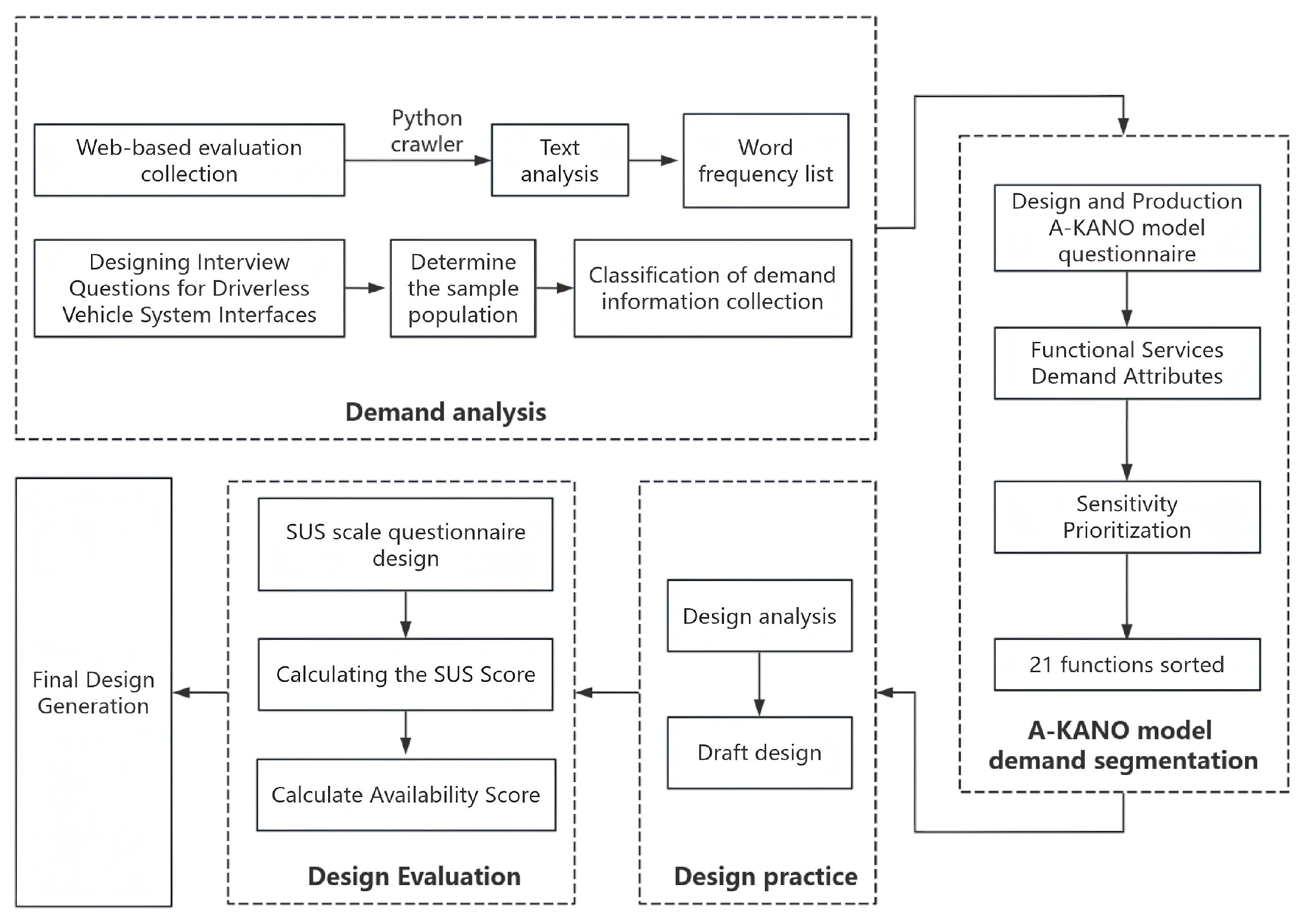
4.2. A-KANO Data Analysis
In this step, we first calculate the average satisfaction with the function , the mean dissatisfaction when the function is absent , and the average weight . , , determine the properties of each function. Secondly, if each respondent is j and the number of respondents is n, then the survey results for each user demand are (n = 153), , and specific calculation steps are as follows:
- 1.
