Foot Strike Pattern Detection Using a Loadsol® Sensor Insole
Abstract
Highlights
- Foot strike pattern detection using the loadsol® sensor insole method achieved high detection accuracy for rearfoot (94.7%) and forefoot (81.8%) strikes compared to a traditional kinematic approach.
- Runners exhibited mixed foot strike patterns, even at constant treadmill speeds, highlighting individual variability in running biomechanics.
- The loadsol® sensor insole shows potential for field-based, step-to-step monitoring of FSP and impact forces, aiding injury prevention and performance analysis.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
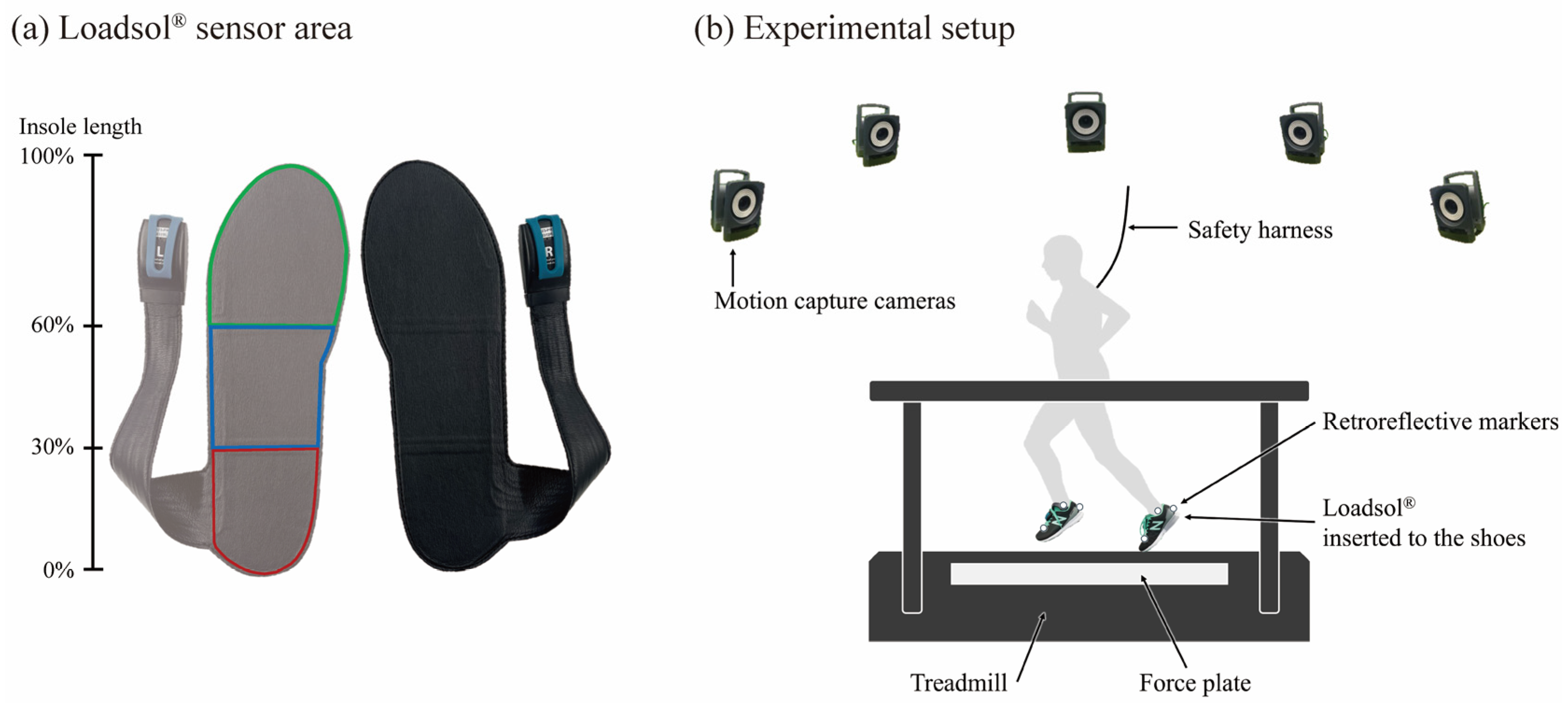
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Procedures
2.3. Data Analysis
- FSPFSA: The foot strike angle (FSA) at the initial foot contact during running was calculated as the angle between the vector from the heel to the metatarsophalangeal markers and Y-axis of the global coordinate system. FSA at initial foot contact was subtracted from the value in the static position [3]. According to a previous study [3], FSPFSA was determined as FFS, MFS, and RFS when FSA < 1.68°, 1.68° < FSA < 8.08°, and 8.08° < FSA, respectively.
