The Synergistic Effect of Electric-Field and Adsorption Enhancement of Amino Acid Carbon Dots Significantly Improves the Detection Sensitivity of SPR Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of Carbon Dots
2.3. Characterizations
2.4. Preparation of Sensing Chip
2.5. Apparatus
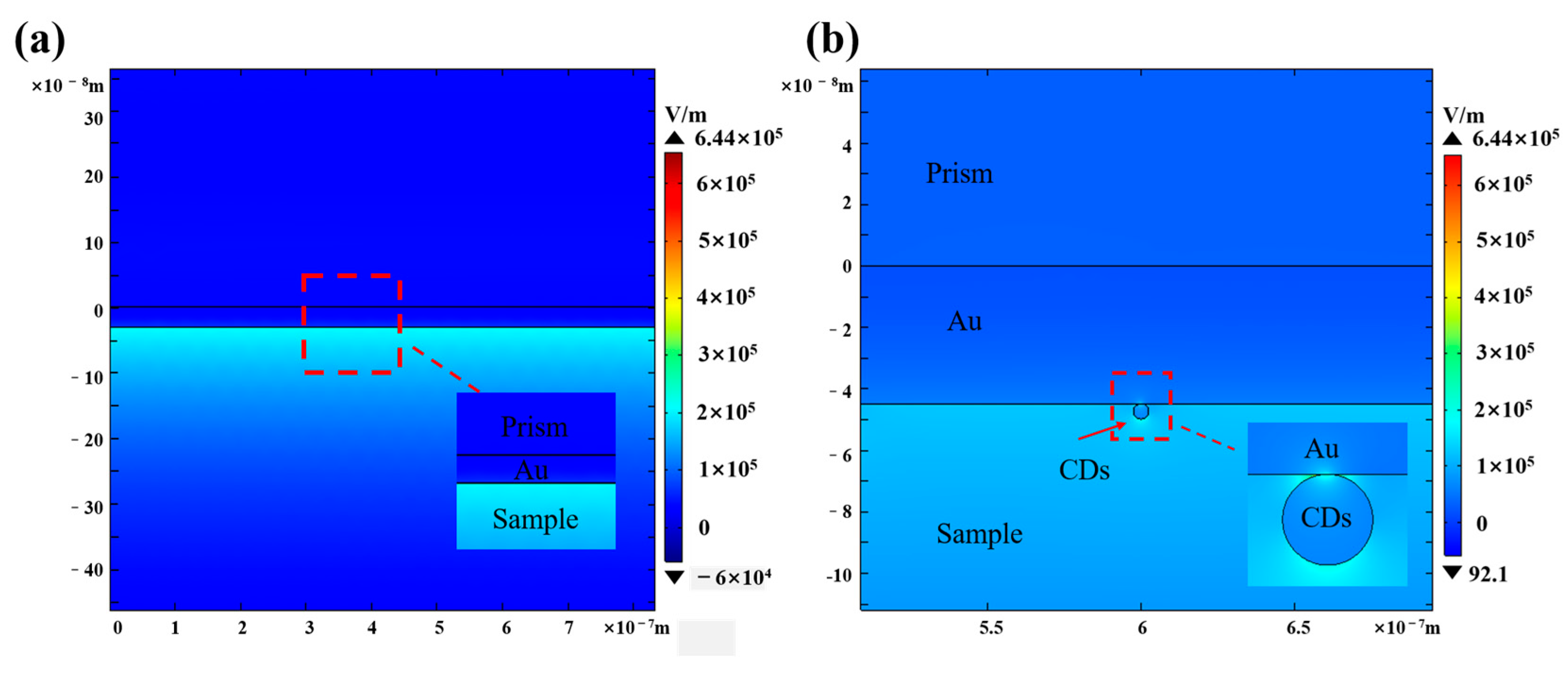
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Omidniaee, A.; Karimi, S.; Farmani, A. Surface Plasmon Resonance-Based SiO2 Kretschmann Configuration Biosensor for the Detection of Blood Glucose. Silicon 2021, 14, 3081–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Hide, M. Diagnosis of immediate-type allergy using surface plasmon resonance. Opt. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, N.I.M.; Fen, Y.W.; Omar, N.A.S.; Saleviter, S.; Daniyal, W.M.E.M.M.; Hashim, H.S.; Nasrullah, M. Nanostructured Chitosan/Maghemite Composites Thin Film for Potential Optical Detection of Mercury Ion by Surface Plasmon Resonance Investigation. Polymers 2020, 12, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Situ, C.; Mooney, M.H.; Elliott, C.T. Advances in surface plasmon resonance biosensor technology towards high-throughput, food-safety analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chang, M.; Yu, X.; Zhou, J.; Shi, Y. SPR humidity dynamic monitoring method via PVA sensing membrane thickness variation and image processing techniques. Photonics Nanostruct.—Fundam. Appl. 2024, 61, 101301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Ouyang, J.; Li, Z.; Shi, C.