Method for Generating Real-Time Indoor Detailed Illuminance Maps Based on Deep Learning with a Single Sensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. A Method for Generating Real-Time Indoor Illuminance Maps with a Single Sensor
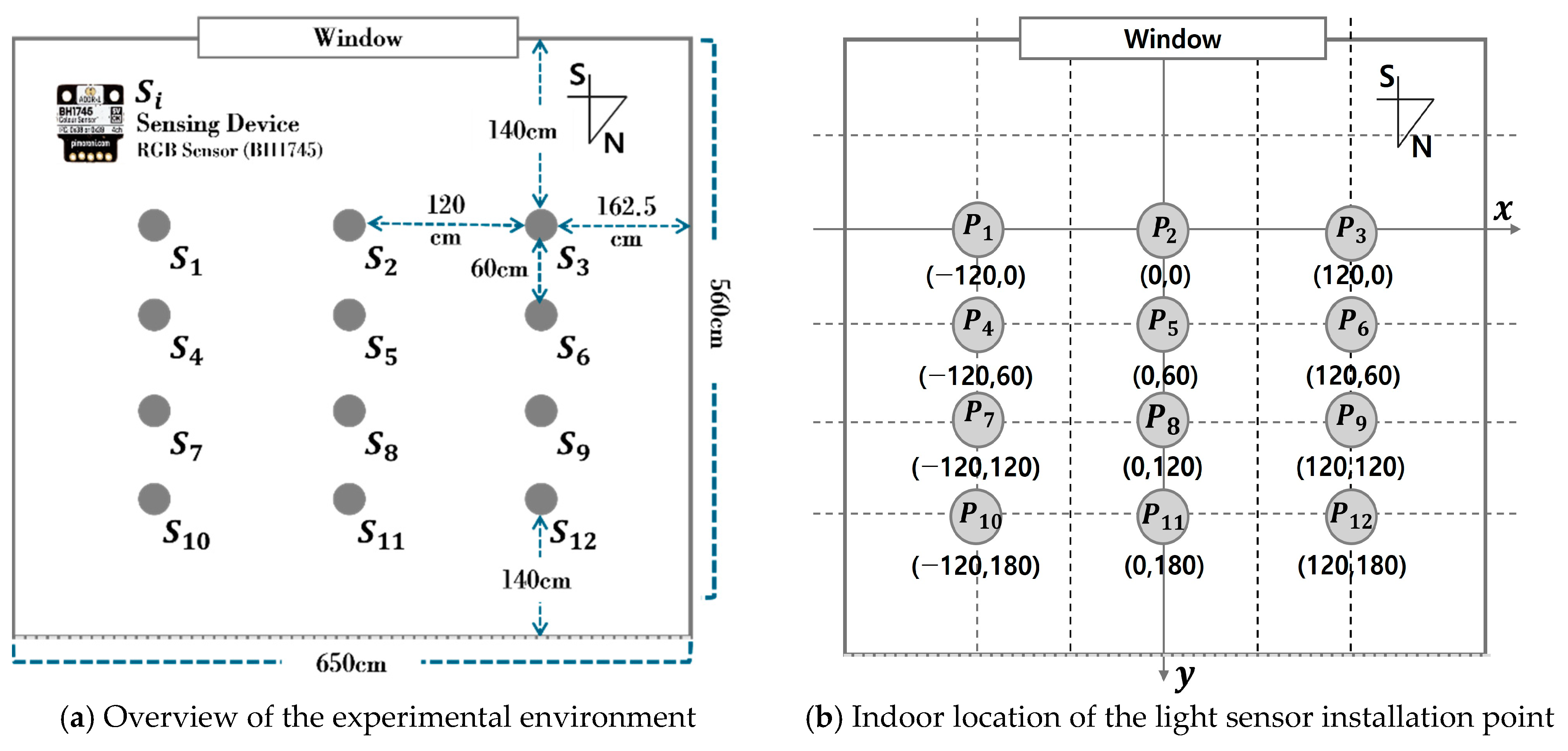
2.1. Building an Experimental Environment and Learning Dataset
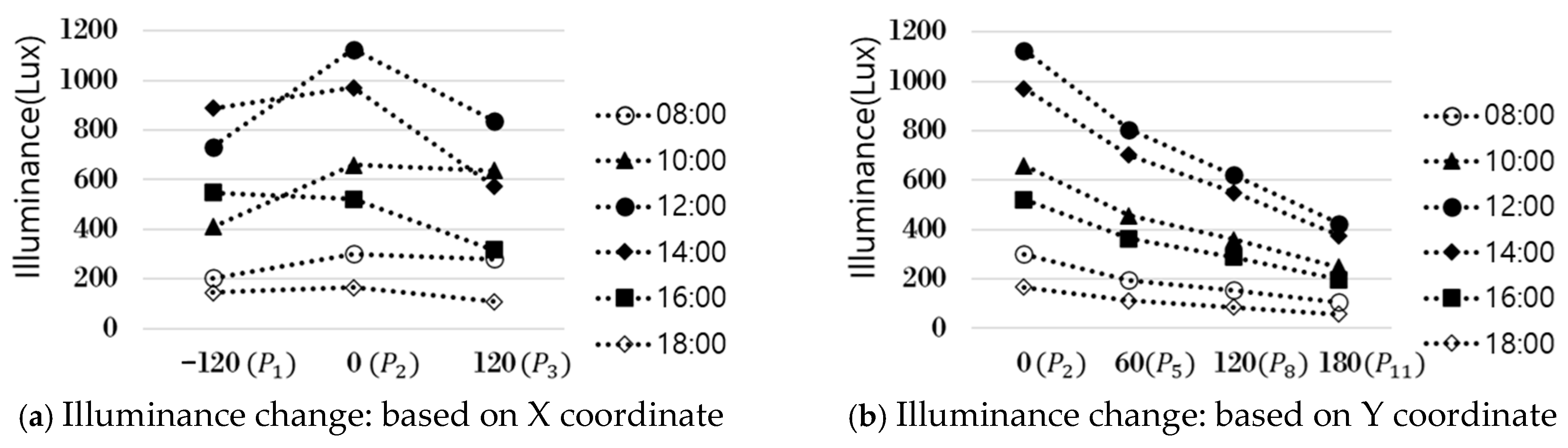
2.2. Correlation Analysis and Selection of Optimal Input Factors
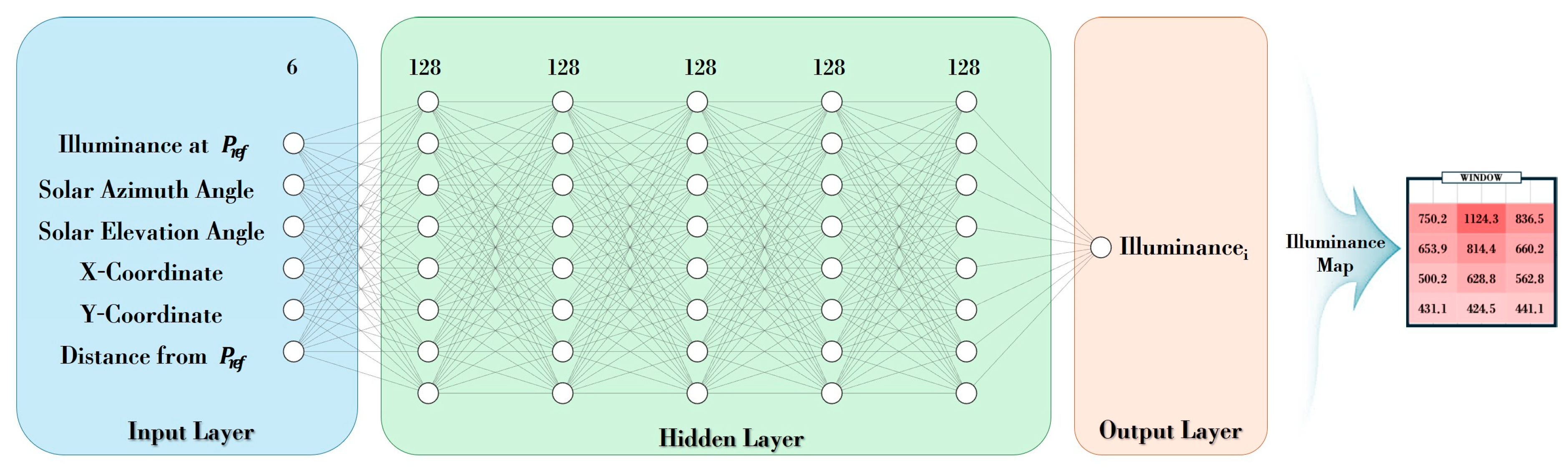
2.3. DNN Model for Generating Indoor Illuminance Maps
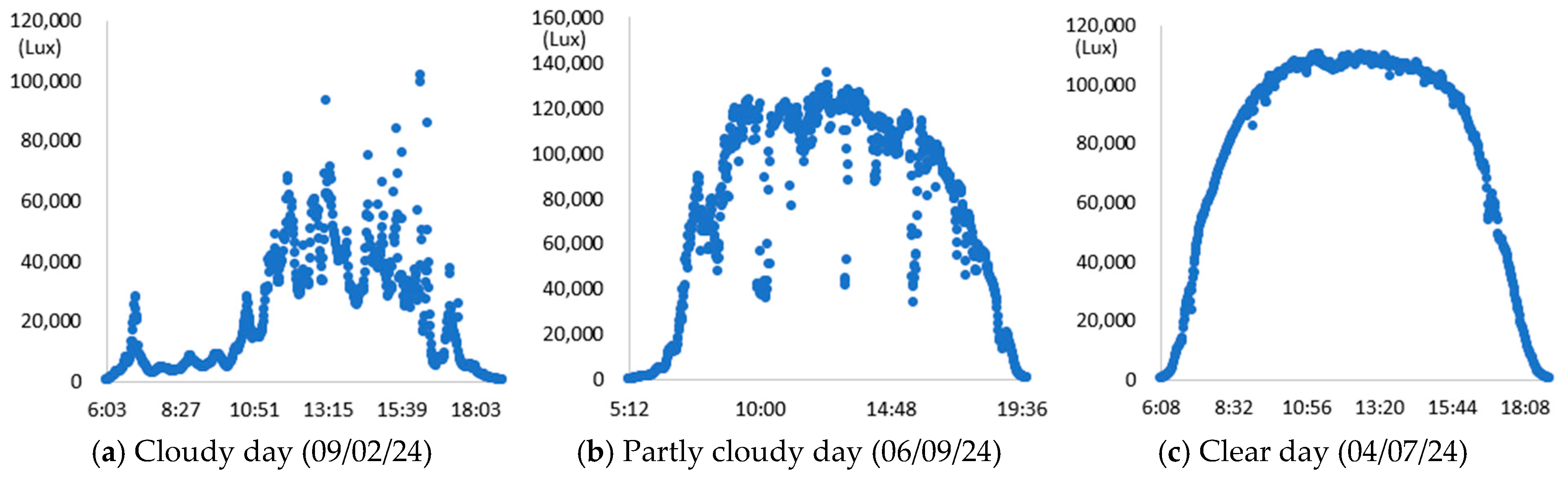
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Kaminska, A.; Ożadowicz, A. Lighting Control Including Daylight and Energy Efficiency Improvements Analysis. Energies 2018, 11, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuera, J.; Hertog, W.; Perálvarez, M.; Polo, J.; Carreras, J. Smart lighting system ISO/IEC/IEEE 21451 compatible. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 2595–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Garg, V. A review of open loop control strategies for shades, blinds and integrated lighting by use of real-time daylight prediction methods. Build. Environ. 2018, 135, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.K.; Park, T.J.; Kang, G.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Song, D. Proposal of the Prediction Equation for Interior Daylight Illuminance. J. Korean Sol. Energy Soc. 2013, 33, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Oh, S.T.; Lim, J.H. Lighting control method based on RIIL to reduce building energy consumption. Energy Rep. 2024, 11, 2090–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, X.; Gao, H. A Distributed Intelligent Lighting Control System Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Oh, S.T.; Lim, J.H. Grid Lighting System for Energy Saving Through Gradation Illuminance Control that Responds Inflow of Natural Light. Mech. Eng. 2022, 7, 284–289. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.H.; Cheung, K.L.; Wong, S.L.; Lam, T.N. An analysis of energy-efficient light fittings and lighting controls. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lin, H.J. Design and implementation of smart home control systems based on wireless sensor networks and power line communications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 62, 4430–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.; Tan, Y.K. Sensorless Illumination Control of a Networked LED-Lighting System Using Feedforward Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.; Yoon, W. A Survey on Energy Conserving Mechanisms for the Internet of Things: Wireless Networking Aspects. Sensors 2015, 15, 24818–24847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellia, L.; Fragliasso, F.; Stefanizzi, E. Why are daylight-linked controls (DLCs) not so spread? A literature review. Build. Environ. 2016, 106, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, M. A review on machine learning algorithms to predict daylighting inside buildings. Sol. Energy 2020, 202, 249–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Jeong, H.D.; Park, S.T.; Kim, S.H. Deep learning. J. KSNVE 2017, 27, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Duan, P.; Zheng, Y.; Cai, W.; Zhang, X. Posting techniques in indoor environments based on deep learning for intelligent building lighting system. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 13674–13682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Ning, C.; Wang, Y.; Duan, W.; Duan, P. Smart lighting control system based on fusion of monocular depth estimation and multi-object detection. Energy Build. 2022, 277, 112485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, N.K.; Karunagaran, G.; Spanos, C.; Tseng, K.J.; Soong, B.H. Smart lighting system using ANN-IMC for personalized lighting control and daylight harvesting. Build. Environ. 2018, 139, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.T.; Ga, D.H.; Lim, J.H. TadGAN-Based Daily Color Temperature Cycle Generation Corresponding to Irregular Changes of Natural Light. Sensors 2022, 22, 7774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le-Thanh, L.; Nguyen-Thi-Viet, H.; Lee, J.; Nguyen-Xuan, H. Machine learning-based real-time daylight analysis in buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 52, 104374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, G.; Han, Z.; Stouffs, R. A predictive model for daylight performance based on multimodal generative adversarial networks. Energy Build. 2024, 305, 113876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.T.; Jeon, G.W.; Lim, J.H. Method of Calculating Short-Wavelength-Ratio-Based Color Temperature Supporting the Measurement of Real-Time Natural Light Characteristics through RGB Sensor. Sensors 2020, 20, 6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podbucki, K.; Suder, J.; Marciniak, T.; Dąbrowski, A. Influence of power supply on airport navigation lamps photometric test accuracy. In Proceedings of the 2023 Signal Processing: Algorithms, Architectures, Arrangements, and Applications (SPA), Poznan, Poland, 20–22 September 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 183–188. [Google Scholar]