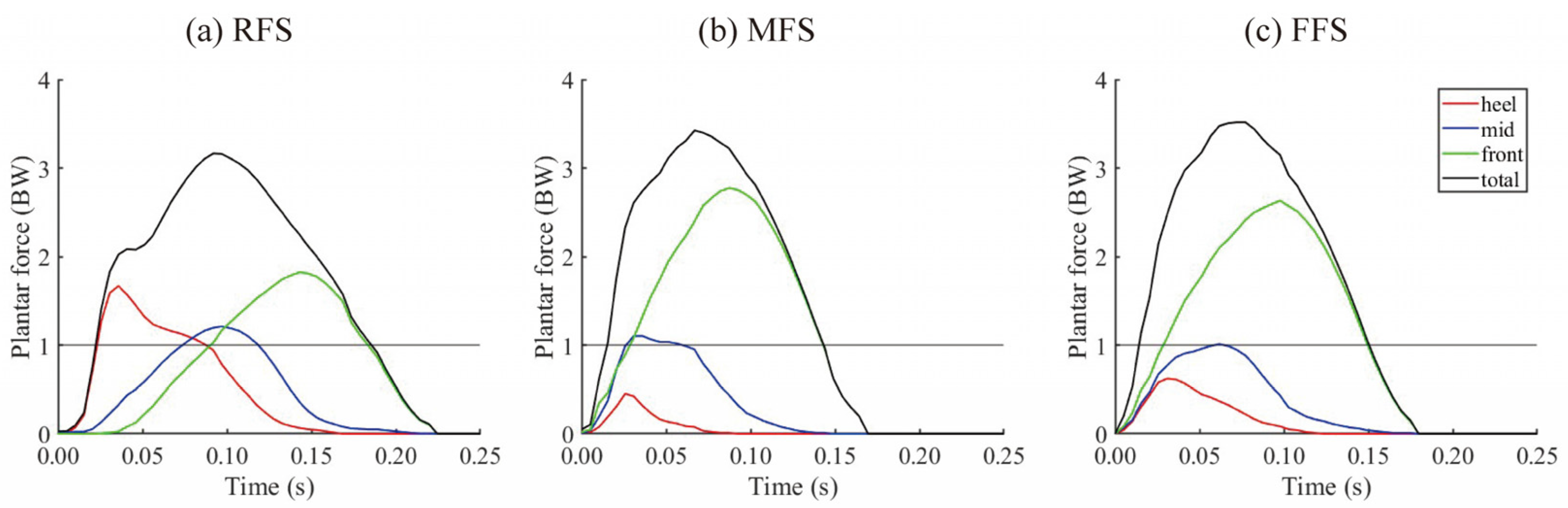
- FSPloadsol: Loadsol® could not measure the center of pressure owing to the limited number of pressure sensors. However, the FSP could be determined by the three pressure sensors in the rear-, mid-, and forefoot areas of the insole. FSPloadsol was defined as RFS, MFS, and FFS when the plantar force exceeded the body weight first in the heel, midfoot, or forefoot area during the first half of the stance phase, respectively.