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J.; Chang, M. Widening of Dynamic Detection Range in Real-Time Angular-Interrogation Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor Based on Anisotropic Van Der Waals Heterojunction. Biosensors 2024, 14, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Xiaolong, Q.; Wanlu, Z.; Yi, L.; Siyu, E.; Zhang, Y.N. Theoretical and experimental characterization of a salinity and temperature sensor employing optical fiber surface plasmon resonance (SPR). Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2020, 48, 601–615. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao-Li, Z.; Yunze, Y.; Shaopeng, W.; Xian-Wei, L. Surface Plasmon Resonance Microscopy: From Single-Molecule Sensing to Single-Cell Imaging. Angew. Chem. (Int. Ed. Engl.) 2020, 59, 1776–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, W.L.; Dereux, A.; Ebbesen, T.W. Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 2003, 424, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manera, M.G.; Colombelli, A.; Rella, R.; Caricato, A.; Cozzoli, P.D.; Martino, M.; Vasanelli, L. TiO2 brookite nanostructured thin layer on magneto-optical surface plasmon resonance transductor for gas sensing applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 053524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siew, M.G.; Susthitha, M.P.; Gurumurthy, H. ZnO for performance enhancement of surface plasmon resonance biosensor: A review. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 012003. [Google Scholar]
- Fusheng, D.; Kai, Z.; Shuwen, Z.; Yufeng, Y. Sensitivity enhanced tunable plasmonic biosensor using two-dimensional twisted bilayer graphene superlattice. Nanophotonics 2023, 12, 1271–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Yangyang, Z.; Hezhen, L.; Junjie, X.; Zhongzheng, Z.; Kwangnak, K.; Hongxia, C. Controllable synthesis of multi-tip spatial gold nanostructures to facilitate SPR enhancement for exosomal PD-L1 assay. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148137. [Google Scholar]
