The TDGL Module: A Fast Multi-Scale Vision Sensor Based on a Transformation Dilated Grouped Layer
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A new standard convolutional unit, GLConv, is designed, and non-zero values are added to the batch variance to enhance the stability of feature information extraction.
- A multi-branch TDGL detection module based on normalized convolutional units is proposed. The TDGL adopts an integrated and more flexible convolutional kernel mechanism, which improves its performance in extracting feature information from targets of multiple sizes with limited computational resources and enhances the detection capability of visual sensors for multi-scale targets on roads.
- Experiments are carried out on the BDD100K benchmark, and the effectiveness of our network is verified.
2. Related Work
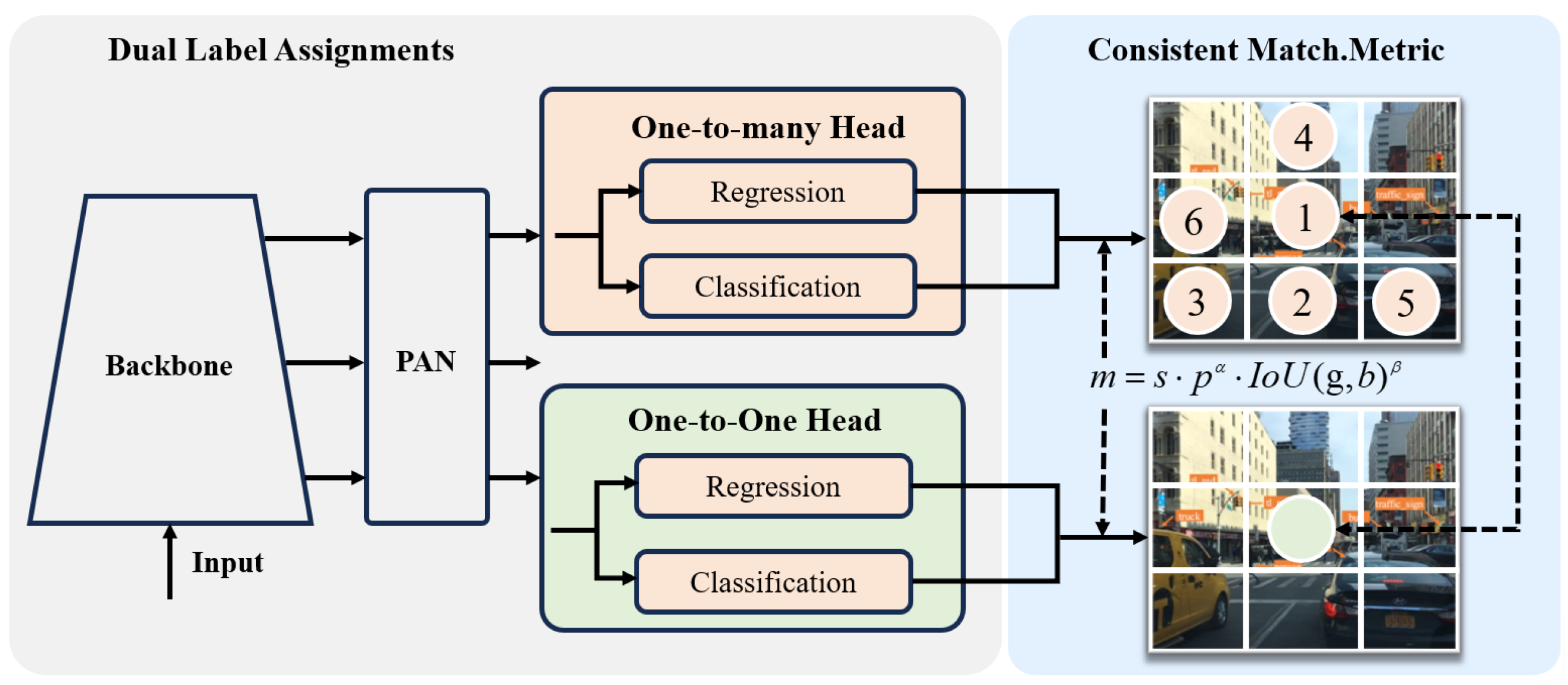
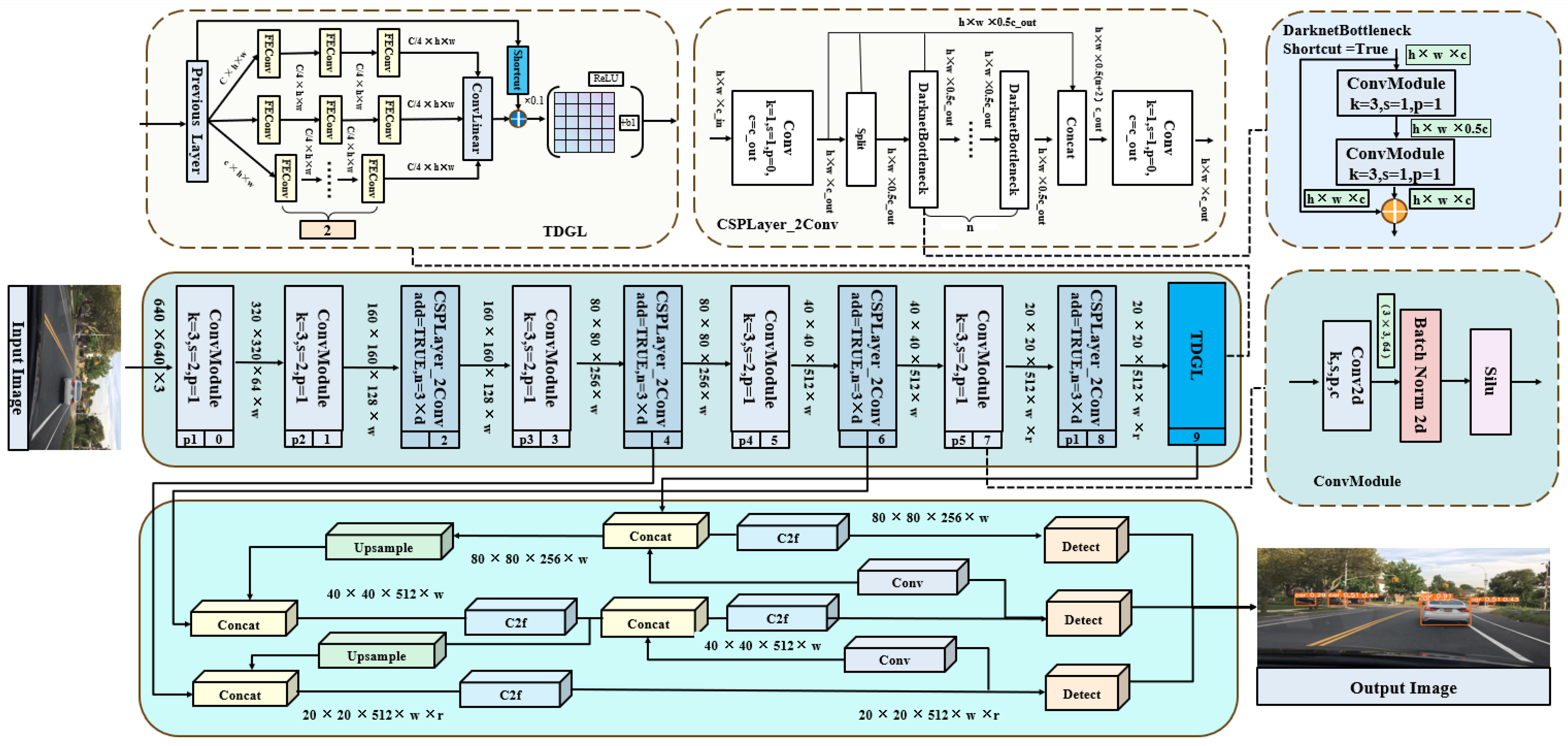
3. Methods
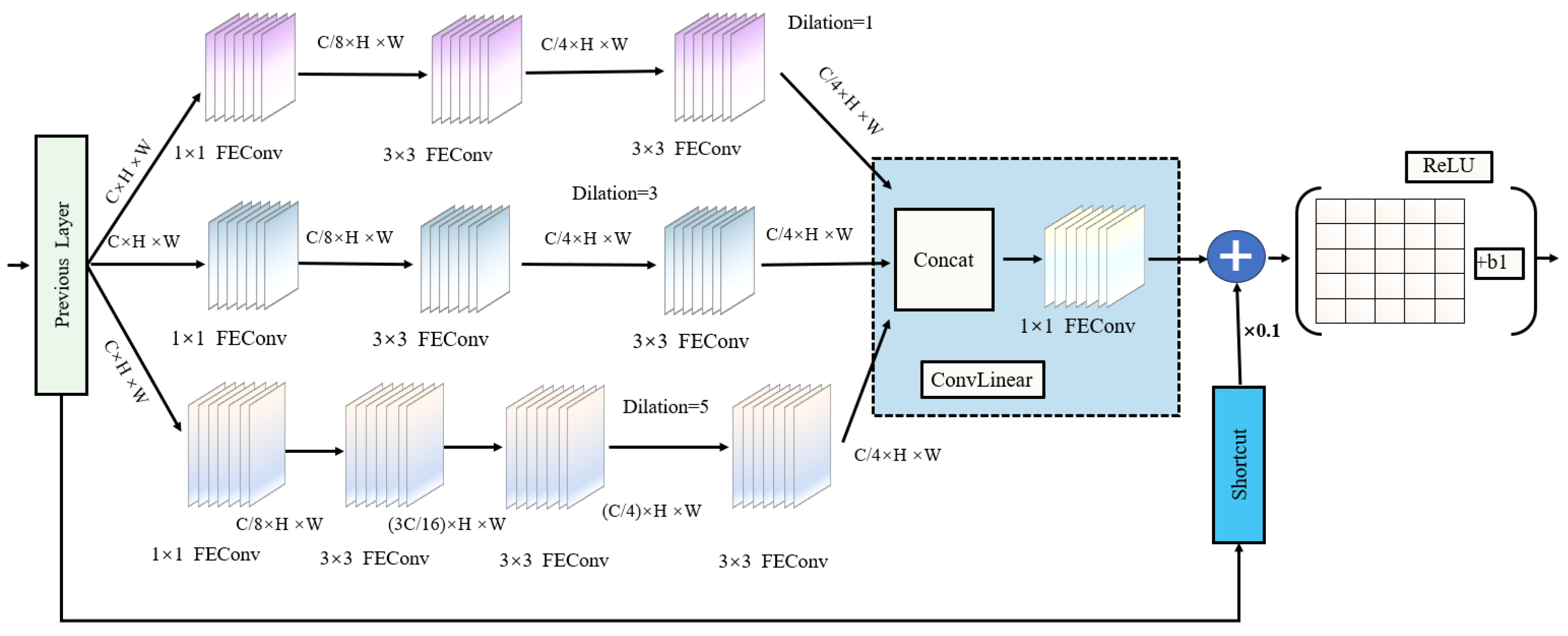
3.1. TDGL Feature Extraction Module
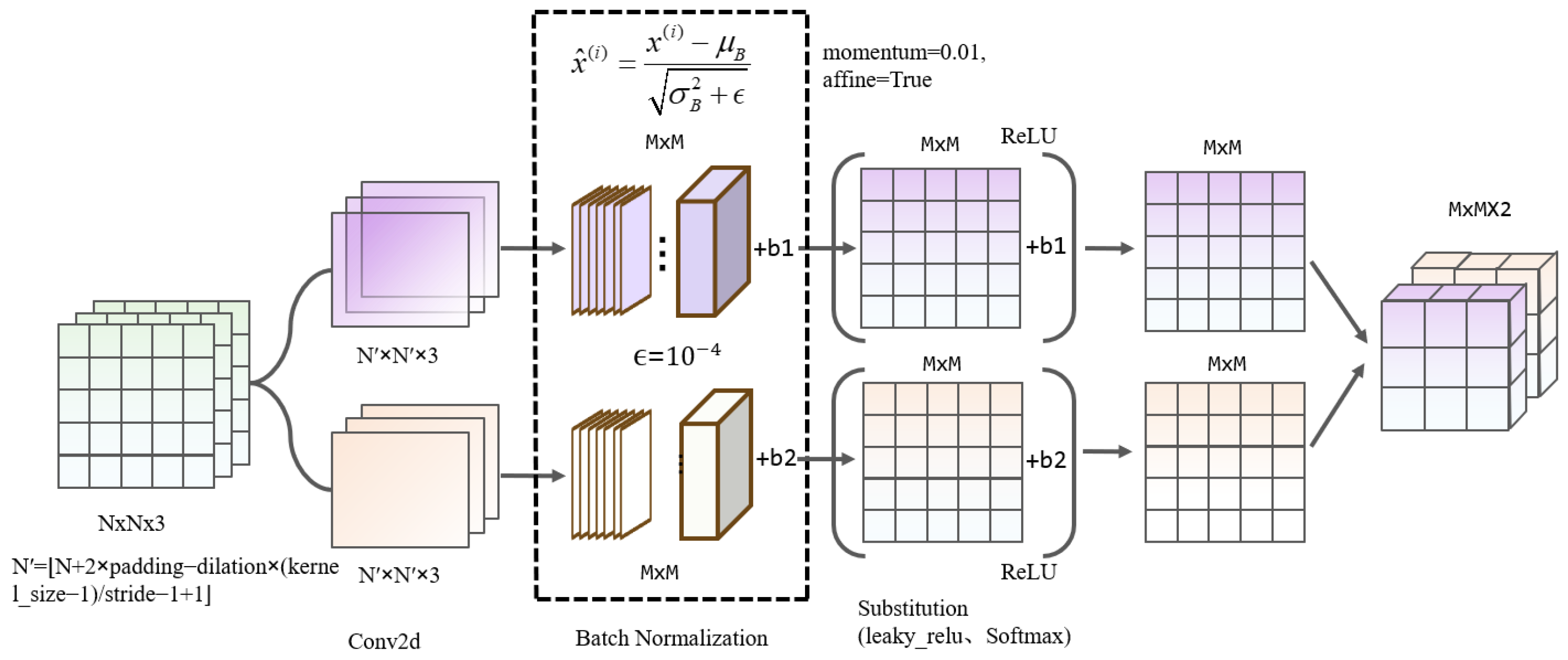
3.2. GL Feature Extraction Convolution
3.3. Training Strategies
4. Experiments
4.1. Training Settings
4.2. Experiments into Replacing Backbone
4.3. Experiments Comparing Our Approach to SOTA Methods
4.4. Ablation Experiments
