Development of a Miniaturized, Automated, and Cost-Effective Device for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sandwich ELISA Protocol
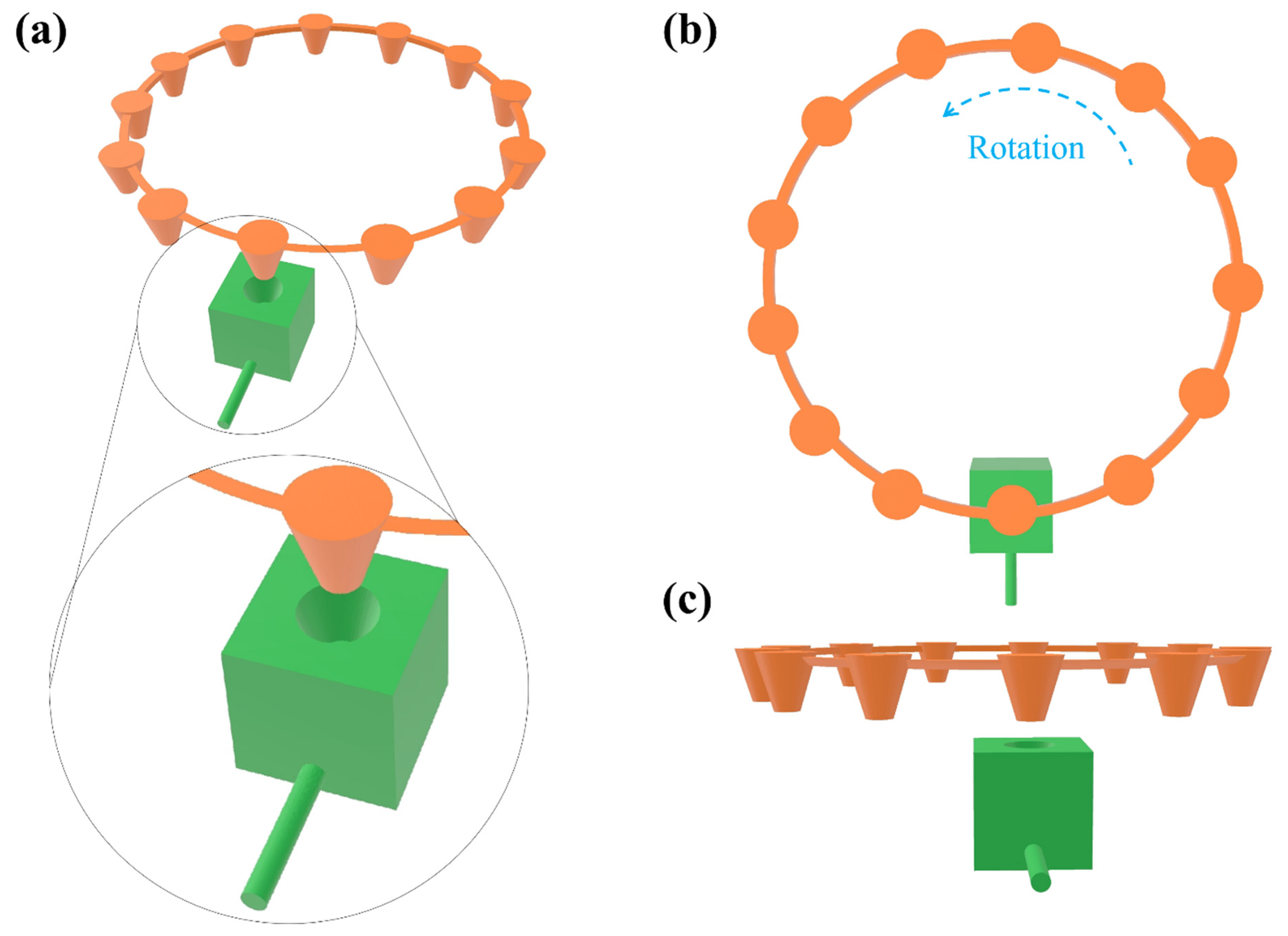
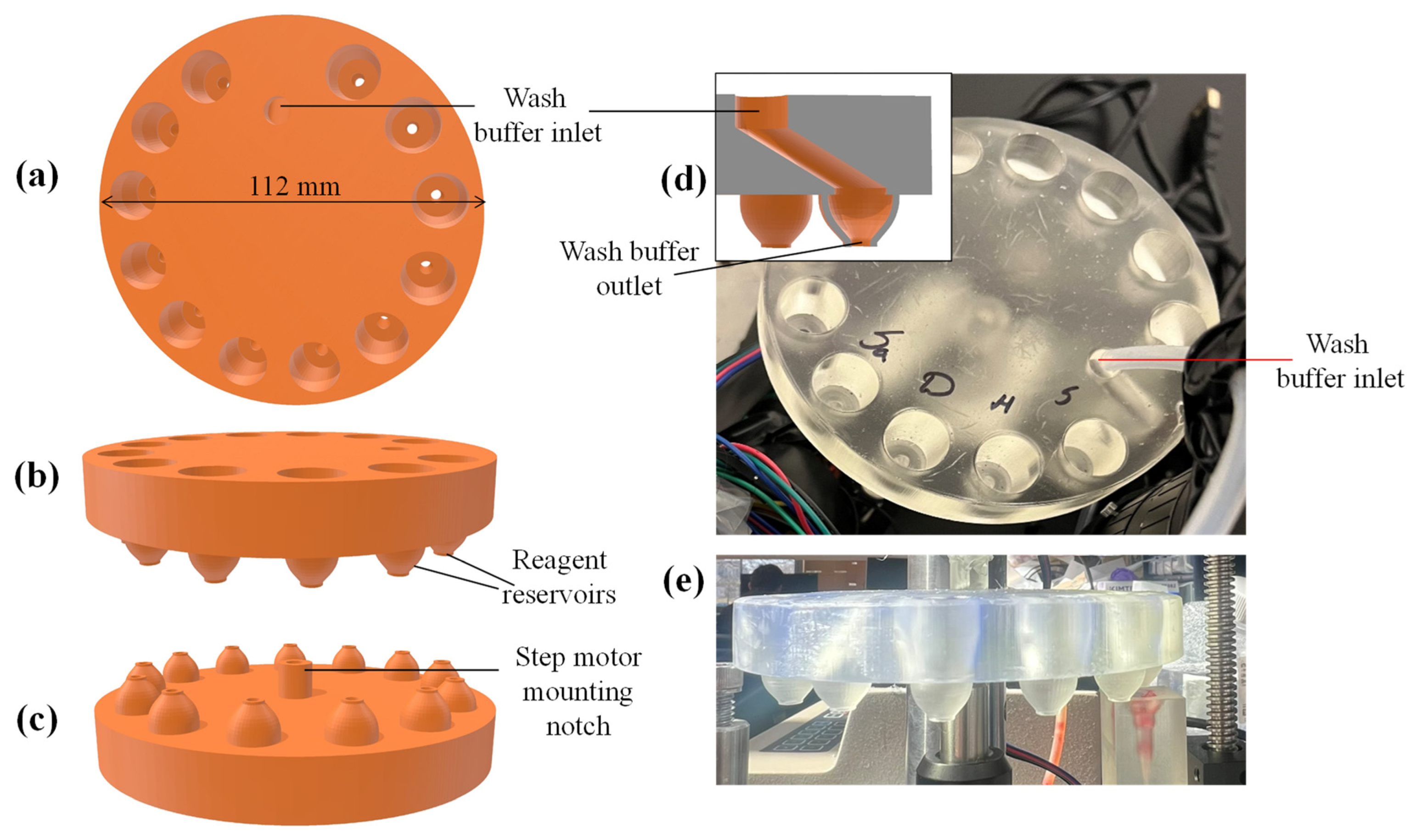
