Impact Evaluation of DME Beacons on BeiDou B2a Signal Reception Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
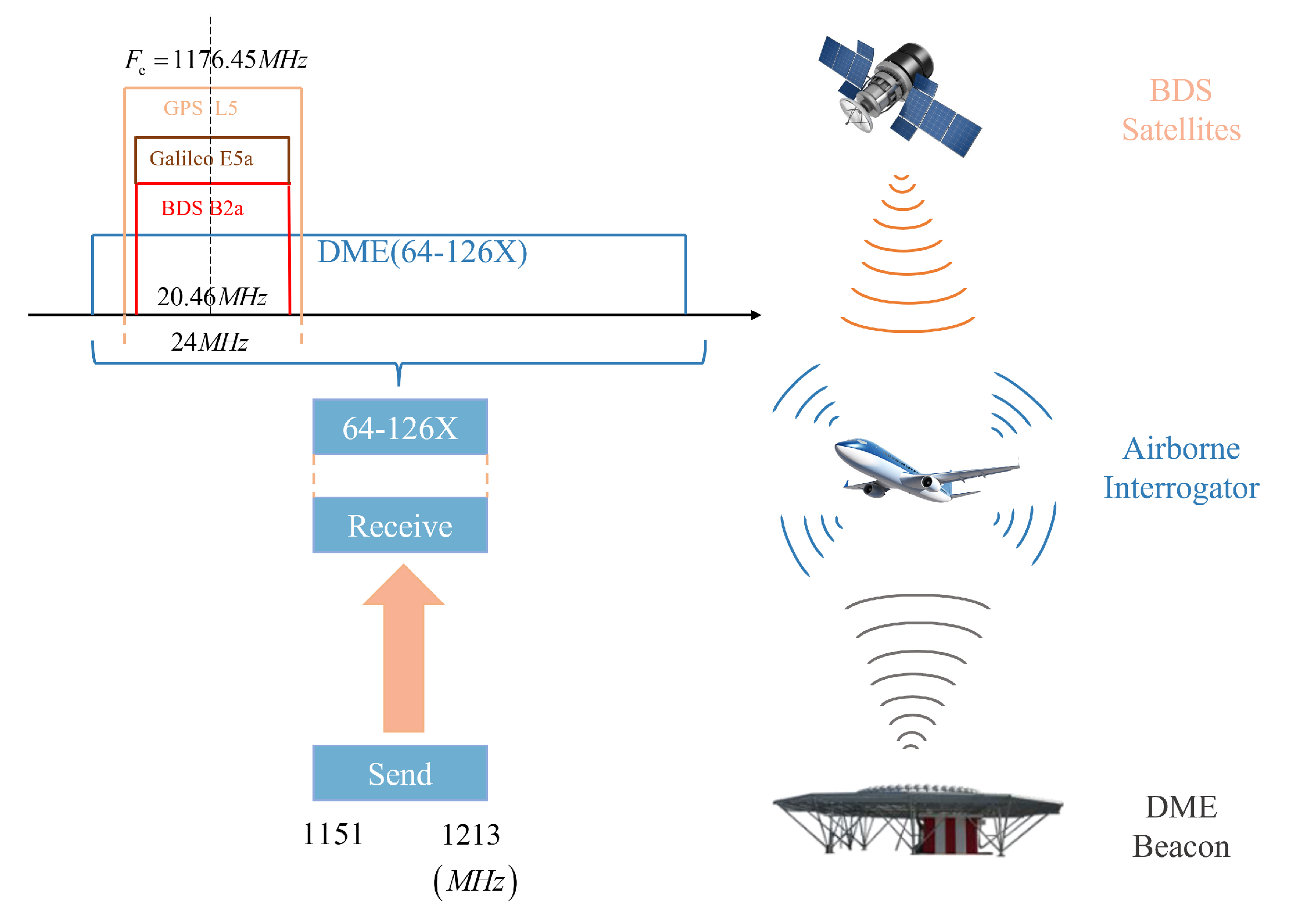
2. DME Interference Model
3. Interference Evaluation Model
3.1. Generic Airborne Civil Aviation BDS Receiver
3.2. Effective Carrier-to-Noise Ratio Degradation
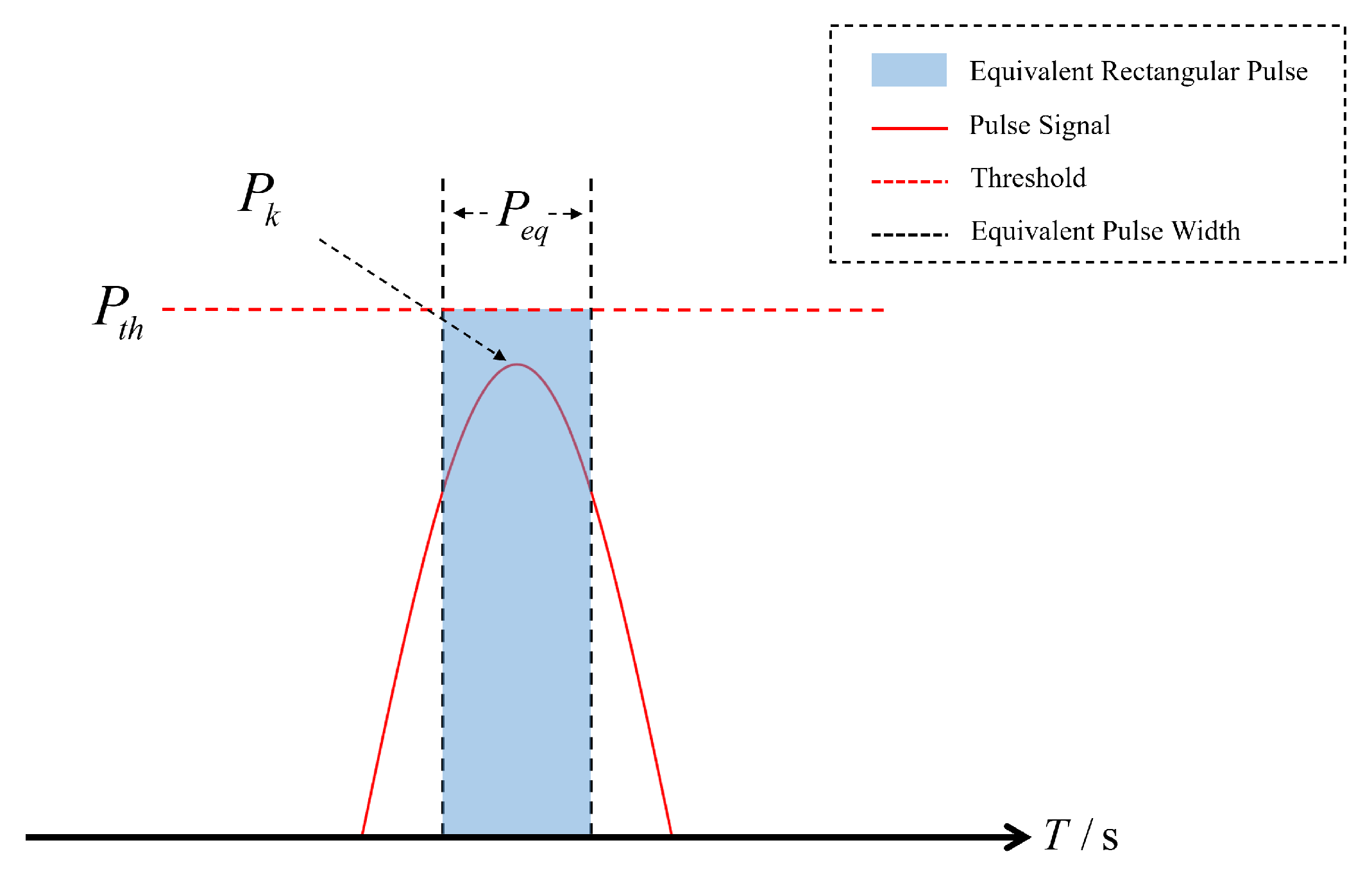
3.2.1. Single DME Signal Interference
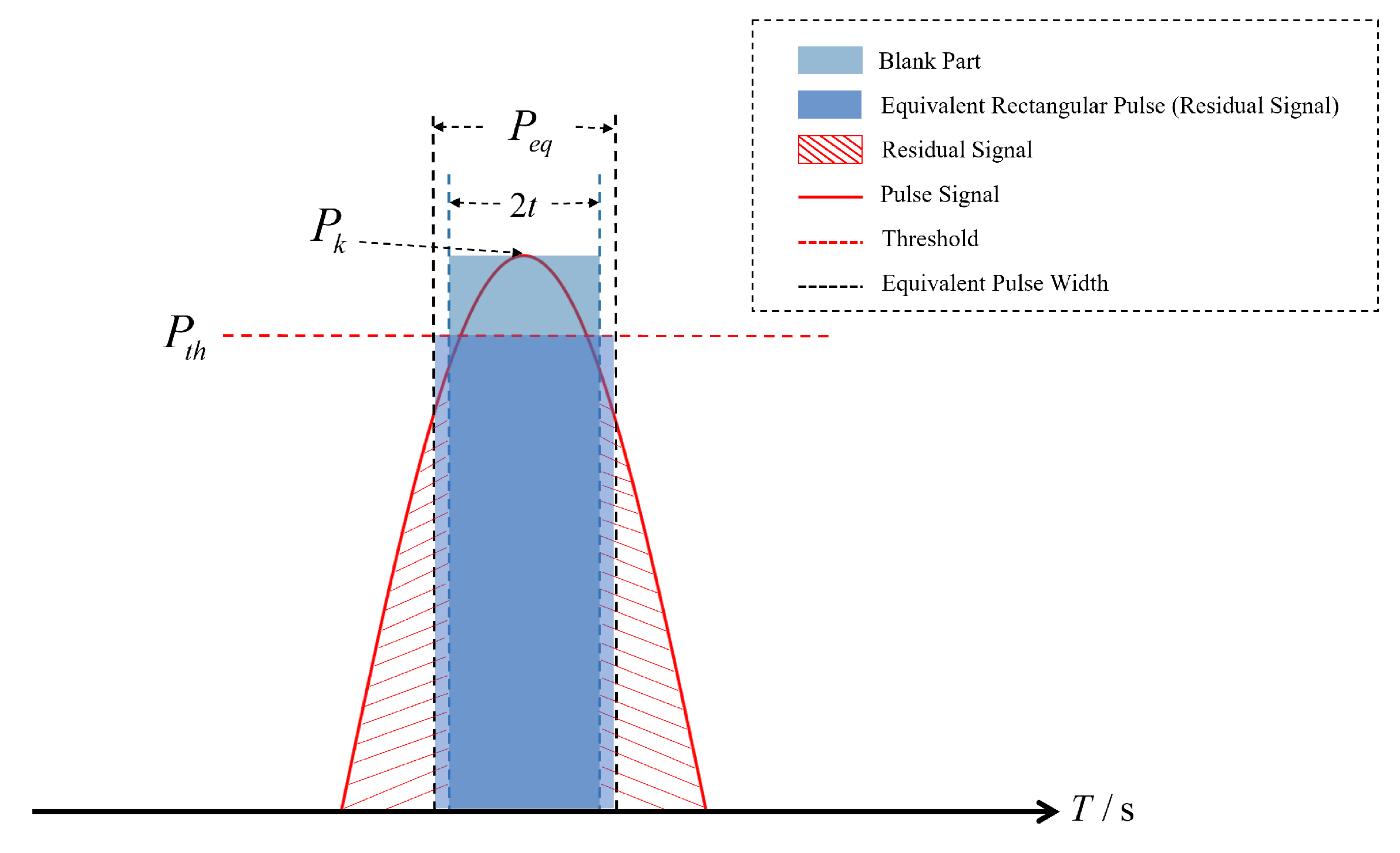
3.2.2. Multiple DME Signal Interference
3.3. B2a Signal Reception Performance Degradation
4. Evaluation of B2a Signal Reception Performance
4.1. DME Signal Reception Power Budget
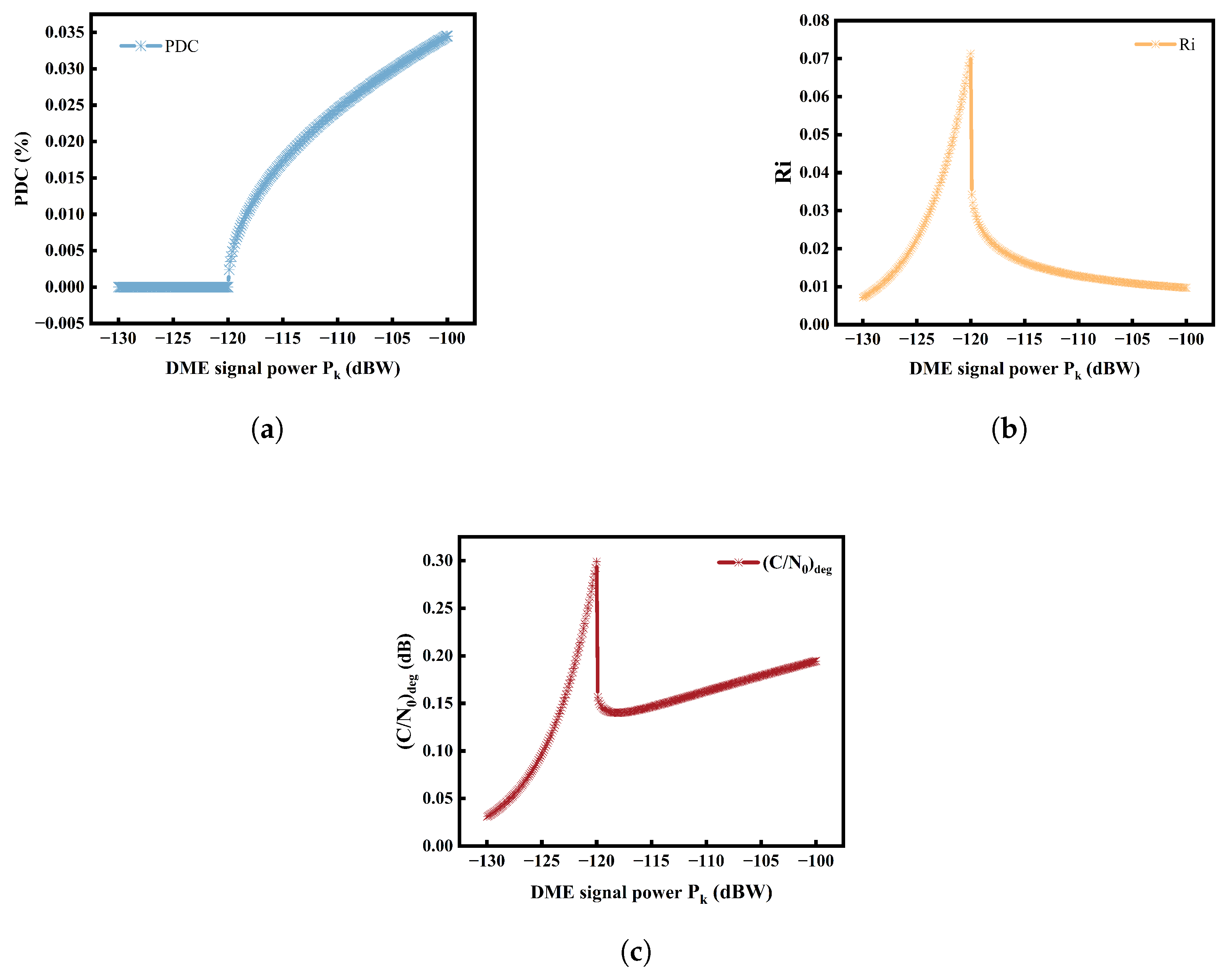
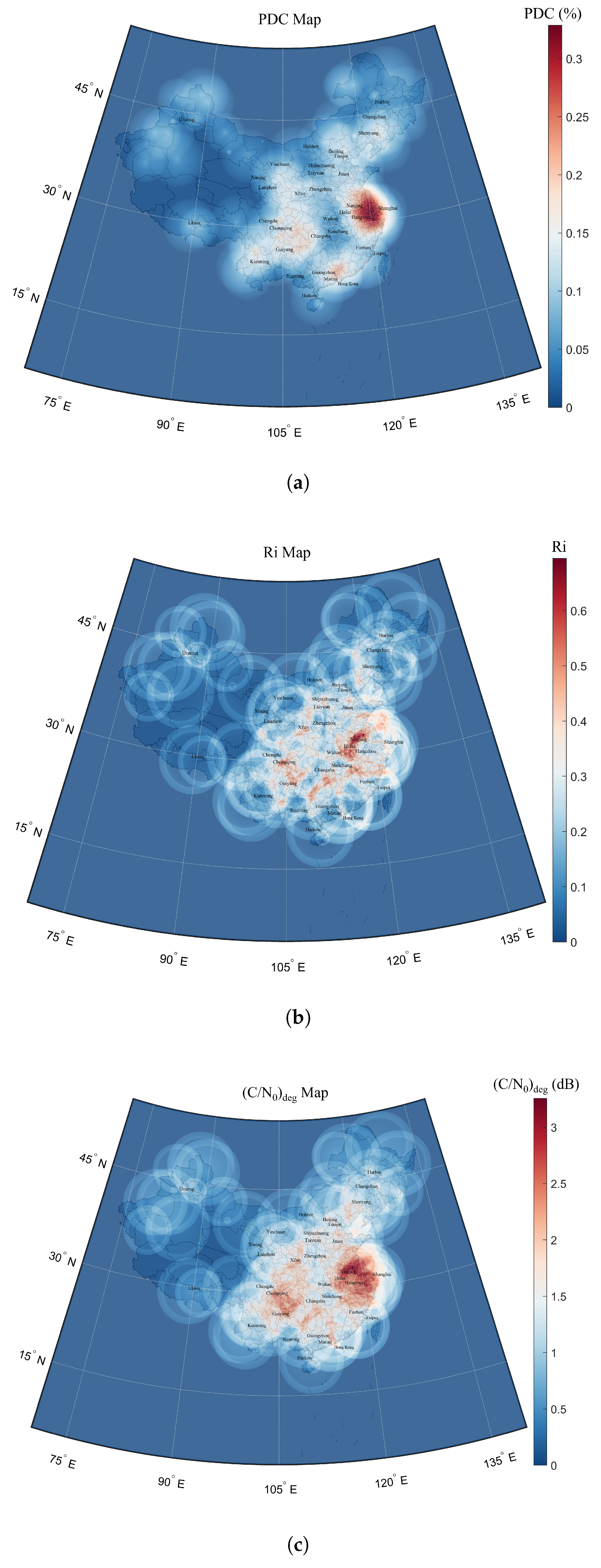
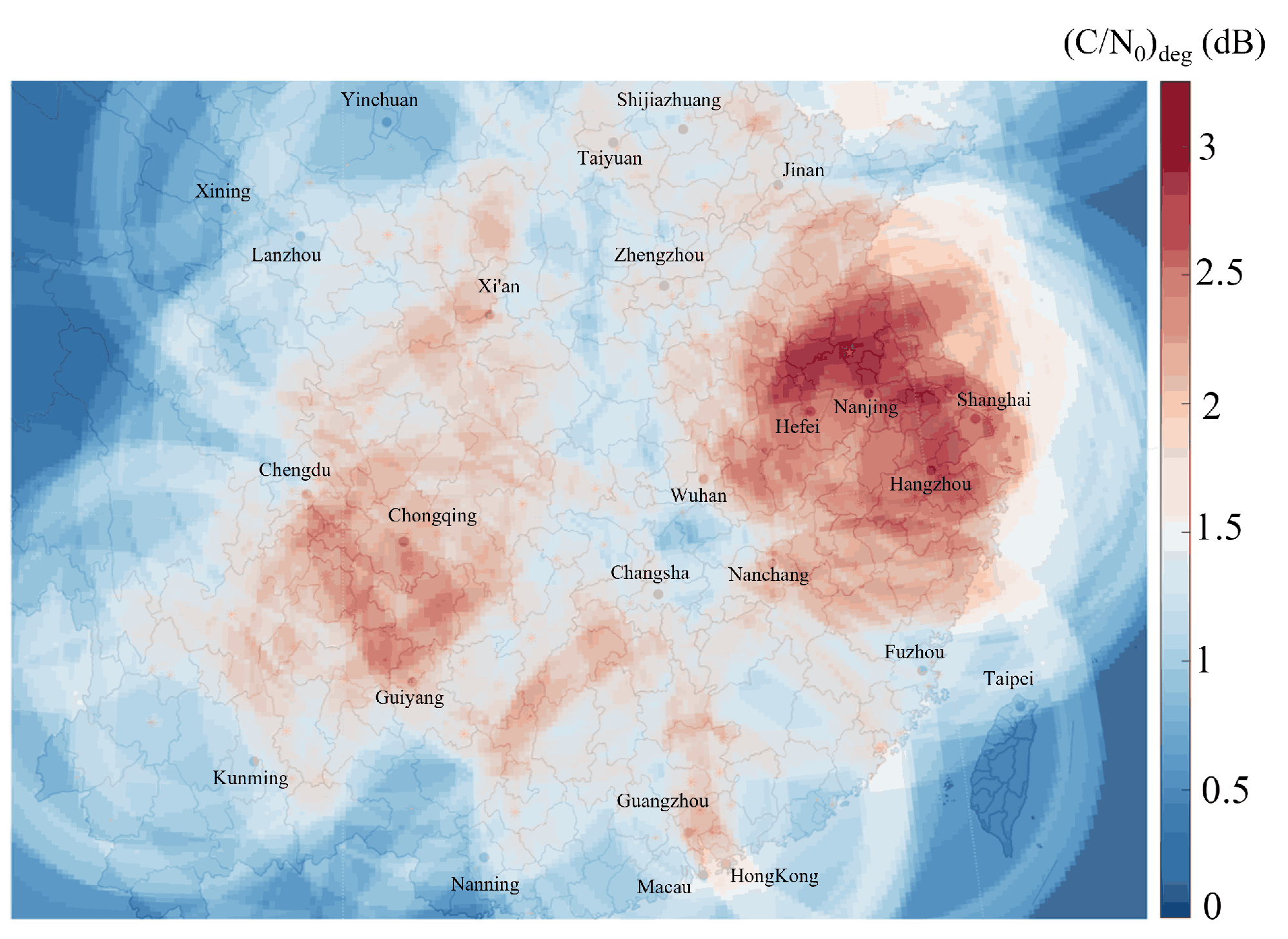
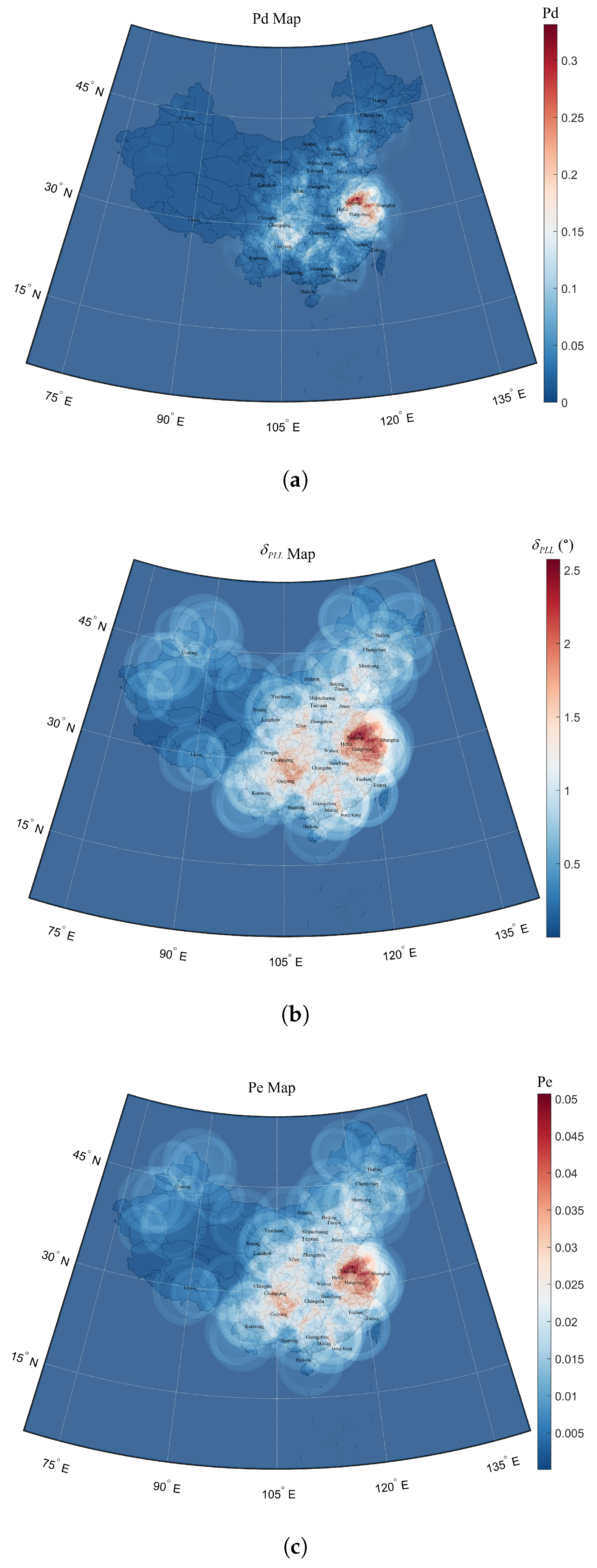
4.2. Evaluation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sokolova, N.; Morrison, A.; Diez, A. Characterization of the GNSS RFI Threat to DFMC GBAS Signal Bands. Sensors 2022, 22, 8587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q. A two-fault detection and elimination approach to the receiver autonomous integrity monitoring. