Large- and Small-Scale Beam-Steering Phased Array Antennas Using Variable Phase BLC for Millimeter-Wave Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design and Analysis
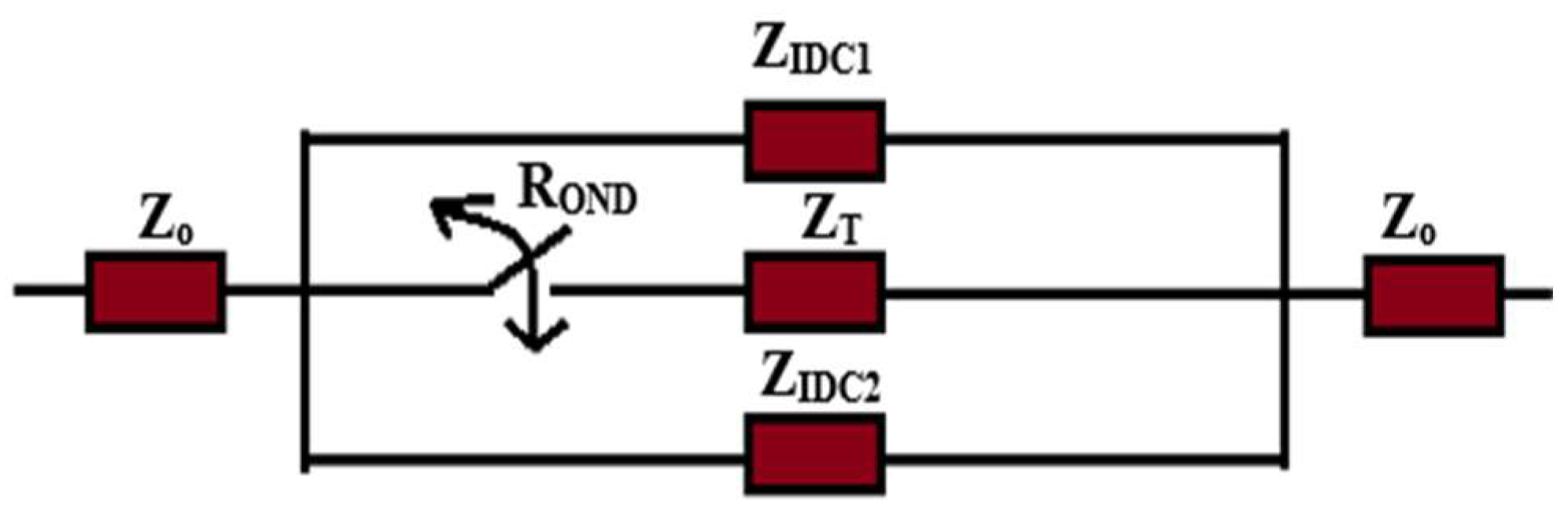
2.1. Variable Phase Transmission Line Module
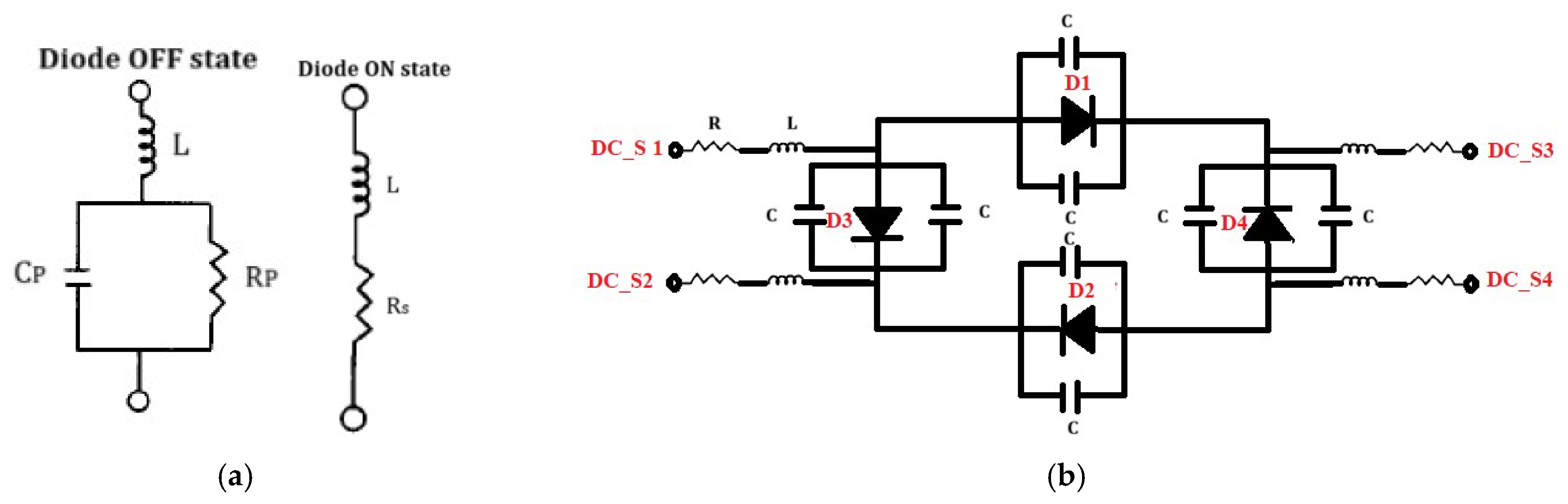
2.2. BLC Circuit Implementation and Evaluation
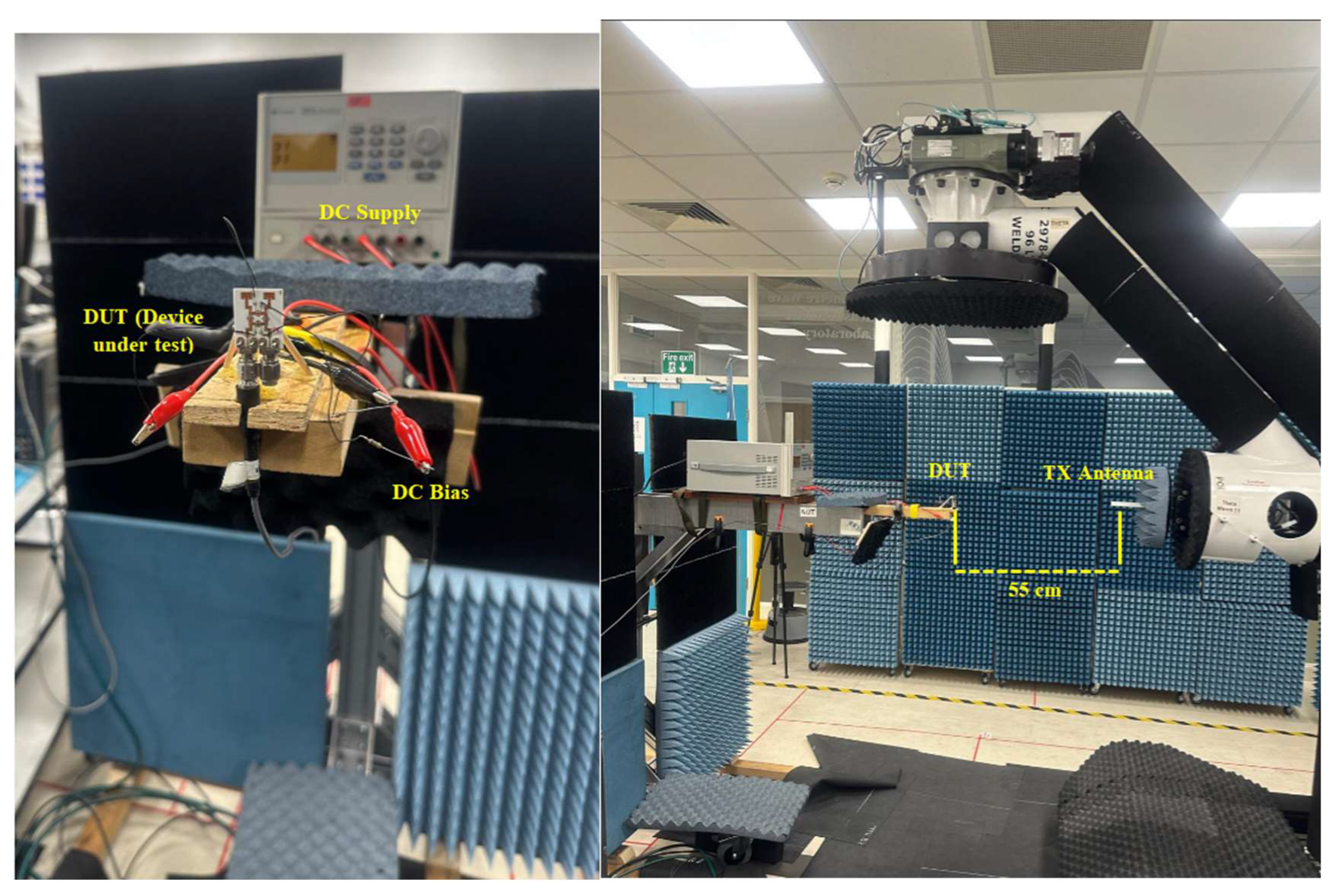
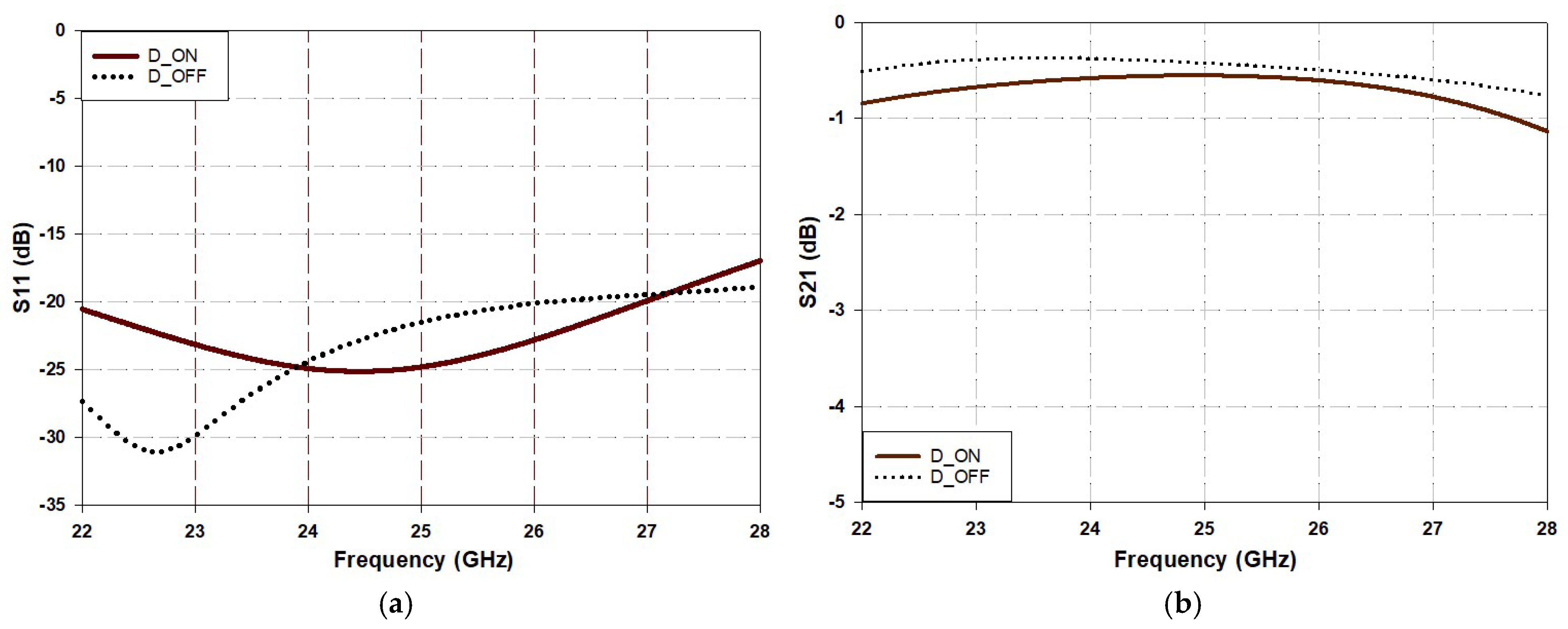
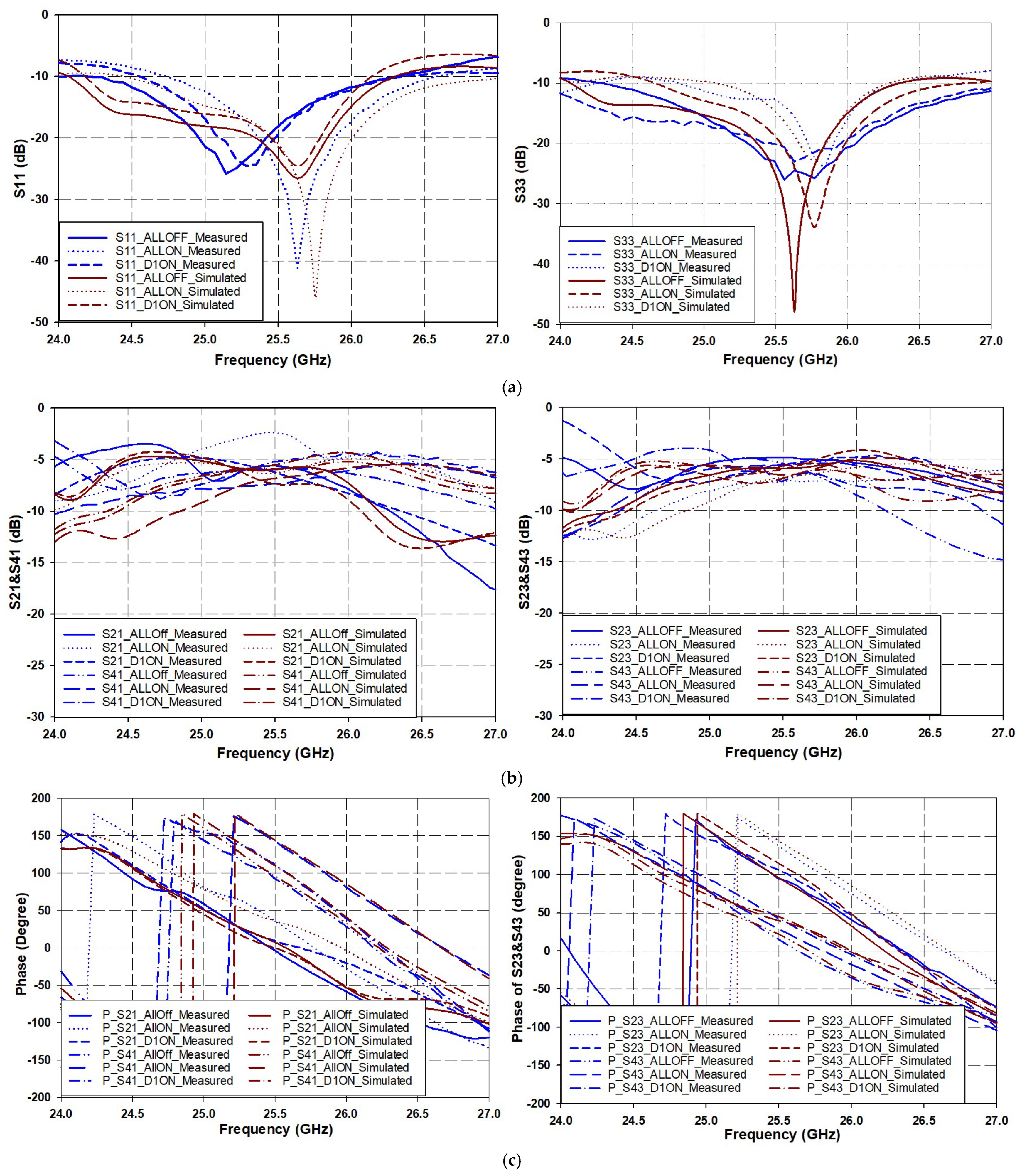
3. Variable Phase BLC Circuit Implementation and Testing
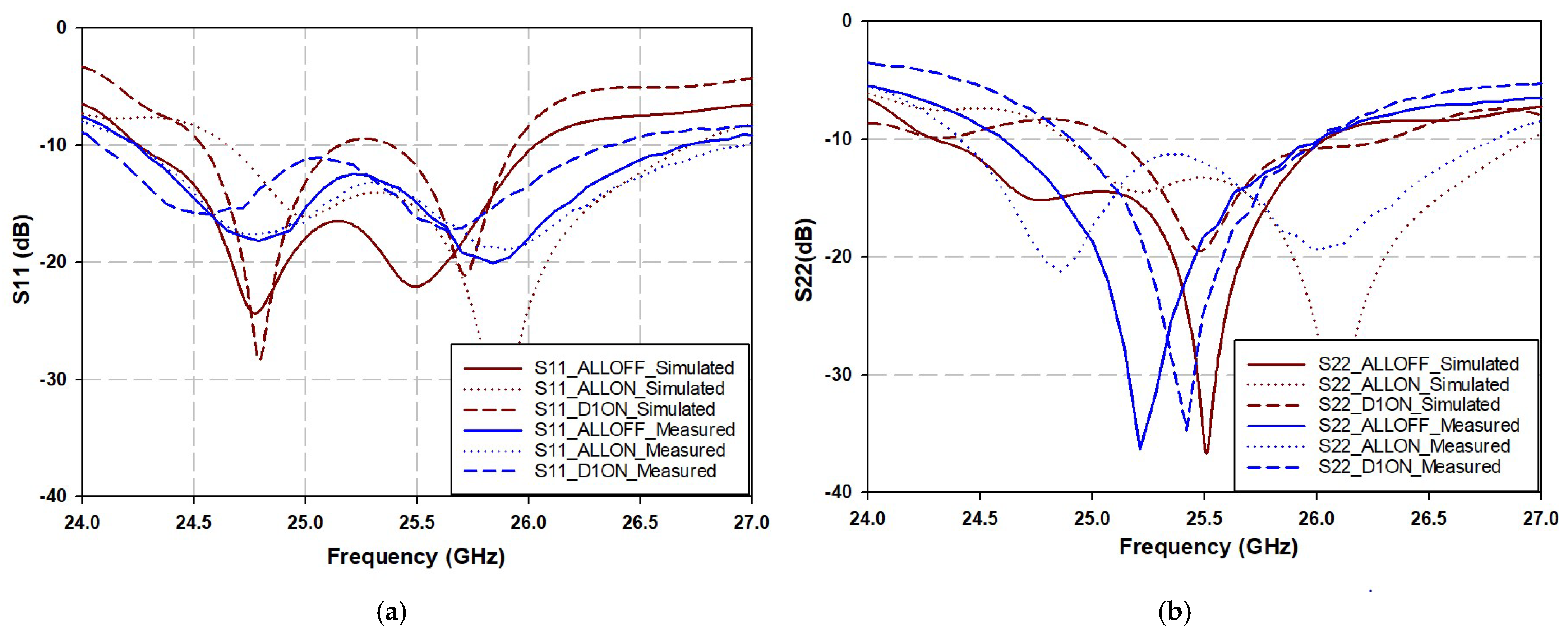
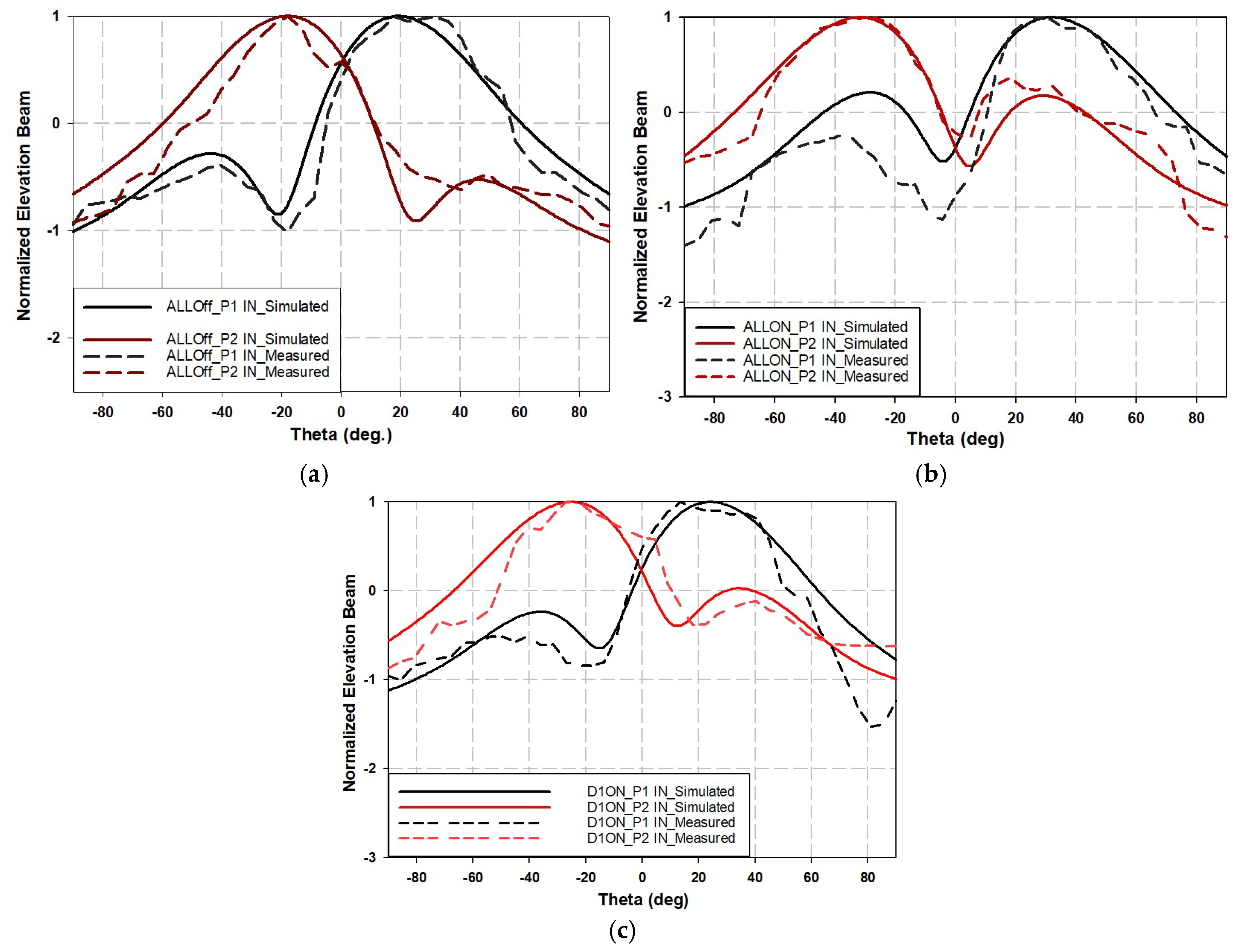
4. Two-Element Phased Array Antennas
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Natarajan, A.; Krishnaswamy, H. Scalable spatial notch suppression in spatio-spectral-filtering MIMO receiver arrays for digital beamforming. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2016, 51, 3152–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, H.B. Fundamental energy limits of digital phased arrays. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2019, 66, 2775–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, S.; Patnaik, S.A.; Sadhu, B.; Sturm, M.; Elbadry, M.; Harjani, R. Multi-beam spatio-spectral beamforming receiver for wideband phased arrays. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2013, 60, 2018–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupakula, B.; Nafe, A.; Zihir, S.; Wang, Y.; Lin, T.-W.; Rebeiz, G. 63.5–65.5-GHz transmit/receive phased-array communication link with 0.5–2 Gb/s at 100–800 m and ±50° scan angles. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2018, 66, 4108–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blass, J. Multidirectional antenna-A new approach to stacked beams. In Proceedings of the 1958 IRE International Convention Record, New York, NY, USA, 21–25 March 1966; pp. 48–50. [Google Scholar]
- Nolen, J. Synthesis of Multiple Beam Networks for Arbitrary Illuminations. Ph.D. Thesis, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, J. Beam-forming matrix simplifies design of electronically scanned antennas. Electron. Des. 1961, 9, 170–173. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Kim, C.-S.; Ahn, D.; Itoh, T. Phase shifter with high phase shifts using defected ground structures. Electron. Lett. 2005, 41, 196–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-Z.; Chen, F.-C.; Chu, Q.-X. A compact broadband 4 × 4 Butler matrix with 360° continuous progressive phase shift. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2023, 71, 3906–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.N.; Ma, T.-G. An Extended 4 × 4 Butler Matrix with Enhanced Beam Controllability and Widened Spatial Coverage. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 66, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.N.; Hoang, T.H.; Ji, K.-J.; Ma, T.-G. A phase distribution network using 2 × 4 Butler matrix for linear/planar beam-scanning arrays. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 133438–133448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Li, P.; Gu, Y.; Arigong, B. Phase shifter-relaxed and control-relaxed continuous steering multiple beamforming 4 × 4 Butler matrix phased array. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2020, 67, 5031–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, X.; Yu, T.; Zhu, L.; Wu, W. Wideband continuously tunable phase shifter with phase slope tunability and low phase error. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2022, 70, 2147–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, M.; Kumar, A.; Aniruddhan, S. A 28GHz reflective-type transmission-line-based phase shifter. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2020, 67, 4641–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-S.; Chang, S.-F.; Chang, C.-C.; Shu, Y.-H. Design of a reflection-type phase shifter with wide relative phase shift and constant insertion loss. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2007, 55, 1862–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaouf, T.M.; Hamdoun, A.; Himdi, M.; Lafond, O.; Ammor, H. Hybrid Coupler Used as Tunable Phase Shifter Based on Varactor Diodes. Micromachines 2024, 15, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryana, J.; Munir, A. Phase reconfigurable hybrid coupler implemented using capacitor-loaded transmission lines. In Proceedings of the 2022 14th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks (CICN), Al-Khobar, Saudi Arabia, 4–6 December 2022; pp. 633–636. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.Y. Simultaneous phase-and frequency-tunable hybrid coupler. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 8088–8097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Abbosh, A.M. A compact tunable directional coupler with continuously tuned differential phase. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2017, 28, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozar, D.M. Microwave Engineering, 4th ed.; University of Massachusetts at Amherst: Amherst, MA, USA; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Yang, W.; Pan, P.; Bai, T.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Z.; Wang, G. Beam Scanning 10 × 10 Phased Array Antenna Using Liquid Crystal Phase Shifters. Prog. Electromagn. Res. Lett. 2023, 108, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Che, W.; Xue, Q. Wide-angle beam-scanning millimeter-wave antenna array using phase-controlled beam-steerable elements. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2024, 72, 3730–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.H.; Yang, X.S. Low-Profile Beam-Steering Metasurface Lens Antenna Utilizing Defocused Array Feed Without Amplitude–Phase Network. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2024, 66, e70064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabarov, S.; Huseynov, R.; Ayyubova, G.S.; Trukhanov, S.; Trukhanov, A.; Aliyev, Y.; Thabethe, T.; Mauyey, B.; Kuterbekov, K.; Kaminski, G. Evaluation of structural characteristics BaFe (12-x) InxO19 hexaferrite compounds at high temperatures. Solid State Commun. 