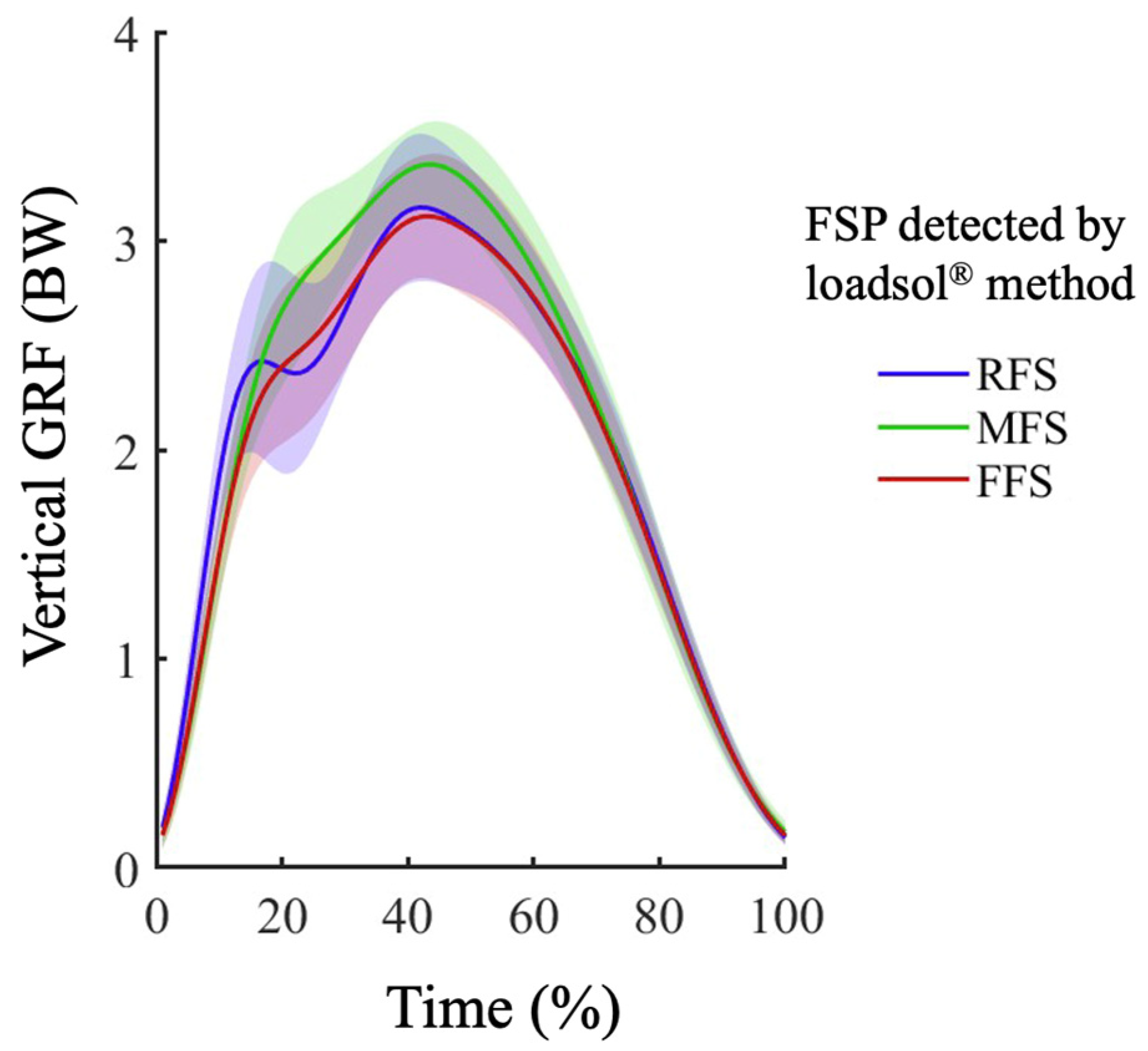
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FSP | Foot strike pattern |
| RFS | Rearfoot strike |
| MFS | Midfoot strike |
| FFS | Forefoot strike |
| GRF | Ground reaction force |
| FSPFSA | Foot strike pattern determined by foot strike angle |
| FSPloadsol | Foot strike pattern determined by loadsol® data |
Appendix A
References
- Lieberman, D.E.; Venkadesan, M.; Werbel, W.A.; Daoud, A.I.; D’andrea, S.; Davis, I.S.; Mang’eni, R.O.; Pitsiladis, Y. Foot Strike Patterns and Collision Forces in Habitually Barefoot versus Shod Runners. Nature 2010, 463, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, H.; Yamauchi, T.; Kraemer, W.J. Foot Strike Patterns of Runners at the 15-Km Point during an Elite-Level Half Marathon. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2007, 21, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, A.R.; Davis, I.S. A Kinematic Method for Footstrike Pattern Detection in Barefoot and Shod Runners. Gait Posture 2012, 35, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavanagh, P.R.; Lafortune, M.A. Ground Reaction Forces in Distance Running. J. Biomech. 1980, 13, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulmala, J.P.; Avela, J.; Pasanen, K.; Parkkari, J. Forefoot Strikers Exhibit Lower Running-Induced Knee Loading than Rearfoot Strikers. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 2306–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshita, T.; Noro, H.; Hata, K.; Yoshida, T.; Fukunaga, T.; Yanagiya, T. Muscle-Tendon Behavior and Kinetics in Gastrocnemius Medialis during Forefoot and Rearfoot Strike Running. J. Appl. Biomech. 2021, 37, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschall, J.S.; Kram, R. Ground Reaction Forces during Downhill and Uphill Running. J. Biomech. 2005, 38, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalski, E.; Li, J.X. Lower Limb Joint Angles and Ground Reaction Forces in Forefoot Strike and Rearfoot Strike Runners during Overground Downhill and Uphill Running. Sports Biomech. 2016, 15, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiberl, W.; Jensen, E.; Merker, J.; Leitel, M.; Schwirtz, A. Accuracy and Precision of Loadsol® Insole Force-Sensors for the Quantification of Ground Reaction Force-Based Biomechanical Running Parameters. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honert, E.C.; Hoitz, F.; Blades, S.; Nigg, S.R.; Nigg, B.M. Estimating Running Ground Reaction Forces from Plantar Pressure during Graded Running. Sensors 2022, 22, 3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, V.M.; Gomes, B.B.; Neto, M.A.; Amaro, A.M. A Systematic Review of Insole Sensor Technology: Recent Studies and Future Directions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xu, X.; Lin, Q.; Xian, D.; Yao, K.