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhan, J.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, K.; Shi, Z.; Zhuo, C. Fast multi-lane detection based on cnn differentiation for adas/ad. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 15290–15300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Zhong, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. Multi-point rcnn for predicting deformation in deep excavation pit surrounding soil mass. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 124808–124818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duth, S.; Vedavathi, S.; Roshan, S. Herbal leaf classification using rcnn, fast rcnn, faster rcnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2023 7th International Conference on Computing, Communication, Control and Automation (ICCUBEA), Pune, India, 18–19 August 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Xian, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, F.; Liao, M.; Madhavan, V.; Darrell, T. Bdd100k: A diverse driving video database with scalable annotation tooling. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.04687. [Google Scholar]
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The pascal visual object classes (voc) challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 88, 303–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part V 13. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Jiang, H.; Chang, L.; Zheng, C. Based on attention mechanism and characteristics of the polymerization of the lane line detection. J. Microelectron. Comput. 2022, 39, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaiarasan, S.; Ravi, R.; Maheswari, D.; Rubavathi, C.Y.; Ramnath, M.; Hemamalini, V. Towards enhanced deep cnn for early and precise skin cancer diagnosis. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2023 International Conference on Networking and Communications (ICNWC), Chennai, India, 5–6 April 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.; Tong, M. Autopilot based on a semi-supervised learning situations of target detection. J. Microelectron. Comput. 2023, 40, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Xu, X.; Liang, A.; Yun, Y.; Li, L.; Hao, F.; Bai, J.; Ma, D. Research on a Lightweight Method for Maize Seed Quality Detection Based on Improved YOLOv8. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 32927–32937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D. Receptive field block net for accurate and fast object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 385–400. [Google Scholar]
- Awais, M.; Iqbal, M.T.B.; Bae, S.H. Revisiting internal covariate shift for batch normalization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 5082–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.Y.; Lee, M.C.; Yang, C.H.; Lee, T.S. Yolo-ore: A deep learning-aided object recognition approach for radar systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 5715–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected crfs. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.7062. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Yu, Y. An internal covariate shift bounding algorithm for deep neural networks by unitizing layers’ outputs. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 8465–8473. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, J. Energy saving based on transformer models with leakyrelu activation function. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2023 13th International Conference on Information Science and Technology (ICIST), Cairo, Egypt, 8–14 December 2023; pp. 623–631. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, J.; Song, W.; Song, C. Research on improved activation function trelu. mall Microcomput. Syst. 2019, 40, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- El Mellouki, O.; Khedher, M.I.; El-Yacoubi, M.A. Abstract layer for leakyrelu for neural network verification based on abstract interpretation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 33401–33413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B. Image classification and detection of cigarette combustion cone based on inception resnet v2. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2020 5th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems (ICCCS), Shanghai, China, 15–18 May 2020; pp. 395–399. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Chi, C.; Yao, Y.; Lei, Z.; Li, S.Z. Bridging the gap between anchor-based and anchor-free detection via adaptive training sample selection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9759–9768. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, B.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zong, F.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. Autoassign: Differentiable label assignment for dense object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.03496. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, D.; Krähenbühl, P. Objects as points. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.07850. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Ye, R.; Wang, P.; Ren, D.; Zuo, W.; Hou, Q.; Cheng, M.M. Localization distillation for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 9407–9416. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, R.; Wang, S.; Yan, D.; Peng, B.; Zhang, T. Video face detection based on improved ssd model and target tracking algorithm. J. Web Eng. 2022, 21, 545–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Tian, T.; Zhao, T.; Li, L.; Zhang, N.; Tian, J. Double fcos: A two-stage model utilizing fcos for vehicle detection in various remote sensing scenes. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 4730–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
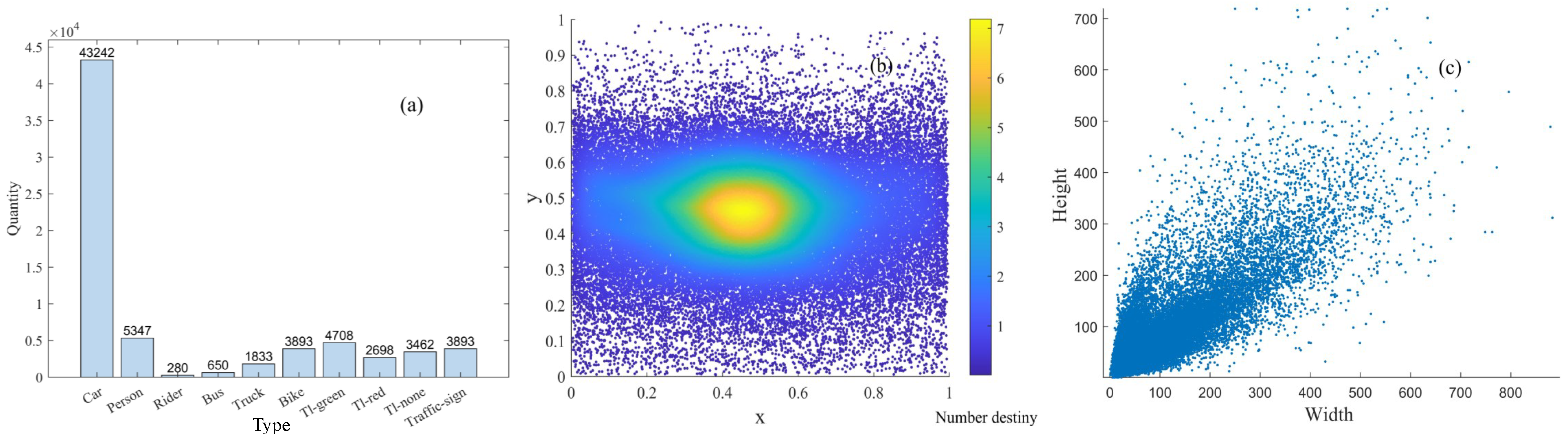
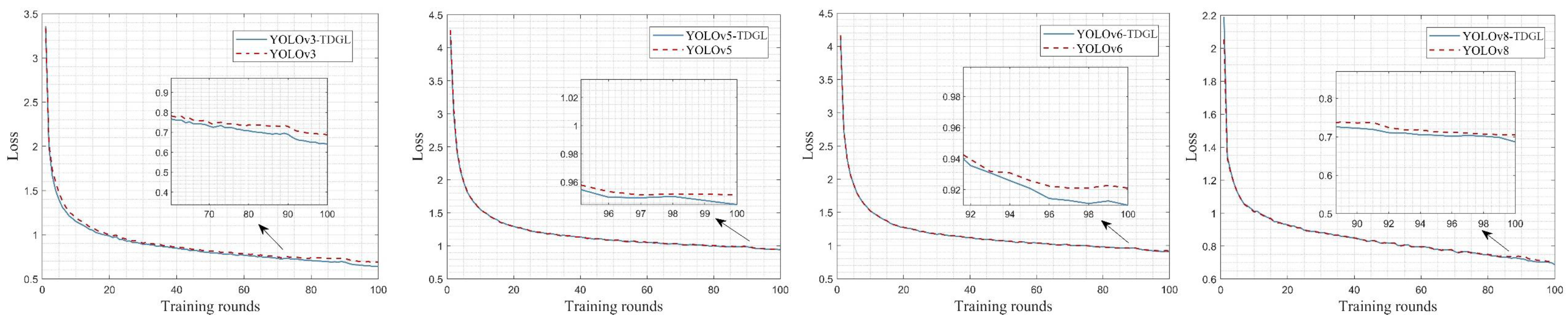

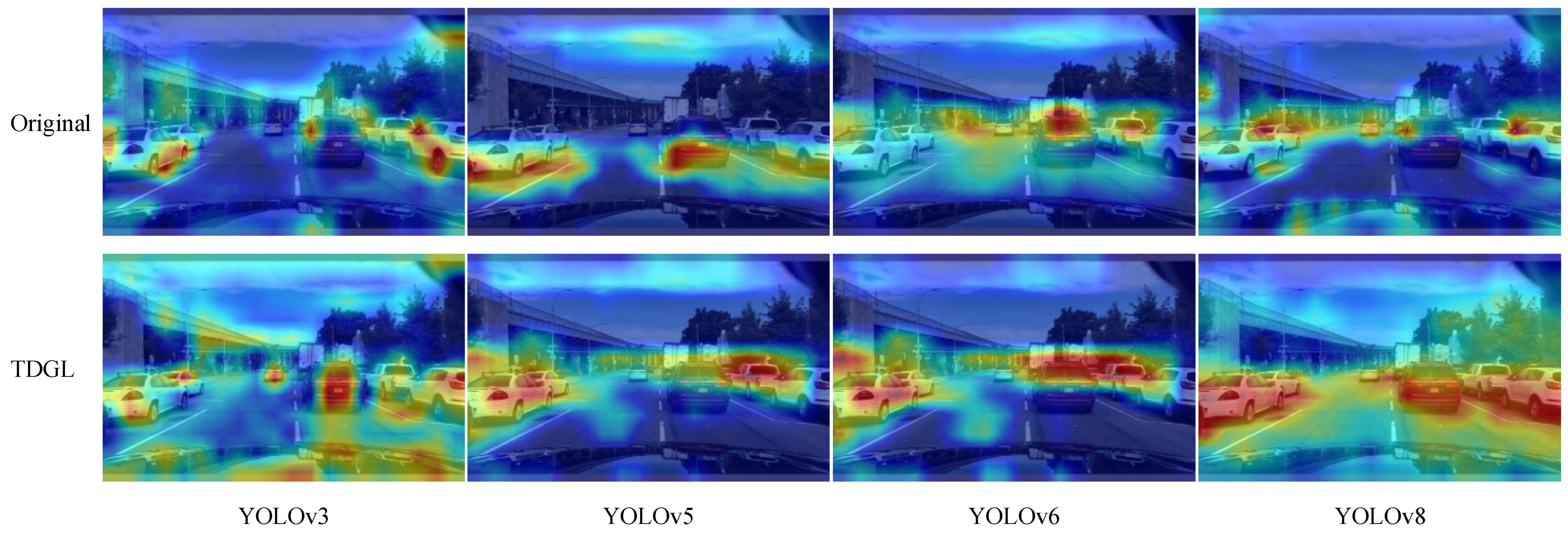
| Hyperparameter | Values |
|---|---|
| epochs | 100 |
