Wavenumber-Domain Joint Estimation of Rotation Parameters and Scene Center Offset for Large-Angle ISAR Cross-Range Scaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
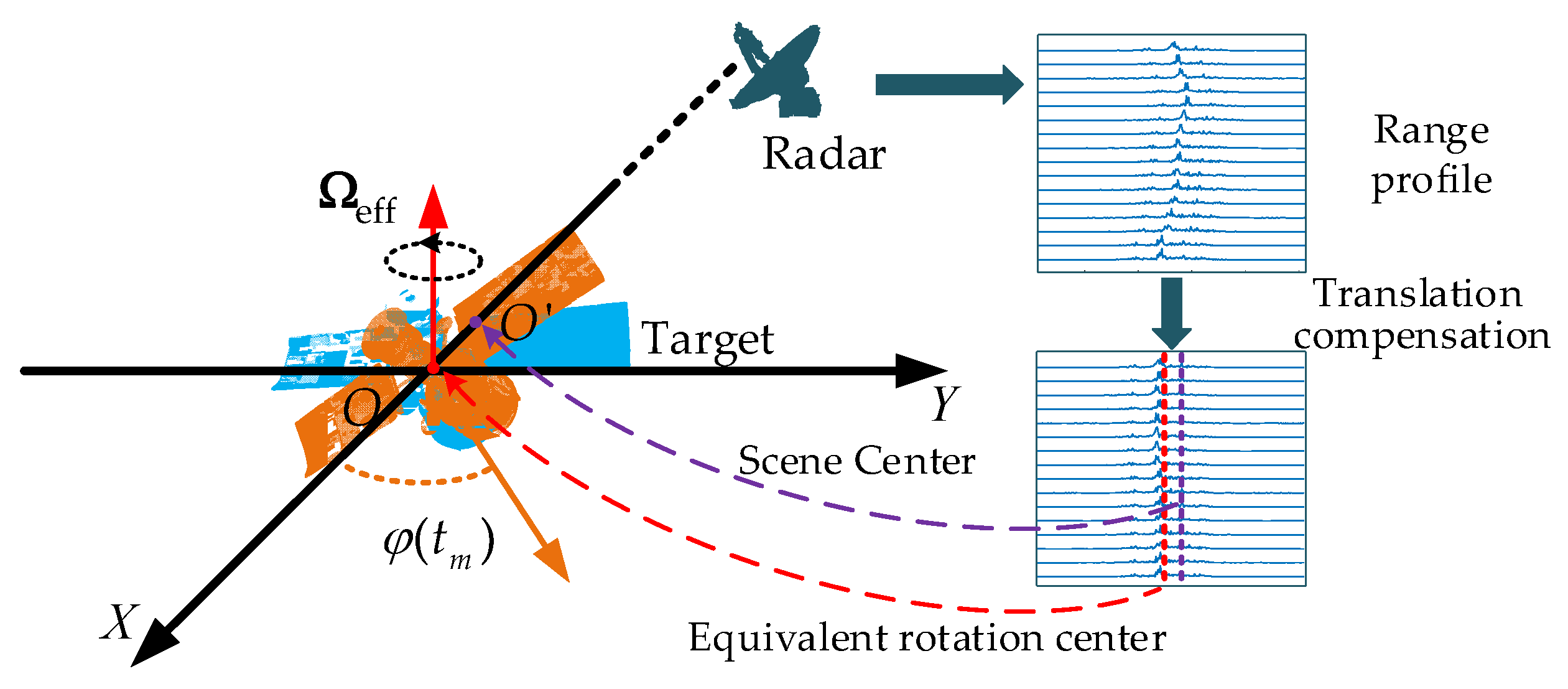
2. ISAR Signal Model
3. Algorithm Description
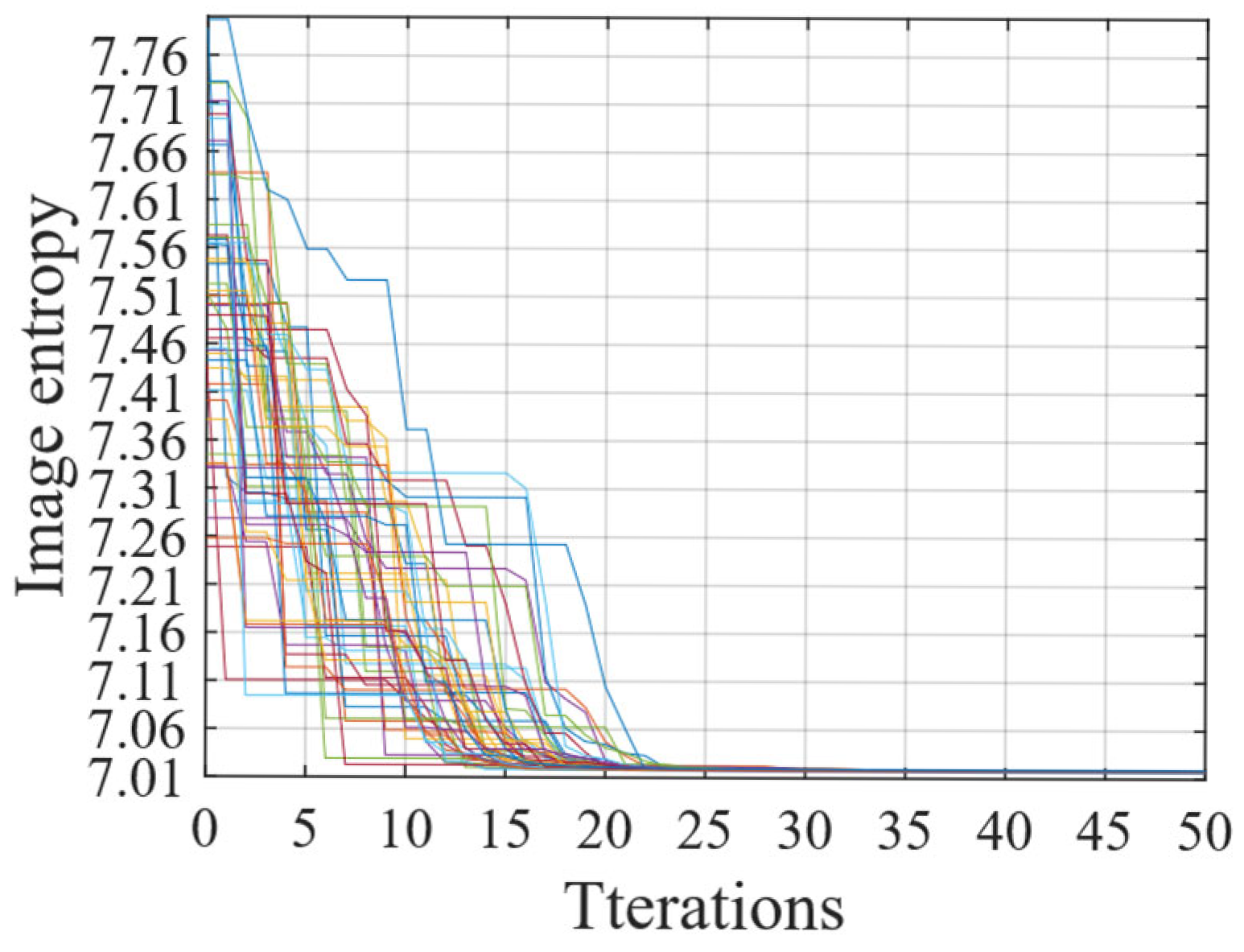
3.1. Joint Estimation of Rotation Parameters and SCO
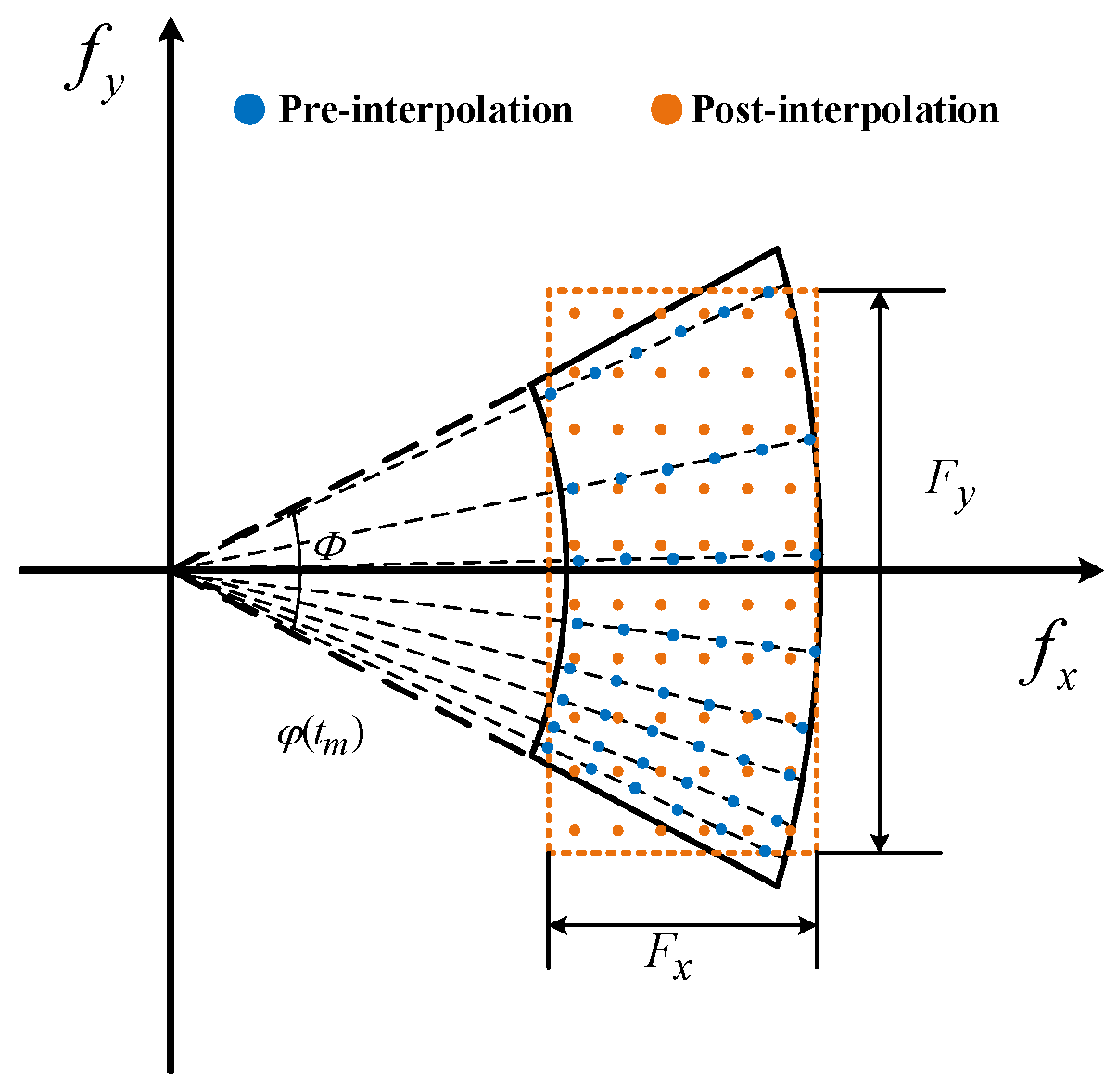
3.2. Cross-Range in the Wavenumber Domain
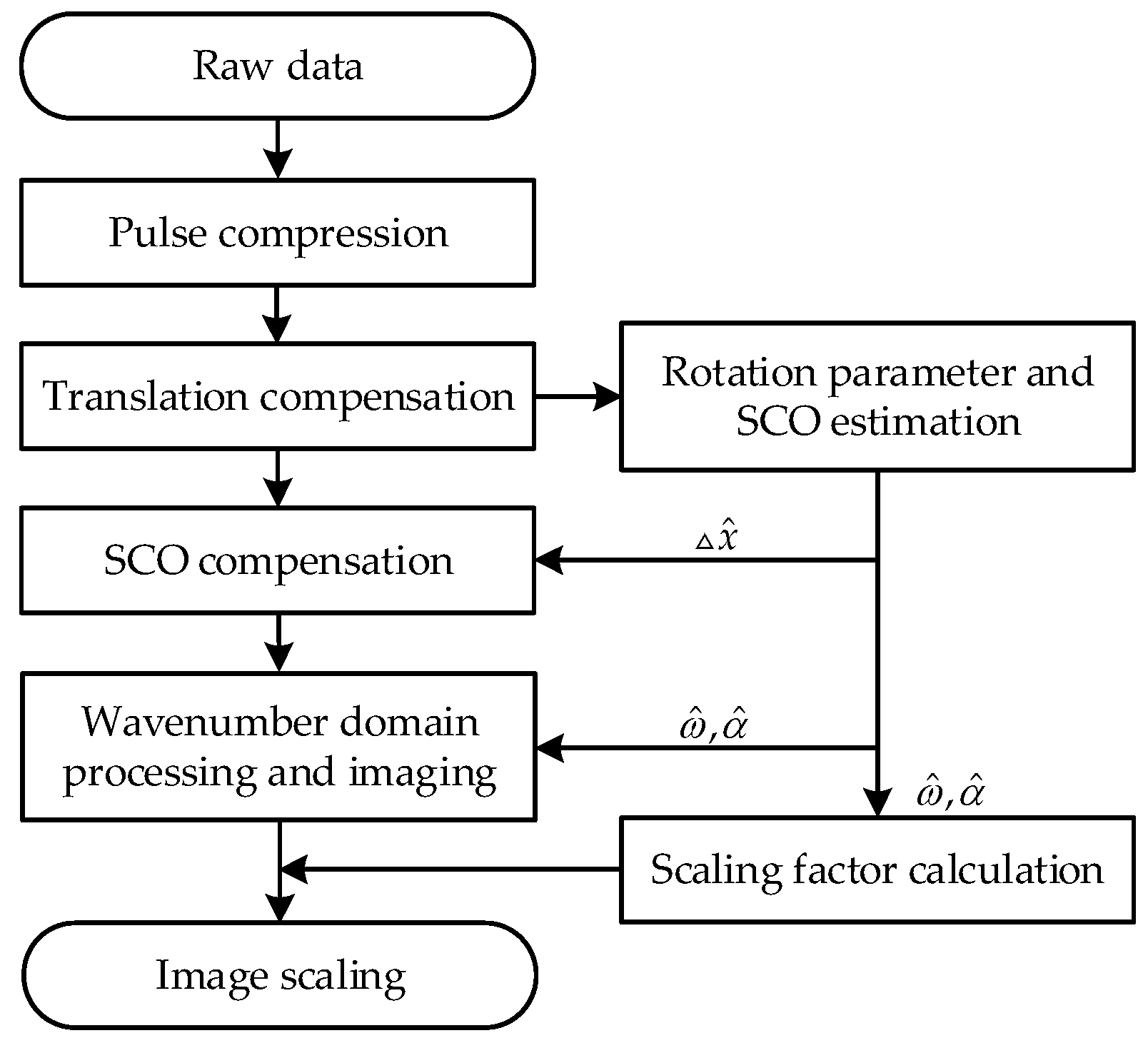
3.3. Overall Structure of the Algorithm
4. Simulation Study
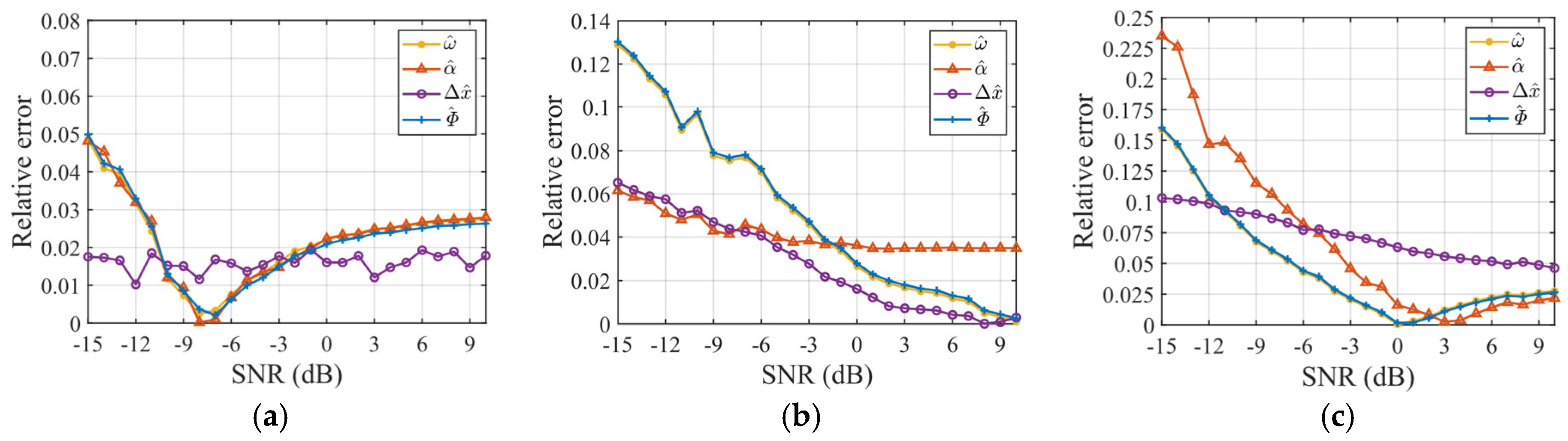
4.1. Simulations Under Varying Rotation Angles
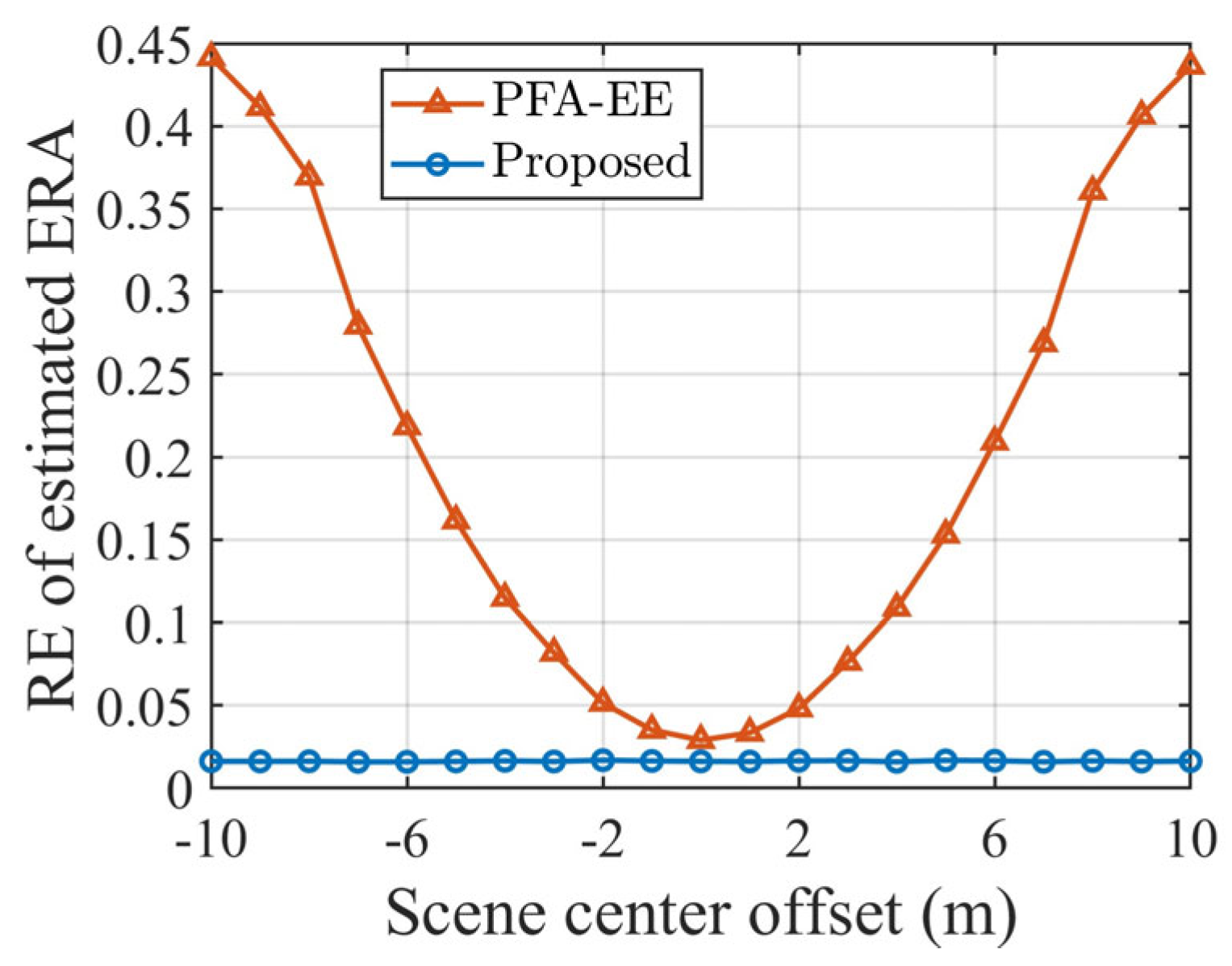
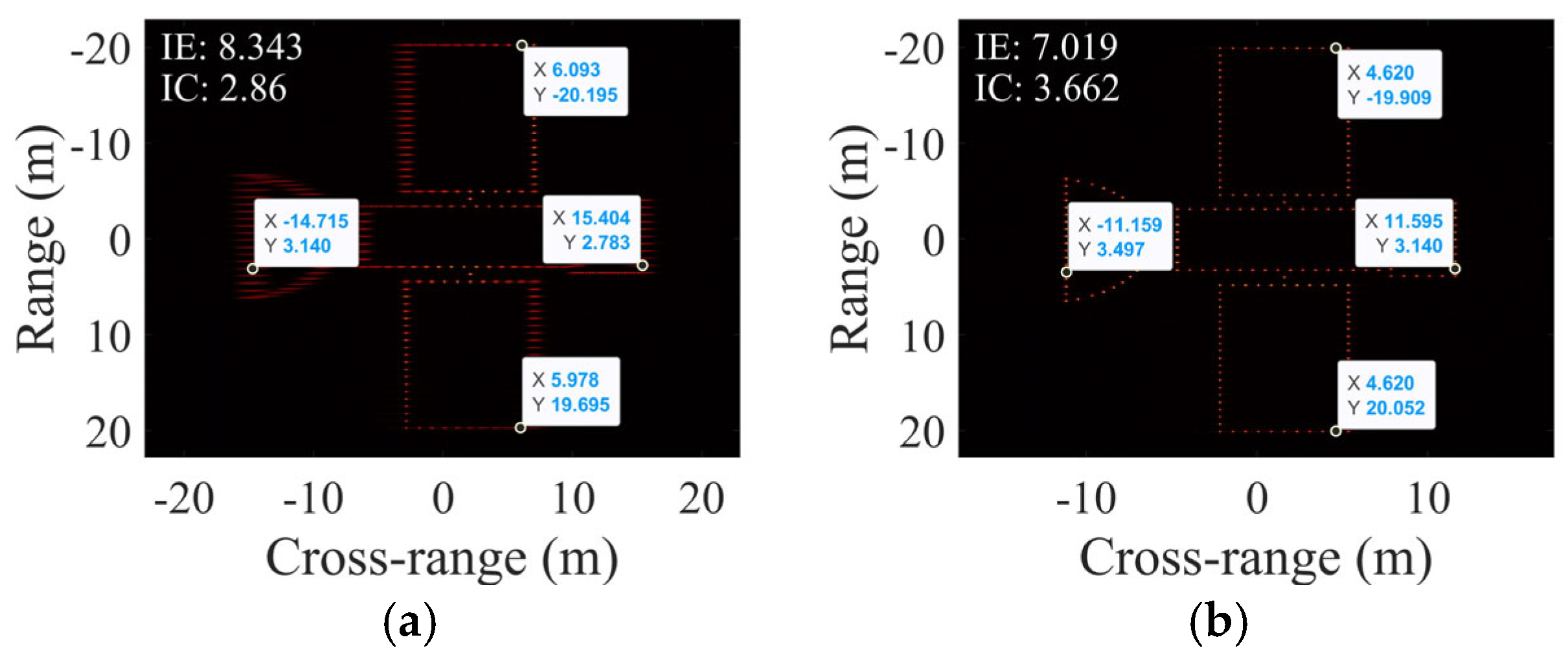
4.2. Simulations with SCO
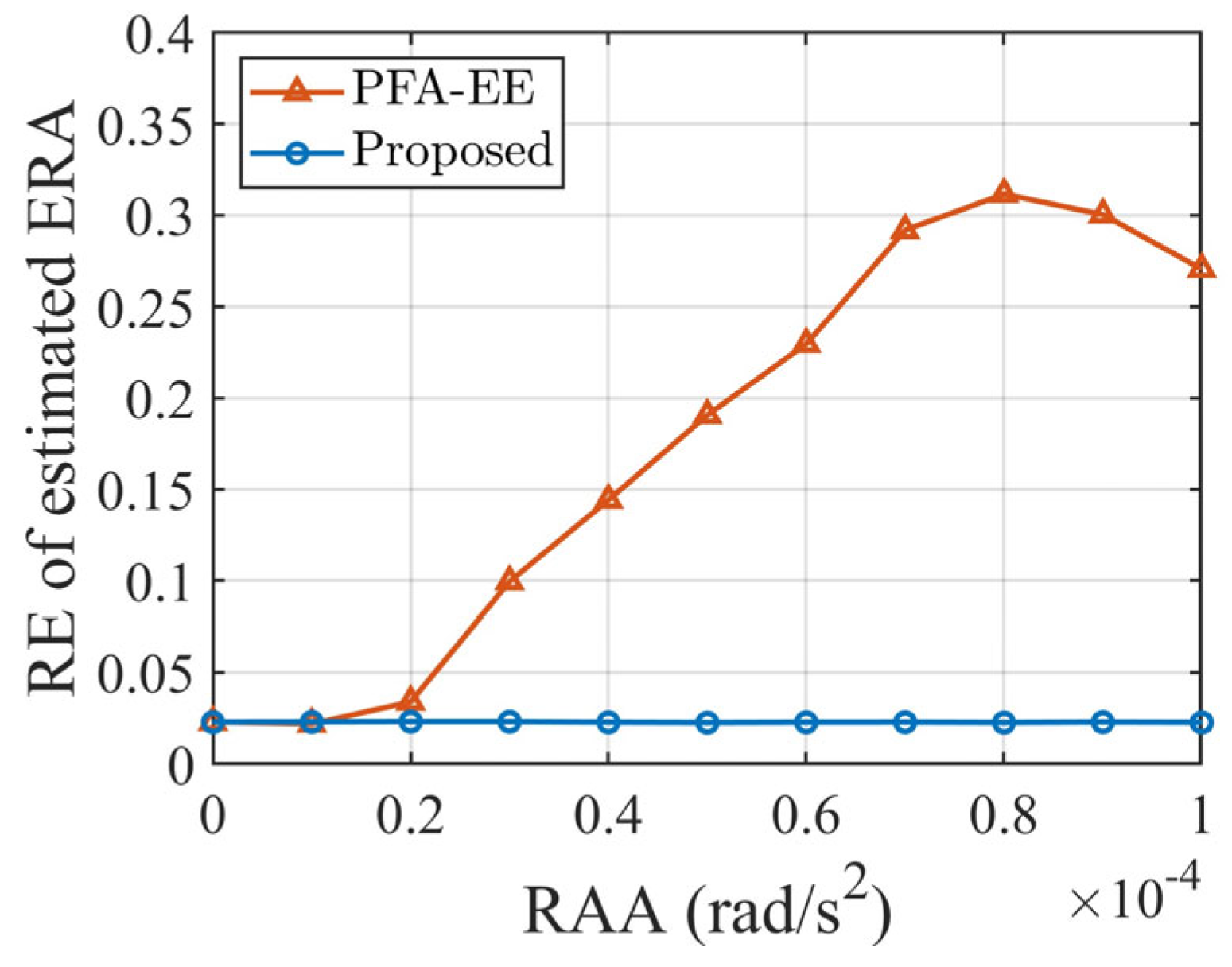
4.3. Simulations with Non-Uniform Rotation
4.4. Simulations with Concurrent SCO and Non-Uniform Rotation
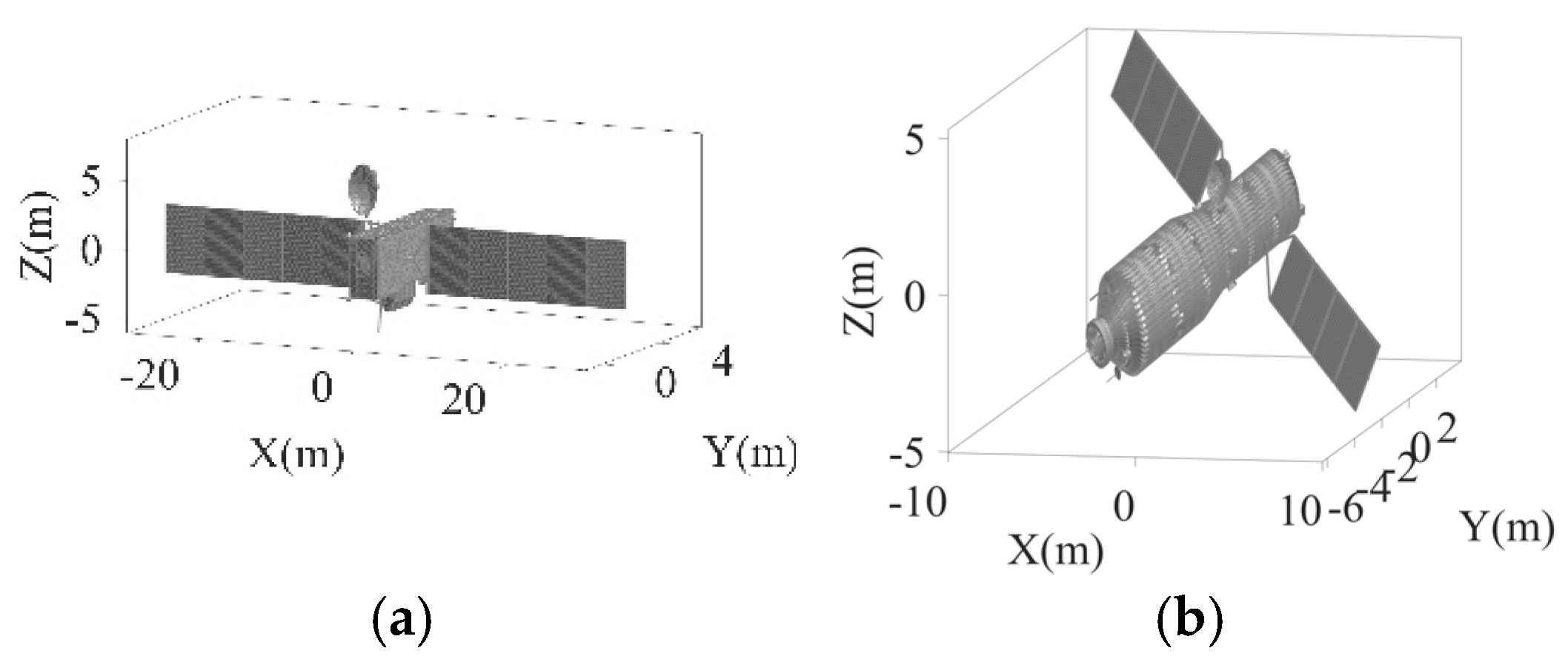
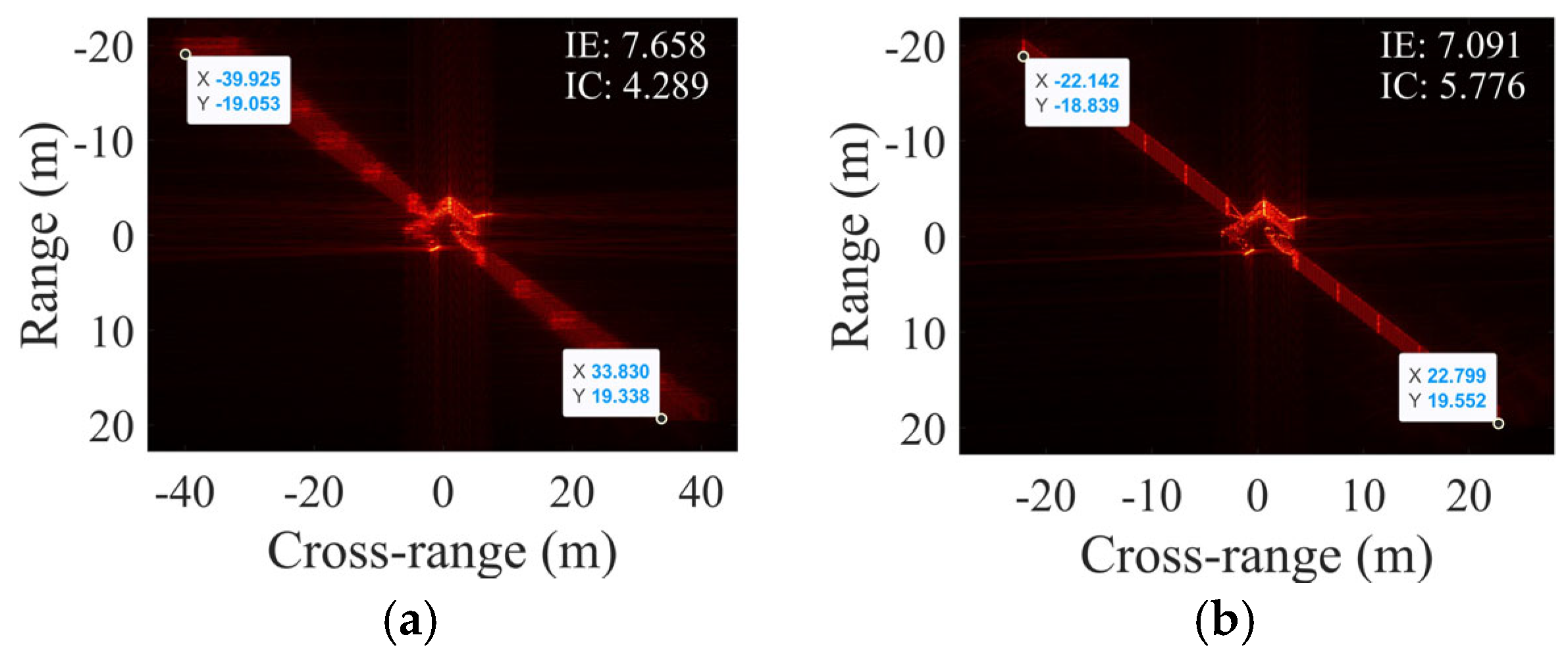
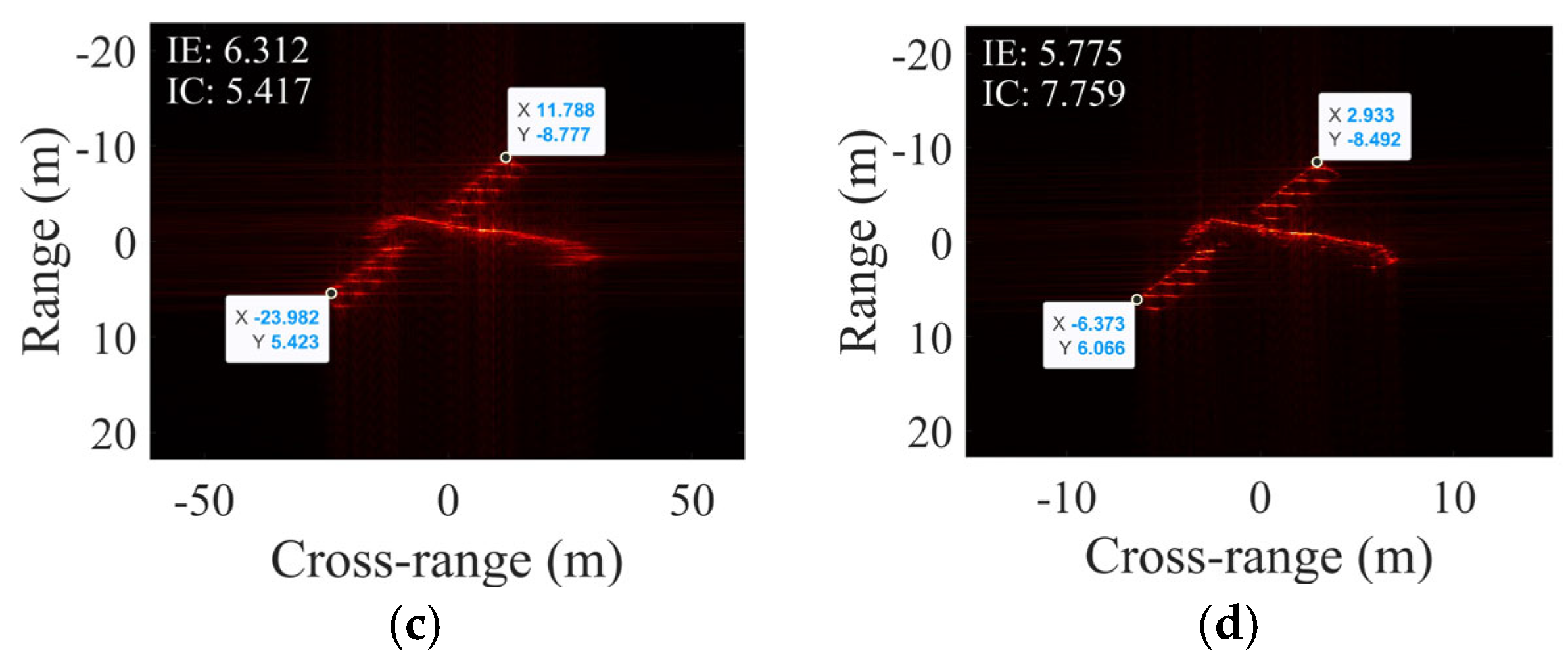
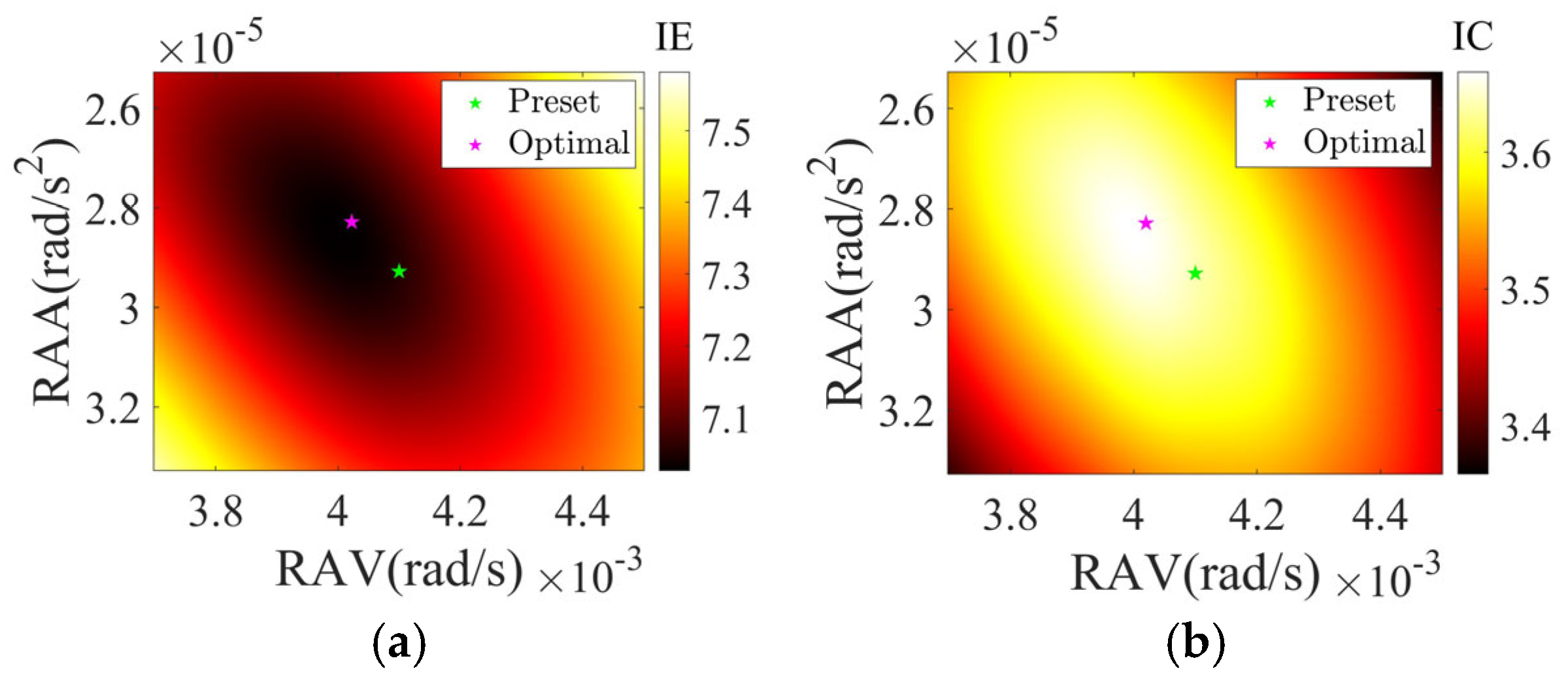
4.5. Simulations with Electromagnetic Computational Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Shao, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, P.; Wei, J. Integration of Super-Resolution ISAR Imaging and Fine Motion Compensation for Complex Maneuvering Ship Targets Under High Sea State. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5222820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Zhang, L.; Du, C.; Wang, X.; Zhong, W. Space Target Attitude Estimation from ISAR Image Sequences with Key Point Extraction Network. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 28, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Martorella, M.; Liu, Q.; Ding, Z.; Giusti, E.; Long, T. Automatic Target Recognition Based on Alignments of Three-Dimensional Interferometric ISAR Images and CAD Models. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2020, 56, 4872–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, B.; Li, Y. Few-Shot Incremental Radar Target Recognition Framework Based on Scattering-Topology Properties. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2024, 37, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Niu, M. Meta-Learner-Based Stacking Network on Space Target Recognition for ISAR Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 12132–12148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Andrews, H.C. Target-Motion-Induced Radar Imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1980, AES-16, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-M.; Xu, J.; Peng, Y.-N.; Wang, X.-T. Cross-Range Scaling for ISAR Based on Image Rotation Correlation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 597–601. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.-S.; Bae, J.-H.; Kang, B.-S.; Kim, K.-T. ISAR Cross-Range Scaling Using Iterative Processing via Principal Component Analysis and Bisection Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 3909–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, J. Efficient Cross-Range Scaling Method via Two-Dimensional Unitary ESPRIT Scattering Center Extraction Algorithm. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Kim, H.-T.; Kim, K.-T. Cross-Range Scaling Algorithm for ISAR Images Using 2-D Fourier Transform and Polar Mapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Wu, R.; Li, Y.; Bao, Z. New ISAR Imaging Algorithm Based on Modified Wigner–Ville Distribution. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2009, 3, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Yang, L.; Bi, G. ISAR Cross-Range Scaling Algorithm Based on LVD. In Proceedings of the 2016 39th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Vienna, Austria, 27–29 June 2016; pp. 643–647. [Google Scholar]
- Martorella, M. Novel Approach for ISAR Image Cross-Range Scaling. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2008, 44, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Su, J.; Tan, X.; Liu, Q.; Liao, G. A Fast Cross-Range Scaling Algorithm for ISAR Images Based on the 2-D Discrete Wavelet Transform and Pseudopolar Fourier Transform. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4231–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Z. ISAR Imaging for Low-Earth-Orbit Target Based on Coherent Integrated Smoothed Generalized Cubic Phase Function. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 1205–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Liang, G.; Zhao, C. Accurate ISAR Scaling for Both Smooth and Maneuvering Targets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 55, 1537–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, R.; Huang, X. Cross-Range Scaling of ISAR Image Generated by the Range-Chirp Rate Algorithm for the Maneuvering Target. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 9124–9131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Q. Rotation Parameters Estimation and Cross-Range Scaling Research for Range Instantaneous Doppler ISAR Images. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 7010–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-C.; Wang, X.-S.; Wang, G.-Y. Scaled Radon-Wigner Transform Imaging and Scaling of Maneuvering Target. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2010, 46, 2043–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xing, M.; Zhang, L.; Sun, G.-C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Bao, Z. Integration of Rotation Estimation and High-Order Compensation for Ultrahigh-Resolution Microwave Photonic ISAR Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 2095–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Xing, M.; Zhang, L.; Mehmood, M.Q.; Yang, L. ISAR Cross-Range Scaling by Using Sharpness Maximization. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Bi, G. Fast ISAR Cross-Range Scaling Using Modified Newton Method. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xing, M.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, L. ISAR Imaging and Cross-Range Scaling for Maneuvering Targets by Using the NCS-NLS Algorithm. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 4889–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Qi, M.-S.; Zhou, F. A Novel Non-Uniform Rotational Motion Estimation and Compensation Method for Maneuvering Targets ISAR Imaging Utilizing Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A. Method and Apparatus for Determining a Cross-Range Scale Factor in Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Systems. U.S. Patent Application No. US07/783,304, 17 November 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Kasilingam, D. Global Range Alignment for ISAR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2003, 39, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y.; Tao, Q.; Zhu, Z. Robust ISAR Range Alignment via Minimizing the Entropy of the Average Range Profile. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 204–208. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Yeo, T.S.; Zheng, B. Weighted Least-Squares Estimation of Phase Errors for SAR/ISAR Autofocus. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 2487–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, D.E.; Eichel, P.H.; Ghiglia, D.C.; Jakowatz, C.V. Phase Gradient Autofocus-a Robust Tool for High Resolution SAR Phase Correction. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.C.; Martorella, M. Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging: Principles, Algorithms and Applications; Institution of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.R. Bilinear Interpolation of Digital Images. Ultramicroscopy 1981, 6, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Fast Entropy Minimization Based Autofocusing Technique for ISAR Imaging. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 3425–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95—International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, D.E. Propagation of Short Radio Waves; IET: London, UK, 1987; Volume 24. [Google Scholar]

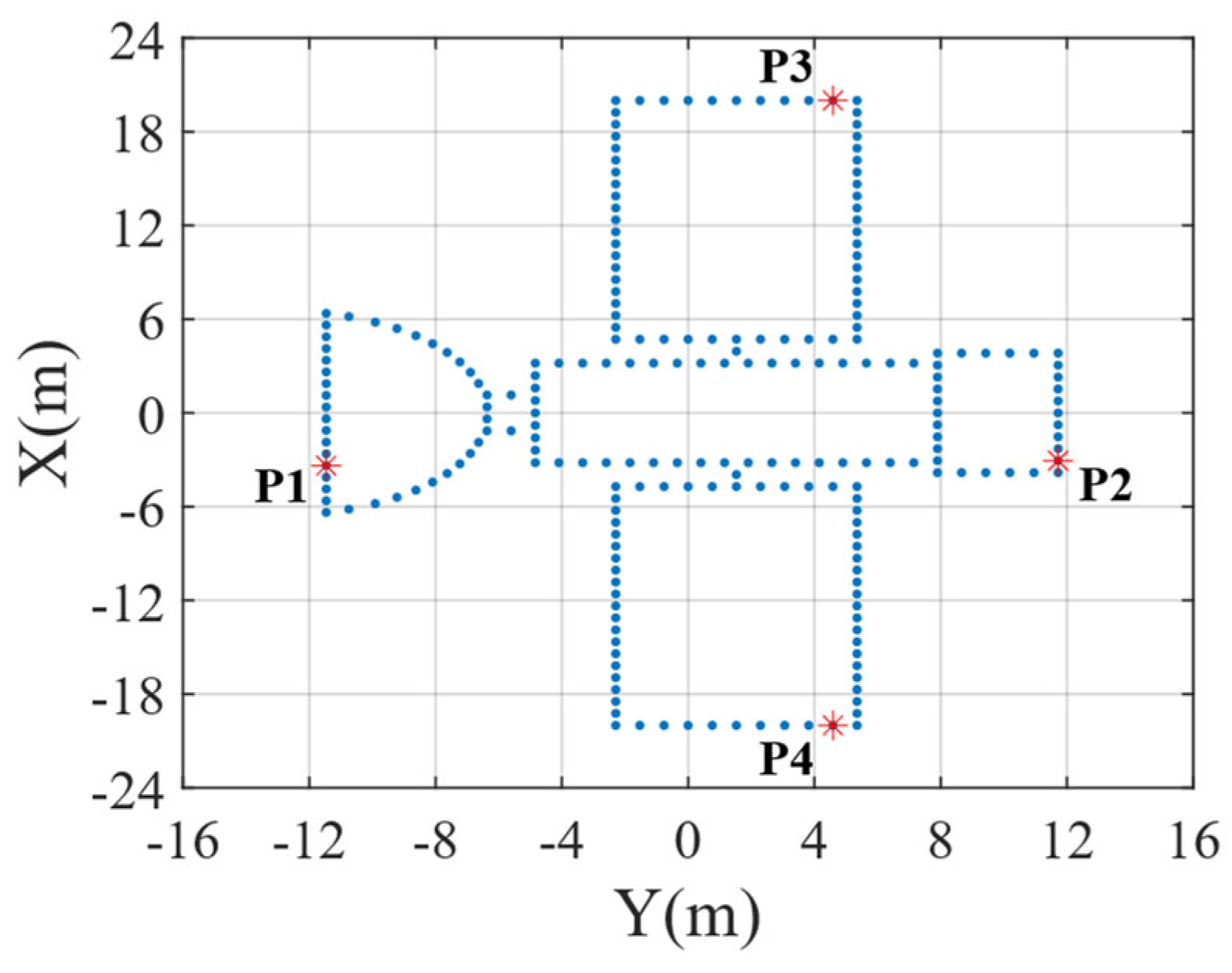
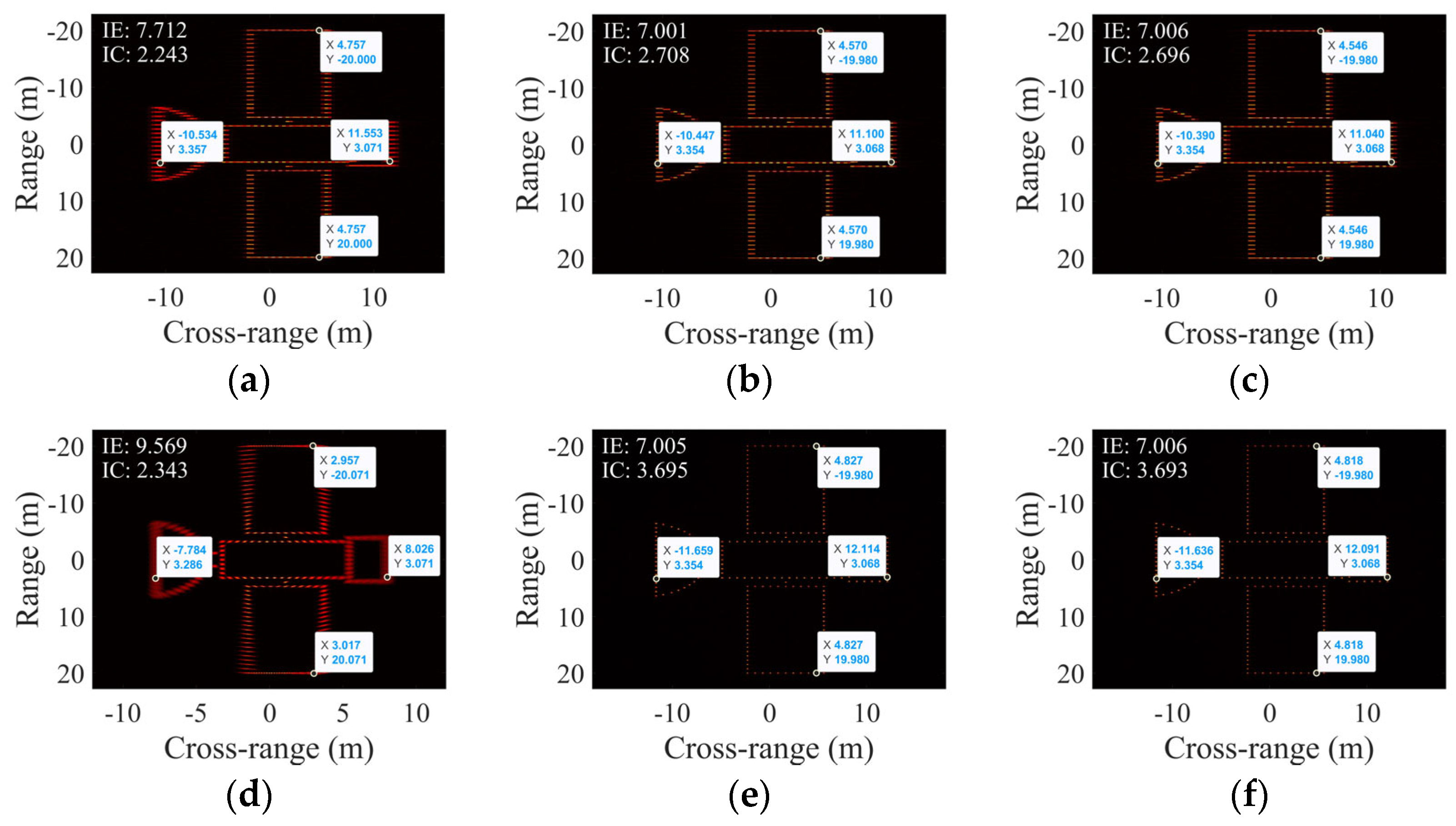



| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Carrier frequency | 16.1 GHz |
| Bandwidth | 2 GHz |
| Pulse width | |
| Dechirping pulse width | |
| PRF | 40 Hz |
| ERA | Estimated RAV (rad/s) | Estimated Length (m) | RE of Estimated Length | Estimated Width (m) | RE of Estimated Width | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5° | 0.00425 | 22.089 | 0.0548 | 40 | 0 | |
| LPFT | 3° | 0.00573 | 16.65 | 0.3267 | 40.142 | 0.0071 |
| 6° | 0.00603 | 15.812 | 0.369 | 40.142 | 0.0071 | |
| 1.5° | 0.00444 | 21.559 | 0.0813 | 39.96 | 0.002 | |
| PFA-EE | 3° | 0.00399 | 23.943 | 0.0379 | 39.96 | 0.002 |
| 6° | 0.004 | 23.775 | 0.295 | 39.96 | 0.002 | |
| 1.5° | 0.00443 | 21.432 | 0.0877 | 39.96 | 0.002 | |