- Shariq, M.; Madkhli, A.Y.; Kawtherali, S.F.; Alshehri, K.; Alasmari, A.; Algarni, Z.S.; Alzahrani, H.S.; Alharbi, S.H.; Idris, M. Recent advancement in development of nitrogen-doped cqds for dye sensitized solar cell and photodetector. Rev. Surf. Interfaces 2025, 59, 105913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, C.; Zhang, M.; Yan, W.; Kang, Z. Multifunctional Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Carbon Dots for Temperature-Responsive Sensor, Information Encryption, and Organelle Imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2405669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.B.; Mirsky, S.K.; Shaked, N.T.; Gazit, E. High Quantum Yield Amino Acid Carbon Quantum Dots with Unparalleled Refractive Index. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 2421–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Yoo, J.; Lim, B.; Kwon, W.; Rhee, S.-W. Improving the functionality of carbon nanodots: Doping and surface functionalization. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. Energy Sustain. 2016, 4, 11582–11603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qandeel, N.A.; El-Masry, A.A.; Eid, M.; Moustafa, M.A.; El-Shaheny, R. Fast one-pot microwave-assisted green synthesis of highly fluorescent plant-inspired S,N-self-doped carbon quantum dots as a sensitive probe for the antiviral drug nitazoxanide and hemoglobin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1237, 340592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrien, R.; Clément, L.; Sandrine, I.; Emmanuelle, L.; Benoit, D.; Emmanuel, L. Surface Control of Doping in Self-Doped Nanocrystals. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 27122–27128. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Xia, B.; Niu, K.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, N. Ultrasensitive optical fiber SPR sensor enhanced by Au-NPs-film modified with functionalized CQDs for label-free detecting cobalt (II) ion. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1320, 343030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhnasab, O.; Moghadam, A.; Eslamifar, Z.; Moghadam, A.H. Fabrication and characterization of chitosan-based bionanocomposite coating reinforced with TiO2 nanoparticles and carbon quantum dots for enhanced antimicrobial efficacy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 296, 139648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, S.; Ghadiri, H.; Dabirmanesh, B.; Khajeh, K. The impact of quantum dot on the SPR detection improvement of molecular interactions between Rap1 interacting factor1 (Rif1) and G4. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2024, 43, 100621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.N.A.; Hidayah, A.N.; Abu, B.M.H.; Naiim, M.N.; Sakinah, M.A.; Md, Z.A.R.; Adzir, M.M.; Gandaryus, S.A.; Kencana, W.T.D.; Yunhan, L.; et al. Polymeric carbon quantum dots as efficient chlorophyll sensor-analysis based on experimental and computational investigation. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 170, 110259. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Ye, S.; Guo, J.; Wang, H.; Yan, W.; Song, J.; Qu, J. Biocompatible carbon dots with low-saturation-intensity and high-photobleaching-resistance for STED nanoscopy imaging of the nucleolus and tunneling nanotubes in living cells. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 3075–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, L.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, F.; Sun, C.; Li, H.; Li, H.; He, Y.; et al. Fluorine-Nitrogen Codoped Carbon Dots for Visualization Imaging of Nucleic Acids via Two-Photon Fluorescence Lifetime Microscopy. Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 5744–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fen, Y.W.; Yunus, W.M.M.; Yusof, N.A. Surface plasmon resonance optical sensor for detection of Pb2+ based on immobilized p-tert-butylcalix[4]arene-tetrakis in chitosan thin film as an active layer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 171–172, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashar, K.E.F.; Wing, F.Y.; Sheh, O.N.A.; Chyi, L.J.Y.; Mohd, D.W.M.E.M. Femtomolar detection of dopamine using surface plasmon resonance sensor based on chitosan/graphene quantum dots thin film. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 263, 120202. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Huang, G.; Song, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, K. Unlocking the potential of chitosan in immunoassay sensor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 350, 123024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zeng, H.; Wu, X.; Li, T.