Biomechanical Effects of a Passive Back-Support Exosuit During Simulated Military Lifting Tasks—An EMG Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
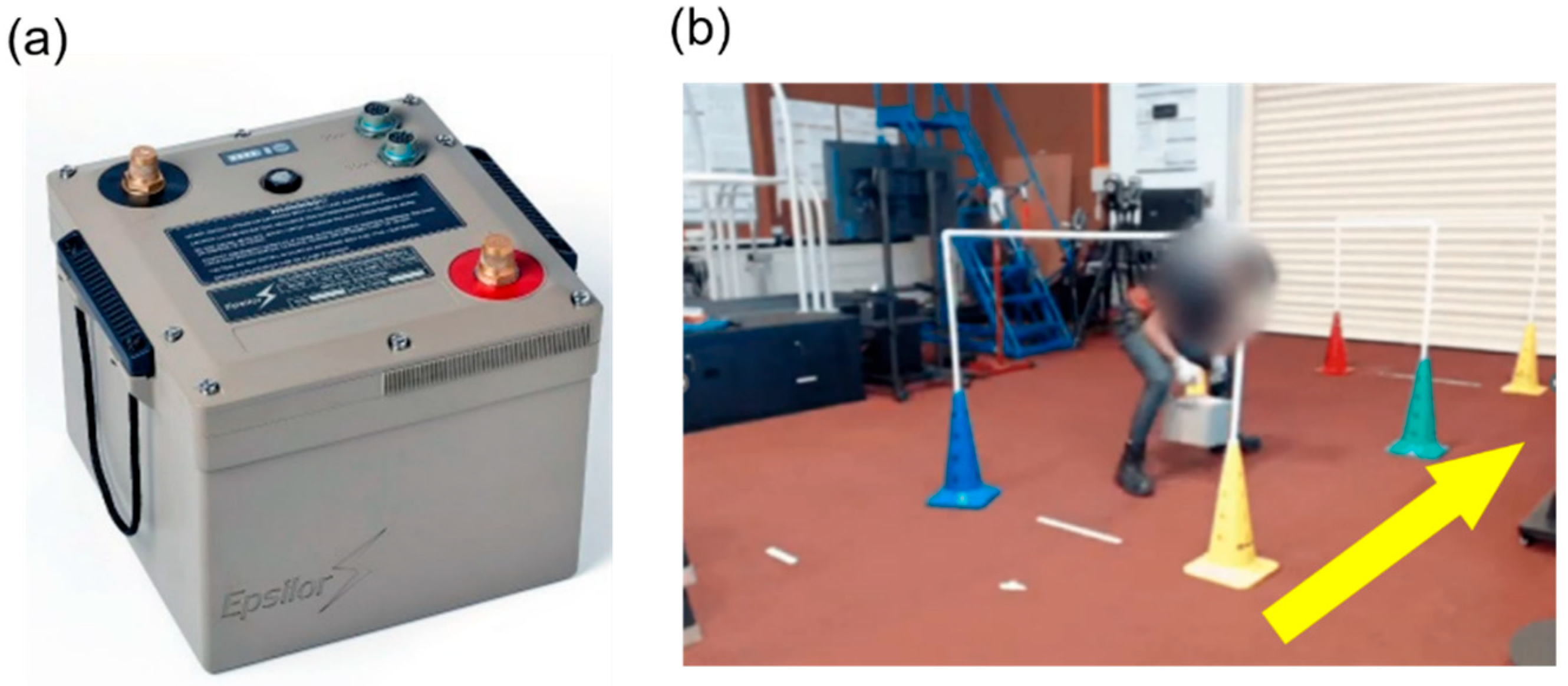
2.2. Back-Support Exosuit
2.3. Participants
2.4. Wireless Surface Electromyography (EMG) System
2.5. Procedures
2.5.1. Skin Preparation
2.5.2. EMG Sensors Placement
2.5.3. EMG Normalisation Task
2.5.4. Vertical Lifting Tasks
2.5.5. Lateral Lifting Task
2.6. Data Processing
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.7.1. Vertical Lifting Tasks
2.7.2. Lateral Lifting Task
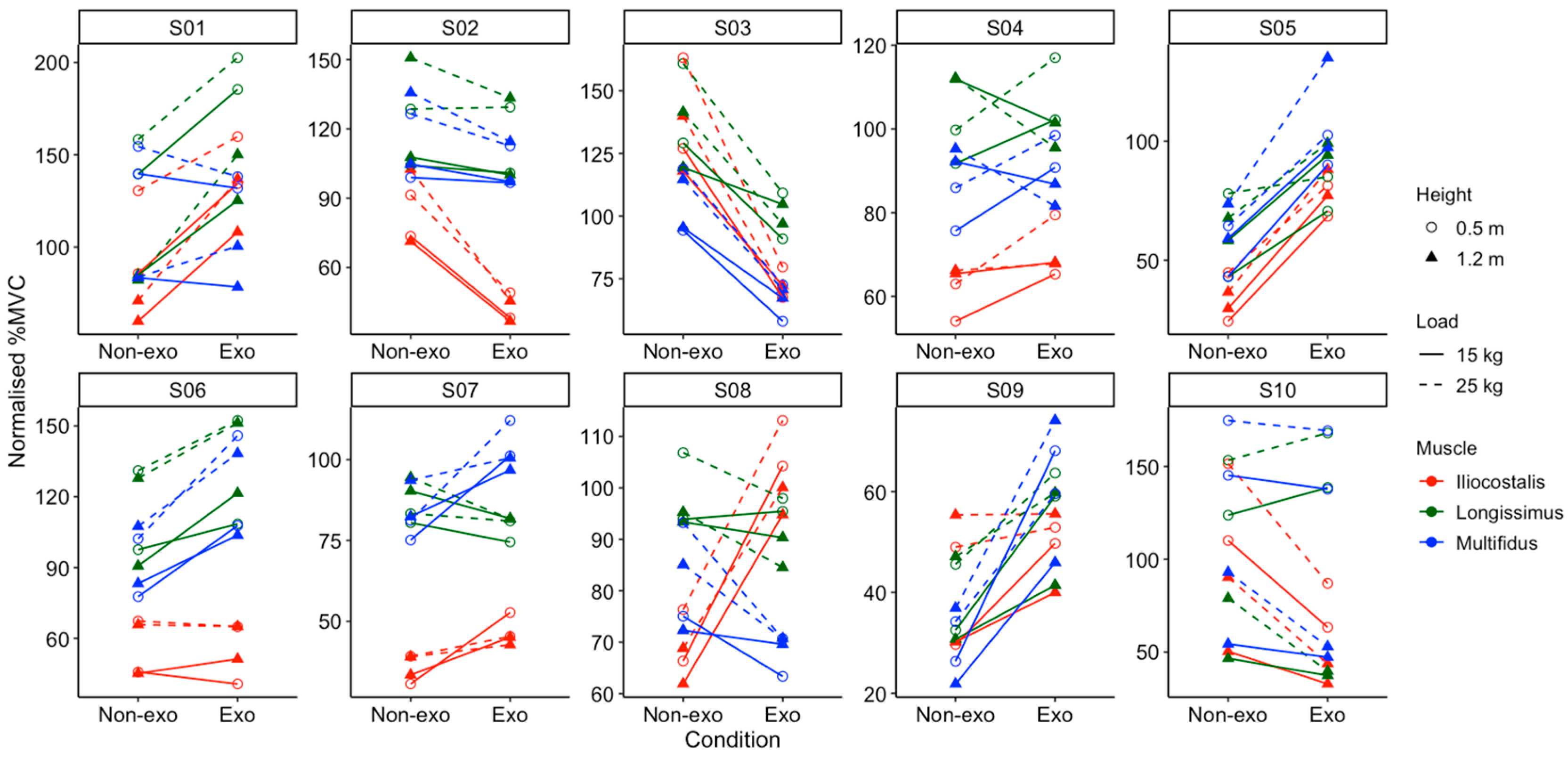
2.7.3. Individual Analysis
3. Results
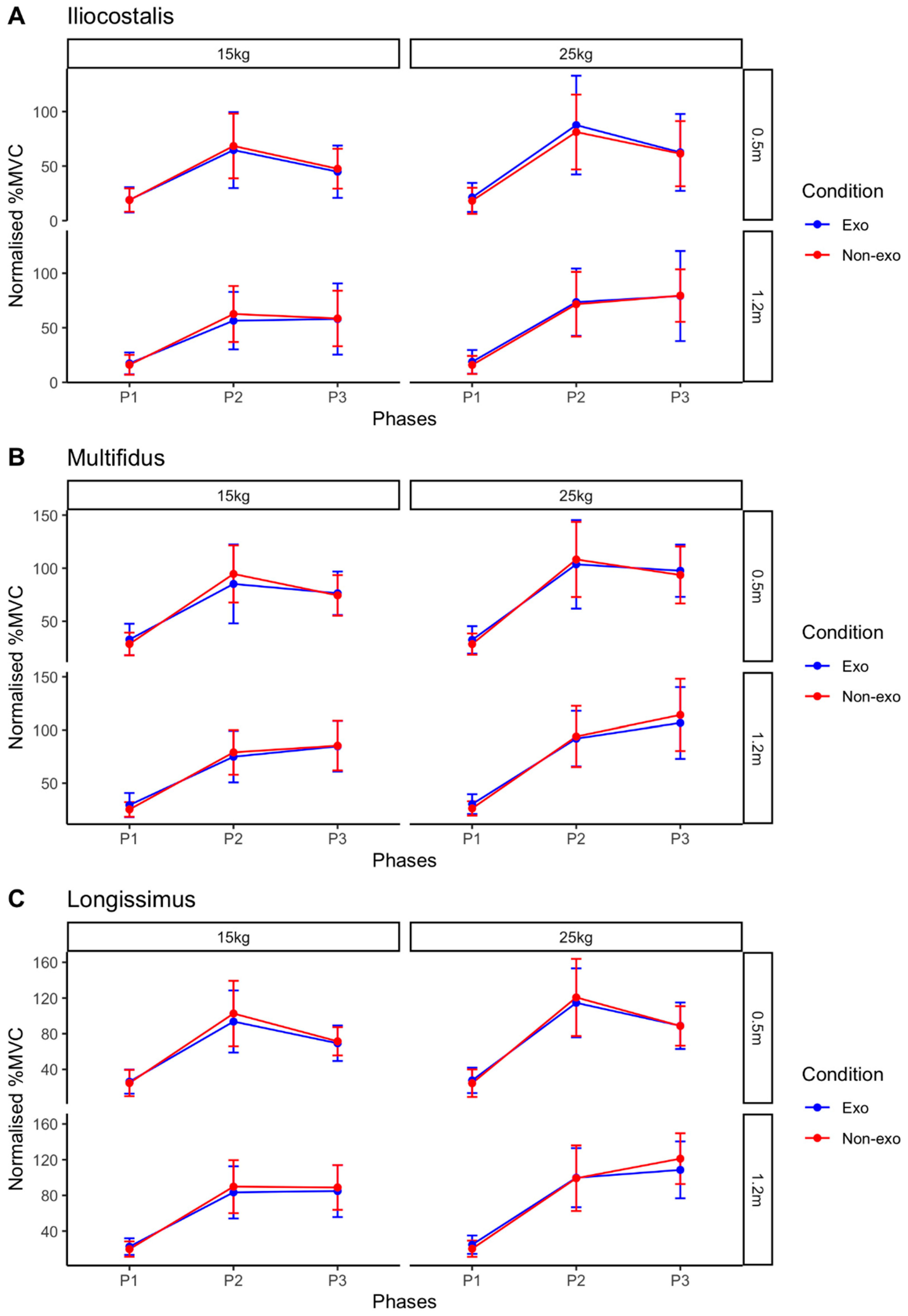
3.1. Vertical Lifting Tasks
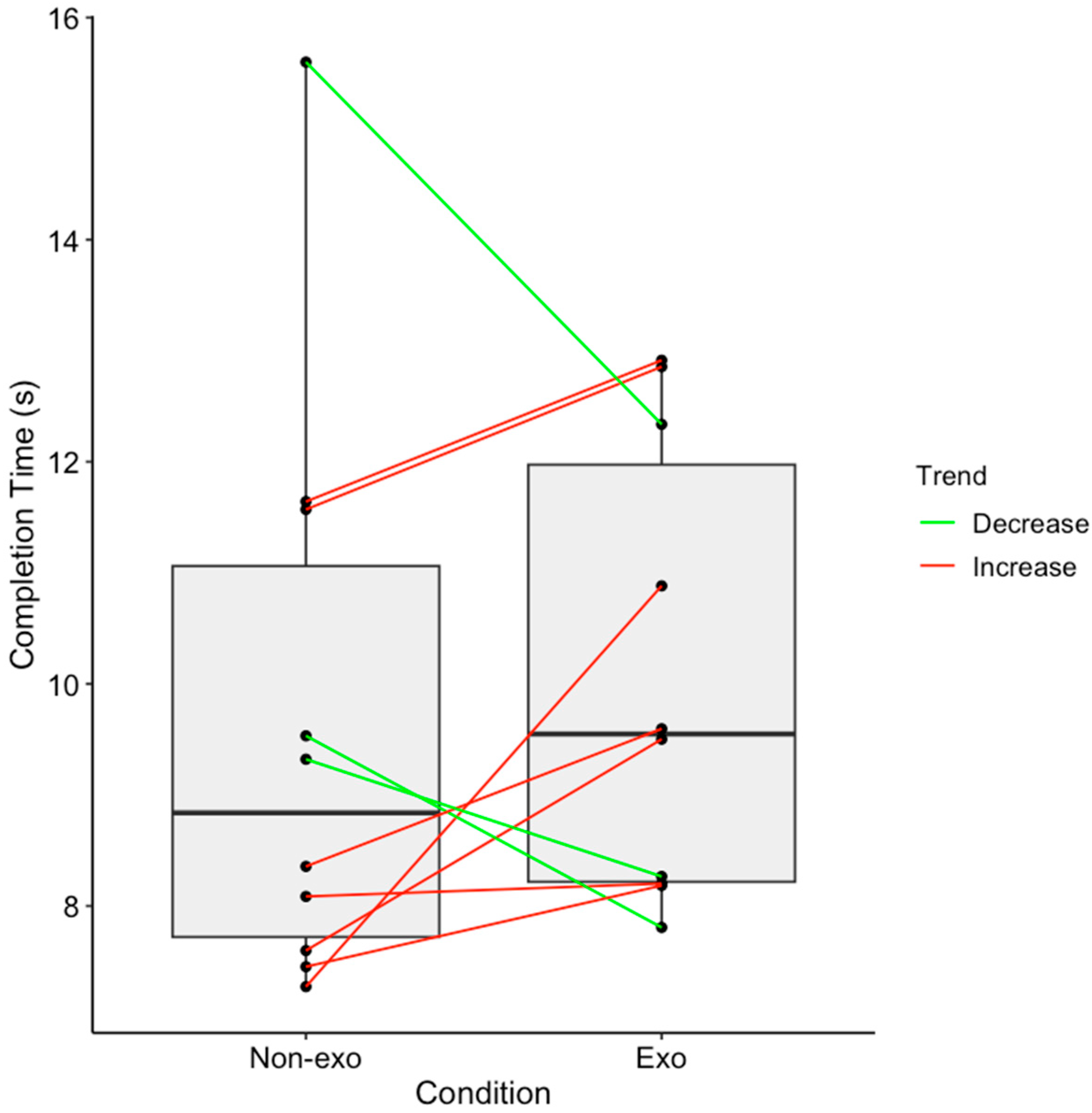
3.2. Lateral Lifting Task
4. Discussion
4.1. Group Responses to Back-Support Exosuit
4.2. Individual Responses to Back-Support Exosuit
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weston, E.B.; Dufour, J.S.; Lu, M.L.; Marras, W.S. Spinal loading and lift style in confined vertical space. Appl. Ergon. 2020, 84, 103021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Costa, B.R.; Vieira, E.R. Risk factors for work-related musculoskeletal disorders: A systematic review of recent longitudinal studies. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2010, 53, 285–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canham-Chervak, M.; Hauret, K.; Hoedebecke, E.; Laurin, M.J.; Cuthie, J. Discharges during U.S. Army Basic Training: Injury Rates and Risk Factors. Mil. Med. 2001, 166, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Manpower. Workplace Safety and Health Report 2021; Ministry of Manpower: Singapore, 2022. Available online: https://www.mom.gov.sg/workplace-safety-and-health/wsh-reports-and-statistics (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Abdoli, E.M.; Agnew, M.J.; Stevenson, J.M. An on-body personal lift augmentation device (PLAD) reduces EMG amplitude of erector spinae during lifting tasks. Clin. Biomech. 2006, 21, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemi, M.M.; Geissinger, J.; Simon, A.A.; Chang, S.E.; Asbeck, A.T. A passive exoskeleton reduces peak and mean EMG during symmetric and asymmetric lifting. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2019, 47, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamsuwan, O.; Milosavljevic, S.; Srinivasan, D.; Trask, C. Potential exoskeleton uses for reducing low back muscular activity during farm tasks. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2020, 63, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Dutta, A.; Dai, F. Exoskeletons for manual material handling—A review and implication for construction applications. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.G.; Reid, C.R.; Rempel, D.D.; Treaster, D. Introduction to the Human Factors Special Issue on User-Centered Design for Exoskeleton. Hum. Factors 2020, 62, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sluijs, R.M.; Wehrli, M.; Brunner, A.; Lambercy, O. Evaluation of the physiological benefits of a passive back-support exoskeleton during lifting and working in forward leaning postures. J. Biomech. 