2024, 386, 115529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabarov, S.; Nabiyeva, A.K.; Samadov, S.; Abiyev, A.; Sidorin, A.; Trung, N.; Orlov, O.; Mauyey, B.; Trukhanov, S.; Trukhanov, A. Study defects formation mechanism in La1-xBaxMnO3 perovskite manganite by positron annihilation lifetime and Doppler broadening spectroscopy. Solid State Ion. 2024, 414, 116640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E. Coupled-strip-transmission-line filters and directional couplers. IRE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1956, 4, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacombe, D.; Cohen, J. Octave-band microstrip dc blocks (short papers). IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1972, 20, 555–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.Y. Analysis of DC blocks using coupled lines. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1975, 23, 773–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünal, Ü.C.; Karaçuha, K.; İmeci, S.T. A simple 90° hybrid branchline coupler with wideband phase balance for 5G applications. J. Electr. Eng. 2024, 75, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.H.; Saad, R.; Khamas, S.K. A novel compact broadband quasi-twisted branch line coupler based on a double-layered microstrip line. Micromachines 2024, 15, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouser Electronics. MA4AGFCP910. 2025. Available online: https://eu.mouser.com/ProductDetail/MACOM/MA4AGFCP910?qs=zQS7eqYV0KSYqG5hb4HNCg%3D%3D&utm_source=octopart&utm_medium=aggregator&utm_campaign=937-MA4AGFCP910&utm_content=MACOM (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Photodata, J. 2025. Available online: https://www.jd-photodata.co.uk/ (accessed on 28 January 2025).



