High-Resolution Localization Using Distributed MIMO FMCW Radars
Abstract
1. Introduction
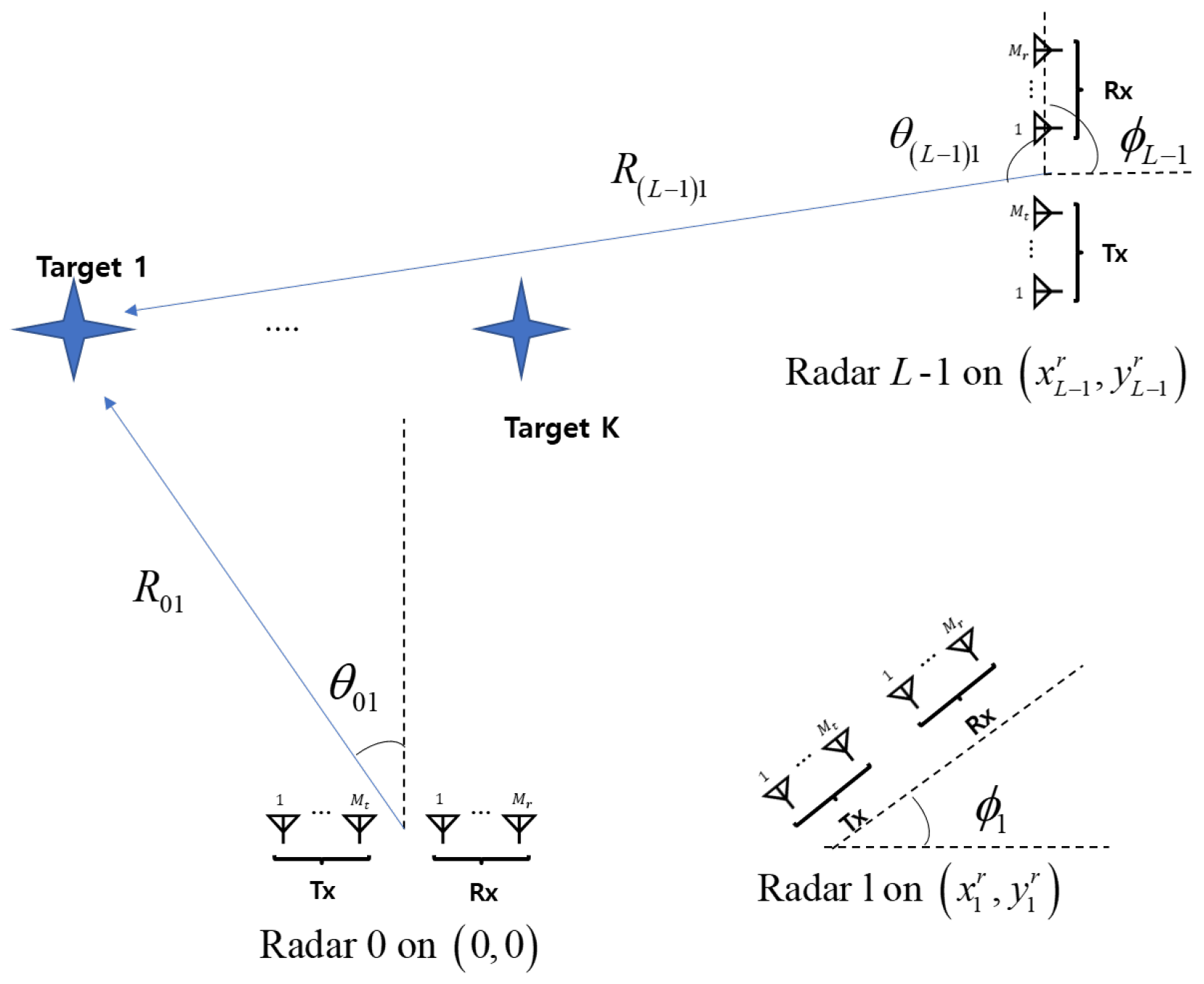
2. System Model for a Distributed FMCW MIMO Radar System
2.1. Transmitted/Received Signal Model for a Distributed FMCW MIMO Radar
2.2. Transforming Received Signals into a Discrete-Time Signal Matrix
3. Target Localization Algorithm with a Single FMCW MIMO Radar
3.1. 2D DFT Based Target Localization and the Resolution Analysis in a Unified Coordinate
3.2. Subspace-Based 2D MUSIC Algorithm with a Single FMCW MIMO Radar
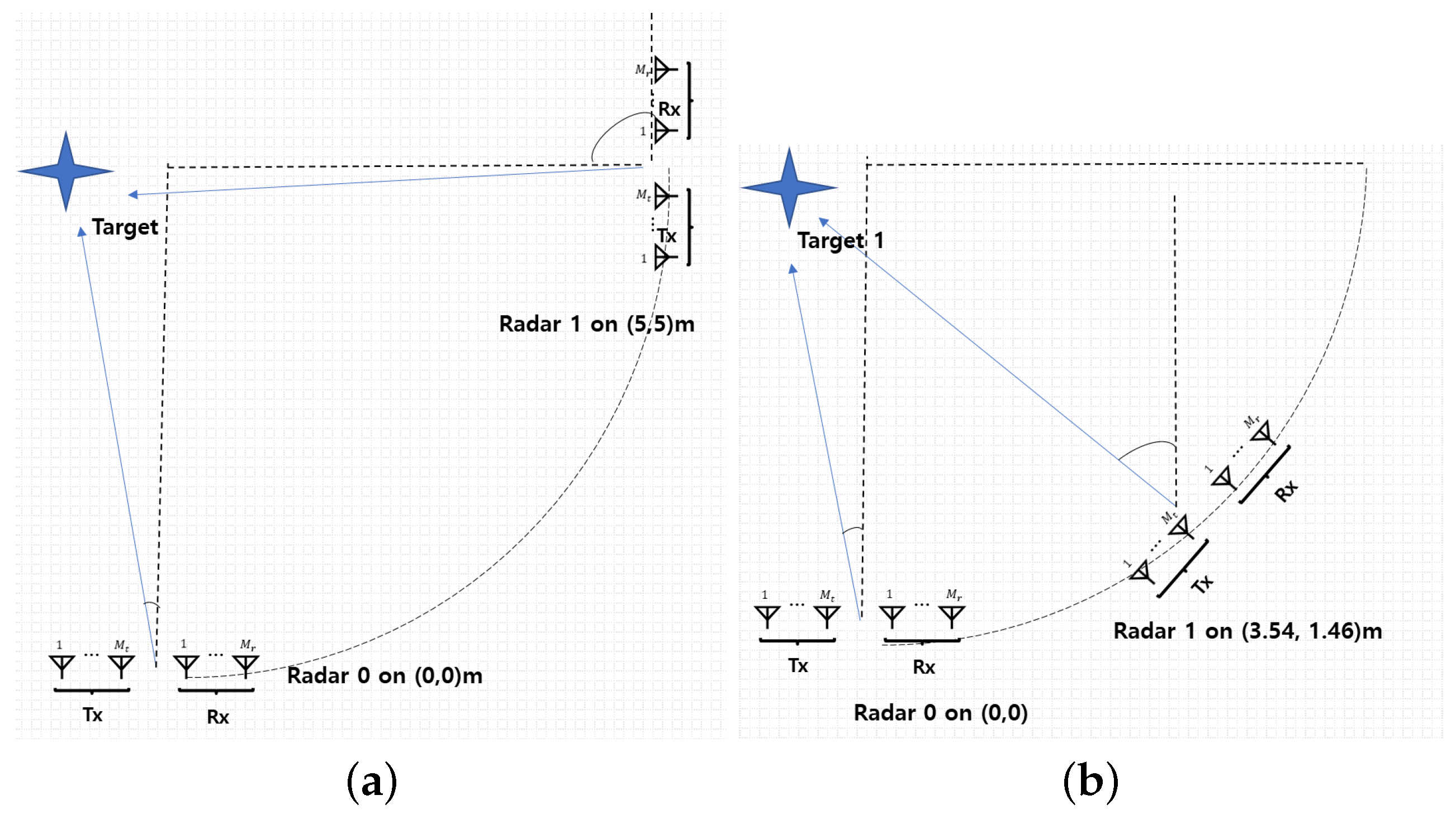
4. Efficient High-Resolution Target Localization Algorithm with Distributed FMCW MIMO Radars
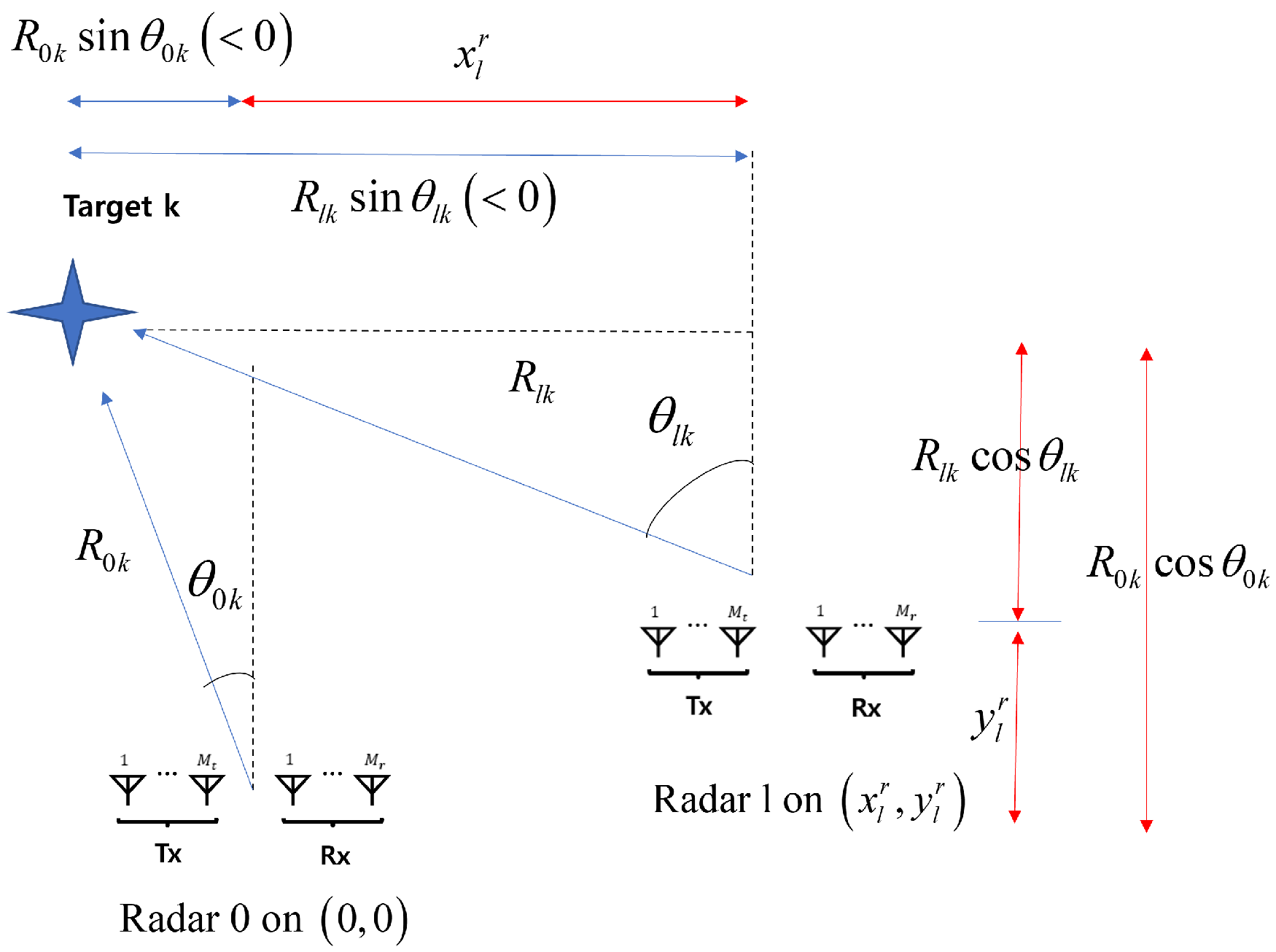
4.1. Target Localization Based on the Transformation of Distributed 2D MUSIC Spectra
4.2. Target Localization Based on the Weighted-Average of Local Estimates in a Unified Coordinate
4.3. Communication Overhead and Computational Complexity Analysis
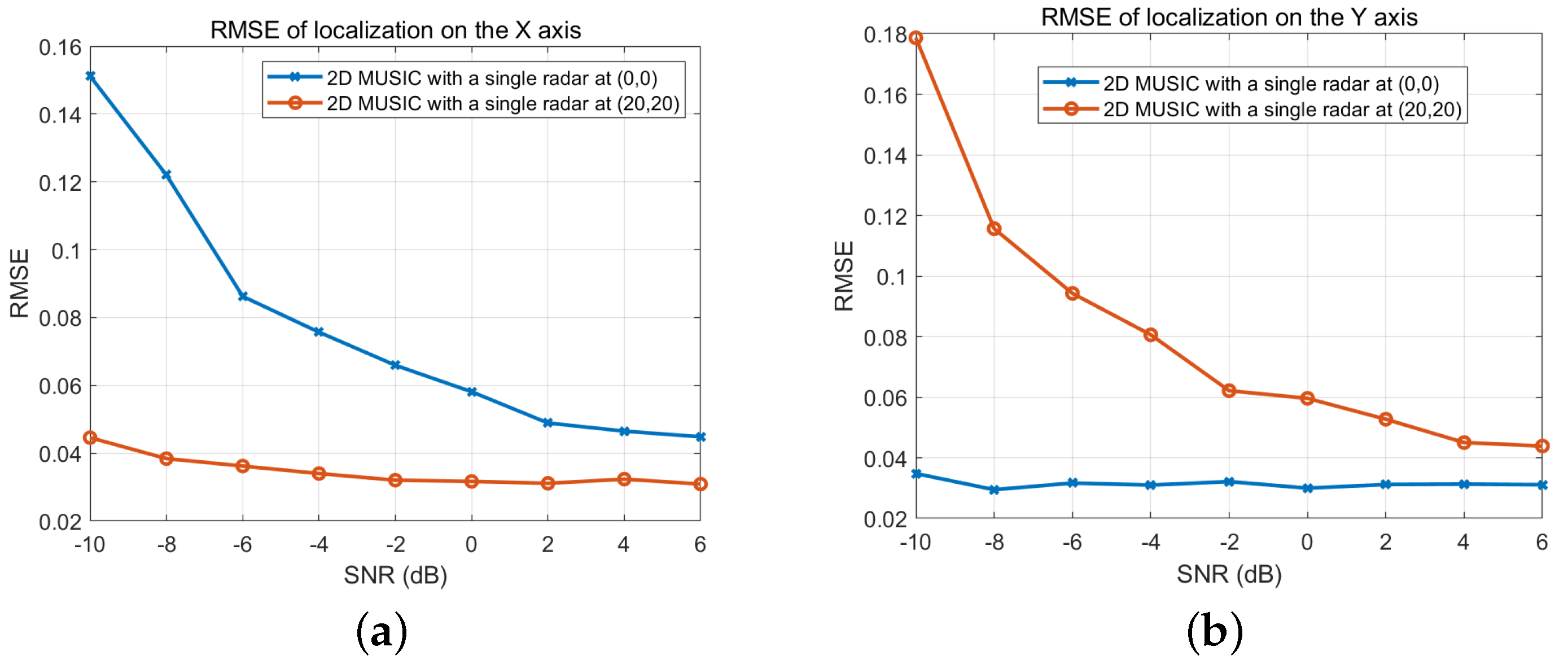
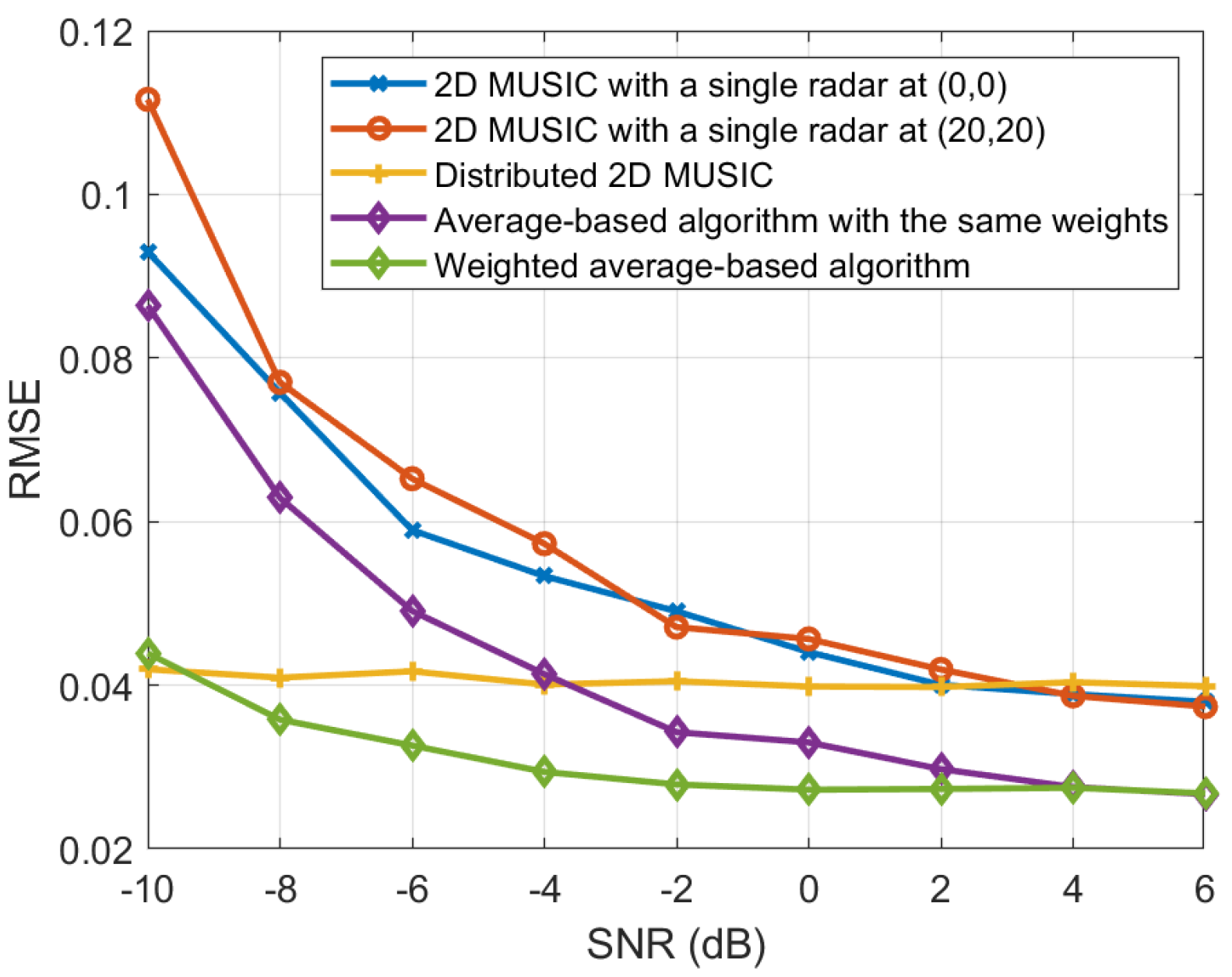
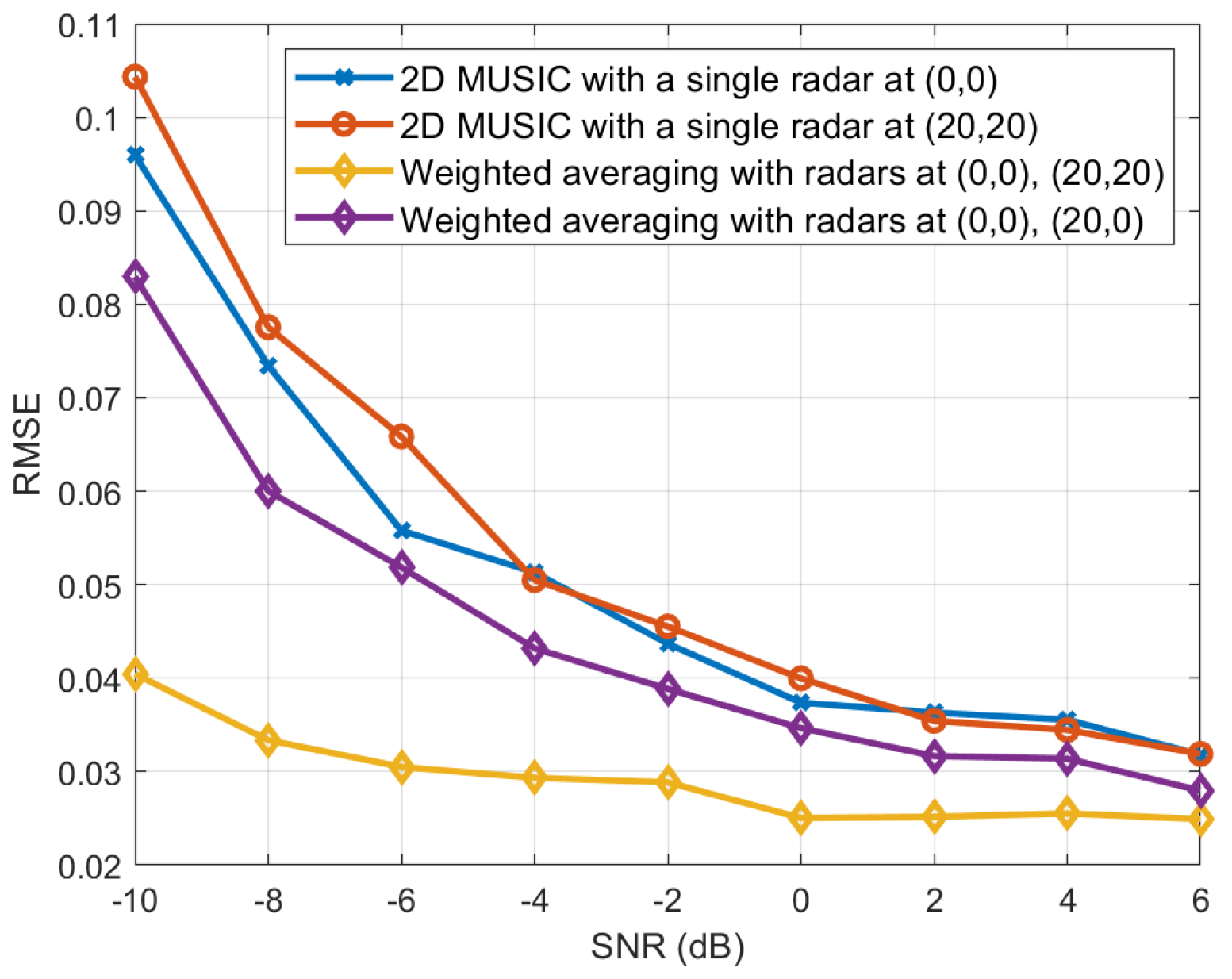
5. Simulation Results
6. Experiment Results
