Validity of Body Composition Estimates in Women Assessed by a Multifrequency Bioelectrical Impedance Device
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Total Body Water by Deuterium Oxide Dilution Technique (D2O)
2.4. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
2.5. Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA)
2.6. Fat-Free Mass Hydration
2.7. Four-Compartment Model
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
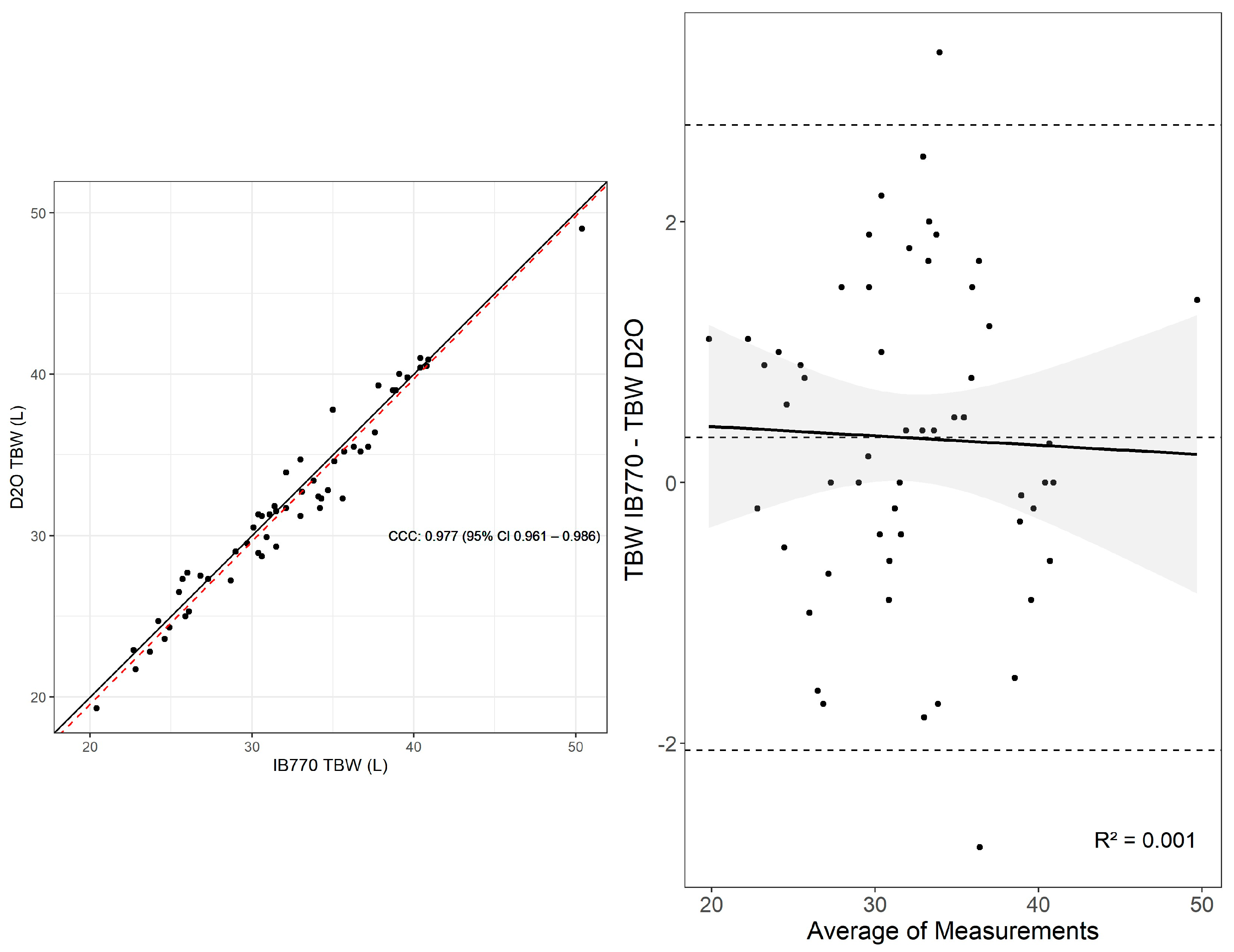
3.1. Total Body Water
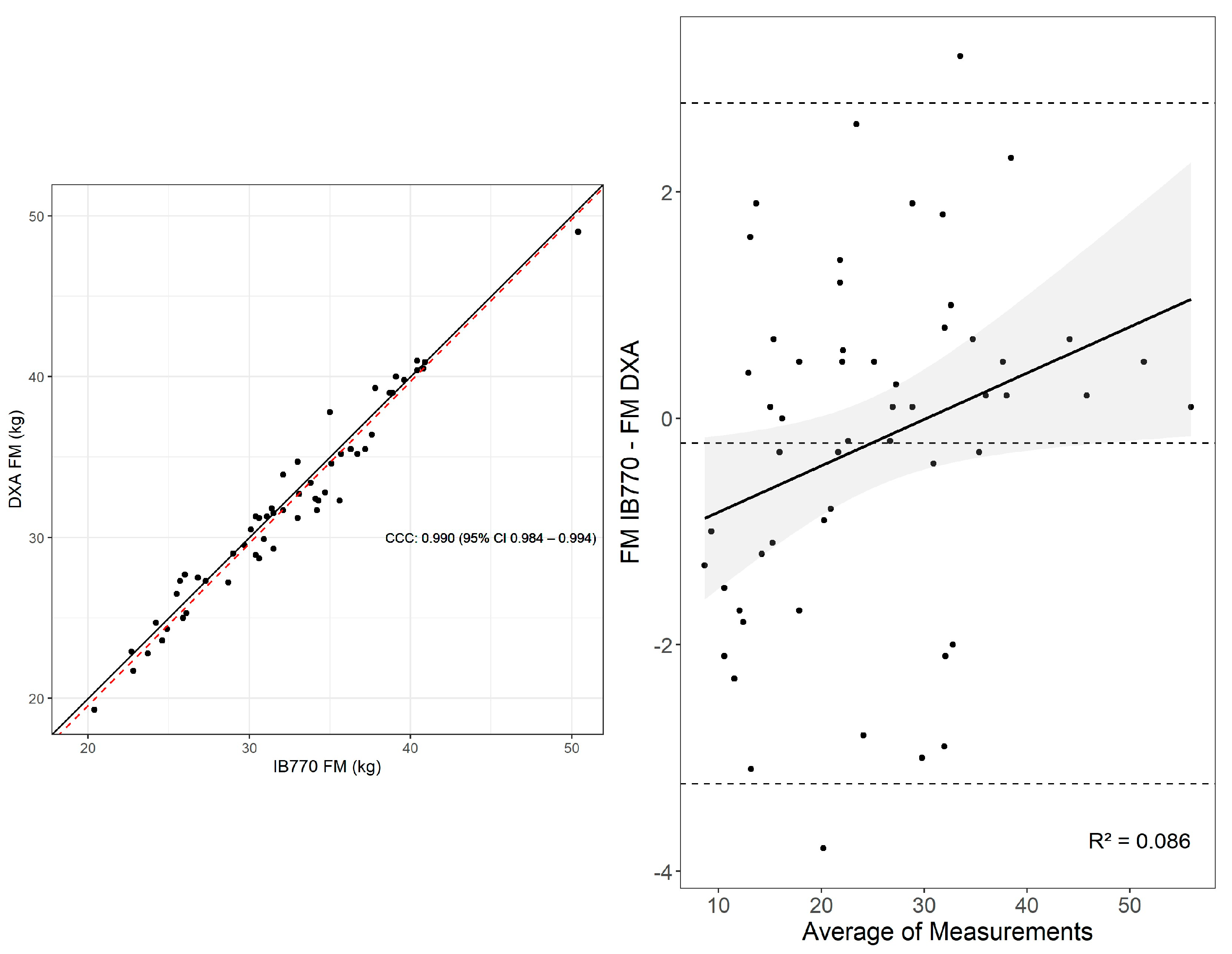
3.2. Fat Mass
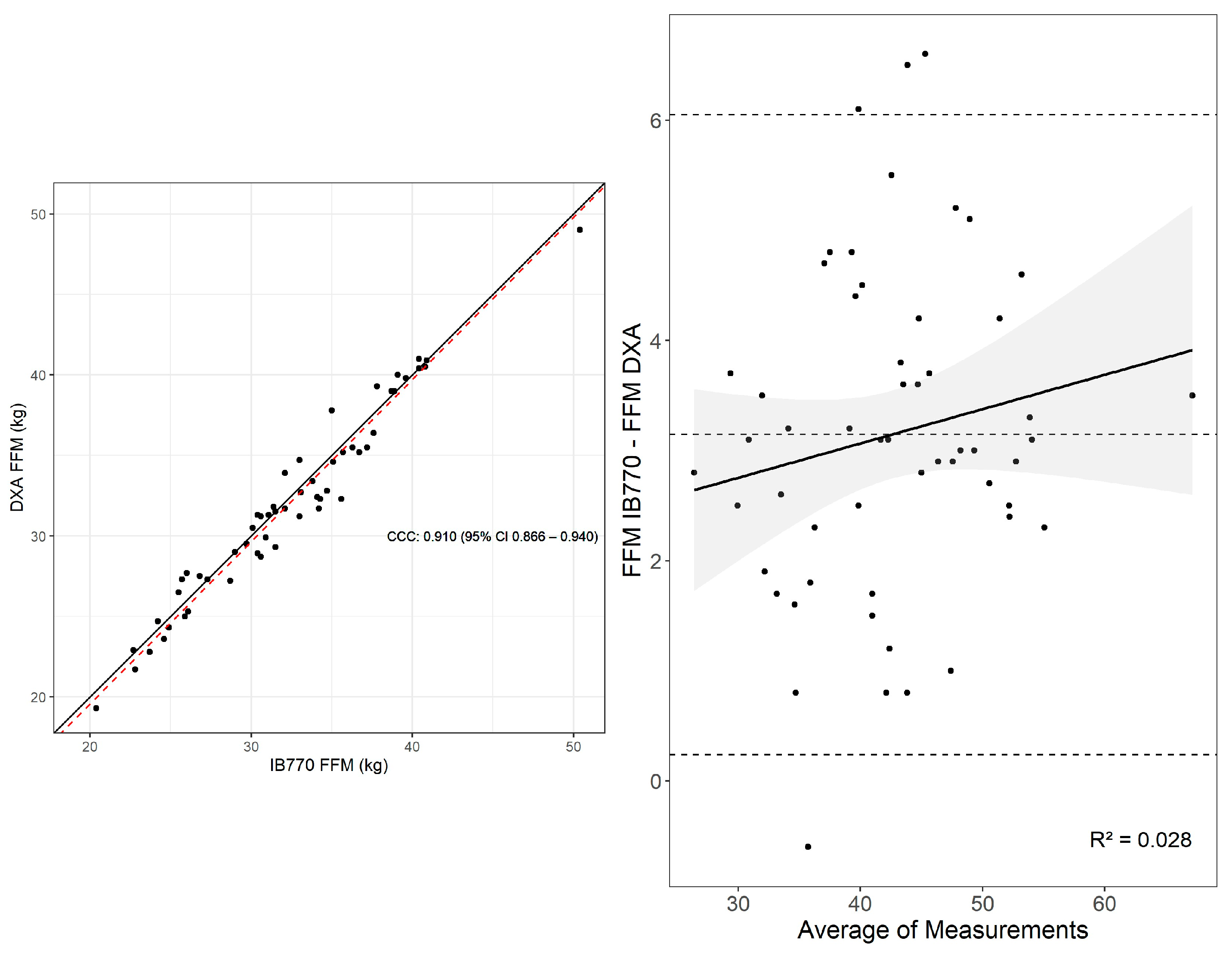
3.3. Fat-Free Mass
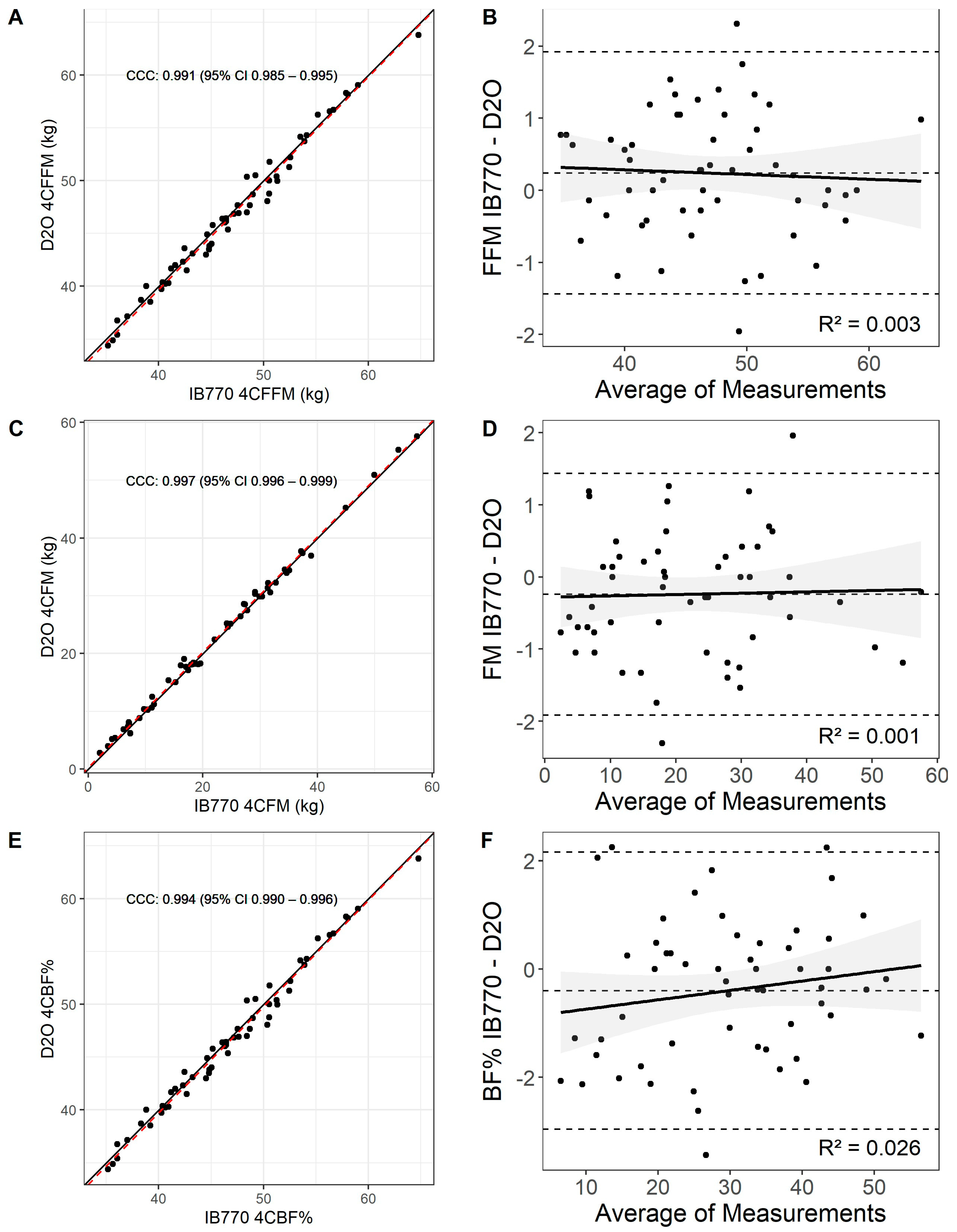
3.4. Four-Compartment Model with Inbody 770 vs. D2O
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IB770 | Inbody 770 |
| D2O | Deuterium oxide |
| TBW | Total body water |
| 4C | Four-compartment model |
| CCC | Lin’s concordance correlation coefficient |
| FM | Fat mass |
| FFM | Fat-free mass |
| BIA | Bioelectrical impedance |
| DXA | Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry |
| BV | Body Volume |
| BMC | Bone mineral content |
References
- Holmes, C.J.; Racette, S.B. The Utility of Body Composition Assessment in Nutrition and Clinical Practice: An Overview of Current Methodology. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, T.; Gallagher, D. Current Body Composition Measurement Techniques. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2017, 24, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.P.; Mulligan, K.; Fan, B.; Sherman, J.L.; Murphy, E.J.; Tai, V.W.; Powers, C.L.; Marquez, L.; Ruiz-Barros, V.; Shepherd, J.A. Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry–Based Body Volume Measurement for 4-Compartment Body Composition123. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golding, P.H. Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) to Measure Bone Mineral Density (BMD) for Diagnosis of Osteoporosis—Experimental Data from Artificial Vertebrae Confirms Significant Dependence on Bone Size. Bone Rep. 2022, 17, 101607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.; De Lucia