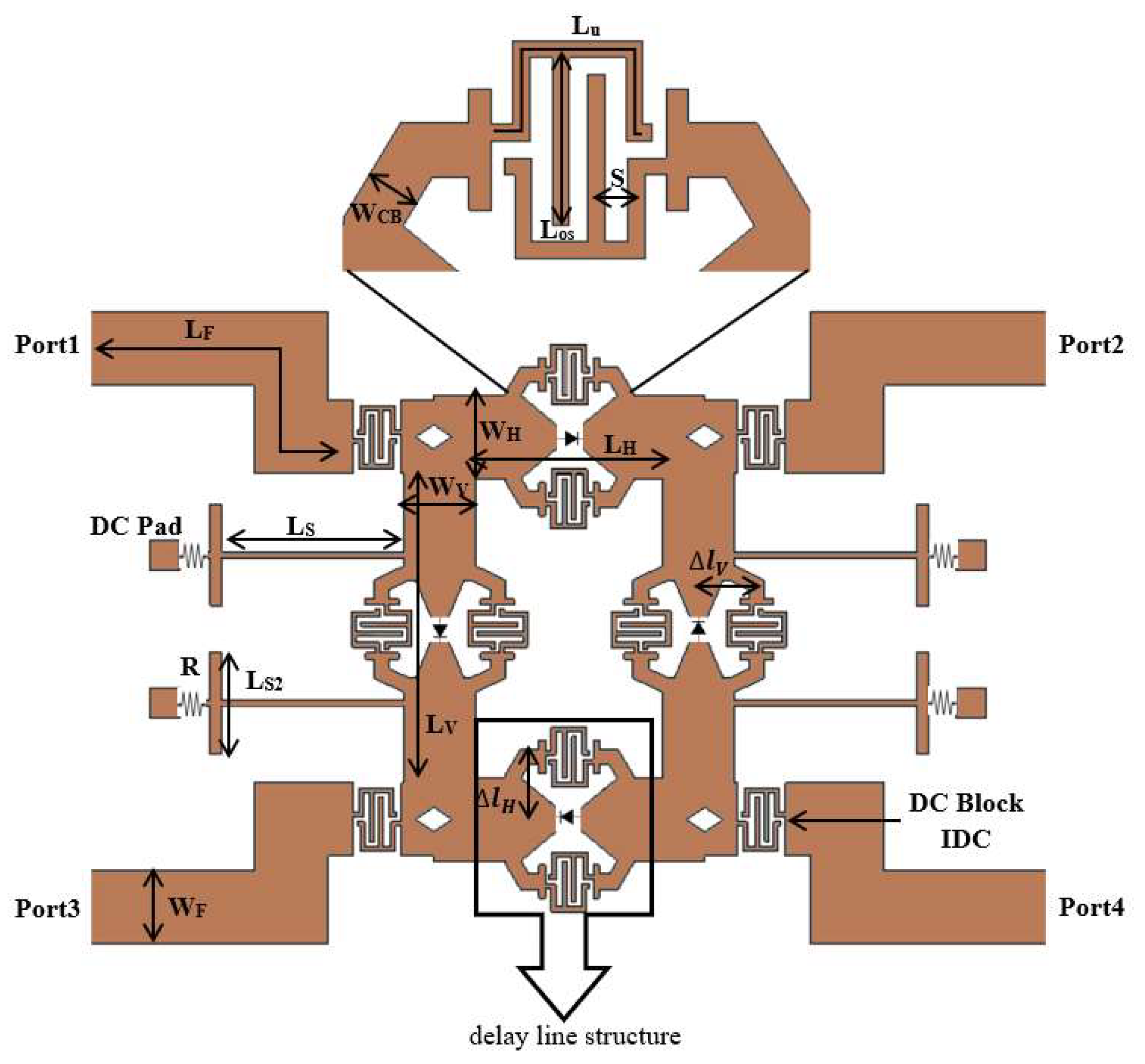
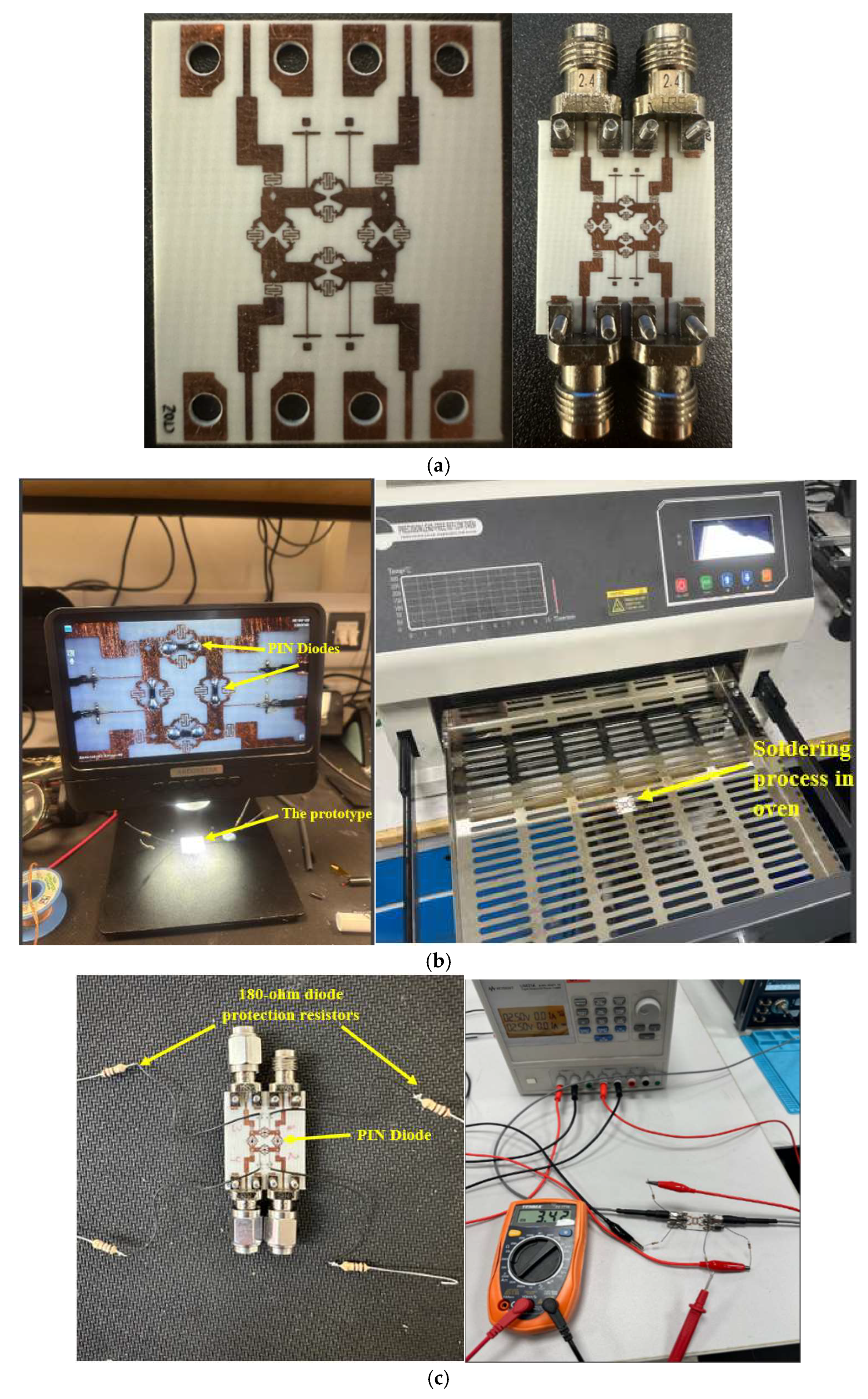
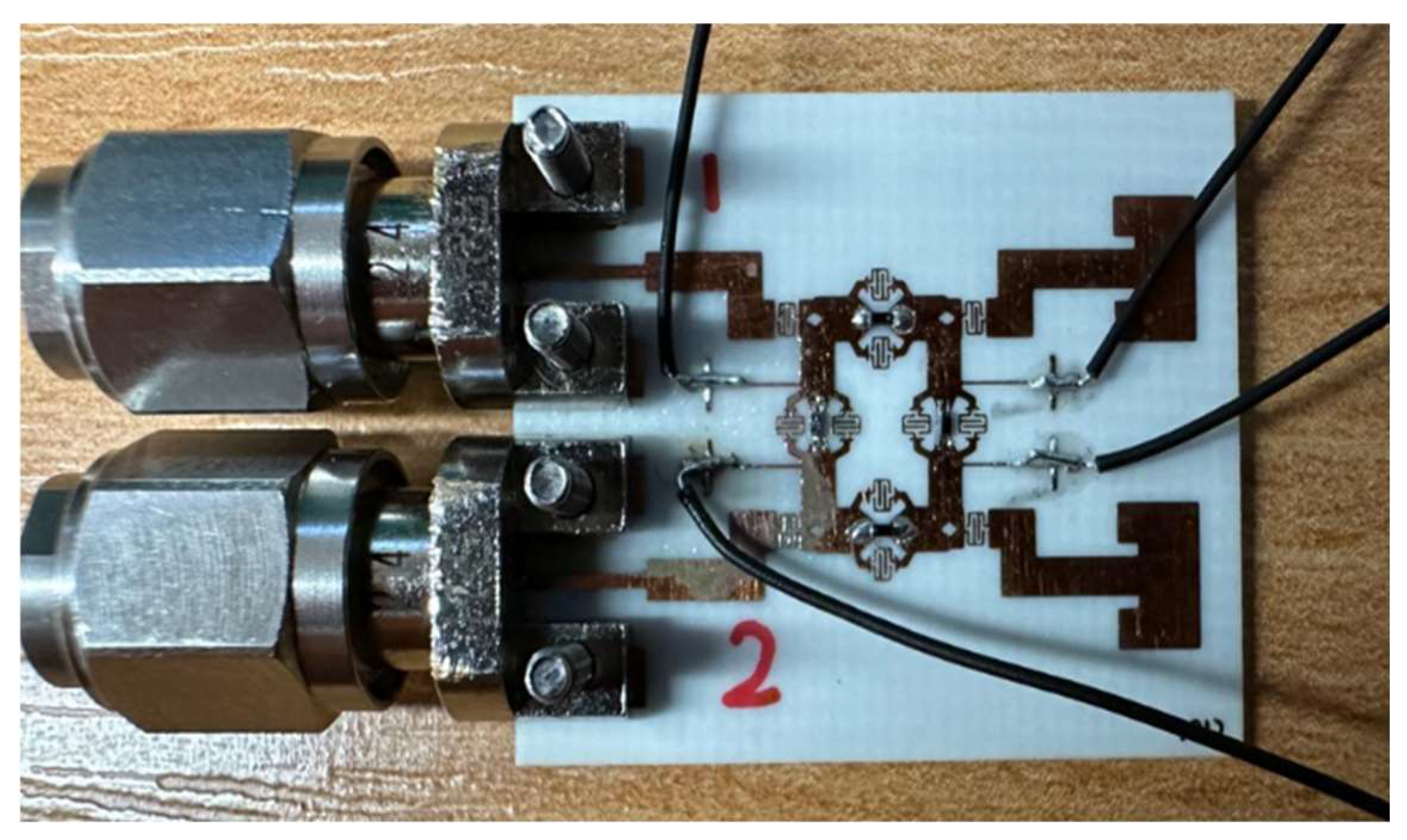

| Parameter | Dimension in mm | Parameter | Dimension in mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| LF | 0.9 | ||
| WF | 1.21 | LS | 2.998 |
| LH | 4.914 | LS2 | 1.66 |
| WH | 1.166 | WCB | 0.25 |
| LV | 3.1 | LOS | 0.756 |
| WV | 1.384 | LU | 1.4835 |
| 1.025 | S | 0.0855 |
| DC Supply Voltages (V) | Diode States | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC_S1 | DC_S2 | DC_S3 | DC_S4 | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | OFF | OFF | OFF | OFF |
| 2.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ON | OFF | ON | OFF |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.5 | OFF | ON | OFF | ON |
| 2.5 | 0 | 0 | 2.5 | ON | ON | ON | ON |
| 0 | 0 | −2.5 | 0 | ON | OFF | OFF | ON |
| 0 | −2.5 | 0 | 0 | OFF | ON | ON | OFF |
| 2.5 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 | ON | OFF | OFF | OFF |
| 2.5 | 0 | 2.5 | 0 | OFF | OFF | ON | OFF |
| PIN Diode Switch States | Input Port 1 | ||||||||||||||
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | RL, −10 BW (GHz) | S21 (dB) | S41 (dB) | ∠S21 | ∠S41 | |||||||
| Meas. | Sim. | Meas. | Sim. | Meas. | Sim. | Meas. | Sim. | Meas. | Sim. | Meas. | Sim. | ||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24–26.3 (2.3) | 24–26.3 (2.3) | −5.6 | −5.9 | −5.8 | −5.8 | −2.5 | 7.5 | 93.9 | 96.3 | 98.8 | 88.8 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 24.7–26.5 (1.8) | 24.4–27 (2.6) | −2.47 | −6.2 | −6.7 | −6.7 | 37.3 | 36.9 | 143.7 | 144.6 | 105.7 | 107.7 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24.4–26.3 (1.9) | 24.1–26.1 (2) | −6.4 | −6.8 | −5.1 | −5.4 | 10.2 | 0.5 | 112.3 | 110.3 | 102 | 109.8 |
