AuNP/Magnetic Bead-Enhanced Electrochemical Sensor Toward Dual Saliva Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
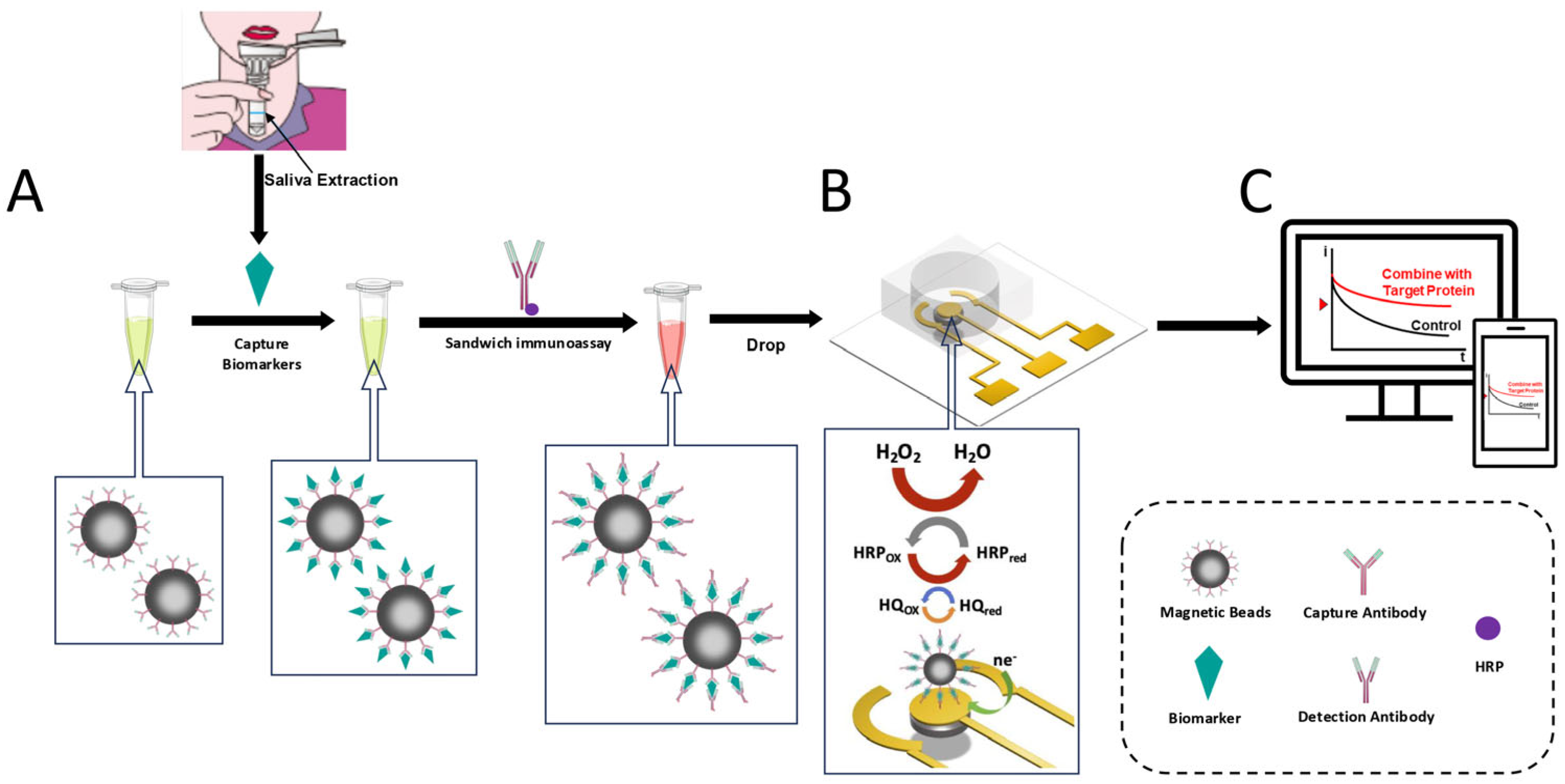
2.2. Immunomagnetic Beads Modification and Assay
2.3. Fabrication of Quartz Substrate-Based Three-Electrodes System
2.4. Fabrication of PDMS Liquid Loading Wells
2.5. Electrochemical Deposition of AuNPs and Characterization
2.6. Electrochemical Detection
3. Results
3.1. Electrochemical Sensor Design
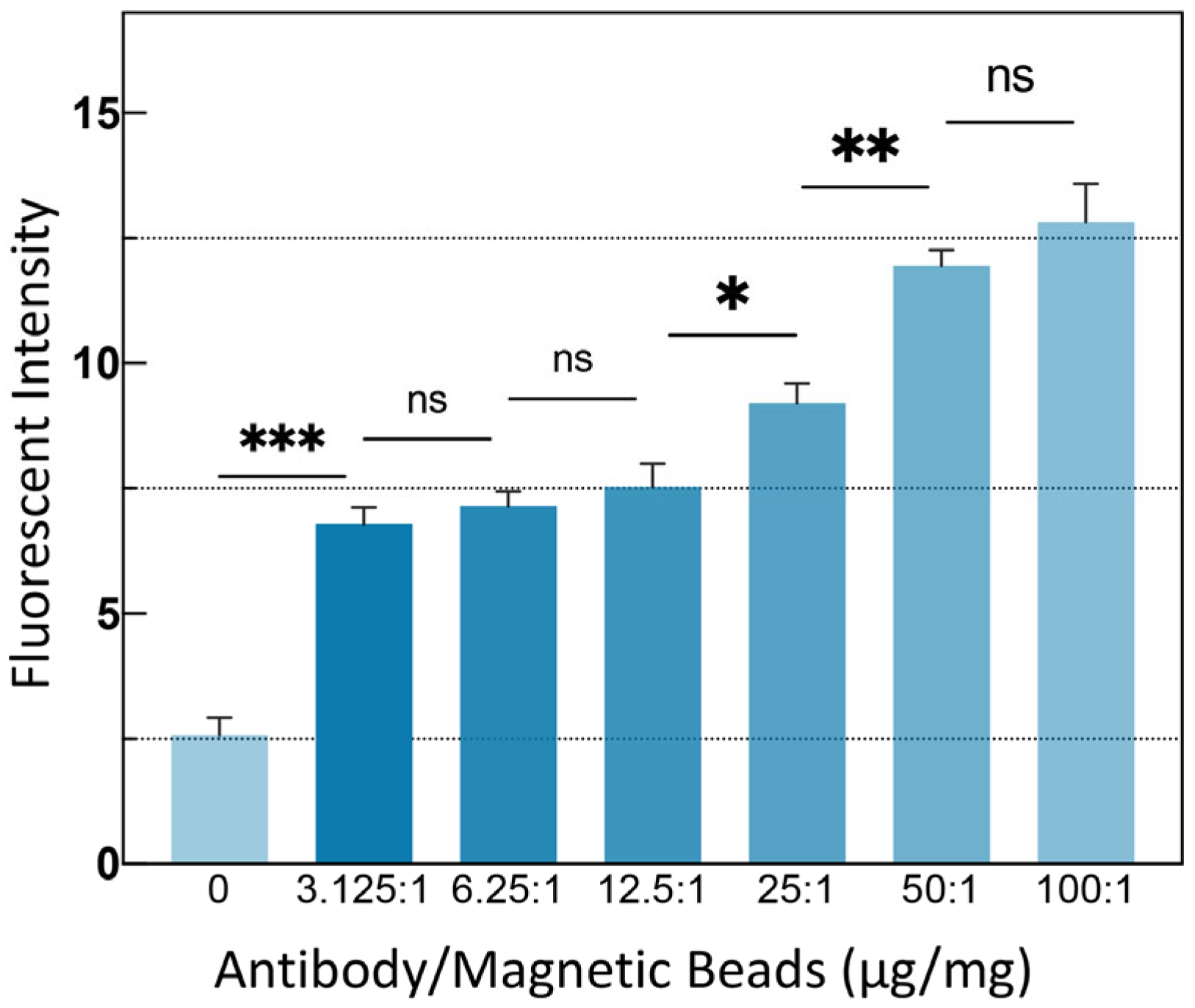
3.2. MB Modification Validity Verification
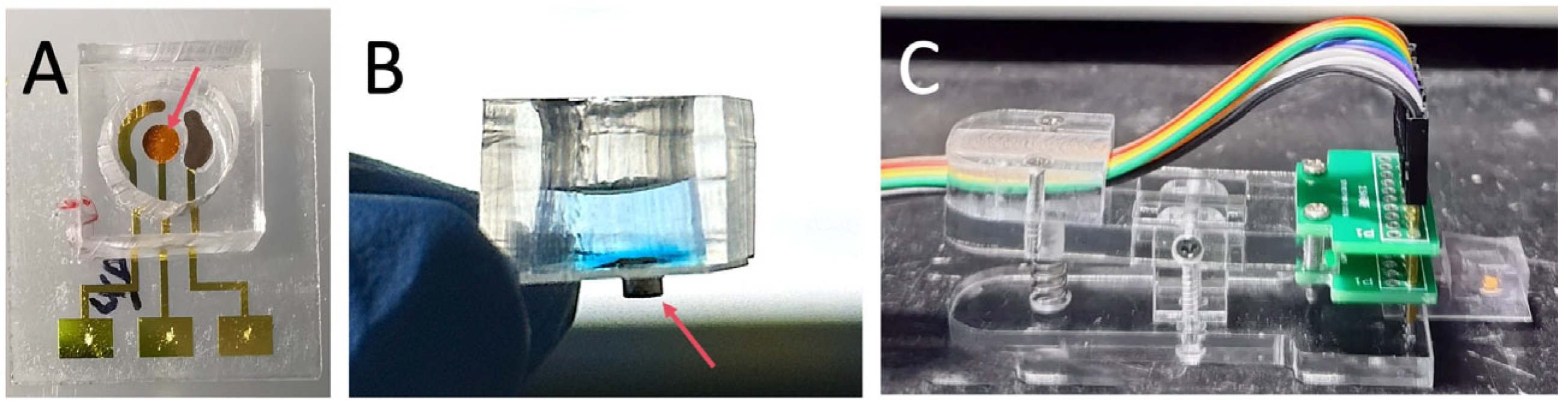
3.3. Fabrication of the Electrochemical Sensor
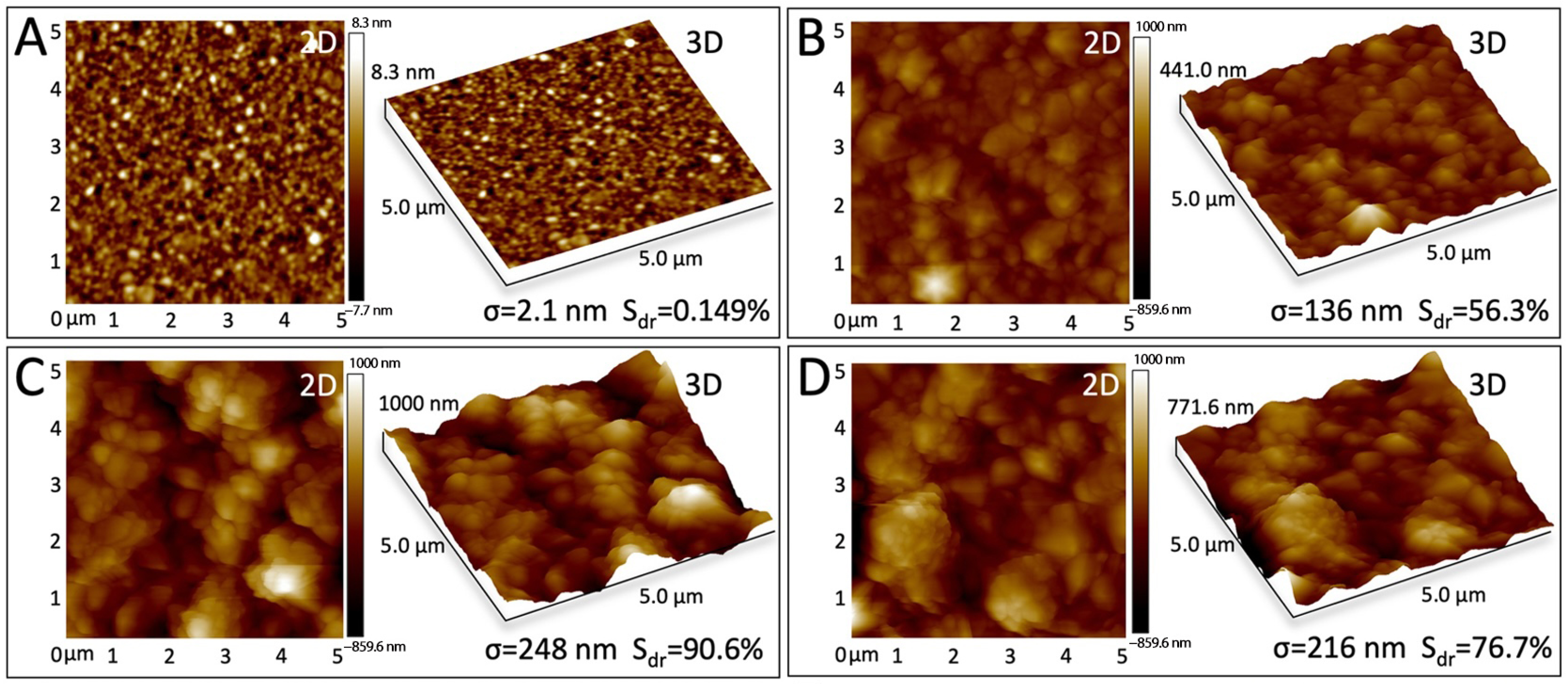
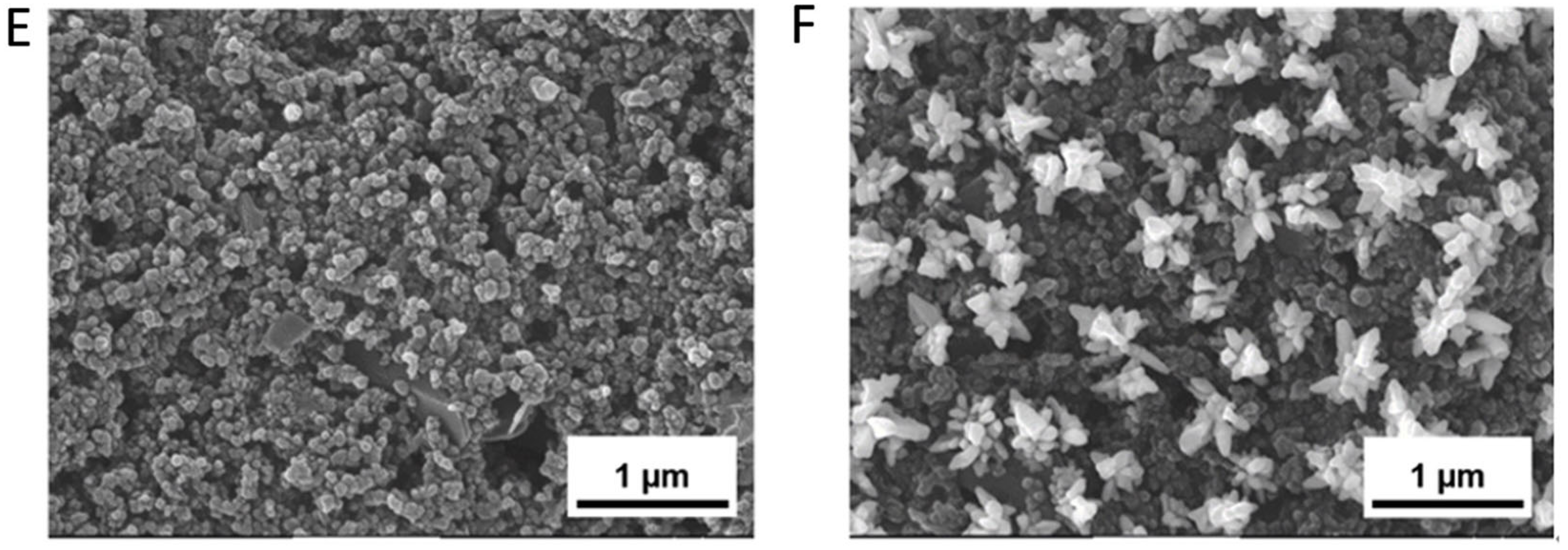
3.4. Modified Electrode Surface Morphology Characterization
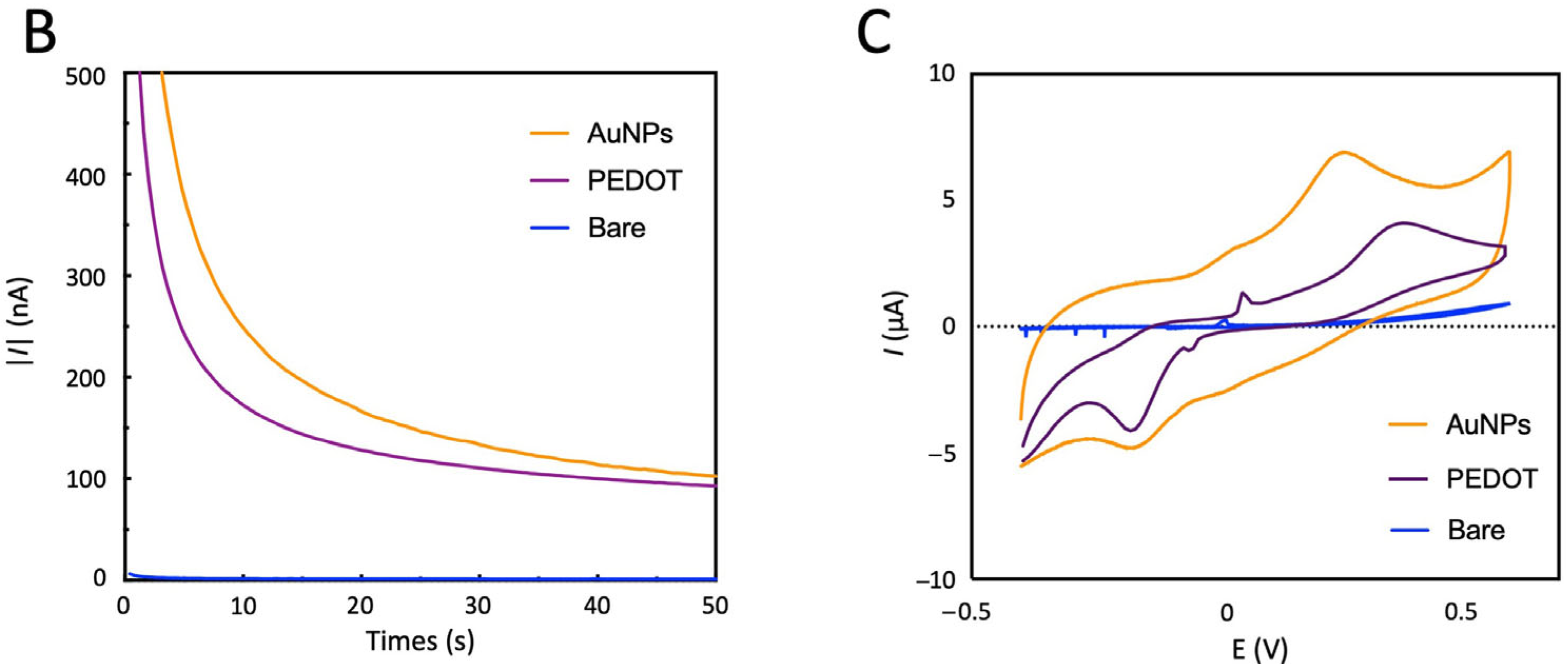
3.5. Modified Electrode Electrochemical Characterization
3.6. Electrochemical Sensor Test Results
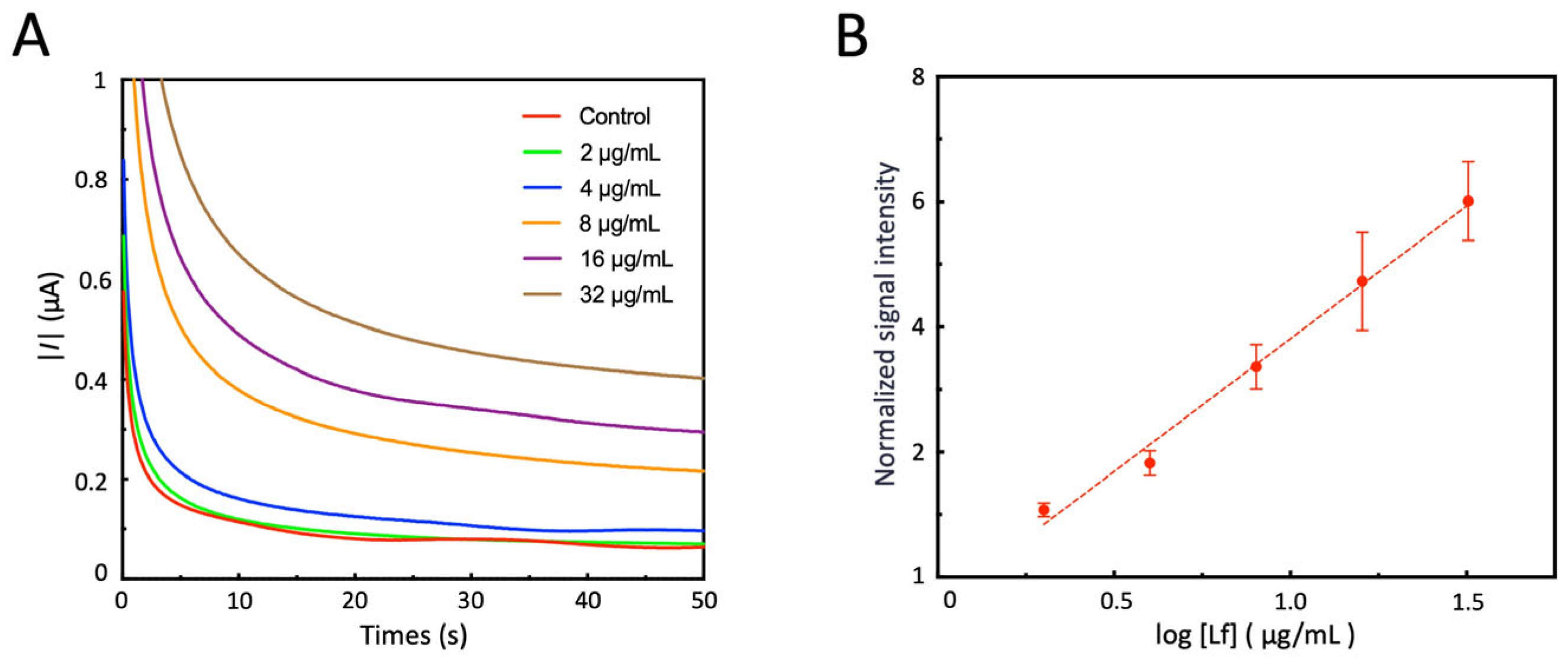
3.7. Detect Lf Using Electrochemical Sensors
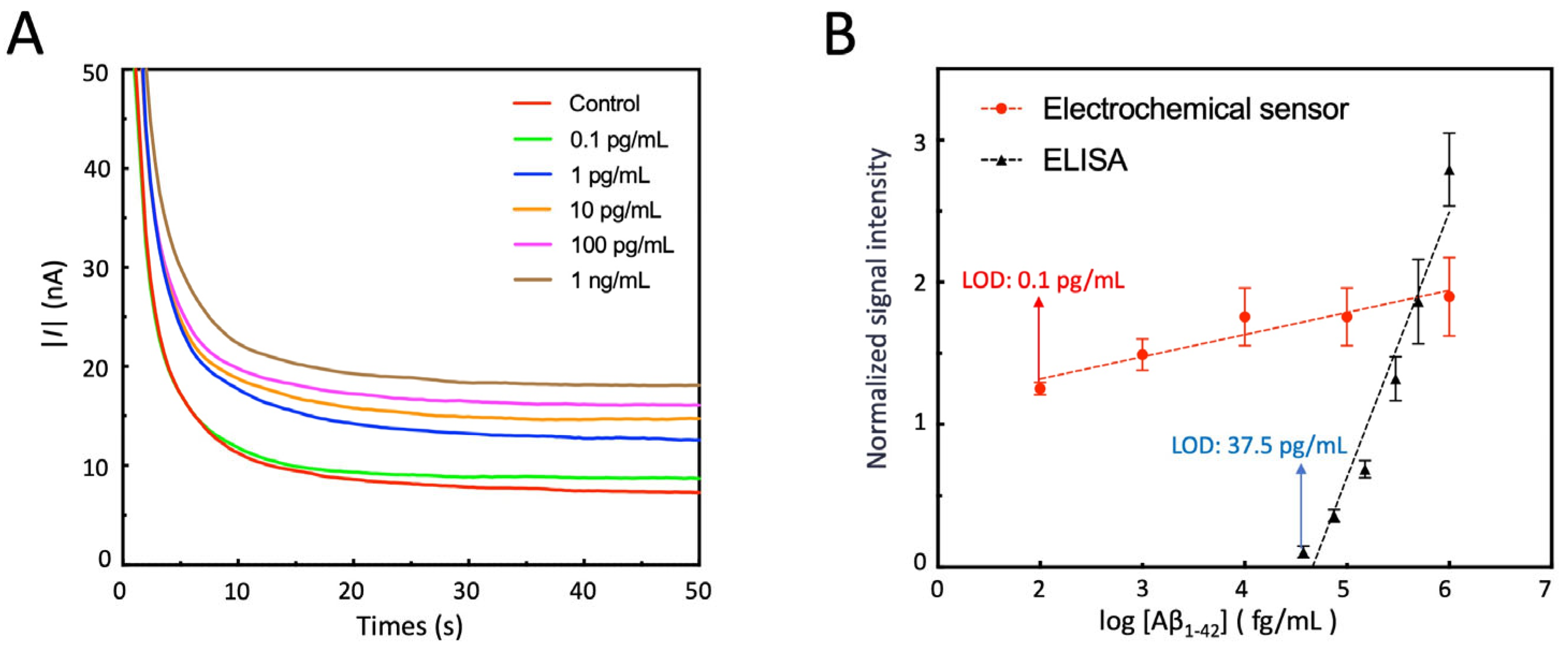
3.8. Detection of Aβ1-42 by Electrochemical Sensor
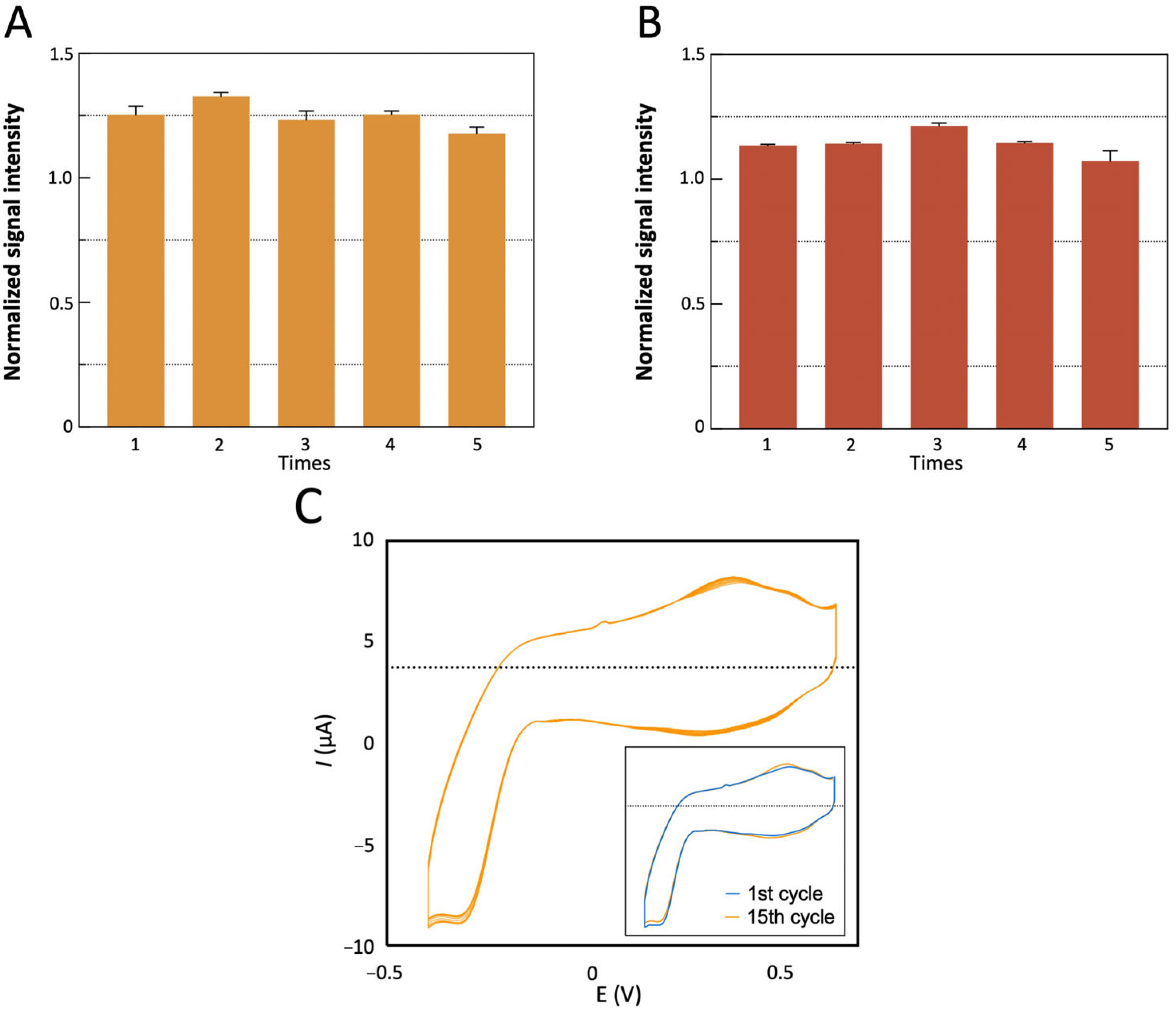
3.9. Test of the Stability and Reproducibility of the Sensor
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| NDD | Neurodegenerative disorder |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| PAMPs | Pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| POCT | Point-of-care testing |
| Aβ1-42 | amyloid β-protein 1-42 |
| Lf | Lactoferrin |
| MBs | Immunomagnetic beads |
| AuNPs | Gold nanoparticles |
| PDMS | Polydimethylsiloxane |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| CV | Cyclic voltammetry |
| DPV | Differential pulse voltammetry |
| ADC | Analog-to-digital converter |
| DAC | Digital-to-analog converter |
| MCU | Microcontroller unit |
| CA | Chronoamperometry |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| EIS | Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
| Sdr | Surface area ratio |
| AFM | Atomic force microscope |
| TMB | 3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine |
| HQ | 1,4-Dihydroxybenzene |
| EIS | Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
References
- Dubois, B.; Hampel, H.; Feldman, H.H.; Scheltens, P.; Aisen, P.; Andrieu, S.; Bakardjian, H.; Benali, H.; Bertram, L.; Blennow, K.; et al. Preclinical Alzheimer’s disease: Definition, natural history, and diagnostic criteria. Alzheimers Dement. 2016, 12, 292–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, B.; Villain, N.; Frisoni, G.B.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Sabbagh, M.; Cappa, S.; Bejanin, A.; Bombois, S.; Epelbaum, S.; Teichmann, M.; et al. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations of the International Working Group. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F. Integrated Positron Emission Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Imaging in clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 145, 110017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groot, C.; Grothe, M.J.; Mukherjee, S.; Jelistratova, I.; Jansen, I.; van Loenhoud, A.C.; Risacher, S.L.; Saykin, A.J.; Mac Donald, C.L.; Mez, J.; et al. Differential patterns of gray matter volumes and associated gene expression profiles in cognitively-defined Alzheimer’s disease subgroups. Neuroimage Clin. 2021, 30, 102660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzman, B.A.; Massoud, T.F. Standard Fluoroscopic and Computed Tomography-Guided Lumbar Punctures. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2025, 35, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, R.; Haraty, H.; Salame, Z.; Fares, Y.; Ojcius, D.M.; Said Sadier, N. Salivary biomarkers for the diagnosis and monitoring of neurological diseases. Biomed. J. 2018, 41, 63–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnowska, S.; Baran, T.; Wilinska, I.; Sienicka, P.; Cabaj-Wiater, I.; Knas, M. Human saliva as a diagnostic material. Adv. Med. Sci. 2018, 63, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, M.; Gonzales-Portillo, I.; Borlongan, C.V. Saliva, an easily accessible fluid as diagnostic tool and potent stem cell source for Alzheimer’s Disease: Present and future applications. Brain Res. 2020, 1727, 146535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleerup, H.S.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Simonsen, A.H. Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease in Saliva: A Systematic Review. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 4761054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, J.; Xiong, W.; Luo, Y.; Feng, H.; Zhou, H.; Peng, Y.; He, Y.; Ye, Q. The oral-brain axis: Can periodontal pathogens trigger the onset and progression of Alzheimer’s disease? Front Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1358179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.B.; Choi, Y.Y.; Song, W.K.; Song, K.B. Antibody-based magnetic nanoparticle immunoassay for quantification of Alzheimer’s disease pathogenic factor. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 051205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, C.; Butchart, J. Systemic inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 898–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antequera, D.; Moneo, D.; Carrero, L.; Bartolome, F.; Ferrer, I.; Proctor, G.; Carro, E. Salivary Lactoferrin Expression in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 749468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carro, E.; Bartolome, F.; Bermejo-Pareja, F.; Villarejo-Galende, A.; Molina, J.A.; Ortiz, P.; Calero, M.; Rabano, A.; Cantero, J.L.; Orive, G. Early diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease based on salivary lactoferrin. Alzheimers Dement 2017, 8, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reseco, L.; Atienza, M.; Fernandez-Alvarez, M.; Carro, E.; Cantero, J.L. Salivary lactoferrin is associated with cortical amyloid-beta load, cortical integrity, and memory in aging. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettazzi, F.; Enayati, L.; Sanchez, I.C.; Motaghed, R.; Mascini, M.; Palchetti, I. Electrochemical bioassay for the detection of TNF-alpha using magnetic beads and disposable screen-printed array of electrodes. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.P.; Yang, T.H.; Wang, J.C.; Chuang, H.S. Recent Trends and Innovations in Bead-Based Biosensors for Cancer Detection. Sensors 2024, 24, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezabakhsh, A.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Fathi, F. Surface plasmon resonance biosensors for detection of Alzheimer’s biomarkers; an effective step in early and accurate diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 167, 112511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.K.; Hwang, I.J.; Cha, M.G.; Kim, H.I.; Yim, D.; Jeong, D.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, J.H. Reaction Kinetics-Mediated Control over Silver Nanogap Shells as Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Nanoprobes for Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers. Small 2019, 15, e1900613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavatski, S.; Khinevich, N.; Girel, K.; Redko, S.; Kovalchuk, N.; Komissarov, I.; Lukashevich, V.; Semak, I.; Mamatkulov, K.; Vorobyeva, M.; et al. Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy of Lactoferrin Adsorbed on Silvered Porous Silicon Covered with Graphene. Biosensors 2019, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korecka, M.; Shaw, L.M. Mass spectrometry-based methods for robust measurement of Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers in biological fluids. J. Neurochem. 2021, 159, 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnello, L.; Piccoli, T.; Vidali, M.; Cuffaro, L.; Lo Sasso, B.; Iacolino, G.; Giglio, V.R.; Lupo, F.; Alongi, P.; Bivona, G.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers measured by chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay for Alzheimer disease diagnosis. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investg. 2020, 80, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Yang, J.; Hu, C.; Dong, J.; Tang, H.; Zhou, B.; Wen, B.; Xiao, Z.; Zhu, M.; Cai, J.; et al. Multi-biomarker combination detection system for diagnosis and classification of dry eye disease by imaging of a multi-channel metasurface. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 248, 115933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehdari Vais, R.; Yadegari, H.; Heli, H.; Sattarahmady, N. A β-Amyloid((1-42)) Biosensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Poly-Pyrrole for Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2021, 11, 215–228. [Google Scholar]