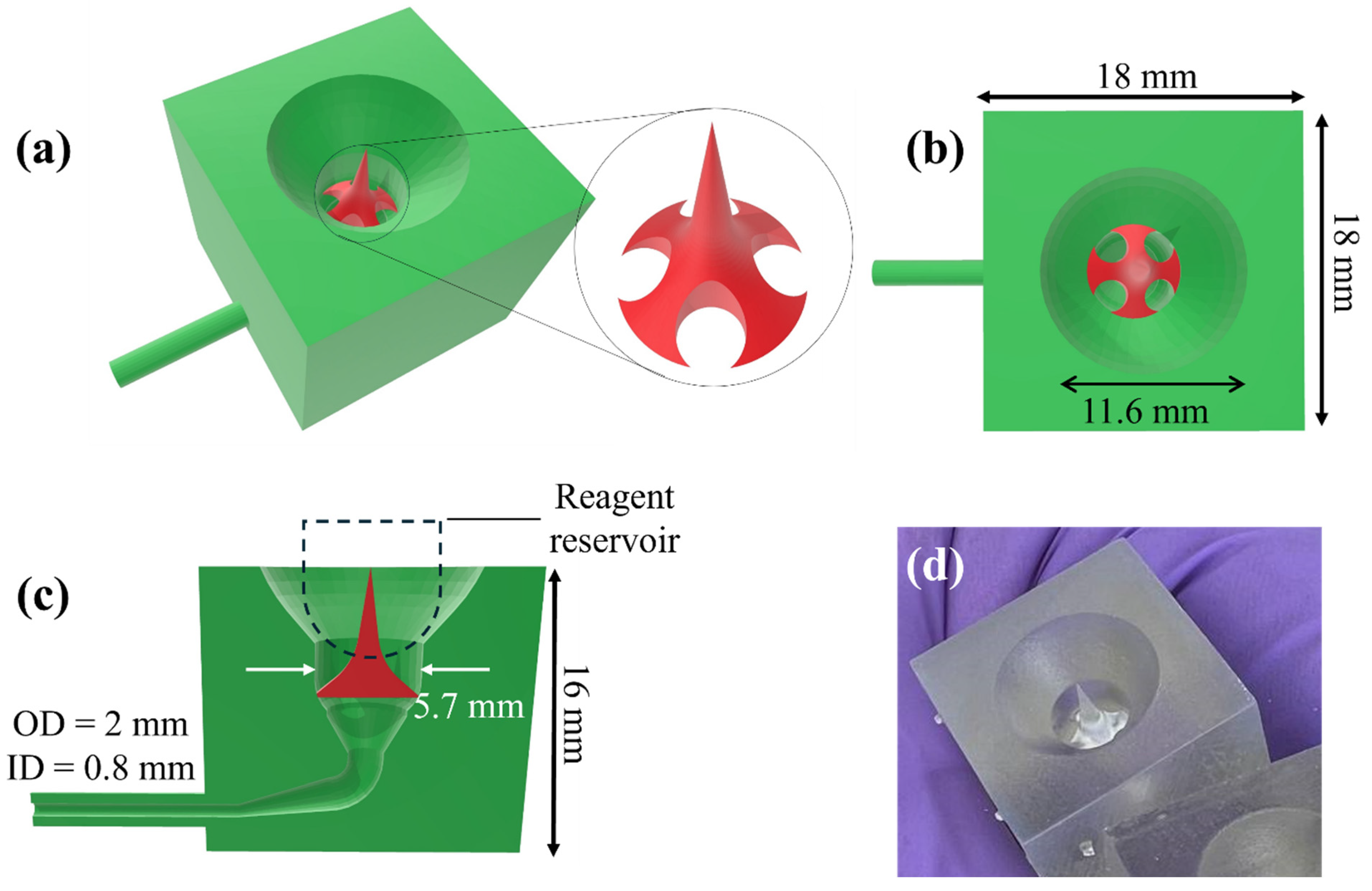
2.3. Design of Components
2.4. 3D Printing
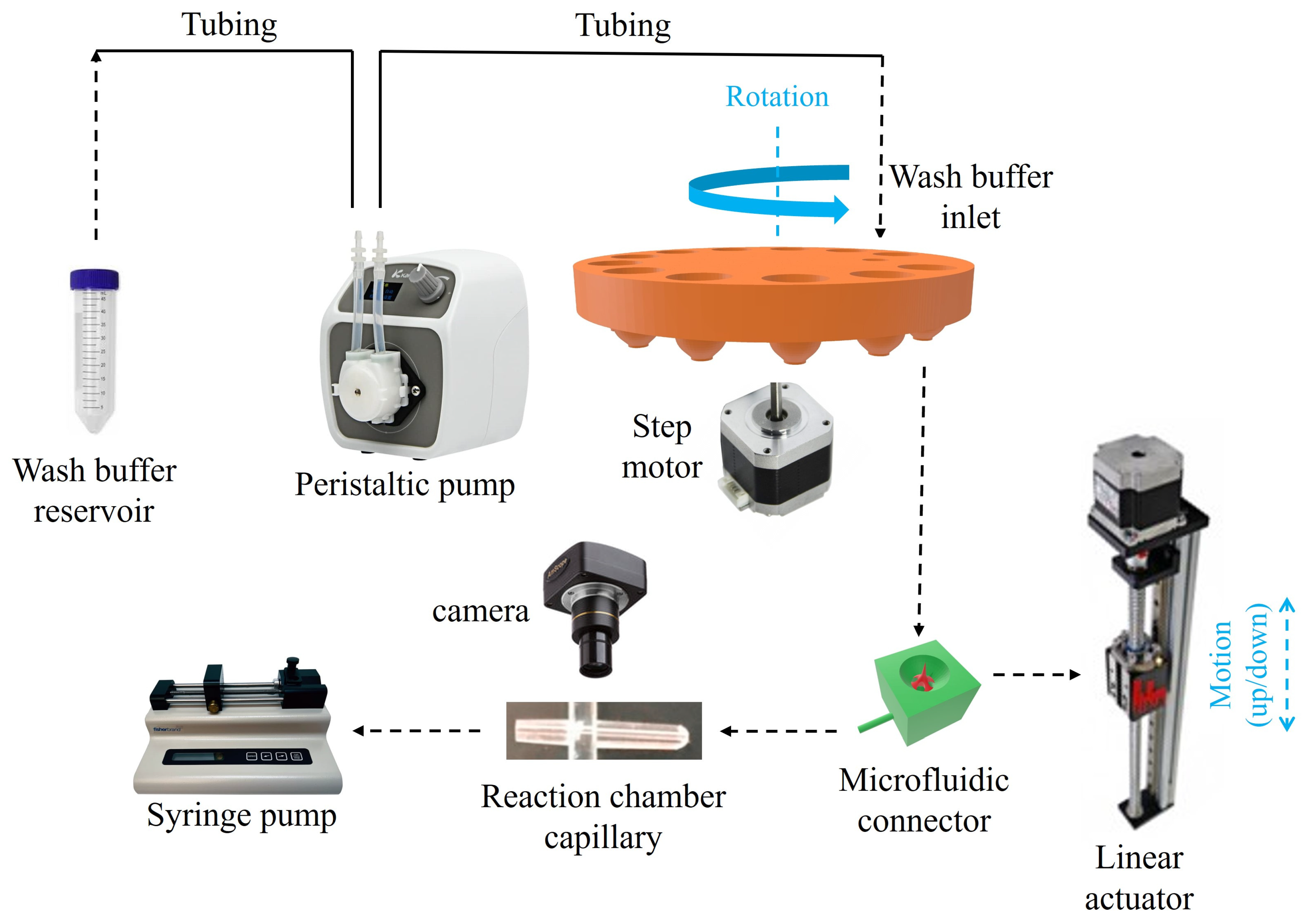
2.5. Assembly and Operation of a Complete System
2.6. Preparation of Disposables
2.7. Cost of Components
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. IL-6 Detection
3.2. Discsussion
4. Conclusions and Future Work
- For reservoir disks, which account for the significant portion of the disposable cost, a highly durable 3D printing resin such as the Tough 2000 Resin ($149 per liter from Formlabs) can be used for more durable printing of much thinner disks for reduced material cost and higher printing speed. The reservoir disks can also be manufactured with injection molding, which significantly reduces the cost per piece.
