Filamentary Convolution for SLI: A Brain-Inspired Approach with High Efficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Convolution for Spoken Language Identification
2.2. Deep Learning-Based Frameworks for Spoken Language Identification
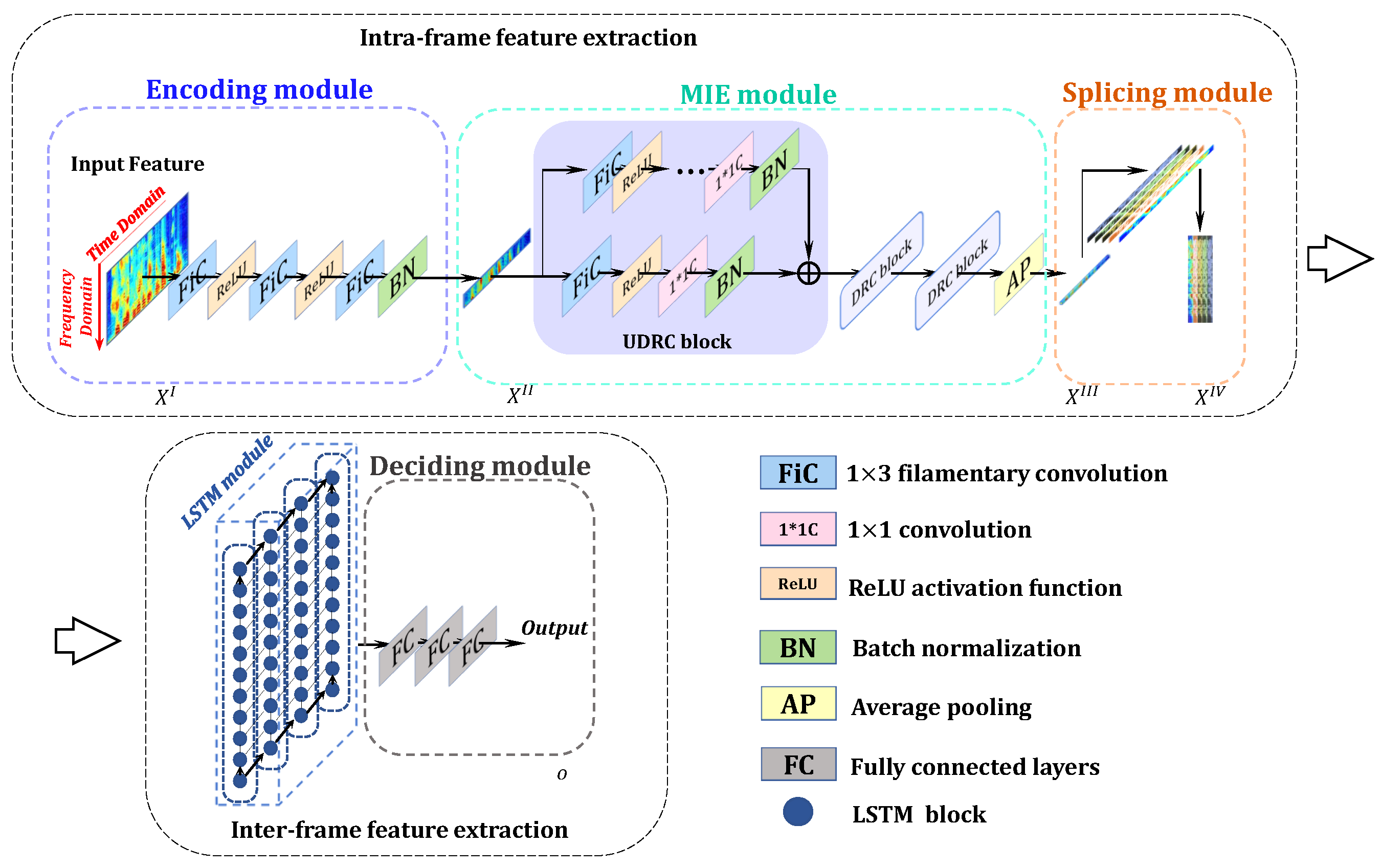
3. Proposed Framework
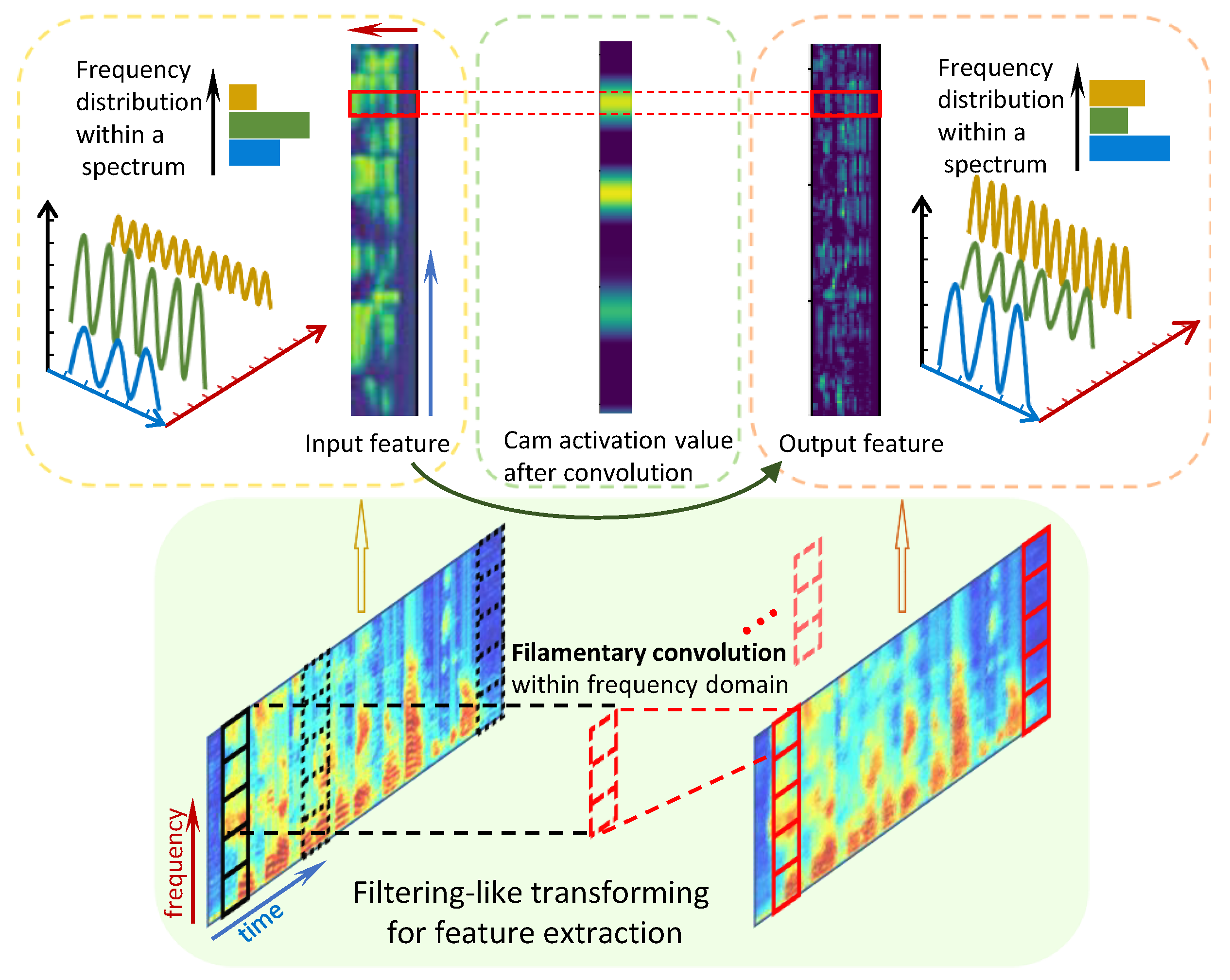
3.1. Definition of Filamentary Convolution
3.2. Implementation Structure for Filamentary Convolution
3.3. Parallel Processing Within Spectrum
3.4. Maintaining Details Among Frames
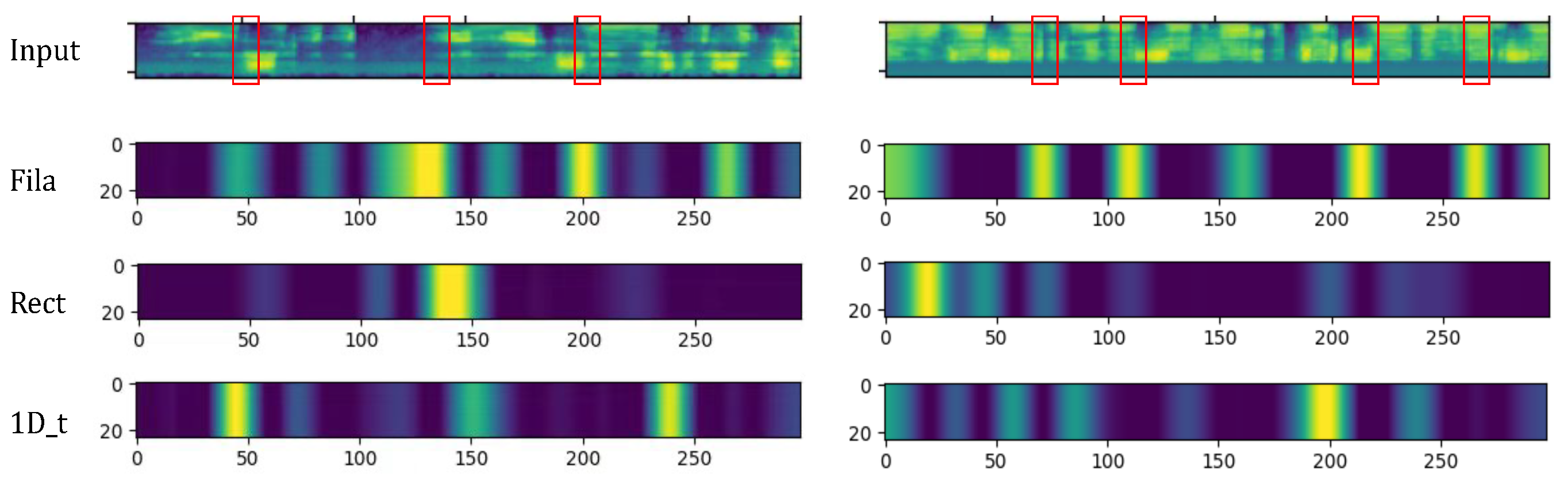
3.4.1. Retaining Detailed Temporal Characteristics
3.4.2. Continuity Evaluation for TFAFs
4. Experiment
4.1. Experimental Setup
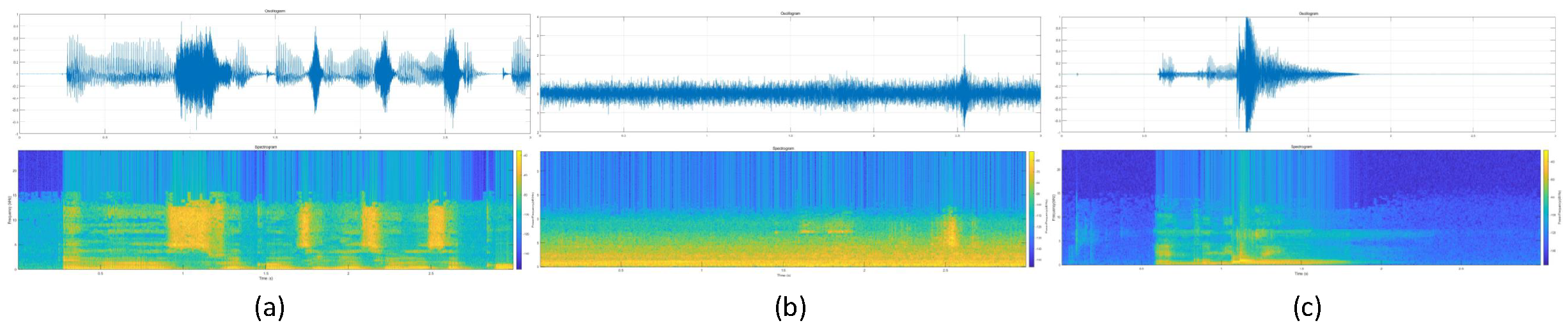
4.1.1. Dataset
4.1.2. Baseline System
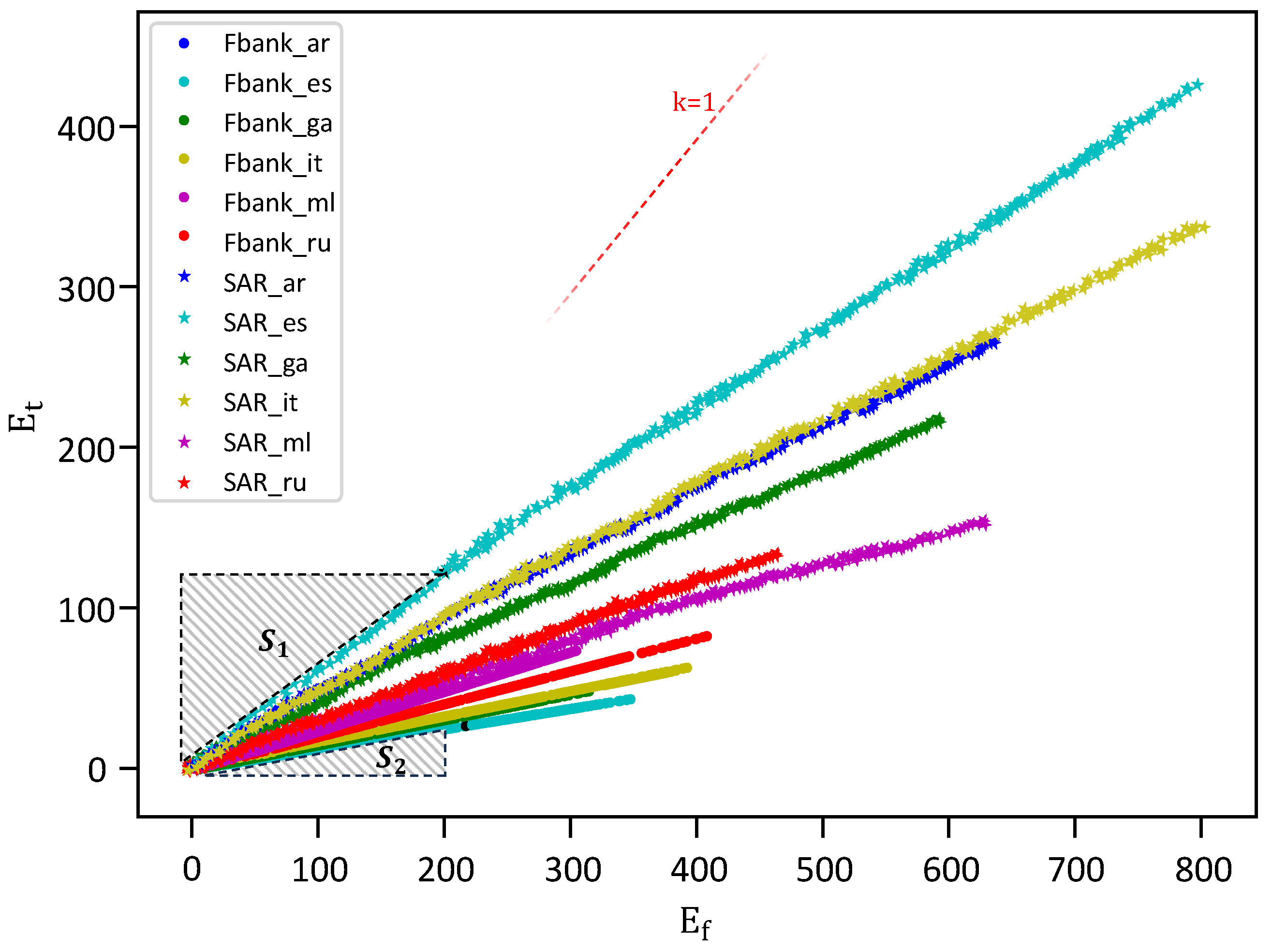
4.1.3. Incremental Efficiency
4.1.4. TFAF Generation
4.2. Ablation Evaluation
4.2.1. Experiments on Different Input Features
4.2.2. Experiments on Voice Activity Detection
4.2.3. Experiments on Components of CNN-LSTM Framework with Filamentary Convolution
4.2.4. Experiments on Filamentary Convolution
4.3. Cross-Method Comparison
4.3.1. Comparison Among SLI-Based Systems
4.3.2. Further Validation Among Other Acoustic-Based Models
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Raw Data of SLR
Appendix A.1.1. Common Voice and OpenSLR
| Language | Code | Voice | Hours | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Validation | |||
| Abkhaz | ab | 14 | 1 | <1 |
| Arabic | ar | 672 | 77 | 49 |
| Assamese | as | 17 | <1 | <1 |
| Breton | br | 157 | 16 | 7 |
| Catalan | ca | 5376 | 748 | 623 |
| Hakha Chin | cnh | 297 | 5 | 2 |
| Czech | cs | 353 | 45 | 36 |
| Chuvash | cv | 92 | 16 | 4 |
| Welsh | cy | 1382 | 124 | 95 |
| German | de | 12659 | 836 | 77 |
| Dhivehi | dv | 167 | 19 | 18 |
| Greek | el | 118 | 13 | 6 |
| English | en | 66173 | 2181 | 1686 |
| Esperanto | eo | 574 | 102 | 90 |
| Spanish | es | 19484 | 579 | 324 |
| Estonian | et | 543 | 27 | 19 |
| Basque | eu | 1028 | 131 | 89 |
| Persian | fa | 3655 | 321 | 282 |
| Finnish | fi | 27 | 1 | 1 |
| French | fr | 12953 | 682 | 623 |
| Frisian | fy | 467 | 46 | 14 |
| Irish | ga | 101 | 5 | 3 |
| Hindi | hi | 31 | <1 | <1 |
| Sorbian | hsb | 19 | 2 | 2 |
| Hungrian | hu | 47 | 8 | 8 |
| Interlingua | ia | 36 | 8 | 6 |
| Indonesian | id | 219 | 17 | 9 |
| Italian | it | 5729 | 199 | 158 |
| Japanese | ja | 235 | 5 | 3 |
| Georgian | ka | 44 | 3 | 3 |
| Kabyle | kab | 1309 | 622 | 525 |
| Luganda | lg | 76 | 8 | 3 |
| Lithuanian | lt | 30 | 4 | 2 |
| Latvian | lv | 99 | 7 | 6 |
| Mongolian | mn | 376 | 17 | 11 |
| Maltese | mt | 171 | 15 | 7 |
| Dutch | nl | 1012 | 63 | 59 |
| Odia | or | 34 | 7 | <1 |
| Punjabi | pa | 26 | 2 | <1 |
| Polish | pl | 2647 | 129 | 108 |
| Portuguese | pt | 1120 | 63 | 50 |
| Romansh Sursilvan | rm-sursilv | 78 | 9 | 5 |
| Romansh Vallader | rm-vallader | 39 | 3 | 2 |
| Romanian | ro | 130 | 9 | 6 |
| Russian | ru | 1412 | 130 | 111 |
| Kinyarwanda | rw | 410 | 1510 | 1183 |
| Sakha | sah | 42 | 6 | 4 |
| Sovenian | sl | 82 | 7 | 5 |
| Swedish | sv | 222 | 15 | 12 |
| Tamil | ta | 266 | 24 | 14 |
| Thai | th | 182 | 12 | 8 |
| Turkish | tr | 678 | 22 | 20 |
| Tatar | tt | 185 | 28 | 26 |
| Ukrainian | uk | 459 | 43 | 30 |
| Vietnamese | vi | 62 | 1 | <1 |
| Votic | vot | 3 | <1 | <1 |
| Chinese(China) | zh_CN | 3501 | 78 | 56 |
| Chinese(Hong Kong) | zh_HK | 2536 | 100 | 50 |
| Chinese(Taiwan) | zh_TW | 1444 | 78 | 55 |
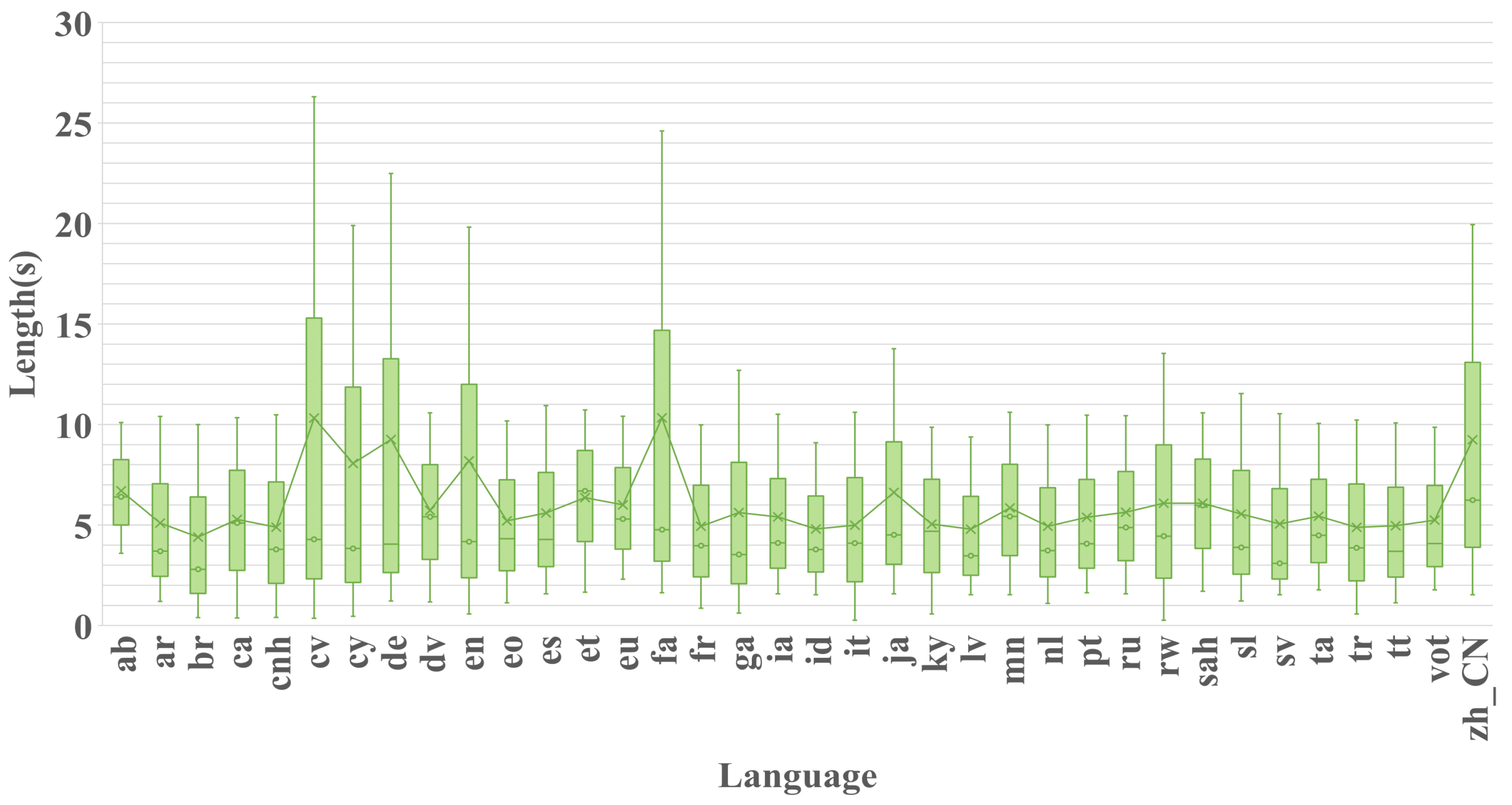