| optimizer | Auto |
| optimizer weight decay | 0.0005 |
| initial learning rate | 0.01 |
| final learning rate | 0.01 |
| imgsz | 640 |
| box loss gain | 7.5 |
| cls loss gain | 0.5 |
| dfl loss gain | 1.5 |
| warmup-epochs | 3.0 |
| warmup-momentum | 0.8 |
| warmup-bias-lr | 0.10 |
| mosaic augmentation | 10 |
| image HSV—saturation augmentation | 0.7 |
| image HSV—value augmentation | 0.4 |
| image HSV—hue augmentation | 0.015 |
| number of images per batch | 16 |
| Methods | Conv | #Param | FLOPs | Precision/% | Recall/% | mAP@0.5/% | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv3-tiny | — | 12.1M | 18.9G | 38.7 | 21.3 | 19.7 | 61 |
| YOLOv3-TDGL | GLConv | 9.7M | 18.2G | 44.2 | 21.9 | 21.0 | 55 |
| YOLOv5 | — | 2.5M | 7.1G | 36.6 | 27.3 | 25.7 | 50 |
| YOLOv5-TDGL | GLConv | 2.6M | 7.2G | 42.3 | 27.6 | 26.6 | 43 |
| YOLOv6 | — | 4.2M | 11.8G | 39.7 | 26.2 | 25.1 | 64 |
| YOLOv6-TDGL | Conv + BN | 4.3M | 11.9G | 38.6 | 25.0 | 24.8 | 54 |
| YOLOv6-TDGL | GLConv | 4.4M | 11.9G | 39.3 | 26.3 | 26.6 | 53 |
| YOLOv8 | — | 3.0M | 8.1G | 55.5 | 35.5 | 39.0 | 65 |
| Faster-RCNN [4] | — | 37.3M | 92.8G | 26.4 | 33.4 | 26.8 | 27 |
| YOLOv8-TDGL | Conv + BN | 3.0M | 8.1G | 55.1 | 34.3 | 38.5 | 57 |
| YOLOv8-TDGL | GLConv | 3.1M | 8.2G | 55.9 | 37.3 | 40.3 | 58 |
| Methods | Backbone | #Param | FLOPs | Precision/% | Recall/% | mAP@0.5/% | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATSS [23] | ResNet-50 | 30.7M | 92.1G | 24.6 | 35.4 | 22.9 | 34 |