Calculate the average satisfaction rate for a certain function
:
- 2.
Calculate the mean dissatisfaction without a function
:
- 3.
Calculate the mean value of a certain function weight
:
In order to seek the quality weight classification of functional services, the satisfaction of each function can be represented by the vector
, where i is the function, and
.
represents the value of the two-dimensional satisfaction of the function from the origin to the function, namely the functional importance;
represents the angle between the function and the X axis, that is, user satisfaction. The calculation formula is as follows:
The distance interval of
and the angle range of
are shown in
Table 6.
In the A-KANO model proposed by Qianli Xu, the core of the model is the introduction of KANO Index and KANO Classifier to realize the quantitative analysis of customers’ needs. KANO Index calculates the customer’s “Importance” and “Satisfaction” of each demand through questionnaire survey and data analysis,. The size of the vector (
) is called the Importance index, and the angle (
) is called the Satisfaction index. Importance indicates the degree of customer’s attention to the demand, and Satisfaction indicates the degree of customer’s satisfaction with the demand fulfilment. KANO Classifier is based on the calculation results of KANO Index, and customer needs are divided into four categories: charismatic needs, expected needs, basic needs and undifferentiated needs. Based on the results of data statistics, the vector score interval of Equation (
5) can be divided into demand attributes, on the basis of the distance interval and the angle range of the A-Kano model analysis diagram, as shown in
Figure 2. Among them, the basic needs are the minimum requirements that customers think the product or service must have; if these are missing, this will lead to extreme customer dissatisfaction and even if these needs are met, it will not significantly improve customer satisfaction. Desired needs are the ones that the customer expects to have, and if they are met, they will bring a certain degree of satisfaction, but they will not exceed the customer’s expectations. Charismatic needs are the ones that the customer does not have a clear expectation of, but once they are provided, they will bring significantly increased satisfaction, even beyond the customer’s expectations. No difference requirements have no significant impact on customer satisfaction; whether they are met or not, the customer will not have a special reaction. The order of function prioritization is as follows: basic requirements, desired requirements, attractive requirements, and no difference requirements.
Using the calculation formula of A-Kano model, the statistical results of the survey data of various requirements of the driverless vehicle system interface are shown in
Table 6.
In the A-KANO model proposed by Qianli Xu, the magnitude of the vector (
) is called the importance index, and the angle (
) is called the satisfaction index. Based on the data statistics results, according to the vector score of Formula (5) which can be divided into demand attributes, on the basis of distance range of
and
, we drew an A-Kano model analysis diagram, as shown in
Figure 2. User demand is grouped into four categories: attractive demand, expected demand, basic demand and no difference demand. The function priority development order is as follows: basic demand, expected demand, attractive demand, and no difference demand [
40].
4.5. VR Design Practice
The current design practice scheme is a flat, picture-based display effect. Considering the user-prioritized experience of its unmanned system interface, in the design and evaluation stage, VR technology is utilized to present the unmanned vehicle in a virtualized manner, simulating a relatively real vehicle driving environment for experience. This is in order to enhance the user’s real experience of the unmanned vehicle system interface at the same time as combining it with the SUS scale to carry out user evaluation in order to obtain more accurate assessment data.
This paper focuses on the driverless vehicle system interface, i.e., the passenger interaction screen. In the market research, the passenger interaction screen is mainly placed behind the front seats of the vehicle, and passengers only ride in the second row. The interface design is shown in
Figure 3. In view of this characteristic, in the design and construction of the VR environment, the passenger interface module of the virtual unmanned vehicle is mainly interactively realized, and the system interface is set up in two presentation modes. Then, the vehicle driving and interaction interface are linked in order to achieve a real driverless vehicle system interface interaction environment; the system environment is shown in
Figure 4.