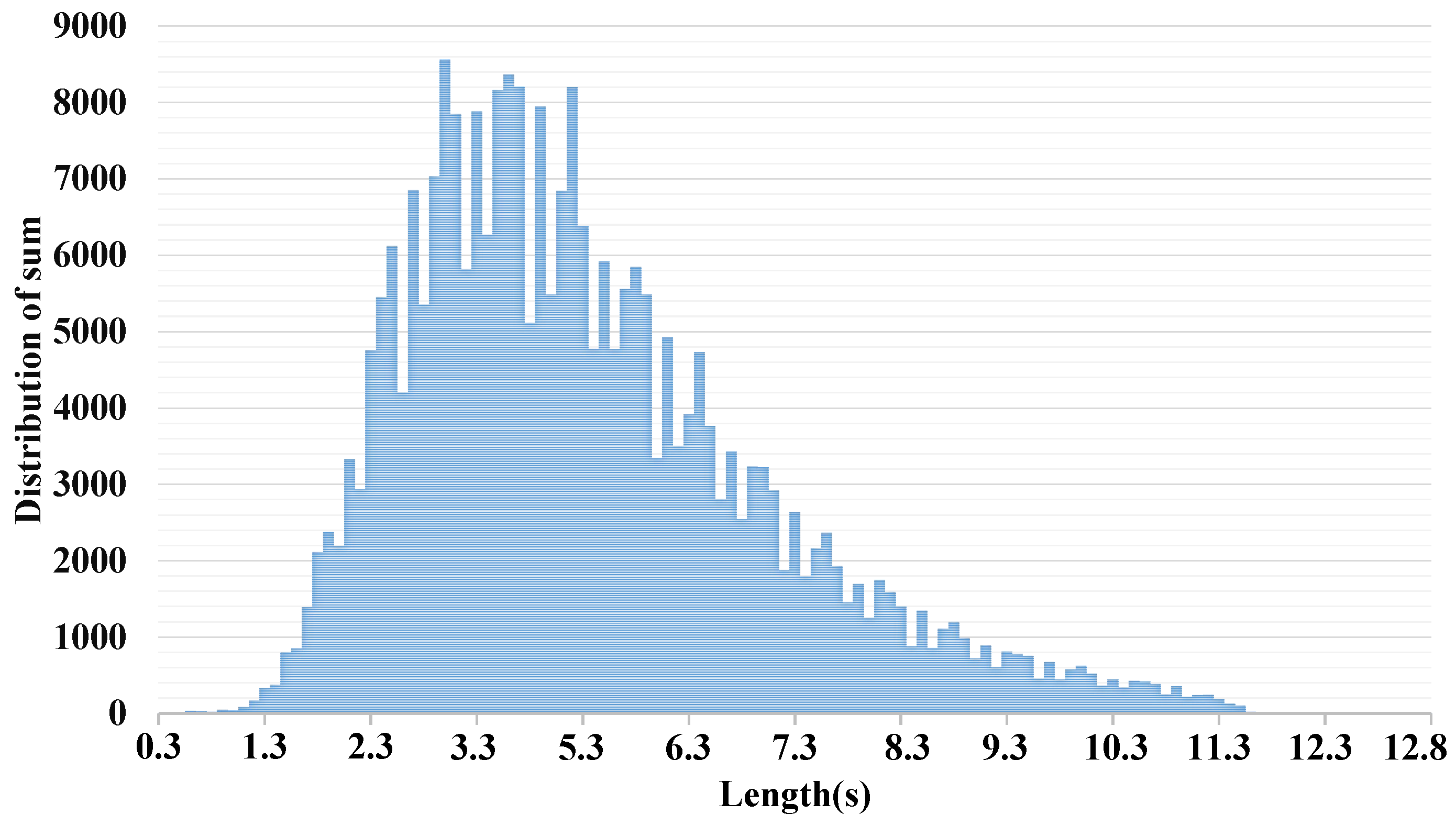
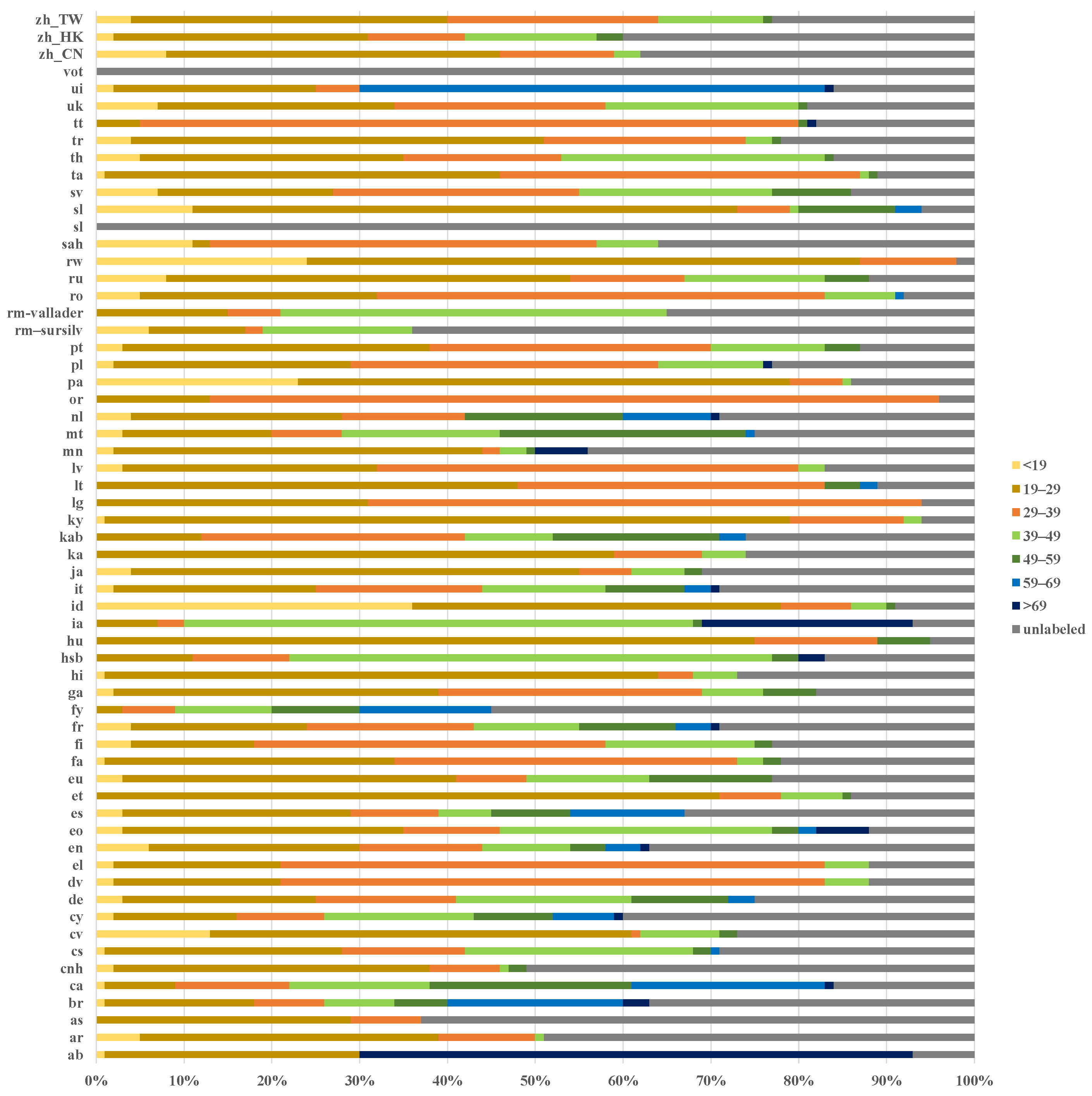
Appendix A.1.2. Dataset Involved in This Experiment
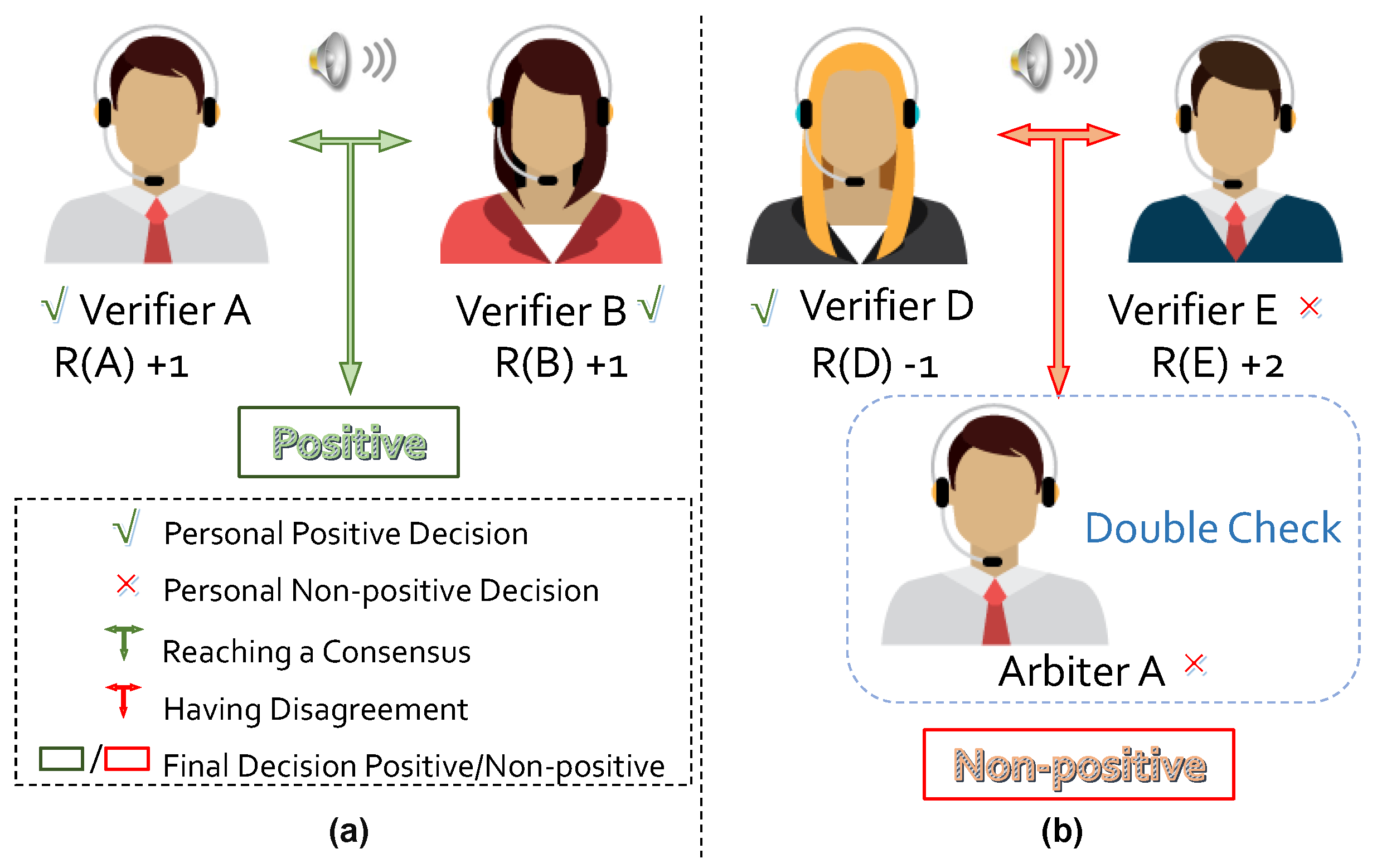
Appendix A.1.3. Our Proposed Corpus Refining Method
| Algorithm A1 Procedure of corpus refinement. |
| 1. Generation of determination reference: (1) Composing the dataset by randomly selecting M audio recordings from all the recordings to be refined; (2) Distinguishing the valid and invalid data of by the voting of L people; (3) Recording the voting result as a determination reference. 2. Referee selection: (1) Inviting N participants to distinguish the valid and invalid data of ; (2) Comparing the determination result of each participant with ; (3) Selecting the referee who achieves the highest accuracy. 3. Data examination: (1) Selecting any two different people from the remaining participants to compose examination groups, where the members of each group are denoted as and ; (2) Equally dividing the total K recordings of corpus into subsets , where each consists of recordings; (3) Inviting each group of examiners to examine the validity of the recordings of the corresponding . For each : for do Examining by and ; if and achieve agreement then if is invalid then Removing from ; end if else Inviting the referee for final determination; if is invalid then Removing from ; end if end if end for 4. Corpus refinement: Refining with the updated . |
Appendix A.1.4. Our Proposed Corpus Refining Method
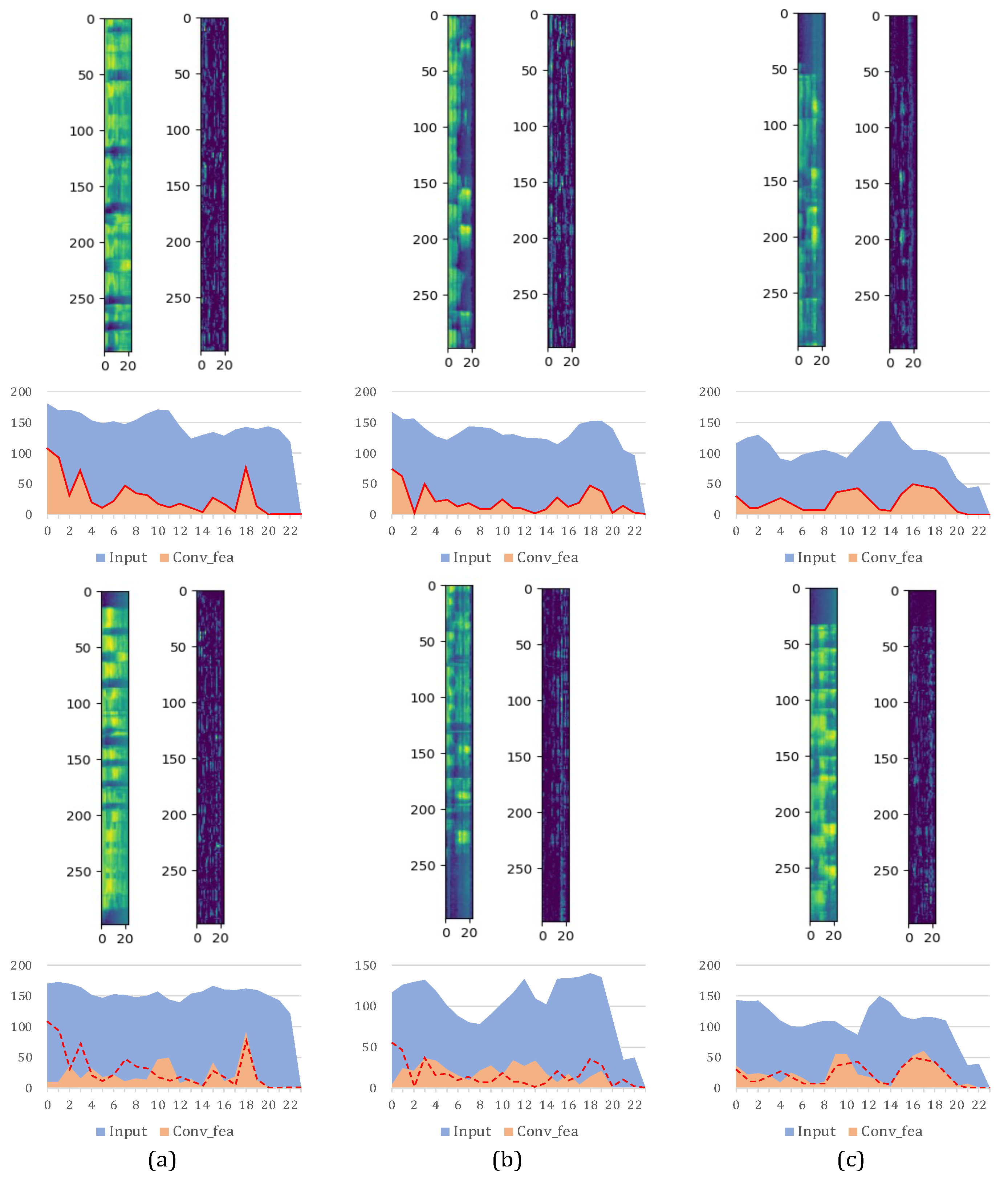
Appendix A.1.5. Characteristics of Clear Samples
References
- Fontolan, L.; Morillon, B.; Liégeois-Chauvel, C.; Giraud, A.L. The contribution of frequency-specific activity to hierarchical information processing in the human auditory cortex. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litovsky, R. Chapter 3—Development of the auditory system. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 129, pp. 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edeline, J.M.; Weinberger, N.M. Subcortical adaptive filtering in the auditory system: Associative receptive field plasticity in the dorsal medial geniculate body. Behav. Neurosci. 1991, 105, 154–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, S.; van der Zwaag, W.; Miller, L.M.; Clarke, S.; Saenz, M. Tuning In to Sound: Frequency-Selective Attentional Filter in Human Primary Auditory Cortex. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 1858–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4489–4497. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V.; Funkhouser, T. Dilated residual networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 472–480. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Romero, D.; McCree, A. Stacked Long-Term TDNN for Spoken Language Recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2016, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 September 2016; International Speech Communication Association (ISCA): Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 3226–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Song, Y.; Mcloughlin, I.; Dai, L.R. LID-Senones and Their Statistics for Language Identification. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2018, 26, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; McLoughlin, I.; Yan, Y. A New Time-Frequency Attention Mechanism for TDNN and CNN-LSTM-TDNN, with Application to Language Identification. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech 2019), Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2019; International Speech Communication Association (ISCA): Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 4080–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lee, K.A.; Wang, Q.; Li, H. Golden gemini is all you need: Finding the sweet spots for speaker verification. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2024, 32, 2324–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; He, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhu, J.; Yang, F. Disentangle Estimation of Causal Effects from Cross-Silo Data. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2024—2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–19 April 2024; pp. 6290–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, F.; Reynolds, D.; Dehak, N. Deep neural network approaches to speaker and language recognition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2015, 22, 1671–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Moreno, I.; Gonzalez-Dominguez, J.; Martinez, D.; Plchot, O.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, J.; Moreno, P. On the use of deep feedforward neural networks for automatic language identification. Comput. Speech Lang. 2016, 40, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhen, Y.; Li, P.; Hu, X.; Yang, L. Optical Fiber Vibration Signal Recognition Based on the EMD Algorithm and CNN-LSTM. Sensors 2025, 25, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralikrishna, H.; Sapra, P.; Jain, A.; Dinesh, D.A. Spoken Language Identification Using Bidirectional LSTM Based LID Sequential Senones. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding Workshop (ASRU), Singapore, 14–18 December 2019; pp. 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liao, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, P.; Huang, J.; Xu, P.; Fu, B.; Zhu, Q.; Lai, X. MAL-Net: A Multi-Label Deep Learning Framework Integrating LSTM and Multi-Head Attention for Enhanced Classification of IgA Nephropathy Subtypes Using Clinical Sensor Data. Sensors 2025, 25, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Han, D.; Zhou, S.; Fu, X.; Li, H. An Improved Software Source Code Vulnerability Detection Method: Combination of Multi-Feature Screening and Integrated Sampling Model. Sensors 2025, 25, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yang, K.; Fu, S.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Marsic, I. Hybrid attention based multimodal network for spoken language classification. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics (COLING 2018), Santa Fe, NM, USA, 20–26 August 2018; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 2379–2390. [Google Scholar]
- Padi, B.; Mohan, A.; Ganapathy, S. End-to-end Language Recognition Using Attention Based Hierarchical Gated Recurrent Unit Models. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 5966–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Garcia, P.; Khong, A.; Styles, S.; Khudanpur, S. PHO-LID: A Unified Model Incorporating Acoustic-Phonetic and Phonotactic Information for Language Identification. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.12366. [Google Scholar]
