, 21, 22–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13713–13722. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Wu, E. ParameterNet: Parameters Are All You Need for Large-Scale Visual Pretraining of Mobile Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 15751–15761. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Lu, H.; Fu, H.; Cao, Z. Learning to Upsample by Learning to Sample. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 6027–6037. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Yeh, I.-H.; Mark Liao, H.-Y. YOLOv9: Learning What You Want to Learn Using Programmable Gradient Information. In Proceedings of the 18th European Conference on Computer Vision—ECCV 2024, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Leonardis, A., Ricci, E., Roth, S., Russakovsky, O., Sattler, T., Varol, G., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]





| Hardware/Software | Configuration | Training Parameter | Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | Intel Core i7-9750H | Initial learning rate | 0.01 |
| GPU | NVIDIA RTX4090D | Momentum | 0.937 |
| Python | 3.8.10 | Weight decay | 0.0005 |
| Pytorch | 2.0.0 | Bach size | 16 |
| Cuda | 11.8 | Learning epoch | 200 |
| Model | P | R | mAP@0.5 | mAP@[0.5:0.95] | IOU | F1 | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv11 | 0.893 | 0.794 | 0.853 | 0.553 | 0.725 | 0.841 | 2834763 |
| YOLO-AR | 0.939 | 0.879 | 0.912 | 0.601 | 0.832 | 0.908 | 2672504 |
| Model | Parameters (Million) | Model Size (MB) | FLOPs (G) |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8 | 3.26 | 6.46 | 12.1 |
| YOLOv9 [40] | 27.84 | 106.91 | 159.1 |
| U-Net [41] | 24.89 | 94.97 | 361.85 |
| SegNet [42] | 29.46 | 337.45 | 327.13 |
| FCN [43] | 18.64 | 269.74 | 203.99 |
| YOLO-AR | 2.67 | 5.58 | 23.2 |
| Model | P | R | mAP@0.5 | IOU | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8 | 0.887 | 0.786 | 0.842 | 0.714 | 0.833 |
| YOLOv9 [40] | 0.893 | 0.804 | 0.851 | 0.733 | 0.846 |
| U-Net [41] | 0.873 | 0.838 | 0.820 | 0.747 | 0.855 |
| FCN [42] | 0.966 | 0.821 | 0.822 | 0.798 | 0.888 |
| SegNet [43] | 0.941 | 0.714 | 0.718 | 0.683 | 0.812 |
| YOLO-AR | 0.939 | 0.879 | 0.912 | 0.832 | 0.908 |
| YOLOv11 | DCCA | ADown | DNeck | P | R | mAP@0.5 | mAP@[0.5:0.95] | IOU | F1 | Parameters (Million) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✓ | × | × | × | 0.893 | 0.794 | 0.853 | 0.553 | 0.725 | 0.841 | 2.83 |
| ✓ | ✓ | × | × | 0.892 | 0.806 | 0.861 | 0.565 | 0.734 | 0.847 | 2.93 |
| ✓ | × | ✓ | × | 0.891 | 0.788 | 0.848 | 0.539 | 0.719 | 0.836 | 2.49 |
| ✓ | × | × | ✓ | 0.925 | 0.863 | 0.899 | 0.564 | 0.801 | 0.893 | 2.91 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | × | 0.891 | 0.801 | 0.856 | 0.564 | 0.730 | 0.844 | 2.57 |
| ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ | 0.923 | 0.866 | 0.902 | 0.574 | 0.808 | 0.894 | 2.99 |
| ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ | 0.930 | 0.866 | 0.902 | 0.581 | 0.813 | 0.897 | 2.57 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.939 | 0.879 | 0.912 | 0.601 | 0.832 | 0.908 | 2.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Jiang, T.; Xi, Z.; Yin, F.; Wang, X. YOLO-AR: An Improved Artificial Reef Segmentation Algorithm Based on YOLOv11. Sensors 2025, 25, 5426. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175426
Wu Y, Jiang T, Xi Z, Yin F, Wang X. YOLO-AR: An Improved Artificial Reef Segmentation Algorithm Based on YOLOv11. Sensors. 2025; 25(17):5426. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175426
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yuxiang, Tingchen Jiang, Zhi Xi, Fei Yin, and Xiuping Wang. 2025. "YOLO-AR: An Improved Artificial Reef Segmentation Algorithm Based on YOLOv11" Sensors 25, no. 17: 5426. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175426
APA StyleWu, Y., Jiang, T., Xi, Z., Yin, F., & Wang, X. (2025). YOLO-AR: An Improved Artificial Reef Segmentation Algorithm Based on YOLOv11. Sensors, 25(17), 5426. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175426