The VR driverless vehicle system is realized using UE5, which mainly tests the interactive functions of the interface to assist the experiencer in evaluating the system interface, the main test functions of which include route navigation, driving surroundings, audio/video playback, ride instructions, file processing, and other functions. The research object carrier for this study is a driverless vehicle. The current market mainly exists in the form of online vehicles, mainly serving passengers. Therefore, in the VR system design, with reference to the traditional cab passengers’ travel logic, the task scene is designed as a passenger travel taxi scene and the core experience logic is that the passengers enter the vehicle, enter the purpose of the vehicle, the vehicle starts to drive, and the surrounding situation is presented; the experience of the music and other entertainment functions, the experience of office functions, and the end of the trip are assessed. In the simulated driving trip, a voice assistant will be incorporated to assist driving to clarify the purpose of the test experiment.
User needs were obtained through web crawling technology and interview methods, and the A-Kano model was employed to quantify the weight of system interface requirements during the ride experience of autonomous vehicles. Based on the derived priority of these needs, the page layout and richness of functional modules of design elements were reasonably arranged, with visual elements such as color, size, and font thickness used to emphasize the demand factors with higher weight values.
This design optimizes the autonomous vehicle system interface to cater to the diversified usage needs of passengers during the ride. In terms of the safety module, journey safety is a core element in both automotive and interface design. To mitigate personal safety issues arising from program errors or vehicle collisions during the trip, three core functions are provided: emergency assistance, passenger information, and a VR journey scene. In particular, there exist four modules, including a security module, functional module, entertainment functional module and visual design module. Firstly, emergency assistance enables urgent calls for help regarding personal safety issues during the journey, including both audible signals to external individuals and dialing for assistance to traffic police, emergency personnel, and firefighters. Secondly, passenger information educates passengers on relevant riding precautions and safety knowledge. Lastly, the VR journey scene displays real-time surroundings of the vehicle, reducing visual blind spots for rear passengers and enhancing their psychological sense of security. Furthermore, passenger financial security is a crucial factor in enhancing overall security. During the alighting phase, passengers are reminded of forgotten items and asked to confirm retrieval, thereby safeguarding their property. In the basic functional modules, to facilitate route selection or temporary changes during the ride, the map function firstly integrates options for temporary boarding and alighting, VR journey scene road conditions, and route selection. Secondly, to enhance riding comfort, functions for seat rotation adjustment, seat massage, and air conditioning control are provided, allowing adjustment of the seatback angle and cabin environment temperature. For overseas passengers, multiple language options are available to meet the needs of users with language recognition difficulties. Additionally, an AI voice assistant is integrated to provide chat services and voice control operations during the ride, alleviating fear triggered by the empty driver’s seat at night. Moreover, basic office functions such as Word, Excel, PPT, and notes are included in the interface design to accommodate temporary file modifications, along with a time display function to replace the need for checking the time on a mobile phone for convenience. Finally, to address issues such as unrecognized traffic police gestures, vehicle stagnation, and door opening failures during the journey, a remote assistance function is designed to provide remote personnel control, compensating for poor user-prioritized experiences caused by program errors. In the entertainment functional module, the autonomous vehicle system interface integrates entertainment functions such as music listening, karaoke, gaming, and video playback, aiming to alleviate boredom during the ride and enhance the passenger experience. The interface includes apps like NetEase Cloud Music, Bingo Pop, Quanmin K-Song, and iQIYI, allowing users to log in and load their entertainment information. Given that music listening has the highest sensitivity among entertainment modules, it is designed as a widget on the homepage, with other functional widgets presented in a sliding page-turning format following the music listening function. In the visual design module, to highlight UI graphics and ensure easy recognition, the contrast between the background and graphics is firstly enhanced in the graphic design. Simultaneously, the size contrast principle of Gestalt psychology is applied, and graphic design is simplified to avoid the accumulation of visual information and elements. Secondly, personalized themes and layouts, such as bright mode and dark mode, are provided to cater to the specific usage habits and preferences of business people and young users. Lastly, to improve the learning efficiency of safety information prompts, animations are added to the prompts, while maintaining a text format as well. This diversified approach ensures that passengers have a basic understanding of riding information.