- Back, J.W.; Ko, J.S.; Choi, J.S.; Jang, M.G.; Kang, S.J.; Chung, D.H. Efficiency analysis of PV tracking system with PSA algorithm. In Proceedings of the Korean Institute of IIIuminating and Electrical Installation Engineers Conference, Yongpyong, Republic of Korea, 7–8 May 2009; The Korean Institute of IIIuminating and Electrical Installation Engineers: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2009; pp. 412–415. [Google Scholar]
- NOAA Solar Position Calculator. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Last Modified 9 March 2025. Available online: https://gml.noaa.gov/grad/solcalc/azel.html (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Wanas, N.; Auda, G.; Kamel, M.S.; Karray, F. On the optimal number of hidden nodes in a neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 25–28 May 1998; Volume 2, pp. 918–921. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Chen, L. A novel approach for determining the optimal number of hidden layer neurons for FNN’s and its application in data mining. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information Technology and Applications (ICITA 2008), Cairns, QLD, Australia, 23–26 June 2008. [Google Scholar]



| Time | Solar Information | Illuminance (Lux) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Azimuth | Elevation | – | |||||||||
| 03/29/24 06:32 | 86.62 | 1.58 | 15 | 20 | – | 16 | 28 | 22 | 7 | 6 | 7 |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 03/29/24 09:52 | 121.58 | 39.75 | 379 | 614 | – | 392 | 471 | 646 | 338 | 329 | 400 |
| 03/29/24 09:53 | 121.82 | 39.92 | 388 | 635 | – | 390 | 470 | 634 | 341 | 327 | 399 |
| – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 09/01/24 12:30 | 295.24 | −17.98 | 504 | 766 | – | 440 | 512 | 548 | 369 | 319 | 331 |
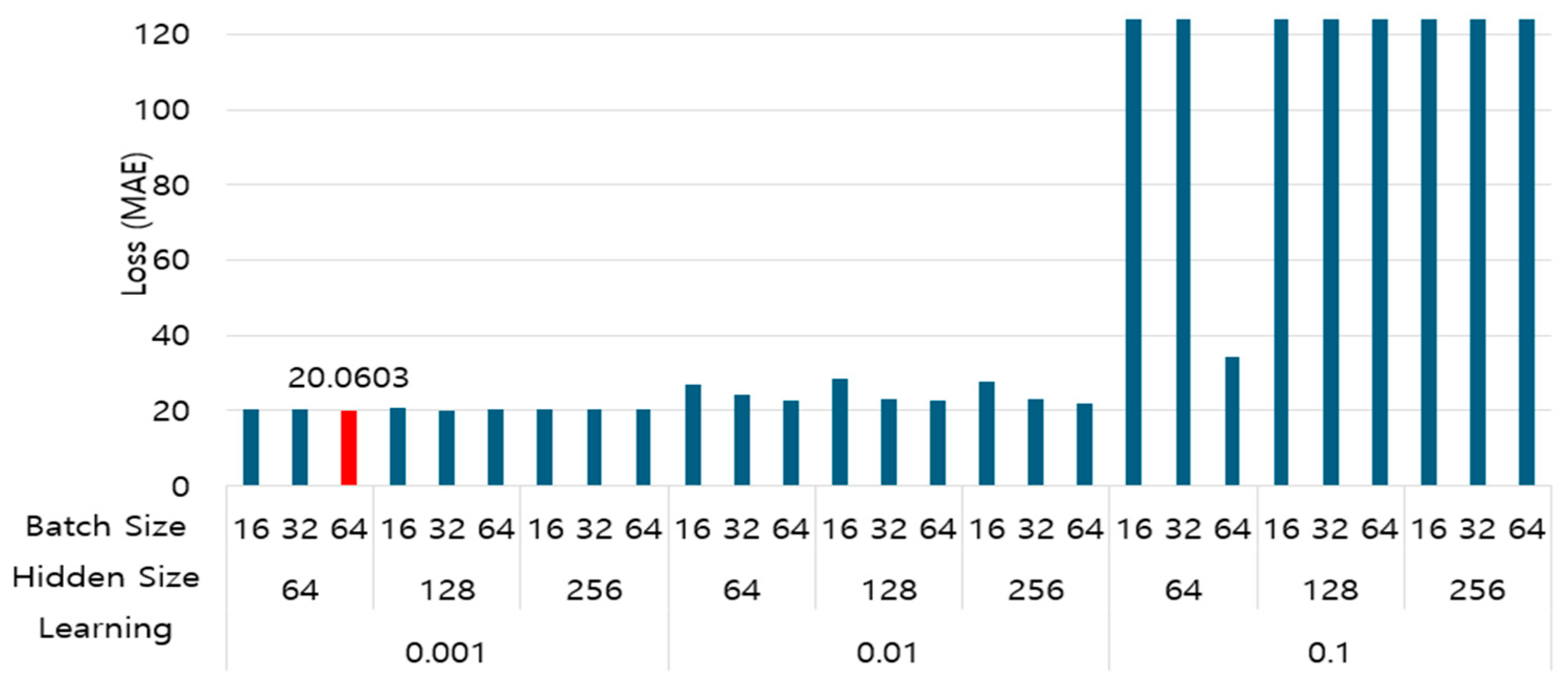
| Hyperparameter | Batch Size | Hidden Size | Learning Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Value | [16, 32, 64] | [64, 128, 256] | [0.1, 0.01, 0.001] |