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setlak, L.; Kowalik, R. Study and Analysis of Interference Signals of the LTE System of the GNSS Receiver. Sensors 2021, 21, 4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y. Research on GNSS Space Signal Interference Evaluation and Mitigation Methods. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Radoš, K.; Brkić, M.; Begušić, D. Recent advances on jamming and spoofing detection in GNSS. Sensors 2024, 24, 4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China Satellite Navigation Office. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Space Signal Interface Control File Public Service Signal B2a (Version 1.0); China Satellite Navigation Office: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- International Civil Aviation Organization. Annex 10—Aeronautical Telecommunications—Volume I—Radio Navigational Aids; ICAO: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hegarty, C.; Kim, T.; Ericson, S.; Reddan, P.; Morrissey, T.; Van Dierendonck, A. Methodology for determining compatibility of GPS L5 with existing systems and preliminary results. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of The Institute of Navigation (1999), Cambridge, MA, USA, 27–30 June 1999; pp. 635–644. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, M.; Kim, T.; Hegarty, C.J.; Devincentis, J.; Ericson, S.D. Validation of the Feasibility of Coexistence of the New Civil GPS Signal (L5) with Existing Systems; Technical Report, Project No. 02011103-03; The MITRE Corporation: McLean, VA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gault, N.; Chabory, A.; Garcia-Pena, A.; Macabiau, C. DME/TACAN Multipath Impact on GNSS L5/E5a Airborne Receivers Part II: Air-Ground Channel Model and Application. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 6765–6786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestarquit, L.; Dulery, C.; Prévost, R.; Iervolino, M. Mitigation of TACAN/DME Interferences for L5/E5 Space-borne GNSS Receivers in LEO. First Simulation Results with Focus on Radio-Occultation Missions. In Proceedings of the NAVITEC 2022, ESA/ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 5–7 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Grabowski, J. Validation of GPS L5 coexistence with DME/TACAN and link-16 systems. In Proceedings of the 16th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GPS/GNSS 2003), Portland, OR, USA, 9–12 September 2003; pp. 1455–1469. [Google Scholar]
- DO-292; Assessment of Radio Frequency Interference Relevant to the GNSS L5/E5A Frequency Band. RTCA, Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 20 July 2004.