2023, 149, 111489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, A.S.; Näf, M.; Baltrusch, S.J.; Kingma, I.; Rodriguez-Guerrero, C.; Babič, J.; de Looze, M.P.; van Dieën, J.H. Biomechanical evaluation of a new passive back support exoskeleton. J. Biomech. 2020, 105, 109795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goršič, M.; Song, Y.; Dai, B.; Novak, D. Evaluation of the HeroWear Apex back-assist exosuit during multiple brief tasks. J. Biomech. 2021, 126, 110620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goršič, M.; Song, Y.; Dai, B.; Novak, V.D. Short-term effects of the Auxivo LiftSuit during lifting and static leaning. Appl. Ergon. 2022, 102, 103765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slaughter, P.R.; Rodzak, K.M.; Fine, S.J.; Ice, C.C.; Wolf, D.N.; Zelik, K.E. Evaluation of U.S. Army Soldiers wearing a back exosuit during a field training exercise. Wearable Technol. 2023, 4, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Refai, M.I.; Moya-Esteban, A.; Van Zijl, L.; Van Der Kooij, H.; Sartori, M. Benchmarking commercially available soft and rigid passive back exoskeletons for an industrial workplace. Wearable Technol. 2024, 5, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arauz, P.G.; Chavez, G.; Reinoso, V.; Ruiz, P.; Ortiz, E.; Cevallos, C.; Garcia, G. Influence of a passive exoskeleton on kinematics, joint moments, and self-reported ratings during a lifting task. J. Biomech. 