| Proposed algorithm | 3° | 0.00399 | 23.846 | 0.0331 | 39.96 | 0.002 |
| 6° | 0.004 | 23.729 | 0.272 | 39.96 | 0.002 |
| Estimated RAV (rad/s) | Estimated SCO (m) | Estimated Length (m) | RE of Estimated Length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFA-EE | 0.0031 | - | 30.722 | 0.377 |
| Proposed algorithm | 0.004 | 4.901 | 23.744 | 0.028 |
| Estimated RAV (rad/s) | Estimated RAA (rad/s2) | Estimated Length (m) | RE of Estimated Length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFA-EE | 0.00444 | - | 21.418 | 0.0883 |
| Proposed algorithm | 0.004 | 2.85 × 10−5 | 22.749 | 0.0218 |
| Estimated RAV (rad/s) | Estimated RAA (rad/s2) | Estimated SCO (m) | Estimated Length (m) | RE of Estimated Length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFA-EE | 0.0032 | - | - | 30.121 | 0.347 |
| Proposed algorithm | 0.004 | 2.85 × 10−5 | 4.9 | 22.757 | 0.0214 |
| Target | Estimated RAV (rad/s) | Estimated RAA (rad/s2) | Estimated SCO (m) | Estimated Length (m) | RE of Estimated Length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFA-EE | 1 | 0.00239 | - | - | 86.877 | 0.4479 |
| Proposed algorithm | 1 | 0.0041 | 2.82 × 10−5 | 5.0446 | 59.106 | 0.0293 |
| PFA-EE | 2 | 8.963 × 10−4 | - | - | 43.734 | 1.277 |
| Proposed algorithm | 2 | 0.00392 | 2.77 × 10−5 | 4.951 | 19.641 | 0.0221 |
| Estimated RAV (rad/s) | Estimated RAA (rad/s2) | Estimated SCO (m) | Estimated Length (m) | RE of Estimated Length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target 1 | 0.0045 | 2.754 × 10−5 | 4.741 | 58.206 | 0.0299 |
