QP-Adaptive Dual-Path Residual Integrated Frequency Transformer for Data-Driven In-Loop Filter in VVC
Abstract
1. Introduction
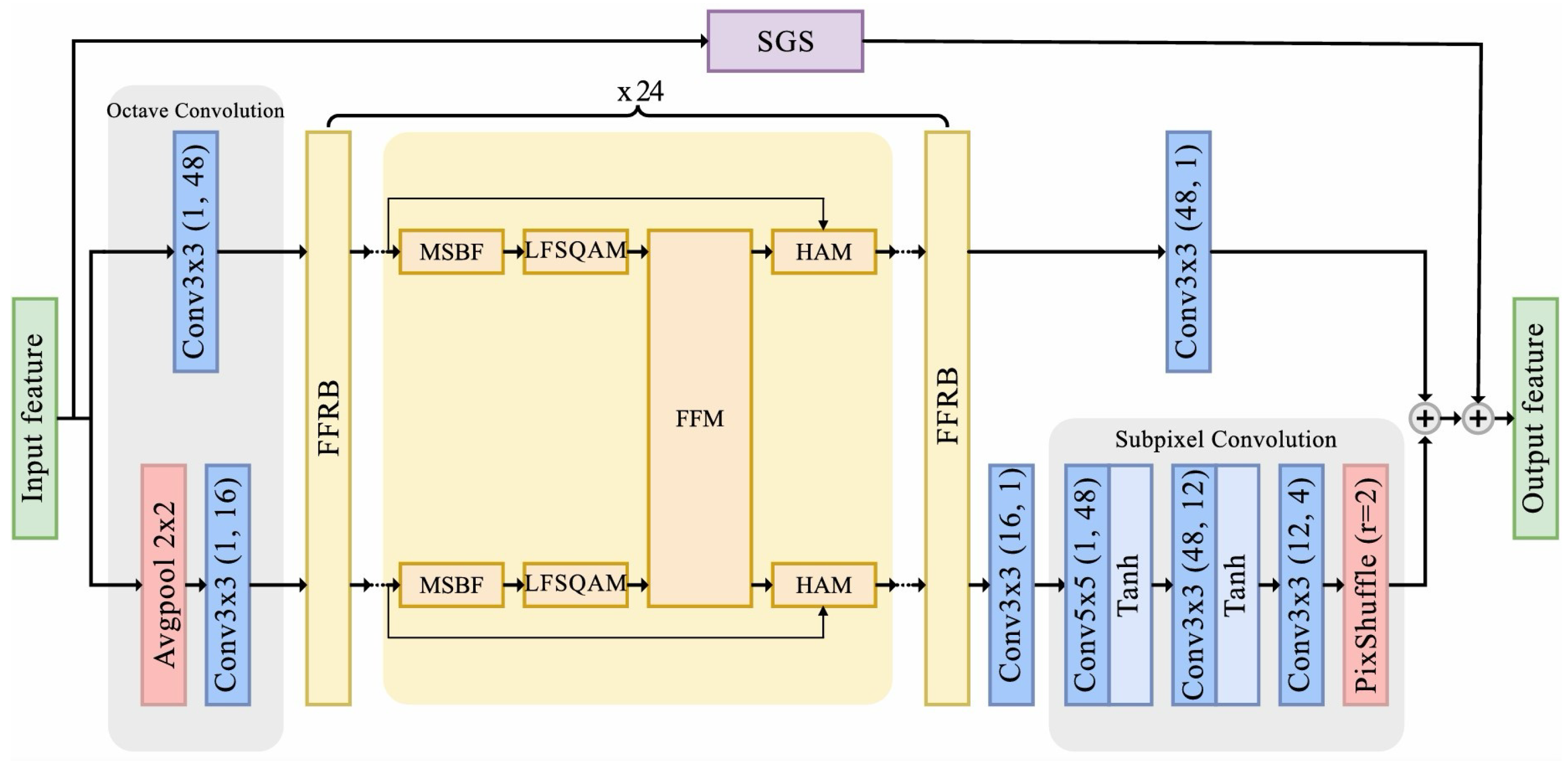
- Our LFFCNN utilizes octave convolution to separate features into high- and low-frequency components, reducing the computational complexity. It incorporates a proposed frequency fusion residual block (FFRB) with four fundamental modules: MSBF for multiscale feature extraction, LFSQAM for QP adaptation, FFM for frequency information exchange, and HAM for the spatial and channel attention mechanism. Notably, LFFCNN achieves comparable BD rate reductions to QA-Filter [36] while reducing the parameter count by 32%.