| AutoAssign [24] | ResNet-50 | 31.4M | 95.2G | 28.3 | 34.8 | 27.0 | 33 |
| YOLOv3-tiny | Tiny-Darknet | 12.1M | 18.9G | 38.7 | 21.3 | 19.7 | 61 |
| Faster-RCNN [4] | ResNet-50 | 37.3M | 92.8G | 26.4 | 33.4 | 26.8 | 27 |
| CenterNet [25] | ResNet-50 | 25.8M | 45.6G | 29.9 | 37.4 | 29.0 | 32 |
| Localization Distillation [26] | ResNet-18 | 10.1M | 18.2G | 22.6 | 30.4 | 20.7 | 38 |
| YOLOv5 | CSPDarknet | 2.5M | 7.1G | 36.6 | 27.3 | 25.7 | 50 |
| SSD300 [27] | VGG | 21.6M | 31.2G | 24.3 | 31.9 | 18.6 | 45 |
| FCOS [28] | ResNet-50 | 27.2M | 38.9G | 27.1 | 39.7 | 25.6 | 36 |
| Generalized Focal Loss | ResNet-50 | 23.8M | 25.8G | 27.0 | 34.3 | 25.3 | 29 |
| RetinaNet | ResNet-18 | 12.2M | 16.8G | 24.6 | 33.7 | 22.7 | 40 |
| Ours | CSPDarknet | 3.1M | 8.2G | 55.9 | 37.3 | 40.3 | 58 |
| Groups | Expansion Rate | Relu | Softmax | L_relu | Depth | Channel | Precision/% | Recall/% | mAP@0.95/% | mAP@0.5/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | — | — | — | — | 3\3\4 | 4 | 55.5 | 35.5 | 19.3 | 39.0 |
| 2 | 1\4\6 | — | √ | — | 3\3\4 | 4 | 51.1 | 38.1 | 19.4 | 39.8 |
| 3 | 1\4\6 | — | — | √ | 3\3\4 | 4 | 57.3 | 36.3 | 19.6 | 39.9 |
| 4 | 1\4\6 | √ | — | — | 3\3\4 | 4 | 51.7 | 37.6 | 19.9 | 39.4 |
| 5 | 1\2\4 | √ | — | — | 3\3\4 | 4 | 55.7 | 35.5 | 19.1 | 38.9 |
| 6 | 1\2\4 | — | √ | — | 3\3\4 | 4 | 56.3 | 36.7 | 19.3 | 39.4 |
| 7 | 1\2\4 | — | — | √ | 3\3\4 | 4 | 56.2 | 37.5 | 19.3 | 39.8 |