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, M.; Chen, L.; Pan, K.; Guo, X. Chitosan-based porous composites embedded with molybdenum disulfide nanosheets for removal of mercury from wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 285, 138379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.C.; Vieira, I.C.; Peralta, R.A.; Neves, A. Development of a biomimetic chitosan film-coated gold electrode for determination of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid and uric acid. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 7152–7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilang, G.; Silvia, C.; Ganes, S.; Aep, P.; Nugraha, N.; Joel, H.; Isa, A.; Valentino, K.Y.; Brian, Y. The revelation of glucose adsorption mechanisms on hierarchical metal-organic frameworks using a surface plasmon resonance sensor. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 4428–4444. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, R.; Yan, X.; Hu, T.; Li, H.; Cheng, T. Carbon Dots-Based Surface Plasmon Resonance Manganese Ion Fiber Sensor for Multi-Use Scenarios. Photonic Sens. 2025, 15, 250311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosddi, N.N.M.; Fen, Y.W.; Omar, N.A.S.; Anas, N.A.A.; Hashim, H.S.; Ramdzan, N.S.M.; Fauzi, N.I.M.; Anuar, M.F.; Daniyal, W.M.E.M.M. Glucose detection by gold modified carboxyl-functionalized graphene quantum dots-based surface plasmon resonance. Optik 2021, 239, 166779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
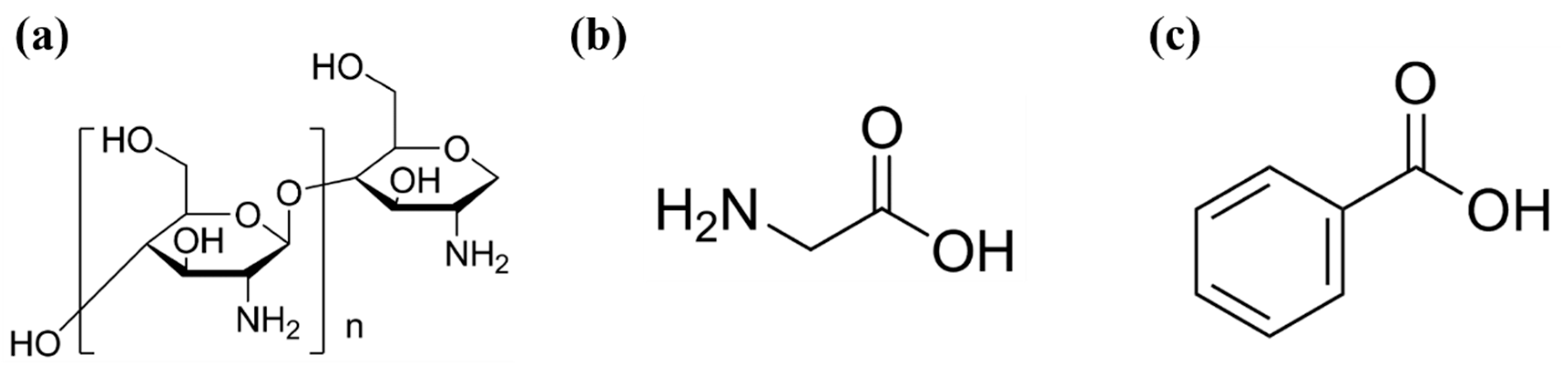




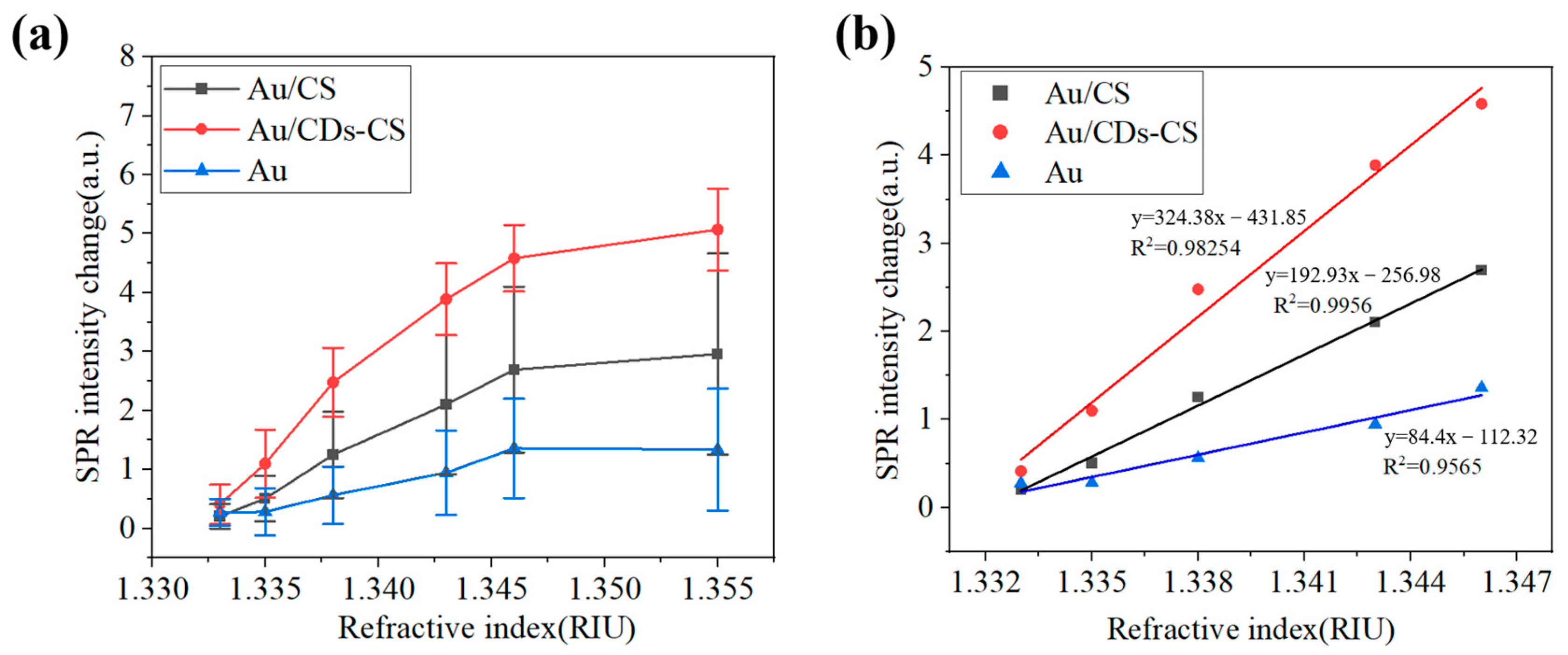
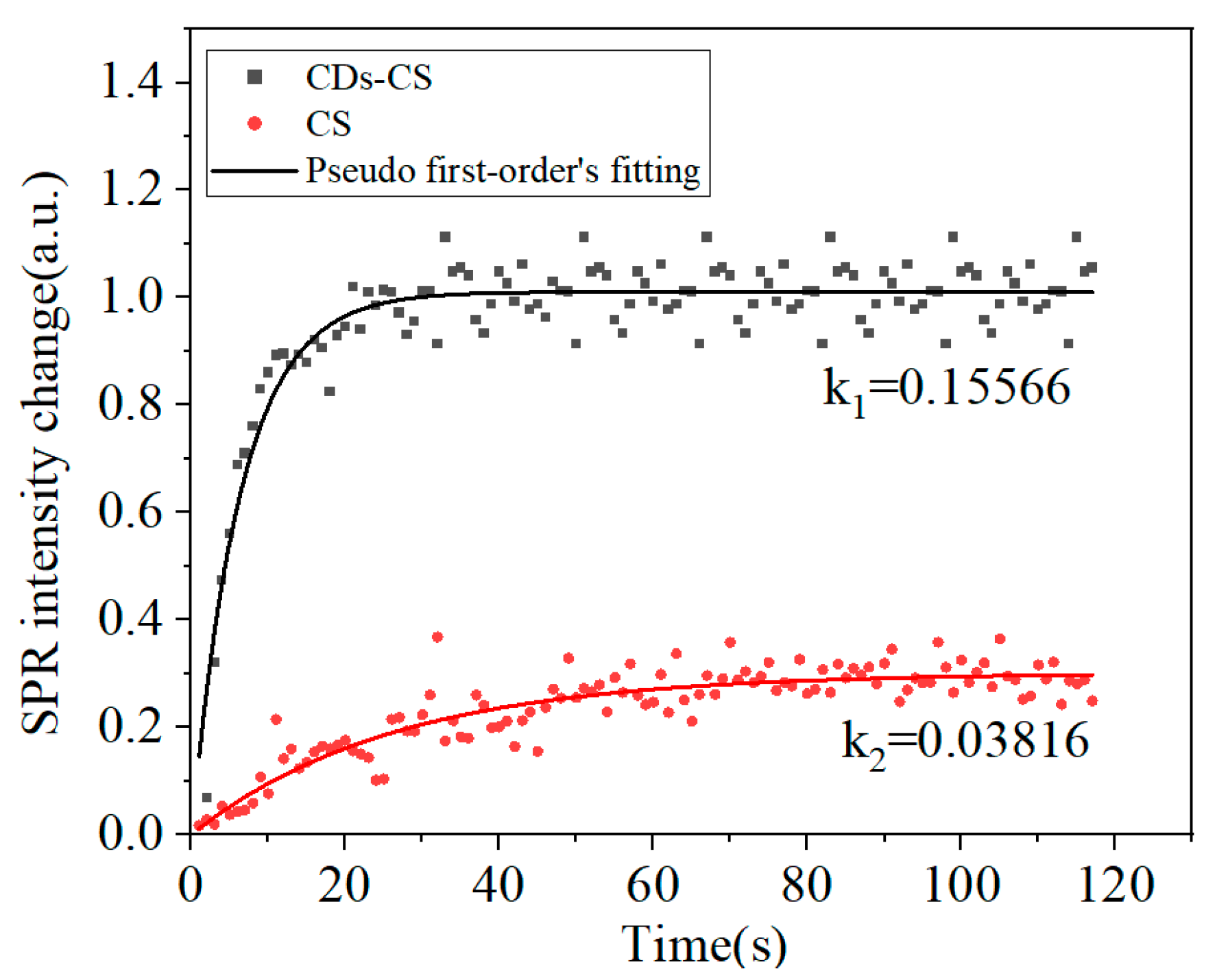
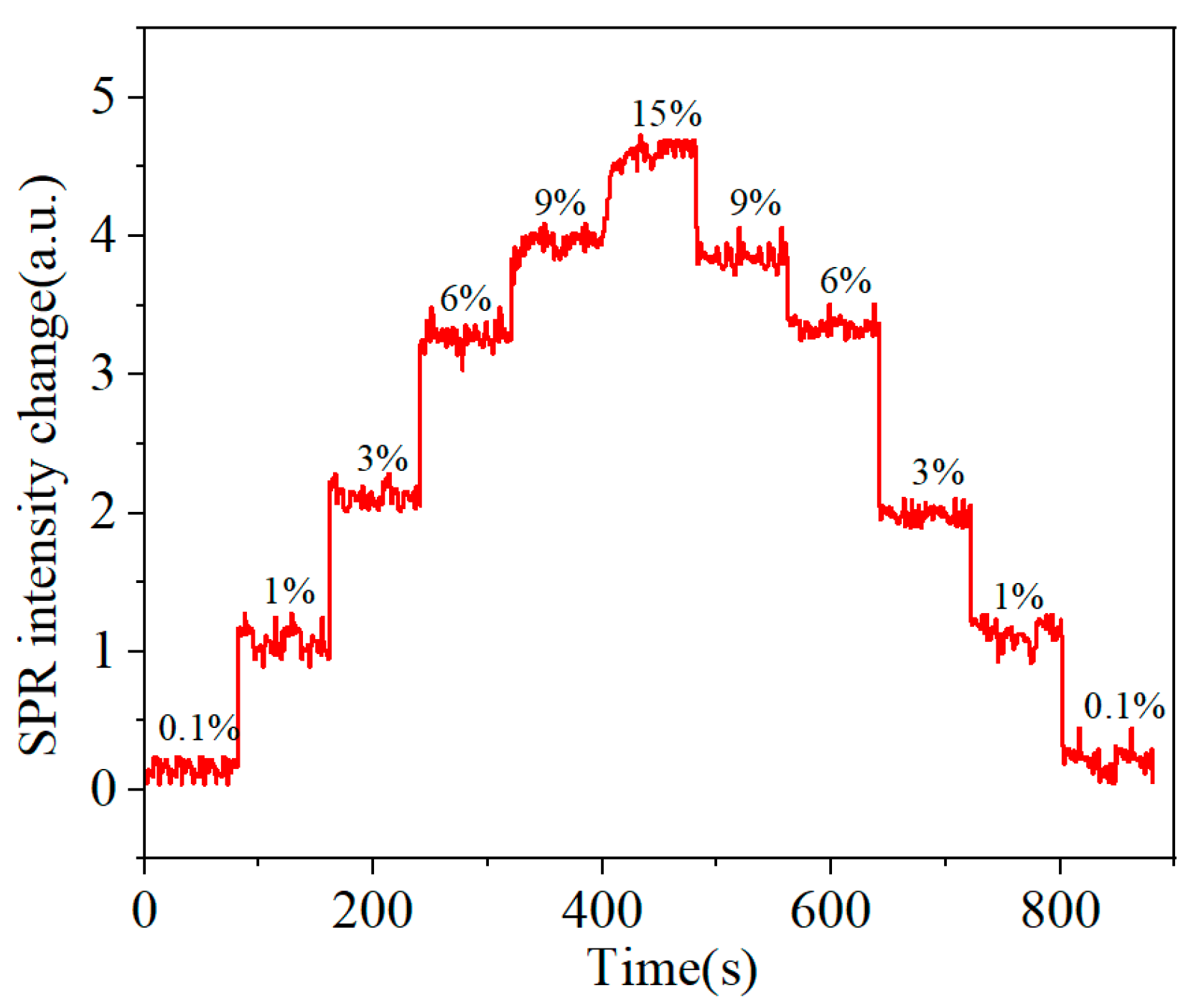
| Materials | Target | Sensitivity | Magnification (Ag/Au) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag/NCDs-PVA | Chlorophyll | 1.90 nm/ppm | 850% | [23] |
| Au/CDs | Mn2+ | 6.383 nm/lg(ppb) | - | [32] |