- LFFCNN enhances local features, whereas SGS leverages Swin transformers to capture long-range dependencies and global contexts. This complementary design significantly improves DRIFT’s performance. Experimental results demonstrate that integrating SGS enhances the BD rate reduction by an additional 1% in intra mode compared to LFFCNN alone.
- A quantization parameter estimator (QPE) is proposed to mitigate double enhancement effects. This addition significantly enhances DRIFT’s coding efficiency, yielding a 0.59% improvement in the BD rate reduction for the inter mode.
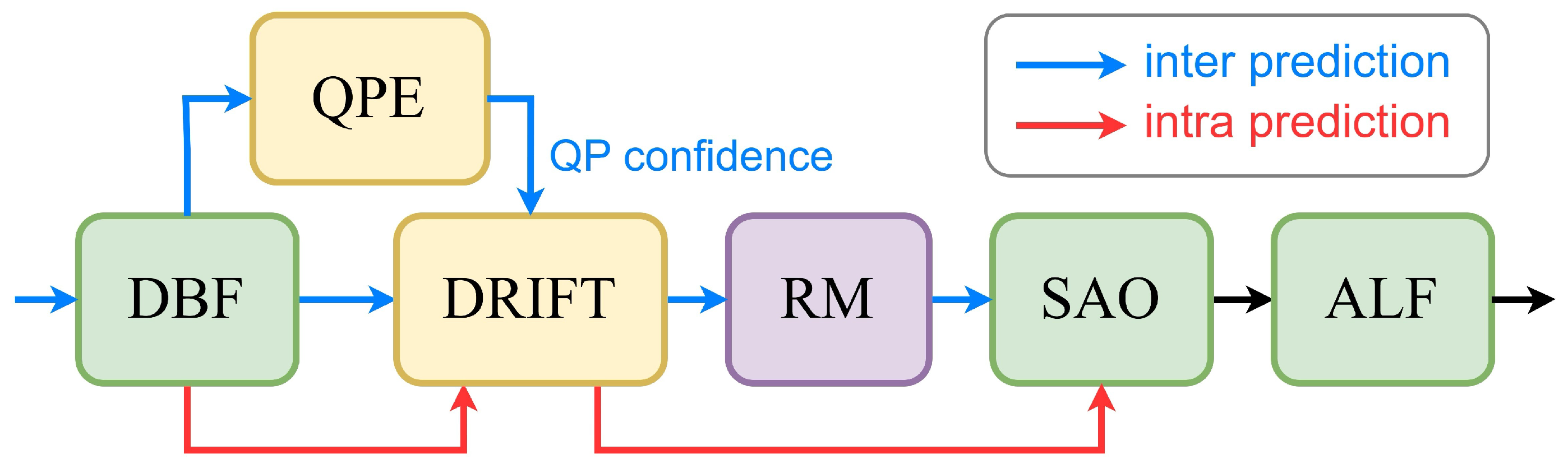
- The proposed DRIFT, which is an AI-enabled method, is beneficial in improving the quality of the reconstructed image on M-IOT devices that support VVC standards.
2. Related Work
2.1. CNN-Based In-Loop Filters
2.2. Vision Transformer
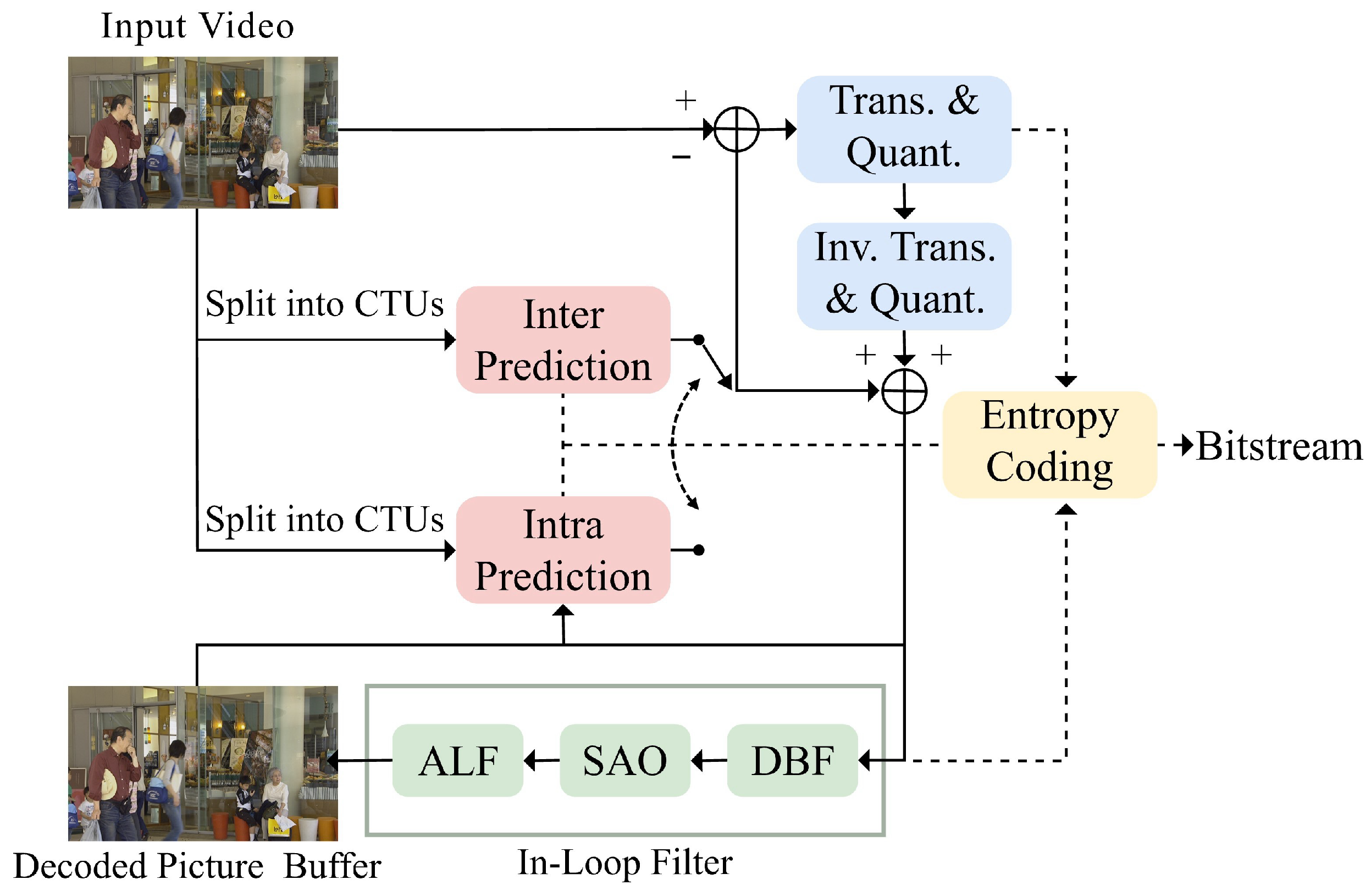
3. Proposed Method
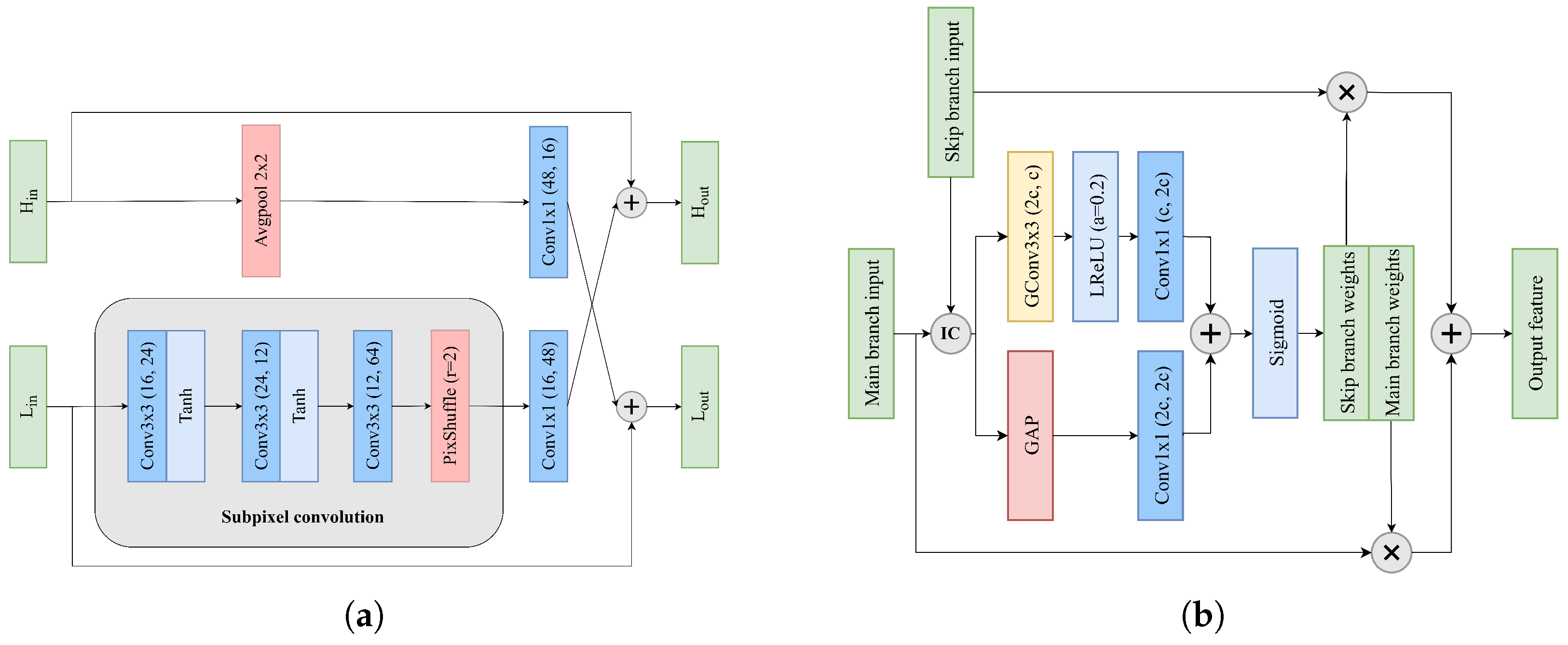
3.1. Network Architecture
3.1.1. Octave Convolution
3.1.2. Feature Fusion Residual Blocks
3.1.3. Reconstruction Layers
3.1.4. SwinIR Transformer Global Skip
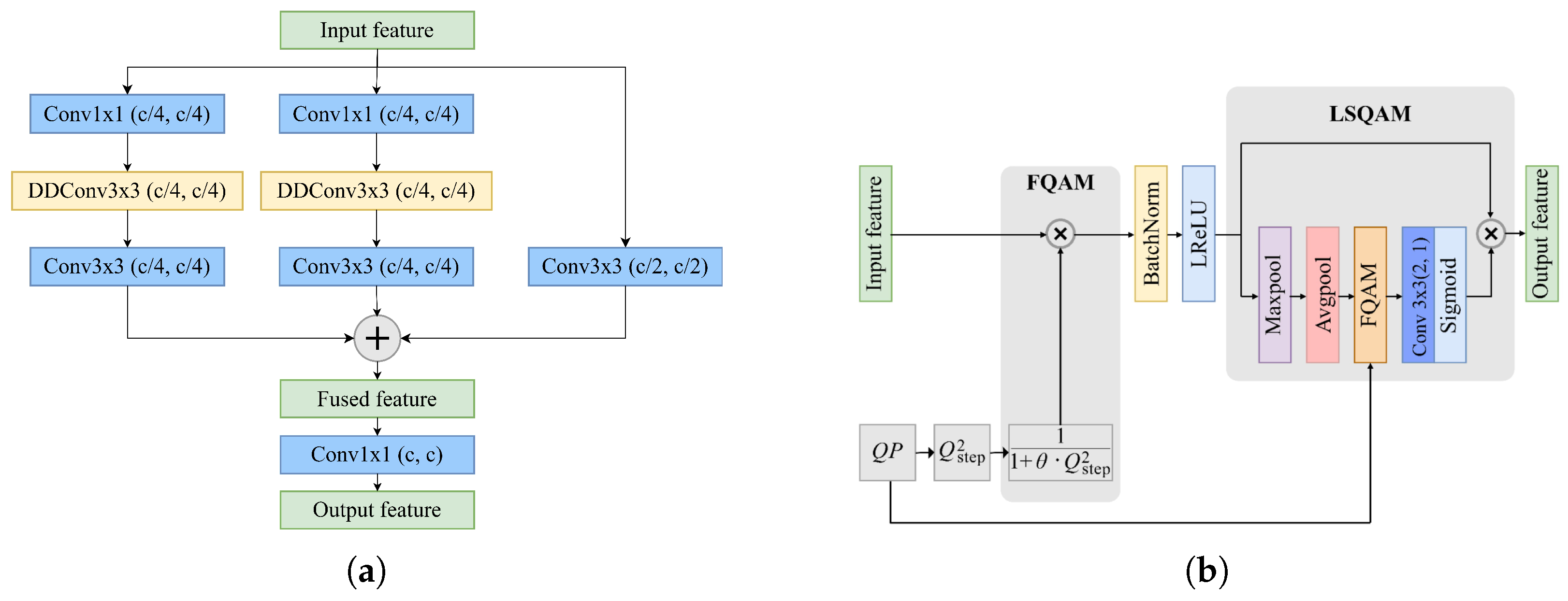
3.2. Details of FFRB
3.2.1. Multiscale Branch Fusion
3.2.2. Lightweight FSQAM
3.2.3. Frequency Fusion Module
3.2.4. Hybrid Attention Module
3.3. Quantization Parameter Estimator
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.2. Objective Evaluation
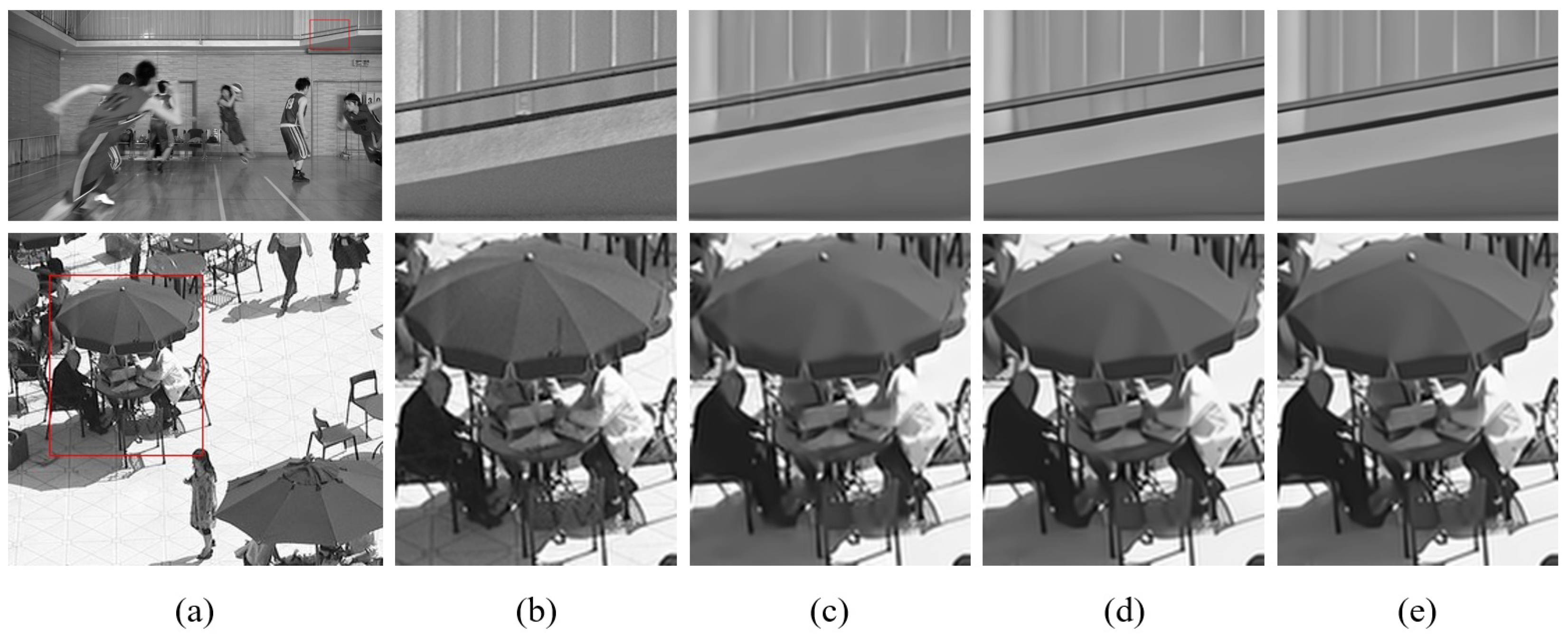
4.3. Subjective Evaluation
4.4. Complexity Evaluation
4.5. Ablation Study
4.5.1. Effectiveness of QPE
4.5.2. Effectiveness of SGS
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Yun, J. M2M service platforms: Survey, issues, and enabling technologies. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 16, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Jiang, T.; Han, Z. A survey of emerging M2M systems: Context, task, and objective. IEEE Internet Things J. 2016, 3, 1246–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, A.; Atzori, L. Managing the quality of experience in the multimedia Internet of Things: A layered-based approach. Sensors 2016, 16, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauman, A.; Qadri, Y.A.; Amjad, M.; Zikria, Y.B.; Afzal, M.K.; Kim, S.W. Multimedia Internet of Things: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 8202–8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaafia, S.; Khemiri, R.; Messaoud, S.; Ben Ahmed, O.; Sayadi, F.E. Deep learning-based video quality enhancement for the new versatile video coding. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 14135–14149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, J.; Jeong, S.Y.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, B.G. Attention-based bi-prediction network for versatile video coding (vvc) over 5g network. Sensors 2023, 23, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, H.; Jiang, Z.; He, T.; Wu, Y. A Survey on Recent Advances in Video Coding Technologies and Future Research Directions. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2025, 2, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, G.J.; Ohm, J.R.; Han, W.J.; Wiegand, T. Overview of the high efficiency video coding (HEVC) standard. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2012, 22, 1649–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bross, B.; Wang, Y.K.; Ye, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, J.; Sullivan, G.J.; Ohm, J.R. Overview of the versatile video coding (VVC) standard and its applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 3736–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, I.; Cabarat, P.L.; Menard, D.; Hamidouche, W.; Déforges, O. Energy Efficient VVC Decoding on Mobile Platform. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 25th International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP), Poitiers, France, 27–29 September 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, A.; Roma, N.; Chavarrías, M.; Dias, T.; Pescador, F.; Aranda, V. GPU-based parallelisation of a versatile video coding adaptive loop filter in resource-constrained heterogeneous embedded platform. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2023, 20, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yu, S.; Zhou, L.; Chen, W.; Zhao, T.; Wang, Z. PEA265: Perceptual assessment of video compression artifacts. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 30, 3898–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, M.; Yang, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, T. Toward Efficient Video Compression Artifact Detection and Removal: A Benchmark Dataset. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 10816–10827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Chen, W.; Lin, J.; Zhao, T.; Lin, C.W. Video compression artifacts removal with spatial-temporal attention-guided enhancement. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 26, 5657–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, P.; Joch, A.; Lainema, J.; Bjontegaard, G.; Karczewicz, M. Adaptive deblocking filter. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2003, 13, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.M.; Alshina, E.; Alshin, A.; Huang, Y.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Tsai, C.Y.; Hsu, C.W.; Lei, S.M.; Park, J.H.; Han, W.J. Sample adaptive offset in the HEVC standard. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2012, 22, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Yamakage, T.; Chong, I.S.; Huang, Y.W.; Fu, C.M.; Itoh, T.; Watanabe, T.; Chujoh, T.; Karczewicz, M.; et al. Adaptive loop filtering for video coding. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2013, 7, 934–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.C.; Park, M.K.; Kang, M.G. Super-resolution image reconstruction: A technical overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2003, 20, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wen, J.; Fei, L.; Zhang, Z. Review of video and image defogging algorithms and related studies on image restoration and enhancement. IEEE Access 2015, 4, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Fei, L.; Zheng, W.; Xu, Y.; Zuo, W.; Lin, C.W. Deep learning on image denoising: An overview. Neural Netw. 2020, 131, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, T.; Galpin, F.; Bordes, P. Iterative training of neural networks for intra prediction. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 30, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Kang, D.U.; Kim, J.; Chun, S.Y. Multi-temporal recurrent neural networks for progressive non-uniform single image deblurring with incremental temporal training. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 327–343. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Kwong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Generative adversarial network-based intra prediction for video coding. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 22, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Liu, D.; Li, B.; Ma, S.; Wu, F.; Gao, W. Deep network-based frame extrapolation with reference frame alignment. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 31, 1178–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murn, L.; Blasi, S.; Smeaton, A.F.; Mrak, M. Improved CNN-based learning of interpolation filters for low-complexity inter prediction in video coding. IEEE Open J. Signal Process. 2021, 2, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Zhang, P.; Peng, B.; Ling, N.; Lei, J. A CNN-based fast inter coding method for VVC. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 28, 1260–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xu, M.; Tang, R.; Chen, Y.; Xing, Q. DeepQTMT: A deep learning approach for fast QTMT-based CU partition of intra-mode VVC. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 5377–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathariya, B.; Li, Z.; Van der Auwera, G. Joint Pixel and Frequency Feature Learning and Fusion via Channel-wise Transformer for High-Efficiency Learned In-Loop Filter in VVC. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 34, 4070–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathariya, B.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Coban, M. Multi-stage spatial and frequency feature fusion using transformer in cnn-based in-loop filter for vvc. In Proceedings of the 2022 Picture Coding Symposium (PCS), San Jose, CA, USA, 7–9 December 2022; pp. 373–377. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, O.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Z. Swin Transformer-Based In-Loop Filter for VVC Intra Coding. In Proceedings of the 2024 Picture Coding Symposium (PCS), Taichung, Taiwan, 12–14 June 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Liu, D.; Wu, F. A convolutional neural network approach for post-processing in HEVC intra coding. In Proceedings of the MultiMedia Modeling: 23rd International Conference, MMM 2017, Reykjavik, Iceland, 4–6 January 2017; Proceedings, Part I 23. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Soh, J.W.; Park, J.; Ahn, B.; Lee, H.S.; Moon, Y.S.; Cho, N.I. A pseudo-blind convolutional neural network for the reduction of compression artifacts. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2019, 30, 1121–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Kong, L.; Chen, G.; Liu, Z.; Fang, Y. A switchable deep learning approach for in-loop filtering in video coding. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2019, 30, 1871–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Yi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jeon, B.; Kwong, S. Efficient in-loop filtering based on enhanced deep convolutional neural networks for HEVC. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 5352–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Yao, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Xie, D.; Pu, S. A practical convolutional neural network as loop filter for intra frame. In Proceedings of the 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Athens, Greece, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 1133–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Sun, H.; Katto, J.; Zeng, X.; Fan, Y. QA-Filter: A QP-adaptive convolutional neural network filter for video coding. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 3032–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Cao, J.; Sun, G.; Zhang, K.; Van Gool, L.; Timofte, R. Swinir: Image restoration using swin transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 1833–1844. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, S.; Jia, S. Dual self-attention Swin transformer for hyperspectral image super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 3275146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, K.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Q. Trinity-Net: Gradient-guided Swin transformer-based remote sensing image dehazing and beyond. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 3285228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Liu, T.; Liu, K. SUNet: Swin transformer UNet for image denoising. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.14009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Sun, H.; Katto, J.; Zeng, X.; Fan, Y. A convolutional neural network-based low complexity filter. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.02733. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, H.; Xu, B.; Yan, Z.; Kalantidis, Y.; Rohrbach, M.; Yan, S.; Feng, J. Drop an octave: Reducing spatial redundancy in convolutional neural networks with octave convolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3435–3444. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, R.; Sun, L.; Liu, Z.; Lu, H.; Pang, C.; Luo, X. MADNet: A fast and lightweight network for single-image super resolution. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 51, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagoruyko, S.; Komodakis, N. Learning to compare image patches via convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4353–4361. [Google Scholar]