2024, 162, 111886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Sluijs, R.M.; Rodriguez-Cianca, D.; Sanz-Morère, C.B.; Massardi, S.; Bartenbach, V.; Torricelli, D. A method to quantify the reduction of back and hip muscle fatigue of lift-support exoskeletons. Wearable Technol. 2023, 4, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, W.F.; Silver, P.H.S. The function of the erectores spinae muscles in certain movements and postures in man*. J. Physiol. 1955, 129, 184–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Kong, P.W. Low Back and Lower-Limb Muscle Performance in Male and Female Recreational Runners with Chronic Low Back Pain. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2015, 45, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermens, H.J. European Recommendations for Surface ElectroMyoGraphy: Results of the SENIAM Project; Roessingh Research and Development BV: Enschede, The Netherlands, 1999; p. 122. [Google Scholar]
- Chalard, A.; Belle, M.; Montané, E.; Marque, P.; Amarantini, D.; Gasq, D. Impact of the EMG normalization method on muscle activation and the antagonist-agonist co-contraction index during active elbow extension: Practical implications for post-stroke subjects. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2020, 51, 102403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Jo, M.E. Comparison of maximum voluntary isometric contraction of the biceps on various posture and respiration conditions for normalization of electromyography data. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 3007–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Visser, J.; Mans, E.; De Visser, M.; Van Den Berg-Vos, R.M.; Franssen, H.; de Jong, J.; Berg, L.v.D.; Wokke, J.; de Haan, R. Comparison of maximal voluntary isometric contraction and hand-held dynamometry in measuring muscle strength of patients with progressive lower motor neuron syndrome. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2003, 13, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, P.W.; Kan, T.Y.W.; Mohamed Jamil, R.A.G.B.; Teo, W.P.; Pan, J.W.; Halim, N.H.A.; Maricar, H.K.A.B.; Hostler, D. Functional versus conventional strength and conditioning programs for back injury prevention in emergency responders. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 918315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, P.W.; Kan, T.Y.W.; Mohamed Jamil, R.A.G.B.; Teo, W.P.; Pan, J.W.; Halim, N.H.A.; Maricar, H.K.A.B.; Hostler, D. Low back pain and biomechanical characteristics of back muscles in firefighters. Ergonomics 2024, 67, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Goršič, M.; Feng, Z.; Cordova, H.; Li, L.; Dai, B.; Novak, V. Effects of a back-assist exosuit in lab-based approximations of construction tasks performed by novices and experienced construction workers. Ergonomics 2025, 68, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanca, M.; Arnau, J.; García-Castro, F.; Alarcón, R.; Bono, R. Non-normal Data in Repeated Measures ANOVA: Impact on Type I Error and Power. Psicothema 2023, 1, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchiotti, M.T.; Weston, E.B.; Knapik, G.G.; Dufour, J.S.; Marras, W.S. Impact of two postural assist exoskeletons on biomechanical loading of the lumbar spine. Appl. Ergon. 2019, 75, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