- Desplanques, B.; Thienpondt, J.; Demuynck, K. Ecapa-tdnn: Emphasized channel attention, propagation and aggregation in tdnn based speaker verification. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.07143. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, S.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, L.; Chen, Q. CAM++: A Fast and Efficient Network for Speaker Verification Using Context-Aware Masking. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.00332. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wang, H.; Cheng, L.; Chen, Q.; Qi, J. An enhanced res2net with local and global feature fusion for speaker verification. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.12838. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, P.; Patil, H.A.; Guido, R.C. Vulnerability issues in Automatic Speaker Verification (ASV) systems. EURASIP J. Audio Speech Music. Process. 2024, 2024, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Huang, Z.; Sun, Q. Federated Subgraph Learning via Global-Knowledge-Guided Node Generation. Sensors 2025, 25, 2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhu, S.; Xie, T.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, B. Filamentary Convolution for Spoken Language Identification: A Brain-Inspired Approach. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2024—2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–19 April 2024; pp. 9926–9930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Pan, Y. Evaluation of Dataset Distribution and Label Quality for Autonomous Driving System. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 21st International Conference on Software Quality, Reliability and Security Companion (QRS-C), Hainan, China, 6–10 December 2021; pp. 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, T.; Cole, R.A.; Noel, B. The OGI 22 Language Telephone Speech Corpus. In Proceedings of the 4th European Conference on Speech Communication and Technology (Eurospeech 1995), Madrid, Spain, 18–21 September 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Muthusamy, Y.K.; Cole, R.A.; Oshika, B.T. The OGI multi-language telephone speech corpus. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (ICSLP 1992), Banff, AB, Canada, 13–16 October 1992; International Speech Communication Association (ISCA): Geneva, Switzerland, 1992; pp. 895–898. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Li, L.; Tang, D.; Chen, Q. AP16-OL7: A multilingual database for oriental languages and a language recognition baseline. In Proceedings of the 2016 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 13–16 December 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Wang, D.; Chen, Q. AP18-OLR Challenge: Three Tasks and Their Baselines. In Proceedings of the 2018 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–15 November 2018; pp. 596–600. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Wang, D.; Song, L. AP19-OLR Challenge: Three Tasks and Their Baselines. In Proceedings of the 2019 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Lanzhou, China, 18–21 November 2019; pp. 1917–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, B.; Zhi, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Hong, Q.; Wang, D. Oriental Language Recognition (OLR) 2020: Summary and Analysis. In Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (INTERSPEECH 2021), Brno, Czech Republic (Virtual), 30 August–3 September 2021; International Speech Communication Association (ISCA): Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 3251–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, E.; Uchimoto, K.; Isahara, H. The NICT JLE Corpus: Exploiting the language learners’ speech database for research and education. Int. J. Comput. Internet Manag. 