Enhanced Distributed Energy-Efficient Clustering (DEEC) Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks: A Modular Implementation and Performance Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. WSNs Background
2.1. Communication in WSNs
- -
- Sensing Unit: This unit includes sensors and Analog-to-Digital converters (ADCs) to measure and digitise physical phenomena.
- -
- Processing Unit: A microcontroller or microprocessor typically processes sensor data and manages communication protocols.
- -
- Communication Unit: A wireless transceiver that enables data exchange between nodes and the base station.
- -
- Power Unit: Often powered by batteries, with energy harvesting mechanisms (e.g., solar panels) increasingly integrated to extend network lifetime.
2.2. Key Characteristics and Challenges
- -
- Energy Efficiency: Since sensors are often battery-powered in the network, energy efficiency is crucial for their hardware, communication methods, and data processing. This helps data processing algorithms to maximise network lifetime without needing battery replacements.
- -
- Scalability: As the number of nodes increases, maintaining efficient communication and data aggregation becomes complex.
- -
- Reliability: Ensuring robust communication in the presence of interference, node failures, or environmental obstacles is critical.
- -
- Security: WSNs can be targeted for various types of attacks, such as eavesdropping or data tampering, as well as denial-of-service attacks. This means that it is essential to have lightweight security measures in place to protect the data and communication without overburdening the system.
3. Related Works
4. DEEC
4.1. Energy Model
4.2. Cluster Head Selection
5. Improved DEEC Protocol
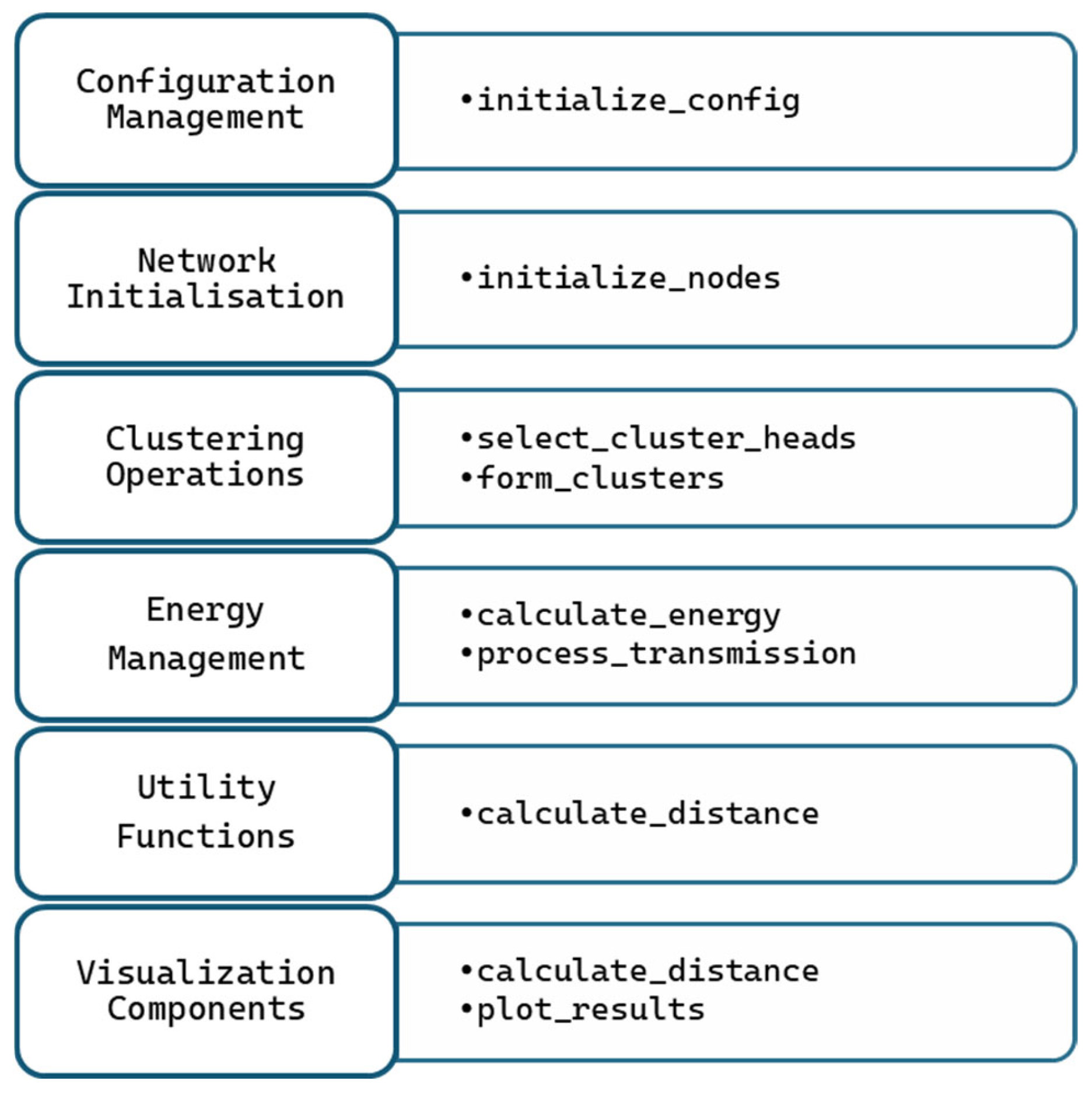
5.1. Component Analysis
- Main Controller: The simulation in MATLAB® begins by initialising the network configuration and setting up the sensor nodes. This includes defining node positions, assigning initial energy levels, and configuring the base station location. The following list shows the main steps of the Improved DEEC Protocol Algorithm.