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, Z. The Flexible and Distributed Pressure Sensor with 64 Units for On-Line Gait Recognition Analysis. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2023, 223, 113726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, D.A. Biomechanics and Motor Control of Human Movement, 4th ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 9780470398180. [Google Scholar]
- Rottier, T.D.; Allen, S.J. The Influence of Swing Leg Technique on Maximum Running Speed. J. Biomech. 2021, 126, 110640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perl, D.P.; Daoud, A.I.; Lieberman, D.E. Effects of Footwear and Strike Type on Running Economy. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2012, 44, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, E.R.; Rooney, B.D.; Derrick, T.R. Rearfoot and Midfoot or Forefoot Impacts in Habitually Shod Runners. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.M.; Bonanno, D.R.; Hart, H.F.; Barton, C.J. What Are the Benefits and Risks Associated with Changing Foot Strike Pattern During Running? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Injury, Running Economy, and Biomechanics. Sports Med. 2019, 50, 885–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, K.; Noro, H.; Takeshita, T.; Yamazaki, Y.; Yanagiya, T. Leg Stiffness during Running in Highly Cushioned Shoes with a Carbon-Fiber Plate and Traditional Shoes. Gait Posture 2022, 95, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, A.; Takeshita, T.; Yanagiya, T. Differences in Sprinting Performance and Kinematics between Preadolescent Boys Who Are Fore/Mid and Rear Foot Strikers. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Speed | FSPloadsol | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RFS | MFS | FFS | |||
| FSPFSA | Slow (12 km/h) | RFS (n = 74) | 86.5% (n = 64) | 12.2% (n = 9) | 1.4% (n = 1) |
| MFS (n = 133) | 33.1% (n = 44) | 39.1% (n = 52) | 27.8% (n = 37) | ||
| FFS (n = 153) | 2.0% (n = 3) | 9.2% (n = 14) | 88.9% (n = 136) | ||
| Medium (15 km/h) | RFS (n = 102) | 97.1% (n = 99) | 2.9% (n = 3) | 0.0% (n = 0) | |
| MFS (n = 122) | 21.3% (n = 26) | 43.4% (n = 53) | 35.2% (n = 43) | ||
| FFS (n = 136) | 0.0% (n = 0) | 22.1% (n = 30) | 77.9% (n = 106) | ||
| Fast (20 km/h) | RFS (n = 106) | 98.1% (n = 104) | 0.0% (n = 0) | 1.9% (n = 2) | |
| MFS (n = 130) | 51.5% (n = 67) | 29.2% (n = 38) | 19.2% (n = 25) | ||
| FFS (n = 124) | 11.3% (n = 14) | 11.3% (n = 14) | 77.4% (n = 96) | ||
| All speeds | RFS (n = 282) | 94.7% (n = 267) | 4.3% (n = 12) | 1.1% (n = 3) | |
| MFS (n = 385) | 35.6% (n = 137) | 37.1% (n = 143) | 27.3% (n = 105) | ||
| FFS (n = 413) | 4.1% (n = 17) | 14.0% (n = 58) | 81.8% (n = 338) |