- Garcia-Pena, A.; Macabiau, C.; Novella, G.; Julien, O.; Mabilleau, M.; Durel, P. RFI GNSS L5/E5a Mask Derivation. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2020), Online, 22–25 September 2020; pp. 188–205. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Pena, A.; Macabiau, C.; Julien, O.; Mabilleau, M.; Durel, P. Impact of DME/TACAN on GNSS L5/E5a receiver. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Technical Meeting of The Institute of Navigation, San Diego, CA, USA, 21–24 January 2020; pp. 207–221. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, Q.; Guo, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y. Evaluation of the Effects of the DME Beacons on BDS B2a Signals in China Hotspots. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Technical Meeting of The Institute of Navigation, Long Beach, CA, USA, 24–26 January 2023; pp. 385–398. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, K.; Dan, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z. Research on the Impact of DME on the Integrity of BDS B2a Signal. In Proceedings of the 36th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2023), Denver, CO, USA, 11–15 September 2023; pp. 1890–1904. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.M.; Xu, F.; Li, S.C. The Interference Analysis and Evaluation of DME to BeiDou-3/B2a. In Proceedings of the China Satellite Navigation Conference, Jinan, China, 22–24 May 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 305–321. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Pena, A.; Julien, O.; Macabiau, C.; Mabilleau, M.; Durel, P. GNSS degradation model in presence of continuous wave and pulsed interference. Navigation 2021, 68, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyaegbu, E.; Brodin, G.; Cooper, J.; Aguado, E.; Boussakta, S. An integrated pulsed interference mitigation for GNSS receivers. J. Navig. 2008, 61, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X. Research on GNSS Radio Frequency Compatibility and the Impact of High-Power Amplifier Nonlinear Effects. PhD Thesis, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Lu, Z.; Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, Z. Impact of Narrowband and Pulse Interference on Carrier-to-Noise Ratio of Satellite Navigation Signals. GNSS World China 2021, 46, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Pena, A.; Julien, O.; Gakne, P.V.; Macabiau, C.; Mabilleau, M.; Durel, P. Efficient DME/TACAN blanking method for GNSS-based navigation in civil aviation. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2019), Miami, FL, USA, 16–20 September 2019; pp. 1438–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Pena, A.; Macabiau, C.; Ashley, J.; Baraban, D.; Durel, P.; Mabilleau, M. Model and observation of the impact of JTIDS/MIDS on GNSS C/N0 degradation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Portland, OR, USA, 20–23 April 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 584–595. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Pena, A.; Novella, G.; Macabiau, C. C/N0 degradation in presence of chirp interference: Statistical, real and estimated C/N0. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novella, G.; Garcia-Pena, A.; Macabiau, C. C/N0 degradation in presence of chirp interference: Theoretical model. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Lyu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Ke, Y. Design of GNSS Spoofing Detection Algorithm Using Carrier-to-Noise Ratio. J. Navig. Position. 2022, 10, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Razavi, A.; Gebre-Egziabher, D.; Akos, D.M. Carrier loop architectures for tracking weak GPS signals. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2008, 44, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pany, T. Navigation Signal Processing for GNSS Software Receivers; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- ITU-R. Calculation Method to Determine Aggregate Interference Parameters of Pulsed RF Systems Operating in and Near the Bands 1164–1215 MHz and 1215–1300 MHz That May Impact Radio Navigation-Satellite Service Airborne and Ground-Based Receivers Operating in Those Frequency Bands; Technical Report; International Telecommunication Union, Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R): Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]




| Distance (km) | |
|---|---|
| 50 | 0.05 |
| 100 | 0.1 |
| 500 | 0.18 |
| 300 | 0.3 |
| 350 | 0.5 |
| Region | Latitude and Longitude | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 39.9° E, 116.3° N | 0.14 | 0.23 | 1.52 |
| Hefei | 31.9° E, 117.3° N | 0.23 | 0.39 | 2.55 |
| Nanjing | 32.1° E, 118.1° N | 0.26 | 0.35 | 2.64 |
| Shanghai | 31.4° E, 121.8° N | 0.25 | 0.38 | 2.65 |
| Chengdu | 30.6° E, 104.1° N | 0.17 | 0.28 | 1.88 |
| Chongqing | 29.9° E, 106.8° N | 0.18 | 0.35 | 2.17 |
| Guangzhou | 23.3° E, 113.4° N | 0.22 | 0.28 | 2.12 |
| Maximum | 32.9° E, 118.4° N | 0.23 | 0.63 | 3.25 |
| Region | Latitude and Longitude | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 39.9° E, 116.3° N | 3 | 1.06 | 1.8 |