- Configuration Management: Configuration parameters for mathematical models are shown in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1 Improved DEEC Protocol |
| Input: N—Total number of sensor nodes E0—Initial energy of a normal node α—Additional energy factor for advanced nodes β—Additional energy factor for super nodes Popt—Optimal probability of a node becoming a cluster head area_x—Width of the sensor network area area_y—Height of the sensor network area max_rounds—Maximum number of simulation rounds Output: metrics—Network performance metrics (packets sent, network lifetime, throughput, packet loss, average energy, dead nodes, cluster heads) begin 1: InitializeNodes(N, E0, α, β) // Step 1: Initialization 2: SetBaseStation(area_x / 2, area_y / 2) 3: for round ← 1 to max_rounds do // Step 2: Simulation Loop 4: for each node i ∈ AliveNodes do // Step 3: Cluster Head Selection 5: Pi ← Popt × (node[i].energy / avg_network_energy) 6: if Uniform (0,1) < Pi then 7: node[i].is_CH ← true 8: end if 9: end for 10: for each node ∈ NonClusterHeads do // Step 4: Cluster Formation 11: nearest_CH ← FindNearestClusterHead(node) 12: JoinCluster(node, nearest_CH) 13: end for 14: for each node ∈ Nodes do // Step 5: Data Transmission 15: if node.is_CH = true then 16: ReceiveFromMembers(node) 17: AggregateData(node) 18: TransmitToBaseStation(node) 19: else 20: TransmitToClusterHead(node) 21: end if 22: end for 23: for each node ∈ Nodes do // Step 6: Energy Update 24: node.energy ← node.energy − energy_consumed 25: if node.energy ≤ 0 then 26: node.alive ← false 27: end if 28: end for 29: UpdatePerformanceMetrics(round) // Step 7: Metrics Update 30: end for 31: metrics ← GenerateFinalResults() 32: return metrics end |
- Energy Model: The energy consumption of nodes during data transmission and reception is calculated as shown in Equation (4). It uses a realistic model that switches between free-space and multi-path propagation based on the transmission distance.
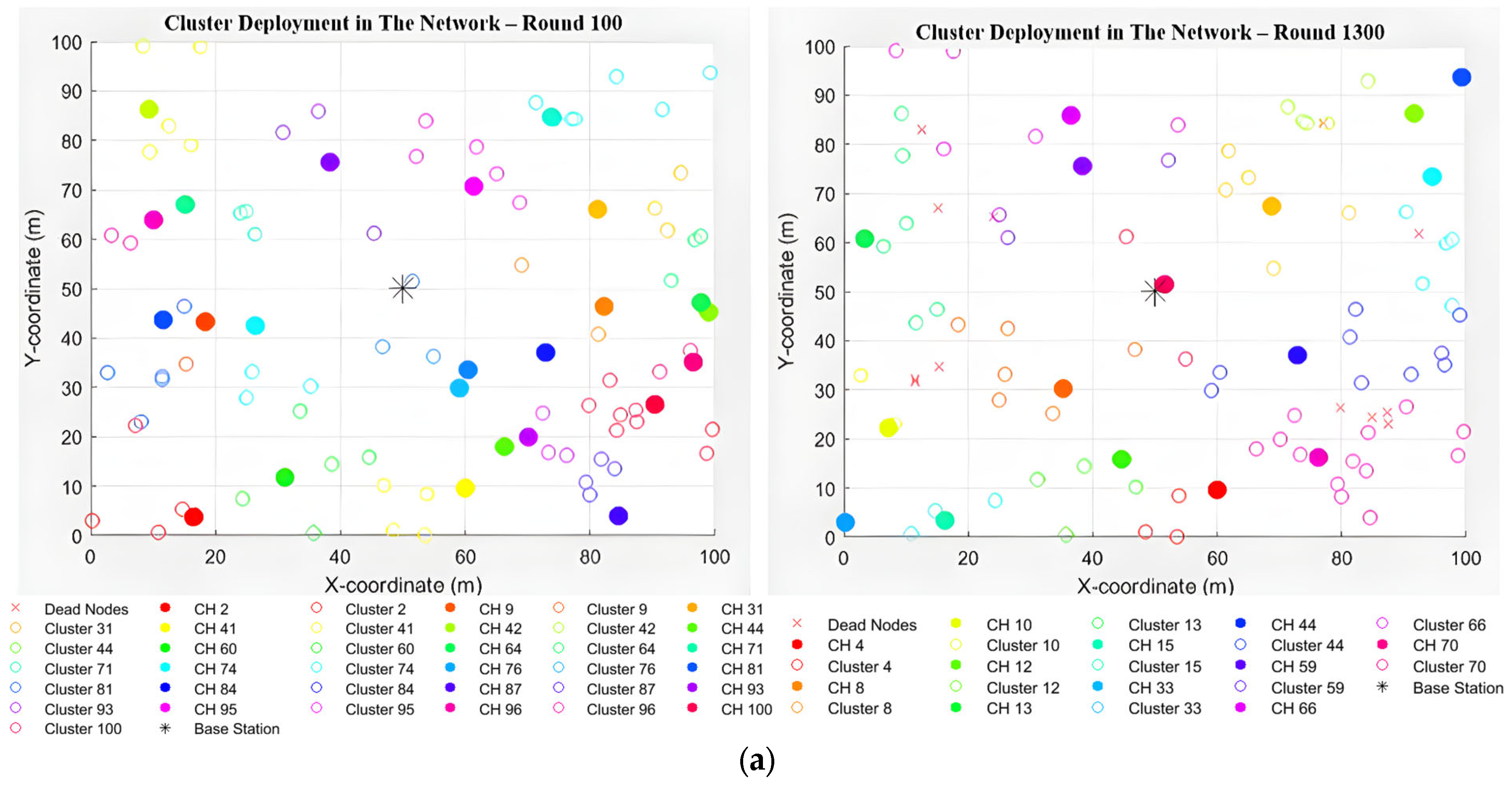
- Cluster Head Selection: This module dynamically selects cluster heads (CHs) based on the residual energy of nodes and the network’s average energy. It ensures fair rotation of CHs to balance the energy load. The probability of node i becoming a cluster head can be calculated from Equation (5):
