Simulative Analysis of Stimulated Raman Scattering Effects on WDM-PON Based 5G Fronthaul Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis of SRS Non-Linearity Impairment
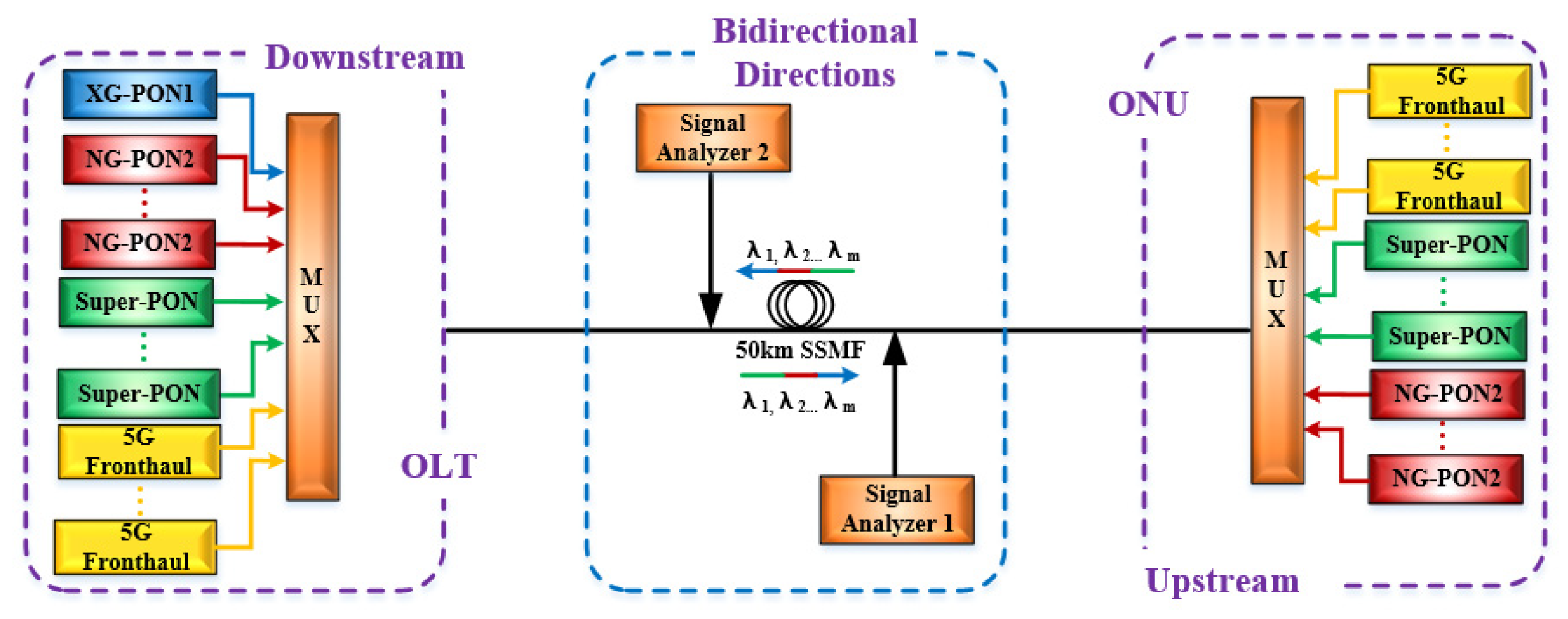
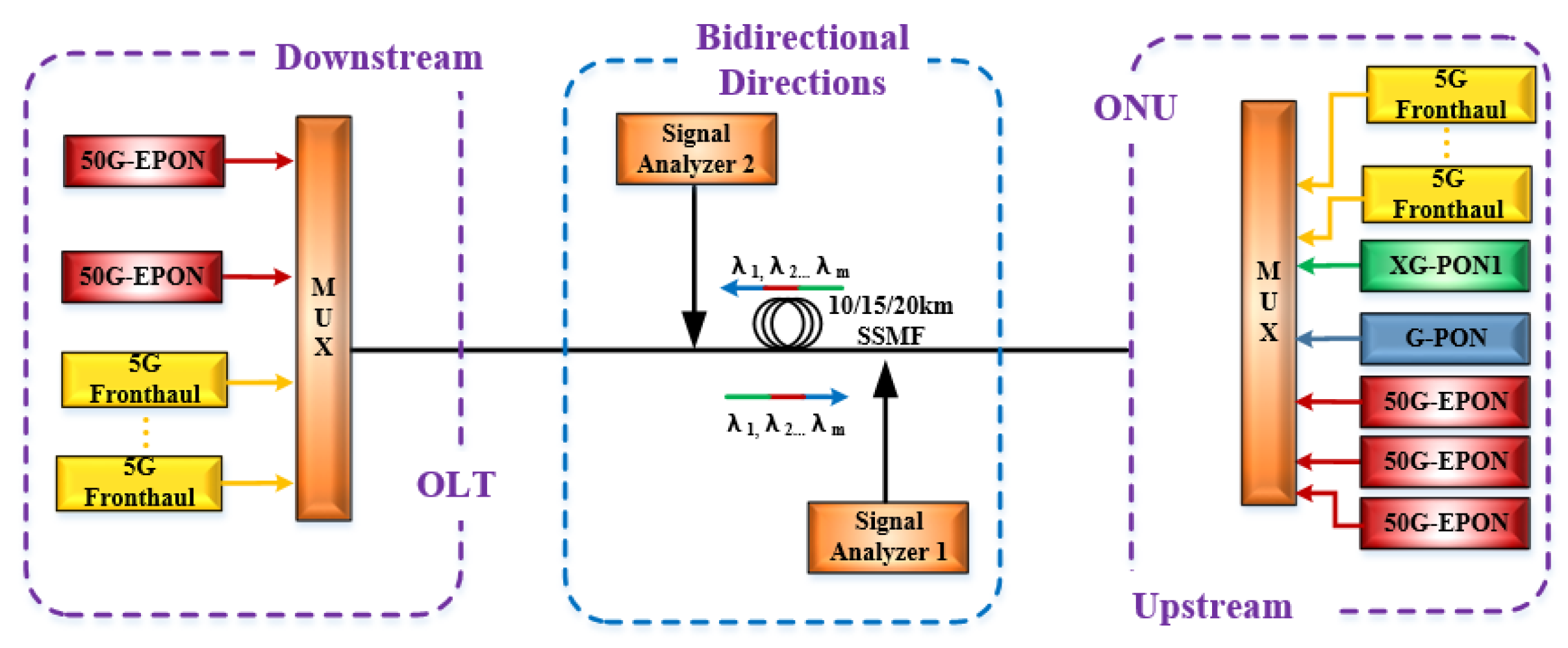
3. Simulation Setup
4. Results
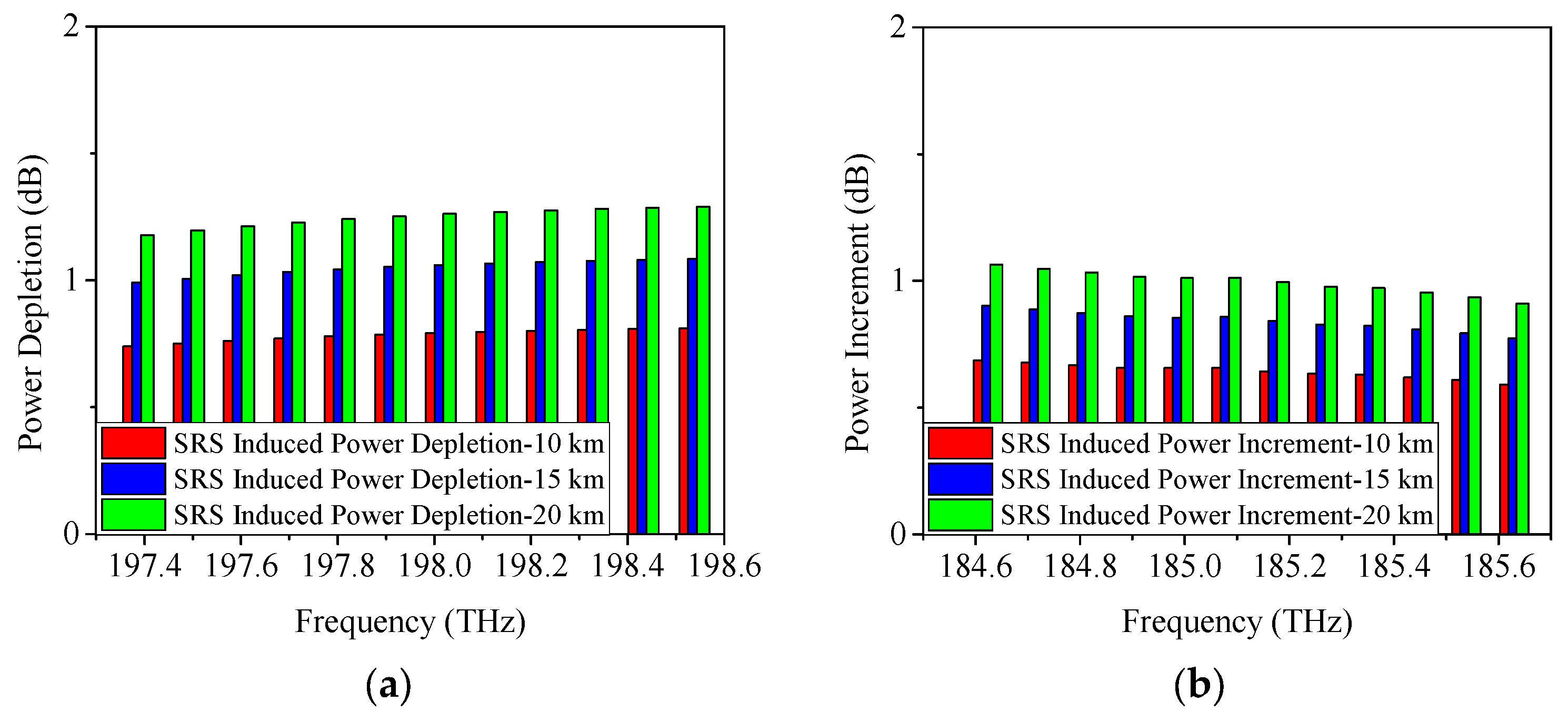
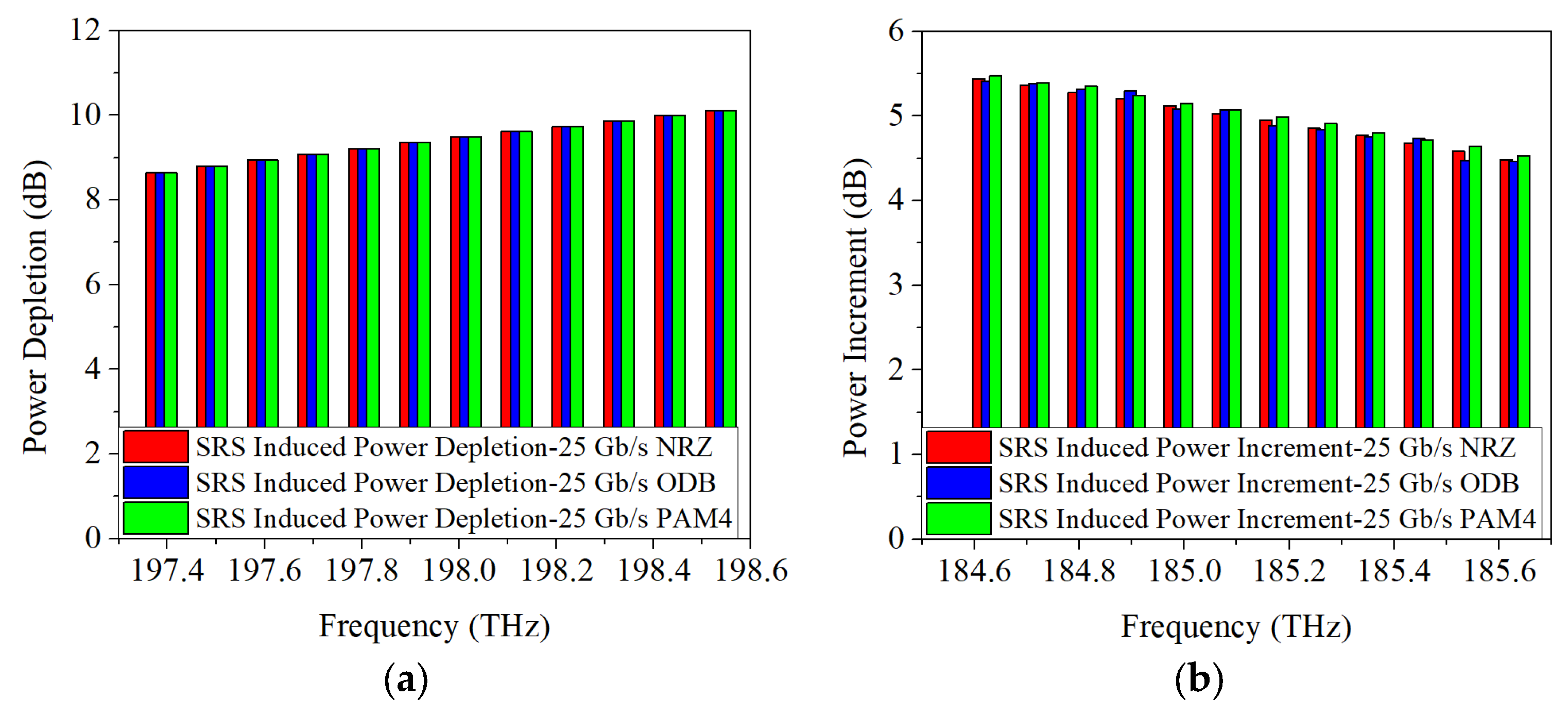