2004, 12, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Matejka, P.; Burget, L.; Glembek, O.; Schwarz, P.; Hubeika, V.; Fapso, M.; Mikolov, T.; Plchot, O. BUT system description for NIST LRE 2007. In Proceedings of the 2007 NIST Language Recognition Evaluation Workshop, Cebu City, Philippines, 22–25 October 2007; National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2007; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Abad, A. The L2F language recognition system for NIST LRE 2011. In Proceedings of the 2011 NIST Language Recognition Evaluation Workshop, Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 13–15 December 2011; National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Plchot, O.; Matejka, P.; Novotnỳ, O.; Cumani, S.; Lozano-Diez, A.; Slavicek, J.; Diez, M.; Grézl, F.; Glembek, O.; Kamsali, M.; et al. Analysis of BUT-PT Submission for NIST LRE 2017. In Proceedings of the Odyssey, Les Sables d’Olonne, France, 26–29 June 2018; pp. 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami, K.; Wang, L.; Dyer, C.; Blunsom, P.; Oord, A.v.d. Learning robust and multilingual speech representations. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.11128. [Google Scholar]
- Valk, J.; Alumäe, T. VOXLINGUA107: A Dataset for Spoken Language Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), Shenzhen, China, 19–22 January 2021; pp. 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardila, R.; Branson, M.; Davis, K.; Kohler, M.; Meyer, J.; Henretty, M.; Morais, R.; Saunders, L.; Tyers, F.; Weber, G. Common Voice: A Massively-Multilingual Speech Corpus. In Proceedings of the 12th Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Marseille, France, 11–16 May 2020; pp. 4218–4222. [Google Scholar]
- Bartz, C.; Herold, T.; Yang, H.; Meinel, C. Language Identification Using Deep Convolutional Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Neural Information Processing (ICONIP 2017), Guangzhou, China, 14–18 November 2017; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 880–889. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Q.; Cao, Y.; Iqbal, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Plumbley, M.D. Panns: Large-scale pretrained audio neural networks for audio pattern recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2020, 28, 2880–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekruksavanich, S.; Jitpattanakul, A.; Sitthithakerngkiet, K.; Youplao, P.; Yupapin, P. Resnet-se: Channel attention-based deep residual network for complex activity recognition using wrist-worn wearable sensors. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 51142–51154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.H.; Cheng, M.M.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, M.H.; Torr, P. Res2net: A new multi-scale backbone architecture. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Module | Unit | Layer | Input_Size | Output_Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Encoding | Convolution | Conv_1 | 50 × 1 × 298 × 23 | 50 × 16 × 298 × 12 |
| Conv_2 | 50 × 16 × 298 × 12 | 50 × 64 × 298 × 7 | ||
| Conv_3 | 50 × 64 × 298 × 7 | 50 × 128 × 298 × 4 | ||
| Conv_4 | 50 × 128 × 298 × 4 | 50 × 128 × 298 × 4 | ||
| MIE | UDRC1_Shallow | Conv_1 | 50 × 128 × 298 × 4 | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 |
| ReLu | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | ||
| BatchNormal | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | ||