| Target 2 | 0.00425 | 3.236 × 10−5 | 4.572 | 19.191 | 9.891 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, B.; Zhu, W.; Pang, H.; Li, C.; Qui, L.; Yan, J.; Ma, F.; Liu, Y. Wavenumber-Domain Joint Estimation of Rotation Parameters and Scene Center Offset for Large-Angle ISAR Cross-Range Scaling. Sensors 2025, 25, 3444. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113444
Zhu B, Zhu W, Pang H, Li C, Qui L, Yan J, Ma F, Liu Y. Wavenumber-Domain Joint Estimation of Rotation Parameters and Scene Center Offset for Large-Angle ISAR Cross-Range Scaling. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3444. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113444
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Bakun, Weigang Zhu, Hongfeng Pang, Chenxuan Li, Lei Qui, Jinhai Yan, Fanyin Ma, and Yijia Liu. 2025. "Wavenumber-Domain Joint Estimation of Rotation Parameters and Scene Center Offset for Large-Angle ISAR Cross-Range Scaling" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3444. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113444
APA StyleZhu, B., Zhu, W., Pang, H., Li, C., Qui, L., Yan, J., Ma, F., & Liu, Y. (2025). Wavenumber-Domain Joint Estimation of Rotation Parameters and Scene Center Offset for Large-Angle ISAR Cross-Range Scaling. Sensors, 25(11), 3444. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113444