| Au/CGDs-NCC | Glucose | - | [33] | |
| Au/Qdot-StAv | G-quadruplexes(DNA) | 494.94% | [22] | |
| Au/CDs-CS | NaCl | 167.28 a.u./RIU | 247.8% | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouyang, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Shi, C.; Li, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chang, M. The Synergistic Effect of Electric-Field and Adsorption Enhancement of Amino Acid Carbon Dots Significantly Improves the Detection Sensitivity of SPR Sensors. Sensors 2025, 25, 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25133903
Ouyang J, Yu X, Wang M, Wang L, Li Z, Shi C, Li H, Yuan Y, Zhou J, Chang M. The Synergistic Effect of Electric-Field and Adsorption Enhancement of Amino Acid Carbon Dots Significantly Improves the Detection Sensitivity of SPR Sensors. Sensors. 2025; 25(13):3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25133903
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuyang, Jing, Xiantong Yu, Mengjie Wang, Longfei Wang, Zhao Li, Chaojun Shi, Hao Li, Yufeng Yuan, Jun Zhou, and Min Chang. 2025. "The Synergistic Effect of Electric-Field and Adsorption Enhancement of Amino Acid Carbon Dots Significantly Improves the Detection Sensitivity of SPR Sensors" Sensors 25, no. 13: 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25133903
APA StyleOuyang, J., Yu, X., Wang, M., Wang, L., Li, Z., Shi, C., Li, H., Yuan, Y., Zhou, J., & Chang, M. (2025). The Synergistic Effect of Electric-Field and Adsorption Enhancement of Amino Acid Carbon Dots Significantly Improves the Detection Sensitivity of SPR Sensors. Sensors, 25(13), 3903. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25133903