Rolfe, E.; Sleigh, A.; Kivisild, T.; Behbehani, K.; Wareham, N.J.; Brage, S.; Mohammad, T. Validity of Visceral Adiposity Estimates from DXA against MRI in Kuwaiti Men and Women. Nutr. Diabetes 2017, 7, e238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glickman, S.G.; Marn, C.S.; Supiano, M.A.; Dengel, D.R. Validity and Reliability of Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry for the Assessment of Abdominal Adiposity. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 97, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith-Ryan, A.E.; Mock, M.G.; Ryan, E.D.; Gerstner, G.R.; Trexler, E.T.; Hirsch, K.R. Validity and Reliability of a 4-Compartment Body Composition Model Using Dual Energy x-Ray Absorptiometry-Derived Body Volume. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeller, D.A.; van Santen, E.; Peterson, D.W.; Dietz, W.; Jaspan, J.; Klein, P.D. Total Body Water Measurement in Humans with 18O and 2H Labeled Water. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1980, 33, 2686–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obuchowska, A.; Standyło, A.; Kimber-Trojnar, Ż.; Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B. The Possibility of Using Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Pregnant and Postpartum Women. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaski, H.C.; Johnson, P.E.; Bolonchuk, W.W.; Lykken, G.I. Assessment of Fat-Free Mass Using Bioelectrical Impedance Measurements of the Human Body. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1985, 41, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, U.G.; Bosaeus, I.; De Lorenzo, A.D.; Deurenberg, P.; Elia, M.; Gómez, J.M.; Heitmann, B.L.; Kent-Smith, L.; Melchior, J.-C.; Pirlich, M.; et al. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis--Part I: Review of Principles and Methods. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 1226–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.R. Body Composition in Athletes and Sports Nutrition: An Examination of the Bioimpedance Analysis Technique. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, S54–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widen, E.M.; Gallagher, D. Body Composition Changes in Pregnancy: Measurement, Predictors and Outcomes. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, G.J.; Blue, M.N.M.; Hirsch, K.R.; Saylor, H.E.; Gould, L.M.; Nelson, A.G.; Smith-Ryan, A.E. Validation of InBody 770 Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Compared to a Four-Compartment Model Criterion in Young Adults. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2021, 41, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Deurenberg, P.; Wang, W.; Pietrobelli, A.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Heymsfield, S.B. Hydration of Fat-Free Body Mass: New Physiological Modeling Approach. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, E995–E1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blue, M.N.M.; Tinsley, G.M.; Hirsch, K.R.; Ryan, E.D.; Ng, B.K.; Smith-Ryan, A.E. Validity of Total Body Water Measured by Multi-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Devices in a Multi-Ethnic Sample. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 54, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speakman, J.R.; Yamada, Y.; Sagayama, H.; Berman, E.S.F.; Ainslie, P.N.; Andersen, L.F.; Anderson, L.J.; Arab, L.; Baddou, I.; Bedu-Addo, K.; et al. A Standard Calculation Methodology for Human Doubly Labeled Water Studies. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Kotler, D.P.; Wielopolski, L.; Withers, R.T.; Pierson, R.N.; Heymsfield, S.B. Multicomponent Methods: Evaluation of New and Traditional Soft Tissue Mineral Models by in Vivo Neutron Activation Analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.I.-K. A Concordance Correlation Coefficient to Evaluate Reproducibility. Biometrics 1989, 45, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakens, D.; Scheel, A.M.; Isager, P.M. Equivalence Testing for Psychological Research: A Tutorial. Adv. Methods Pract. Psychol. Sci. 2018, 1, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, K.; Nakamura, H.; Kouda, K.; Fujita, Y.; Mase, T.; Momoi, K.; Nishiyama, T. Similarities and Discrepancies between Commercially Available Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis System and Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry for Body Composition Assessment in 10-14-Year-Old Children. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, G.M.; Park, K.-S.; Saenz, C.; Mehra, A.; Esco, M.R.; Czerwinski, S.A.; Nickerson, B.S. Deuterium Oxide Validation of Bioimpedance Total Body Water Estimates in Hispanic Adults. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1221774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SHAPIRO, S.S.; WILK, M.B. An Analysis of Variance Test for Normality (Complete Samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breusch, T.S.; Pagan, A.R. A Simple Test for Heteroscedasticity and Random Coefficient Variation. Econometrica 1979, 47, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistical Methods for Assessing Agreement between Two Methods of Clinical Measurement. Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, A.R. SimplyAgree: An R Package and Jamovi Module for Simplifying Agreement and Reliability Analyses. J. Open Source Softw. 2022, 7, 4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldi, D.; Bennett, J.P.; Quon, B.K.; Liu, Y.E.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Kelly, T.; Shepherd, J.A. Agreement and Precision of Deuterium Dilution for Total Body Water and Multicompartment Body Composition Assessment in Collegiate Athletes. J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 2048–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardena, R.; Wijetunga, W.M.U.A.; Ranasinghe, P.; Wanninayake, L.; Wickramasinghe, V.P. Assessment of Body Composition in Sri Lankan Adults: Development and Validation of Bioelectrical Impedance Prediction Equation. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartorio, A.; Malavolti, M.; Agosti, F.; Marinone, P.G.; Caiti, O.; Battistini, N.; Bedogni, G. Body Water Distribution in Severe Obesity and Its Assessment from Eight-Polar Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 59, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rush, E.C.; Plank, L.D.; Lubree, H.; Bhat, D.S.; Ganpule, A.; Yajnik, C.S. Gains in Body Mass and Body Water in Pregnancy and Relationships to Birth Weight of Offspring in Rural and Urban Pune, India. J. Nutr. Sci. 2022, 11, e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loan, M.D.; Kopp, L.E.; King, J.C.; Wong, W.W.; Mayclin, P.L. Fluid Changes during Pregnancy: Use of Bioimpedance Spectroscopy. J. Appl. Physiol. 