- Cluster Formation: This module assigns nodes to the nearest CH and calculates the distance between two nodes D(x,y), where x,y are coordinates of a set of nodes, such as x = {x1, x2, …… xn}, y = {y1, y2, …… yn}. Euclidean distance will be used, which can be calculated from Equation (7). It ensures that no CH is overloaded with too many nodes. The cluster information will be formatted as shown in Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 2 Cluster Formation in the Improved DEEC Protocol | |
| Input: Nodes—Array of sensor nodes with coordinates (x, y) and cluster head status CH_nodes—Set of nodes designated as cluster heads non_CH_nodes—Set of nodes that are not cluster heads max_cluster_size—Maximum number of nodes allowed per cluster (for load balancing) Output: cluster_assignments: Updated cluster membership for all nodes begin 1: for each node i ∈ nodes do // Step 1: Initialise cluster membership 2: to nodes[i].cluster_head ← null 3: nodes[i].distance_to_CH ← ∞ 4: end for 5: for each node i ∈ non_CH_nodes do // Step 2: Computation of optimal cluster 6: min_distance ← ∞ 7: nearest_CH ← null 8: end for 9: for each node j ∈ CH_nodes do // Step 3: Evaluation of distances to all available CHs 10: distance ← √((nodes[i].x − nodes[j].x)2 + (nodes[i].y − nodes[j].y)2) 11: if distance < min_distance and IsClusterLoadBalanced(j, max_cluster_size) then 12: min_distance ← distance 13: nearest_CH ← j 14: end if 15: end for 16: if nearest_CH ≠ null then // Step 4: Assignment of node to optimal CH 17: nodes[i].cluster_head ← nearest_CH 18: nodes[i].distance_to_CH ← min_distance 19: nodes[nearest_CH].cluster_members.add(i) cluster head 20: end if 21: cluster_assignments ← nodes 22: return cluster_assignments end |
5.2. Mathematical Framework
5.2.1. Initial Energy Allocation in a Heterogeneous Network
5.2.2. Derivation of the Optimal Number of Clusters
5.2.3. Role of Node Tiers in DEEC Operation
- -
- Normal nodes (Ei = E0): Perform sensing and intra-cluster data transmission. Rarely selected as CHs in later rounds because of their limited residual energy.
- -
- Advanced nodes (Ei = E0 (1 + α)): Possess additional energy (αE0) that increases their probability of becoming CHs. Act as relay nodes when neighbouring normal nodes deplete their energy.