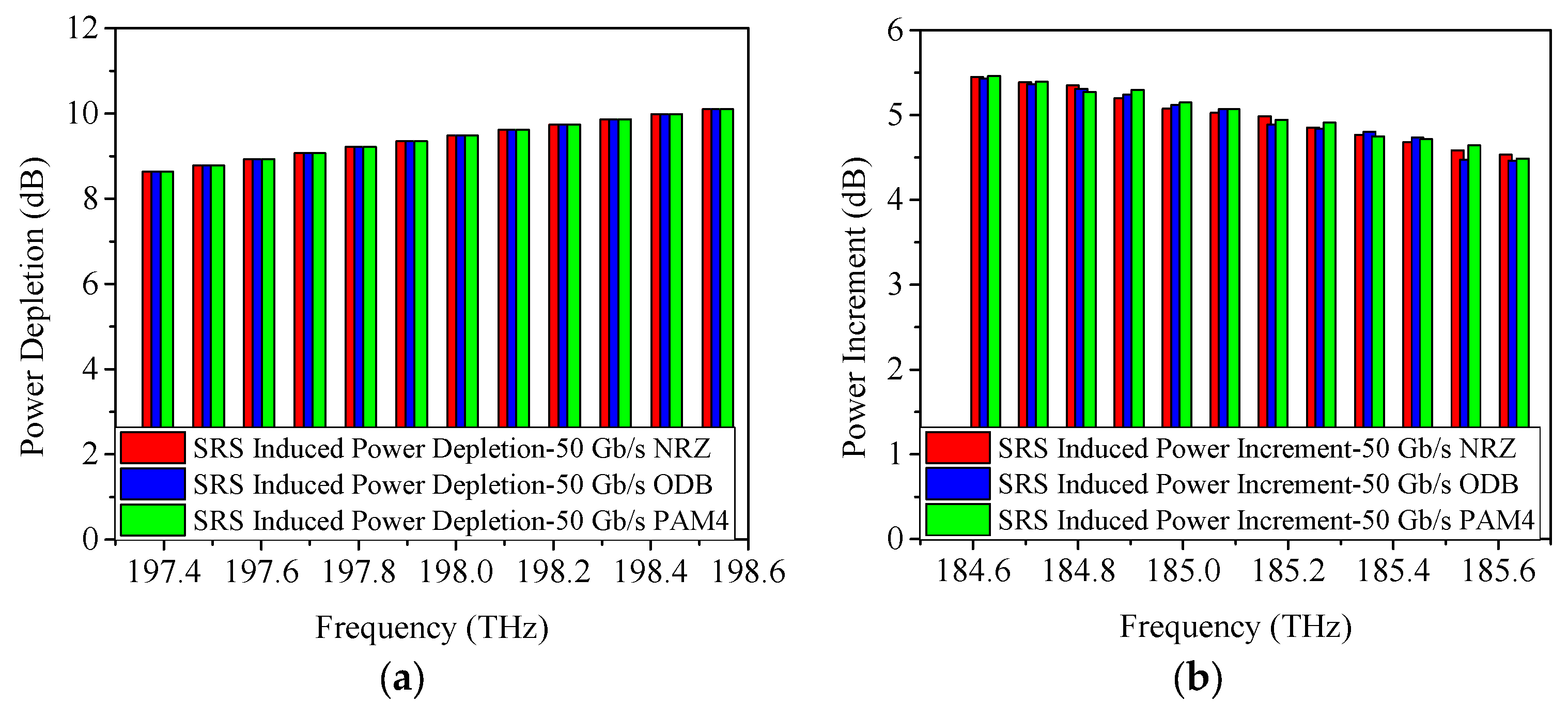
4.1. SRS-Induced Power Changes in C-Band Allocation Scheme
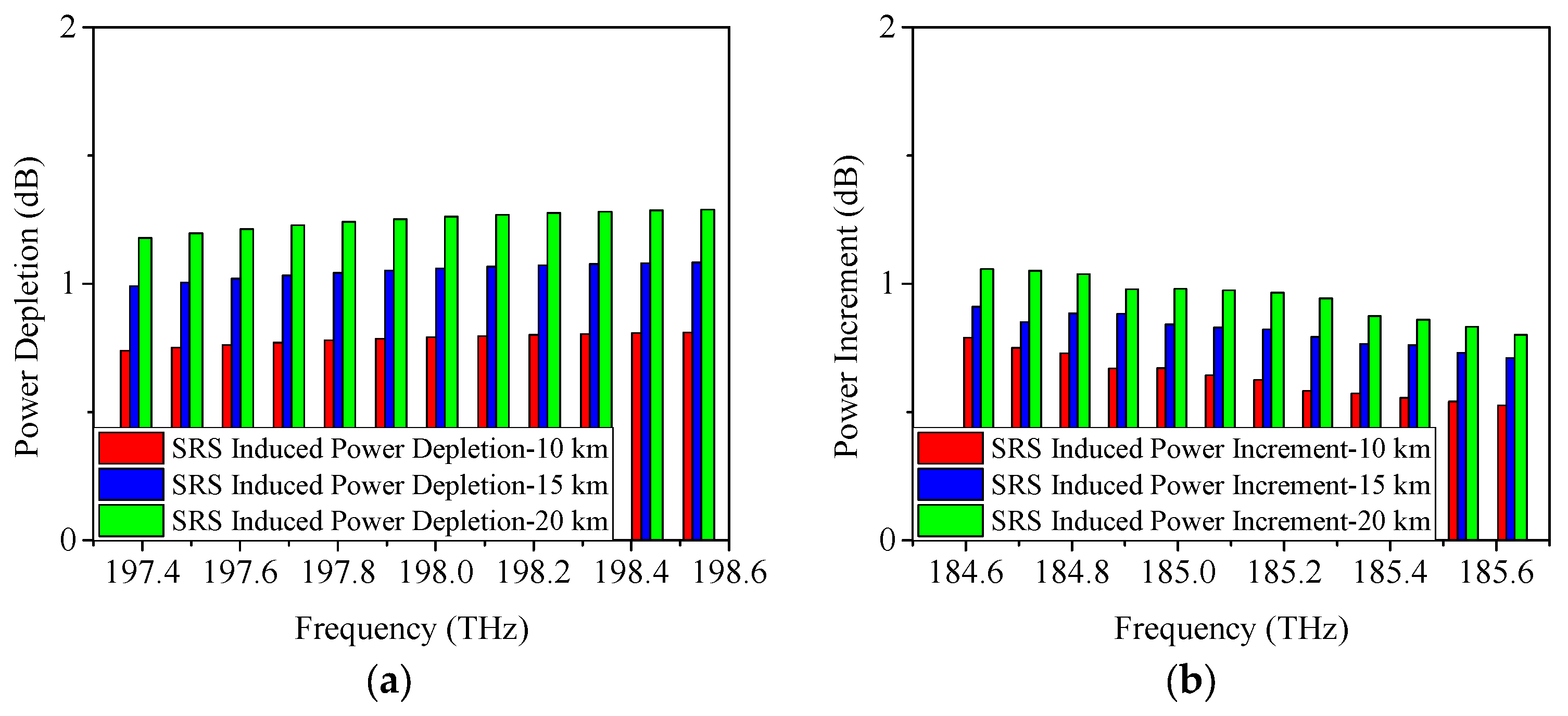
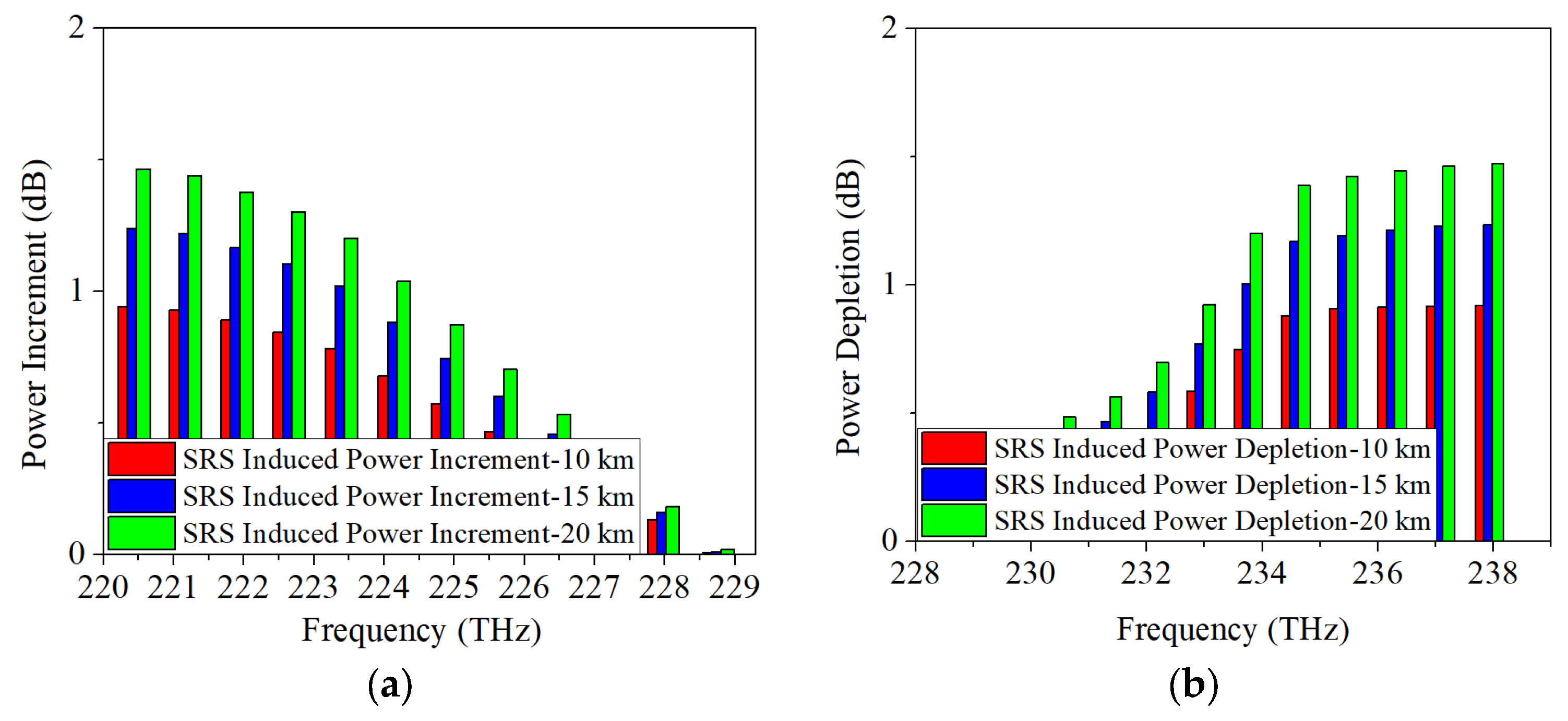
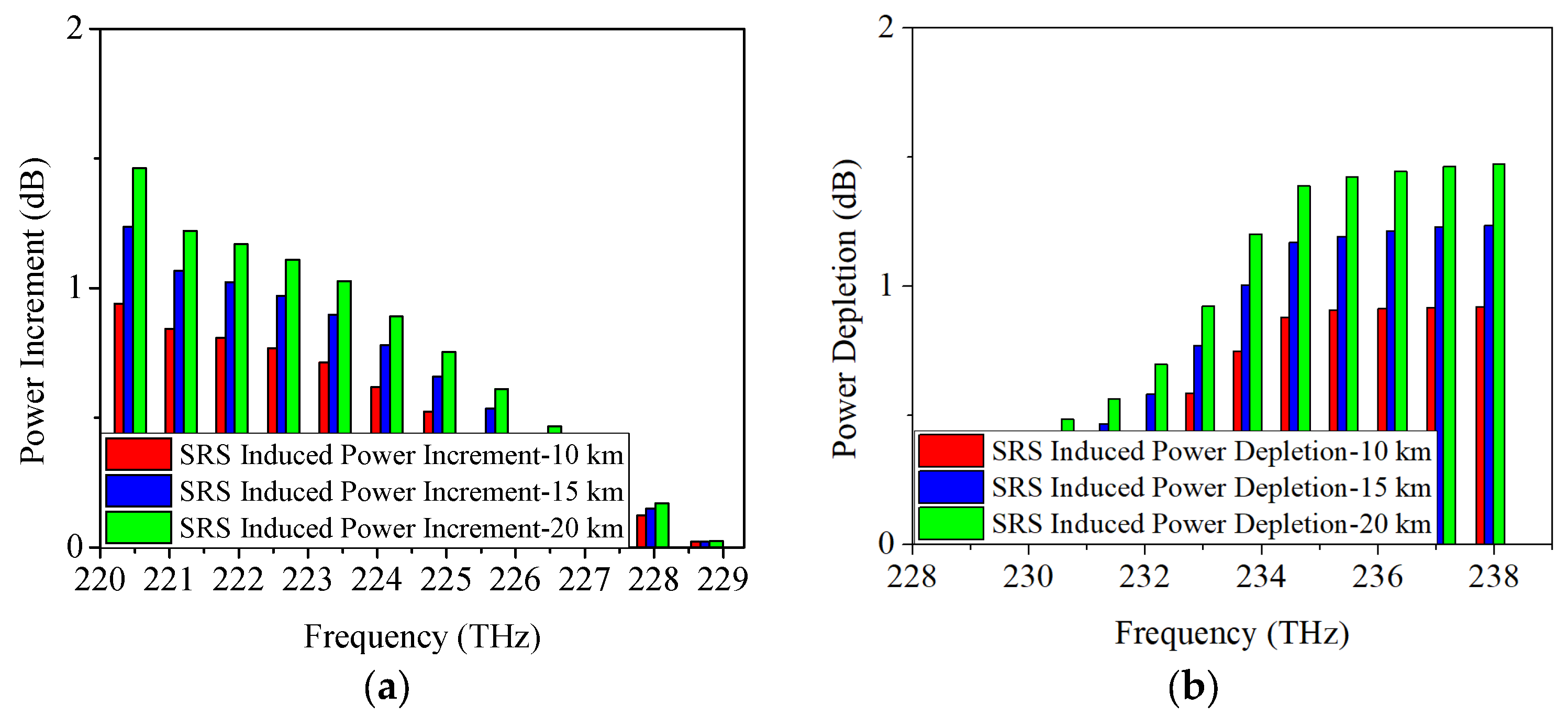
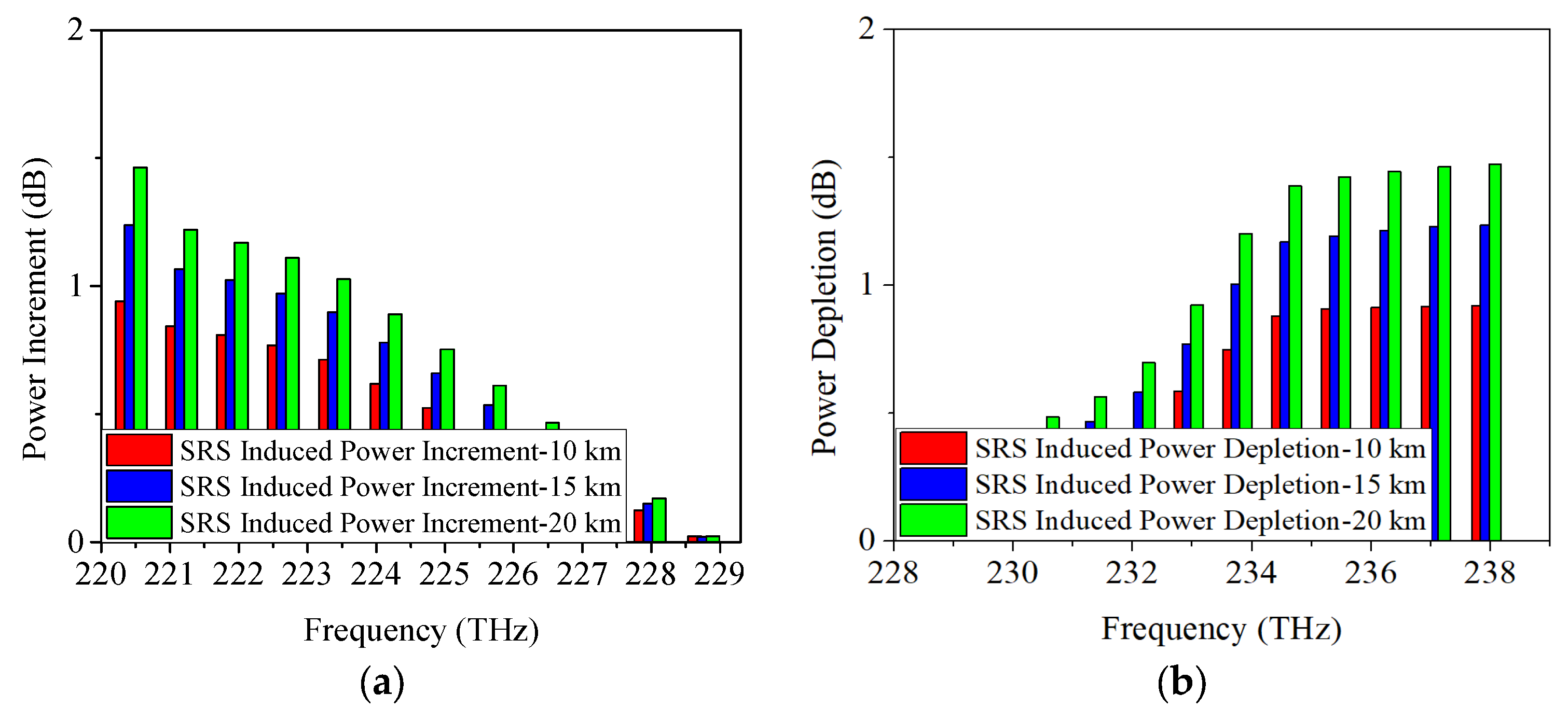
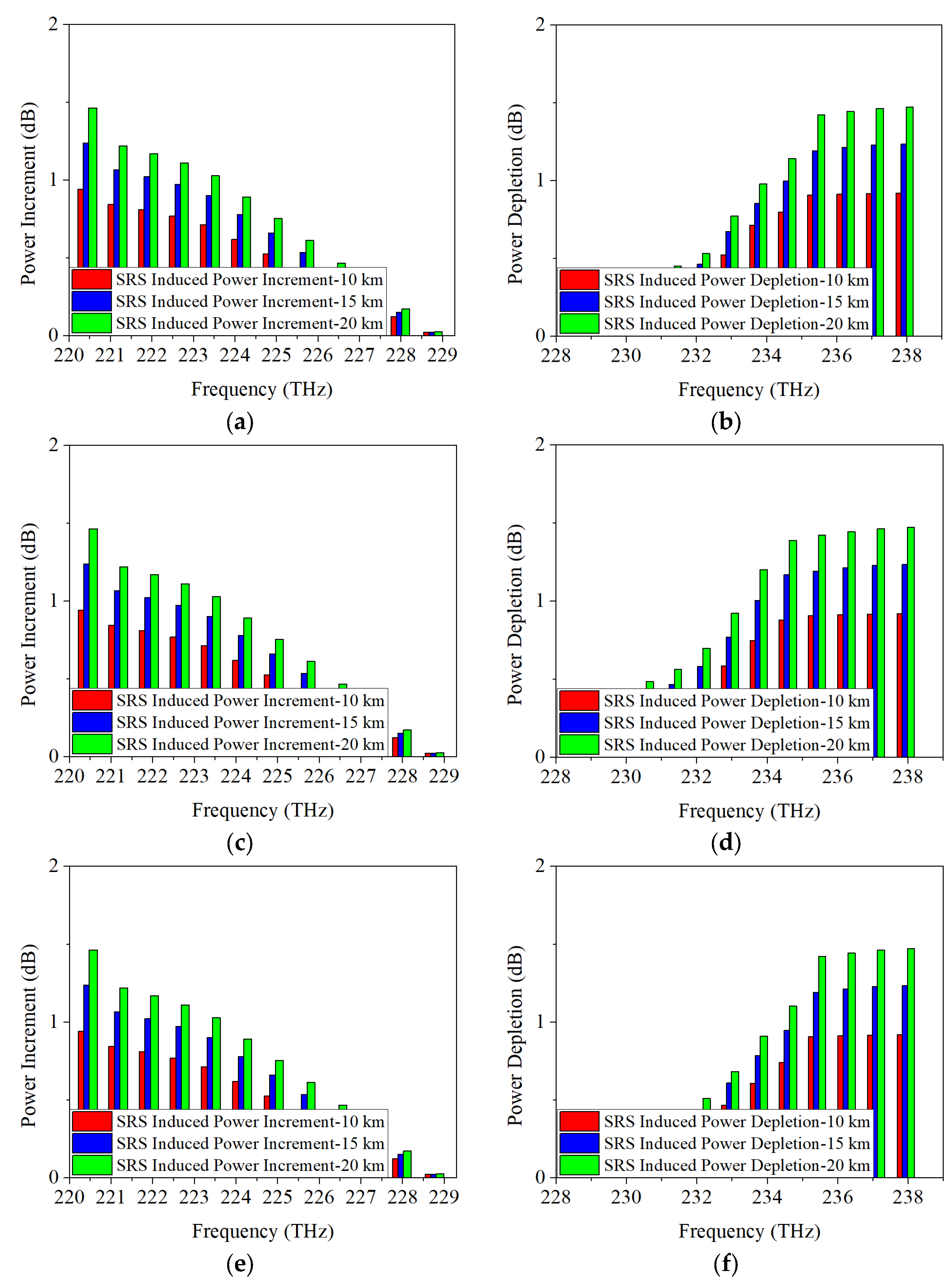
4.2. SRS-Induced Power Changes in O-Band Allocation Scheme
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Lima, C.; Belot, D.; Berkvens, R.; Bourdoux, A.; Dardari, D.; Guillaud, M.; Isomursu, M.; Lohan, E.-S.; Miao, Y.; Barreto, A.N. Convergent communication, sensing and localization in 6G systems: An overview of technologies, opportunities and challenges. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 26902–26925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgios, G.; Dimitrios, J.; Angelos, M.; Michael, D. The advantage of the 5G network for enhancing the Internet of Things and the evolution of the 6G network. Sensors 2024, 24, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H. Global Industry Vision 2025. Available online: https://www.huawei.com/cn/news/2018/4/Huawei-Global-Industry-Vision-2025 (accessed on 17 April 2018).