- For microfluidic connectors, it would be difficult to use injection molding for mass production with the current design. We can stay with the current 3D printing method with more durable resin described above. Or we can re-design the microfluidics (along with the embedded needle) that are more amicable for injection molding.
- For reaction chambers, instead of using capillaries with a circular cross section, microfluidic channels (or chambers) fabricated on a planar surface can be implemented, which is more suitable for mass production. More reaction channels can be added to accommodate multiplexed detection.
- The dimensions of the reservoir wells and all microfluidic channels can be reduced further to reduce reagent consumption.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharafeldin, M.; Davis, J.J. Point of Care Sensors for Infectious Pathogens. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B., Jr.; Hassan, U.; Seymour, C.; Angus, D.C.; Isbell, T.S.; White, K.; Weir, W.; Yeh, L.; Vincent, A.; Bashir, R. Point-of-care sensors for the management of sepsis. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engvall, E. The ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, B.; Cortazar, B.; Tseng, D.; Ozkan, H.; Feng, S.; Wei, Q.; Chan, R.Y.; Burbano, J.; Farooqui, Q.; Lewinski, M.; et al. Cellphone-Based Hand-Held Microplate Reader for Point-of-Care Testing of Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7857–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Svedendahl, M.; Duyne, R.P.; Kall, M. Plasmon-enhanced colorimetric ELISA with single molecule sensitivity. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 1826–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhou, T.; Yin, B.; He, P. Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric ELISA for quantification of ractopamine. Mikrochim. Acta 2018, 185, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Huang, Z.; Liu, X.; Bi, J.; Shu, Z.; Xiao, A.; Wang, J. Colorimetric ELISA based on urease catalysis curcumin as a ratiometric indicator for the sensitive determination of aflatoxin B(1) in grain products. Talanta 2022, 246, 123495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Huang, X.; Yu, R.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, Y. Fluorescence ELISA for sensitive detection of ochratoxin A based on glucose oxidase-mediated fluorescence quenching of CdTe QDs. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 936, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, W.; Peng, W.; Zhao, Q.; Piao, J.; Zhang, B.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Gong, X.; Chang, J. Enhanced Fluorescence ELISA Based on HAT Triggering Fluorescence “Turn-on” with Enzyme-Antibody Dual Labeled AuNP Probes for Ultrasensitive Detection of AFP and HBsAg. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 9369–9377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breault-Turcot, J.; Poirier-Richard, H.P.; Couture, M.; Pelechacz, D.; Masson, J.F. Single chip SPR and fluorescent ELISA assay of prostate specific antigen. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 4433–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Krel, M.; Dolgov, E.; Park, S.; Li, X.; Wu, W.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhang, J.; Khaing Oo, M.K.; Perlin, D.S.; et al. Rapid and quantitative detection of SARS-CoV-2 specific IgG for convalescent serum evaluation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Tan, X.; Khaing Oo, M.K.; Kulkarni, G.; Ilgen, M.A.; Fan, X. Rapid and sensitive detection of drugs of abuse in sweat by multiplexed capillary based immuno-biosensors. Analyst 2020, 145, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; David, A.; Day, J.; Tang, H.; Dixon, E.R.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Y.C.; Khaing Oo, M.K.; Shikanov, A.; Fan, X. Rapid Mouse Follicle Stimulating Hormone Quantification and Estrus Cycle Analysis Using an Automated Microfluidic Chemiluminescent ELISA System. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 2327–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapsford, K.E.; Francis, J.; Sun, S.; Kostov, Y.; Rasooly, A. Miniaturized 96-well ELISA chips for staphylococcal enterotoxin B detection using portable colorimetric detector. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dessel, W.; Vandenbussche, F.; Staes, M.; Goris, N.; De Clercq, K. Assessment of the diagnostic potential of immuno-RCA in 96-well ELISA plates for foot-and-mouth disease virus. J. Virol. Methods 2008, 147, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, B.S.; Vincent, A.L. Detection and Titration of Influenza A Virus Neuraminidase Inhibiting (NAI) Antibodies Using an Enzyme-Linked Lectin Assay (ELLA). Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2123, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, Y.; Kita, K.; Tsugaru, M.; Hotta, K.; Kojima, T.; Noritake, K.I. Generic UPLC-MS/MS and Gyrolab assays with blood microsampling for pharmacokinetic assessments of therapeutic antibodies in mice. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2024, 241, 115993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstrom, J. Gyrolab Immunoassays: Miniaturization, Automation, and Integration into a Rapid Workflow. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2612, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Manen-Brush, K.; Zeitler, J.; White, J.R.; Younge, P.; Willis, S.; Jones, M. Improving Chinese hamster ovary host cell protein ELISA using Ella((R)): An automated microfluidic platform. Biotechniques 2020, 69, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, U.; Mackeben, K.; Stubenrauch, K. Use of Ella((R)) to facilitate drug quantification and antidrug antibody detection in preclinical studies. Bioanalysis 2019, 11, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, E.R.; Jariwala, P.; Rector, K.; Gibbons, W.E.; Zarutskie, P.W.; Devaraj, S. Validation of the picoAMH assay on the Dynex DS2 platform. Pract. Lab. Med. 2019, 17, e00140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, G.; Moheysen-Zadeh, M.; Heinrich, J.; Staack, R.F. Platform switching from ELISA to Gyrolab: A novel generic reagent omits the need to change critical reagents. Bioanalysis 2016, 8, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, T.; Mawatari, K.; Sato, K.; Tokeshi, M.; Kitamori, T. A micro-ELISA system for the rapid and sensitive measurement of total and specific immunoglobulin E and clinical application to allergy diagnosis. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clotilde, L.M.; Bernard, C.T.; Sequera, D.E.; Karmali, A.; Fusellier, A.; Carter, J.M. Dynex: Multiplex ELISA technology. J. Lab. Autom. 2012, 17, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.S.; Lee, J.N.; Park, J.M.; Lee, J.G.; Kim, S.; Cho, Y.K.; Ko, C. A fully automated immunoassay from whole blood on a disc. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, T.H.; Yates, P.D.; Chunyk, A.G.; Joyce, A.P.; Wu, A.; Pop-Damkov, P.; Zhang, Y.; Dreher, E.A.; Tylaska, L.A.; Wentland, J.A.; et al. Feasibility of Singlet Analysis for Ligand Binding Assays: A Retrospective Examination of Data Generated Using the Gyrolab Platform. AAPS J. 2016, 18, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, Y.; Yu, S.; Li, N.; Yao, H.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Q.; Wu, R.; et al. Ultrasensitive point-of-care multiplex diagnosis for influenza virus based robust quantum dot microsphere-lateral flow immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 273, 117187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ao, L.; Hu, R.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Jiang, C.; Gao, G.; Shen, Z.; Hu, J.; Wang, J. Kiwi-Inspired Rational Nanoarchitecture with Intensified and Discrete Magneto-Fluorescent Functionalities for Ultrasensitive Point-of-Care Immunoassay. Small 2024, 20, e2402676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Porter, R.; Zhou, X.; Snozek, C.L.; Yang, E.H.; Wang, S. Microfluidic Digital Immunoassay for Point-of-Care Detection of NT-proBNP from Whole Blood. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 10569–10576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.C.; Hurst, B.; Martiszus, I.; Hausman, M.S.; Sarwat, S.; Schapiro, J.M.; Rowell, S.; Lituev, A. Semi-quantitative, high throughput analysis of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies: Measuring the level and duration of immune response antibodies post infection/vaccination. Vaccine 2021, 39, 5688–5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasca, D.; Reidy, L.; Romero, M.; Diaz, A.; Cray, C.; Kahl, K.; Blomberg, B.B. The majority of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies in COVID-19 patients with obesity are autoimmune and not neutralizing. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dysinger, M.; Marusov, G.; Fraser, S. Quantitative analysis of four protein biomarkers: An automated microfluidic cartridge-based method and its comparison to colorimetric ELISA. J. Immunol. Methods 2017, 451, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macis, D.; Aristarco, V.; Johansson, H.; Guerrieri-Gonzaga, A.; Raimondi, S.; Lazzeroni, M.; Sestak, I.; Cuzick, J.; DeCensi, A.; Bonanni, B.; et al. A Novel Automated Immunoassay Platform to Evaluate the Association of Adiponectin and Leptin Levels with Breast Cancer Risk. Cancers 2021, 13, 3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bio-Techne Ltd. Ella Automated Immunoassay System. Available online: https://www.bio-techne.com/p/simple-plex/ella-automated-immunoassay-system_600-100 (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- DYNEX Technologies Ltd. DYNEX ELISA Systems. Available online: https://www.dynextechnologies.com/systems (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Berthold Technologies Ltd. Crocodile 5-in-One ELISA miniWorkstation. Available online: https://www.berthold.com/ (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Gold Standard Diagnostics Ltd. The BOLT ELISA/CLIA Processor. Available online: https://www.goldstandarddiagnostics.com/bolt.html (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- BIOBASE Ltd. China. BIOBASE 1000 ELISA System. Available online: https://www.biobase.cc/Auto-ELISA-Processor-BIOBASE1000-pd40186305.html (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- GYROS Protein Technologies Ltd. Gyrolab Automated Immunoassay Solutions. Available online: https://www.gyrosproteintechnologies.com/ (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- DAS Ltd. Italy. DAS ELITE Systems. Available online: https://dasitaly.com/en/ape-if-elite-eng/ (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Lutteri, L.; Aldenhoff, M.C.; Cavalier, E. Evaluation of the new Sebia free light chain assay using the AP22 ELITE instrument. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 487, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmane, S.; Kendre, P.; Mahajan, H.; Jain, S. Stereolithography 3D printing technology in pharmaceuticals: A review. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2021, 47, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Kachoie, P.; Pourgholami, M.H.; Richardson, D.R.; Morris, D.L. Gene of the month: Interleukin 6 (IL-6). J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 67, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knupfer, H.; Preiss, R. Significance of interleukin-6 (IL-6) in breast cancer (review). Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 102, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.; Fatima, R.; Assaly, R. Elevated interleukin-6 and severe COVID-19: A meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 2283–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdinasab, M.; Lamy de la Chapelle, M.; Marty, J.L. Recent Progresses in Optical Biosensors for Interleukin 6 Detection. Biosensors 2023, 13, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, L.; Bendali, A.; Pereiro, I.; Azimani, M.; Dumas, S.; Malaquin, L.; Mai, T.D.; Descroix, S. Modular microfluidic system for on-chip extraction, preconcentration and detection of the cytokine biomarker IL-6 in biofluid. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbar, M.; Wu, Y.; Subramony, J.A.; Liu, G. Sensitive Colorimetric Detection of Interleukin-6 via Lateral Flow Assay Incorporated Silver Amplification Method. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 778269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhou, L.; Huang, G.; Shen, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, C.; Kim, A.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, W.; Dai, S.; et al. Enhanced Label-Free Nanoplasmonic Cytokine Detection in SARS-CoV-2 Induced Inflammation Using Rationally Designed Peptide Aptamer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 48464–48475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Biosensor Name | Price ($) | Company | Dimensions (cm) | Volume (L) | Weight (Kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELLA [34] | ~52,000 | Bio-Techne | 38 × 54 × 26 | 53 | >20 (estimated) |
| DYNEX DS2 [35] | ~73,000 | DYNEX Technologies | 54 × 68 × 66 | 242 | 48 |
| DYNEX DSX [35] | ~130,000 | DYNEX Technologies | 106 × 91 × 80 | 476 | 136 |
| DYNEX Agility [35] | ~170,000 | DYNEX Technologies | 90 × 123 × 125 | 1384 | 296 |
| Crocodile ELISA [36] | ~29,000 | Berthold | ~40 × 40 × 40 | ~64 | >20 (estimated) |
| The Bolt [37] | ~37,000 | Axiom Medical Supplies | 48 × 53 × 56 | 142 | 27 |
| BIOBASE1000 [38] | ~11,000 | Biobase | 93 × 69 × 86 | 552 | 130 |
| Gyrolab xPlore [39] | 172,000 | Gyrolab | 54 × 58 × 64 | 200 | 80 |
| Gyrolab xPand [39] | 385,000 | Gyrolab | 121 × 67 × 82 | 665 | 160 |
| DAS APE IF ELITE [40] | ~61,000 | DAS | 113 × 77 × 75 | 653 | 120 |
| DAS AP22 ELITE [40,41] | ~46,000 | DAS | 62 × 83 × 72 | 370 | 85 |
| This work | ~1200 (manufacturing cost) | - | 19 × 24 × 14 | <6.4 | <3 |
| Part | Item Price ($) | Count | Total Price ($) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arduino Uno REV3 | 27.60 | 2 | 55.20 |
| TB6600 stepper motor driver | 9.98 | 2 | 19.96 |
| FUYU FSL30 linear stage | 83.00 | 1 | 83.00 |
| Iverntech Nema 17 stepper motor | 12.99 | 1 | 12.99 |
| Fujinon HF12.5SA-1 C-Mount 12.5 mm lens | 268.00 | 1 | 268.00 |
| AmScope MU Series 5.3MP CMOS C-mount microscope camera | 534.99 | 1 | 534.99 |
| Peristaltic Pump 12V dc Kamoer DKCP | 66.00 | 1 | 66.00 |
| Handmade syringe pump (estimated) | 130.00 | 1 | 130.00 |
| Wefomey 72W Universal Power Supply | 18.99 | 1 | 18.99 |
| Breadboard + wires (estimated) | <10.00 | 1 | 10.00 |
| Total | - | - | ~1200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aalizadeh, M.; Yang, S.; Guntur, S.; Potluri, V.; Kulkarni, G.; Fan, X. Development of a Miniaturized, Automated, and Cost-Effective Device for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Sensors 2025, 25, 5262. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175262
Aalizadeh M, Yang S, Guntur S, Potluri V, Kulkarni G, Fan X. Development of a Miniaturized, Automated, and Cost-Effective Device for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Sensors. 2025; 25(17):5262. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175262
Chicago/Turabian StyleAalizadeh, Majid, Shuo Yang, Suchithra Guntur, Vaishnavi Potluri, Girish Kulkarni, and Xudong Fan. 2025. "Development of a Miniaturized, Automated, and Cost-Effective Device for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay" Sensors 25, no. 17: 5262. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175262
APA StyleAalizadeh, M., Yang, S., Guntur, S., Potluri, V., Kulkarni, G., & Fan, X. (2025). Development of a Miniaturized, Automated, and Cost-Effective Device for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Sensors, 25(17), 5262. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25175262