- Agustsson, E.; Timofte, R. Ntire 2017 challenge on single image super-resolution: Dataset and study. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 126–135. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1026–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Nah, S.; Baik, S.; Hong, S.; Moon, G.; Son, S.; Timofte, R.; Lee, K.M. NTIRE 2019 Challenge on Video Deblurring and Super-Resolution: Dataset and Study. In Proceedings of the The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 721, 8026–8037. [Google Scholar]
- Suehring, K.; Li, X. Common Test Conditions and Software Reference Configurations, document JVET-G1010; Joint Video Exploration Team (JVET): Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]


| Class | Sequence | IACNN [32] | SEFCNN [33] | EDCNN [34] | QA-Filter [36] | DRIFT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 (3840 × 2160) | Tango2 | −0.97 | −2.42 | −2.78 | −3.82 | −5.23 |
| FoodMarket4 | −1.26 | −3.82 | −3.66 | −6.02 | −6.93 | |
| Campfire | −0.93 | −1.71 | −1.92 | −2.59 | −3.15 | |
| A2 (3840 × 2160) | CatRobot1 | −1.90 | −3.43 | −3.77 | −5.01 | −5.91 |
| DaylightRoad2 | −1.10 | −2.08 | −2.33 | −3.03 | −3.97 | |
| ParkRunning3 | −1.58 | −2.95 | −3.26 | −4.40 | −5.17 | |
| B (1920 × 1080) | MarketPlace | −1.60 | −2.99 | −3.44 | −4.50 | −5.51 |
| RitualDance | −3.33 | −5.96 | −6.50 | −8.00 | −9.38 | |
| Cactus | −1.70 | −2.97 | −3.44 | −4.47 | −5.29 | |
| BasketballDrive | −0.93 | −2.38 | −2.94 | −4.03 | −5.53 | |
| BQTerrace | −0.99 | −1.76 | −2.08 | −2.63 | −3.54 | |
| C (832 × 480) | BasketballDrill | −4.11 | −6.86 | −7.40 | −9.16 | −10.90 |
| BQMall | −3.01 | −5.08 | −5.59 | −6.65 | −8.03 | |
| PartyScene | −2.29 | −3.38 | −3.56 | −4.25 | −4.98 | |
| RaceHorses | −1.32 | −2.10 | −2.38 | −2.88 | −3.95 | |
| D (416 × 240) | BasketballPass | −3.80 | −6.44 | −6.88 | −8.19 | −9.43 |
| BQSquare | −3.45 | −5.37 | −5.66 | −6.52 | −8.07 | |
| BlowingBubbles | −3.23 | −4.73 | −4.97 | −5.84 | −6.78 | |
| RaceHorses | −3.87 | −5.15 | −5.41 | −6.01 | −7.11 | |
| E (1280 × 720) | FourPeople | −3.39 | −5.68 | −6.17 | −7.55 | −9.22 |
| Johnny | −2.79 | −4.87 | −5.40 | −6.91 | −8.31 | |
| KristenAndSara | −2.92 | −4.79 | −5.26 | −6.46 | −7.85 | |
| Average | −2.29 | −3.95 | −4.31 | −5.41 | −6.56 | |
| Class | IACNN [32] | SEFCNN [33] | EDCNN [34] | QA-Filter [36] | DRIFT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 Average | −1.52 | −3.04 | −3.16 | −3.07 | −3.30 |