| Category | Comparison of Calculated Results and Actual Measurements: Illuminance (Lux) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 9:00 | 12:00 | 15:00 | 18:00 | |||||||||
| Date | Position | Calculation | Measurement | Error | Calculation | Measurement | Error | Calculation | Measurement | Error | Calculation | Measurement | Error |
| 09/02/24 (cloudy day) | P1 | 63.9 | 57.6 | 6.3 | 553.7 | 593.6 | 39.9 | 575.4 | 451.6 | 123.8 | 71.8 | 89.5 | 17.7 |
| P3 | 59.6 | 71.5 | 11.9 | 595.1 | 493.9 | 101.2 | 363.5 | 355.3 | 8.1 | 61.5 | 54.1 | 7.4 | |
| P4 | 50.3 | 57.7 | 3.3 | 485.5 | 475.7 | 9.8 | 465 | 311.7 | 153.3 | 52.6 | 72.5 | 19.9 | |
| P5 | 57.7 | 62.7 | 5 | 582.8 | 565 | 17.8 | 431.2 | 372.1 | 59 | 58.6 | 73 | 14.4 | |
| – | |||||||||||||
| P12 | 31.5 | 34.6 | 3.1 | 317.6 | 256.6 | 61 | 220.3 | 188.5 | 31.8 | 31.1 | 30.6 | 0.5 | |
| MAE | 4.88 (MAPE: 9.43%) | 45.39 (MAPE: 12.56%) | 59.95 (MAPE: 21.36%) | 10.00 (MAPE: 16.63%) | |||||||||
| 06/09/24 (partly cloudy day) | P1 | 334.5 | 353.2 | 18.8 | 466.5 | 516.4 | 49.9 | 464.4 | 470.5 | 6.1 | 187.3 | 187.1 | 0.2 |
| P3 | 424.6 | 434.2 | 9.6 | 513.9 | 515.3 | 1.3 | 342.8 | 348.5 | 5.7 | 149.7 | 150.5 | 0.8 | |
| P4 | 285.8 | 357.1 | 0.1 | 393.2 | 419.2 | 26 | 365.7 | 366.6 | 0.9 | 151.7 | 143.2 | 8.6 | |
| P5 | 357.1 | 306 | 3.1 | 479.7 | 487.2 | 7.5 | 377.3 | 379.4 | 2.1 | 149 | 146 | 3 | |
| – | |||||||||||||
| P12 | 204.4 | 205.3 | 0.8 | 254.7 | 271.8 | 17.1 | 195.4 | 188.6 | 6.8 | 82.3 | 81.4 | 0.9 | |
| MAE | 5.07 (MAPE: 2.11%) | 15.21 (MAPE: 4.07%) | 5.44 (MAPE: 2.11%) | 2.65 (MAPE: 2.26%) | |||||||||
| 04/07/24 (clear day) | P1 | 294.9 | 294.5 | 0.4 | 750.2 | 732.5 | 17.7 | 728.3 | 739.4 | 11.1 | 146.0 | 143.9 | 2.0 |
