Gesture-Based Secure Authentication System Using Triboelectric Nanogenerator Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TENG Experiment Configuration
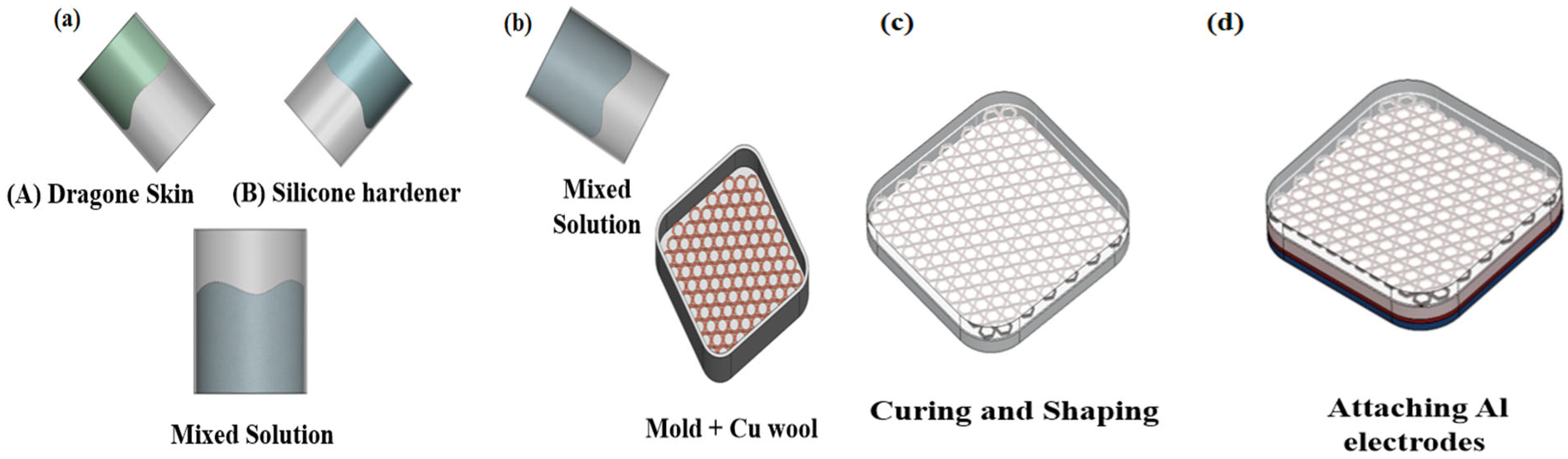
2.2. Fabrication of the TENG Sensor
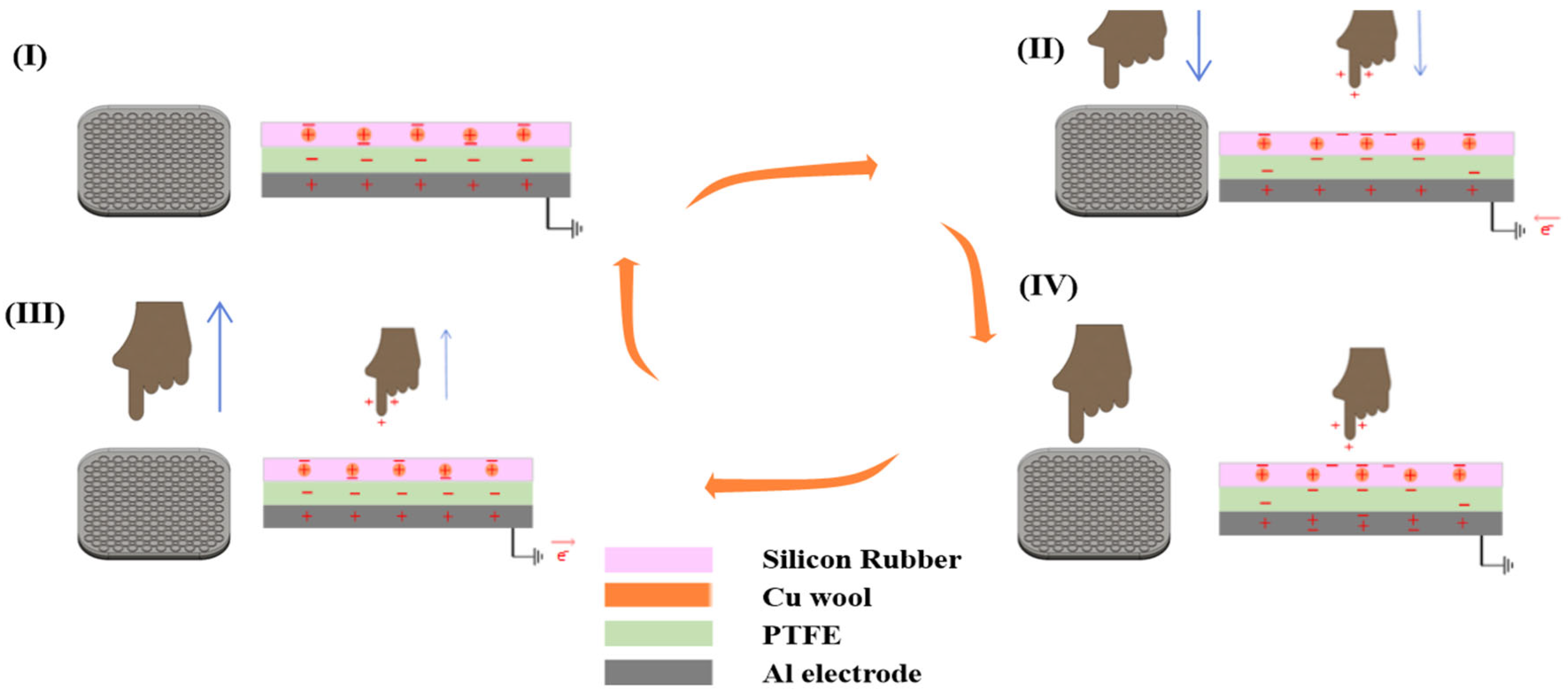
2.3. TENG Operating Principles and Mechanisms
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Triboelectric Sensor Outputs According to Pressure
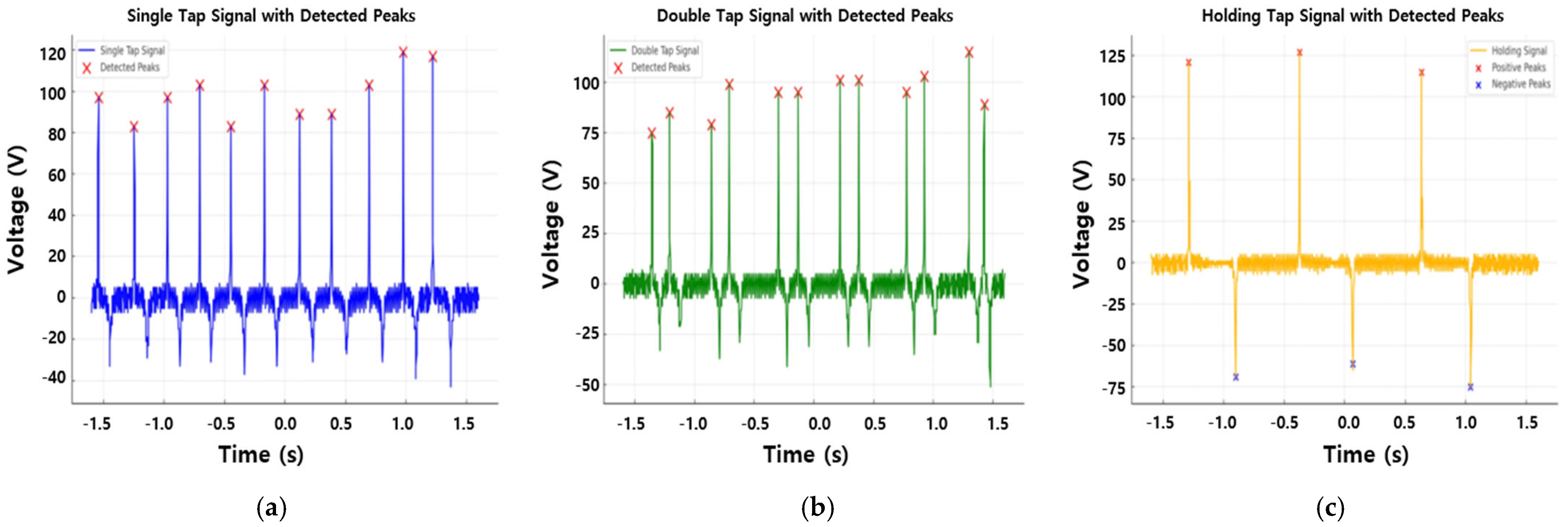
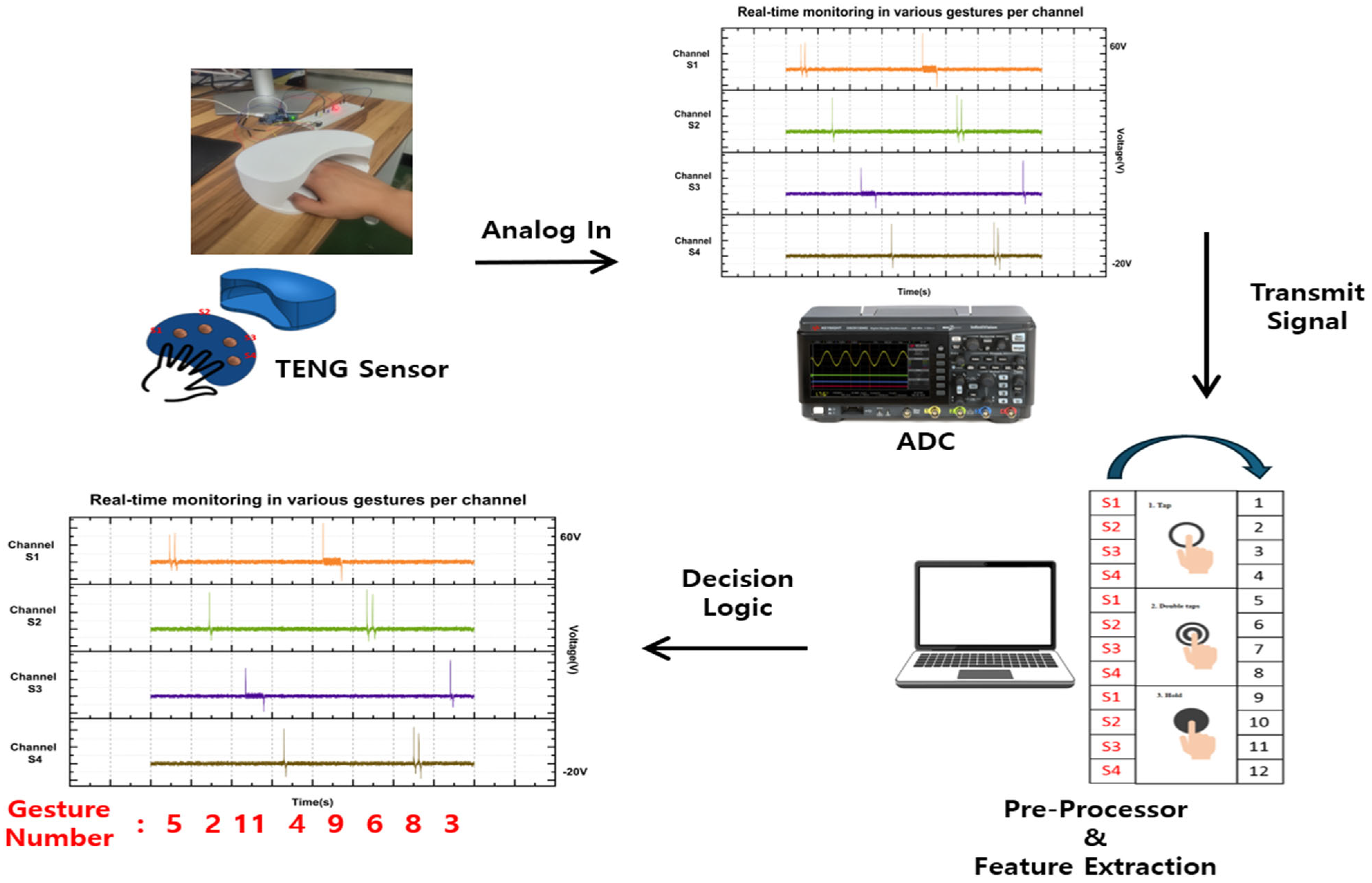
3.2. Signal Analysis and Signal Processing Mechanism for Gesture Signal Recognition
3.3. Development of Threshold-Based Gesture Classification Algorithm
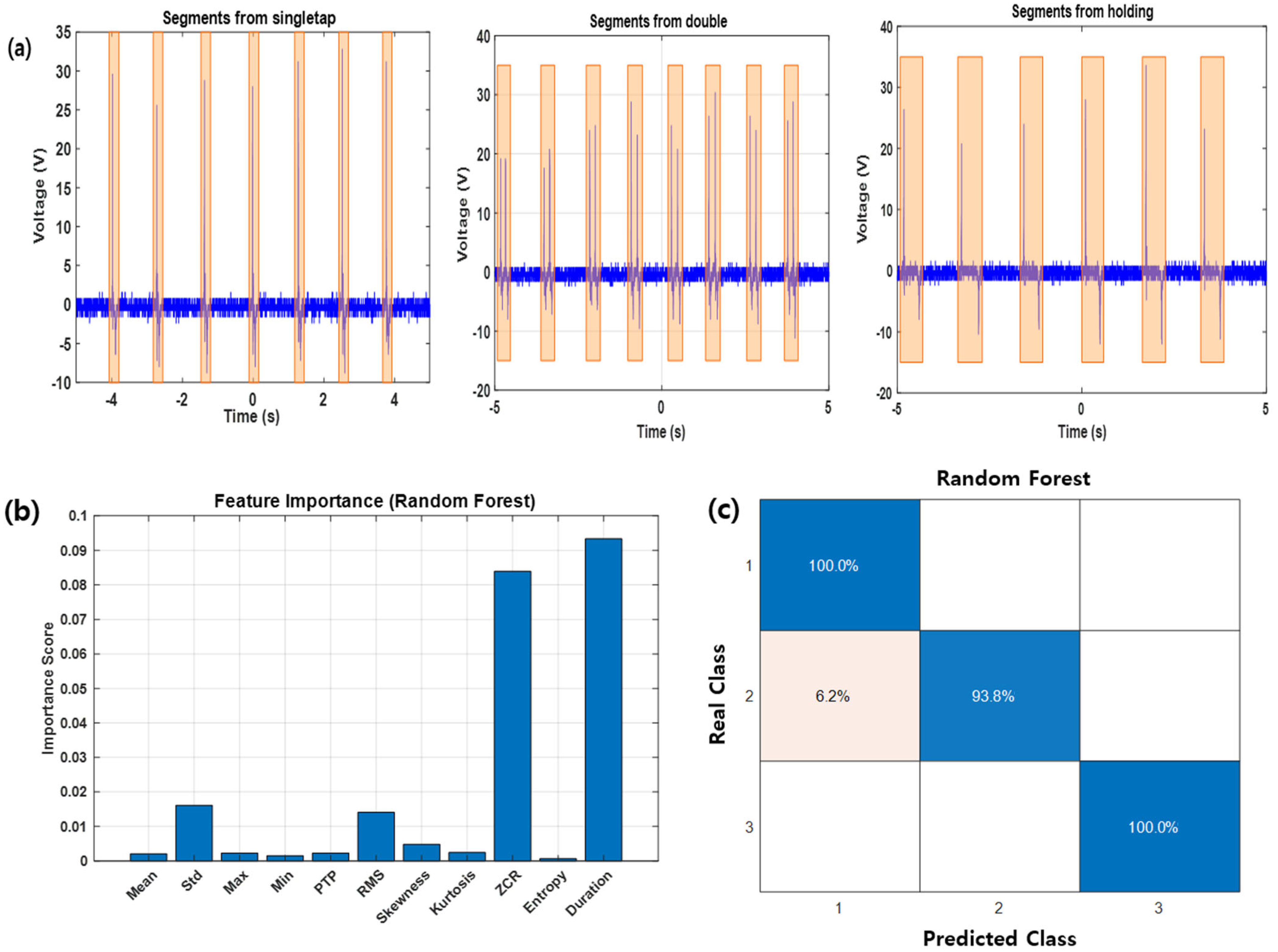
3.4. Machine Learning-Based Gesture Classification Using Automatically Labeled Segments
3.5. Application of Gesture Recognition for Secure Certification
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahamed, J.; Rajan, A.V. Internet of Things (IoT): Application Systems and Security Vulnerabilities; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wayman, J.L. Fundamentals of Biometric Authentication Technologies. Int. J. Image Graph. 2001, 01, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhishek, A.M.; Patnaik, L.M.; Manjunathswamy, B.E.; Thriveni, J.; Venugopal, K.R. Multimodal Biometric Authentication Using ECG and Fingerprint. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2015, 111, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab Hassani, F.; Lee, C.; Mogan, R.P.; Gammad, G.G.L.; Wang, H.; Yen, S.