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasch, J.; Topak, E.; Schnabel, R.; Zwick, T.; Weigel, R.; Waldschmidt, C. Millimeter-Wave Technology for Automotive Radar Sensors in the 77 GHz Frequency Band. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2012, 60, 845–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankiraman, M. Design of Multi-Frequency CW Radars; SciTech Publishing: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2007; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Stove, A.G. Linear FMCW Radar Techniques. IEE Proc. F—Radar Signal Process. 1992, 139, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakobyan, G.; Yang, B. High-Performance Automotive Radar: A Review of Signal Processing Algorithms and Modulation Schemes. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2019, 36, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, K.K. Low-Complexity Joint Extrapolation-MUSIC-Based 2-D Parameter Estimator for Vital FMCW Radar. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 2205–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, J.; Chun, J. Weighted Two-Dimensional Root MUSIC for Joint Angle-Doppler Estimation With MIMO Radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 55, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Zheng, W.; Xia, Z.; Wang, Y. Localization of Near-Field Sources: A Reduced-Dimension MUSIC Algorithm. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 1422–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y.; Hwang, S.S. Cascade AOA Estimation Algorithm Based on Flexible Massive Antenna Array. Sensors 2020, 20, 6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Xu, K.; Feng, D.; Wu, C.Q.; Hou, A.; Yin, X. A Fast Algorithm for 2D DOA Estimation Using an Omnidirectional Sensor Array. Sensors 2017, 17, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amine, I.M.; Seddik, B. 2-D DOA Estimation Using MUSIC Algorithm with Uniform Circular Array. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th IEEE International Colloquium on Information Science and Technology (CiSt), Tangier, Morocco, 24–26 October 2016; pp. 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, R.; Rogier, H. A Hybrid UCA-RARE/Root-MUSIC Approach for 2-D Direction of Arrival Estimation in Uniform Circular Arrays in the Presence of Mutual Coupling. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2007, 55, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Zhang, X.; Lai, X.; Ali, F.; Shi, X. Low-Complexity 2D-DOD and 2D-DOA Estimation in Bistatic MIMO Radar Systems: A Reduced-Dimension MUSIC Algorithm Approach. Sensors 2024, 24, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aal Dhaheb, L.T.H.; Muzlifah Mahyuddin, N. A Low Computational Complexity for 2D MUSIC Algorithm in Massive MIMO Systems. In Proceedings of the 2021 8th International Conference on Computer and Communication Engineering (ICCCE), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 22–23 June 2021; pp. 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisto, M.A.; Dell’Aversano, A.; Brancaccio, A.; Russo, I.; Solimene, R. A Computationally Light MUSIC Based Algorithm for Automotive RADARs. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2024, 10, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.H.; Jung, D.H.; Kim, D.C.; Ham, J.W.; Park, S.O. A Distributed FMCW Radar System Based on Fiber-Optic Links for Small Drone Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Huang, C.; Su, Y. A Coherent Signal Processing Method for Distributed Radar System. In Proceedings of the 2016 Progress in Electromagnetic Research Symposium (PIERS), Shanghai, China, 8–11 August 2016; pp. 2226–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Long, T. Wideband Distributed Coherent Aperture Radar. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Radar Conference, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 19–23 May 2014; pp. 1114–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurwanz, M.; Oettinghaus, S.; Mietzner, J.; Hoeher, P.A. Reducing On-Board Interference and Angular Ambiguity Using Distributed MIMO Radars in Medium-Sized Autonomous Air Vehicle. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2024, 39, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wen, G.; Liang, Y.; Luo, D.; Jian, H. Multitarget Enumeration and Localization in Distributed MIMO Radar Based on Energy Modeling and Compressive Sensing. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2023, 59, 4493–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Lee, J.; Park, J.; Kim, H.; You, S. Distributed Two-Dimensional MUSIC for Joint Range and Angle Estimation with Distributed FMCW MIMO Radars. Sensors 2021, 21, 7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, L.; Hehao, N.; Yuanzhi, H.; Kang, A.; Xudong, Z.; Zheng, C.; Pei, X. Self-powered absorptive reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for securing satellite-terrestrial integrated networks. China Commun. 2024, 21, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ma, R.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, R.; Cai, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, J. Improving Age of Information for Covert Communication With Time-Modulated Arrays. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 1718–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commin, H.; Manikas, A. Virtual SIMO Radar Modelling in Arrayed MIMO Radar. In Proceedings of the Sensor Signal Processing for Defence (SSPD 2012), London, UK, 25–27 September 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1986, 34, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, J. High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis. Proc. IEEE 1969, 57, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Haardt, M.; Greco, M.S.; Mecklenbräuker, C.F.; Willett, P. Twenty-Five Years of Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing: A review of progress to date and potential research directions. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2023, 40, 80–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahafza, B.R. Radar Systems Analysis and Design Using MATLAB; CRC Press, Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wax, M.; Kailath, T. Detection of signals by information theoretic criteria. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1985, 33, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünwald, P.D.; Myung, I.J.; Pitt, M.A. Advances in Minimum Description Length: Theory and Applications; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wannebo, A. Hardy inequalities. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 1990, 109, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
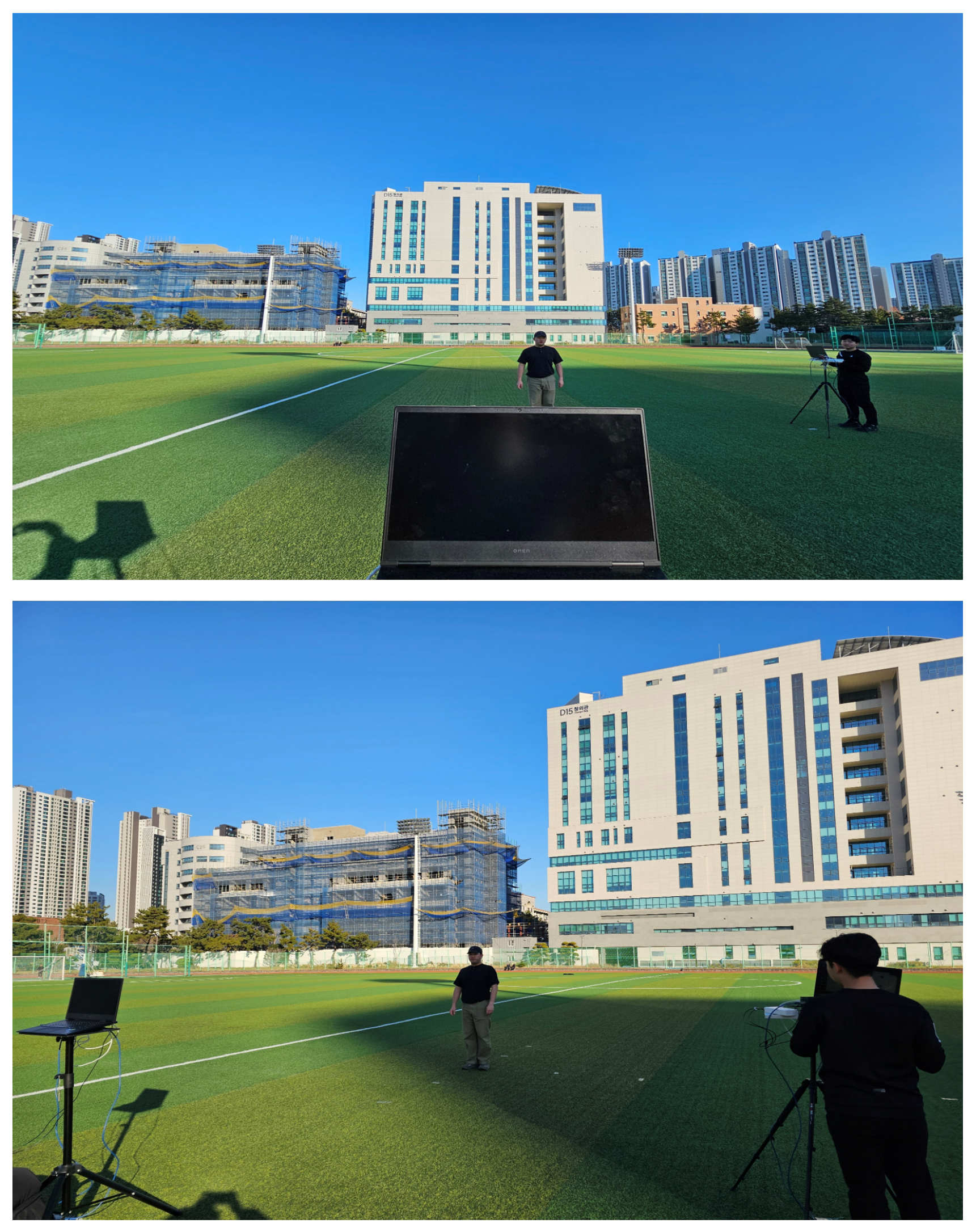




| Method | Data per Frame | Reduction Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Signal Fusion [15,16,17] | 4.2 MB | 1 |
| MUSIC Spectrum Fusion [20] | 369 KB | 11.4× |
| Proposed Method | 8 bytes/target | 525,000× |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Type of Signal waveform | Linear Chirped waveform |
| Chirp BW | 1279.2 (Mhz) |
| Number of Chirps per frame | 256 |
| Number of Chirp Loops | 128 |
| Range resolution | 0.1172 (m) |
| Velocity resolution | 0.0470 (m/s) |
| Tx power | 12 dBm |
| Sampling Rate | 6000 ksps |
| RMSE | Target Locations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ϵx,ϵy) | (0, 5)m | (0, 4)m | (0, 6)m | (1, 5)m |
| Radar at m | ||||
| Radar at m | ||||
| RMSE | Target Locations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | m | m | m | |
| 2D MUSIC with a single | 0.224 | 0.151 | 0.173 | 0.135 |
| radar at m | ||||
| 2D MUSIC with a single | 0.137 | 0.111 | 0.192 | 0.149 |
| radar at m | ||||
| Equal-weight combining with | 0.130 | 0.083 | 0.192 | 0.130 |
| radars at /m | ||||
| Equal-weight combining with | 0.149 | 0.110 | 0.011 | 0.076 |
| radars at /m | ||||
| Proposed weighted averaging with | 0.115 | 0.060 | 0.127 | 0.085 |
| radars at /m | ||||
| Proposed weighted averaging with | 0.069 | 0.057 | 0.094 | 0.044 |
| radars at /m | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.; Chung, S.; Park, J.; Huang, Y. High-Resolution Localization Using Distributed MIMO FMCW Radars. Sensors 2025, 25, 3579. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25123579
Park H, Chung S, Park J, Huang Y. High-Resolution Localization Using Distributed MIMO FMCW Radars. Sensors. 2025; 25(12):3579. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25123579
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Huijea, Seungsu Chung, Jaehyun Park, and Yang Huang. 2025. "High-Resolution Localization Using Distributed MIMO FMCW Radars" Sensors 25, no. 12: 3579. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25123579
APA StylePark, H., Chung, S., Park, J., & Huang, Y. (2025). High-Resolution Localization Using Distributed MIMO FMCW Radars. Sensors, 25(12), 3579. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25123579