- Negahdary, M.; Heli, H. An electrochemical peptide-based biosensor for the Alzheimer biomarker amyloid-β((1-42)) using a microporous gold nanostructure. Mikrochim. Acta. 2019, 186, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negahdary, M.; Heli, H. An ultrasensitive electrochemical aptasensor for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, using a fern leaves-like gold nanostructure. Talanta 2019, 198, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitka, O.; Krizkova, S.; Skalickova, S.; Dospivova, D.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R. Microfluidic tool coupled with electrochemical assay for detection of lactoferrin isolated by antibody-modified paramagnetic beads. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 2120–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negahdary, M.; Veloso, W.B.; Bacil, R.P.; Buoro, R.M.; Gutz, I.G.R.; Paixão, T.R.L.C.; do Lago, C.L.; Sakata, S.K.; Meloni, G.N.; França, M.C.; et al. Aptasensing of beta-amyloid (Aβ(1−42)) by a 3D-printed platform integrated with leaf-shaped gold nanodendrites. Sens. Actuators B 2023, 393, 134130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Yuan, W.; Kang, Y.; Xie, J.; Hu, F.; Li, C.M. Biomass-Derived Hierarchical Nanoporous Carbon with Rich Functional Groups for Direct-Electron-Transfer-Based Glucose Sensing. ChemElectroChem 2016, 3, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Angnes, L.; Sattarahmady, N.; Negahdary, M.; Heli, H. Electrochemical Immunosensors Developed for Amyloid-Beta and Tau Proteins, Leading Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biosensors 2023, 13, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Molazemhosseini, A.; Liu, C.C. In Vitro Quantified Determination of beta-Amyloid 42 Peptides, a Biomarker of Neuro-Degenerative Disorders, in PBS and Human Serum Using a Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Gold Film Biosensor. Biosensors 2017, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, J.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Ganapathy, D.; Atchudan, R.; Habila, M.A.; Nallaswamy, D. 2D MXene/graphene nanocomposite preparation and its electrochemical performance towards the identification of nicotine level in human saliva. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbagh, M.N.; Shi, J.; Lee, M.; Arnold, L.; Al-Hasan, Y.; Heim, J.; McGeer, P. Salivary beta amyloid protein levels are detectable and differentiate patients with Alzheimer’s disease dementia from normal controls: Preliminary findings. BMC Neurol. 