| UDRC1_Deep | Conv_1 | 50 × 128 × 298 × 4 | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | |
| ReLu | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | ||
| Conv_2 | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | ||
| ReLu | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | ||
| Conv_3 | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | ||
| BatchNormal | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | ||
| UDRC2 | / | 50 × 512 × 298 × 4 | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | |
| UDRC3 | / | 50 × 256 × 298 × 4 | 50 × 128 × 298 × 4 | |
| Pooling | Avg_Pool | 50 × 128 × 298 × 4 | 50 × 128 × 74 × 1 | |
| LSTM | LSTM | LSTM | 50 × 128 × 74 | 50 × 128 × 50 |
| Decision | Full_Connect | FC_1 | 50 × 6400 | 50 × 64 |
| FC_2 | 50 × 64 | 50 × 128 | ||
| FC_3 | 50 × 128 | 50 × 256 | ||
| FC_4 | 50 × 256 | 50 × 44 |
| Threshold (T) (T/256 %) | Convolution Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filamentary | 1D_t | Rectangular | ||
| Amount () | 76 (30%) | 3.54 | 3.27 | 3.33 |
| 127 (50%) | 2.23 | 2.05 | 2.05 | |
| 191 (75%) | 1.22 | 1.04 | 1.13 | |
| Proportion (%) | 76 (30%) | 25.87 | 23.91 | 24.35 |
| 127 (50%) | 16 | 15 | 15 | |
| 191 (75%) | 8.91 | 7.61 | 8.26 | |
| Threshold(T) (T/256 %) | Convolution Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filamentary | 1D_t | Rectangular | ||
| Amount () | 76 (30%) | 3.16 | 2.99 | 2.90 |
| 127 (50%) | 1.93 | 1.90 | 1.75 | |
| 191 (75%) | 1.01 | 0.99 | 0.93 | |
| Proportion (%) | 76 (30%) | 26.7 | 25.3 | 24.6 |
| 127 (50%) | 16.3 | 16.0 | 14.8 | |
| 191 (75%) | 8.5 | 8.4 | 7.89 | |
| Language | Code | Amount | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Train | Test | Validation | ||
| Arabic | ar | 2246 | 1350 | 400 | 400 |
| Breton | br | 1979 | 1200 | 350 | 350 |
| Bu-Ninkada * | bu * | 2065 | 1250 | 400 | 400 |
| Catalan | ca | 2894 | 1700 | 550 | 550 |
| Hakha Chin | cn(cnh) | 2831 | 1700 | 550 | 550 |
| Chuvash | cv | 2948 | 1750 | 550 | 550 |
| Welsh | cy | 2138 | 1300 | 400 | 400 |
| German | de | 2331 | 1400 | 450 | 450 |
| Dhivehi | dv | 2282 | 1350 | 450 | 450 |
| English | en | 2346 | 1400 | 450 | 450 |
| Esperanto | eo | 2312 | 1750 | 550 | 550 |
| Spanish | es | 2320 | 1400 | 450 | 450 |
| Estonian | et | 2309 | 1400 | 450 | 450 |
| Basque | eu | 2314 | 1400 | 450 | 450 |
| Persian | fa | 2309 | 1400 | 450 | 450 |
| French | fr | 2233 | 1300 | 400 | 400 |
| Irish | ga | 2814 | 1700 | 550 | 550 |
| Gujarat * | gu * | 2334 | 1400 | 450 | 450 |
| Interlingua | ia | 2352 | 1400 | 450 | 450 |
| Iban * | ib * | 1779 | 1050 | 350 | 350 |
| Indonesian | id | 2256 | 1350 | 450 | 450 |
| Italian | it | 2257 | 1350 | 450 | 450 |
| Japanese | ja | 2323 | 1400 | 450 | 450 |
| Javanese * | jv * | 1701 | 1050 | 300 | 300 |
| Khmer * | km * | 2287 | 1350 | 450 | 450 |
| Kannada * | kn * | 1760 | 1050 | 350 | 350 |
| Slovenian * | si * | 2033 | 1200 | 400 | 400 |
| Latvian | lv | 2317 | 1400 | 450 | 450 |
| Malayalam * | ml * | 2316 | 1400 | 450 | 450 |
| Mongolian | mn | 2112 | 1300 | 400 | 400 |
| Nepali * | ne * | 1540 | 900 | 300 | 300 |
| Dutch | nl | 2277 | 1350 | 450 | 450 |
| Portuguese | pt | 2278 | 1350 | 450 | 450 |
| Russian | ru | 2338 | 1400 | 450 | 450 |
| Sakha | sa(sah) | 2977 | 1750 | 550 | 550 |
| Sovenian | sl | 2275 | 1350 | 450 | 450 |
| Sundanese * | su * | 1563 | 950 | 300 | 300 |
| Swedish | sv | 2970 | 1750 | 550 | 550 |
| Tamil | ta | 2326 | 1400 | 450 | 450 |
| Telugu * | te * | 2324 | 1400 | 450 | 450 |