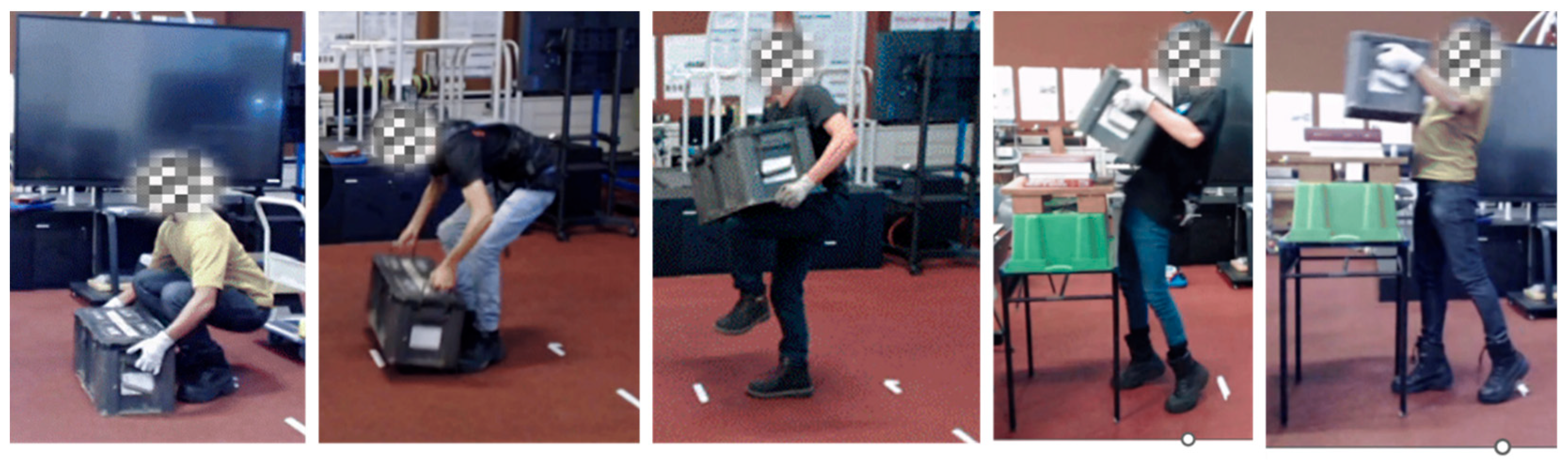







| Participants | Age (Years) | Body Mass (kg) | Height (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S01 | 23 | 60.6 | 173 |
| S02 | 28 | 72.5 | 181 |
| S03 | 26 | 58.5 | 179 |
| S04 | 43 | 99.0 | 185 |
| S05 | 27 | 83.2 | 172 |
| S06 | 37 | 67.5 | 170 |
| S07 | 37 | 92.3 | 177 |
| S08 | 45 | 94.0 | 179 |
| S09 | 30 | 50.9 | 179 |
| S10 | 29 | 48.0 | 160 |
| Mean (SD) | 32.1 (7.0) | 72.6 (17.6) | 175.5 (6.6) |
| Range | 23–45 | 48.0–94.0 | 160–185 |
| Muscle | Height (m) | Load (kg) | Phases | Conditions | Phases | Interaction | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1: Lowering | P2: Lift and Forward | P3: End | ||||||||||||
| Non-Exo (% MVC) | Exo (% MVC) | Non-Exo (% MVC) | Exo (% MVC) | Non-Exo (% MVC) | Exo (% MVC) | p | p | p | ||||||
| Iliocostalis | 0.5 | 15 | 19.03 ± 11.60 | 18.85 ± 10.67 | 64.71 ± 34.87 | 68.46 ± 29.72 | 44.86 ± 23.95 | 47.58 ± 18.31 | 0.773 | 0.01 | <0.001 | 0.797 | 0.902 | 0.011 |
| 25 | 21.32 ± 13.29 | 18.19 ± 12.00 | 87.63 ± 45.31 | 81.26 ± 34.36 | 62.58 ± 35.29 | 61.42 ± 29.87 | 0.705 | 0.017 | <0.001 | 0.761 | 0.868 | 0.016 | ||
| 1.2 | 15 | 17.29 ± 10.05 | 16.02 ± 9.14 | 56.52 ± 26.30 | 62.64 ± 25.72 | 58.03 ± 32.61 | 58.56 ± 25.46 | 0.802 | 0.007 | <0.001 | 0.752 | 0.633 | 0.050 | |
| 25 | 18.74 ± 10.83 | 15.88 ± 8.31 | 73.54 ± 30.83 | 71.60 ± 29.73 | 79.13 ± 41.29 | 79.53 ± 24.04 | 0.873 | 0.003 | <0.001 | 0.859 | 0.949 | 0.006 | ||