| P3 | 434.6 | 447.2 | 12.6 | 836.5 | 837.0 | 0.5 | 434.9 | 426.5 | 8.4 | 112.7 | 109.2 | 3.6 | |
| P4 | 242.8 | 235.1 | 7.7 | 653.9 | 640.4 | 13.5 | 563.6 | 581.2 | 17.6 | 118.5 | 115.2 | 3.3 | |
| P5 | 320.6 | 306.0 | 14.7 | 814.4 | 803.9 | 10.4 | 528.6 | 519.4 | 9.2 | 111.9 | 111.6 | 0.4 | |
| – | |||||||||||||
| P12 | 194.4 | 200.8 | 6.4 | 441.1 | 452.5 | 11.4 | 268.4 | 268.1 | 0.3 | 58.5 | 58.7 | 0.2 | |
| MAE | 6.38 (MAPE: 2.69%) | 7.27 (MAPE: 1.44%) | 6.91 (MAPE: 2.07%) | 2.38 (MAPE: 1.89%) | |||||||||
| Time | 09:00 | 12:00 | 15:00 | 18:00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) Measurement |  |  | 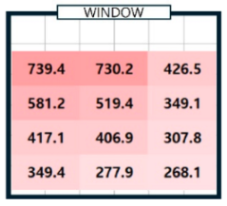 |  |
| (b) Calculation |  |  | 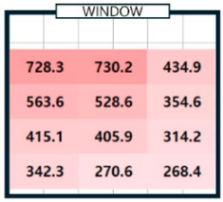 | 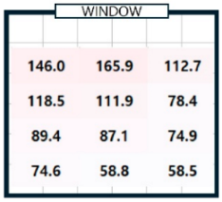 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, S.-T.; Lee, Y.-B.; Lim, J.-H. Method for Generating Real-Time Indoor Detailed Illuminance Maps Based on Deep Learning with a Single Sensor. Sensors 2025, 25, 5154. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165154
Oh S-T, Lee Y-B, Lim J-H. Method for Generating Real-Time Indoor Detailed Illuminance Maps Based on Deep Learning with a Single Sensor. Sensors. 2025; 25(16):5154. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165154
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Seung-Taek, You-Bin Lee, and Jae-Hyun Lim. 2025. "Method for Generating Real-Time Indoor Detailed Illuminance Maps Based on Deep Learning with a Single Sensor" Sensors 25, no. 16: 5154. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165154
APA StyleOh, S.-T., Lee, Y.-B., & Lim, J.-H. (2025). Method for Generating Real-Time Indoor Detailed Illuminance Maps Based on Deep Learning with a Single Sensor. Sensors, 25(16), 5154. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165154