| A2 Average | −1.96 | −3.17 | −3.41 | −3.42 | −4.56 |
| B Average | −1.64 | −2.79 | −3.10 | −3.44 | −3.67 |
| C Average | −1.93 | −2.93 | −3.13 | −3.18 | −3.63 |
| D Average | −3.27 | −4.63 | −4.83 | −4.65 | −5.45 |
| E Average | −2.70 | −4.21 | −4.59 | −5.22 | −5.60 |
| Overall Average | −2.17 | −3.46 | −3.70 | −3.83 | −4.83 |
| Method | Parameters (M) |
|---|---|
| IACNN [32] | 0.37 |
| SEFCNN [33] | 2.57 |
| EDCNN [34] | 18.20 |
| QA-Filter [36] | 1.78 |
| LFFCNN | 1.22 |
| DRIFT | 2.09 |
| Class | QA-Filter [36] | DRIFT |
|---|---|---|
| B | 103.56 | 110.59 |
| C | 103.14 | 110.00 |
| D | 107.45 | 109.74 |
| E | 105.01 | 118.08 |
| Average | 104.79 | 112.38 |
| Class | LFFCNN | DRIFT |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | −3.16 | −3.79 |
| A2 | −5.22 | −5.96 |
| B | −3.79 | −4.28 |
| C | −3.84 | −4.56 |
| D | −5.58 | −6.00 |
| E | −5.67 | −6.36 |
| Average | −4.59 | −5.18 |
| Class | QA-Filter [36] | LFFCNN | DRIFT |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | −4.31 | −4.20 | −5.04 |
| A2 | −3.03 | −3.20 | −3.97 |
| B | −4.73 | −4.68 | −5.85 |
| C | −5.74 | −6.10 | −6.97 |
| D | −6.64 | −7.13 | −7.85 |
| E | −6.97 | −7.40 | −8.46 |
| Average | −5.56 | −5.79 | −6.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yeh, C.-H.; Ni, C.-T.; Huang, K.-Y.; Wu, Z.-W.; Peng, C.-P.; Chen, P.-Y. QP-Adaptive Dual-Path Residual Integrated Frequency Transformer for Data-Driven In-Loop Filter in VVC. Sensors 2025, 25, 4234. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134234
Yeh C-H, Ni C-T, Huang K-Y, Wu Z-W, Peng C-P, Chen P-Y. QP-Adaptive Dual-Path Residual Integrated Frequency Transformer for Data-Driven In-Loop Filter in VVC. Sensors. 2025; 25(13):4234. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134234
Chicago/Turabian StyleYeh, Cheng-Hsuan, Chi-Ting Ni, Kuan-Yu Huang, Zheng-Wei Wu, Cheng-Pin Peng, and Pei-Yin Chen. 2025. "QP-Adaptive Dual-Path Residual Integrated Frequency Transformer for Data-Driven In-Loop Filter in VVC" Sensors 25, no. 13: 4234. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134234
APA StyleYeh, C.-H., Ni, C.-T., Huang, K.-Y., Wu, Z.-W., Peng, C.-P., & Chen, P.-Y. (2025). QP-Adaptive Dual-Path Residual Integrated Frequency Transformer for Data-Driven In-Loop Filter in VVC. Sensors, 25(13), 4234. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134234