1995, 78, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Most, J.; Marlatt, K.L.; Altazan, A.D.; Redman, L.M. Advances in Assessing Body Composition during Pregnancy. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, K.M.; Kafali, S.G.; Shih, S.-F.; Artura, A.M.; Masamed, R.; Elashoff, D.; Wu, H.H.; Calkins, K.L. Pregnancies Complicated by Gestational Diabetes and Fetal Growth Restriction: An Analysis of Maternal and Fetal Body Composition Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Perinatol. 2023, 43, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maw, G.J.; Mackenzie, I.L.; Taylor, N.A. Redistribution of Body Fluids during Postural Manipulations. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1995, 155, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLester, C.N.; Nickerson, B.S.; Kliszczewicz, B.M.; McLester, J.R. Reliability and Agreement of Various InBody Body Composition Analyzers as Compared to Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry in Healthy Men and Women. J. Clin. Densitom. 2020, 23, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonio, J.; Kenyon, M.; Ellerbroek, A.; Carson, C.; Tyler-Palmer, D.; Burgess, V.; Angeli, G.; Silver, T.; Jiannine, L.; Peacock, C. Body Composition Assessment: A Comparison of the Bod Pod, InBody 770, and DXA. J. Exerc. Nutr. 2019, 2, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Antonio, J.; Kenyon, M.; Ellerbroek, A.; Carson, C.; Burgess, V.; Tyler-Palmer, D.; Mike, J.; Roberts, J.; Angeli, G.; Peacock, C. Comparison of Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) Versus a Multi-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance (InBody 770) Device for Body Composition Assessment after a 4-Week Hypoenergetic Diet. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2019, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, A.W.; Nindl, L.J.; Soto, L.D.; Pazmino, A.; Looney, D.P.; Tharion, W.J.; Robinson-Espinosa, J.A.; Friedl, K.E. High Precision but Systematic Offset in a Standing Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) Compared with Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA). BMJ Nutr. Prev. Health 2022, 5, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahav, Y.; Goldstein, N.; Gepner, Y. Comparison of Body Composition Assessment across Body Mass Index Categories by Two Multifrequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Devices and Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry in Clinical Settings. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duren, D.L.; Sherwood, R.J.; Czerwinski, S.A.; Lee, M.; Choh, A.C.; Siervogel, R.M.; Chumlea, W.C. Body Composition Methods: Comparisons and Interpretation. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2008, 2, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumlea, W.C.; Schubert, C.M.; Sun, S.S.; Demerath, E.; Towne, B.; Siervogel, R.M. A Review of Body Water Status and the Effects of Age and Body Fatness in Children and Adults. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2007, 11, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tinsley, G.M.; Moore, M.L.; Rafi, Z.; Griffiths, N.; Harty, P.S.; Stratton, M.T.; Benavides, M.L.; Dellinger, J.R.; Adamson, B.T. Explaining Discrepancies Between Total and Segmental DXA and BIA Body Composition Estimates Using Bayesian Regression. J. Clin. Densitom. 2021, 24, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đorđević, S.; Hadzovic, M.; Lilic, A.; Jorgić, B.; Jelenković, L.; Stojiljković, N.; Katanic, B.; Stankovic, M. Effects of Non-Compliance with the Protocol on InBody 770 in Students of Different Training. Sport Mont 2024, 22, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiose, K.; Yamada, Y.; Motonaga, K.; Sagayama, H.; Higaki, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Takahashi, H. Segmental Extracellular and Intracellular Water Distribution and Muscle Glycogen after 72-h Carbohydrate Loading Using Spectroscopic Techniques. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 121, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch, A.; Ben-Yehuda, A.; Rouach, V.; Maier, A.B.; Greenman, Y.; Izkhakov, E.; Stern, N.; Eldor, R. Validation of a Multi-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Device for the Assessment of Body Composition in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. Nutr. Diabetes 2022, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, R.T.; Ebbert, J.O.; Croghan, I.; Nanda, S.; Schroeder, D.R.; Teigen, L.M.; Velapati, S.R.; Mundi, M.S. The Comparison of Segmental Multifrequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis and Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry for Estimating Fat Free Mass and Percentage Body Fat in an Ambulatory Population. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2021, 45, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, G.M.; Harty, P.S.; Stratton, M.T.; Smith, R.W.; Rodriguez, C.; Siedler, M.R. Tracking Changes in Body Composition: Comparison of Methods and Influence of Pre-Assessment Standardisation. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 127, 1656–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellakis, S.; Skoufas, E.; Simitsopoulou, E.; Migdanis, A.; Migdanis, I.; Prelorentzou, T.; Louka, A.; Moschonis, G.; Bountouvi, E.; Androutsos, O. Changes in Body Weight and Body Composition during the Menstrual Cycle. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2023, 35, e23951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuikman, M.A.; McKay, A.K.A.; Minahan, C.; Harris, R.; Elliott-Sale, K.J.; Stellingwerff, T.; Smith, E.S.; McCormick, R.; Tee, N.; Skinner, J.; et al. Effect of Menstrual Cycle Phase and Hormonal Contraceptives on Resting Metabolic Rate and Body Composition. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2024, 34, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, L.E.; Muñoz, C.X.; Armstrong, E.M. Distinguishing Low and High Water Consumers-A Paradigm of Disease Risk. Nutrients 2020, 12, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleck, S.J.; Hayes, A.; Stadler, G.; Goesch, T.; Goldammer, M.; Braun, S. Urine Specific Gravity Effect on Total and Segmental Body Composition Validity of Multifrequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Compared With Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2021, 35, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.