| Hefei | 31.9° E, 117.3° N | 17 | 1.91 | 3.6 |
| Nanjing | 32.1° E, 118.1° N | 19 | 1.99 | 3.8 |
| Shanghai | 31.4° E, 121.8° N | 19 | 2.01 | 3.8 |
| Chengdu | 30.6° E, 104.1° N | 7 | 1.35 | 2.4 |
| Chongqing | 29.9° E, 106.8° N | 10 | 1.59 | 2.9 |
| Guangzhou | 23.3° E, 113.4° N | 10 | 1.55 | 2.8 |
| Maximum | 32.9° E, 118.4° N | 33 | 2.57 | 5.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Cui, J.; Ma, Z.; Duan, Z. Impact Evaluation of DME Beacons on BeiDou B2a Signal Reception Performance. Sensors 2025, 25, 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25123763
Li Y, Cui J, Ma Z, Duan Z. Impact Evaluation of DME Beacons on BeiDou B2a Signal Reception Performance. Sensors. 2025; 25(12):3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25123763
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yicheng, Jinli Cui, Zhenyang Ma, and Zhaobin Duan. 2025. "Impact Evaluation of DME Beacons on BeiDou B2a Signal Reception Performance" Sensors 25, no. 12: 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25123763
APA StyleLi, Y., Cui, J., Ma, Z., & Duan, Z. (2025). Impact Evaluation of DME Beacons on BeiDou B2a Signal Reception Performance. Sensors, 25(12), 3763. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25123763