- -
- Super nodes (Ei = E0 (1 + β)): Highest initial energy reserve; dominate CH selection in the network’s later life. Often placed in strategically important positions (e.g., far from the BS) to reduce overall multi-hop path length.
5.3. Performance Metrics
- -
- Network Lifetime: The time until all nodes die.
- -
- Stability Period: The time until the first node dies.
- -
- Throughput: The number of packets successfully delivered to the BS.
- -
- Packet Loss: The number of packets lost during transmission.
5.4. Communication Protocol
- -
- Cluster Head (CH) Selection: Nodes probabilistically determine if they become CHs based on their residual and average network energy (Equation (5)). If a node’s probability exceeds a threshold (Equation (6)), it becomes a CH.
- -
- CH Advertisement: The elected CHs broadcast an advertisement message, which includes their IDs, to all nodes within their communication range.
- -
- Cluster Formation: Non-CH nodes receive these advertisements and choose the closest CH to join based on the Euclidean distance (Equation (7)), ensuring no CH is overloaded.
- -
- Data Transmission: Member nodes transmit their data to the CH.
- -
- Data Aggregation: The CH aggregates the data received from its member nodes to reduce redundancy and energy consumption.
- -
- Transmission to Base Station: The CH transmits the aggregated data to the base station.
- -
- Energy Model: Energy consumption is calculated using free-space and multi-path propagation models (Equation (4)), accounting for the distance between nodes.
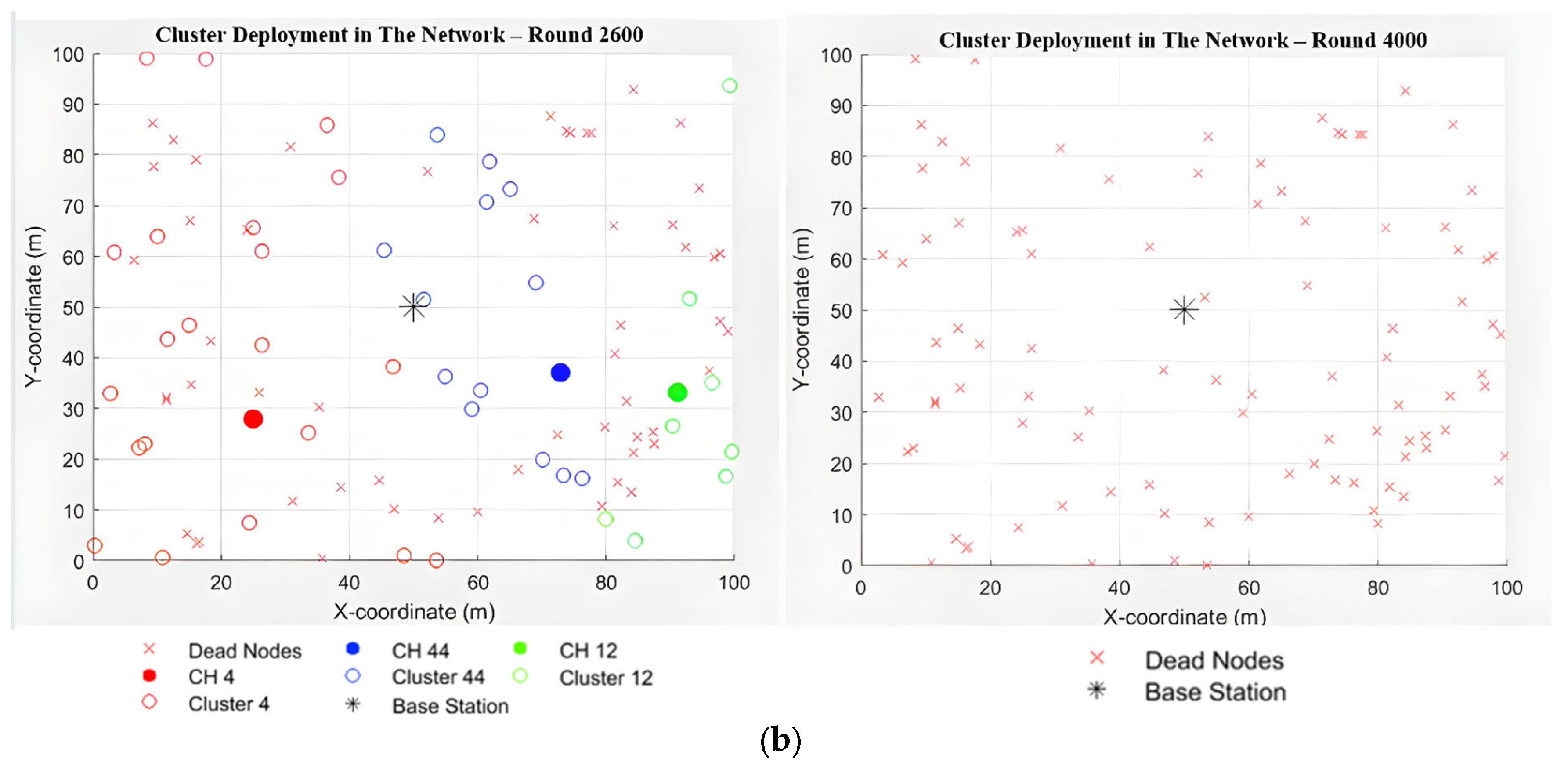
6. Results
6.1. Results Analysis
- Throughput: The number of packets successfully sent to the base station.
