FBStrNet: Automatic Fetal Brain Structure Detection in Early Pregnancy Ultrasound Images
Abstract
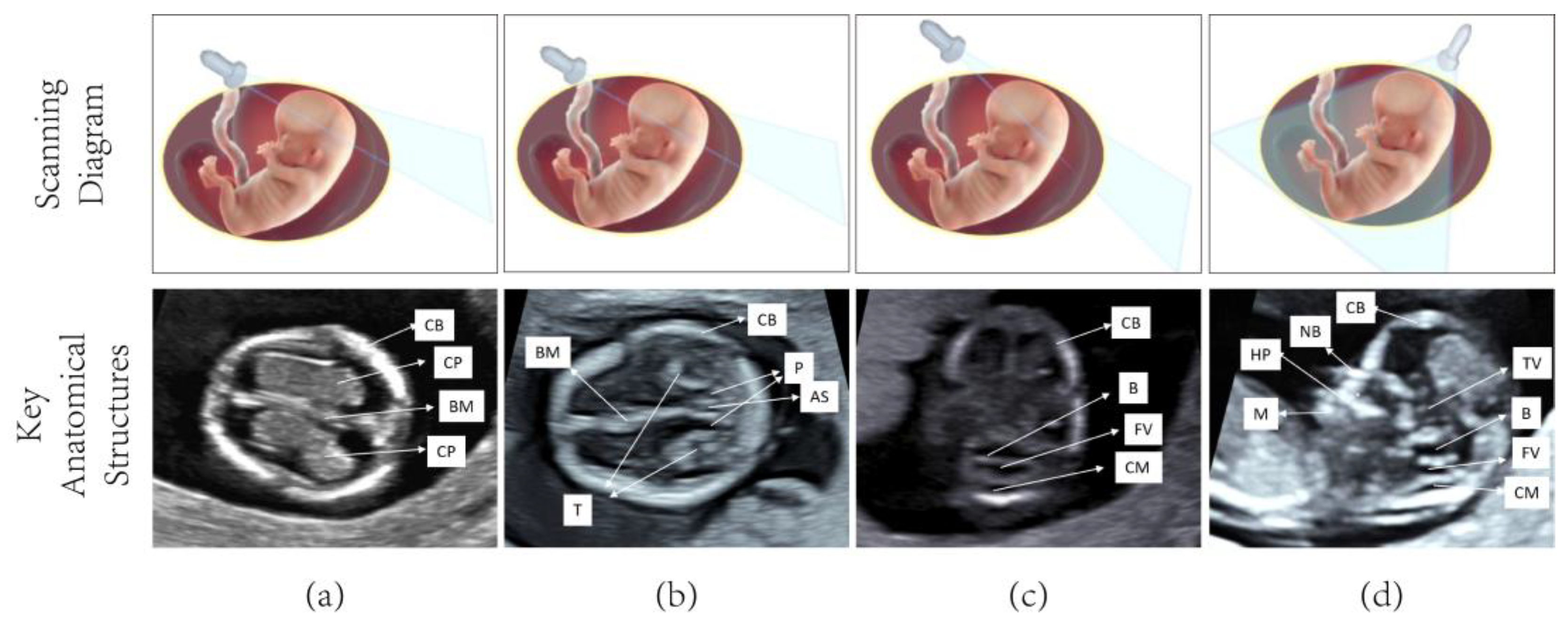
1. Introduction
- (1)
- This study addresses the challenge of automatic detection of KASs in FBUS images through FBStrNet, an innovative multi-task deep learning framework.
- (2)
- By integrating YOLOv5 with a feature fusion strategy, FBStrNet achieves unprecedented precision in detecting 12 critical anatomical structures, significantly improving both detection accuracy and computational efficiency.
- (3)
- Experimental results demonstrate the model’s exceptional robustness under low signal-to-noise ratio conditions, making it a valuable assistive tool for sonographers to identify key structures in real-time, thereby enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of fetal brain development assessments.