| Multifidus | 0.5 | 15 | 32.71 ± 14.84 | 28.51 ± 10.67 | 85.13 ± 37.17 | 94.57 ± 26.93 | 76.33 ± 20.54 | 74.33 ± 19.14 | 0.865 | 0.003 | <0.001 | 0.817 | 0.275 | 0.134 |
| 25 | 32.37 ± 12.98 | 28.39 ± 10.07 | 103.60 ± 41.76 | 108.20 ± 35.37 | 97.57 ± 24.61 | 93.54 ± 26.84 | 0.881 | 0.003 | <0.001 | 0.810 | 0.628 | 0.050 | ||
| 1.2 | 15 | 29.34 ± 11.35 | 25.21 ± 6.97 | 74.89 ± 24.26 | 79.02 ± 21.05 | 84.70 ± 23.77 | 85.28 ± 23.36 | 0.970 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.785 | 0.598 | 0.056 | |
| 25 | 30.20 ± 9.31 | 26.17 ± 6.69 | 91.89 ± 26.17 | 93.90 ± 28.82 | 106.58 ± 33.72 | 114.15 ± 33.97 | 0.806 | 0.007 | <0.001 | 0.825 | 0.625 | 0.051 | ||
| Longissimus | 0.5 | 15 | 26.29 ± 13.48 | 24.82 ± 14.66 | 93.61 ± 34.75 | 102.63 ± 36.65 | 69.31 ± 19.93 | 71.51 ± 15.86 | 0.463 | 0.061 | <0.001 | 0.828 | 0.367 | 0.105 |
| 25 | 27.76 ± 14.20 | 24.56 ± 15.42 | 114.57 ± 38.57 | 120.64 ± 43.18 | 88.88 ± 26.01 | 88.68 ± 22.13 | 0.892 | 0.002 | <0.001 | 0.829 | 0.440 | 0.087 | ||
| 1.2 | 15 | 22.64 ± 9.29 | 19.83 ± 8.60 | 83.40 ± 29.18 | 89.81 ± 29.64 | 84.85 ± 29.17 | 88.93 ± 25.03 | 0.521 | 0.047 | <0.001 | 0.774 | 0.412 | 0.094 | |
| 25 | 24.84 ± 10.34 | 20.27 ± 9.15 | 99.80 ± 33.12 | 99.20 ± 36.69 | 108.53 ± 31.85 | 121.13 ± 28.36 | 0.658 | 0.023 | <0.001 | 0.832 | 0.322 | 0.118 | ||
| Muscle | Conditions | Conditions | Sides | Interaction | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Exo | Exo | |||||||||
| Left (% MVC) | Right (% MVC) | Left (% MVC) | Right (% MVC) | p | p | p | ||||