| PIN Diode Switch States | Input Port 3 | ||||||||||||||
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | RL, −10 BW (GHz) | S21 (dB) | S41 (dB) | ∠S21 | ∠S41 | |||||||
| Meas. | Sim. | Meas. | Sim. | Meas. | Sim. | Meas. | Sim. | Meas. | Sim. | Meas. | Sim. | ||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24.2–27 (2.8) | 24.06–26.3 (2.24) | −4.8 | −5.2 | −5.3 | −5.6 | 95.4 | 96.2 | 16.2 | 22.3 | 79.2 | 73.9 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 24–27 (3) | 24.6–26.9 (2.3) | −6.5 | −6.3 | −5.9 | −6.3 | 138.9 | 144.6 | 29.6 | 40 | 109.3 | 104.6 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24.8–26.3 (1.5) | 25–26.3 (1.3) | −5.5 | −5.4 | −6.6 | −6.5 | 106.8 | 115 | 43.9 | 45.3 | 62.9 | 69.7 |
| Reference | Operating Frequency (GHz) | Return Loss dB | Isolation dB | Need for External Phase Shift Circuit | Phase Shift Step Size | Phase Difference Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [8] | 2 | 20 | - | Yes | ~10° | 151°–(−56°) |
| [9] | 2.4 | 20 | 20 | Yes | Continues | 360° |
| [10] | 2.4 | 20 | 20 | Yes | 22.5° | −90°–(+90°) |
| [11] | 2.4 | 15 | 15 | Yes | 60°~90° | 180–(−135°) |
| [16] | 3.5 | 10 | 17 | Yes | Continues | 52°120° |
| [19] | 1 | 10 | 12 | No | Continues | 45°135° |
| This Work | 25.5 | 10 | 15 | No | 70°~110° | −3°~145° |
| Diode States | Results | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | S11 (GHz) Simulated | S11 (GHz) Measured | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Feeding from Port 1 | 24.2–26 | 24.2–26.7 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 24.6–26.7 | 24.2–26.9 | |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24.5–25.9 | 24.1–26.3 | |