- Doorgakant, B.; Fowdur, T.P.; Akinsolu, M.O. End-to-End Power Models for 5G Radio Access Network Architectures with a Perspective on 6G. Mathematics 2025, 13, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y. Research on 5G optical transport schemes. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 332, 042015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlQahtani, D.; El-Naha, F. WDM-PON Free Space Optical (FSO) System Utilizing LDPC Decoding for Enhanced Cellular C-RAN Fronthaul Networks. Photonic 2025, 12, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yu, P.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z. Simulation and experimental investigation of nonlinear effects in 5G fronthaul transmission system based on WDM-PON architecture. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2021, 65, 102628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.K.; Garg, A.K. Analysis with gain and power for better coverage of FTTH network using WDM-PON architecture. J. Optics 2023, 756, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, C.; Song, Z.; Du, H.; Liu, Z.; Tang, J.; Meng, Y.; Tang, M. Design and fabrication of 125-μm standard cladding diameter heterogeneous 8-core fiber with ultra-low crosstalk for C-band transmission. J. Light. Technol. 2024, 42, 5681–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houtsma, V.; Borkowski, R.; Mahadevan, A.; van Veen, D. Dispersion-tolerant 100 Gb/s downstream PON With 38 dB power budget and low-complex equalization. J. Light. Technol. 2024, 11, 4096–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudino, R.; Curri, V.; Capriata, S. Propagation impairments due to Raman effect on the coexistence of GPON, XG-PON, RF-video and TWDM-PON. In Proceedings of the 39th European Conference and Exhibition on Optical Communication (ECOC), London, UK, 22–26 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Curri, V.; Capriata, S.; Gaudino, R. Outage probability due to stimulated Raman scattering in GPON and TWDM-PON coexistence. In Proceedings of the 2014 Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exhibition (OFC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–13 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; He, H.; Hu, W. Power depletion and crosstalk induced by stimulated Raman scattering in WDM fronthaul. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2016, 28, 1069–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, H.; Hu, W. Theoretical and experimental analysis of Interchannel crosstalk between TWDM and fronthaul wavelengths due to stimulated Raman scattering. OPT. Express 2015, 23, 8809–8817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, P.; Ye, N.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Y. Simulation investigation of XPM and SRS effect on upgraded Super-PON systems. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2021, 67, 102121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Saleem, A. Investigation of stimulated Raman scattering effect on designing of NG-EPON systems. Opt. Eng. 2021, 60, 126101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximidis, R.; Vagionas, C.; Kalfas, G.; Leiba, Y.; Miliou, A.; Pleros, N. A 51 Gb/s reconfigurable mmWave fiber-wireless C-RAN supporting 5G/6G MNO network sharing. J. Light. Technol. 2023, 41, 4705–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayad, A.; Cinkler, T.; Rak, J. Toward 6G optical fronthaul: A survey on enabling technologies and research perspectives. J. Light. Technol. 2025, 27, 629–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kaur, G.; Islam, M.T.; Kaler, R.S. Broadband Connectivity in 5G and Beyond: Next Generation Networks; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, W.; Alexander, L.; Giese, E. Nonlinear Optics, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.R. Principles of Nonlinear Optics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, G.P. Nonlinear Fiber Optics, 5th ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, R.; Wang, Y.; Demarest, K.; Allen, C. Frequency response of cross-phase modulation in multispan WDM optical fiber systems. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 1998, 10, 1271–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulides, D.N.; Jander, R.B. Evolution of stimulated Raman crosstalk in wavelength division multiplexed systems. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 1996, 8, 1722–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSanti, C.; Du, L.; Guarin, J.; Bone, J.; Lam, C.F. Super-PON: An evolution for access networks. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2020, 12, D66–D77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, J.; Bidkar, S.; Straub, M.; Thomas, P.; Bonk, R. Efficient transport of eCPRI fronthaul over PON. In Proceedings of the 2023 Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exhibition (OFC), San Diego, CA, USA, 5–9 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Seki, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kanno, A.; Tetsuya, K.; Izutsu, M.; Nakajima, H. Suppression of third-order harmonics in two-tone signals using cascaded Mach-Zehnder modulators. In Proceedings of the Microwave Photonics (MWP) and the 2014 9th Asia-Pacific Microwave Photonics Conference (APMP) 2014 International Topical Meeting, Sapporo, Japan, 20–23 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Hu, W. Optical access networks for fixed and mobile applications [Invited Tutorial]. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2024, 16, A118–A135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Zheng, J.; Dong, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, L.; Zeng, H.; Luo, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, X. Improved dispersion tolerance for 50G-PON downstream transmission via receiver-side equalization. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference 2019, San Diego, CA, USA, 3–7 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Houtsma, V.; Veen, D. Higher-speed PONs based on data center technology and optics [Invited]. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2024, 16, A98–A104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
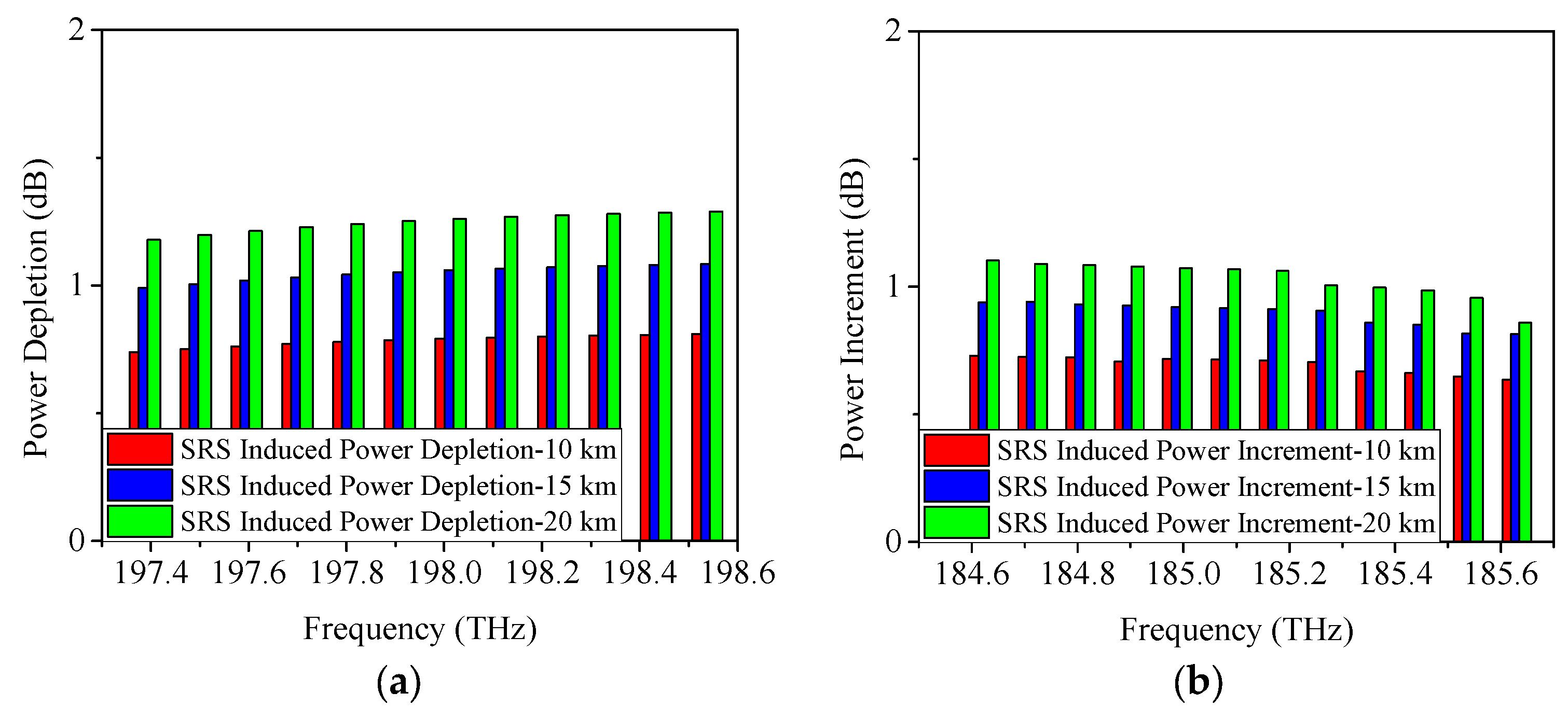
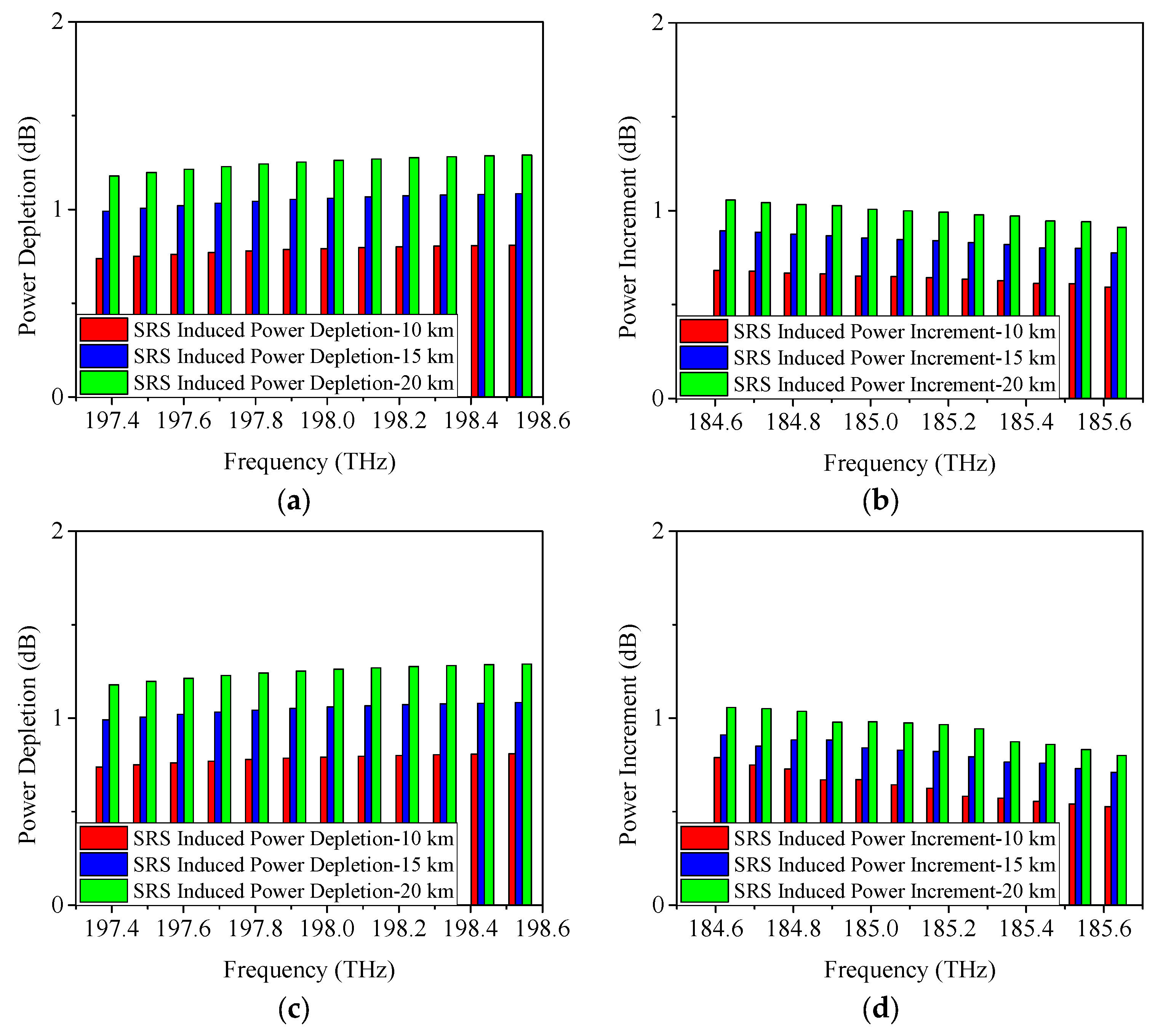
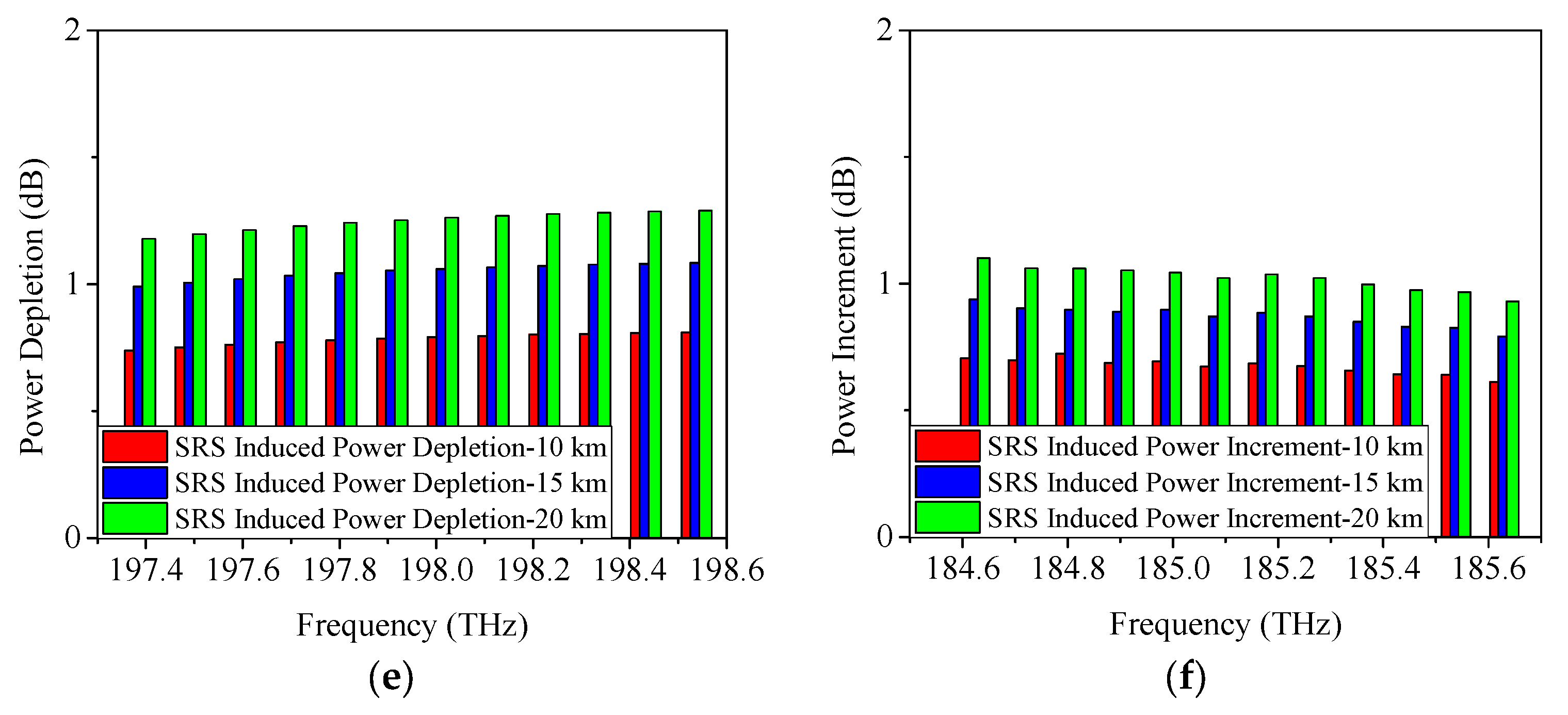
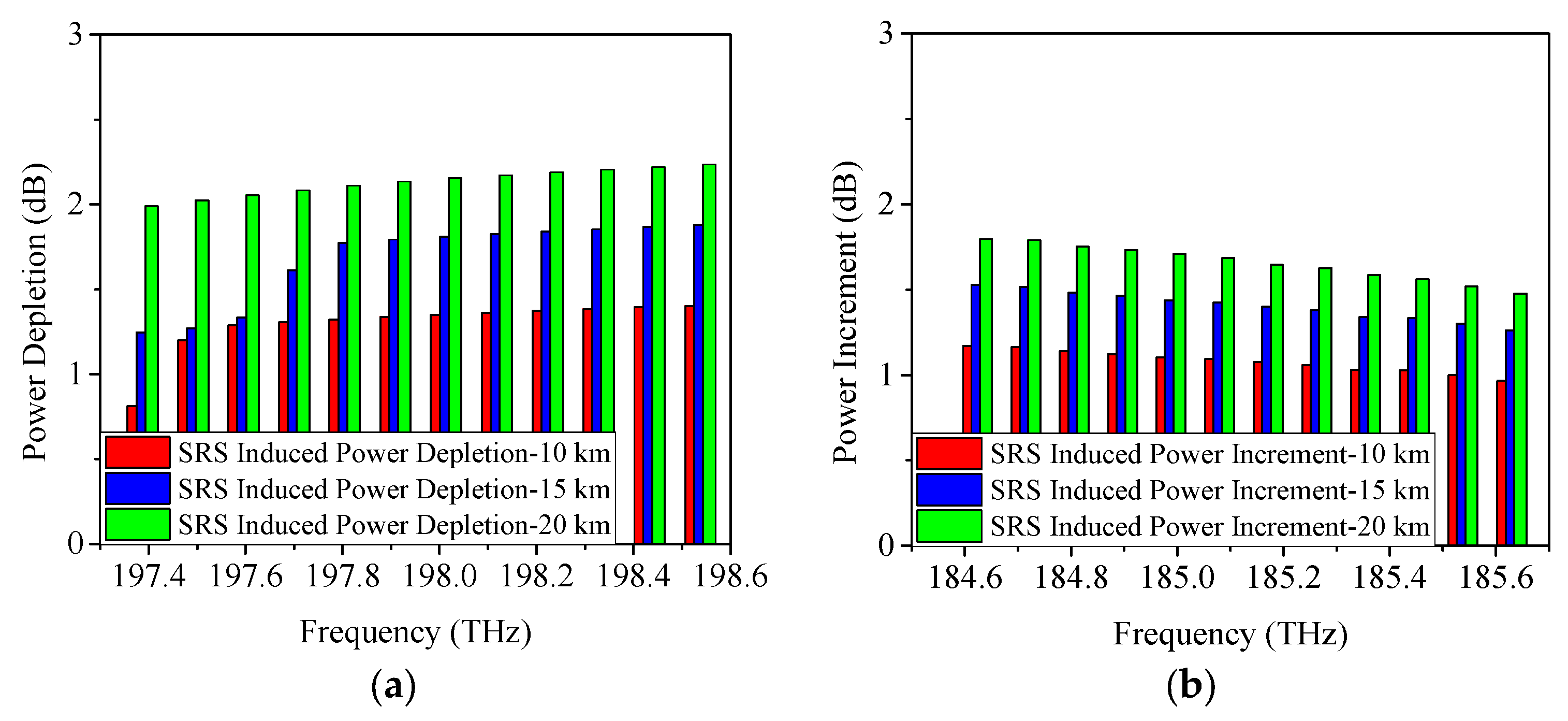
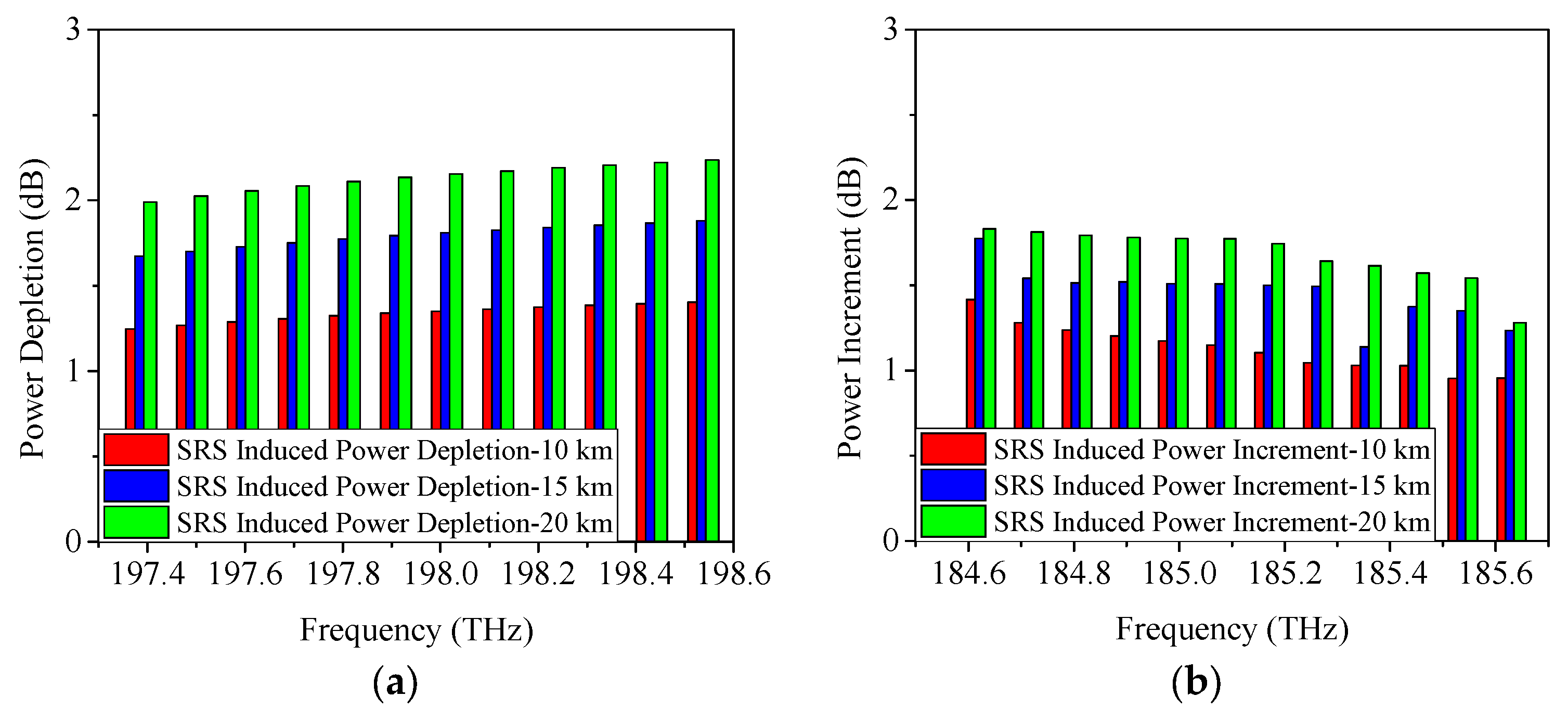
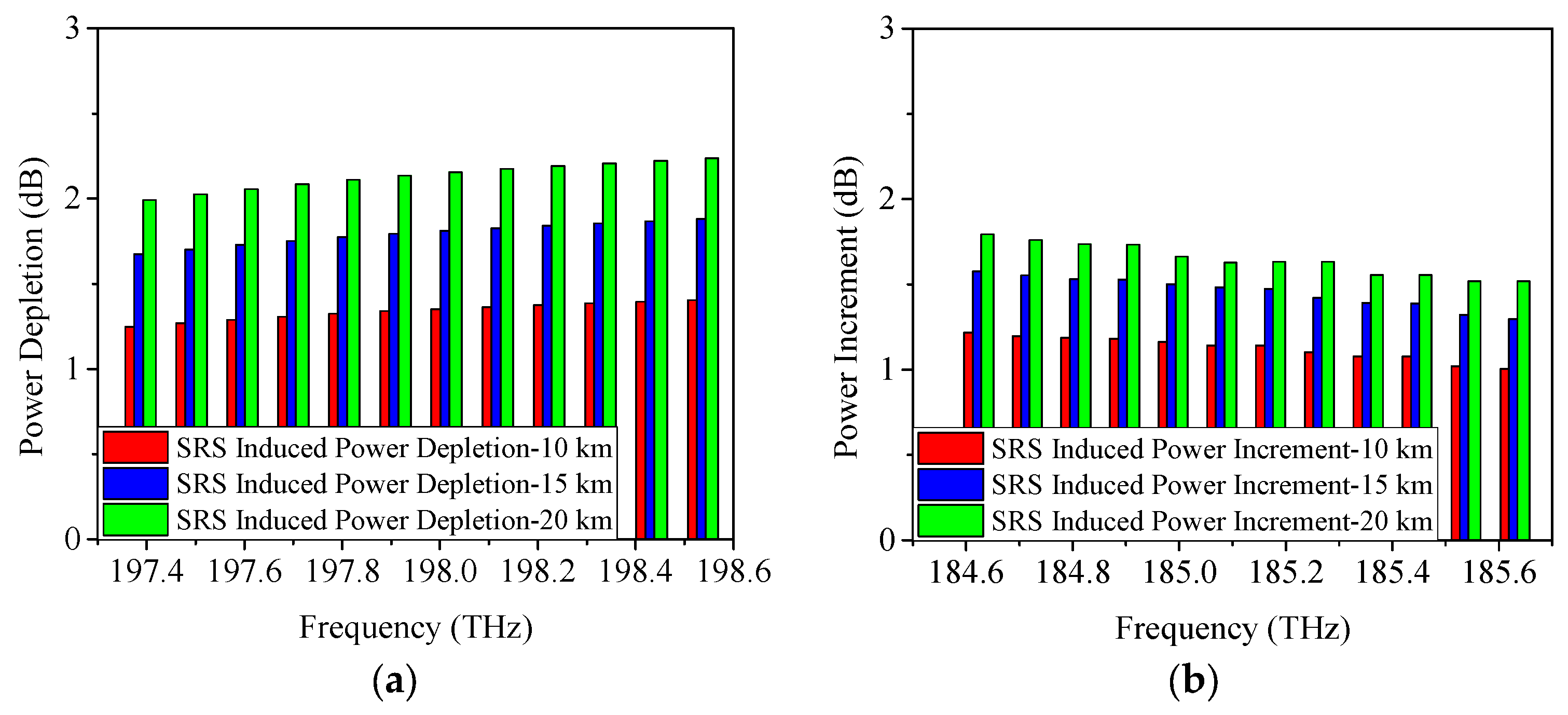
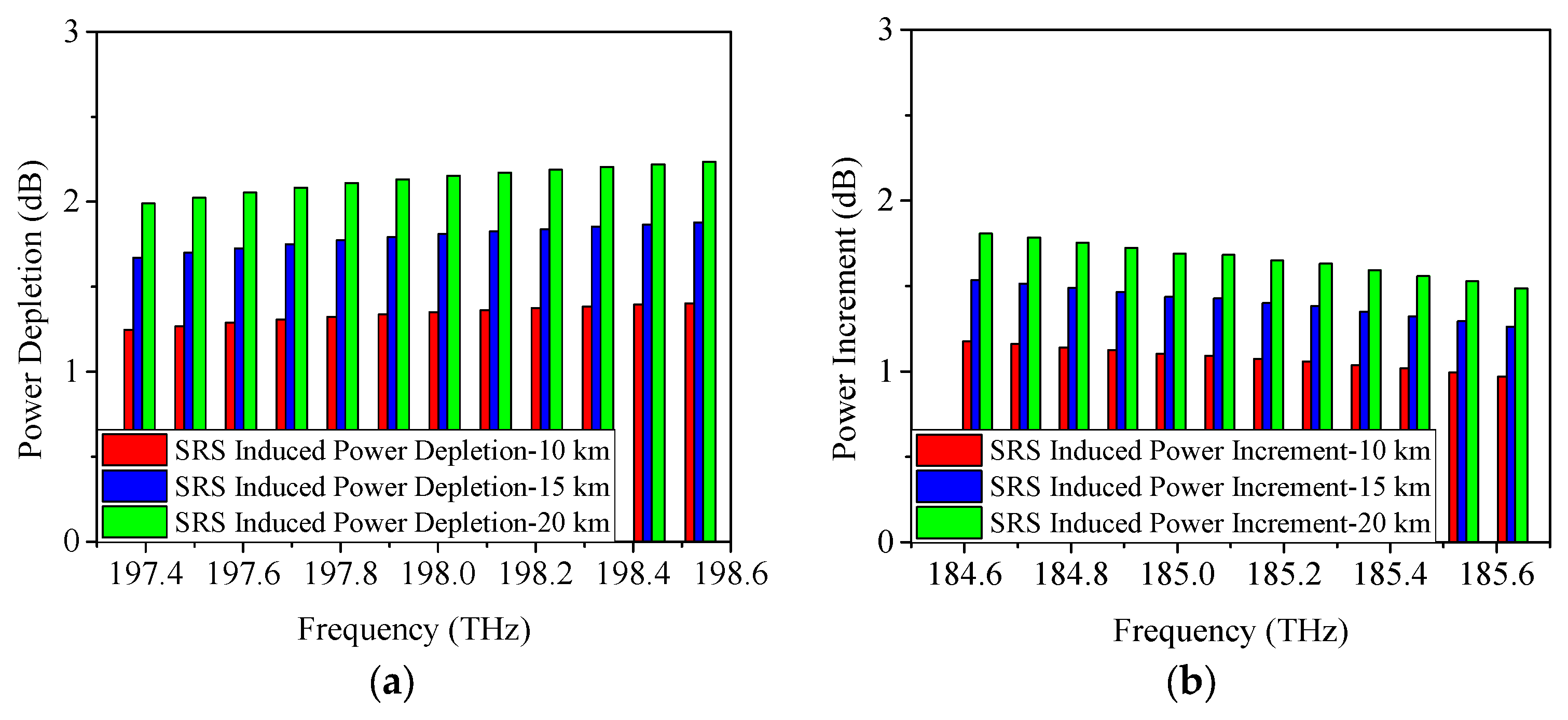
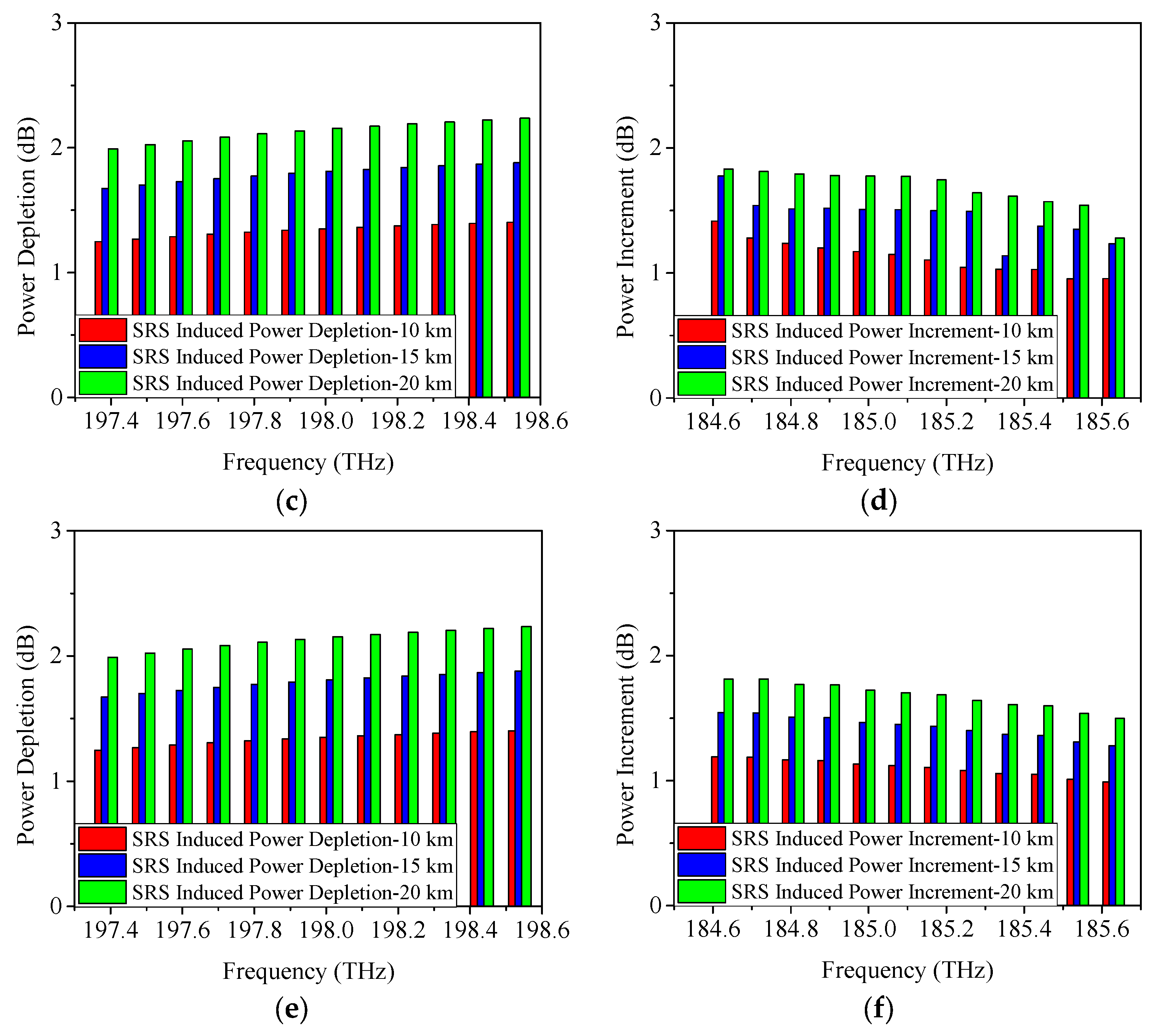
| Serial Number | Approximate Condition |
|---|---|
| 1 | All channels lie within the linear portion of the Raman gain profile and are equally separated in the spectral domain |