- Packet Loss: The number of packets lost during transmission.
- Network Lifetime: The average residual energy of the network.
6.2. Comparative Analysis with Recent DEEC Approaches
6.2.1. Network Lifetime and Stability Period
6.2.2. Throughput and Energy Efficiency
6.2.3. Scalability
7. Discussion
- The cluster head probability is proportional to the node’s residual energy and inversely proportional to the total network energy.
- It includes a threshold (Ti) to ensure fair CH rotation over rounds.
- -
- The Main Controller initialises the network and coordinates the simulation process.
- -
- The Configuration Management module provides the necessary parameters for the Energy Model and Cluster Head Selection modules.
- -
- The Energy Model calculates energy consumption and updates the residual energy of nodes, which is used by the Cluster Head Selection module.
- -
- The Cluster Head Selection module determines CHs and sends this information to the Cluster Formation module.
- -
- The Cluster Formation module assigns nodes to CHs and updates the network topology.
- -
- The Performance Metrics module evaluates the protocol’s performance based on data from all other modules.
- -
- The Visualisation module generates real-time plots illustrating the network’s status and performance.
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heinzelman, A.; Chandrakasan, A.; Balakrishnan, H. Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, 7 January 2000; Volume 2, p. 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vançin, S.; Erdem, E. Threshold balanced sampled DEEC model for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2018, 2018, 4618056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsafi, S.; Talab, S.A. Implementation of DEEC, DDEEC, EDEEC and TDEEC protocols using MATLAB in wireless sensor network. Int. J. Adv. Netw. Appl. 2020, 12, 4596–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Singh, S. Constrains and their Impacts for Improving Latency of DEEC based Routing Protocols for IOT-WSN. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Automation (ICCCA), Arad, Romania, 17–19 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, A.; Kumar, A.; Mandoria, H.; Pandey, B. Study and analysis of deec protocols in hetergeneous wsns using matlab. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2016, 3, 1902–1907. [Google Scholar]
- Banita, B. Comparative Analysis of Mobility based DEEC Protocol to Optimise the Efficiency in Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 11th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence), Noida, India, 28–29 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jibreel, F.; Daabo, I.M.; Aziz, A.A. Distance-Distributed Energy Efficient Clustering (D-DEEC) Routing Protocol for Wireless Sensor Network. Asian J. Res. Comput. Sci. 2024, 17, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibreel, F. Improved Enhanced Distributed Energy Efficient Clustering (iE-DEEC) scheme for heterogeneous wireless sensor network. Int. J. Eng. Res. Adv. Technol. (IJERAT) 2019, 5, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Ryait, H.S.; Gupta, A.K. Performance analysis of ATTEMPT, SIMPLE and DEEC routing protocols in WBAN. Int. J. Latest Trends Eng. Tech. 2015, 6, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Redjimi, K.; Boulaiche, M.; Redjimi, M. DEEC and EDEEC routing protocols for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks: A brief comparative study. In International Conference on Deep Learning, Artificial Intelligence and Robotics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jangra, R.; Kait, R. DEEC Protocol with ACO Based Cluster Head Selection in Wireless Sensor Network. In International Conference on Computing Science, Communication and Security; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, R.K.; Mishra, R. Analysis of DEEC deviations in heterogeneous WSNs: A survey. In Computer Communication, Networking and IoT: Proceedings of ICICC 2020; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, A.A.; Swaminathan, A.; Brundha; Pajila, B. A comparative analysis of LEACH, TEEN, SEP and DEEC in hierarchical clustering algorithm for WSN sensors. In Intelligent Communication Technologies and Virtual Mobile Networks: ICICV 2019; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 395–403. [Google Scholar]
- Juwaied, A.; Jackowska-Strumillo, L. Improving Performance of Cluster Heads Selection in DEC Protocol Using K-Means Algorithm for WSN. Sensors 2024, 24, 6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juwaied, A.; Jackowska-Strumillo, L.; Sierszeń, A. Enhancing Clustering Efficiency in Heterogeneous Wireless Sensor Network Protocols Using the K-Nearest Neighbours Algorithm. Sensors 2025, 25, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juwaied, A.; Jackowska-Strumiłło, L.; Sierszeń, A. Modified TEEN Protocol in Wireless Sensor Network Using KNN Algorithm. In Image Processing and Communications Challenges 10. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference, IP&C’2018, Bydgoszcz, Poland, 14–16 November 2018; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 892, pp. 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Koyuncu, H.; Tomar, G.S.; Sharma, D. A New Energy Efficient Multitier Deterministic Energy-Efficient Clustering Routing Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks. Symmetry 2020, 12, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiq, A.; Ghazwani, Y.J. Hybrid Optimized Deep Neural Network-Based Intrusion Node Detection and Modified Energy Efficient Centralized Clustering Routing Protocol for Wireless Sensor Network. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2024, 70, 6303–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhao, H.; Fan, F.; Liu, G.; Xu, Q.; Nazir, S. An Enhanced Intrusion Detection Model Based on Improved KNN in WSNs. Sensors 2022, 22, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheshwar, K.; Suraparaju, V.; Almelu, M. Energy Efficient Heterogeneous WNS Clustering Using Machine Learning. Smart Moves J. Ijosci. 2021, 7, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, H.H.; Hashem, Z.M. Comparison of the new version of DEEC protocol to extend WSN lifetime. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2023, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, P.; Bhardwaj, D. Evaluating Energy Efficiency and Performance of WSN Routing Protocols: A Comparative Study of LEACH, DEEC, DDEEC, and EESAA. In International Conference on Sustainable and Innovative Solutions for Current Challenges in Engineering & Technology; Springer: Singapore, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Malik, A. hetDEEC: Heterogeneous DEEC protocol for prolonging lifetime in wireless sensor networks. J. Inf. Optim. Sci. 2017, 38, 699–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, N.; Mardani, A.; Mohan, P.; Mishra, A.; Ezhumalai, P. A fuzzy logic and DEEC protocol-based clustering routing method for wireless sensor networks. AIMS Math. 2023, 8, 8310–8331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagga, S.; Chawla, N.; Sharma, D.K.; Kukreja, D. Fuzzy Logic based Clustering Algorithm to Improve DEEC Protocol in Wireless Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (GUCON), New Delhi, India, 27–28 September 2019; pp. 212–216. [Google Scholar]
- Nehra, V.; Sharma, A.K.; Tripathi, R.K. I-DEEC: Improved DEEC for blanket coverage in heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. J. Ambient. Intell. Human Comput. 2020, 11, 3687–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Nehra, V. Trade-off analysis for different Sink locations in DEEC Protocol. In Proceedings of the 2022 Second International Conference on Computer Science, Engineering and Applications (ICCSEA), Gunupur, India, 8 September 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, B.; Senthilkumar, C. An effective delay reduction routing protocol for WSN using optimised distributed energy efficient clustering (O-DEEC) protocol compared with DEEC protocol. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Greater Noida, India, 2024; Volume 2816. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, M. Design of a distributed energy-efficient clustering algorithm for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Comput. Commun. 2006, 29, 2230–2237. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.; Ching, P.C. Energy efficiency for proactive eavesdropping in cooperative cognitive radio networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 13443–13457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
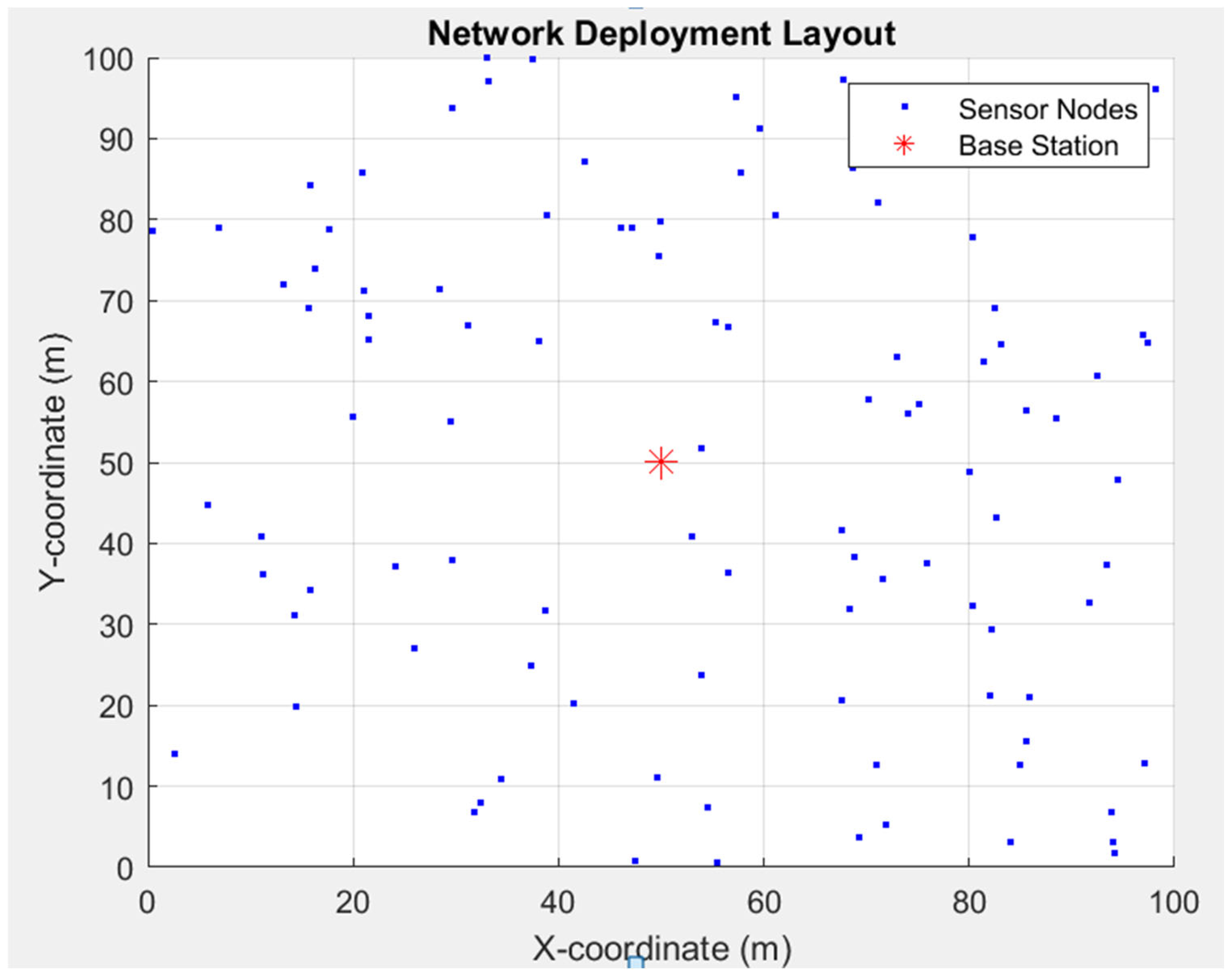

| No | Parameters | Definition | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | x × y | 100 m × 100 m | Area of network, dimensions |
| 2 | n | 100 | Number of nodes in the network |
| 3 | Rmax | 4000 | Maximum number of rounds |
| 4 | Popt | 0.1 | The probability of a node becoming CH |
| 5 | Eelec | 50 nJ/bit | Energy dissipation per bit |
| 6 | Efs | 10 pJ/bit/m2 | Energy dissipation for free space |
| 7 | Emp | 0.0013 pJ/bit/m4 | Energy dissipation for multi-path delay |
| 8 | ERx | 50 nJ/bit | Receiving energy of the sensor |
| 9 | ED | 5 nJ/bit/message | Data aggregation energy |