| 8 | 1\3\5 | √ | — | — | 3\3\4 | 4 | 53.7 | 37.2 | 19.2 | 39.3 |
| 9 | 1\3\5 | — | √ | — | 3\3\4 | 4 | 54.2 | 37.2 | 19.0 | 39.1 |
| 10 | 1\4\6 | — | √ | — | 4\4\5 | 8 | 54.9 | 35.3 | 18.7 | 38.2 |
| 11 | 1\2\4 | — | — | √ | 4\4\5 | 8 | 53.3 | 34.4 | 18.2 | 37.3 |
| 12 | 1\2\4 | — | — | √ | 4\4\5 | 16 | 54.9 | 35.3 | 18.9 | 39.4 |
| 13 | 1\3\5 | — | √ | — | 3\3\4 | 16 | 50.5 | 31.3 | 17.9 | 35.8 |
| 14 | 1\3\5 | √ | — | — | 4\4\5 | 8 | 56.2 | 37.1 | 19.2 | 40.0 |
| 15 | 1\3\5 | — | — | √ | 3\3\4 | 4 | 55.9 | 37.3 | 19.7 | 40.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, L.; Zhu, F.; Wang, Z. The TDGL Module: A Fast Multi-Scale Vision Sensor Based on a Transformation Dilated Grouped Layer. Sensors 2025, 25, 3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113339
Xie L, Zhu F, Wang Z. The TDGL Module: A Fast Multi-Scale Vision Sensor Based on a Transformation Dilated Grouped Layer. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113339
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Leilei, Fenghua Zhu, and Zhixue Wang. 2025. "The TDGL Module: A Fast Multi-Scale Vision Sensor Based on a Transformation Dilated Grouped Layer" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113339
APA StyleXie, L., Zhu, F., & Wang, Z. (2025). The TDGL Module: A Fast Multi-Scale Vision Sensor Based on a Transformation Dilated Grouped Layer. Sensors, 25(11), 3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113339