| S22 (GHz) Simulated | S22 (GHz) Measured | |||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Feeding from Port 2 | 24.2–26 | 24.6–26 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 24.8–27 | 24.4–26.8 | |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25–26.3 | 24.8–26 | |
| Input Port | Diode’s State | Main Beam Direction Angle (deg) | Main Beam AMPLITUDE (dB) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulated | Measured | Simulated | Measured | ||
| 1 | ALL_OFF | 19 | 18 | 7.07 | 5.56 |
| 2 | ALL_OFF | −18 | −18 | 7.09 | 6.8 |
| 1 | ALL_ON | 32 | 27 | 6.9 | 6.03 |
| 2 | ALL_ON | −32 | −27 | 6.9 | 6.6 |
| 1 | D1_ON | 24 | 21 | 6.85 | 5.9 |
| 2 | D1_ON | −25 | −27 | 6.93 | 6.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, F.H.; Khamas, S.K. Large- and Small-Scale Beam-Steering Phased Array Antennas Using Variable Phase BLC for Millimeter-Wave Applications. Sensors 2025, 25, 3714. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25123714
Ahmed FH, Khamas SK. Large- and Small-Scale Beam-Steering Phased Array Antennas Using Variable Phase BLC for Millimeter-Wave Applications. Sensors. 2025; 25(12):3714. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25123714
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Fayyadh H., and Salam K. Khamas. 2025. "Large- and Small-Scale Beam-Steering Phased Array Antennas Using Variable Phase BLC for Millimeter-Wave Applications" Sensors 25, no. 12: 3714. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25123714
APA StyleAhmed, F. H., & Khamas, S. K. (2025). Large- and Small-Scale Beam-Steering Phased Array Antennas Using Variable Phase BLC for Millimeter-Wave Applications. Sensors, 25(12), 3714. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25123714