| 10 | Px | 0.1 | Probability of a node to become a cluster head |
| 11 | L | 4000 bits | Packet size |
| No | Aspect | Original DEEC | Improved DEEC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Energy Model | Simple, single amplification model | Realistic, with free-space and multi-path models |
| 2 | Node Heterogeneity | Homogeneous nodes | Heterogeneous nodes (normal, advanced, super) |
| 3 | Cluster Head Selection | Based on energy/average energy | Probabilistic, with fair rotation and load balancing |
| 4 | Cluster Formation | Nearest CH only | Nearest CH with load balancing |
| 5 | Packet Loss | Not considered | Simulated with a loss probability |
| 6 | Data Aggregation | Not Implemented | Implemented at CHs |
| 7 | Metrics | Basic (dead nodes, CHs, avg. energy) | Comprehensive (throughput, packet loss, lifetime) |
| 8 | Visualisation | Static topology, basic plots | Dynamic topology, detailed plots |
| 9 | Modularity | Minimal | Highly modular |
| 10 | Scalability | Limited | Designed for large-scale networks |
| No | Feature | Original DEEC | Improved DEEC | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
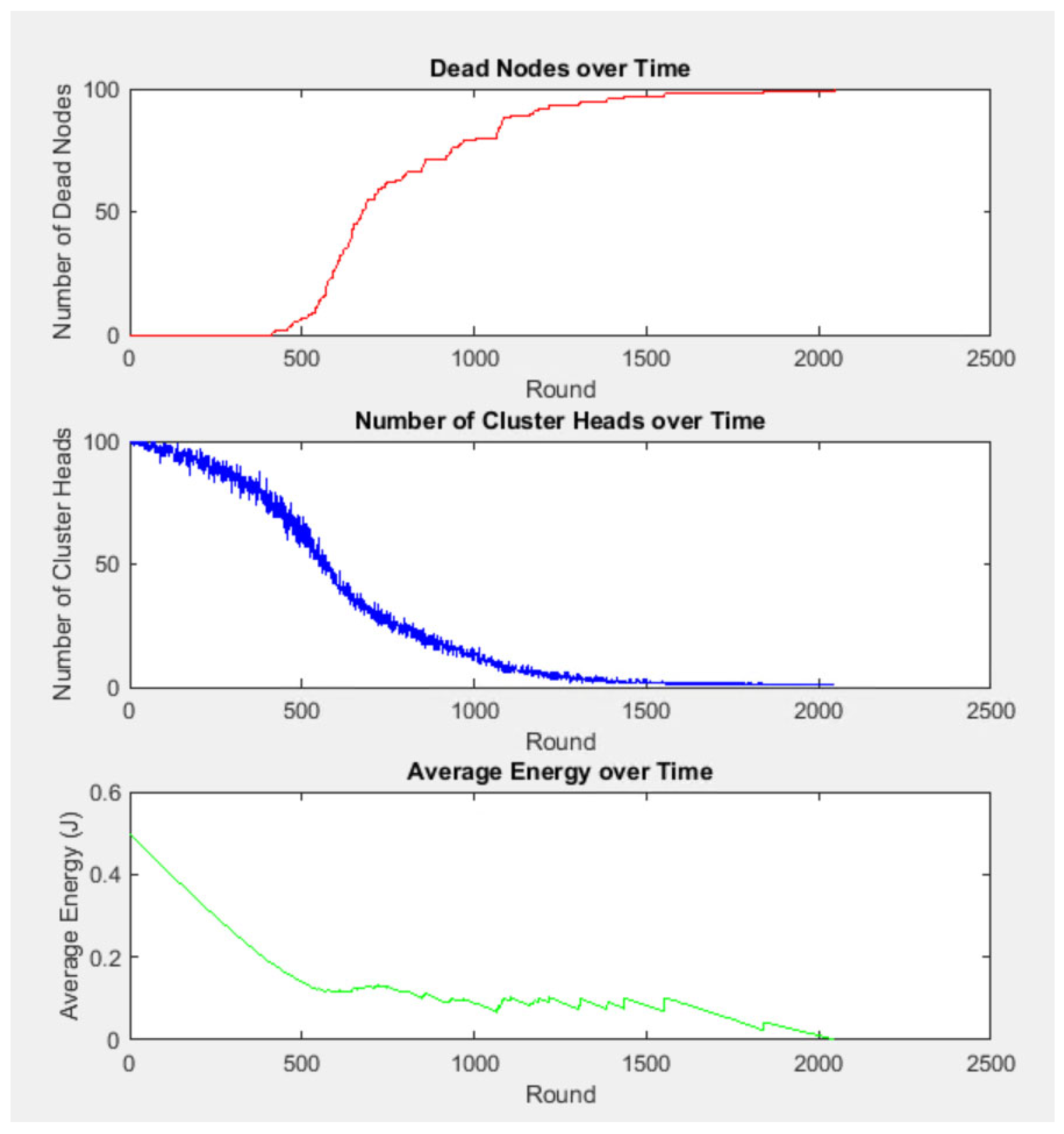
| 1 | First Node Death (FND) | 472 rounds | 1166 rounds | 133% longer stability |
| 2 | Last Node Death (LND) | 2111 rounds | 4000 rounds | 98.5% longer lifetime |
| 3 | Stability Period | 1500 rounds | 2834 rounds | 89% longer stability |
| 4 | Energy Stabilisation | No stabilisation | Stabilises at ~0.2 J | Better energy management |
| 5 | Cluster Head Stability | 1000 rounds | 2000 rounds | 100% longer stability |
| 6 | Network Lifetime | 2111 rounds | 4000 rounds | 100% longer lifetime |
| 7 | Average Energy | Near 0 J at 2111 rounds | Stabilises at 0.26 J after 2000 rounds | Energy conserved longer |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juwaied, A.; Jackowska-Strumillo, L.; Majchrowicz, M. Enhanced Distributed Energy-Efficient Clustering (DEEC) Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks: A Modular Implementation and Performance Analysis. Sensors 2025, 25, 4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134015
Juwaied A, Jackowska-Strumillo L, Majchrowicz M. Enhanced Distributed Energy-Efficient Clustering (DEEC) Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks: A Modular Implementation and Performance Analysis. Sensors. 2025; 25(13):4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134015
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuwaied, Abdulla, Lidia Jackowska-Strumillo, and Michal Majchrowicz. 2025. "Enhanced Distributed Energy-Efficient Clustering (DEEC) Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks: A Modular Implementation and Performance Analysis" Sensors 25, no. 13: 4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134015
APA StyleJuwaied, A., Jackowska-Strumillo, L., & Majchrowicz, M. (2025). Enhanced Distributed Energy-Efficient Clustering (DEEC) Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks: A Modular Implementation and Performance Analysis. Sensors, 25(13), 4015. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25134015