-C.; Thakor, N.V. Toward Self-Control Systems for Neurogenic Underactive Bladder: A Triboelectric Nanogenerator Sensor Integrated with a Bistable Micro-Actuator. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3487–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Che, L.; Liu, J. A High Sensitivity Self-Powered Wind Speed Sensor Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators (TENGs). Sensors 2021, 21, 2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, D.; Cui, S.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, S.; Yin, X. Rationally Designed Dual-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Mechanical Energy by Both Electrostatic Induction and Dielectric Breakdown Effects. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, T. Theoretical Foundations of Triboelectric Nanogenerators (TENGs). Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2020, 63, 1087–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ling, Y.; Yin, R. Fiber/Yarn-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators (TENGs): Fabrication Strategy, Structure, and Application. Sensors 2022, 22, 9716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Dziuban, J.A.; Lee, C.; Sun, L.; Shi, Q.; Li, K.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z. Investigation of Position Sensing and Energy Harvesting of a Flexible Triboelectric Touch Pad. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.-B.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, W.-G.; Tcho, I.-W.; Jin, I.-K.; Han, J.-K.; Kim, D.; Choi, Y.-K. Self-Powered Wearable Keyboard with Fabric Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, P.; Cho, H.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Shrestha, K.; Bhatta, T.; Rana, S.S.; Park, C.; Salauddin, M.; Rahman, M. High-Performance Keyboard Typing Motion Driven Hybrid Nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2021, 88, 106232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R. Machine Learning-Assisted Triboelectric Nanogenerator-Based Self-Powered Sensors. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2024, 5, 101888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; An, S.; Tang, Q.; Guo, H.; Hu, C. Wearable Triboelectric Sensors for Biomedical Monitoring and Human-Machine Interface. iScience 2021, 24, 102027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Duan, X.; Wen, J.; Tian, Q.; Shi, L.; Dong, S.; Peng, L. A Self-Powered Smart Glove Based on Triboelectric Sensing for Real-Time Gesture Recognition and Control. Electronics 2025, 14, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qing, W.; Zhang, D.; Gan, C.; Zhang, J.; Liao, S.; Wei, K.; Zou, H. Flexible Staircase Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Motion Monitoring and Gesture Recognition. Nano Energy 2024, 128, 