| ID | Self- Reported FSP | Slow (12 km/h) | Medium (15 km/h) | Fast (20 km/h) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RFS | MFS | FFS | RFS | MFS | FFS | RFS | MFS | FFS | ||||
| A | FFS/MFS | 0% (n = 0) | 0% (n = 0) | 100% (n = 30) | 0% (n = 0) | 0% (n = 0) | 100% (n = 30) | 0% (n = 0) | 0% (n = 0) | 100% (n = 30) | ||
| B | FFS/MFS | 33% (n = 10) | 27% (n = 8) | 40% (n = 12) | 0% (n = 0) | 60% (n = 18) | 40% (n = 12) | 47% (n = 14) | 40% (n = 12) | 13% (n = 4) | ||
| C | RFS | 93% (n = 28) | 0% (n = 0) | 7% (n = 2) | 100% (n = 30) | 0% (n = 0) | 0% (n = 0) | 90% (n = 27) | 0% (n = 0) | 10% (n = 3) | ||
| D | FFS/MFS | 0% (n = 0) | 87% (n = 26) | 13% (n = 4) | 0% (n = 0) | 73% (n = 22) | 27% (n = 8) | 0% (n = 0) | 73% (n = 22) | 27% (n = 8) | ||
| E | RFS | 100% (n = 30) | 0% (n = 0) | 0% (n = 0) | 100% (n = 30) | 0% (n = 0) | 0% (n = 0) | 97% (n = 29) | 3% (n = 1) | 0% (n = 0) | ||
| F | FFS/MFS | 3% (n = 1) | 23% (n = 7) | 73% (n = 22) | 0% (n = 0) | 33% (n = 10) | 67% (n = 20) | 0% (n = 0) | 3% (n = 1) | 97% (n = 29) | ||
| G | FFS/MFS | 0% (n = 0) | 57% (n = 17) | 43% (n = 13) | 0% (n = 0) | 50% (n = 15) | 50% (n = 15) | 0% (n = 0) | 50% (n = 15) | 50% (n = 15) | ||
| H | RFS | 87% (n = 26) | 0% (n = 0) | 13% (n = 4) | 83% (n = 25) | 10% (n = 3) | 7% (n = 2) | 97% (n = 29) | 3% (n = 1) | 0% (n = 0) | ||
| I | RFS | 0% (n = 0) | 0% (n = 0) | 100% (n = 30) | 50% (n = 15) | 0% (n = 0) | 50% (n = 15) | 100% (n = 30) | 0% (n = 0) | 0% (n = 0) | ||
| J | RFS | 53% (n = 16) | 47% (n = 14) | 0% (n = 0) | 83% (n = 25) | 17% (n = 5) | 0% (n = 0) | 100% (n = 30) | 0% (n = 0) | 0% (n = 0) | ||
| K | FFS/MFS | 0% (n = 0) | 0% (n = 0) | 100% (n = 30) | 0% (n = 0) | 0% (n = 0) | 100% (n = 30) | 0% (n = 0) | 0% (n = 0) | 100% (n = 30) | ||
| L | FFS/MFS | 0% (n = 0) | 3% (n = 1) | 97% (n = 29) | 0% (n = 0) | 40% (n = 12) | 60% (n = 18) | 83% (n = 25) | 0% (n = 0) | 17% (n = 5) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hata, K.; Yamazaki, Y.; Ishikawa, M.; Yanagiya, T. Foot Strike Pattern Detection Using a Loadsol® Sensor Insole. Sensors 2025, 25, 4417. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144417
Hata K, Yamazaki Y, Ishikawa M, Yanagiya T. Foot Strike Pattern Detection Using a Loadsol® Sensor Insole. Sensors. 2025; 25(14):4417. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144417
Chicago/Turabian StyleHata, Keiichiro, Yohei Yamazaki, Misato Ishikawa, and Toshio Yanagiya. 2025. "Foot Strike Pattern Detection Using a Loadsol® Sensor Insole" Sensors 25, no. 14: 4417. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144417
APA StyleHata, K., Yamazaki, Y., Ishikawa, M., & Yanagiya, T. (2025). Foot Strike Pattern Detection Using a Loadsol® Sensor Insole. Sensors, 25(14), 4417. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25144417