| Turkish | tr | 2297 | 1350 | 450 | 450 |
| Tatar | tt | 2330 | 1400 | 450 | 450 |
| Uighur * | yg * | 2332 | 1400 | 450 | 450 |
| Chinese | zh | 2392 | 1450 | 450 | 450 |
| Training Subset | Testing Subset | Avg Acc | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ours | Raw | SLR100 | Voxlingua | ||
| Ours | 0.913 | 0.908 | 0.785 | 0.803 | 0.852 |
| Raw | 0.893 | 0.875 | 0.753 | 0.806 | 0.832 |
| SLR100 | 0.865 | 0.853 | 0.882 | 0.782 | 0.845 |
| Voxlingua | 0.735 | 0.723 | 0.766 | 0.859 | 0.771 |
| Dataset | Consistent Mono-Label | Clear | Clean | Public Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common Voice | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Voxlingua | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| OpenSLR | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| NIST LRE | ✓ | \ | \ | \ |
| Ours | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Unit | Input_Size | Output_Size |
|---|---|---|
| Convolution_1 | 50 × 1 × 298 × 23 | 50 × 16 × 100 × 8 |
| ReLu | 50 × 16 × 100 × 8 | 50 × 16 × 100 × 8 |
| Convolution_2 | 50 × 16 × 100 × 8 | 50 × 64 × 34 × 3 |
| ReLu | 50 × 64 × 34 × 3 | 50 × 64 × 34 × 3 |
| Convolution_3 | 50 × 64 × 34 × 3 | 50 × 128 × 12 × 1 |
| BatchNormal | 50 × 128 × 12 × 1 | 50 × 128 × 12 × 1 |
| LSTM | 50 × 128 × 12 | 50 × 128 × 50 |
| Full_Connect_1 | 50 × 6400 | 50 × 64 |
| Full_Connect_2 | 50 × 64 | 50 × 128 |
| Full_Connect_3 | 50 × 128 | 50 × 256 |
| Full_Connect_4 | 50 × 256 | 50 × 44 |
| Feature | Size | Data Type | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| MFCC | (298,13) | Float32 | Kaldi |
| PLP | (298,12) | Float32 | Kaldi |
| Fbank | (298,23) | Float32 | Kaldi |
| Feature | Kernel Size | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 × 2 + 1 × 3 | 2 × 1 + 3 × 1 | 2 × 2 + 3 × 3 | |
| MFCC | 76.18 | 64.85 | 81.58 |
| PLP | 87.75 | 80.80 | 89.30 |
| Fbank | 92.38 | 83.53 | 91.18 |
| Method | Kernel Size | Database | Period | Params (M) | Acc (%) | Base | IE ↑ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fbank | PLP | MFCC | Params (M) | Acc (%) | ||||||
| Frequency | 1 * 2 + 1 * 3 | ✓ | 1 s | 2.191 | 79.89 | 0.577 | 60.03 | 12.309 | ||
| 3 s | 2.444 | 92.38 | 0.337 | 76.57 | 7.501 | |||||
| ✓ | 1 s | 1.462 | 76.90 | 0.577 | 69.96 | 7.851 | ||||
| 3 s | 1.502 | 87.75 | 0.579 | 82.41 | 5.791 | |||||
| ✓ | 1 s | 1.782 | 61.40 | 0.577 | 50.87 | 8.742 | ||||
| 3 s | 1.822 | 76.18 | 0.579 | 67.15 | 7.262 | |||||
| Time | 2 * 1 + 3 * 1 | ✓ | 1s | 3.305 | 69.20 | 0.577 | 60.03 | 3.365 | ||
| 3 s | 3.306 | 83.53 | 0.337 | 76.57 | 2.344 | |||||
| ✓ | 1 s | 2.895 | 61.73 | 0.577 | 69.96 | –3.550 | ||||
| 3 s | 2.896 | 80.80 | 0.579 | 82.41 | –0.694 | |||||
| ✓ | 1 s | 2.486 | 43.81 | 0.577 | 50.87 | –3.703 | ||||
| 3 s | 2.487 | 64.85 | 0.579 | 67.15 | –1.207 | |||||
| Both | 2 * 2 + 3 * 3 | ✓ | 1s | 3.389 | 80.40 | 0.577 | 60.03 | 7.248 | ||
| 3 s | 3.390 | 91.18 | 0.337 | 76.57 | 4.786 | |||||
| ✓ | 1 s | 3.801 | 75.76 | 0.577 | 69.96 | 1.800 | ||||
| 3 s | 3.806 | 89.30 | 0.579 | 82.41 | 2.136 | |||||
| ✓ | 1s | 3.596 | 61.33 | 0.577 | 50.87 | 3.465 | ||||
| 3 s | 3.601 | 81.58 | 0.579 | 67.15 | 4.775 | |||||
| Dataset | Low-Speech-Ratio Samples | High-Speech-Ratio Samples | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAD | VAD-Free | VAD | VAD-Free | |
| FCK-NN | 0.101 | 0.110 | 0.080 | 0.076 |
| LID_Senones [12] | 0.168 | 0.173 | 0.158 | 0.156 |
| CNN | LSTM | UDRC | ACC(%) ↑ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | ||||