109849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Huo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Yue, D.; Xu, N.; Gu, R.; Wei, L.; Luo, L.; Chen, M. Triboelectric In-Sensor Deep Learning for Self-Powered Gesture Recognition toward Multifunctional Rescue Tasks. Nano Energy 2024, 124, 109465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Niu, H.; Shen, G.; Li, Y. Self-Healing Hydrogel-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator in Smart Glove System for Integrated Drone Safety Protection and Motion Control. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2419809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, J.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Cheng, L.; Huo, Z.; Lei, Y.; Sun, Q. Recent Progress in Self-Powered Wireless Sensors and Systems Based on TENG. Sensors 2023, 23, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Han, Y. Threshold-Based Signal Segmentation for Improved Gesture Classification Accuracy. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2025, 359, 114703. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Ji, S.; Yang, Y.; Yang, C.; Mo, J.; Zhu, J. Machine Learning-Assisted Wearable Sensing for High-Sensitivity Gesture Recognition. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2023, 365, 114877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wei, S.; Zhu, F.; Tian, H.; Liu, B.; Ji, L.; Wang, Z.L. Decoding Lip Language Using Triboelectric Sensors with Deep Learning. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.K.; Ke, K.H. High Contact Surface Area Enhanced Al/PDMS Triboelectric Nanogenerator Using Novel Overlapped Microneedle Arrays and Its Application to Lighting and Self-Powered Devices. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 508, 145310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, G.; Gadegaard, N.; Cochran, P.; Dahiya, R.; Xu, Y.; Mulvihill, D.M. Origin of the Contact Force-Dependent Response of Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2021, 83, 105829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Shin, J.; Yoon, J.; Lim, K.-H.; Sim, G.-D.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, D.H.; Cho, H.; Park, J. Three-Dimensional Skin-Type Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Detection of Two-Axis Robotic-Arm Collision. Nano Energy 2022, 97, 107225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Gong, X. Material Selection and Performance Optimization Strategies for a Wearable Friction Nanogenerator (W-TENG). J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 24454–24481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Lin Wang, Z. Flexible Triboelectric Generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Wen, Z.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.L. Effective Energy Storage from a Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosangadi Prutvi, S.; Korrapati, M.; Gupta, D. Self-Powering Vibration Sensor Based on a Cantilever System with a Single-Electrode Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 