2. Related Work
3. Methodology
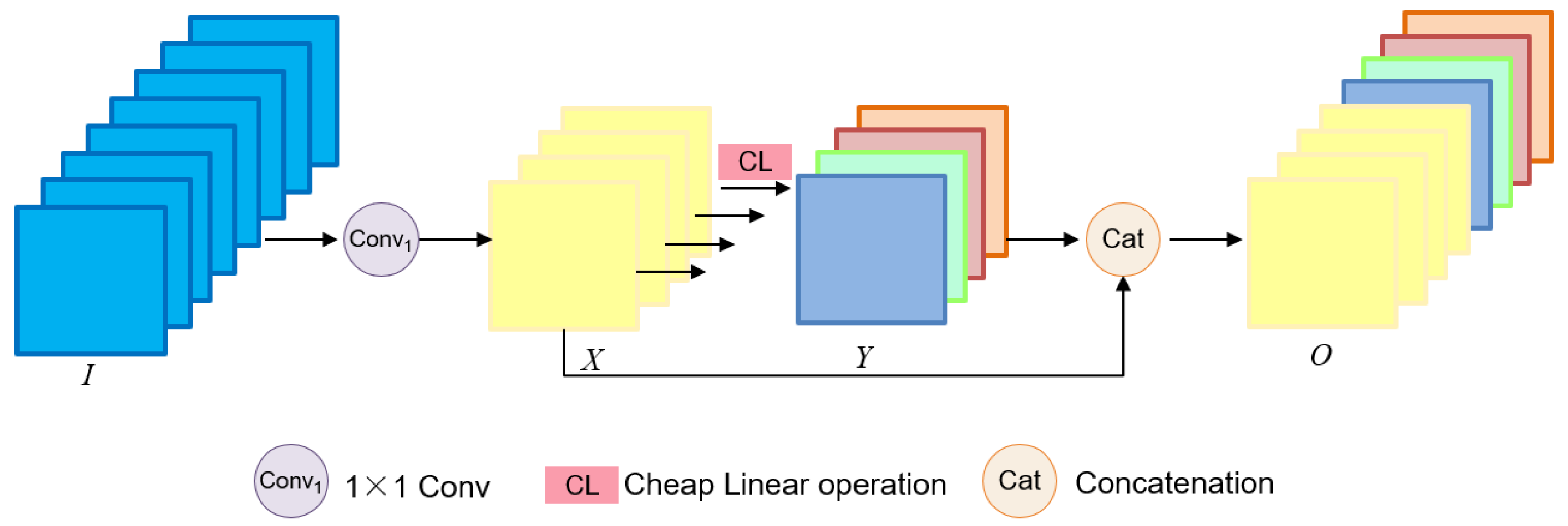
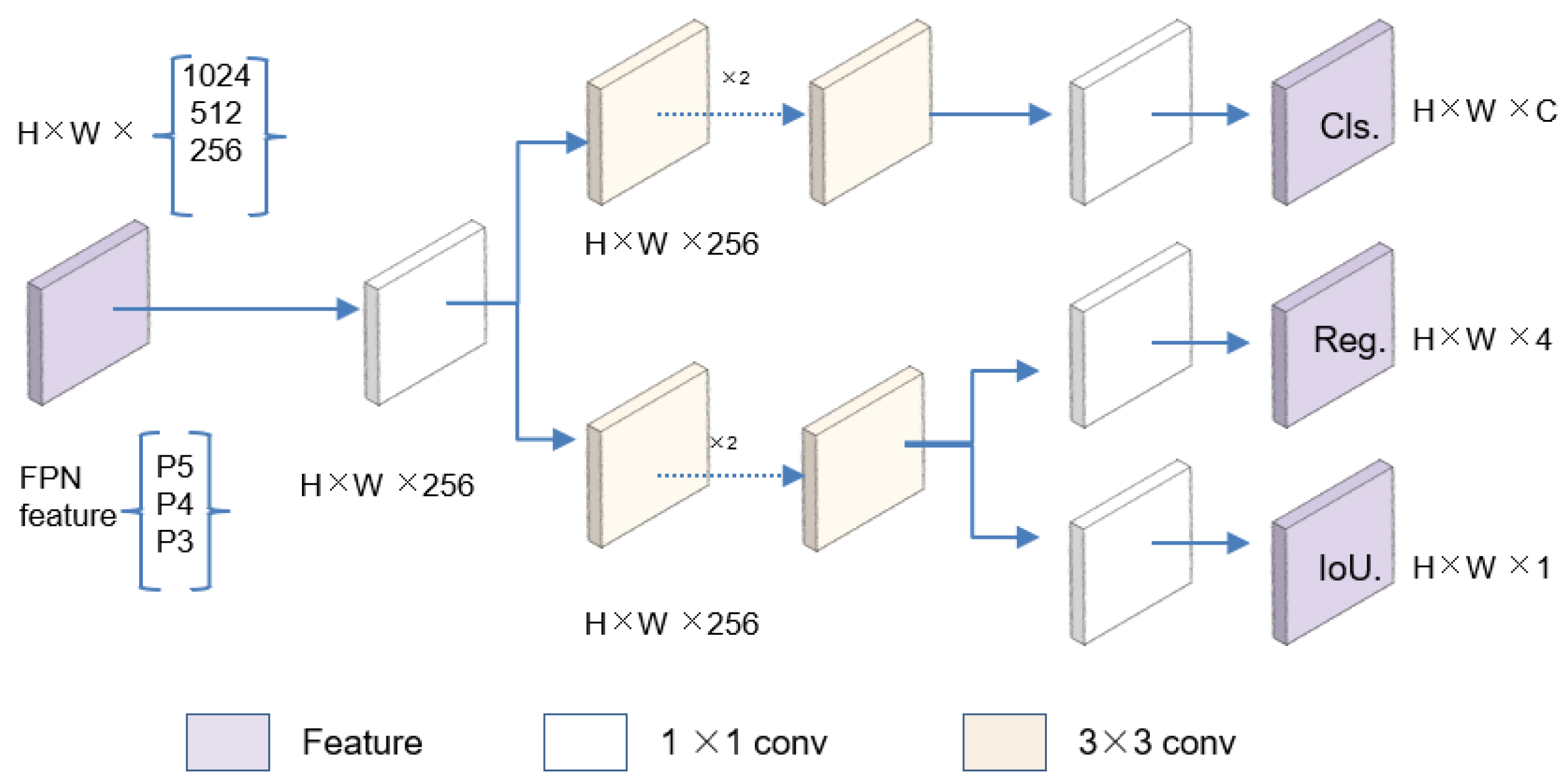
3.1. Model Framework
3.2. Loss Function
3.3. Target Filter
| Algorithm 1. An algorithm for filtering and sorting object detection results. |
| Require: Res, P_Objs Ensure: Filtered_Res ← None, Best_Conf_Res ← None, Res_cp ← None, Top_cp ← None, Res_now ← None. 1: Step 1: Filter_results based on P_Objs 2: for result in Res do 3: if result matches criteria defined by P_Objs then 4: Filtered_Res ← Filtered_Res ∪ {result} 5: end if 6: end for 7: Step 2: Retain results with conf > 0.5 and best per class 8: for each result in Filtered_Res do 9: if result.conf > 0.5 then 10: Best_Class_Res[result.class] ← Update with result ▷ Keep the best result per class 11: end if 12: end for 13: Step 3: Retain top 2 results with the highest confidence for TLVAP with 2 CPs 14: if ”CP” in Res then 15: Res_cp ← FilterResultsByNameCP(Res) 16: Top_cp ← GetTopTwoByConfidence(Res_cp) 17: end if 18: Step 4: Sort, screen and rank the results 19: Res now ← ConcatenateAndRemoveDuplicates(Best_Class_Ress, Top_cp) 20: Res_now ← SortByAscending(Res_now, ’class’) 21: return Res_now |
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
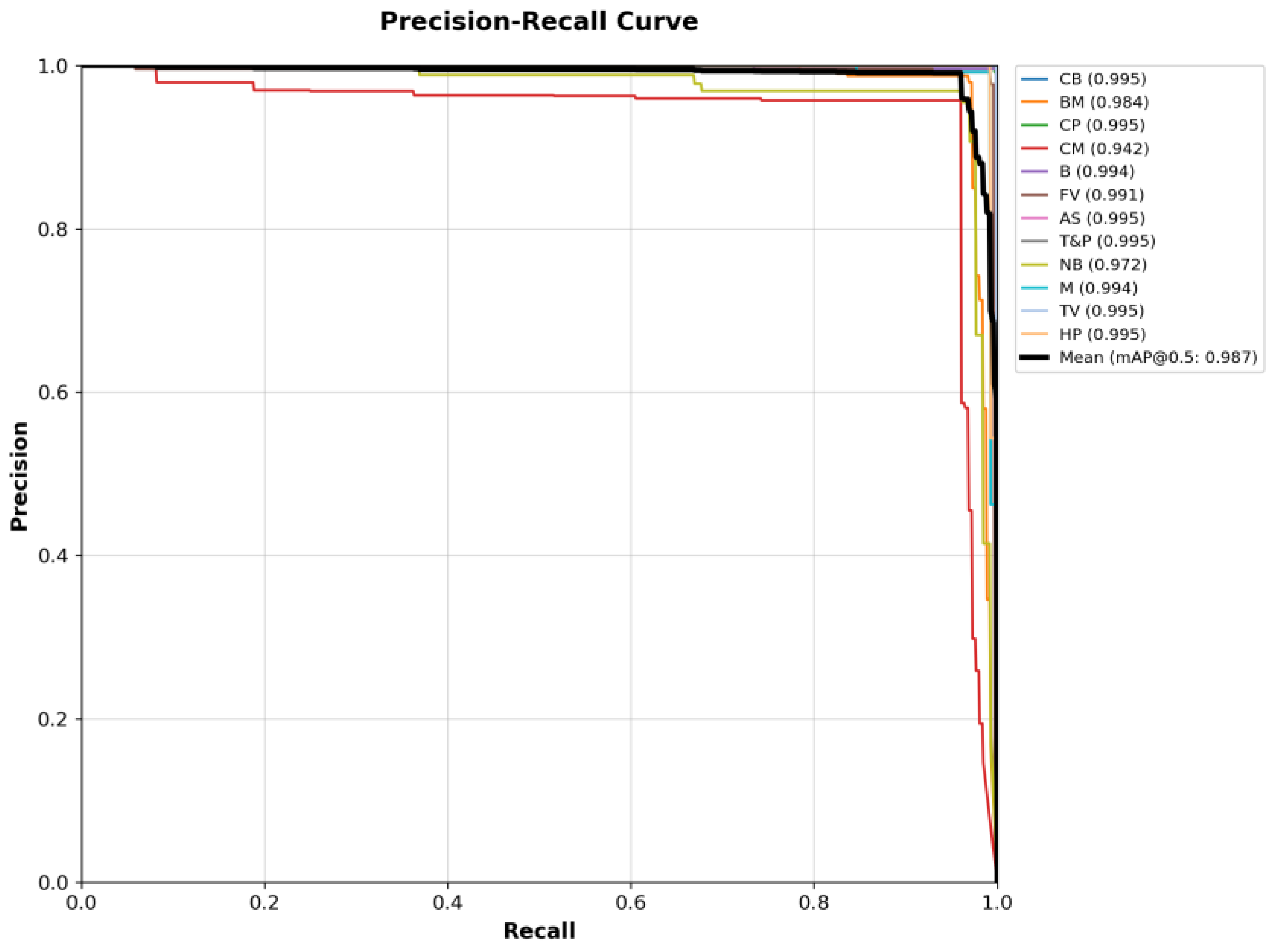
4.3. Experiment Results
4.3.1. Detection Results
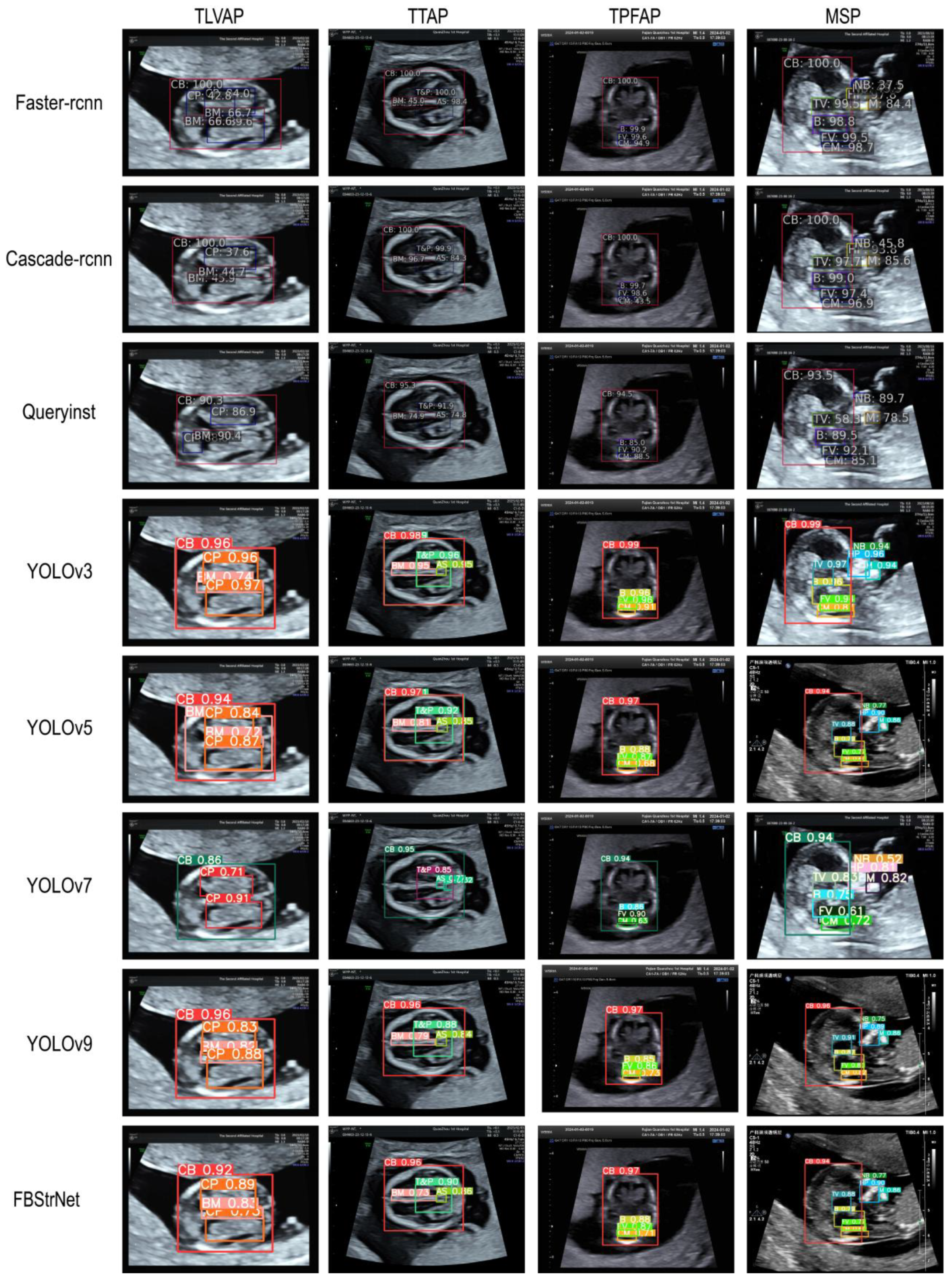
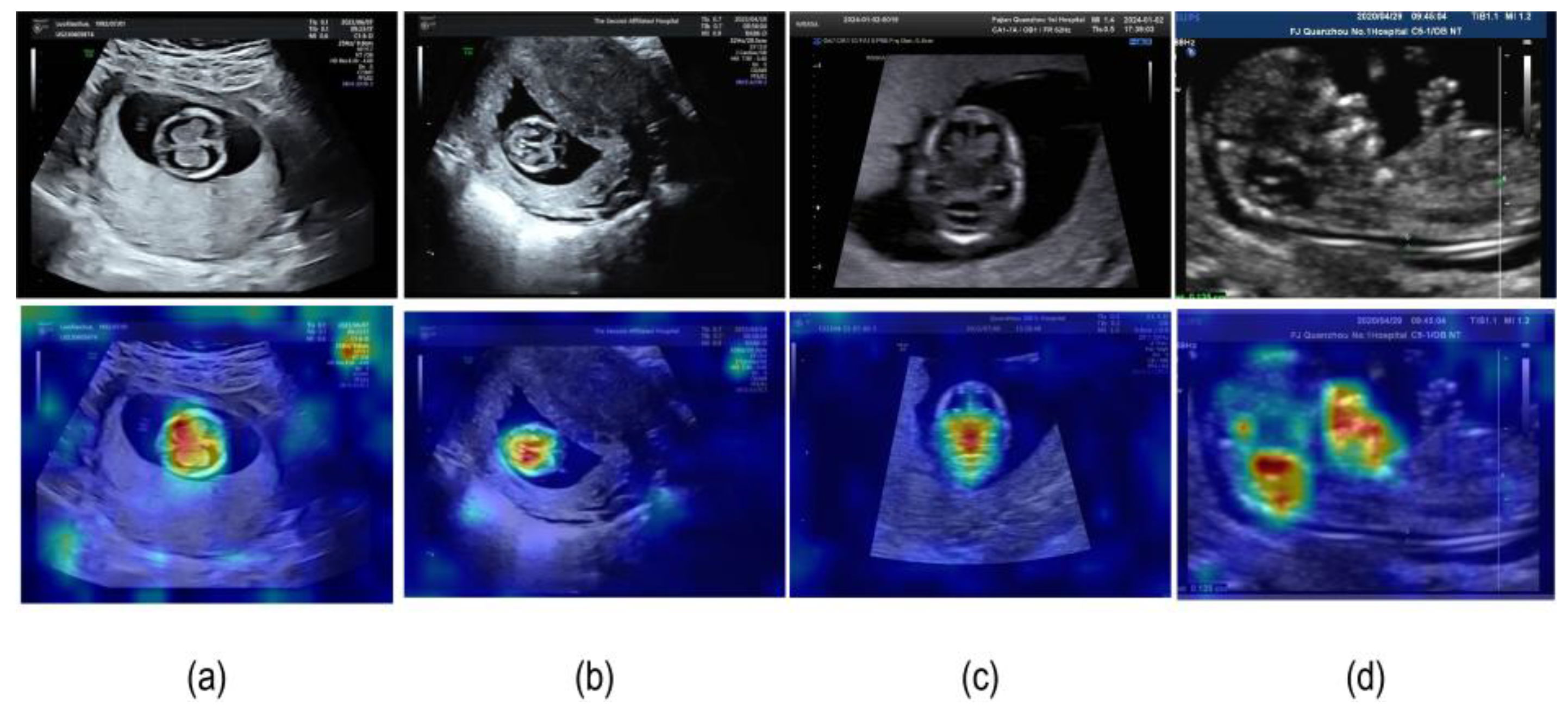
4.3.2. Model Visualization Results
4.4. Ablation Experiments
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yasrab, R.; Fu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Lee, L.H.; Sharma, H.; Drukker, L.; Papageorgiou, A.T.; Noble, J.A. A Machine Learning Method for Automated Description and Workflow Analysis of First Trimester Ultrasound Scans. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2023, 42, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilardo, C.M.; Chaoui, R.; Hyett, J.A.; Kagan, K.O.; Karim, J.N.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; Poon, L.C.; Salomon, L.J.; Syngelaki, A.; Nicolaides, K.H. ISUOG Practice Guidelines (updated): Performance of 11–14-week ultrasound scan. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 61, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, K.M.; Tugarinov, N.; Lechmann, G.; Abi Habib, P.; Cagliyan, E.; Goetzinger, K.R.; Turan, O.M.; Turan, S. The value of detailed first-trimester ultrasound in the era of noninvasive prenatal testing. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 229, 326.e1–326.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Wang, L.; Shang, N.; Hu, X.; He, B.; Liu, X.; Xiang, G.; Zhong, W. Ultrasound measurements of fetal facial profile markers and their associations with congenital malformations during early pregnancy. BMC Pregnancy Childb. 2023, 23, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqub, M.; Kelly, B.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; Noble, J.A. A Deep Learning Solution for Automatic Fetal Neurosonographic Diagnostic Plane Verification Using Clinical Standard Constraints. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 2925–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Lei, T.; Wang, N.; Cai, H.; Xian, J.; He, M.; Zhang, L.; Xie, H. Computer-aided diagnosis for fetal brain ultrasound images using deep convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. 2020, 15, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Yuan, L.; Li, P.; Liu, P. Real-Time Automatic Assisted Detection of Uterine Fibroid in Ultrasound Images Using a Deep Learning Detector. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2023, 49, 1616–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Liu, S.; He, S.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, G.; Liu, P. TUSPM-NET: A multi-task model for thyroid ultrasound standard plane recognition and detection of key anatomical structures of the thyroid. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 163, 107069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L. MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.04381v4. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNetV2: Smaller Models and Faster Training. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.00298. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Li, S.; Ni, D.; Liao, Y.; Wen, H.; Du, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, T.; Lei, B. Multi-task learning for quality assessment of fetal head ultrasound images. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 58, 101548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Luo, H.; Li, K. Automatic quality assessment for 2D fetal sonographic standard plane based on multitask learning. Medicine 2021, 100, e24427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, B.; Li, K.; Li, S.; Zhu, N. Automatic Fetal Ultrasound Standard Plane Recognition Based on Deep Learning and IIoT. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 7771–7780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gofer, S.; Haik, O.; Bardin, R.; Gilboa, Y.; Perlman, S. Machine Learning Algorithms for Classification of First-Trimester Fetal Brain Ultrasound Images. J. Ultras. Med. 2022, 41, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Tan, G.; Wu, F.; Wen, H.; Li, K. Fetal Ultrasound Standard Plane Detection with Coarse-to-Fine Multi-Task Learning. IEEE J. Biomed. Health 2023, 27, 5023–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Yu, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, C.; Zhou, H.; Qiu, C.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Peng, M.; Zhu, G.; et al. Artificial intelligence assistance for fetal development: Evaluation of an automated software for biometry measurements in the mid-trimester. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2024, 24, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Mahmud, M.; Yovera, L. Classification of First Trimester Ultrasound Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network. In Communications in Computer and Information Science; Joaquim, F., Ashish, G., Prates, R.O., Zhou, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 1435, pp. 92–105. [Google Scholar]
- Ryou, H.; Yaqub, M.; Cavallaro, A.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; Noble, J.A. Automated 3-D Ultrasound Image Analysis for First Trimester Assessment of Fetal Health. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 185010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C. GhostNet: More Features from Cheap Operations. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1577–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO Series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Su, X.; Wu, W. Lightweight detection networks for tea bud on complex agricultural environment via improved YOLO v4. Comput. Electron. Agr. 2023, 211, 107955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevorgyan, Z. SIoU Loss: More Powerful Learning for Bounding Box Regression. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.12740. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Li, C.; Guo, H. A lightweight face-assisted object detection model for welding helmet use. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2023, 221, 119764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.M. YOLOv7: Trainable Bag-of-Freebies Sets New State-of-the-Art for Real-Time Object Detectors. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Yeh, I.; Liao, H. YOLOv9: Learning What You Want to Learn Using Programmable Gradient Information. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.13616. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving into High Quality Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6154–6162. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Fang, C.; Shan, Y.; Feng, B.; Liu, W. Instances as Queries. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 6890–6899. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.N.; Wang, N.; He, M.; Zhang, L.H.; Cai, H.M.; Xian, J.B.; Lin, M.F.; Zheng, J.; Yang, Y.Z. Using deep-learning algorithms to classify fetal brain ultrasound images as normal or abnormal. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 56, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Xu, G.; Ding, C.; Jia, W.; Sun, M. Standard Plane Identification in Fetal Brain Ultrasound Scans Using a Differential Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 83821–83830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, T.B.; Kokil, P. Standard fetal ultrasound plane classification based on stacked ensemble of deep learning models. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 122153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka, S.; Włodarczyk, T.; Klasa, A.; Lipa, M.; Sitek, A.; Trzciński, T. FetalNet: Multi-task deep learning framework for fetal ultrasound biometric measurements. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.06943. [Google Scholar]
- Coronado-Gutiérrez, D.; Eixarch, E.; Monterde, E.; Matas, I.; Traversi, P.; Gratacós, E.; Bonet-Carne, E.; Burgos-Artizzu, X.P. Automatic Deep Learning-Based Pipeline for Automatic Delineation and Measurement of Fetal Brain Structures in Routine Mid-Trimester Ultrasound Images. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2023, 50, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Xu, G.; Ding, C.; Jia, W.; Sun, M. Deep Learning-Based Methodology for Recognition of Fetal Brain Standard Scan Planes in 2D Ultrasound Images. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 44443–44451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Train | Test | |
|---|---|---|
| CB | 2518 | 1866 |
| BM | 1251 | 1010 |
| CP | 1266 | 938 |
| CM | 1267 | 856 |
| B | 1267 | 856 |
| FV | 1267 | 856 |
| AS | 618 | 539 |
| T&P | 618 | 539 |
| NB | 649 | 317 |
| M | 649 | 317 |
| TV | 649 | 347 |
| HP | 649 | 347 |
| Model | Precision | Recall | mAP@0.5 | mAP@0.5:0.95 | Parameters (M) | Times (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv3 | 98.6% | 98.6% | 98.3% | 66.4% | 61.5 | 30.9 |
| YOLOv5-n | 98.7% | 98.5% | 98.3% | 65.8% | 1.8 | 8.4 |
| YOLOv5-s | 98.2% | 97.4% | 98.3% | 64.2% | 7.0 | 11.2 |
| YOLOv7 | 94.8% | 95.1% | 96.4% | 56.5% | 36.5 | 65.4 |
| YOLOv7-x | 95.5% | 96.6% | 96.8% | 58.3% | 70.9 | 53.1 |
| YOLOv9-c | 98.3% | 98.5% | 98.8% | 69.0% | 60.8 | 58.5 |