2018, 18, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermejo-Pareja, F.; Antequera, D.; Vargas, T.; Molina, J.A.; Carro, E. Saliva levels of Abeta1-42 as potential biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease: A pilot study. BMC Neurol. 2010, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Fu, X.; Zhu, Z. Microfluidic beads-based immunosensor for sensitive detection of cancer biomarker proteins using multienzyme-nanoparticle amplification and quantum dots labels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.X.; Acha, D.; Shah, A.J.; Hills, F.; Roitt, I.; Demosthenous, A.; Bayford, R.H. Detection of the tau protein in human serum by a sensitive four-electrode electrochemical biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, R.; Xi, F. Enhanced Electrochemiluminescence of Luminol and-Dissolved Oxygen by Nanochannel-Confined Au Nanomaterials for Sensitive Immunoassay of Carcinoembryonic Antigen. Molecules 2024, 29, 4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.L.; Oliveira, D.; Pego, A.P.; Santos, S.D.; Moreira, F.T.C. Electrochemical miRNA-34a-based biosensor for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioelectrochemistry 2023, 154, 108553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xu, L.; Jia, N.; Huang, B.; Tan, L.; Yang, S.; Yao, S. Electrochemical immunoassay for carcinoembryonic antigen using gold nanoparticle-graphene composite modified glassy carbon electrode. Talanta 2013, 116, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Weng, X.; Milcovich, G. Dendritic Gold Nanoparticles Loaded on 3D Graphene-like Surface and Layer-by-Layer Assembly for Enhanced Glucose Biosensing. Biosensors 2025, 15, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ji, C.; Chen, D.; Nie, L. Applications of Gold Nanoparticles in Non-Optical Biosensors. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, P.; Li, J.; Jiang, F.; Meng, J.; Pan, H. Superwettable Dendritic Gold Nanostructured Electrode Arrays for Electrochemical Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbant Assay (ELISA). Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2022, 17, 220828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Liu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Li, P.; Yang, Z. A sensor for glycoproteins based on dendritic gold nanoparticles electrodeposited on a gold electrode and modified with a phenylboronic acid. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2015, 19, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Kulangara, V.; Vareed, T.P.; Melepat, D.P.; Chattothayil, L.; Chullipparambil, S. Variations in the levels of acute-phase proteins and lactoferrin in serum and milk during bovine subclinical mastitis. J. Dairy Res. 2021, 88, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, M.; Halder, A.; Mohammadniaei, M.; Prado, M.; Ashley, J.; Sun, Y. A multivalent aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for biomarker detection in urinary tract infection. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 389, 138644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, P.; Loureiro, J.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Morais, S.; do Carmo Pereira, M. Alzheimer’s disease: Development of a sensitive label-free electrochemical immunosensor for detection of amyloid beta peptide. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 239, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc Le, H.T.; Park, J.; Chinnadayyala, S.R.; Cho, S. Sensitive electrochemical detection of amyloid beta peptide in human serum using an interdigitated chain-shaped electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 144, 111694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, W.; Liu, C.; Zeng, J.; He, Z.; Wang, C.; Yuan, W.; Wang, Q. Flower-like CoO nanowire-decorated Ni foam: A non-invasive electrochemical biosensor for glucose detection in human saliva. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 36, 102083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, T.R.; Erbereli, C.R.; Manzine, P.R.; Magalhães, T.N.C.; Balthazar, M.L.F.; Cominetti, M.R.; Faria, R.C. Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease in Blood Using a Disposable Electrochemical Microfluidic Platform. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, T.R.; Manzine, P.R.; Cominetti, M.R.; Leite, O.D.; Faria, R.C. Electrochemical magneto-immunoassay for detection of ADAM10 Alzheimer’s biomarker using gold nanoparticles as label. Talanta 2024, 266, 125042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boston, P.F.; Gopalkaje, K.; Manning, L.; Middleton, L.; Loxley, M. Developing a simple laboratory test for Alzheimer’s disease: Measuring acetylcholinesterase in saliva—A pilot study. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2008, 23, 439–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.Y.; Watanabe, I.; Kunitake, Y.; Sugataka, K.; Muraoka, T.; Kojima, N.; Kawashima, T.; Yamada, S. Relationship between saliva level of 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol and mental health in the elderly general population. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 62, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navazesh, M. Methods for collecting saliva. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 694, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herr, A.E.; Hatch, A.V.; Throckmorton, D.J.; Tran, H.M.; Brennan, J.S.; Giannobile, W.V.; Singh, A.K. Microfluidic immunoassays as rapid saliva-based clinical diagnostics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5268–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, E.H.; Lathwal, S.; Shah, P.P.; Sikes, H.D. Detection of Biomarkers of Periodontal Disease in Human Saliva Using Stabilized, Vertical Flow Immunoassays. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1589–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.G.; Jung, D.; Kong, S.H. A Lab-on-a-Chip-Based Non-Invasive Optical Sensor for Measuring Glucose in Saliva. Sensors 2017, 17, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, J.M.; Schafer, C.A.; Schafer, J.J.; Farrell, J.J.; Paster, B.J.; Wong, D.T. Salivary biomarkers: Toward future clinical and diagnostic utilities. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Pdel, V.; Grégio, A.M.; Machado, M.A.; de Lima, A.A.; Azevedo, L.R. Saliva composition and functions: A comprehensive review. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2008, 9, 72–80. [Google Scholar]
- Sonuç Karaboğa, M.N.; Sezgintürk, M.K. A nano-composite based regenerative neuro biosensor sensitive to Parkinsonism-associated protein DJ-1/Park7 in cerebrospinal fluid and saliva. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 138, 107734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altuntas, S.; Buyukserin, F. Fabrication of thioflavin-T-modified nanopillared SERS substrates for ultrasensitive beta-amyloid peptide detection. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2018, 49, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Q.; Wei, Y.; Ji, J.; Zhang, W. Progress of new label-free techniques for biosensors: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Liao, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, W. Investigation of Whole and Glandular Saliva as a Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Meroni, M.; Casati, S.; Goldoni, R.; Thomaz, D.V.; Kehr, N.S.; Galimberti, D.; Del Fabbro, M.; Tartaglia, G.M. Salivary biomarkers: Novel noninvasive tools to diagnose chronic inflammation. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2023, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligtenberg, A.J.; Liem, E.H.; Brand, H.S.; Veerman, E.C. The Effect of Exercise on Salivary Viscosity. Diagnostics 2016, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilancio, G.; Cavallo, P.; Lombardi, C.; Guarino, E.; Cozza, V.; Giordano, F.; Palladino, G.; Cirillo, M. Saliva for assessing creatinine, uric acid, and potassium in nephropathic patients. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almadori, G.; Bussu, F.; Galli, J.; Limongelli, A.; Persichilli, S.; Zappacosta, B.; Minucci, A.; Paludetti, G.; Giardina, B. Salivary glutathione and uric acid levels in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2007, 29, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Naruishi, N.; Fukuya, H.; Sakata, J.; Saito, K.; Wakida, S.