075115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.; Niu, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Lin, L.; Liao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, P.K.; et al. Stretchable-Rubber-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Its Application as Self-Powered Body Motion Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3688–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Nie, J.; Zhang, Y. Recent Advances in High Charge Density Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2024, 6, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, A.C.; Guo, H.; Ding, W. Triboelectric Nanogenerator: A Foundation of the Energy for the New Era. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 9, 1802906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Guo, J.; Shao, J.; Xu, Q.; Ding, W.; Wang, Z.L.; Xu, M.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Yu, H. Theoretical Modeling of Contact-Separation Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerators from Initial Charge Distribution. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 2228–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

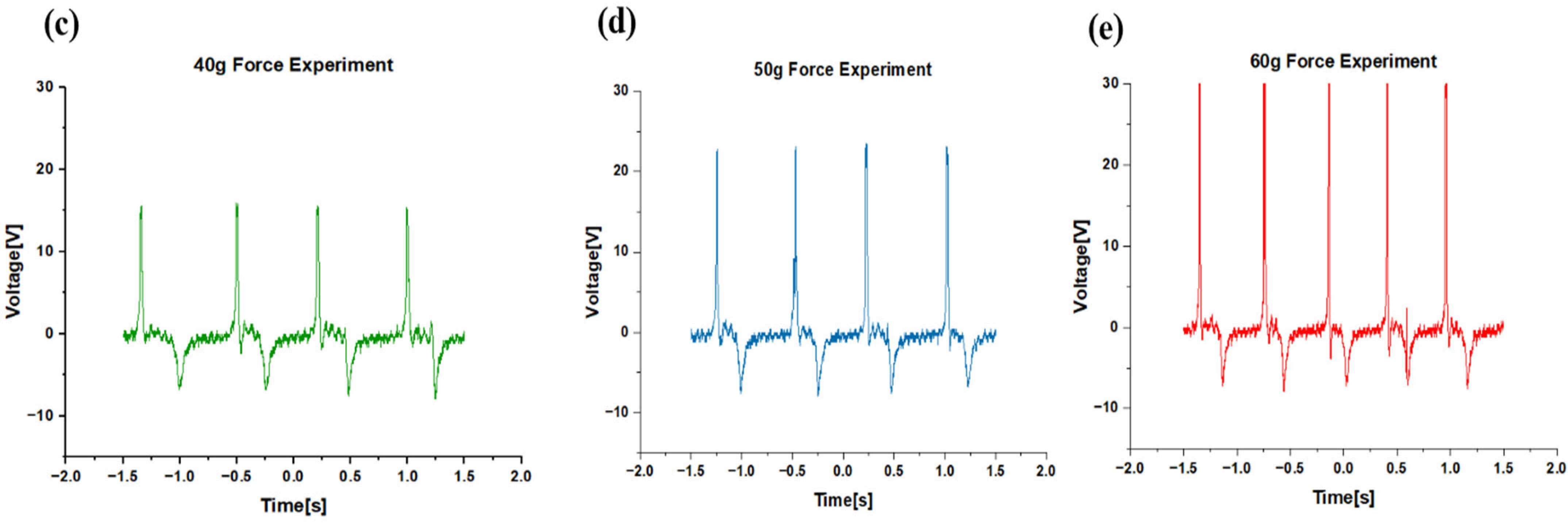



| Force | Stroke Length | Acceleration | Output Voltage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 gf | 20 mm | 17.83 m/s2 | 15 V |
| 50 gf | 25 mm | 22.29 m/s2 | 24 V |
| 60 gf | 30 mm | 26.75 m/s2 | 30 V |