| YOLOv9-e | 98.2% | 98.3% | 98.5% | 69.3% | 69.5 | 62.4 |
| Faster R-CNN | - | - | 91.4% | 57.8% | 41.4 | 56.1 |
| Cascade R-CNN | - | - | 92.0% | 59.8% | 69.4 | 74.5 |
| QueryInst | - | - | 96.1% | 65.9% | 172.5 | 121.0 |
| FBStrNet (Ours) | 98.6% (+0.3%) | 98.5% | 98.7% | 64.3% | 6.9 | 11.5 |
| Ghost | SIoU | Decoupled_Detect | mAP@0.5 | mAP@0.5:0.95 | Parameters (M) | Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline(YOLOv5-s, CIoU) | × | × | 98.3% | 64.2% | 7.0 | 9.8 |
| √ | × | × | 98.4% | 64.6% | 5.1 | 10.0 |
| × | √ | × | 98.9% | 65.6% | 7.0 | 9.8 |
| × | × | √ | 98.8% | 66.4% | 8.8 | 11.6 |
| √ | √ | × | 98.5% | 63.1% | 5.1 | 10.0 |
| √ | × | √ | 98.2% | 64.4% | 6.9 | 11.3 |
| √ | √ | √ | 98.7% | 64.3% | 6.8 | 11.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Liu, P.; Guo, X. FBStrNet: Automatic Fetal Brain Structure Detection in Early Pregnancy Ultrasound Images. Sensors 2025, 25, 5034. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165034
Lin Y, Liu S, Liu Z, Fan Y, Liu P, Guo X. FBStrNet: Automatic Fetal Brain Structure Detection in Early Pregnancy Ultrasound Images. Sensors. 2025; 25(16):5034. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165034
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yirong, Shunlan Liu, Zhonghua Liu, Yuling Fan, Peizhong Liu, and Xu Guo. 2025. "FBStrNet: Automatic Fetal Brain Structure Detection in Early Pregnancy Ultrasound Images" Sensors 25, no. 16: 5034. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165034
APA StyleLin, Y., Liu, S., Liu, Z., Fan, Y., Liu, P., & Guo, X. (2025). FBStrNet: Automatic Fetal Brain Structure Detection in Early Pregnancy Ultrasound Images. Sensors, 25(16), 5034. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25165034