| 2 | The triangular approximation is employed to the Raman gain curve (i.e., the Raman gain is assumed to vary linearly) |
| 3 | |
| 4 | The walk-off effect between wavelengths is ignored |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Wavelengths (5G fronthaul upstream) | 197.4~198.5 THz |
| Wavelengths (5G fronthaul downstream) | 184.6~185.7 THz |
| Channel Spacing | 100 GHz |
| Modulation Format | NRZ, ODB, PAM4 |
| Modulation Rate | 25 Gb/s, 50 Gb/s (5G fronthaul), 10 Gb/s (NG-PON2, Super-PON and XG-PON1) |
| Fiber Attenuation | 0.24 dB/km |
| MUX and DEMUX Insertion Loss | 1.5 dB |
| Chirp Coefficient | 0 |
| Out Power | 8 dBm/channel, 12 dBm/channel (for Super-PON) |
| Chromatic Dispersion of Fiber | 16 ps/(nm·km) |
| Fiber Length | 10 km, 15 km, 20 km, 50 km (for Super-PON) |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Wavelengths (5G fronthaul upstream) | 220.4~229.2 THz |
| Wavelengths (5G fronthaul downstream) | 228.9~237.9 THz |
| Channel Spacing | 800 GHz |
| Modulation Format | NRZ, ODB, PAM4 |
| Modulation Rate | 25 Gb/s, 50 Gb/s (5G fronthaul), 25 Gb/s (50G-EPON), 10 Gb/s (XG-PON1), 1 Gb/s (GPON) |
| Fiber Attenuation | 0.34 dB/km |
| MUX and DEMUX Insertion Loss | 1.5 dB |
| Chirp Coefficient | 0 |
| Out Power | 8 dBm/channel |
| Chromatic Dispersion | 2 ps/(nm·km) |
| Fiber Length | 10 km, 15 km, 20 km |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Wang, S.; Saleem, A. Simulative Analysis of Stimulated Raman Scattering Effects on WDM-PON Based 5G Fronthaul Networks. Sensors 2025, 25, 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103237
Xu Y, Wang S, Saleem A. Simulative Analysis of Stimulated Raman Scattering Effects on WDM-PON Based 5G Fronthaul Networks. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103237
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yan, Shuai Wang, and Asad Saleem. 2025. "Simulative Analysis of Stimulated Raman Scattering Effects on WDM-PON Based 5G Fronthaul Networks" Sensors 25, no. 10: 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103237
APA StyleXu, Y., Wang, S., & Saleem, A. (2025). Simulative Analysis of Stimulated Raman Scattering Effects on WDM-PON Based 5G Fronthaul Networks. Sensors, 25(10), 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103237