-J.; Zhong, W.-H.; Liu, Y.-X.; Miao, H.-Z.; Li, Y.-C.; Ji, M.-H. Sample Size for Assessing Agreement between Two Methods of Measurement by Bland−Altman Method. Int. J. Biostat. 2016, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 4C Model with D2O | 4C Model with IB770 | |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Mass (kg) | 22.28 ± 13.24 | 22.04 ± 13.26 |
| Fat-Free Mass (kg) | 46.63 ± 6.71 | 46.87 ± 6.66 |
| Body Fat % | 29.87 ± 12.16 | 29.47 ± 12.37 |
| TBW (L) | 31.89 ± 5.91 | 32.24 ± 5.87 |
| FFM Hydration | 0.68 ± 0.05 | 0.68 ± 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaplatosch, M.E.; Meireles, J.F.; Amason, J.S.; Dabeer, S.; Kliszczewicz, B.M.; Mangine, G.T.; Barry, V.G.; Gower, B.A.; Ingram, K.H. Validity of Body Composition Estimates in Women Assessed by a Multifrequency Bioelectrical Impedance Device. Sensors 2025, 25, 5037. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165037
Zaplatosch ME, Meireles JF, Amason JS, Dabeer S, Kliszczewicz BM, Mangine GT, Barry VG, Gower BA, Ingram KH. Validity of Body Composition Estimates in Women Assessed by a Multifrequency Bioelectrical Impedance Device. Sensors. 2025; 25(16):5037. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165037
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaplatosch, Mitchell E., Juliana F. Meireles, Janeen S. Amason, Sadaf Dabeer, Brian M. Kliszczewicz, Gerald T. Mangine, Valene G. Barry, Barbara A. Gower, and Katherine H. Ingram. 2025. "Validity of Body Composition Estimates in Women Assessed by a Multifrequency Bioelectrical Impedance Device" Sensors 25, no. 16: 5037. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165037
APA StyleZaplatosch, M. E., Meireles, J. F., Amason, J. S., Dabeer, S., Kliszczewicz, B. M., Mangine, G. T., Barry, V. G., Gower, B. A., & Ingram, K. H. (2025). Validity of Body Composition Estimates in Women Assessed by a Multifrequency Bioelectrical Impedance Device. Sensors, 25(16), 5037. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165037