4.6. Design Evaluation
In industrial usability research, the SUS accounts for 43% of post-study questionnaire usage. Therefore, the SUS was adopted in this study to evaluate product usability. Subsequently, in the subjective evaluation phase, based on the SUS, a questionnaire was designed tailored to the characteristics of the autonomous vehicle system interface, as shown in
Table 8.
The scoring participants included six driverless vehicle experiencers and four interface designers aged 16–55 years old, all of whom had conducted 10–15 experiences per month in driverless vehicles of two brands, Radish Express and Pony Smart. Before starting, the scoring participants were firstly introduced to the work, and secondly we formally started to observe and score the participants’ interface operation of the VR driverless vehicle system. The process was repeated for each participant to evaluate the interface design of the system. Finally, the participant ratings were summarized and collated for calculation as follows: For odd-numbered items (items 1/3/5/7/9): “Raw score”-1. For even-numbered items (items 2/4/6/8/10): 5-“Raw score”, where
,
is the total SUS score, the odd score for the odd number term and
even for the even number term.
Lewis and Sauro [
45] found that there are primarily two factors influencing SUS data. Items 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, and 8 constitute Factor 1, named “Usability,” with a reliability of 0.91, calculated as the total score of these items. Items 4 and 10 constitute Factor
Figure 2, named “Learnability,” with a reliability of 0.7, calculated as the total score of these two items. In order to make the usability and accessibility score compatible with the overall SUS score (both 0–100), the raw data needs to be transformed. Set
as the availability score;
is the accessibility score, namely,
As shown in
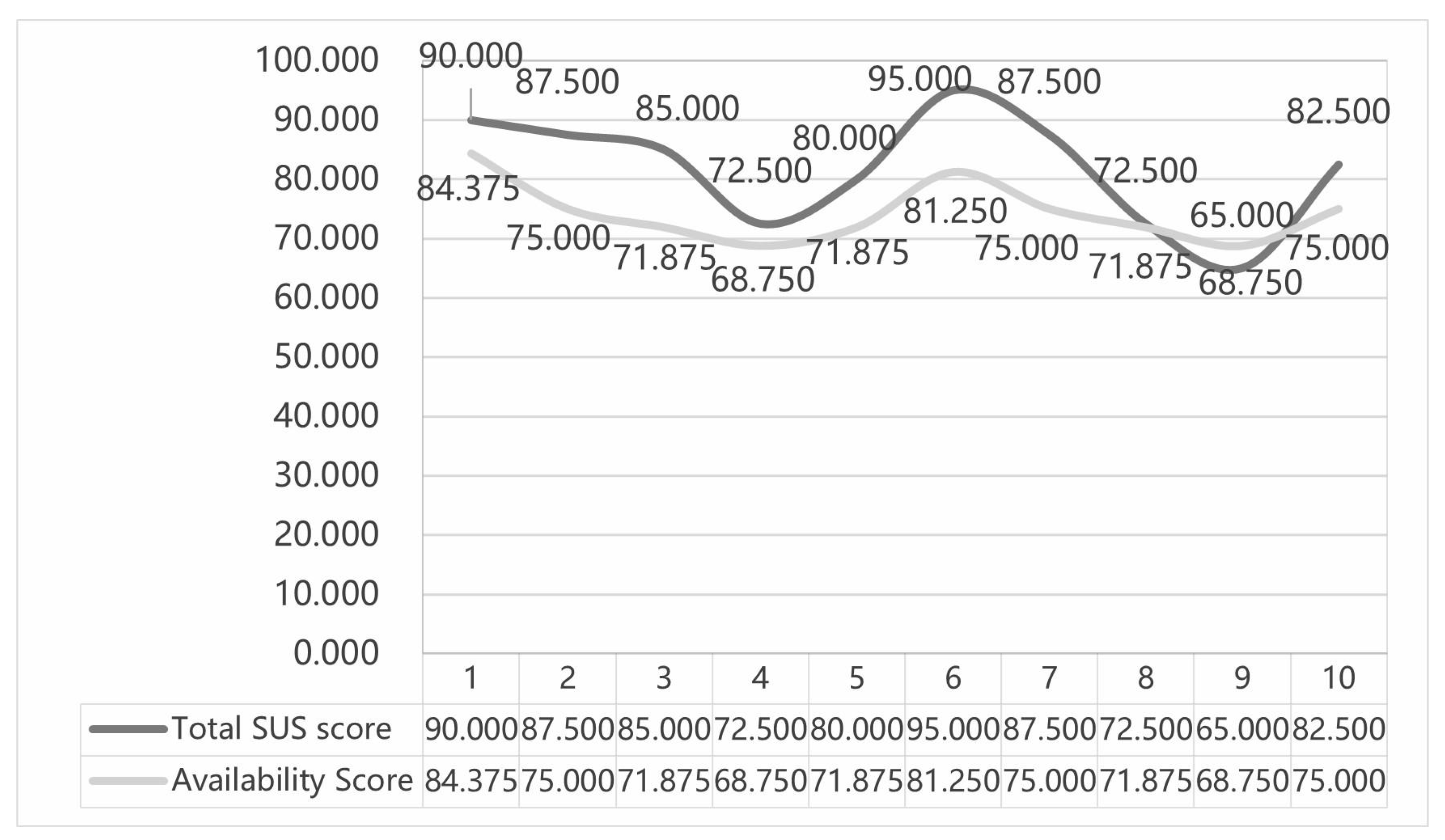
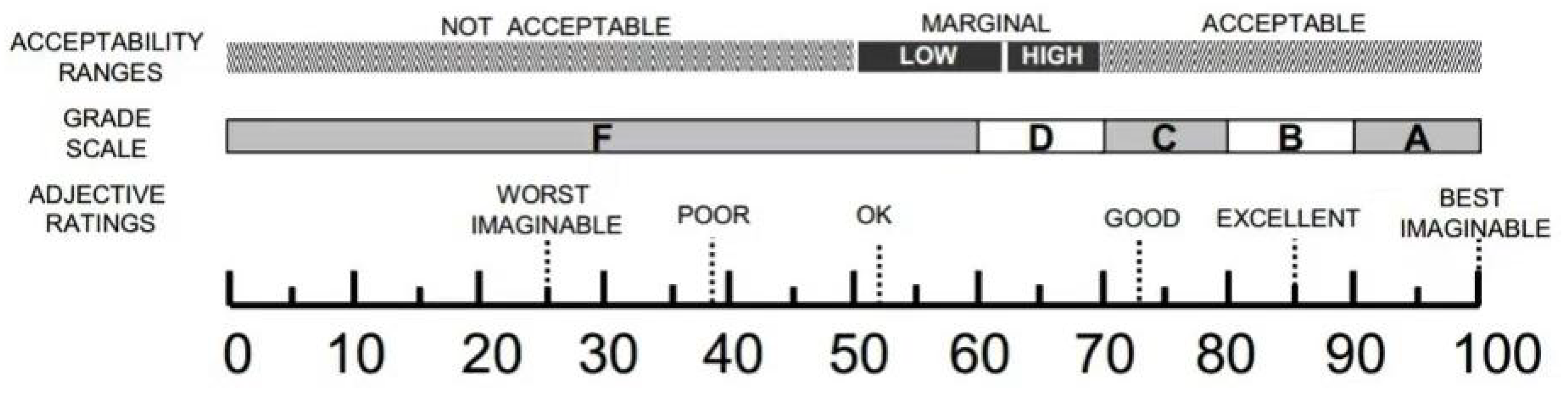
Figure 5, the mean total SUS score for the interface of the autonomous vehicle system is 81.75, and the mean total usability score is 74.375. Based on the SUS scores, the range of acceptability, usability grade and adjective grade was further classified, as shown in
Figure 6. The range of acceptability was acceptable, the usability grade was B and the adjective grade was excellent. Therefore, the product used has higher usability.