| Iliocostalis | 69.03 ± 32.00 | 71.83 ± 35.00 | 53.33 ± 27.28 | 49.63 ± 24.26 | 0.105 | 0.265 | 0.926 | 0.001 | 0.408 | 0.077 |
| Longissimus | 66.19 ± 29.27 | 63.27 ± 24.13 | 58.00 ± 25.93 | 54.16 ± 19.98 | 0.045 * | 0.376 | 0.290 | 0.123 | 0.771 | 0.010 |
| Multifidus | 84.62 ± 25.81 | 88.23 ± 26.82 | 75.50 ± 19.97 | 70.59 ± 23.73 | 0.091 | 0.284 | 0.909 | 0.002 | 0.172 | 0.197 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marican, M.A.; Chandra, L.D.; Tang, Y.; Iskandar, M.N.S.; Lim, C.X.E.; Kong, P.W. Biomechanical Effects of a Passive Back-Support Exosuit During Simulated Military Lifting Tasks—An EMG Study. Sensors 2025, 25, 3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103211
Marican MA, Chandra LD, Tang Y, Iskandar MNS, Lim CXE, Kong PW. Biomechanical Effects of a Passive Back-Support Exosuit During Simulated Military Lifting Tasks—An EMG Study. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103211
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarican, Muhammad Ammar, Lavern Dharma Chandra, Yunqi Tang, Muhammad Nur Shahril Iskandar, Cheryl Xue Er Lim, and Pui Wah Kong. 2025. "Biomechanical Effects of a Passive Back-Support Exosuit During Simulated Military Lifting Tasks—An EMG Study" Sensors 25, no. 10: 3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103211
APA StyleMarican, M. A., Chandra, L. D., Tang, Y., Iskandar, M. N. S., Lim, C. X. E., & Kong, P. W. (2025). Biomechanical Effects of a Passive Back-Support Exosuit During Simulated Military Lifting Tasks—An EMG Study. Sensors, 25(10), 3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103211