| 1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 87.11 | |
| 2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 80.68 | |
| 3 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 88.31 | ||
| 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 89.06 | ||
| 5 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 75.03 | ||
| 6 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 90.31 |
| 7 | ✓ | ✓ | 72.19 | |||
| 8 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 88.15 | |
| 9 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 89.11 | |
| 10 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 92.38 | |
| Kernel Shape | Method | Kernel Size | Overlap | Params (M) | Acc (%) | IE ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Square | Both | 2 × 2 + 3 × 3 | Y | 4.427 | 89.71 | 3.213 |
| N | 3.390 | 91.18 | 4.785 | |||
| 3 × 3 + 3 × 3 | Y | 4.268 | 90.59 | 3.566 | ||
| N | 3.437 | 85.00 | 2.718 | |||
| 4 × 4 + 3 × 3 | Y | 4.333 | 90.91 | 3.588 | ||
| N | 3.500 | 85.00 | 2.664 | |||
| Filamentary | Time | 2 × 1 + 3 × 1 | Y | 3.319 | 80.31 | 1.255 |
| N | 3.306 | 83.53 | 2.344 | |||
| 3 × 1 + 3 × 1 | Y | 3.328 | 80.02 | 1.154 | ||
| N | 3.314 | 82.94 | 2.139 | |||
| 4 × 1 + 3 × 1 | Y | 3.337 | 80.39 | 1.274 | ||
| N | 3.323 | 80.99 | 1.480 | |||
| Frequency | 1 × 2 + 1 × 3 | Y | 2.596 | 88.80 | 5.413 | |
| N | 2.444 | 92.38 | 7.501 | |||
| 1 × 3 + 1 × 3 | Y | 2.400 | 88.71 | 5.883 | ||
| N | 1.626 | 81.54 | 3.858 | |||
| 1 × 4 + 1 × 3 | Y | 2.410 | 88.85 | 5.923 | ||
| N | 1.635 | 88.04 | 8.832 |
| Method | Fbank | PLP | MFCC |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRNN [45] | 77.58 | 82.34 | 69.64 |
| Inception-v3_CRNN [45] | 82.49 | 84.45 | 72.38 |
| LID_Senones [12] | 84.56 | 79.68 | 73.24 |
| Ours | 92.38 | 87.75 | 76.18 |
| Method | Original | Param (M) | Fila | Params (M) | IE ↑ | Square | Params (M) | IE ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECAPA-TDNN [25] | 96.72 | 6.195 | 96.85 | 6.220 | 4.813 | 96.80 | 6.271 | 0.998 |
| campplus [26] | 96.87 | 7.199 | 97.25 | 7.224 | 14.897 | 97.34 | 7.274 | 6.219 |
| Method | Original | Param (M) | Fila | Params (M) | DC ↓ | Time | Params (M) | DC↓ |
| ResnetSE [47] | 96.11 | 7.821 | 93.70 | 5.935 | 1.281 | 93.58 | 5.935 | 1.343 |
| PANNS_CNN10 [46] | 95.36 | 5.244 | 90.76 | 2.122 | 1.474 | 85.73 | 2.122 | 3.085 |
| ERes2Net [27] | 94.19 | 6.619 | 92.59 | 5.676 | 1.690 | 90.96 | 5.676 | 3.423 |
| Res2net [48] | 92.44 | 5.096 | 91.54 | 4.624 | 1.909 | 89.64 | 4.624 | 5.925 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Yang, X.; Xie, T.; Zhu, S.; Zeng, B. Filamentary Convolution for SLI: A Brain-Inspired Approach with High Efficiency. Sensors 2025, 25, 3085. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103085
Zhang B, Yang X, Xie T, Zhu S, Zeng B. Filamentary Convolution for SLI: A Brain-Inspired Approach with High Efficiency. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):3085. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103085
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Boyuan, Xibang Yang, Tong Xie, Shuyuan Zhu, and Bing Zeng. 2025. "Filamentary Convolution for SLI: A Brain-Inspired Approach with High Efficiency" Sensors 25, no. 10: 3085. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103085
APA StyleZhang, B., Yang, X., Xie, T., Zhu, S., & Zeng, B. (2025). Filamentary Convolution for SLI: A Brain-Inspired Approach with High Efficiency. Sensors, 25(10), 3085. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103085