| Gesture | Single Tap | Double Tap | Holding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vp (positive peak voltage) | 60~70 V | 60~70 V | 70~80 V |
| Vn (negative peak voltage) | −30~−40 V | −30~−40 V | −50~−60 V |
| Np (number of peaks) | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Td (time delay) | - | 0.2s | 0.3~0.5 s |
| Key characteristics | Single peak, rapid signal change, short duration | Two consecutive peaks, short tap interval, repeated pattern | Delayed negative peak, large voltage drop, long duration |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, D.; Kim, K.; Shin, J.; Park, J. Gesture-Based Secure Authentication System Using Triboelectric Nanogenerator Sensors. Sensors 2025, 25, 5170. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165170
Han D, Kim K, Shin J, Park J. Gesture-Based Secure Authentication System Using Triboelectric Nanogenerator Sensors. Sensors. 2025; 25(16):5170. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165170
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Doohyun, Kun Kim, Jaehee Shin, and Jinhyoung Park. 2025. "Gesture-Based Secure Authentication System Using Triboelectric Nanogenerator Sensors" Sensors 25, no. 16: 5170. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165170
APA StyleHan, D., Kim, K., Shin, J., & Park, J. (2025). Gesture-Based Secure Authentication System Using Triboelectric Nanogenerator Sensors. Sensors, 25(16), 5170. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165170