-i. Simultaneous determination of nitrite, nitrate, thiocyanate and uric acid in human saliva by capillary zone electrophoresis and its application to the study of daily variations. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1051, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsaeivahid, N.; Grenier, C. Filtered Saliva for Rapid and Accurate Analyte Detection for POC Diagnostics. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Honig, L.S.; Kang, M.S.; Bahl, A.; Sanchez, D.; Reyes-Dumeyer, D.; Manly, J.J.; Dage, J.L.; Lantigua, R.A.; Brickman, A.M.; et al. Risk of Alzheimer’s disease is associated with longitudinal changes in plasma biomarkers in the multi-ethnic Washington Heights-Hamilton Heights-Inwood Columbia Aging Project (WHICAP) cohort. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 1988–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Cummings, J.; Blennow, K.; Gao, P.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Vergallo, A. Developing the ATX(N) classification for use across the Alzheimer disease continuum. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Number of Cycles | ΔIpa (%) | ΔEpa (mV) | ΔIpc (%) | ΔEpc (mV) | Overlap |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (ref) | - | - | - | - | - |
| 15 | 7.49% | −21 | 2.87% | 0 | 95.96% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, P.; Wang, J.; Mao, H.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Sun, T.; Hui, J.; Ma, G. AuNP/Magnetic Bead-Enhanced Electrochemical Sensor Toward Dual Saliva Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 4088. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134088
Zhao P, Wang J, Mao H, Zhou L, Wu Z, Lu Y, Sun T, Hui J, Ma G. AuNP/Magnetic Bead-Enhanced Electrochemical Sensor Toward Dual Saliva Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Detection. Sensors. 2025; 25(13):4088. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134088
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Pengcheng, Jieyu Wang, Hongju Mao, Lin Zhou, Zhenhua Wu, Yunxing Lu, Teng Sun, Jianan Hui, and Guowu Ma. 2025. "AuNP/Magnetic Bead-Enhanced Electrochemical Sensor Toward Dual Saliva Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Detection" Sensors 25, no. 13: 4088. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134088
APA StyleZhao, P., Wang, J., Mao, H., Zhou, L., Wu, Z., Lu, Y., Sun, T., Hui, J., & Ma, G. (2025). AuNP/Magnetic Bead-Enhanced Electrochemical Sensor Toward Dual Saliva Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Detection. Sensors, 25(13), 4088. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134088






